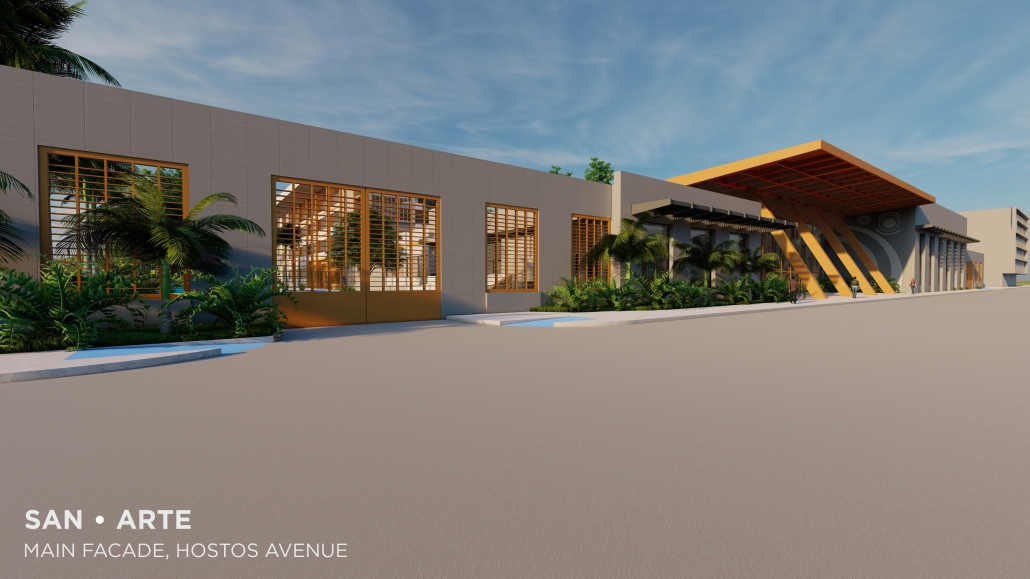
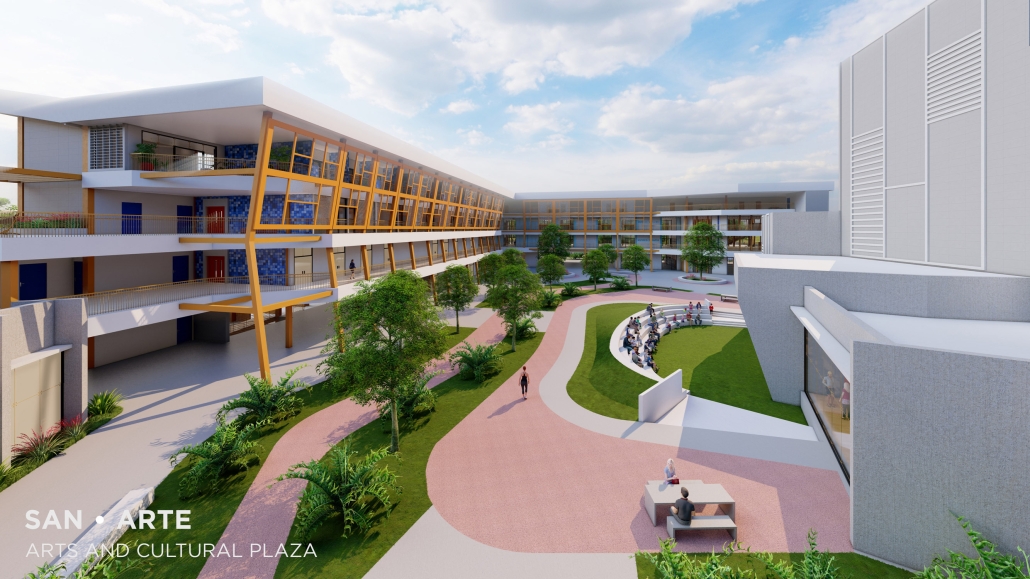
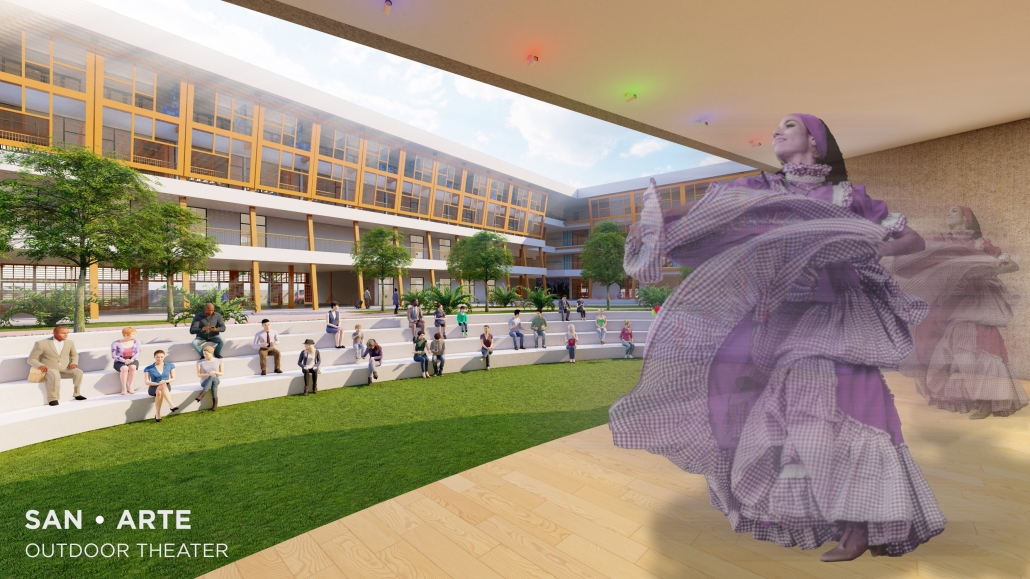
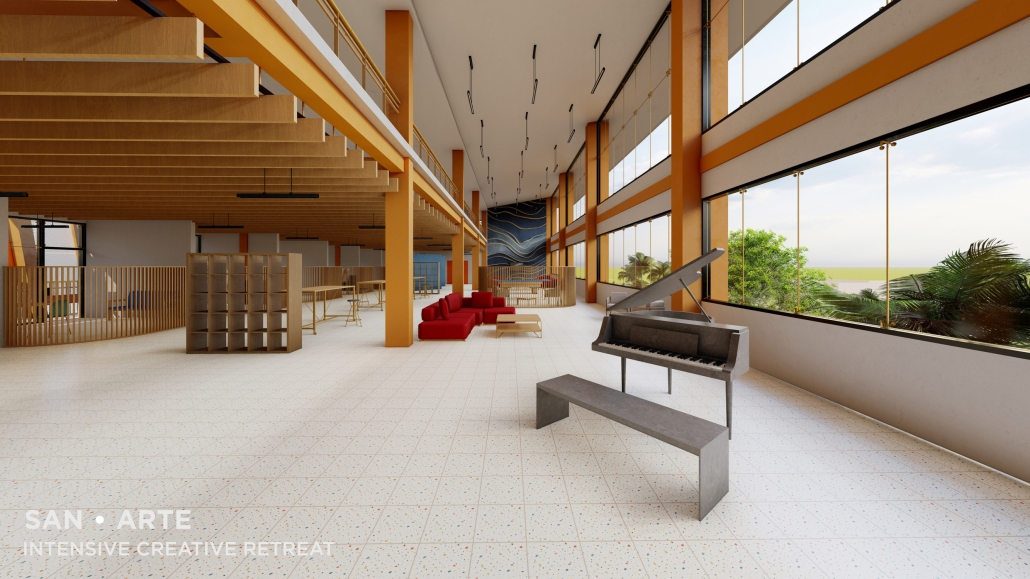
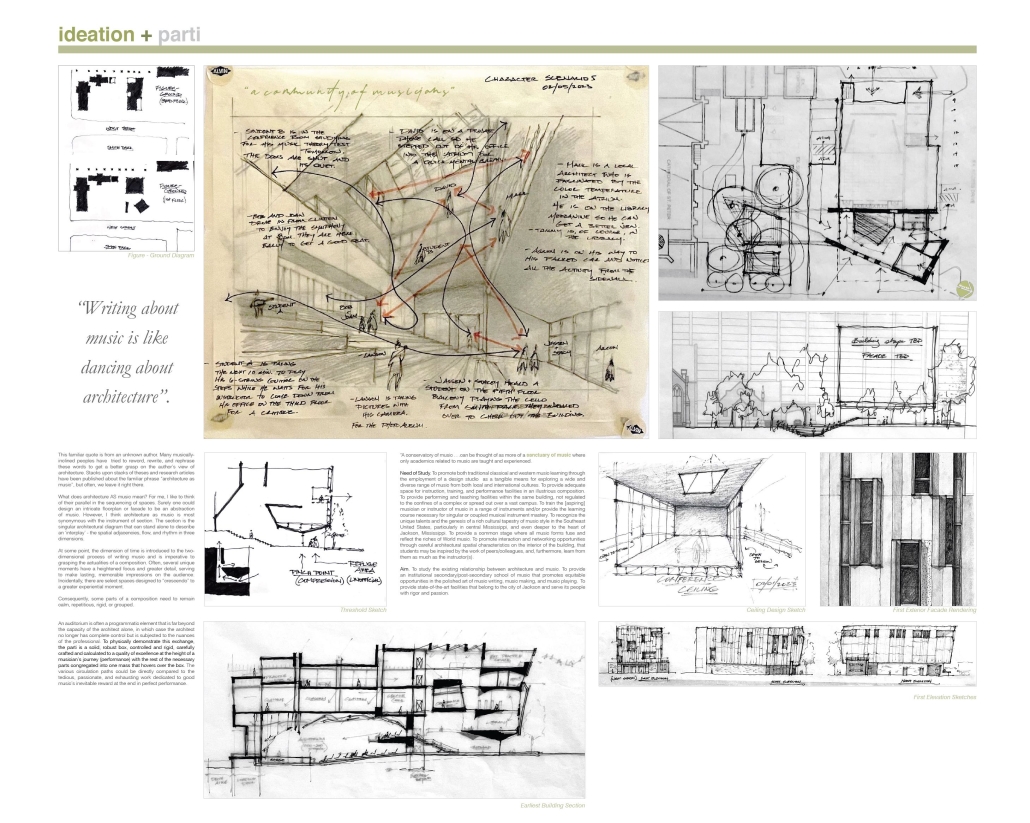
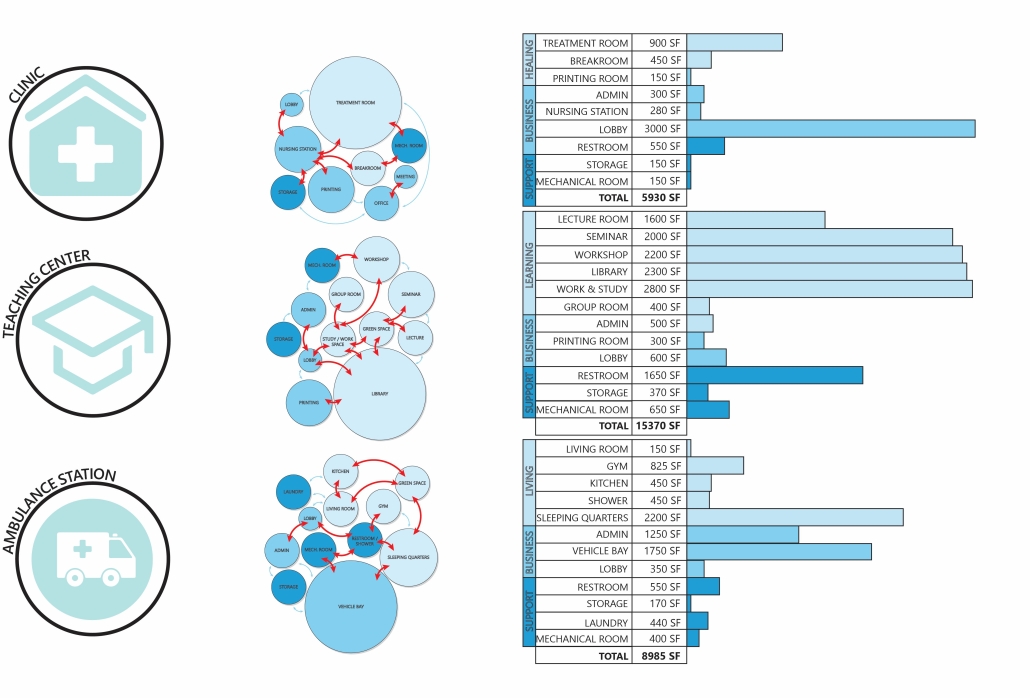
2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part II
In Part II of the 2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase, we take a look at projects that focus on education. From supporting the social integration of neurodivergent students to designing a Makerspace for a university, the featured student work addresses education in various capacities.
Today’s installment includes proposals to build schools and increase the accessibility of education in underserved communities, designs for South Korean Hagwons, and more!
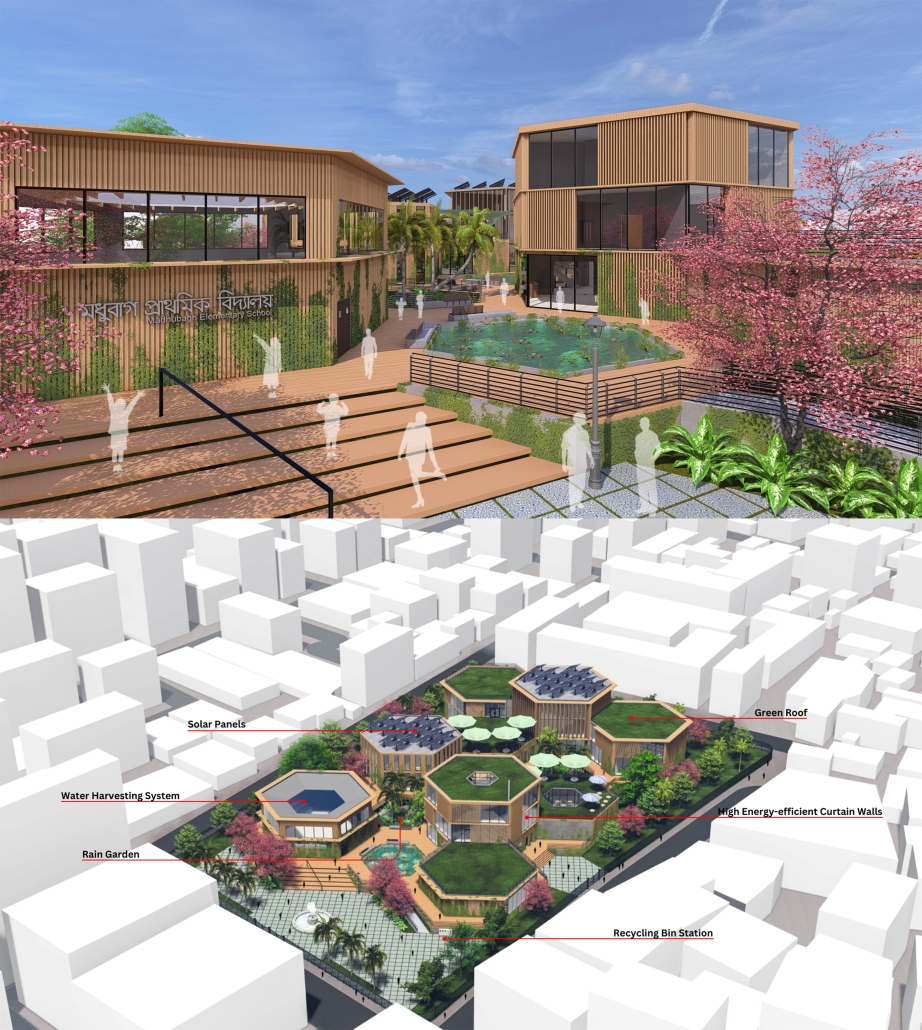
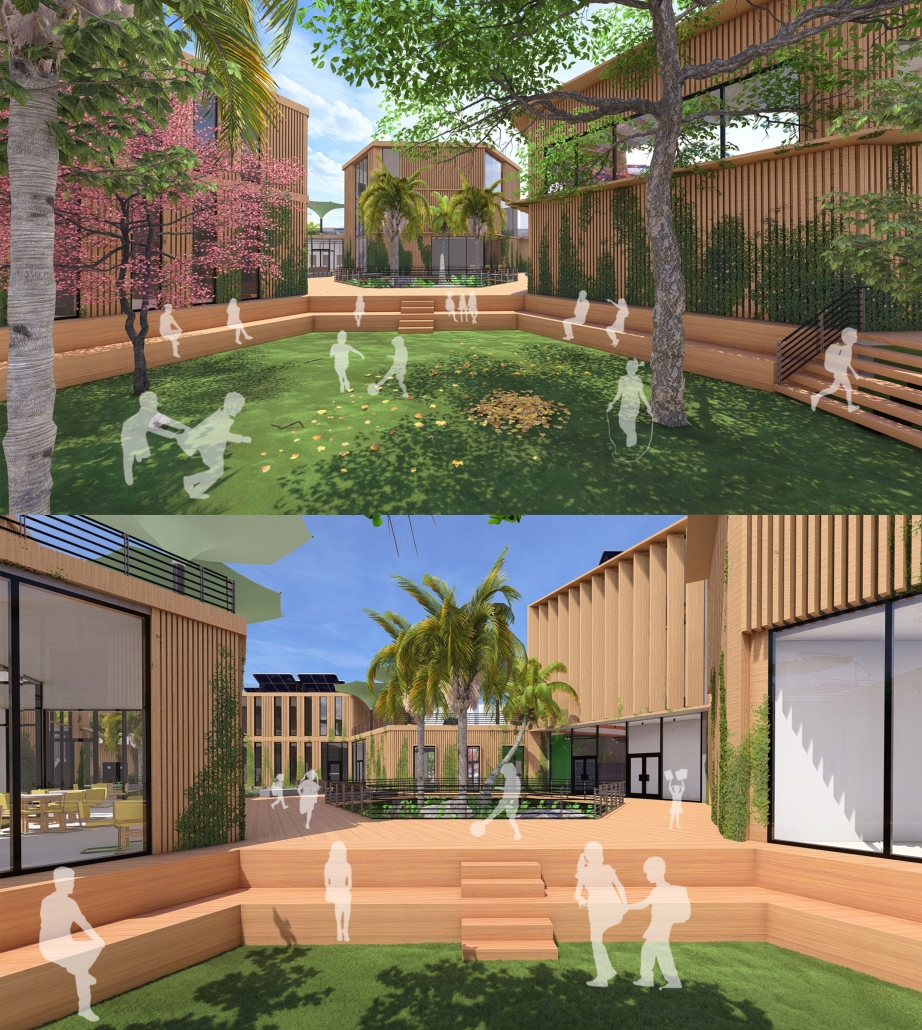
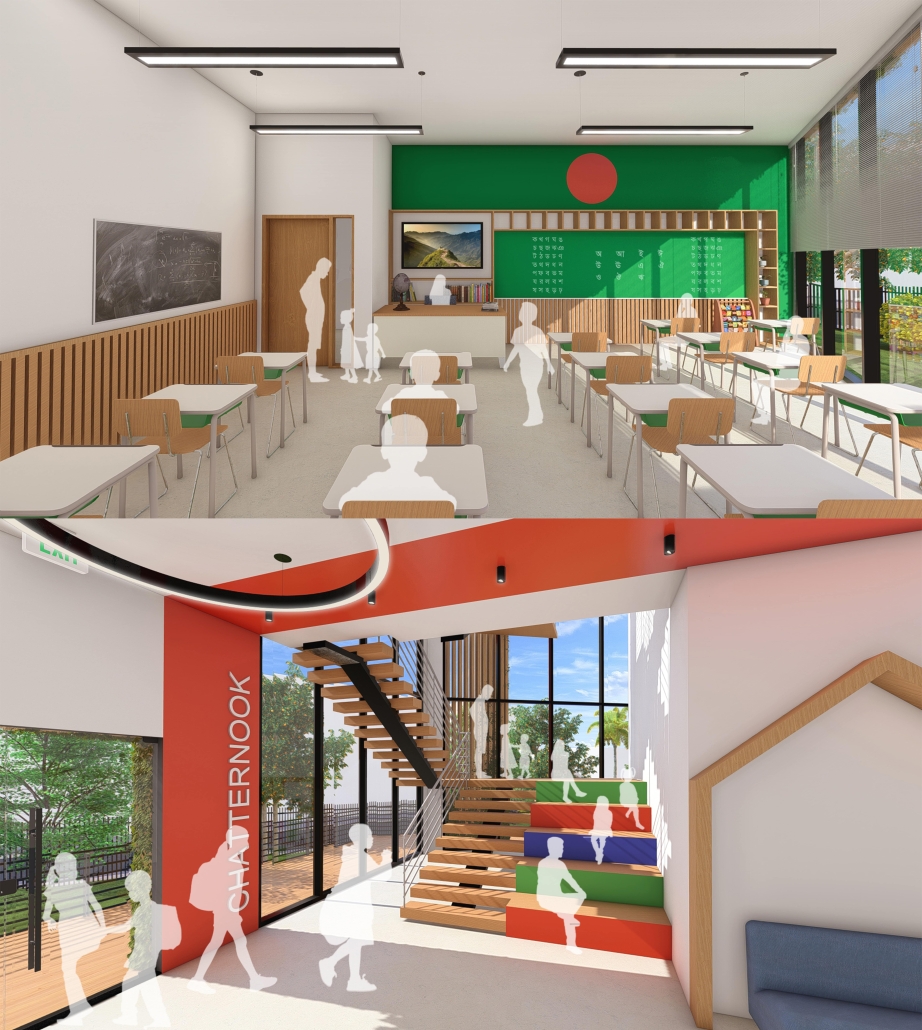
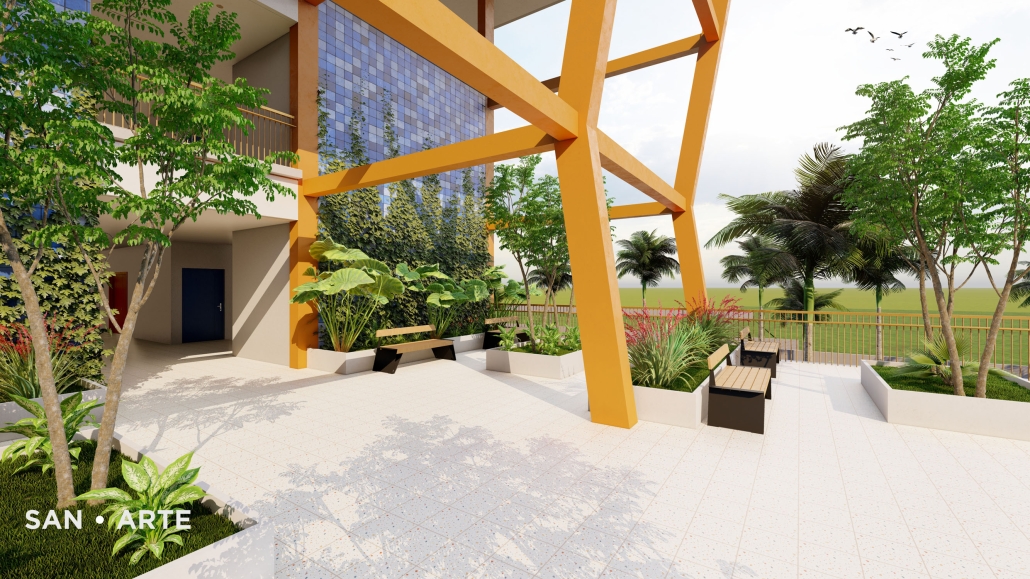
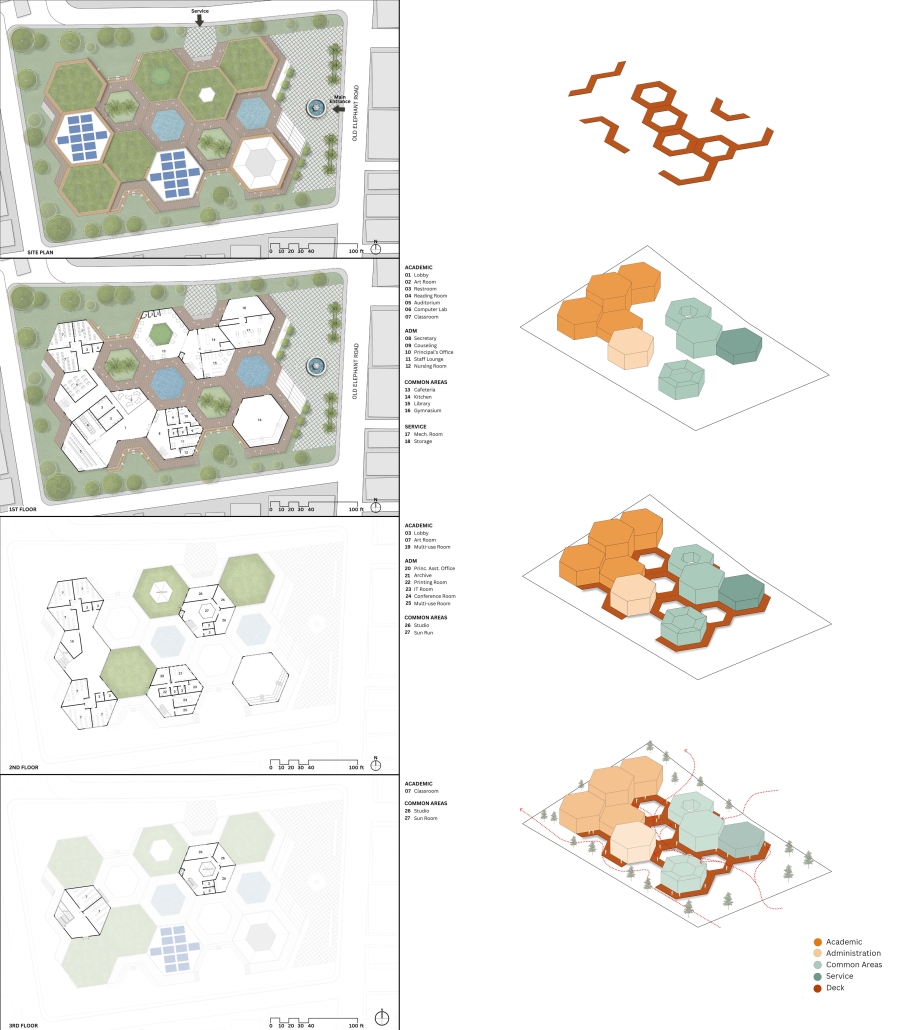
Sustainable School in Bangladesh by Cesar Augusto Borges dos Santos, B.Sc in Architecture ’24
University of District of Columbia | Advisor: Dr. Golnar Ahmadi
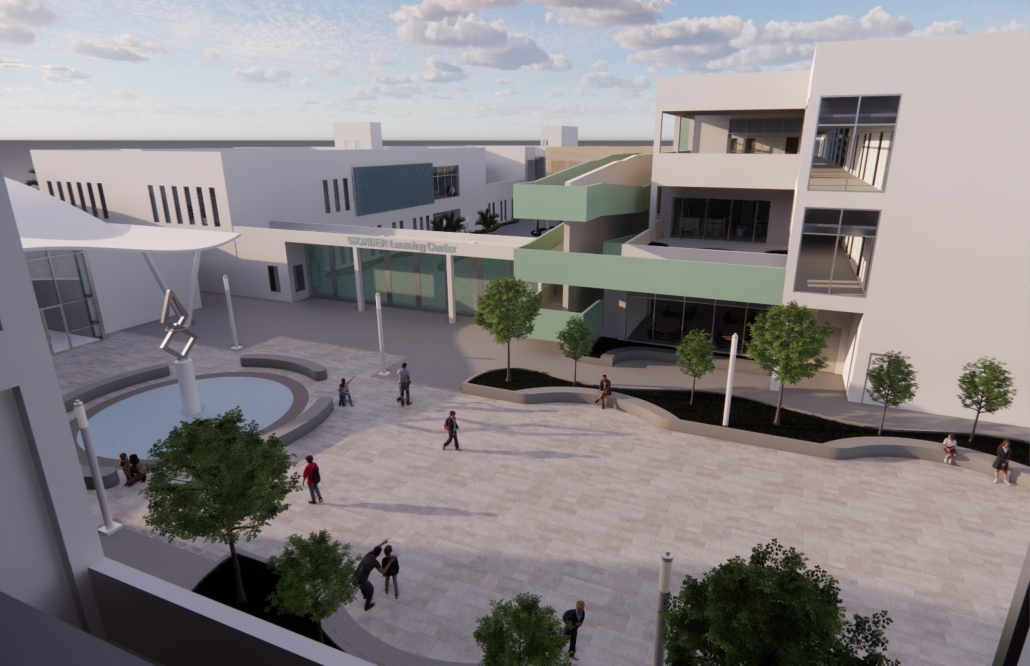
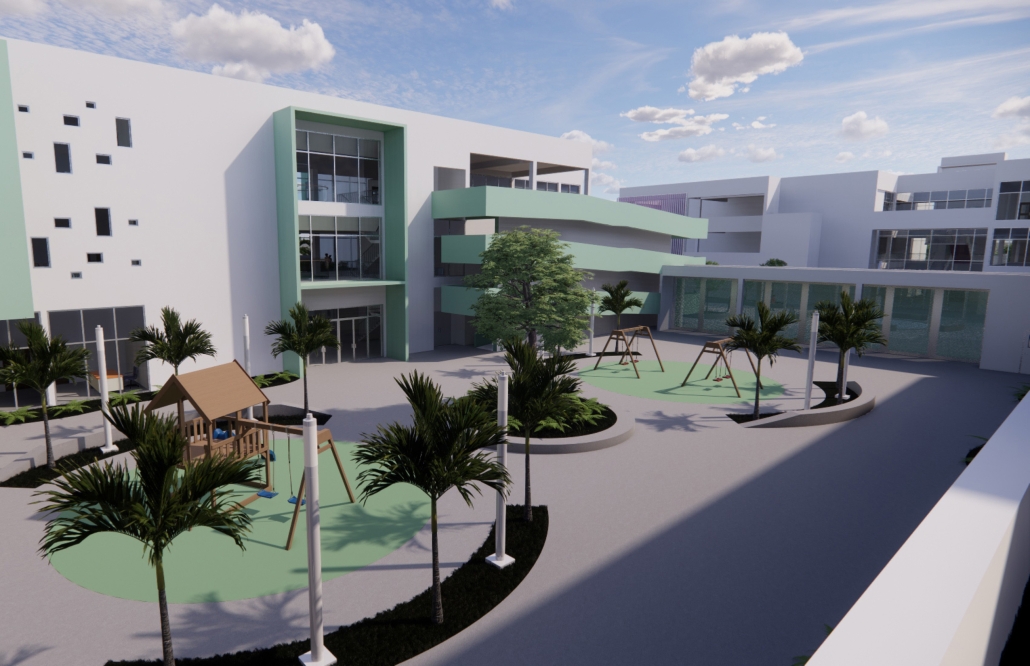
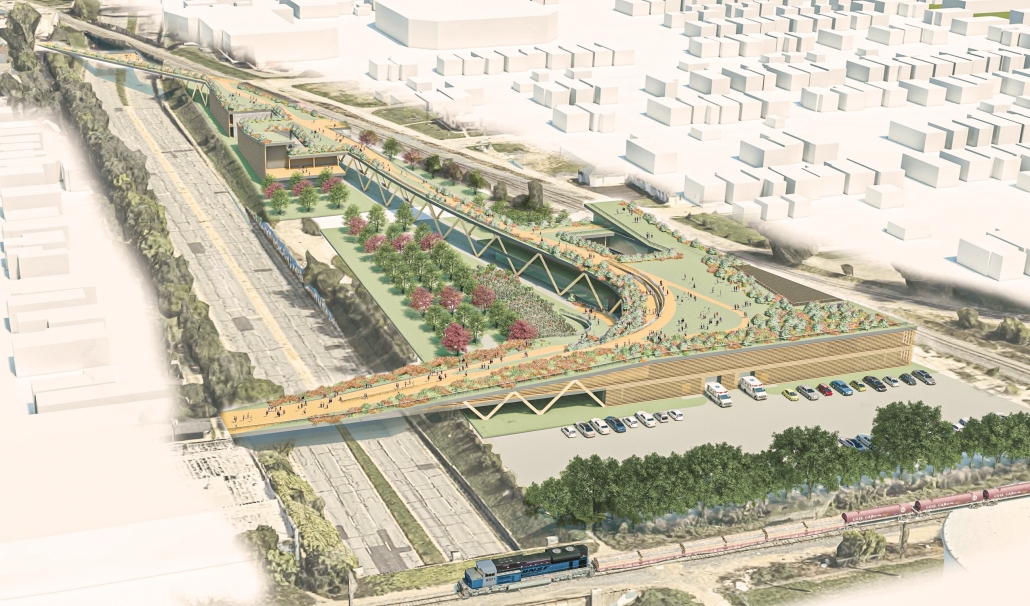
Elin Nordegren once said, “Education is one thing no one can take away from you.” This powerful statement underscores the importance of establishing an elementary school in Modhubagh, a densely populated and predominantly low-income area in Dhaka. Currently, the absence of a local elementary school forces children to embark on long and arduous journeys to reach distant educational institutions. This situation not only hinders their academic progress but also exacerbates the cycle of poverty that grips the community.
According to UNICEF, only 19% of children aged 3-5 in Bangladesh attend an early childhood education program. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for more accessible educational facilities. By constructing a new elementary school in Modhubagh, we can ensure that children have better access to quality education, thereby laying a strong foundation for their future.
The proposed school will serve as a beacon of hope, providing a safe and nurturing environment for the children of Modhubagh. It will offer a comprehensive curriculum designed to foster cognitive, social, and emotional development. Moreover, the establishment of this school will create job opportunities for local residents, further uplifting the community.
In summary, building an elementary school in Modhubagh is a transformative step towards breaking the cycle of poverty and empowering the next generation. This project is not just about constructing a building; it is about building a brighter future for the children and the community as a whole.
Instagram: @Golnarahmadi
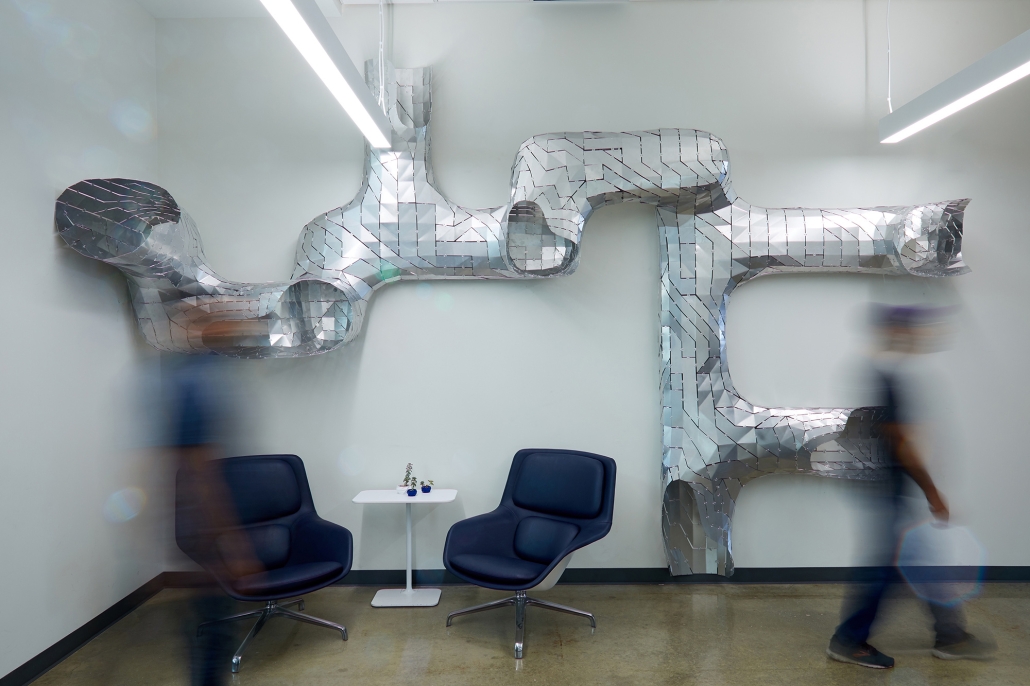
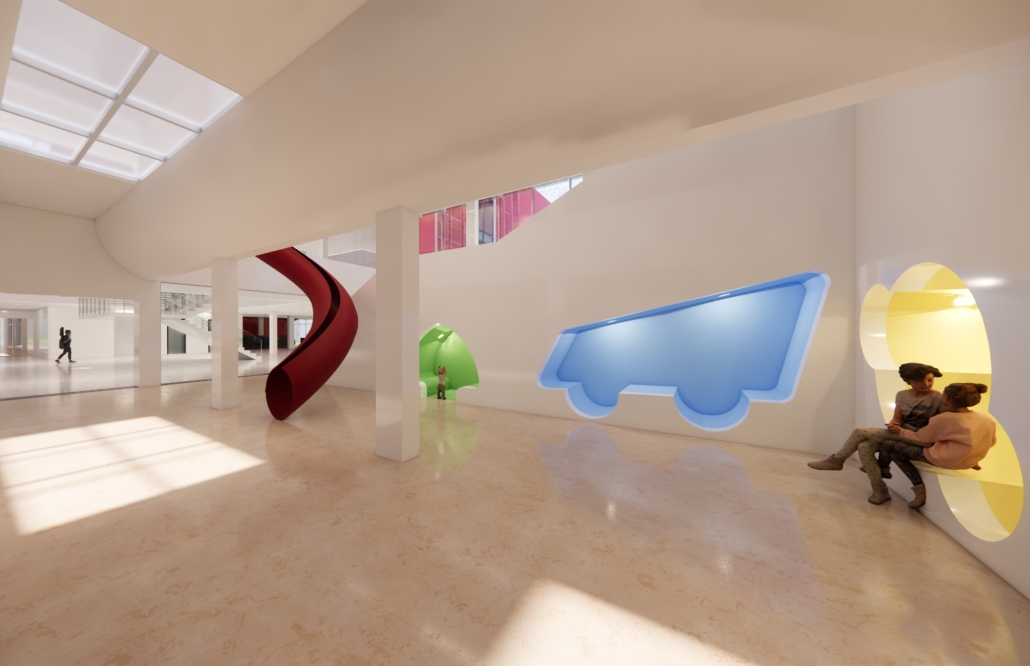
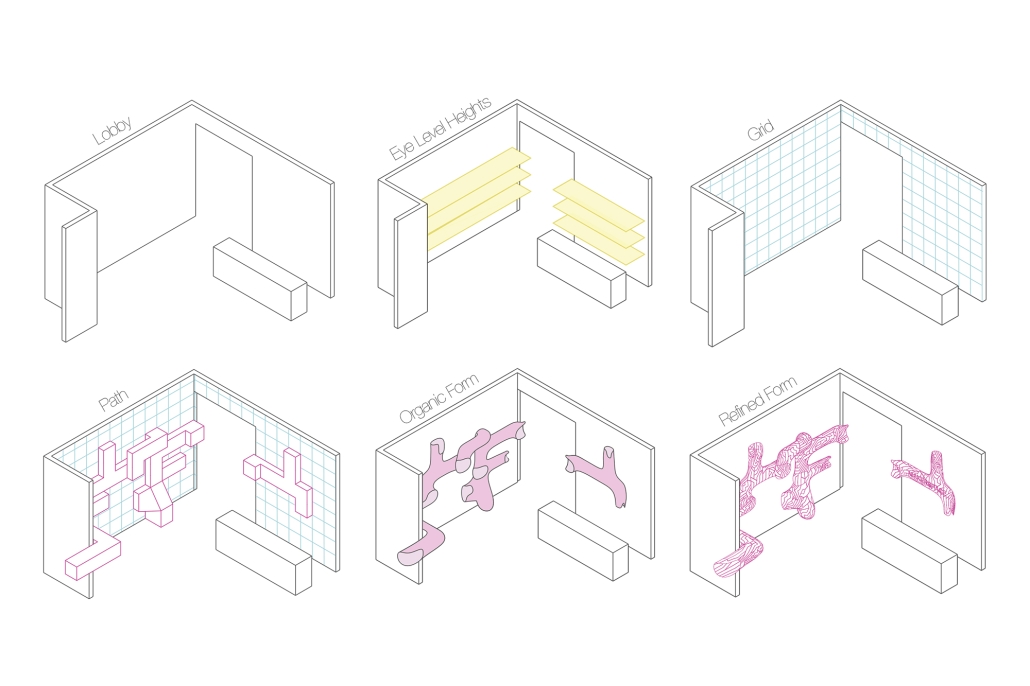
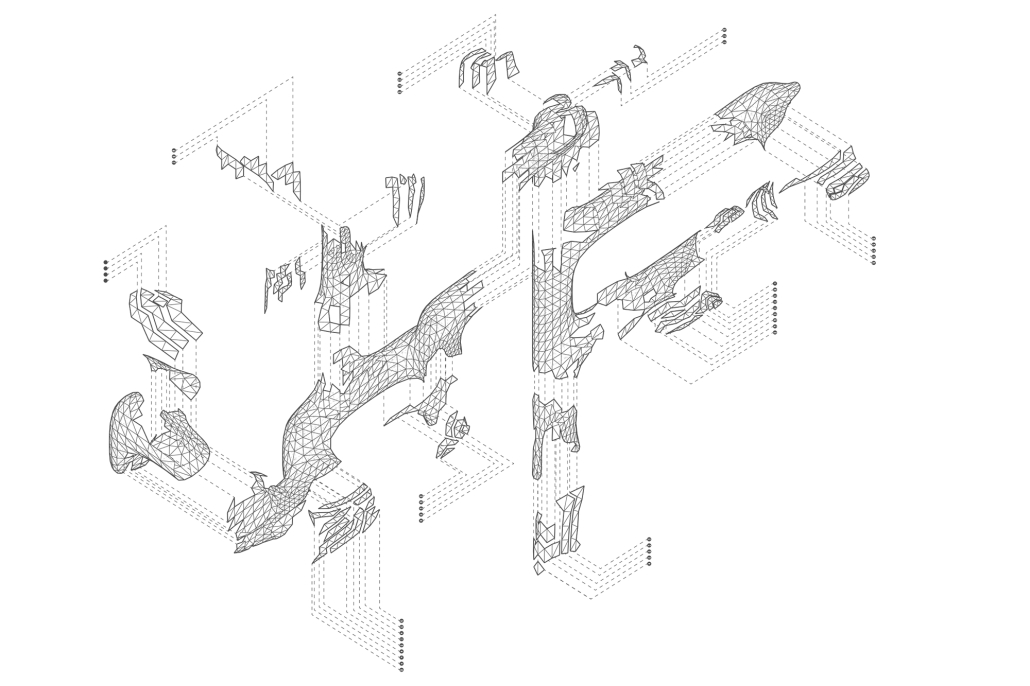
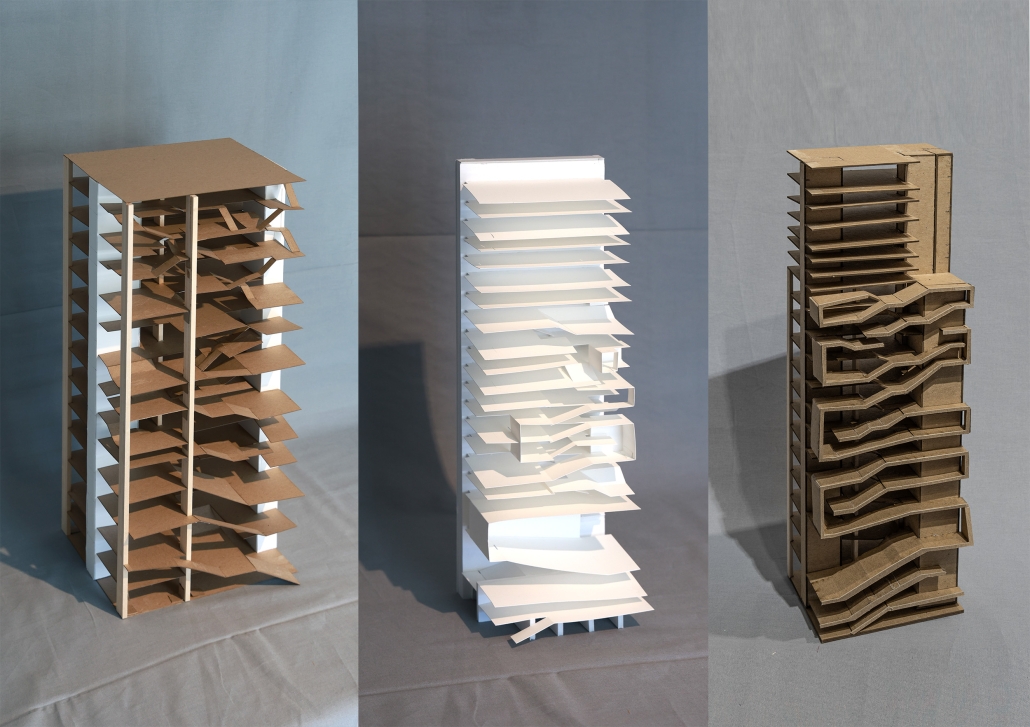
SNAPD by Baraa Abdolkarim, Yusuf Abdul-Rakib, Lauren Cepeda, Alondra Egure, Angel Estrada, Aneida Flores, Luis Flores, Marianne Friedel, Lorena Gonzalez, Brianna Guerra, Douglas Long, Isabel Vera Lopez, Simran Maredia, Kawa Ojo, Bylasan Shalabi, Jesus Sifuentes & Kyndal Thompson, B. Arch ’24
The University of Texas at San Antonio | Advisor: Armando Araiza
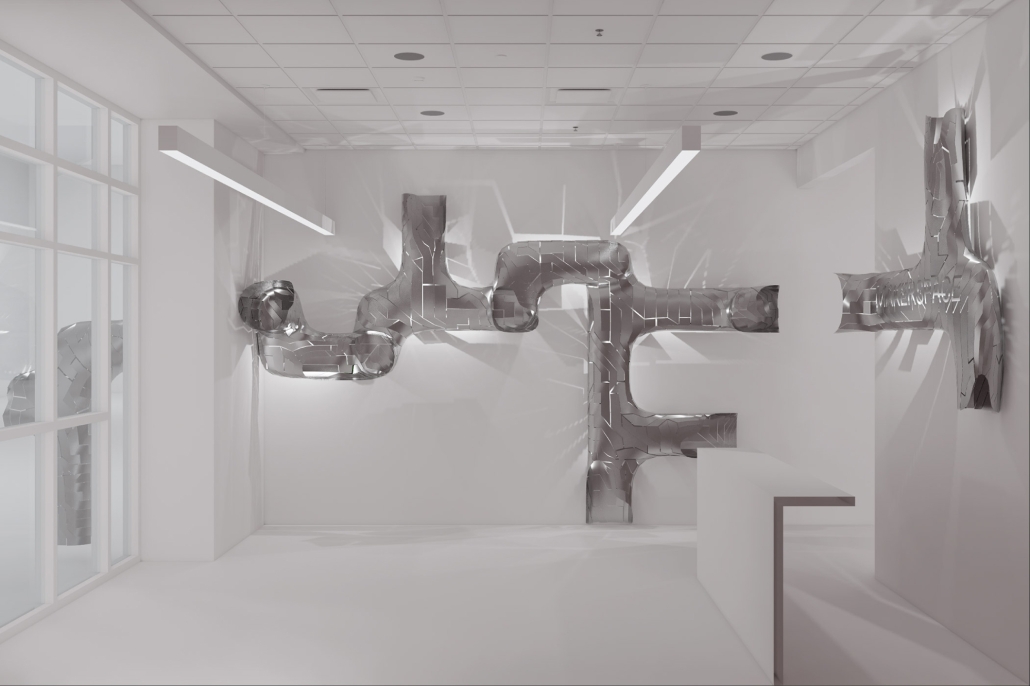
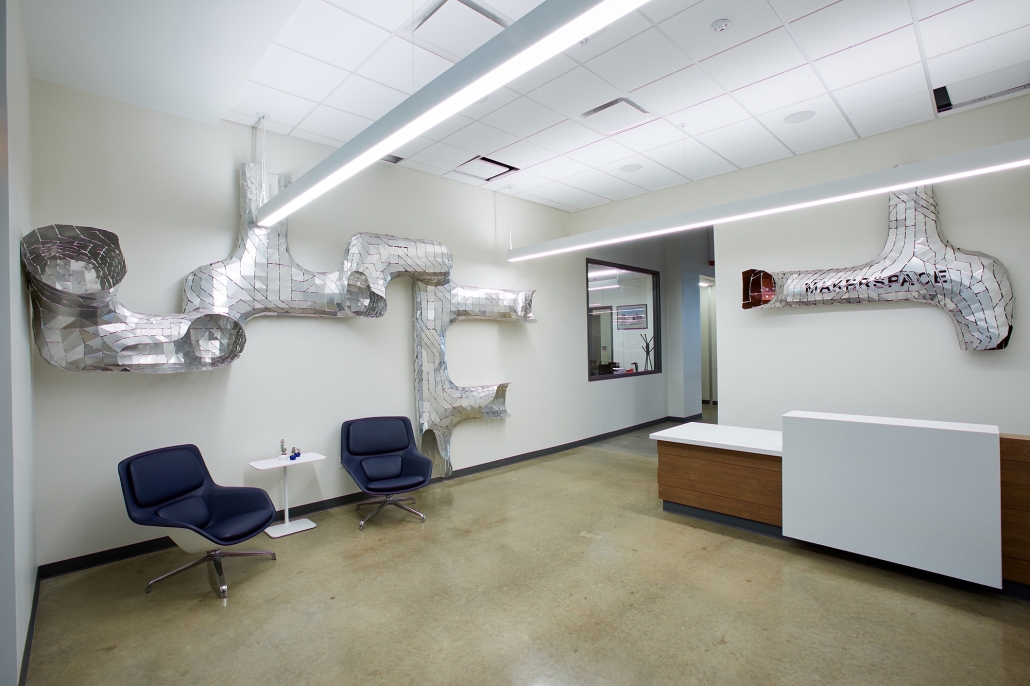
The project was designed for the entrance of the new Makerspace in the newly finished Science and Engineering Building at the UTSA Main Campus. The design allows students from all majors to showcase projects made in the Makerspace as well as welcome students to work on new projects. The studio explored the concept of folding, while transforming 2-dimensional surfaces into 3-dimensional volumes. The volumes organically flow throughout the Makerspace Lobby, displaying the concept of growth and transformation. Color and lights were incorporated into the design in order to illuminate the project and make it feel like an immersive and interactive experience for those entering the Makerspace Lobby.
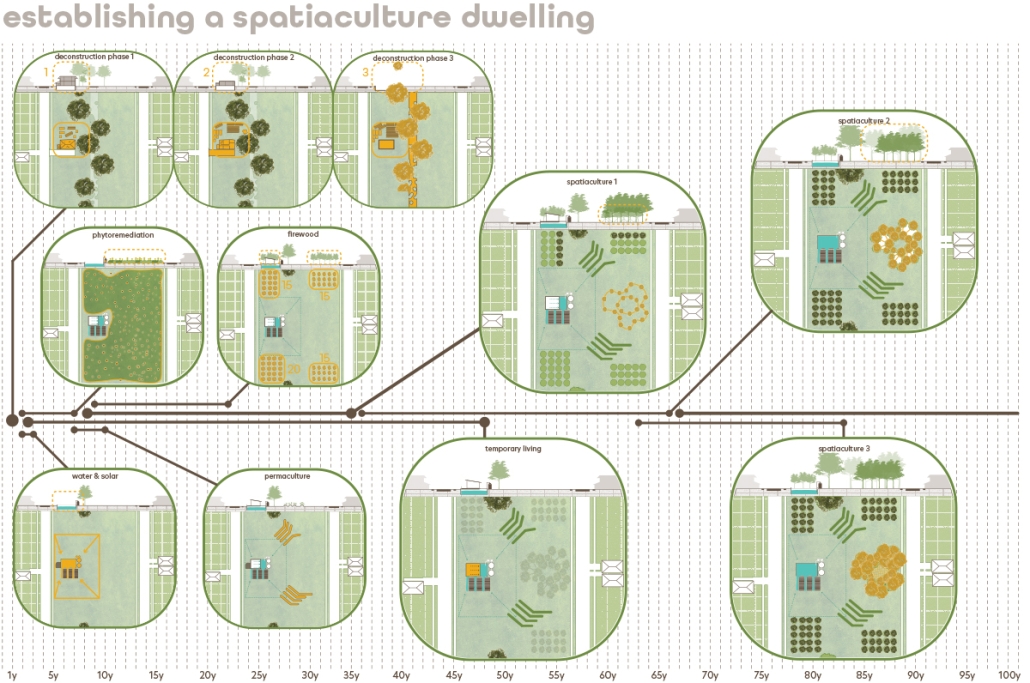
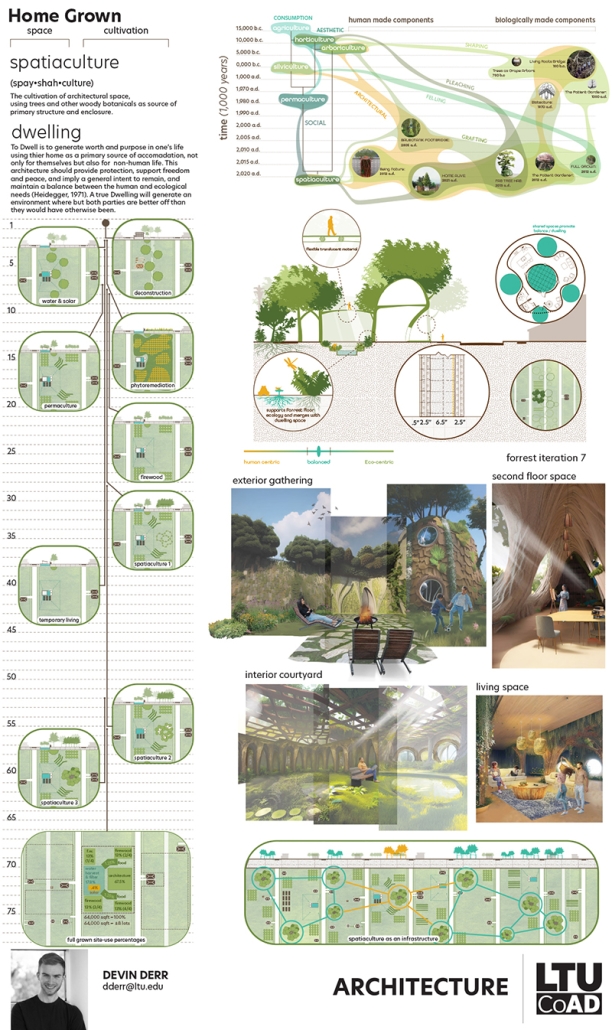
Field Station: A Land Based Elementary School by Huê Bùi, M. Arch ‘24
University of California, Berkeley | Advisors: Neyran Turan (Primary Advisor) & Liz Gálvez
Field Station proposes a land-based elementary school as a response to the growing disconnect between people and land in industrializing rural Vietnam.
Land is big and school is small. Field Station is situated in Bac Giang, Vietnam, and centered around the lychee tree, the region’s key agricultural export. The school is located on an existing field to foster direct, place-based knowledge. The school is realized as a trail, integrating local land maintenance practices into both its pedagogy and architecture.
In the flat topography of the site, lychee trees are grown on mounds to help the roots stay above flood level and protect them from weeds. Field Station comprises interventions around these lychee mounds, organized like an almanac that suggests how architecture can adapt seasonally to facilitate different programs and spatial organizations during different planting stages throughout the year. The scroll drawing experiments with depicting both time and space in a two-dimensional medium. Read from right to left, the drawing aims to depict Field Station at four points of activation: Spring school during flower development, Summer school during harvest, Autumn school during ground preparation, and Winter school during canopy development.
Land time is long and school time is short. Yet both are cyclical, rooted in repetition and resulting in growth. Field Station explores time across scales: the time of a human, a tree, a school year, an annual crop; the time of growth and decay. Using primarily bamboo and lychee bi-products (branches, leaves, fruits), the interventions aim to promote regenerative agriculture through various composting strategies, proposing the restoration of land depleted by mono-crop as an essential component of land education.
Instagram: @nemestudio, @office.for.example, @ucberkeleyarch
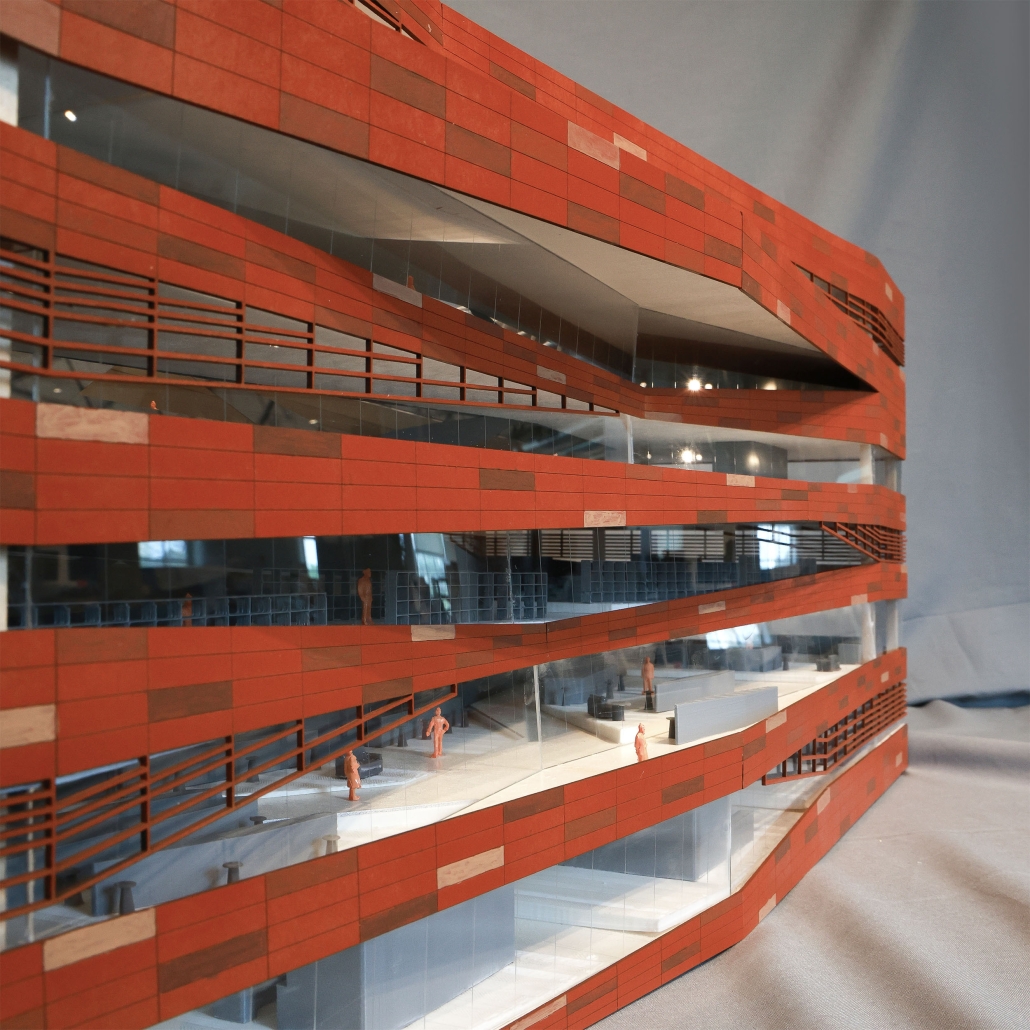
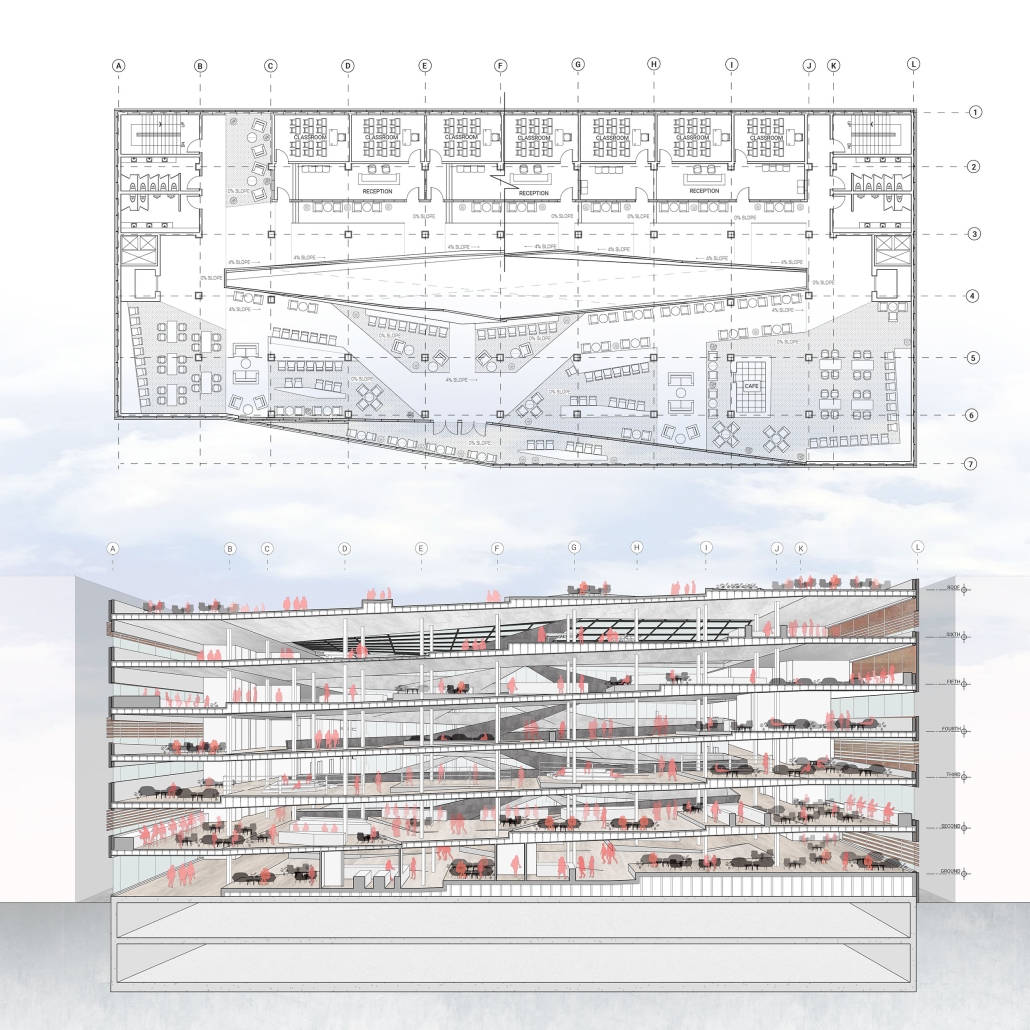
Social Ribbon by Brandon Rosas, Eddie Lam & Huiying Tan, M. Arch ’24
University at Buffalo | Advisor: Jin Young Song
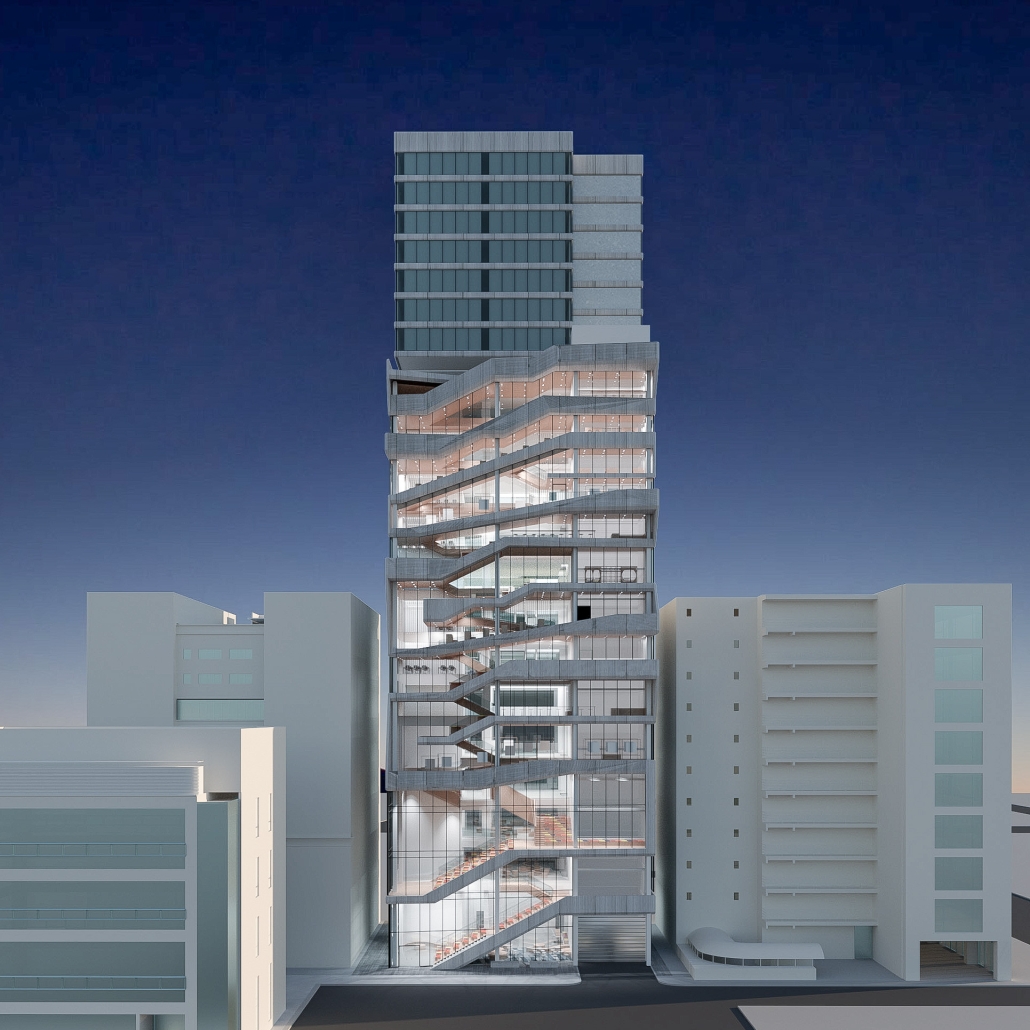
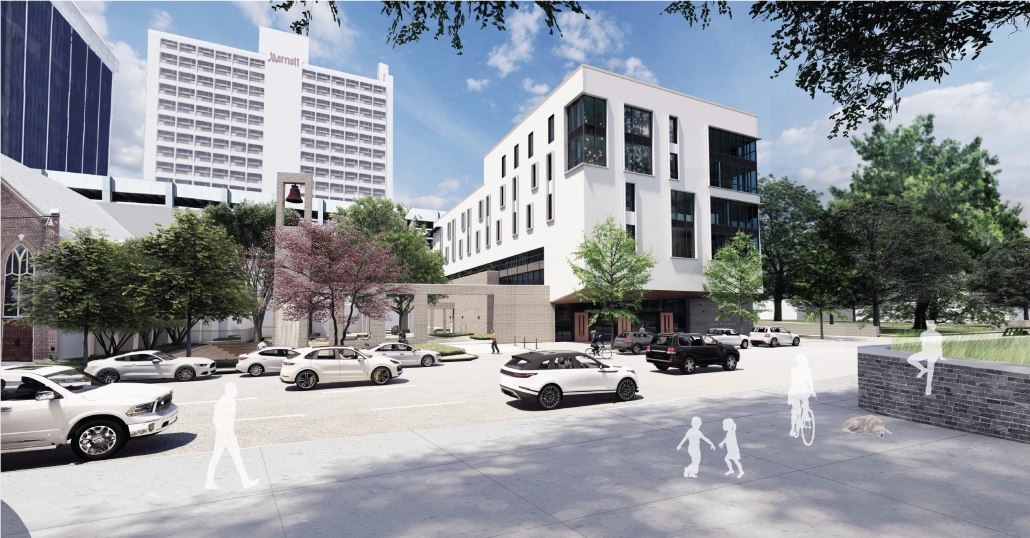
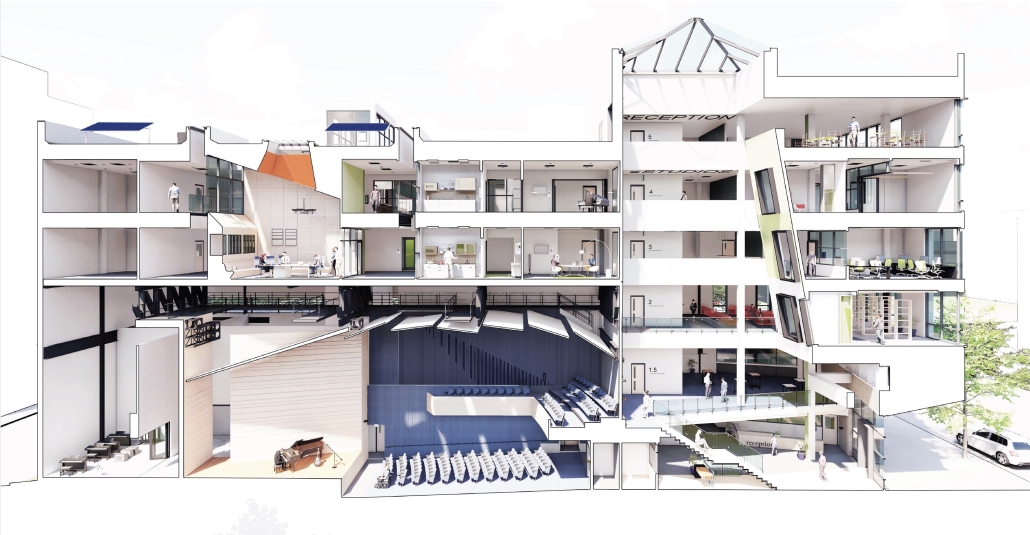
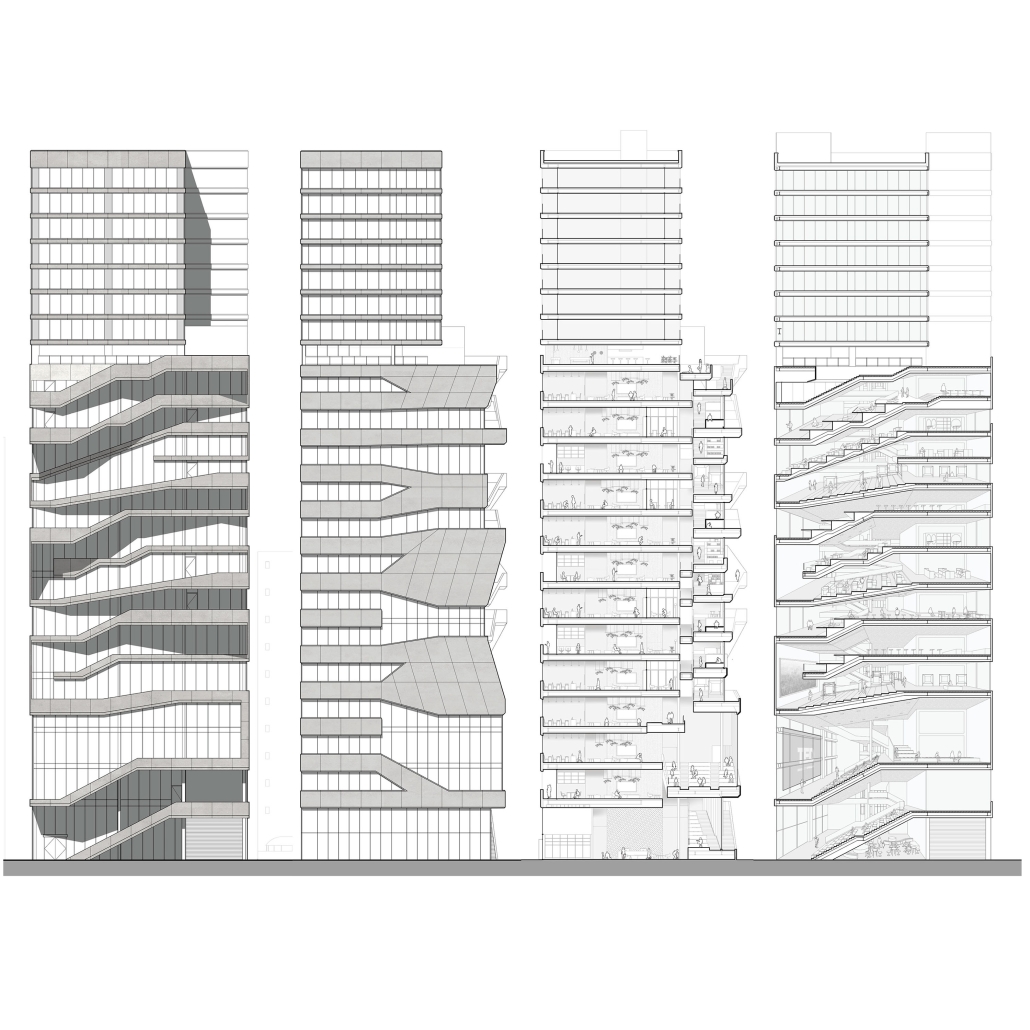
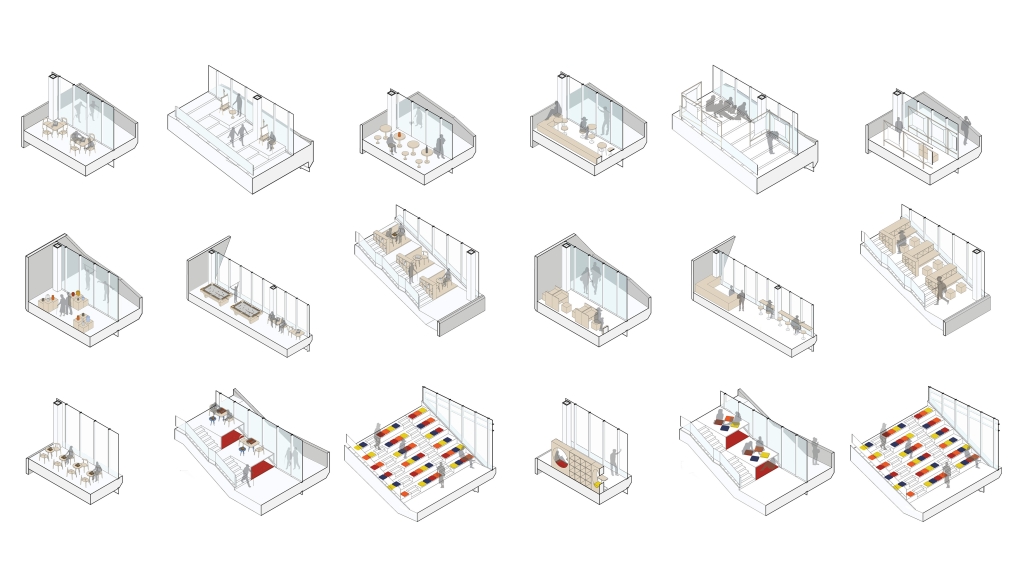
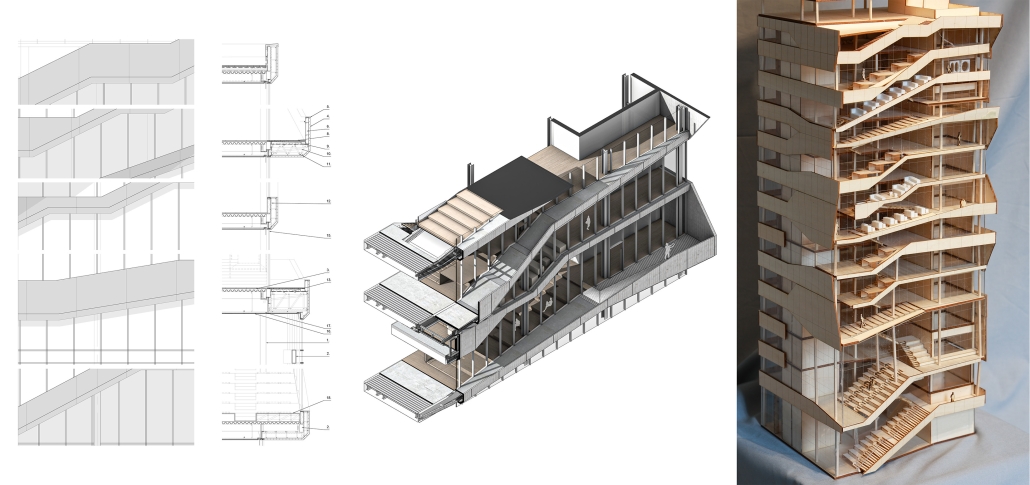
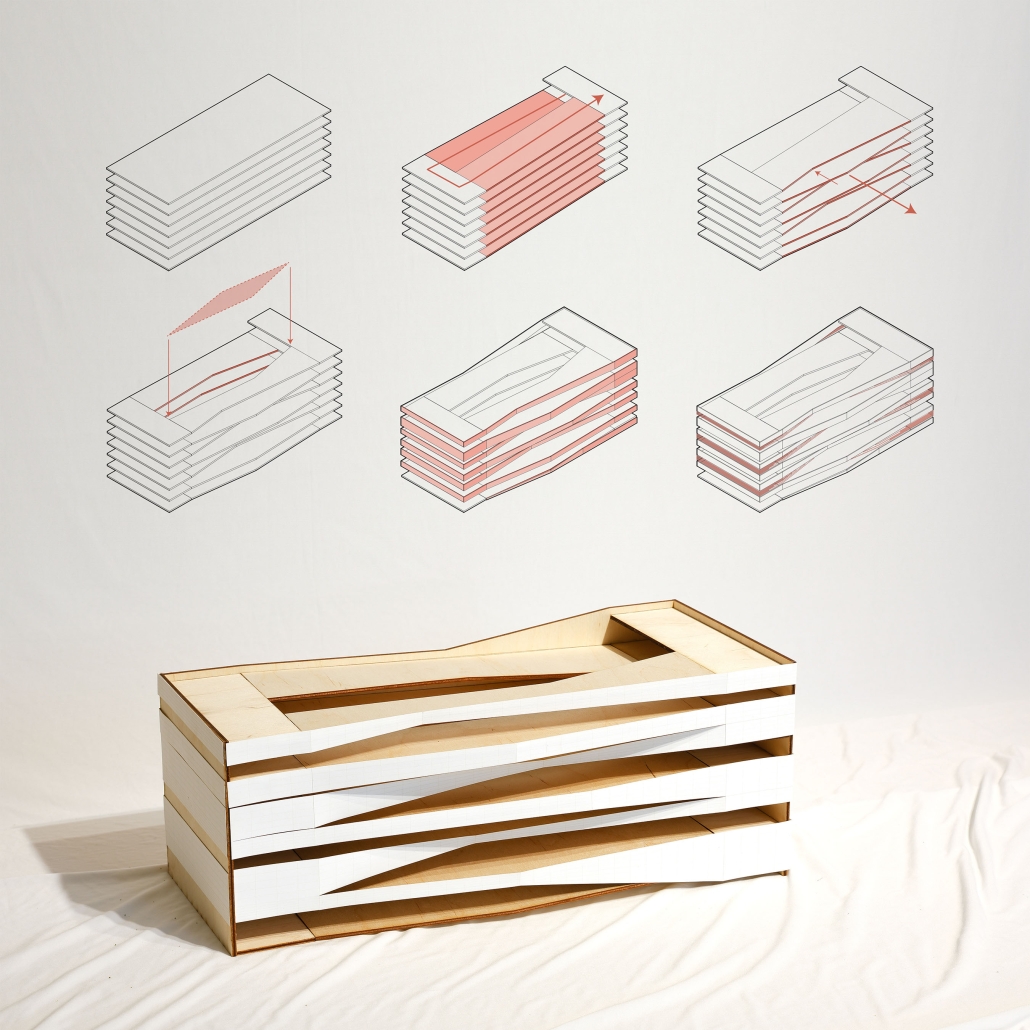
The competitive college entrance process in South Korea has led to the proliferation of Hagwons, after-school private learning institutions. We also observe an emerging trend of commercialized “Study Cafes” in most Hagwon districts. A Study Cafe is a hybrid space between a cafe and a reading room in a library. This project explores a novel integration of Study Cafes into a “vertical school,” maximizing the performance of the cafe space in the context of classroom spaces in Hagwons.
The Study Cafe spaces are all connected as a flow of socialization, like a ribbon. The “social ribbon” is a new vertical school typology featuring vertical and diagonal circulation to encourage social interaction, relaxation, and other diverse activities. This ribbon transforms the Hagwon spaces, creating versatile, programmatic areas that blend the boundaries between levels, including Study Cafes, mini libraries, lounges, and galleries. Accessible from the ground to all levels, the ribbon offers students the freedom to engage in collaborative or private activities, easing the stress of their daily routines. The verticality is designed to provide efficient and diverse behaviors, not only as places but also as means of circulation.
Additionally, the ribbon incorporates a series of angled and protruding balconies that provide outdoor space and shade, enhancing the building’s performance. This design gesture is highlighted on the north façade, serving as a prominent feature that activates both the building’s interior and exterior.
Instagram: @ubuffaloarchplan
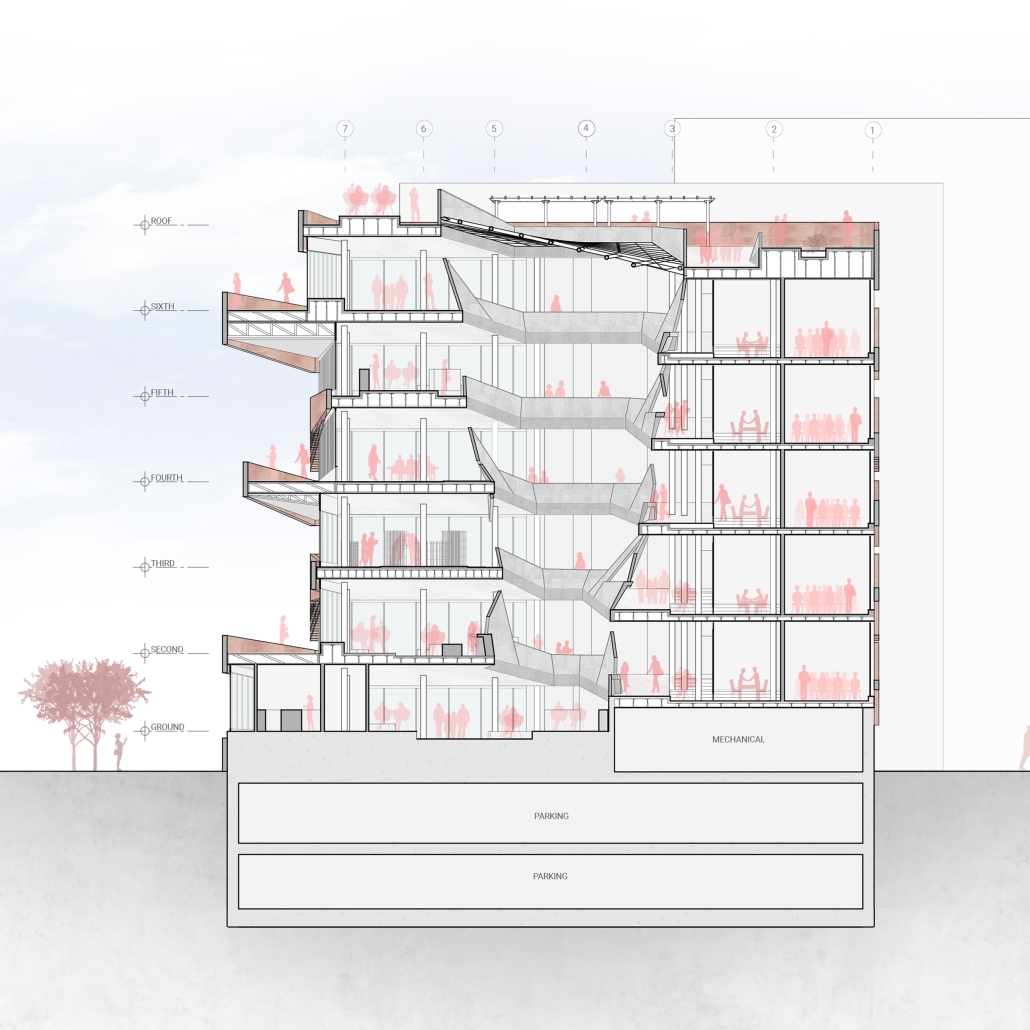
Hagwon On The Move by Toni Vargas, Omar Ibrahim & Staci Tubiolo, M. Arch ’24
University at Buffalo | Advisor: Jin Young Song
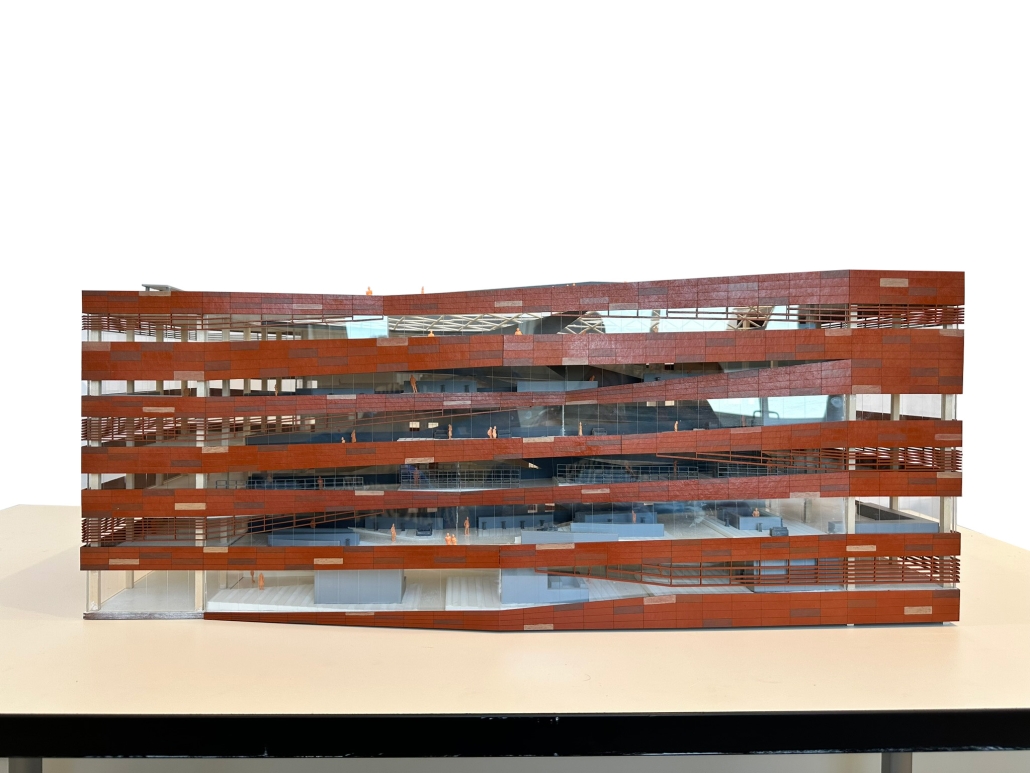
Hagwon On The Move proposes a transformative intervention in the heart of South Korea’s Hagwon (private institutions) culture. We understand that young students have the most interactive, meaningful, and enjoyable social activities ‘before and after’ classes. While the current Hagwon culture focuses on efficient learning, the architecture lacks the sense of a ‘place’ to linger. We aim to extend this particular ‘before and after’ class time as much as possible. Through an extended walking experience within the building, the project redefines the traditional private cram school experience, creating a vibrant, inclusive learning environment for students of all ages.
The building emphasizes the social and physical benefits of walking, inviting users to explore its 7-story structure via a moderate 1:25 continuous ramp. While the north-facing side of the building is reserved for efficient learning spaces, the south-facing side is highly dynamic, accommodating various programs including flexible studying spaces, a library, and activity lounges.
Ascending to the open roof, users are treated to engaging views across the building through a central atrium, transforming the walking experience into a spectacle. The constant change in the angle at which the floor slabs meet the façade introduces double-height balcony spaces, reconnecting users with nature. This shifting, angular design is clad in terracotta panels that mirror the fluidity of the ramp behind and provide shade and thermal comfort. Additionally, terracotta baguettes extend underneath the panels to provide extra shading where needed.
Hagwon on the Move offers students the opportunity to engage with their peers and surroundings in a dynamic setting that contrasts with traditional education spaces. Embracing innovation and community, the project is poised to re-evaluate the learning experience in vertical spaces.
Instagram: @ubuffaloarchplan
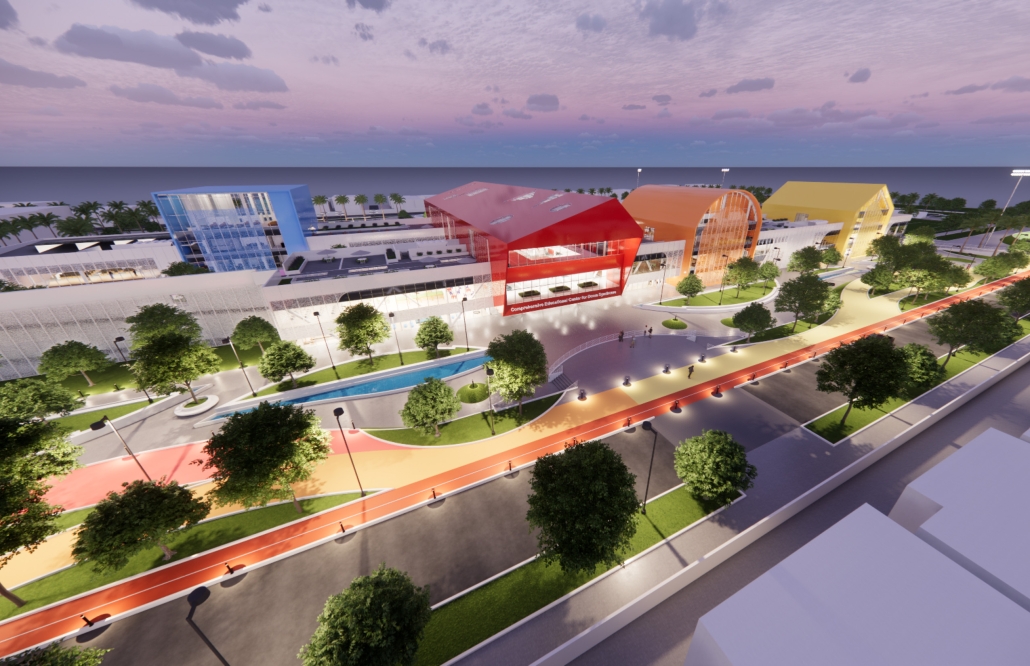
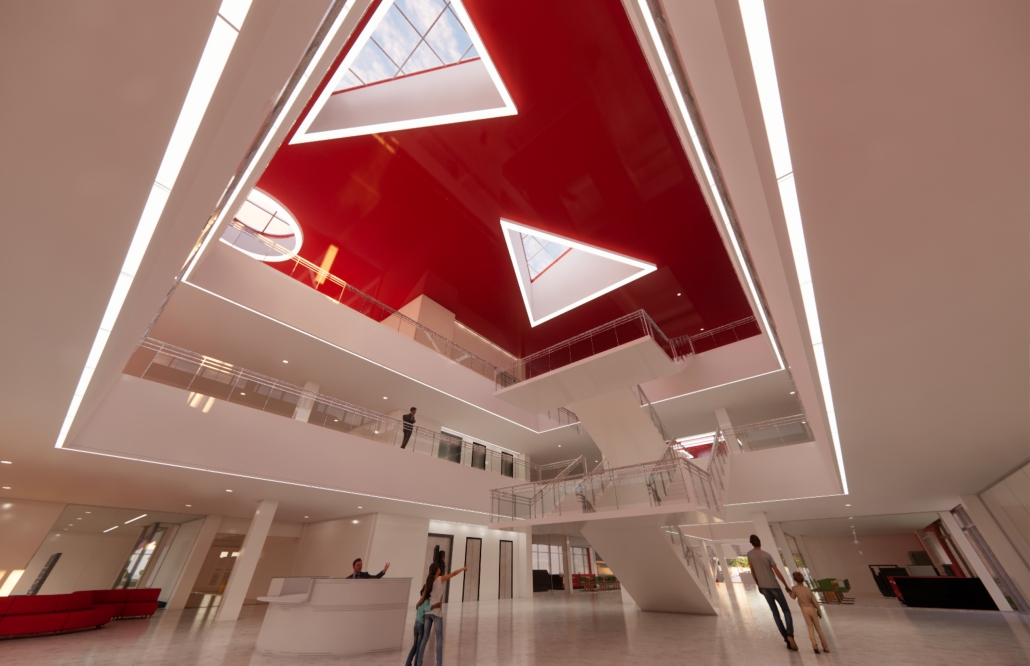
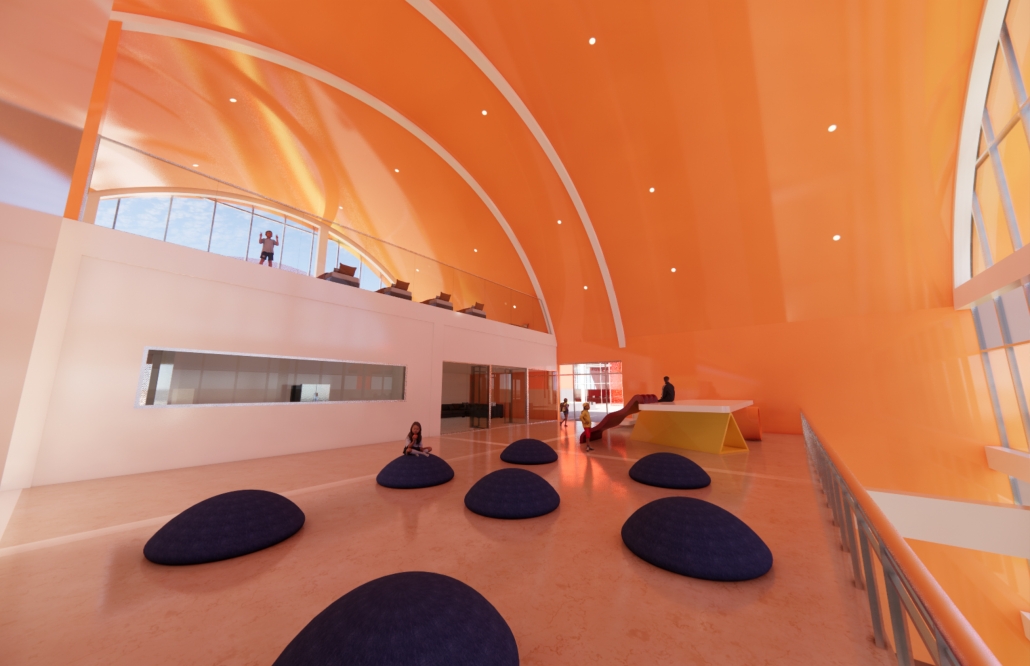
Down Syndrome: A Path to Independence by Luis D. Maldonado-Albertorio, B. Arch ’24
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisors: Pedro A. Rosario-Torres, Juan C. Santiago-Colón & Manuel De Lemos-Zuazaga
Down Syndrome is a condition observed in different parts of the world, and people with this condition are often perceived as incapable of doing what a neurotypical person would do. However, in many cases, these individuals do not achieve independence because appropriate approaches for their integration into society are not adopted. There is a mistaken belief that a simple program will solve their problems. People with Down Syndrome may have intellectual disabilities, motor difficulties, and some distinctive features in their bodies, but this does not mean they cannot improve and advance toward a successful life. It is crucial to work with them from an early age to achieve great results in adulthood.
The project proposes an idea where architecture performs a central role in creating a space specifically designed for people with Down Syndrome to learn and progress towards an independent life.
The architectural proposal is located in Puerto Rico, in the city of Ponce, at a site that is currently an incomplete and abandoned sports complex. This represents an opportunity not only to improve and develop a master plan for the complex but also to implement an educational proposal for children with Down Syndrome. Being located in an existing sports area, the project will help improve the users’ motor skills and allow for the “Special Olympics” to take place for this community, fostering an exchange of experiences and learning between neurotypical individuals and children with Down Syndrome.
From an architectural perspective, the idea is to implement ludic areas that will make learning efficient and enjoyable, helping to improve both mental and motor aspects. Additionally, various programs specifically designed for these users are implemented, such as the simulation of a home, located in volumes of geometric shapes. These colorful geometric shapes aim to help the users clearly identify different spaces.
Instagram: @daniel_albertorio30
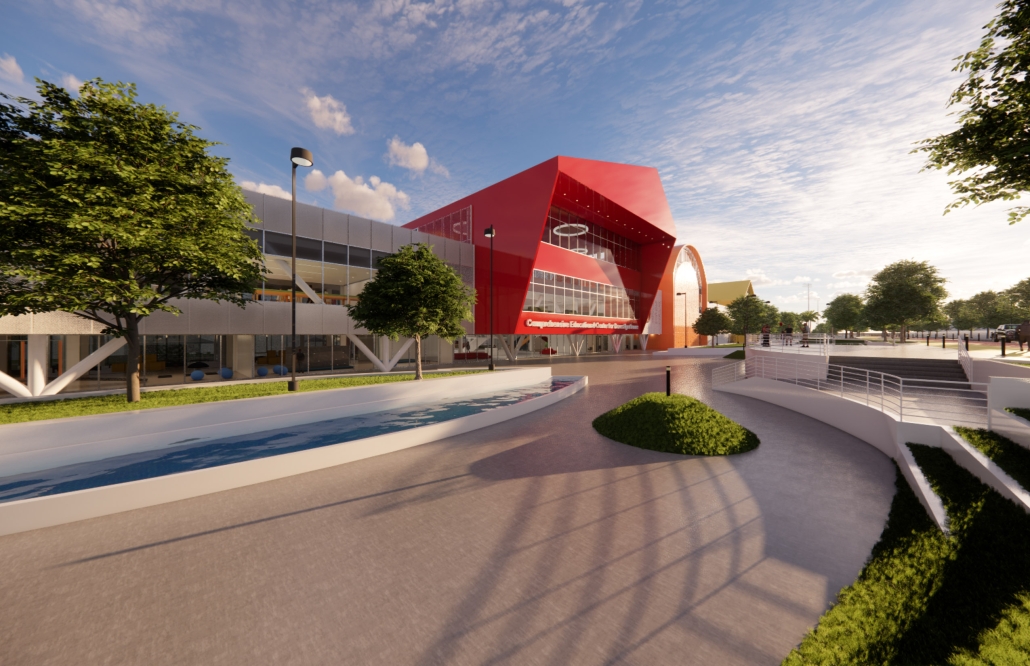
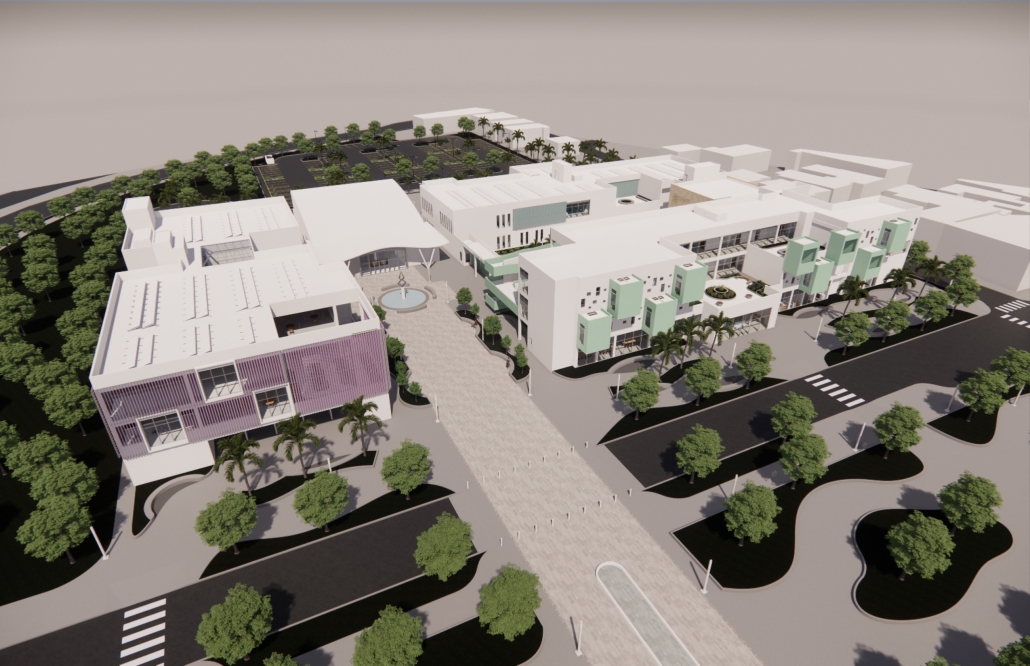
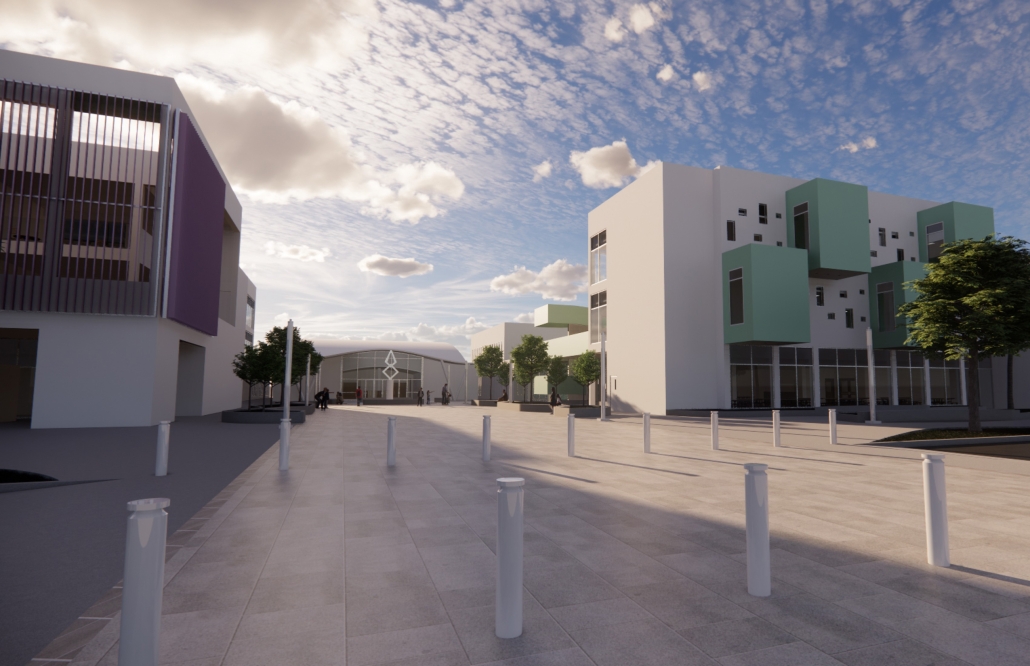
Architecture for Autism Spectrum Disorder: In Search of Social Integration for People with ASD by Jorelma Alfaro-Padilla, B. Arch ’24
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico |Advisors: Pedro A. Rosario-Torres, Juan C. Santiago-Colón & Manuel De Lemos-Zuazaga
Over the years, statistical studies have demonstrated the exponential increase in diagnoses and prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) globally. This is a lifelong condition implying that each diagnosed individual receives personalized treatment, and it is primarily characterized by its impact on individuals’ communication skills. With the growth of this community, the need for spaces that foster the social integration of the autistic community with the neurotypical population has become more apparent. Although the autistic community must be fully attended to, early diagnosis and care allow for the identification of strategies and the insertion of individuals with the condition into environments that enable full development adjusted to their abilities. In this context, architecture becomes a tool for designing spaces that meet the needs of autistic users, such as through the use of sensory design theory, allowing for spaces that promote the social integration of these users.
This architectural proposal is located in the town of Caguas, Puerto Rico, on a lot adjacent to a cluster of existing schools. The proposal comprises a set of structures subdivided according to their use: education, treatment, and integration; leading to the creation of five structures: an amphitheater, a treatment center, a K-12 school, a gymnasium, and a school of fine arts. The placement of these structures seeks the social integration of the autistic community through the creation of a connecting axis that facilitates the creation of spaces for interaction between school communities through urban spaces, as well as the interaction of neurotypical and autistic school communities in the fine arts program. As part of the educational program, the implementation of retreat spaces in classrooms for autistic students was considered, so that in the event of overstimulation or lack of stimuli, they can take a moment to recompose themselves and use a space that, in addition to being designed for their needs, becomes an element for the façade design of the K-12 school. Additionally, the structures feature sensory gardens which, together with the vegetation, provide an outdoor retreat space and an area for social interaction. Architecture, in these respects, becomes a mediator for the social integration of autistic users, enabling interactions among users.
Instagram: @jorelma_a
Stay tuned for Part III!