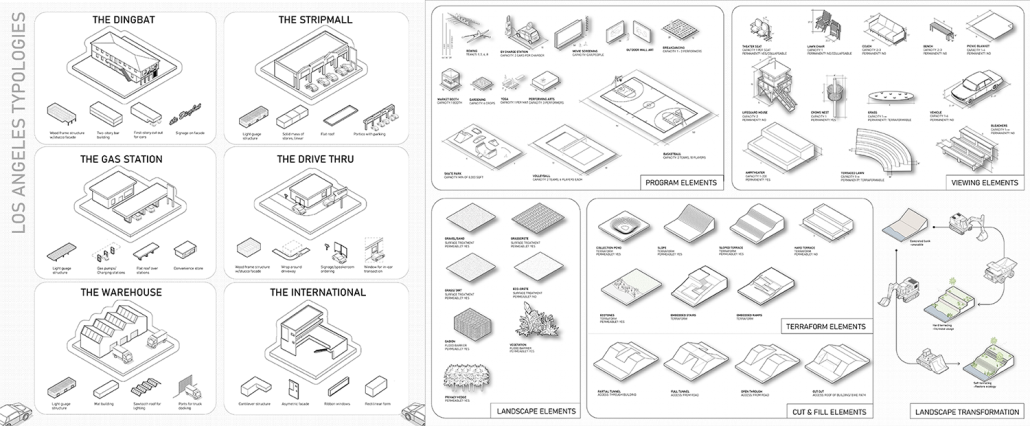
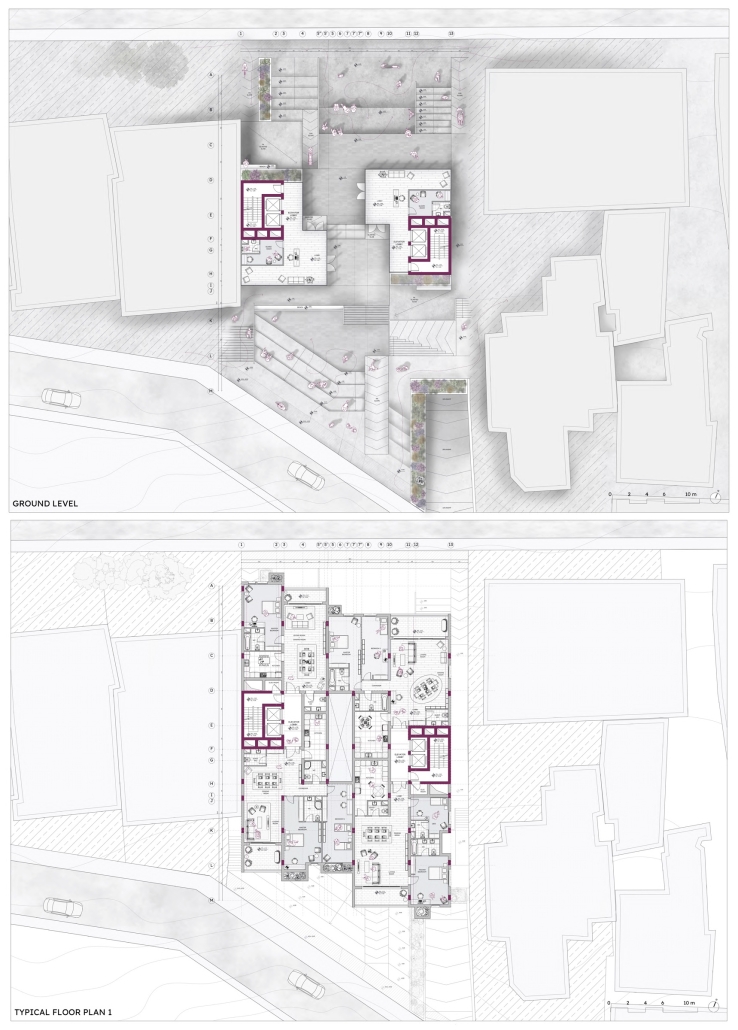
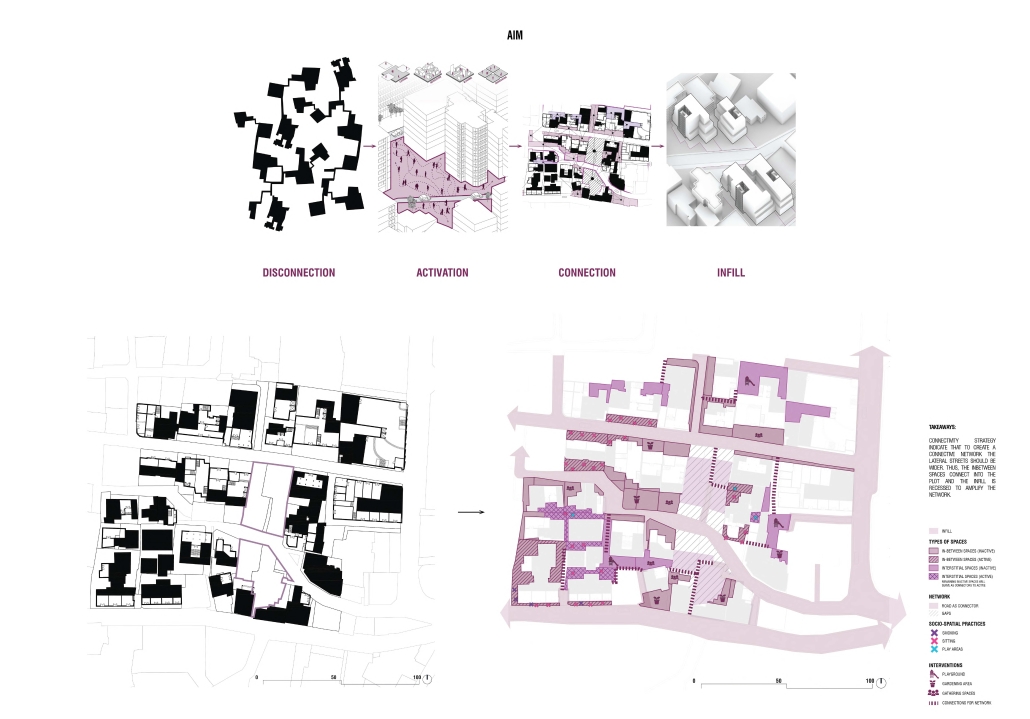
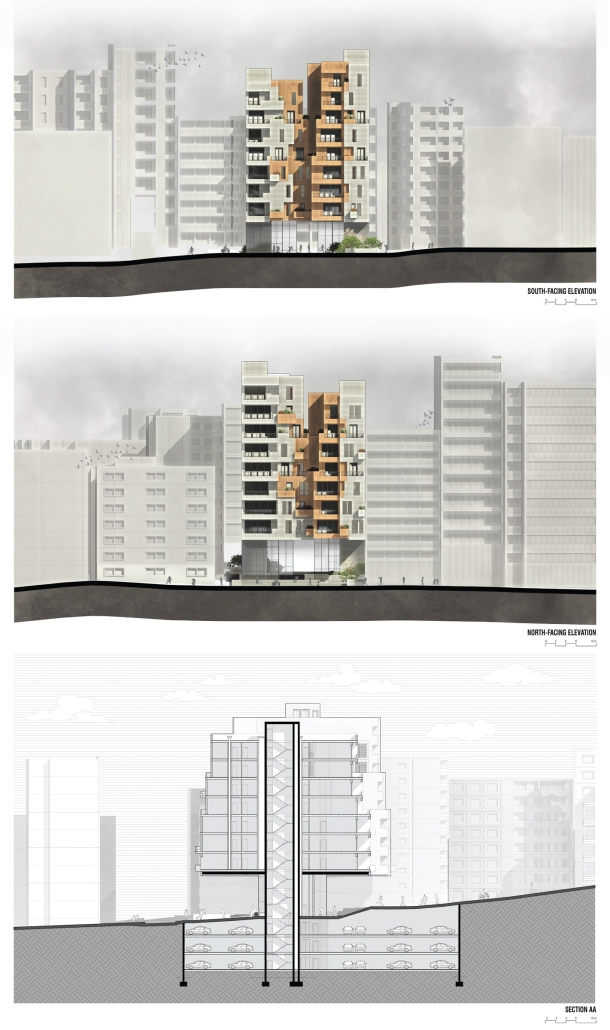
2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XIV
Architecture plays a large role in the restoration and preservation of buildings. The projects featured in Part XIV of the 2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase focus on revitalizing spaces.
Today, we look at various sites, including areas impacted by natural disasters, former industrial zones, federal buildings, and more. Each project blends old and new, demonstrating the ability to recover and reclaim using architecture and design.
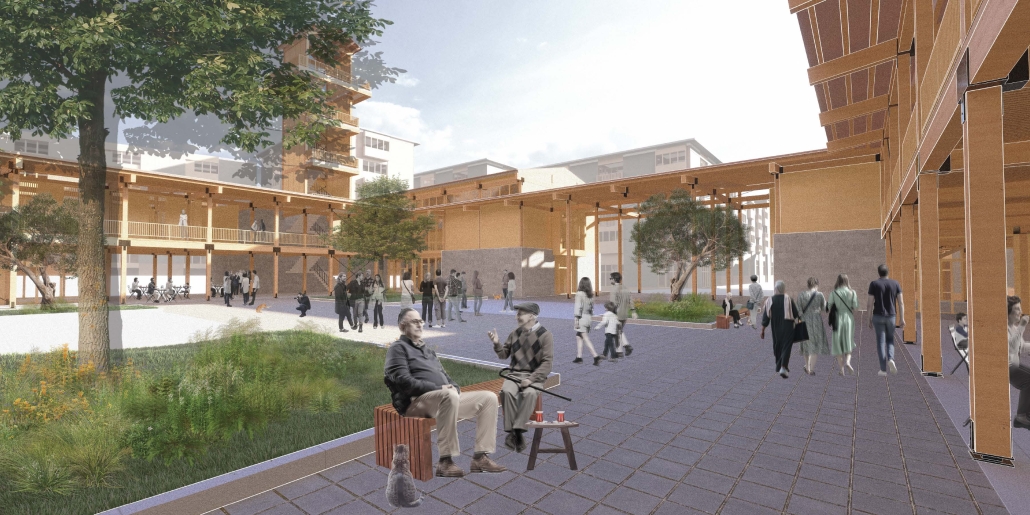
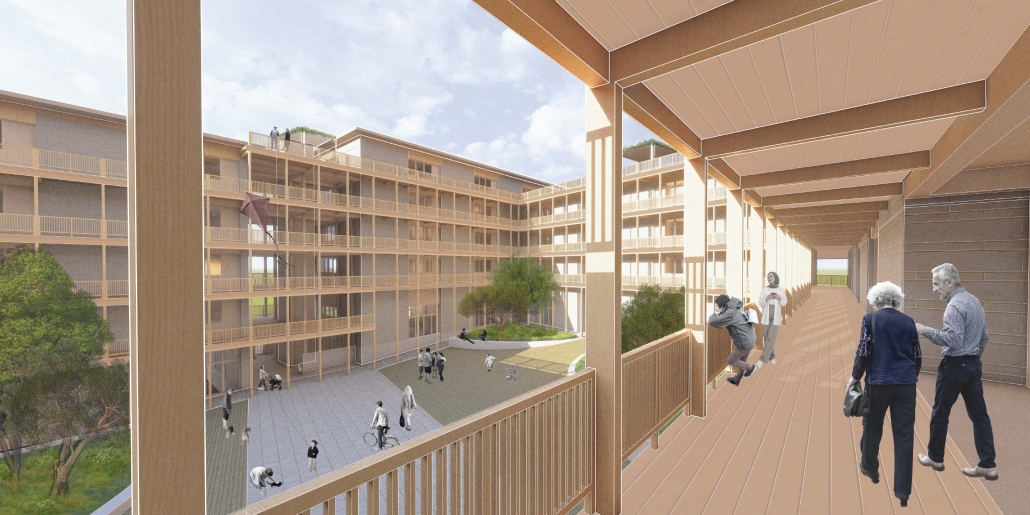
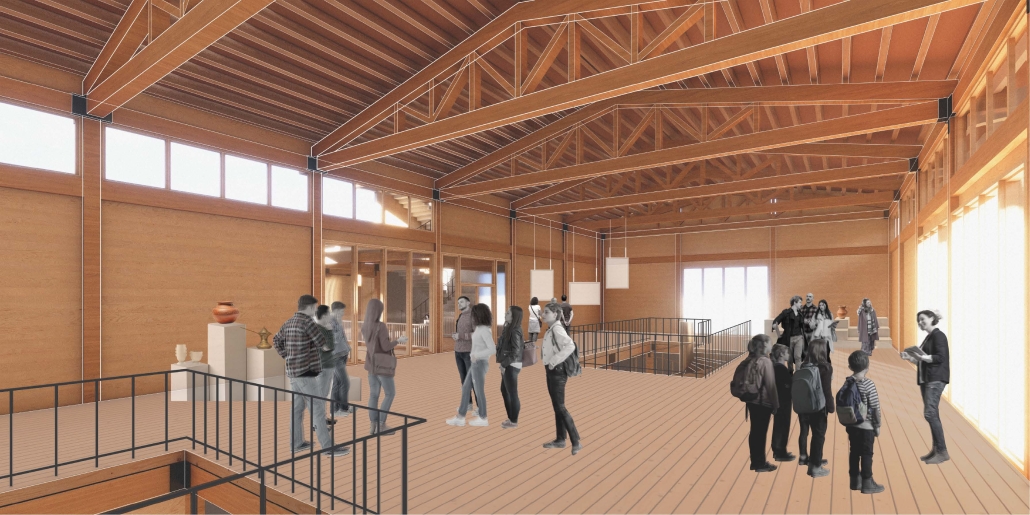
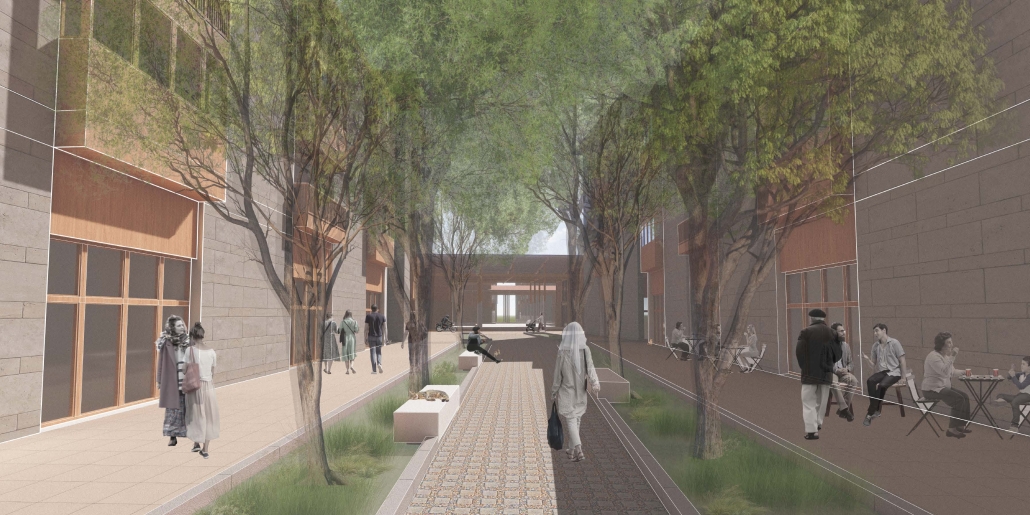
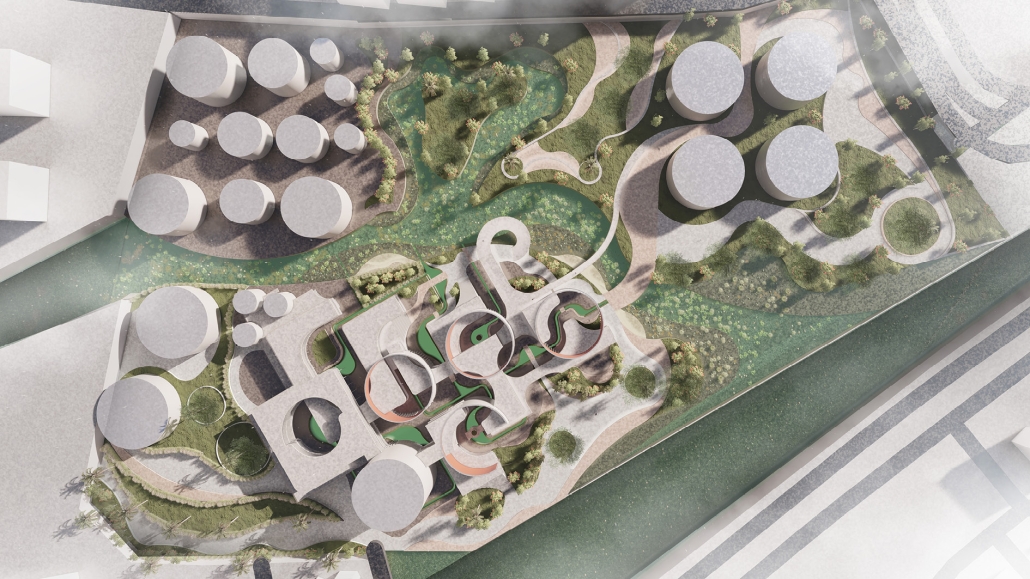
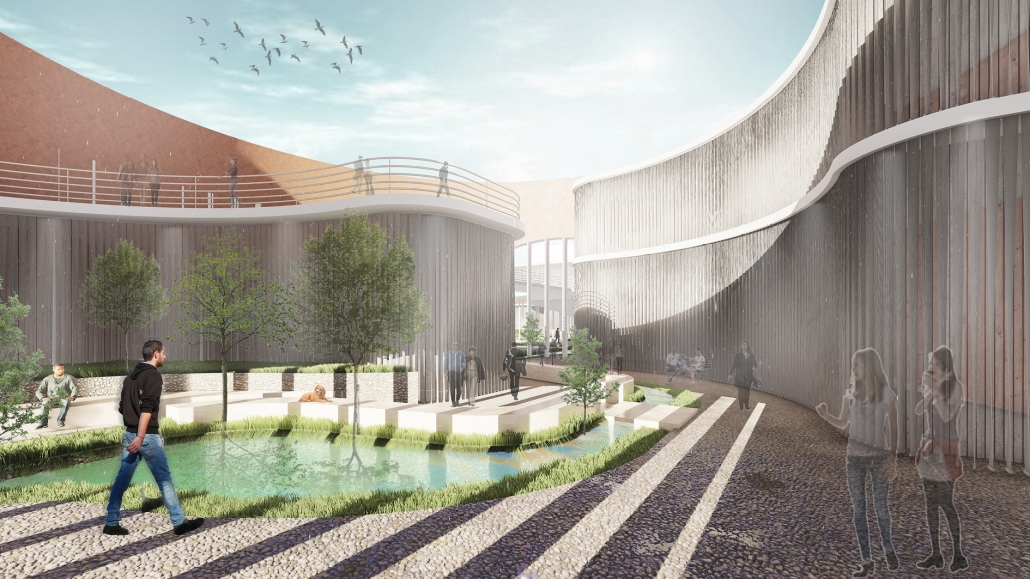
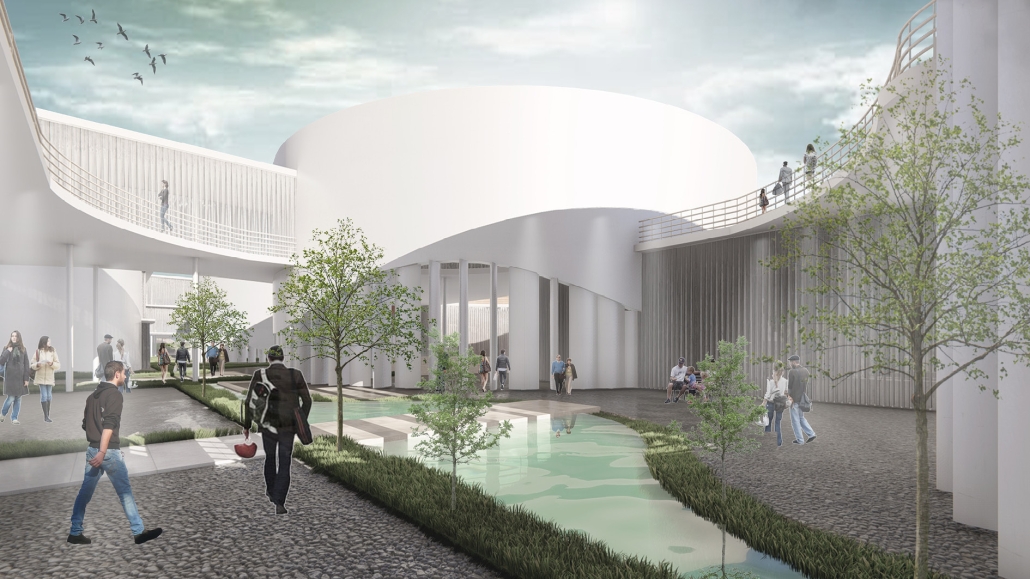
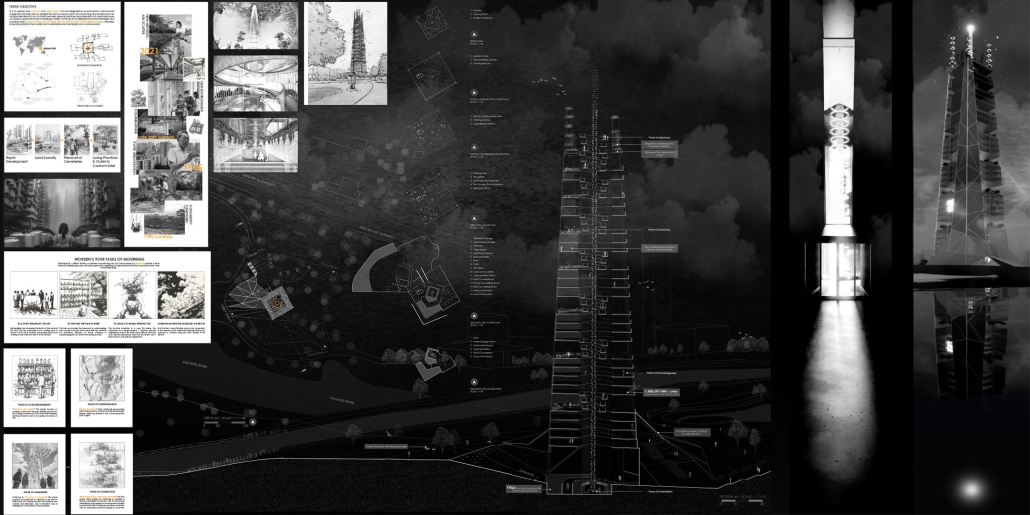
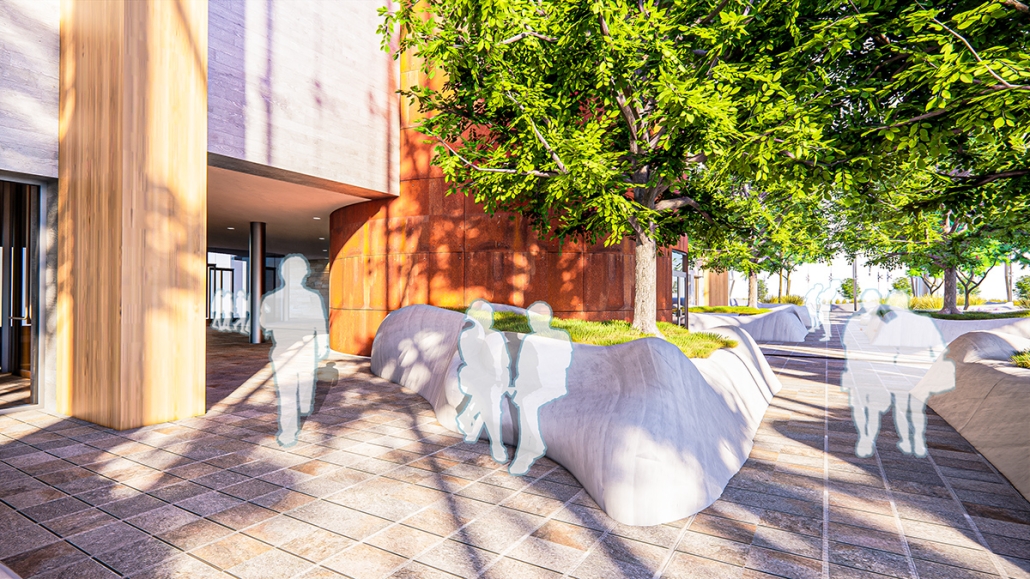
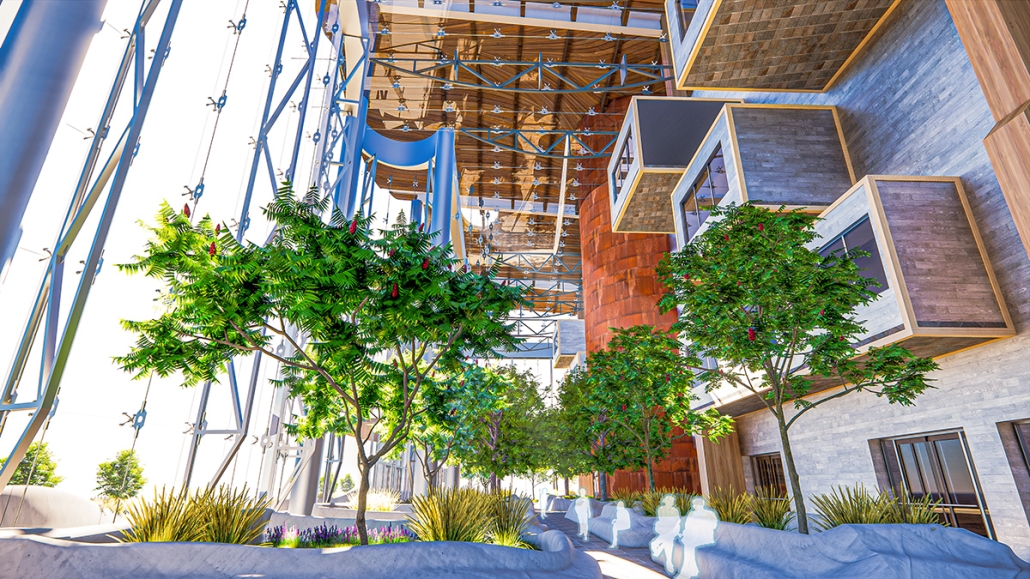
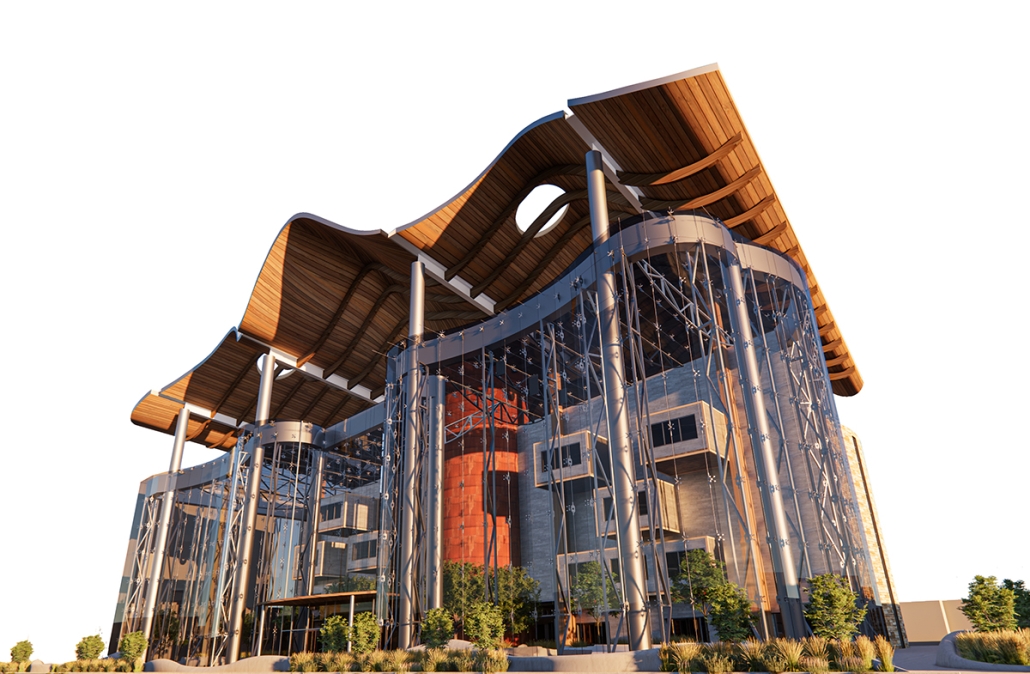
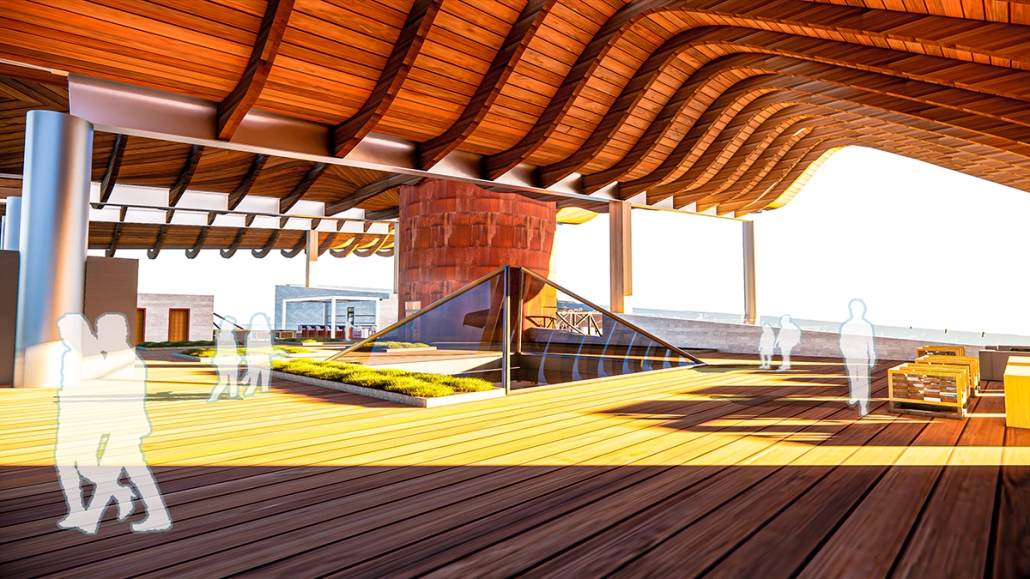
Reclaiming Antakya: Post Disaster Community Recovery for Resilient Futures by Zeynep Dila Demircan, M. Arch ‘24
University of Maryland | Advisor: Ken Filler
The earthquakes that struck Southwestern Turkey and Northern Syria in February 2023 caused extensive damage, ranking among Turkey’s worst disasters in its history. The city of Antakya, especially, suffered severe destruction in its center, resulting in significant losses of lives, culture, and history.
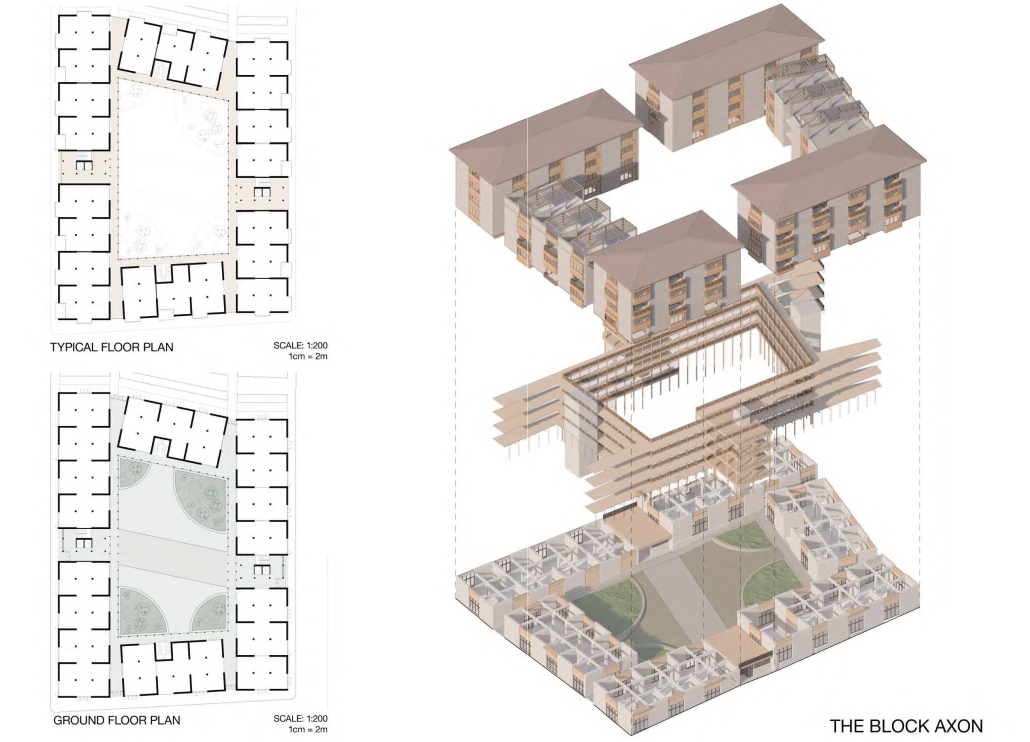
This thesis presents a comprehensive plan to recover and reclaim Antakya’s center, enhancing community resilience through proactive design strategies. It focuses on a specific urban block, a key commercial, residential, and administrative hub across the Asi River and the historical district. The proposal outlines a multi-phased approach to transform this urban block, starting from the post-disaster period and concluding with its complete redevelopment. The phases include recovery, reclamation, reconstruction, and reconnection.
For the recovery phase, temporary shelter and gathering spaces are provided for residents within the grove area existing on the site, while efforts to engage stakeholders in the recovery process begin. Reclamation involves reforming the cleared area based on existing and new street systems, integrating new public streets and courtyards that make up the green infrastructure. Reconstruction involves rebuilding the site in smaller blocks, starting from the middle section and expanding to the upper and lower sections. The reconnection phase focuses on finalizing building blocks and reintegrating them into the larger context.
This includes the creation of a new urban plaza and the introduction of programs aimed at fostering cultural and social resilience, as well as commemorating the earthquake through a memorial space within a community center. The proposal introduces two main building types: The Block, a mixed-use structure with a courtyard for residents, and The Hub, a community center featuring public spaces, a museum, gathering areas, and studios for local crafts practices.
In essence, this thesis aims to not only reconstruct Antakya’s physical infrastructure but also to cultivate resilient communities through place-making strategies. It endeavors to revitalize cultural and social life while fostering trust and collaboration, ultimately laying the groundwork for a robust and resilient future.
This project won the UMD Architecture Thesis – Director’s Award and the ARCC 2023-2024 King Student Medal for Excellence in Architectural + Environmental Design Research.
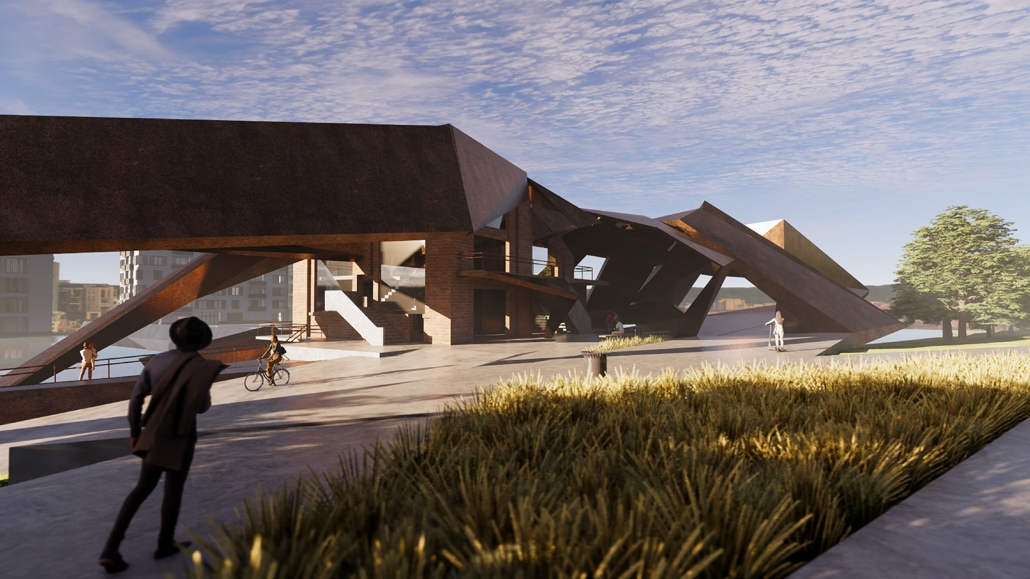
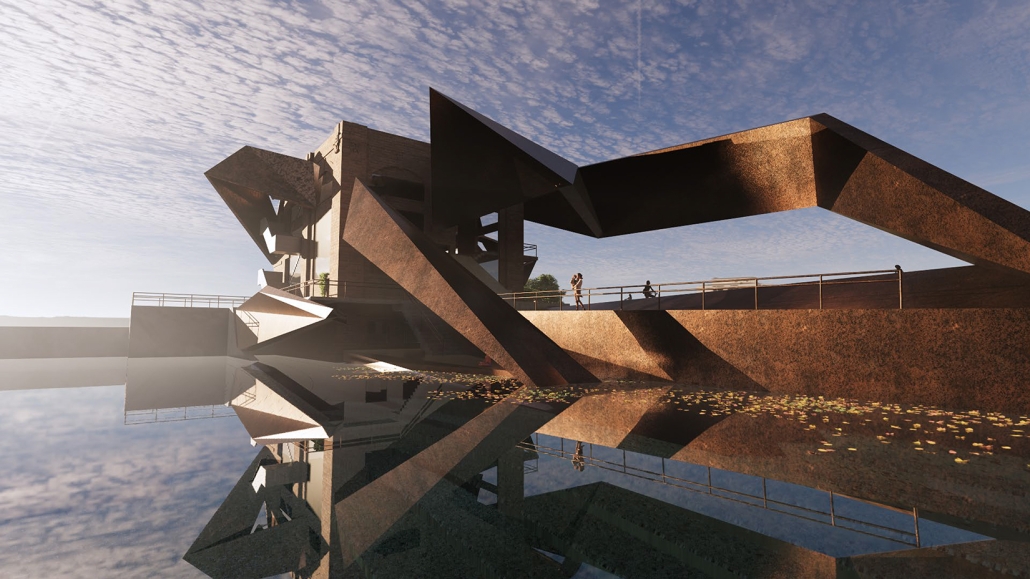
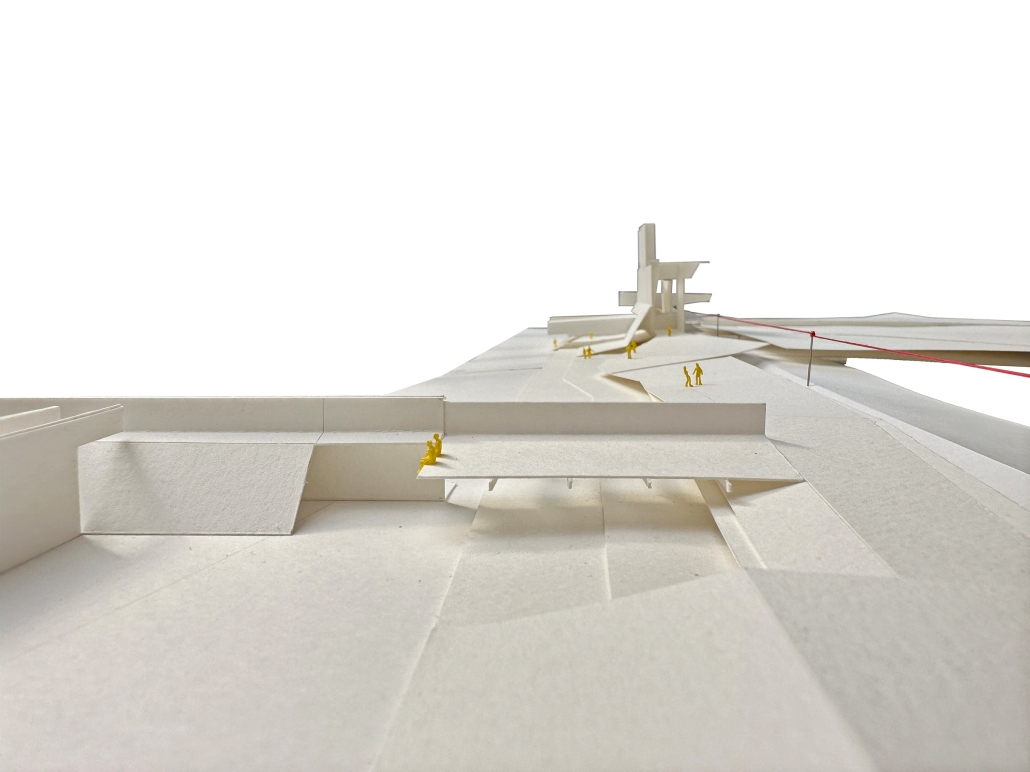
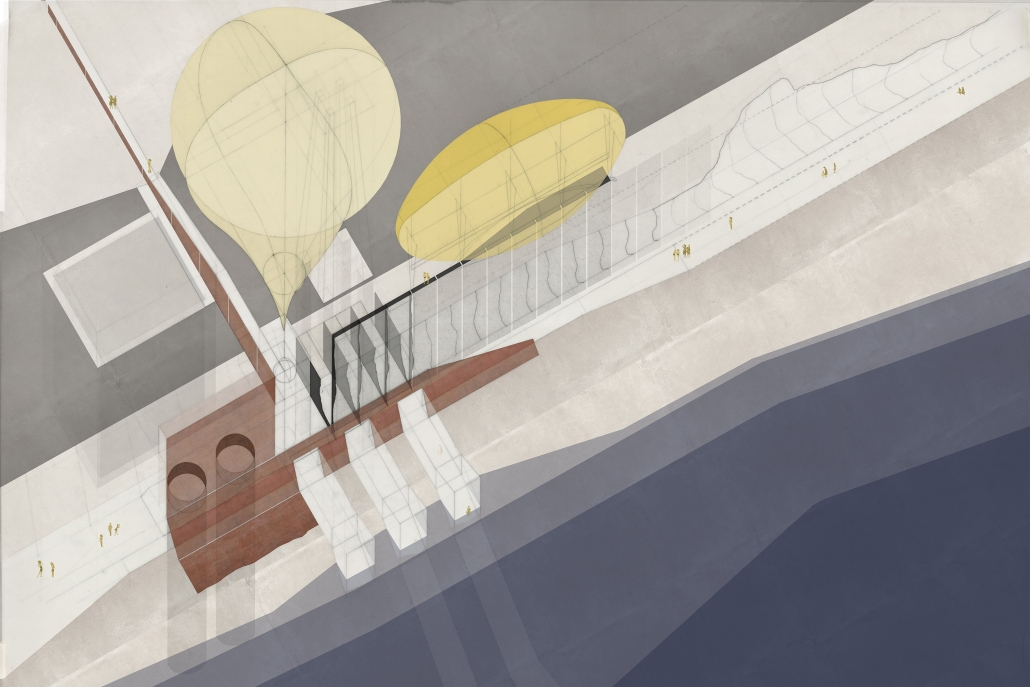
The Topographical Reactivation by Yanbo Zhu, M. Arch ’24
University of Waterloo | Advisors: Mohamad Araji & Shiyu Wei
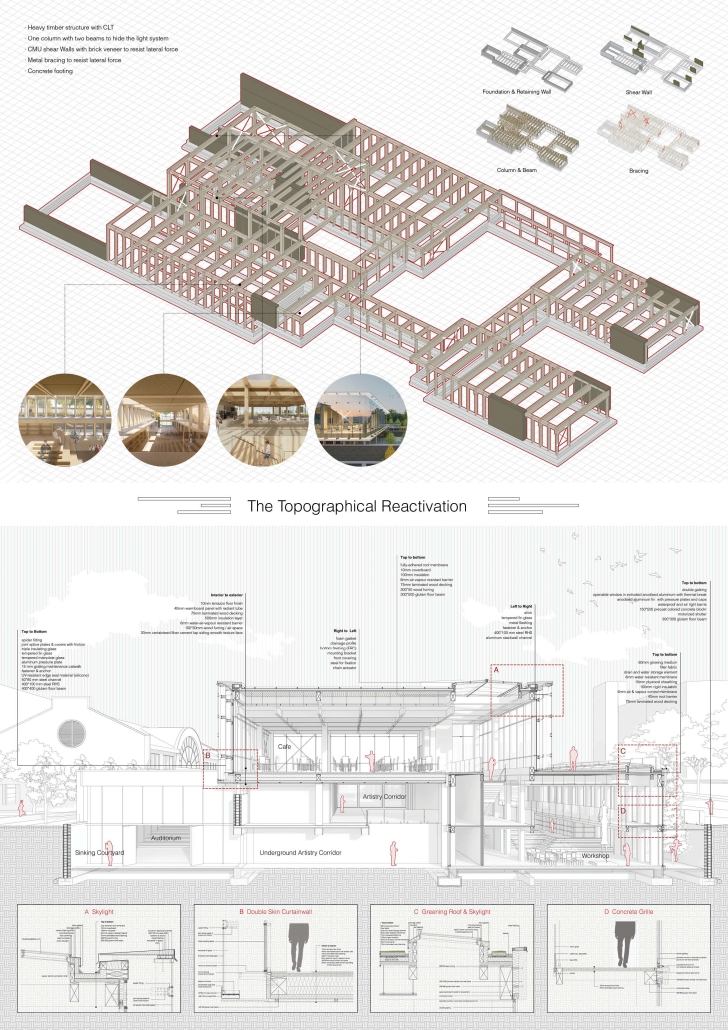
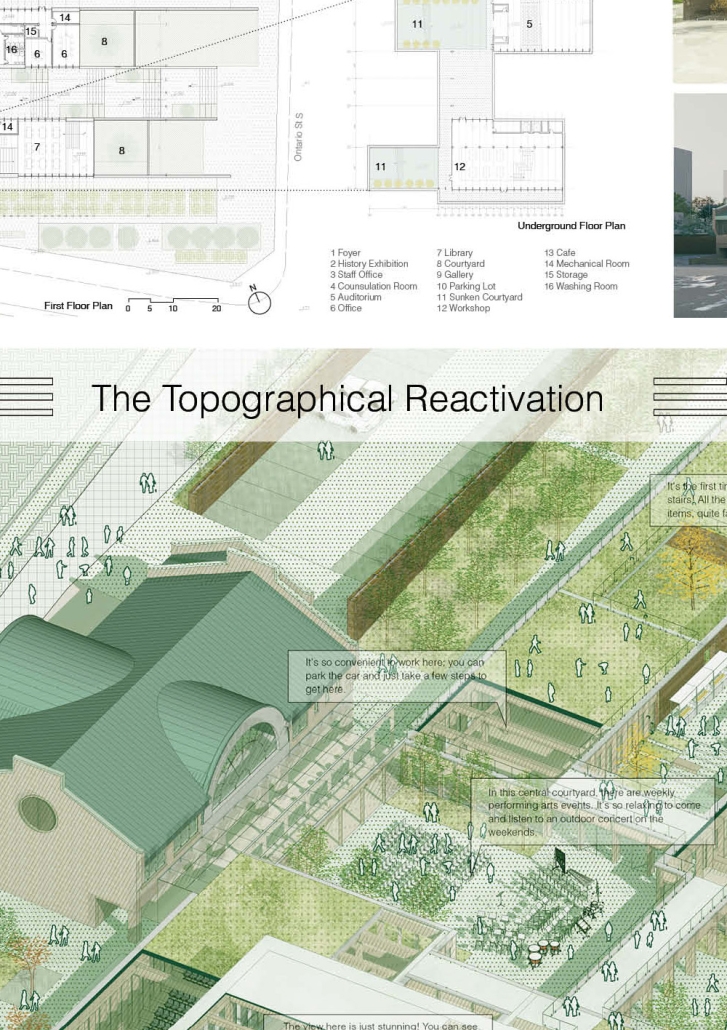
Community Center Design at Kitchener
This design features three keywords: nature, history, and topography.
- NATURE: The site is located in the center of Kitchener, with the expansive Victoria Park to the south. However, due to roadways and parking areas interrupting the flow, it’s challenging for this landscape to permeate the site effectively. Simultaneously, with a site area of 15,000 square meters and a required building area of only 1,500 square meters according to the project brief, the strategy involves integrating small-scale structures with the landscape to address the issue of the site’s excessive scale.
- HISTORY: Within the site, there is an abandoned Charles bus terminal, with its main hall building well-preserved, but the historical elements of its platforms, bus lanes, and connecting corridors are poorly maintained. In the design, preserving the original waiting hall while removing other elements yet continuing its multi-linear spatial configuration is a critical historical stance.
- TOPOGRAPHY: On the eastern side of the site, there is an elevation difference of nearly four meters. In the design, a planted roof is utilized to seamlessly connect, allowing individuals to enter the building from the roof. Simultaneously, the height difference is employed to create outdoor stepped activity areas or sloped gardens. Additionally, to respect historical architecture, a partial sunken approach is employed in spaces like the art gallery and lecture hall, forming various topographical experiences.
This project won the Edward Allen BTES Award and the Second Prize SOPREMA Award.
Instagram: @yanbo_zhu
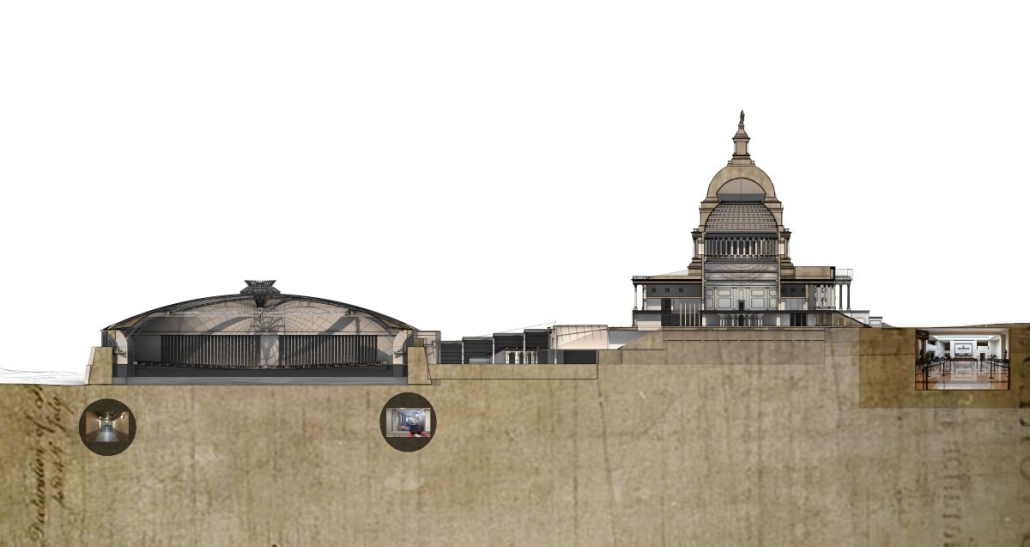
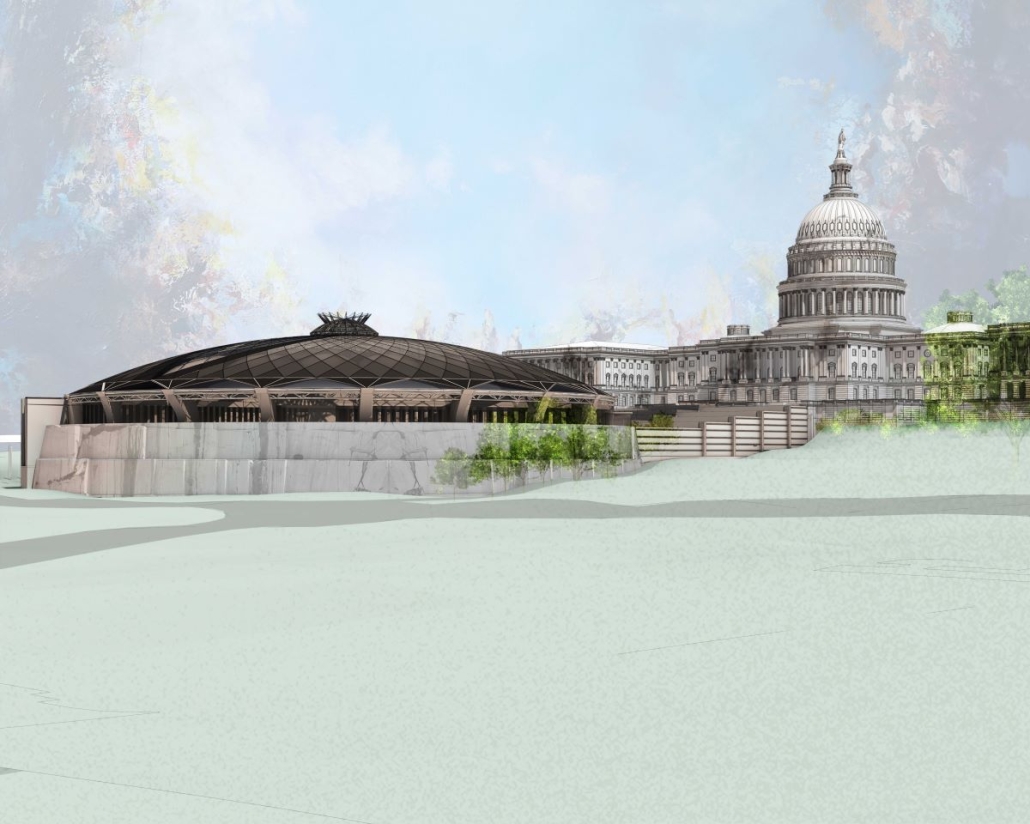
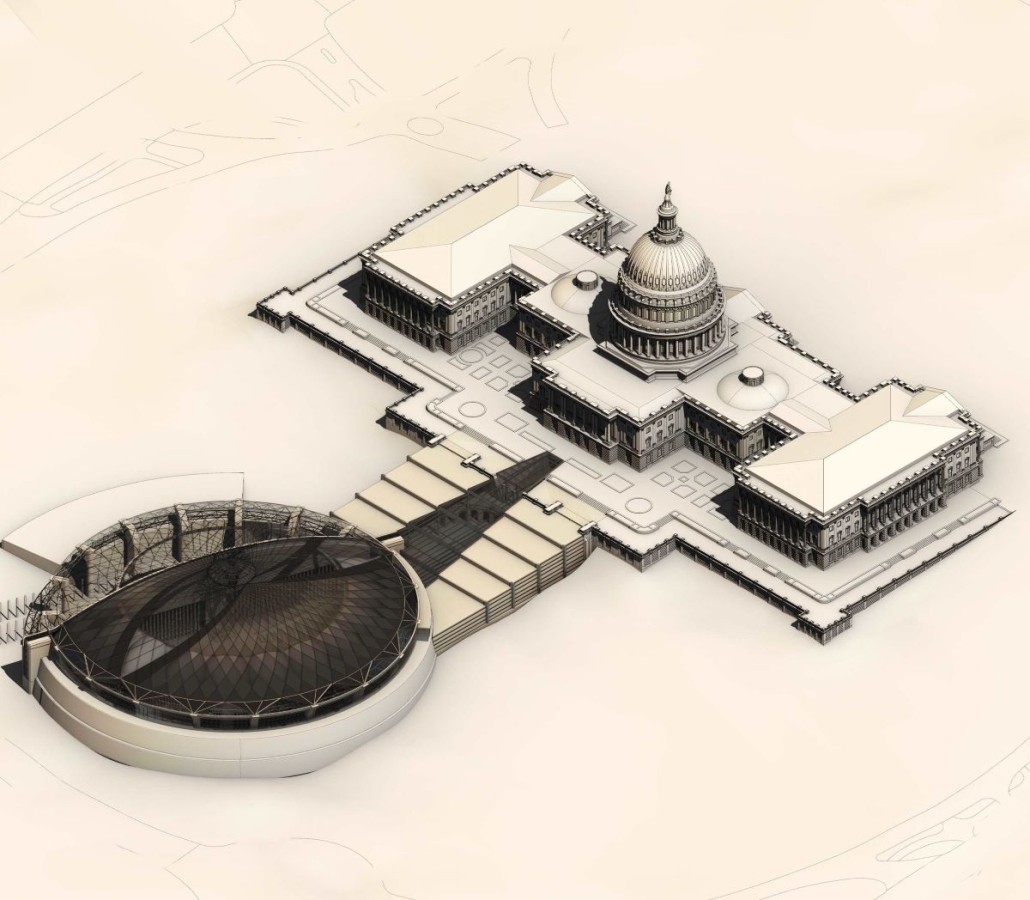
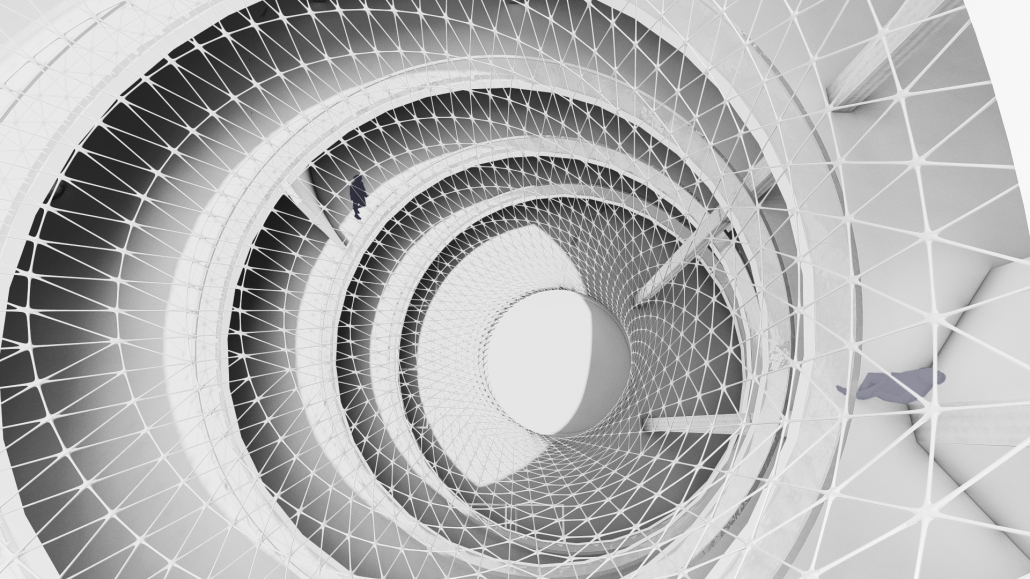
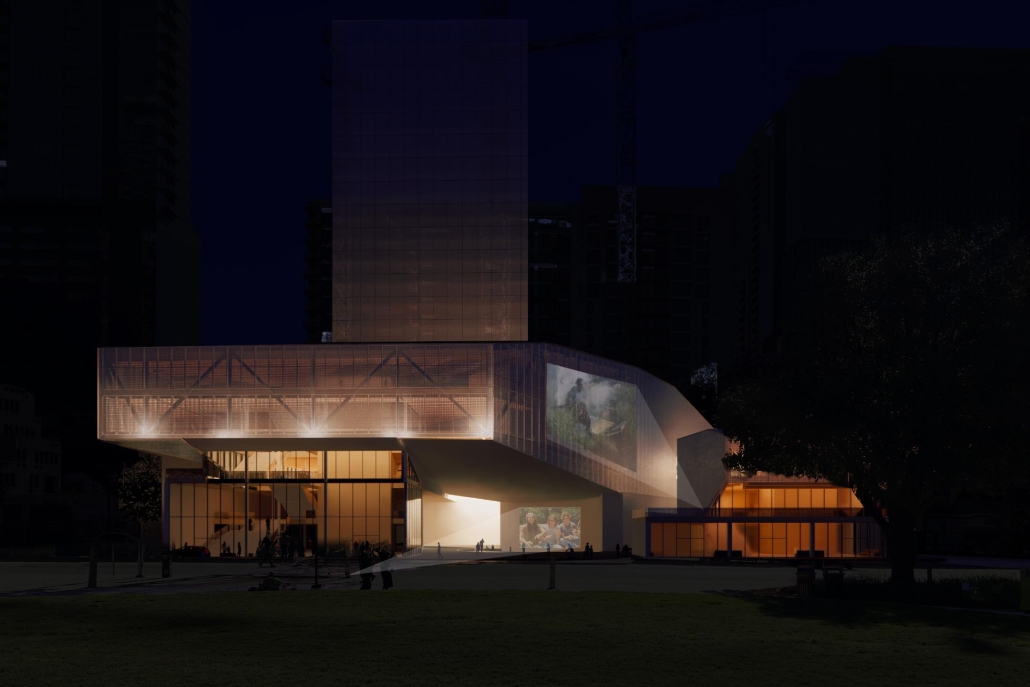
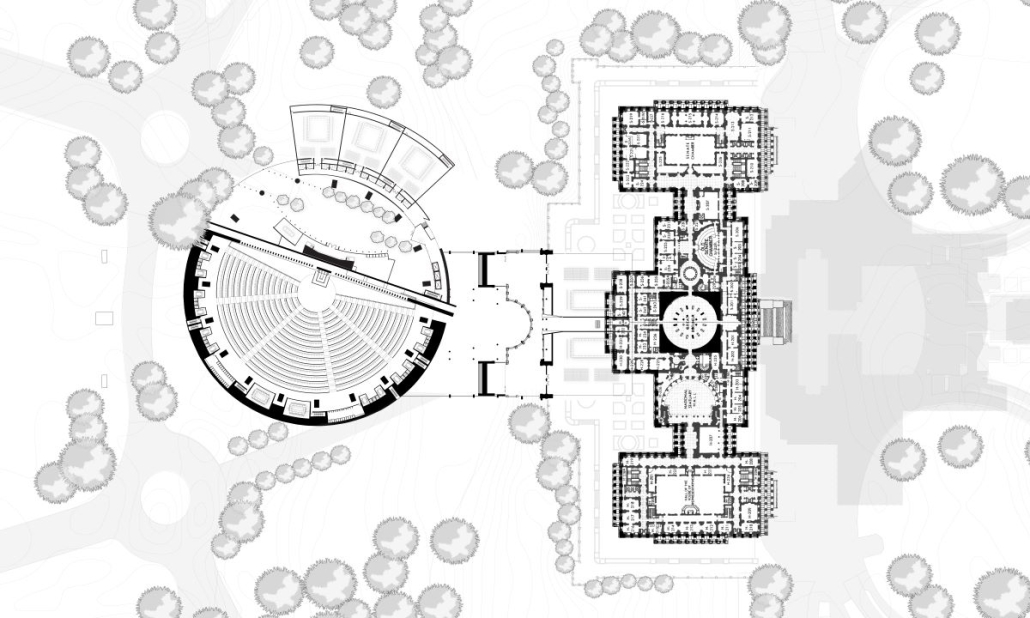
Amending the Capitol by Garrett Krueger, M. Arch ‘24
Virginia Tech | Advisors: Susan Piedmont-Palladino, Paul Emmons & Scott Archer
The United States Capitol Building has long been an iconic symbol of the American government and democracy worldwide. Despite this, the United States has had many major events since 1892, and the Capitol has not had any representation of those events.
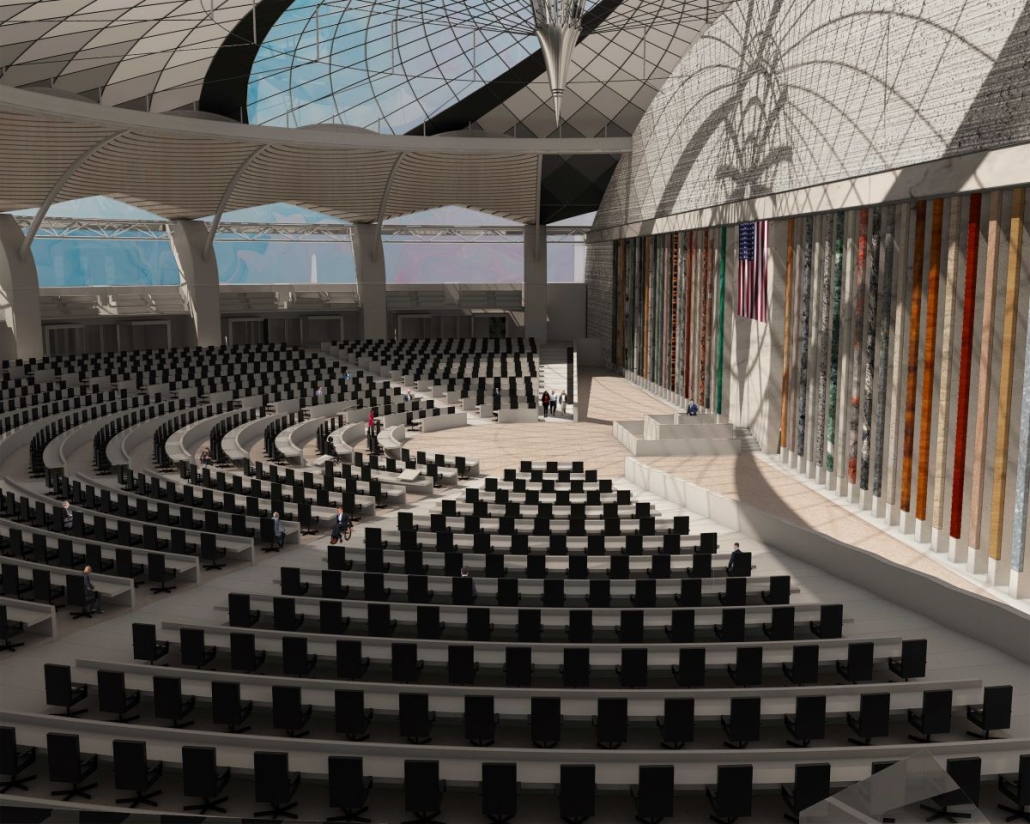
One example of stalled symbols of change is the number of representatives in the House. Since 1913, the House of Representatives in Congress has had 435 representatives, despite the population more than tripling since then. Many have had the idea to increase this number and expand the House. This idea gives an opportunity to design a new, larger chamber for the House to meet in. This thesis proposes a new chamber to redefine the architecture of the Capitol Building and symbolize the century of history that has yet to be represented in the Capitol.
The idea of making a new expansion to the iconic Capitol Building comes with challenges. This thesis was done amid historic turmoil and record lows in productivity in the House. This thesis also begs the question of whether the building that Congress meets in can be part of the solution. The House Chamber, when completed, had no electric lighting, let alone C-SPAN cameras and smartphones in every lawmaker’s pocket. This new extension aims to provide Congress with a workplace designed to address the difficulties it faces in keeping itself in order. As a whole, this thesis is about the idea of representing change. The nature of a democratic government is one of changing ideas and laws, and this project seeks to have the Capitol Building embody that aspect. Thomas Jefferson himself is known for saying rejecting change is like “requiring a man to wear still the coat which fitted him when he was a boy.” Congress needs a new coat.
This project won the WAAC Crystal Award.
Instagram: @vt_waac
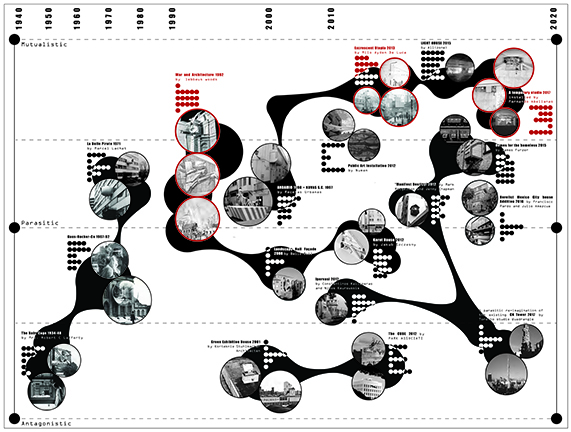
Life, Death, and the Eternal Recurrence of Architecture by Geri Roa Kim & Kelvin Hu, B. Arch ’24
Pratt Institute | Advisors: Adam Elstein, Frank Gesualdi & Ashley Simone
Life, Death, and the Eternal Recurrence of Architecture proposes building anew as a form of preservation. Situated along the Arakawa River Island in Tokyo, this project is a story of a building that has grown over time since 1946. The building undergoes successive replication and revision every few years, each edition is built next to its predecessor, eventually becoming an endless, linear, horizontal skyscraper that constantly reinvents itself through time.
This architectural approach, rooted in preservation, provides a tangible way to experience changes that normally unfold over centuries. Architecture, then, becomes a device to register time.
This project won the Best Degree Project of 2023/2024.
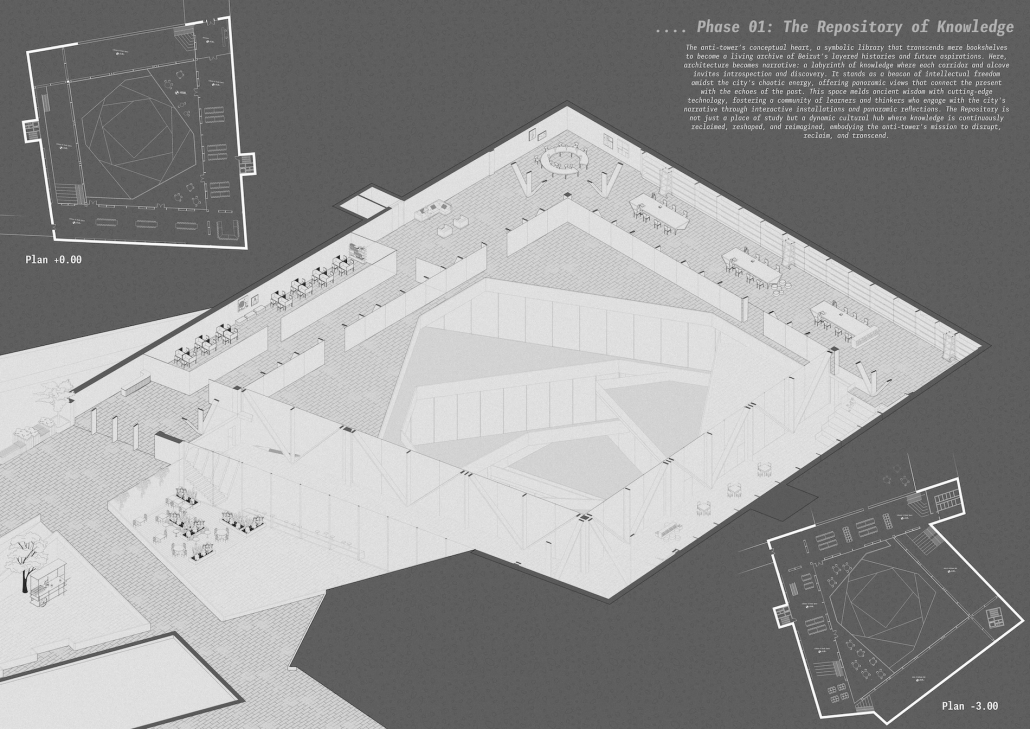
Unbound Beirut: Reimagining Boundaries & Transforming Realities by Sima Fayad, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Makram Al Kadi
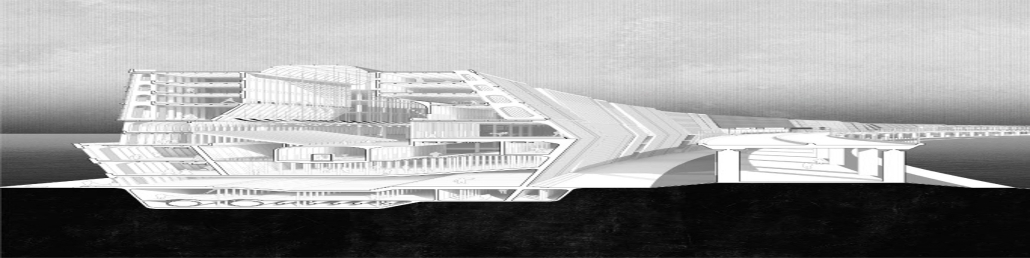
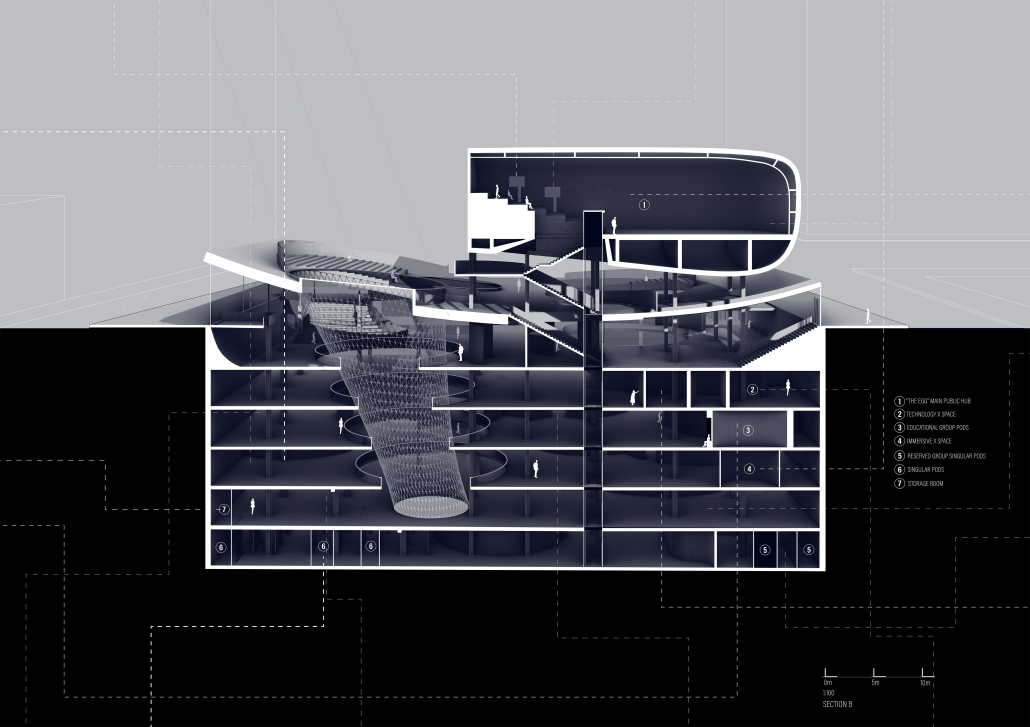
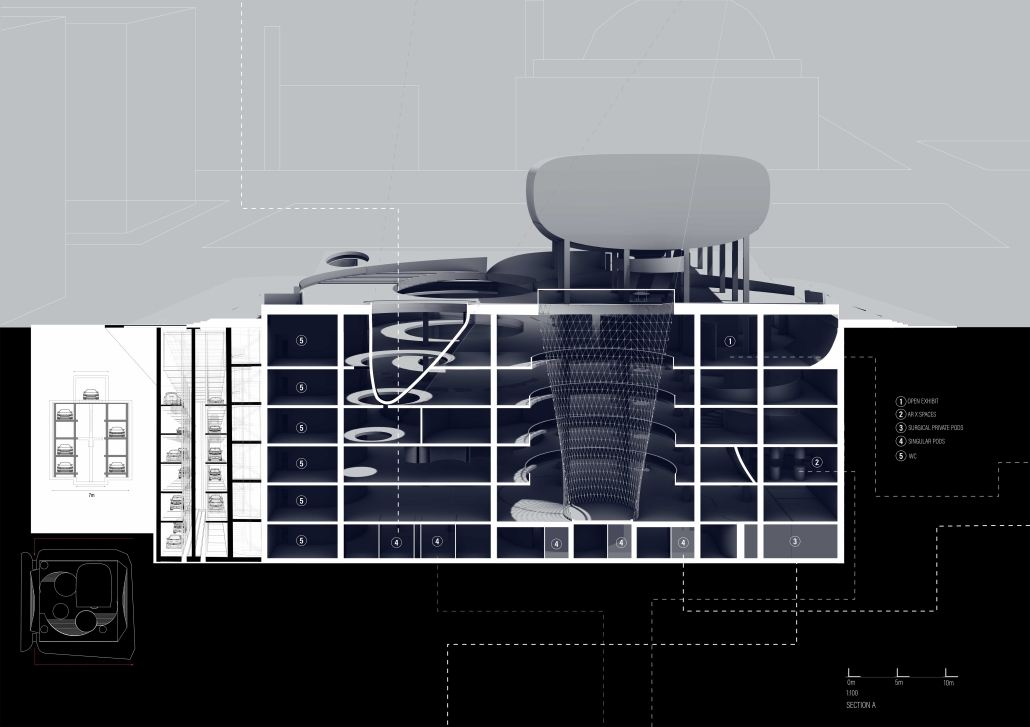
This architectural thesis culminates in transforming Beirut’s iconic dome, The Egg, located in Solidere, into a multifaceted public space. It seamlessly integrates medical, educational, and cultural uses through a harmonious fusion of virtual and physical elements. This design transcends Solidere’s boundaries, fostering interaction among diverse user groups within a dynamic environment. Symbolizing Beirut’s resilience and revival, The Egg blends history with a vibrant future, redefining spatial inhabitation by bridging physical and virtual realms.
At its core, this thesis explores the intersection of physical and virtual spaces, emphasizing the enduring significance of tangible structures while delving into the growing realm of digital environments. It investigates how architects can utilize digital technology to craft emotionally and socially resonant spaces that transcend traditional boundaries. Envisioning a future where architecture integrates seamlessly with digital elements, the study challenges architects to reimagine spatial design.
The introduction lays the foundation by recognizing the pivotal role of physical spaces in our spatial understanding, positioning the thesis at the confluence of the tangible and intangible. As digital technologies increasingly influence our physical reality, this thesis calls on architects to incorporate digital elements such as virtual reality and internet connectivity into their designs. It highlights how these once futuristic concepts are now essential tools for creating visually striking, functional, and socially impactful architectural spaces.
The thesis examines the redevelopment of Beirut’s downtown area, specifically focusing on The Egg, a striking dome in the Solidere district. This site symbolizes Beirut’s resilience and revival post-war, embodying the city’s enduring spirit while highlighting the economic barriers that modern urban landscapes can create. The Egg stands as a testament to Beirut’s cultural heritage, illustrating how architecture can blend the past with a vibrant future, bridging physical and virtual realms to redefine our concept of inhabiting space.
Instagram: @ard_aub
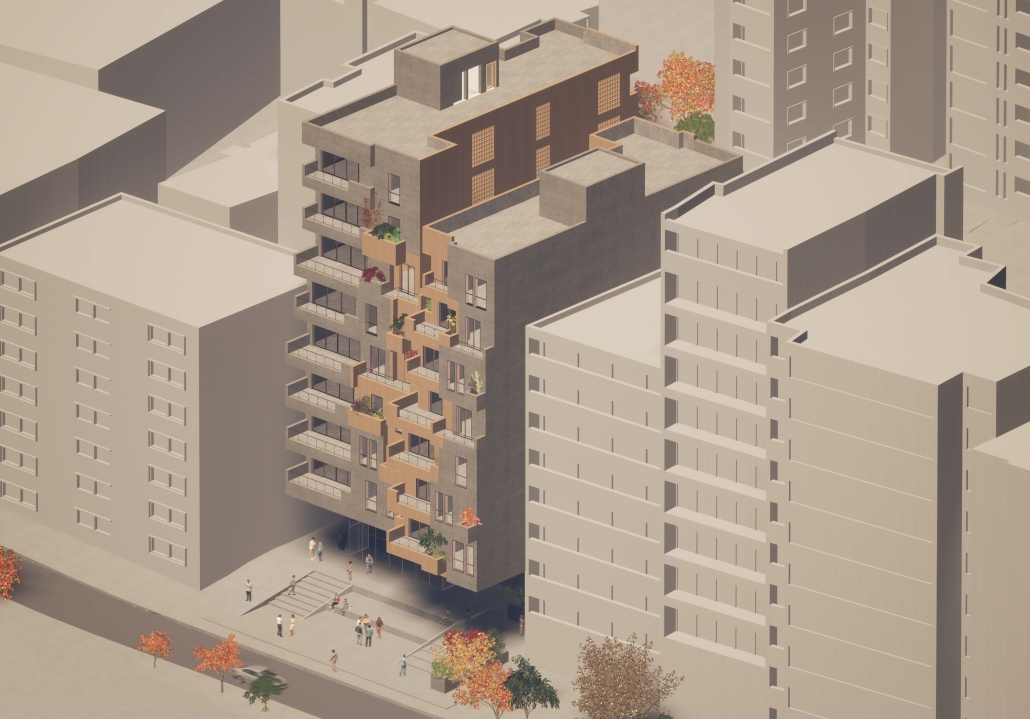
PENINSULAR PAPER CO. by Chase Dietrich, B.S. Arch ’24
Lawrence Technological University | Advisor: Masataka Yoshikawa
The project, PENINSULAR PAPER CO., began with an in-depth site analysis. The design was initially inspired by the natural gathering spots surrounding the existing building. This project aims to renovate and expand the existing structure, guided by the logic of these natural gathering points and the acute angles they form. The contemporary vision for the building’s renovation leverages these convergent points, ensuring the new design seamlessly integrates with the environment while enhancing functionality and aesthetic appeal. By focusing on these natural elements, the project promises a harmonious blend of old and new, creating a revitalized space that respects its historical context and serves modern needs.
This project won the Lawrence Technological University Chair’s Award.
Instagram: @chase.a.dietrich, @masataka.yoshikawa
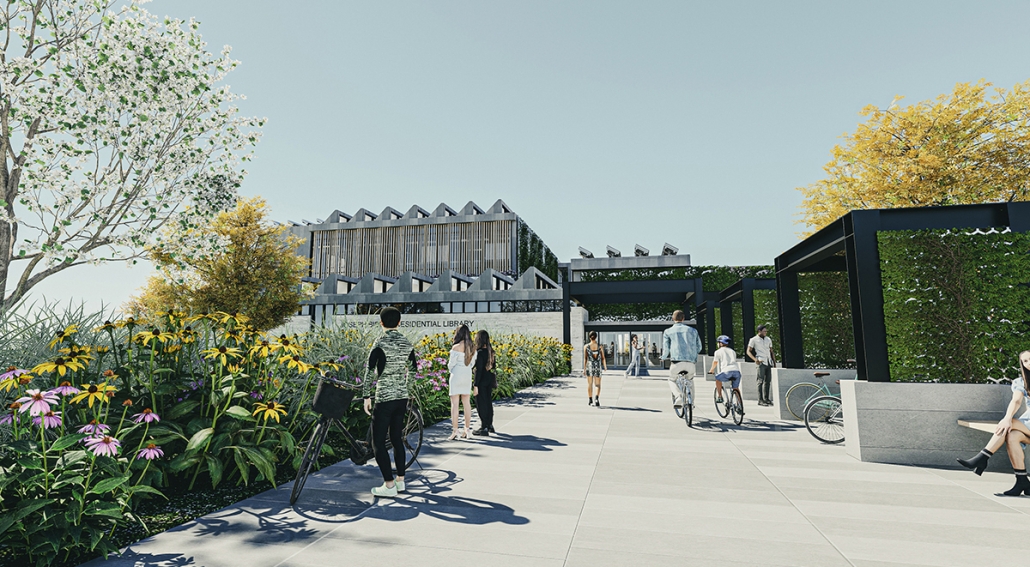
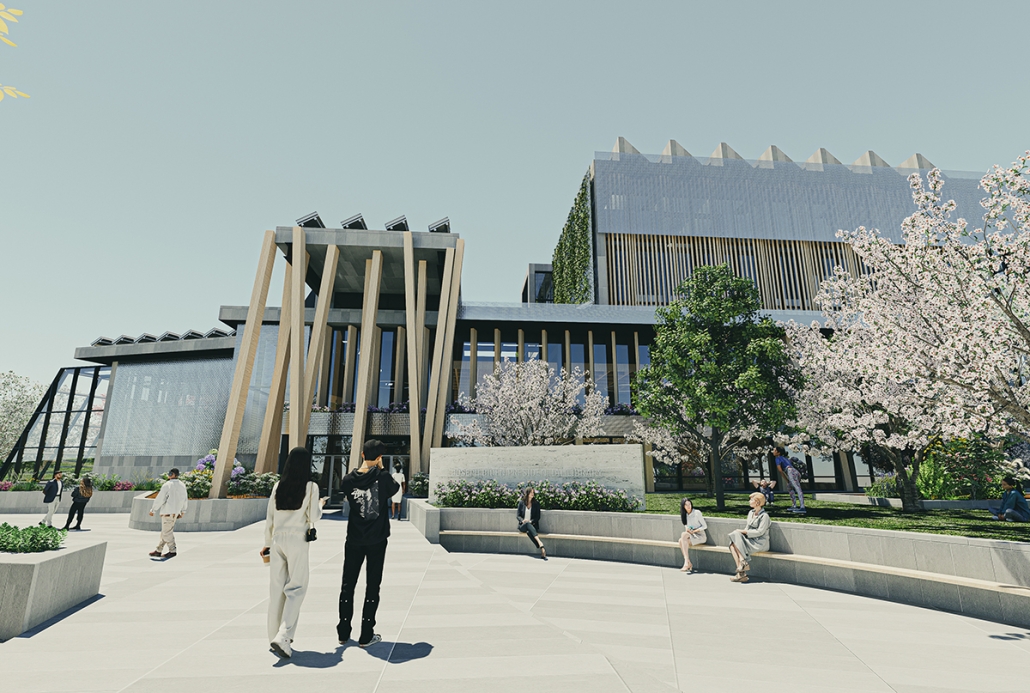
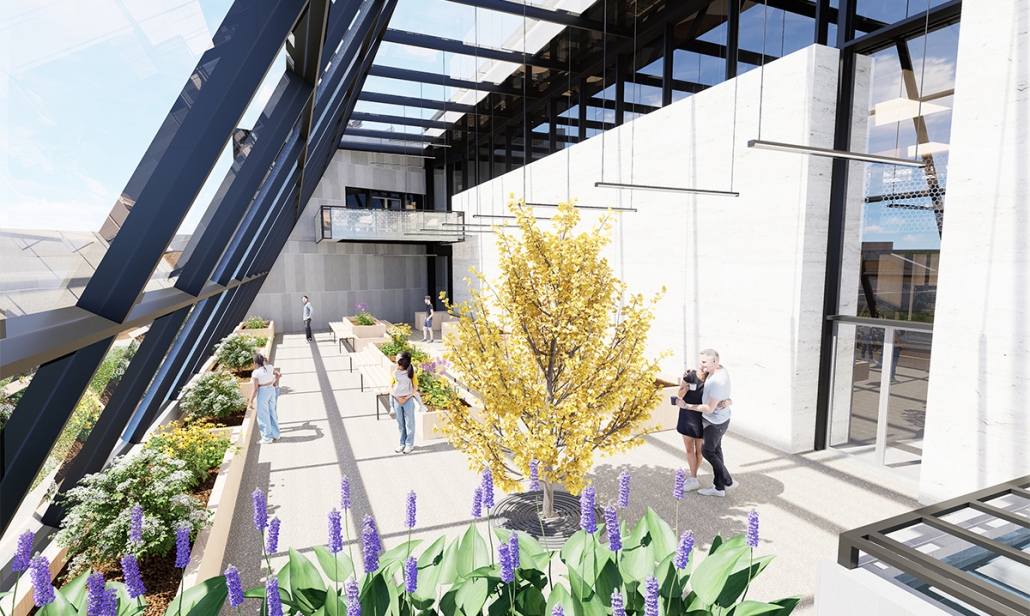
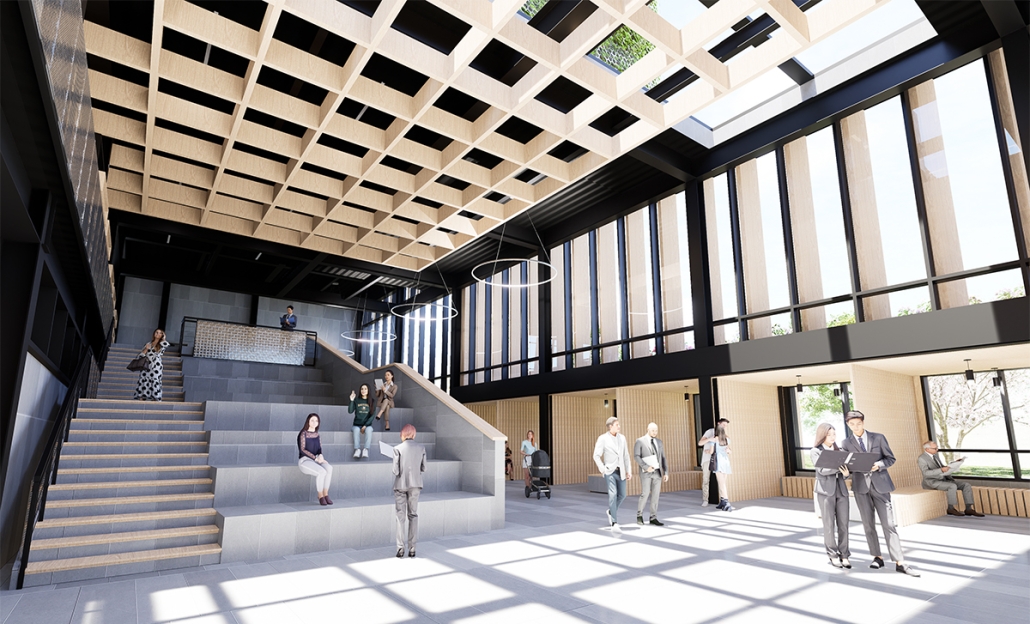
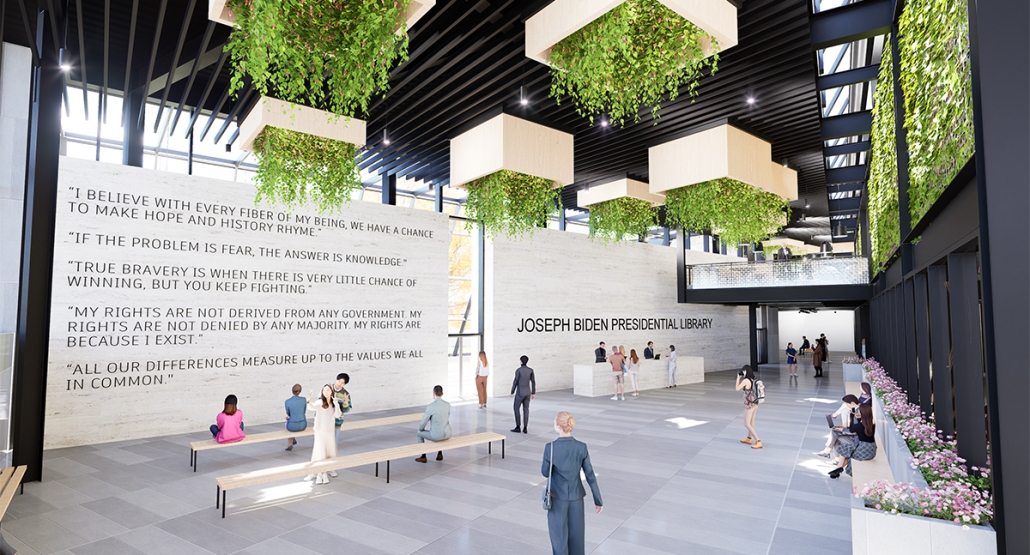
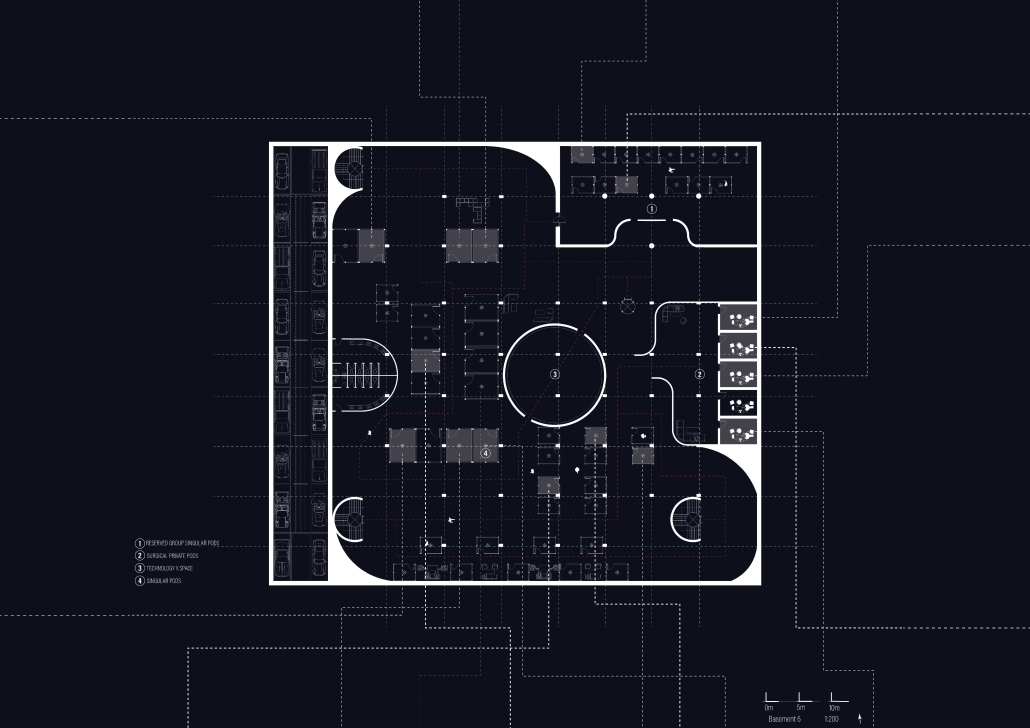
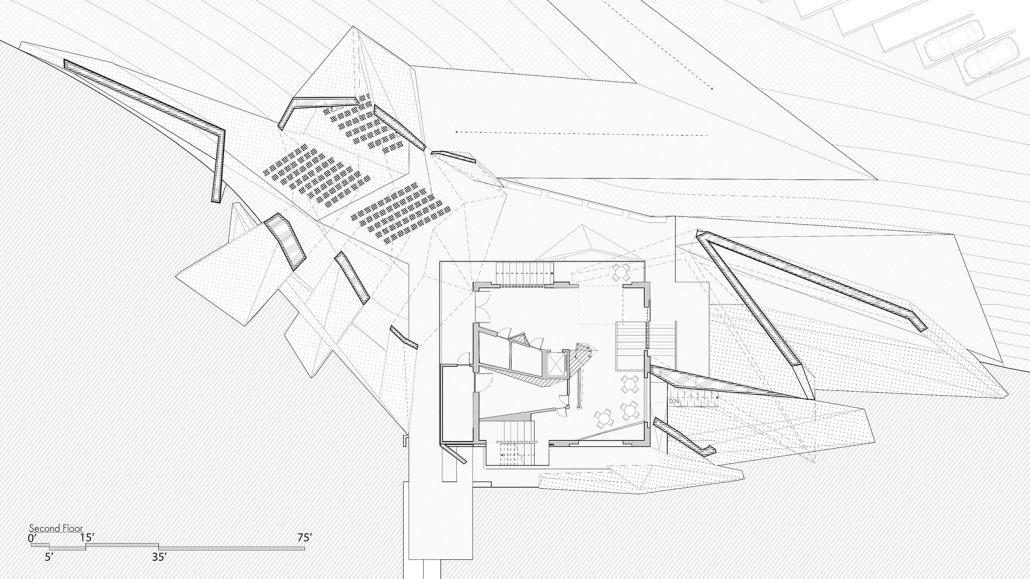
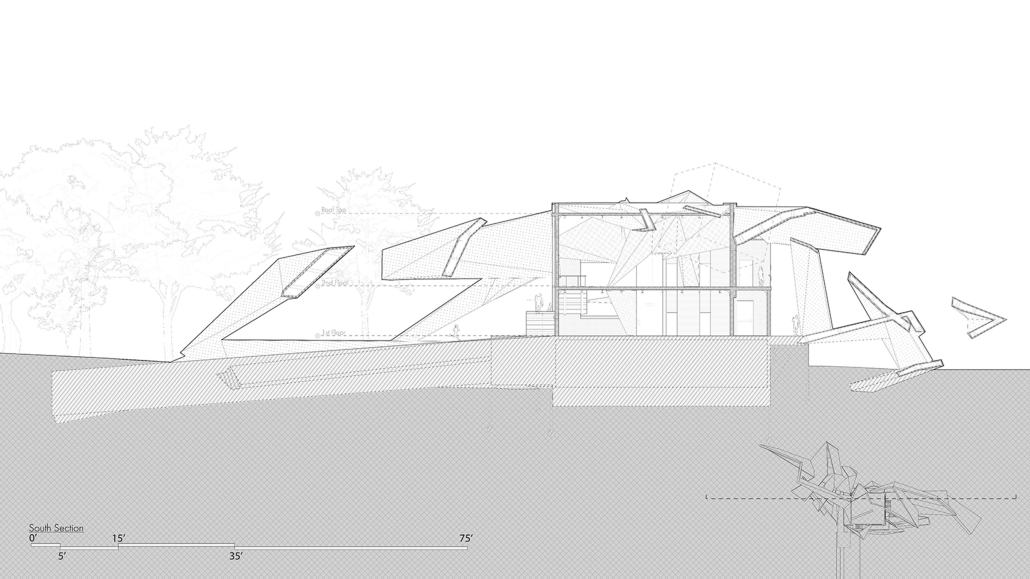
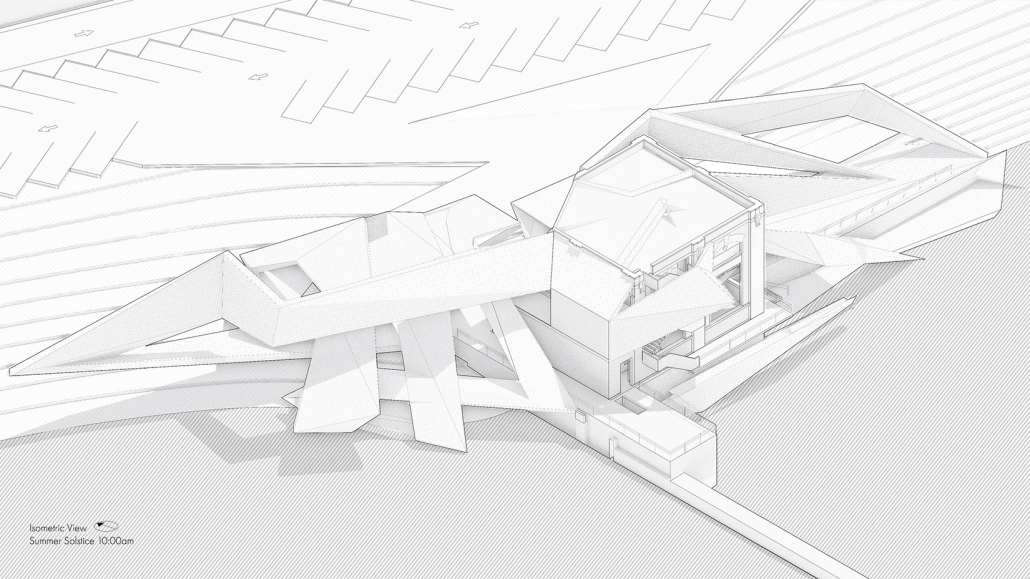
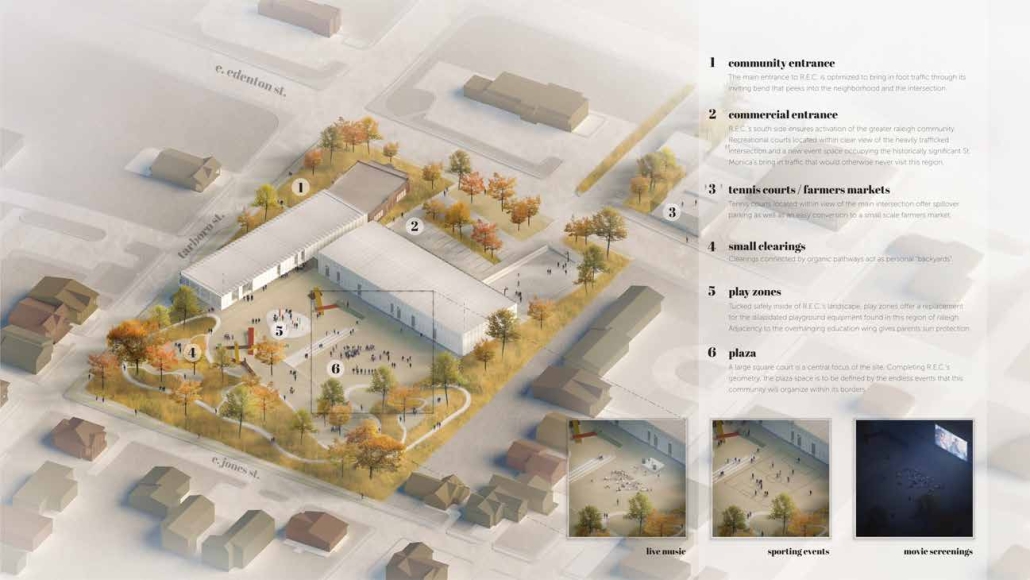
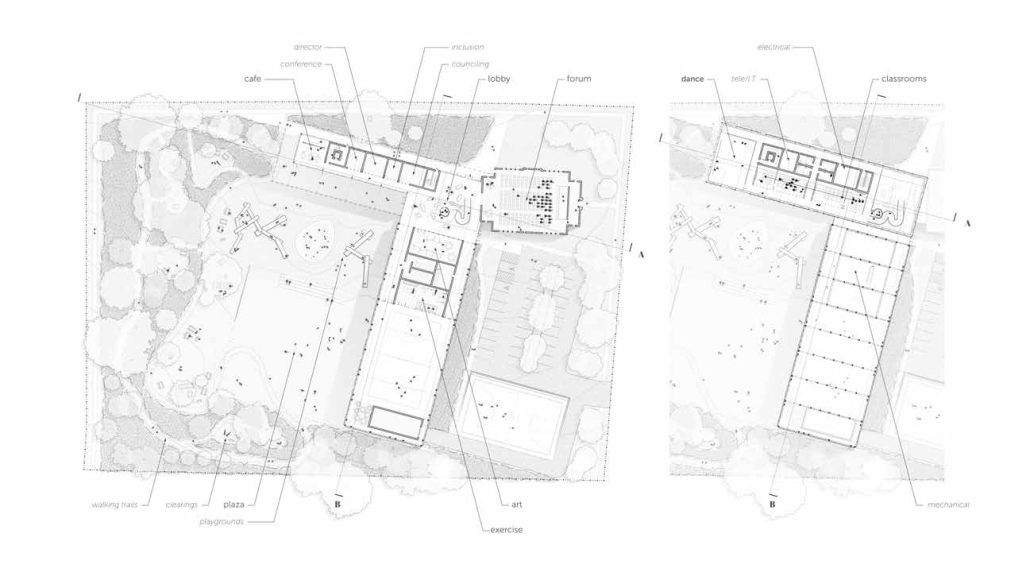
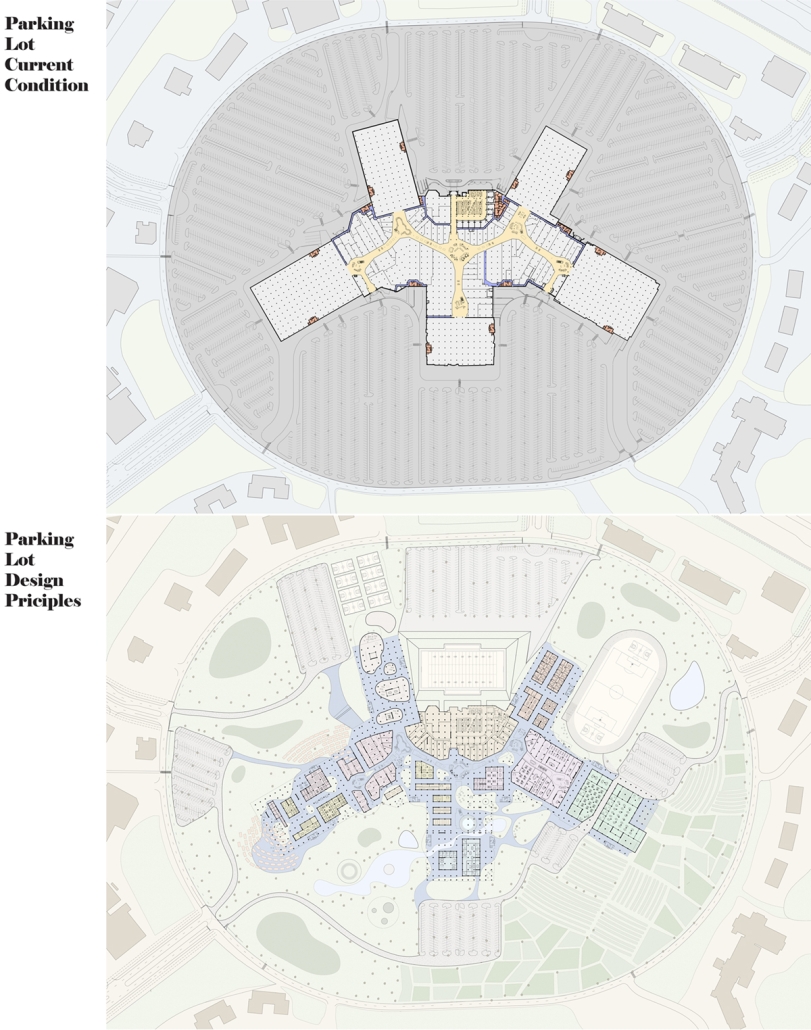
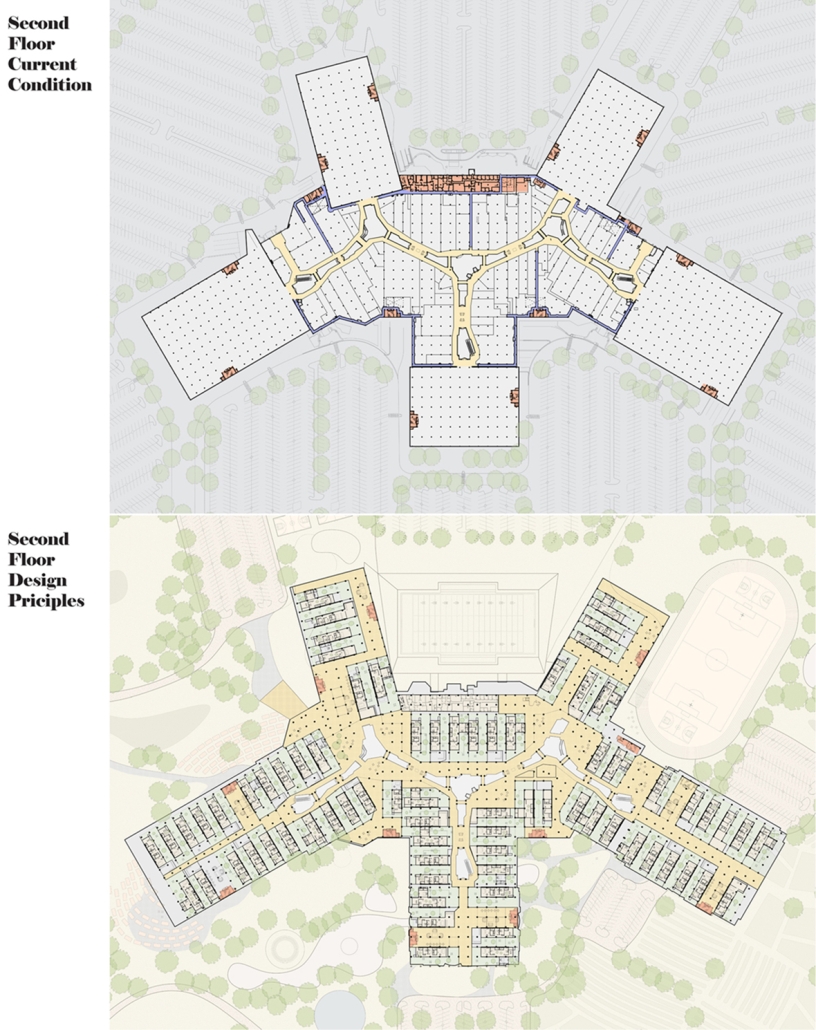
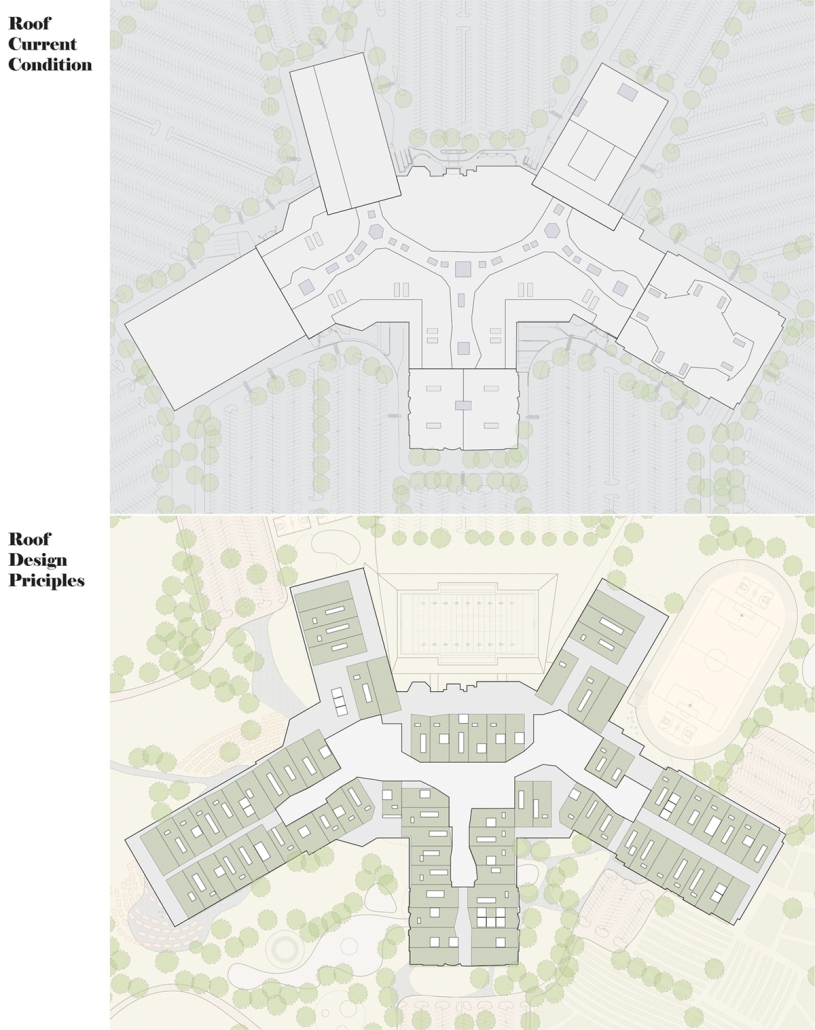
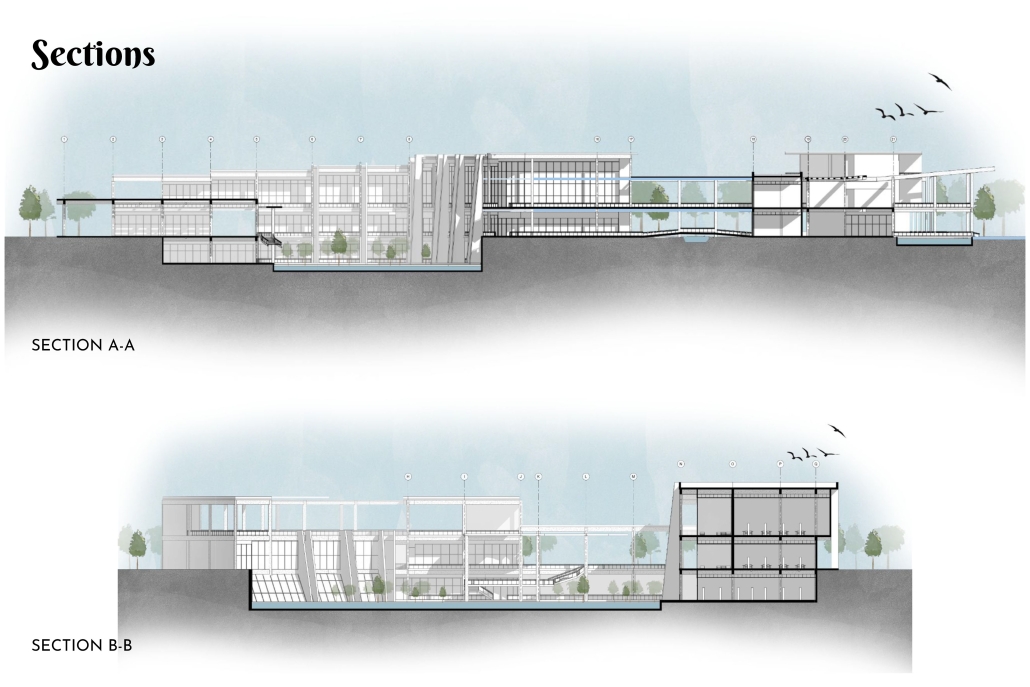
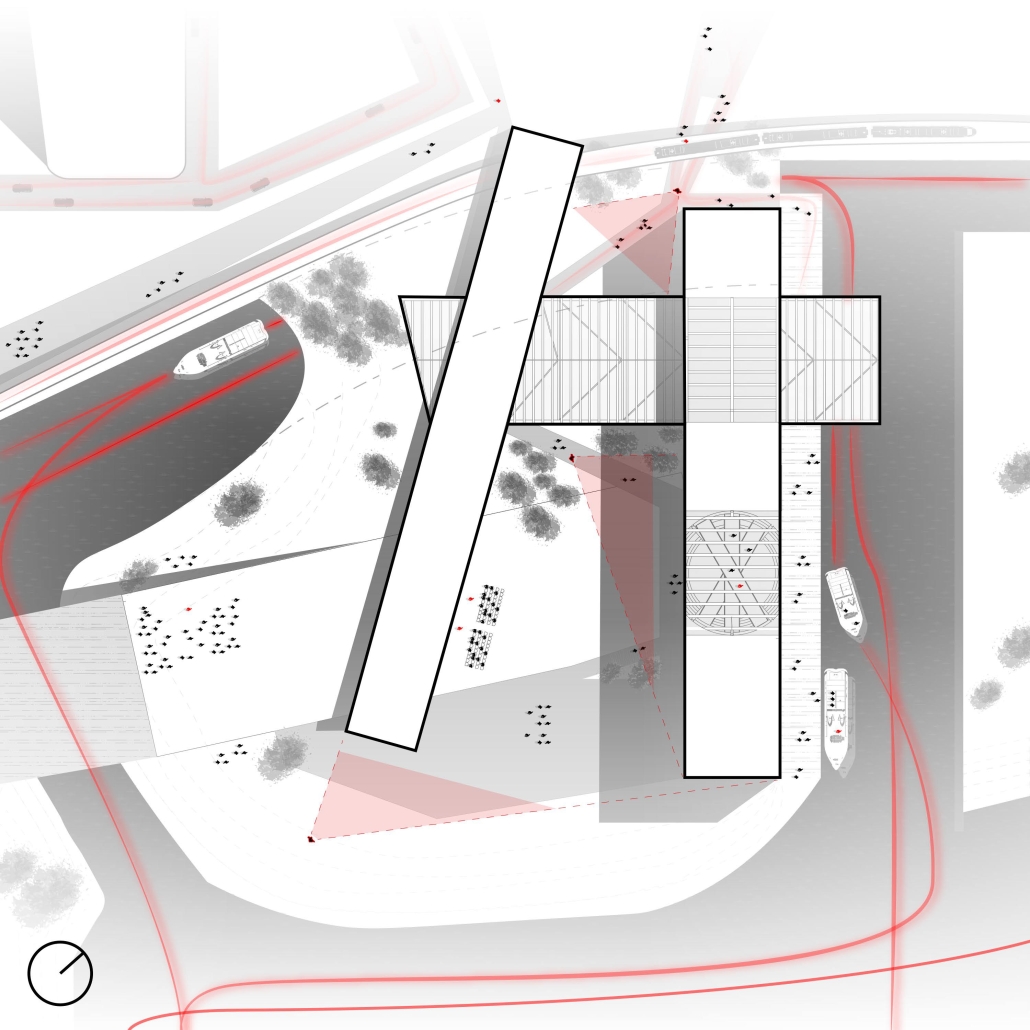
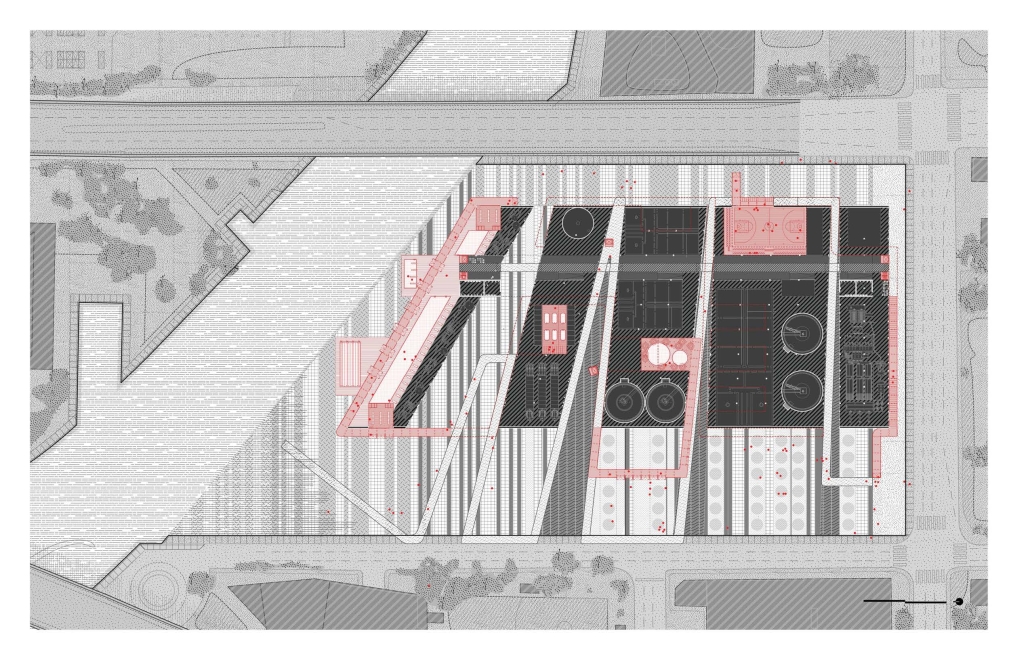
Steamtown Revival by Mason Ramsey, James Gentilesco & Dalton Metzger, B. Arch ’24
Marywood University | Advisors: Jodi La Coe & James Eckler
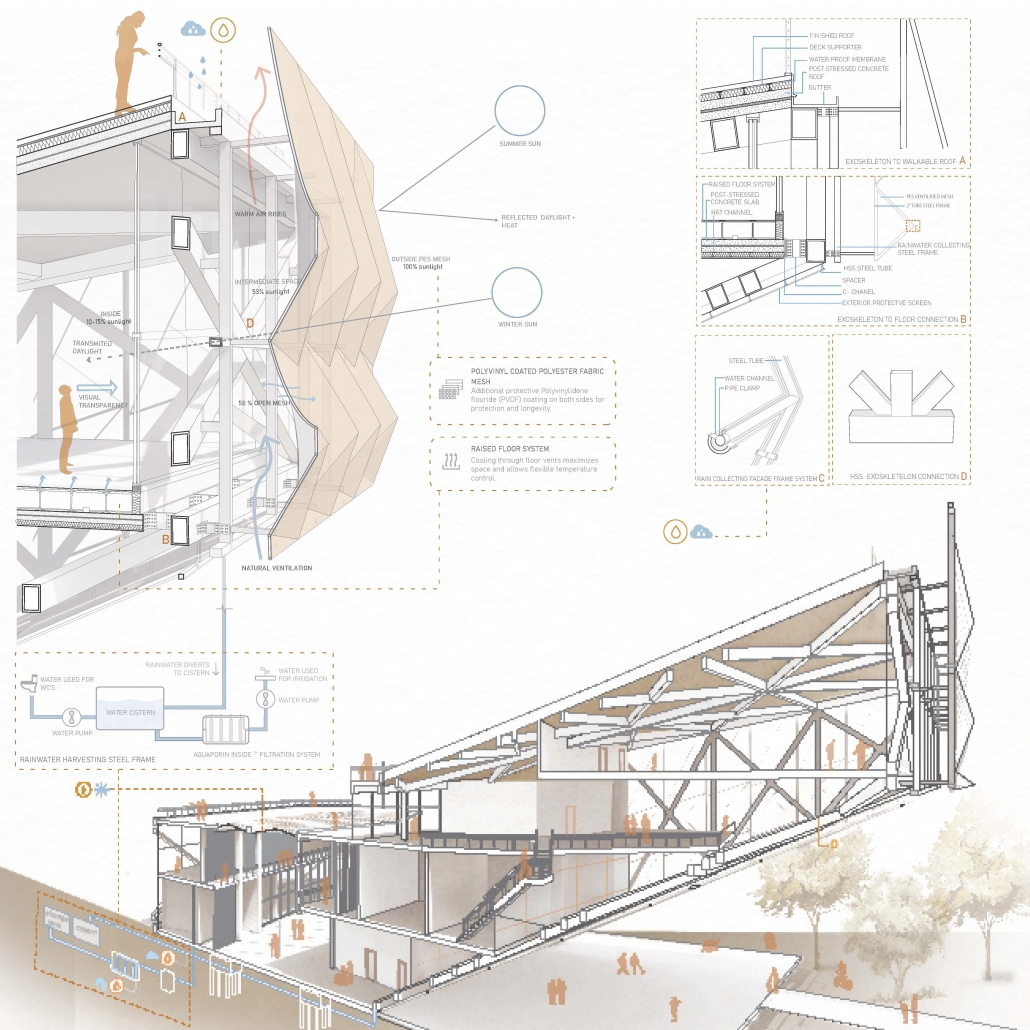
The Joseph Biden Presidential Library uses various design concepts to best represent our president’s values. Green walls, aquaponics, water reuse, and bioswales all work together to visually demonstrate President Biden’s environmental priorities. These are new concepts for the proposed site in Scranton, Pennsylvania, currently occupied by the Steamtown Mall, a development that only hurt the economy and environment of the city, as Jane Jacobs argued. The entire site is to be replaced with biking and walking trails to best integrate the cityscape with nature. Inside this presidential library, one may visit Biden’s museum collection, browse through his personal selection of books, and even request access to presidential archives in this new landmark in a regrowing city.
Instagram: @ramsey_architecture, @gentilesco_architecture, @jodilacoe
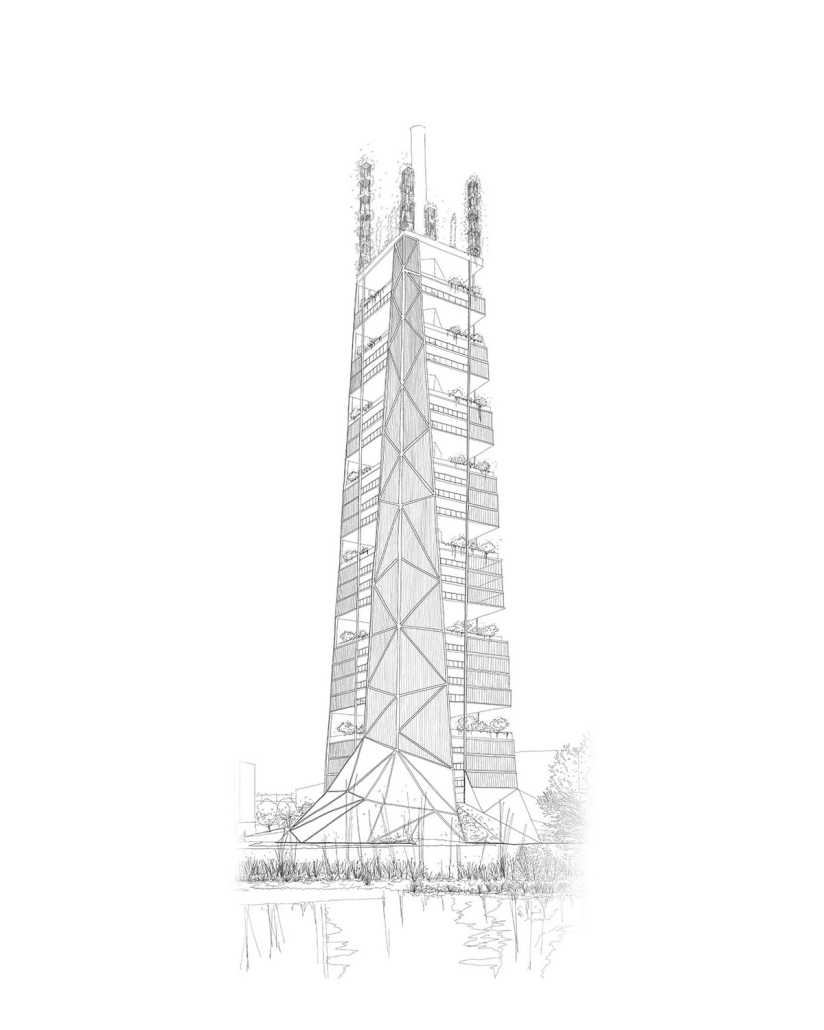
“Navigating Uncertainty” in Lebanon by Karly Abou Dib, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisors: Trevor Ryan Patt & Rana Haddad
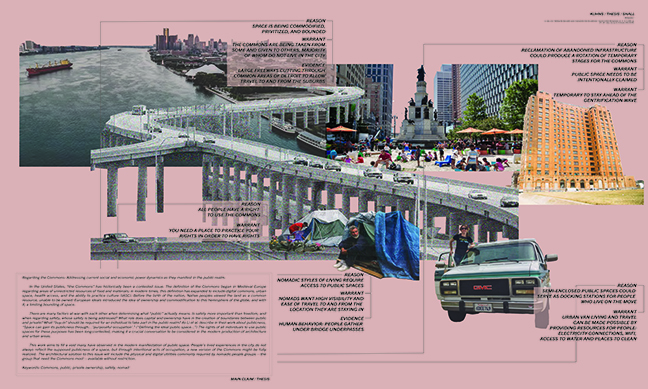
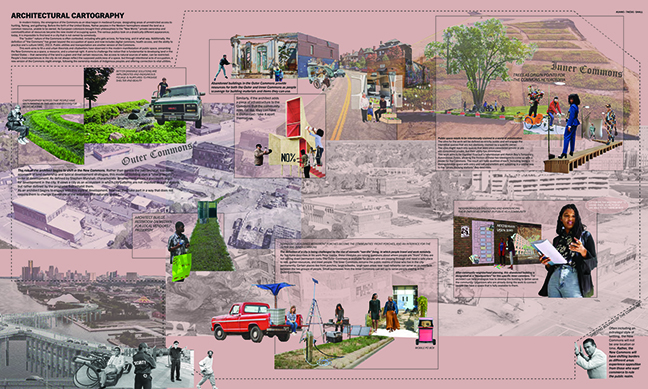
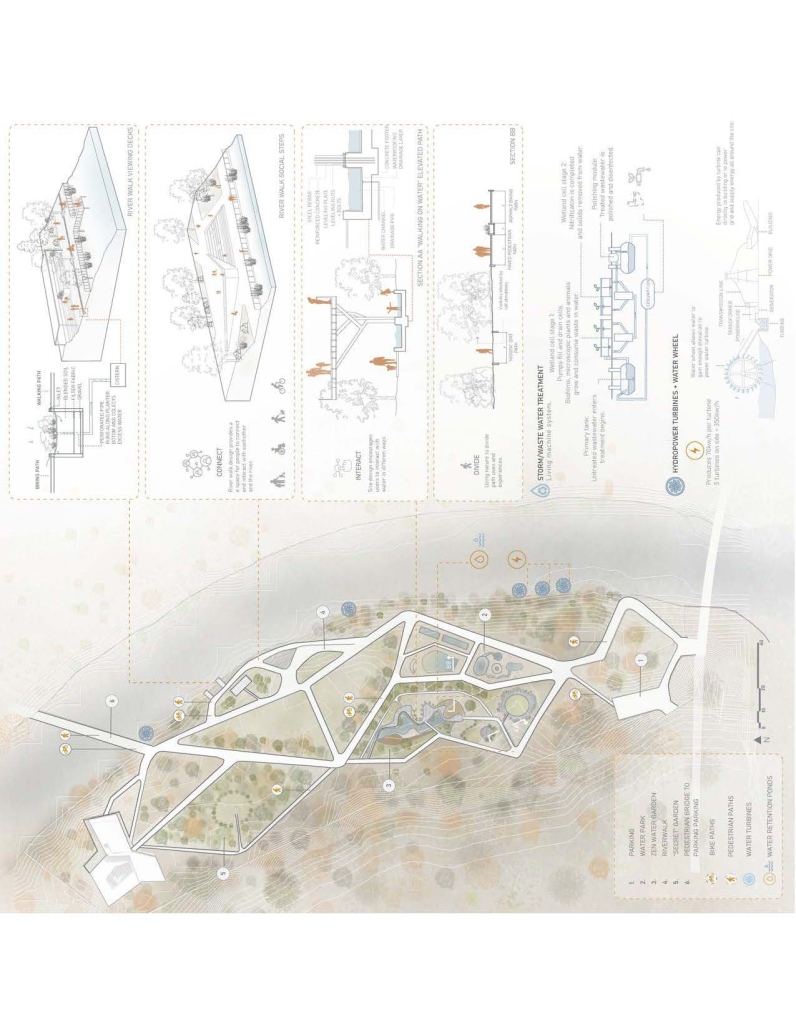
“Navigating Uncertainty” embarks on a detailed exploration of oil terminals, delving into their structural intricacies and temporal dimensions. By examining the historical significance, contemporary functionalities, and future uncertainties of these terminals, the study unfolds a narrative that seeks to craft a transformative blueprint for their decommissioning and sustainable future.
At the heart of this exploration is the concept of transforming challenges into opportunities for innovation through human collaboration. The uncertainty surrounding oil terminals is reimagined as a productive force, driving the evolution of a resilient and environmentally conscious infrastructure. The study proposes a shift from impermeable industrial containers to porous courtyards or “voids” that invite nature to reclaim and transform these spaces. This transformation symbolizes a transition from industrial to ecological, where past structures are enveloped by greenery and become communal spaces that foster biodiversity and community interaction.
Strategically designed “solids” are introduced within these voids, serving as eco-friendly program holders that benefit the environment. These solids house activities such as labs and workshops, green markets, and human energy-powered gyms, directly engage with and enhance their natural surroundings. The design and proportion of these solids vary based on their environmental impact, with programs that have a significant positive effect on nature occupying more prominent spaces.
The interface between the new solids and the voids is filled with community engagement opportunities and pathways that foster educational and cultural experiences. Visitors navigate through these transformed spaces, engaging with layers of information and activity that promote a deeper understanding of sustainability and its impact. This dynamic environment educates and inspires, cultivating a greener mindset among its visitors.
The project transforms an industrial site into a vibrant green space through the development of a porous wetland. This wetland enhances social well-being, supports biodiversity, and aids in natural water treatment and flood mitigation. It serves as an educational hub promoting environmental sustainability and highlights the role of wetlands in urban ecosystems. By integrating water into the site, the wetland mitigates flood risks and improves urban microclimates, showcasing how industrial areas can be reclaimed by nature
Instagram: @ard_aub
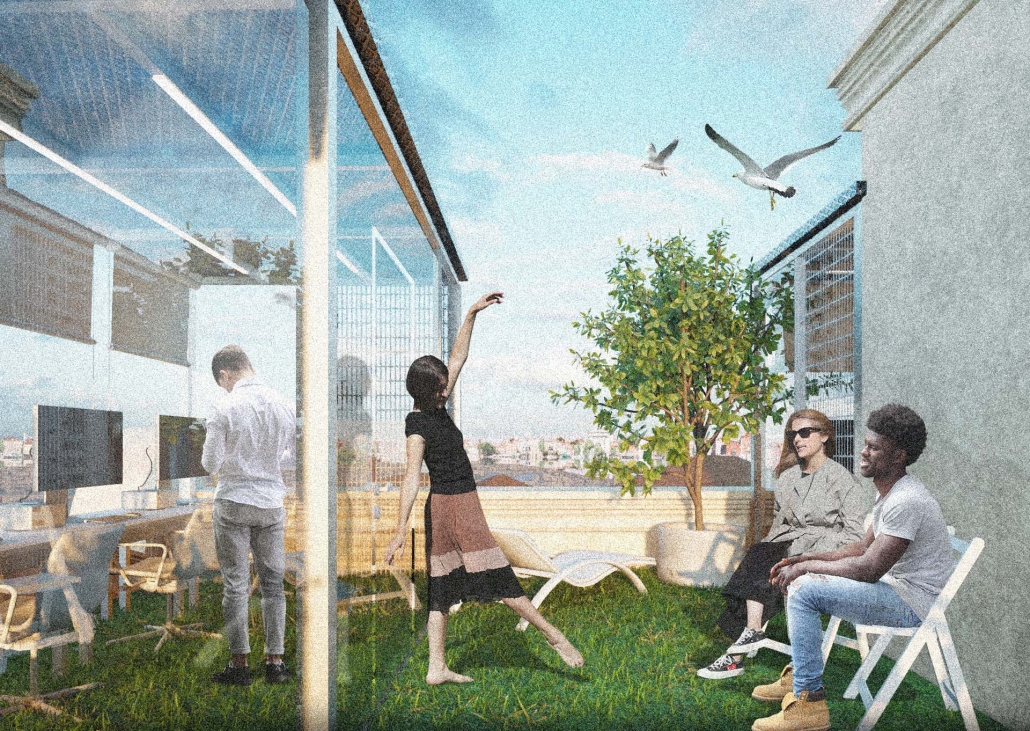
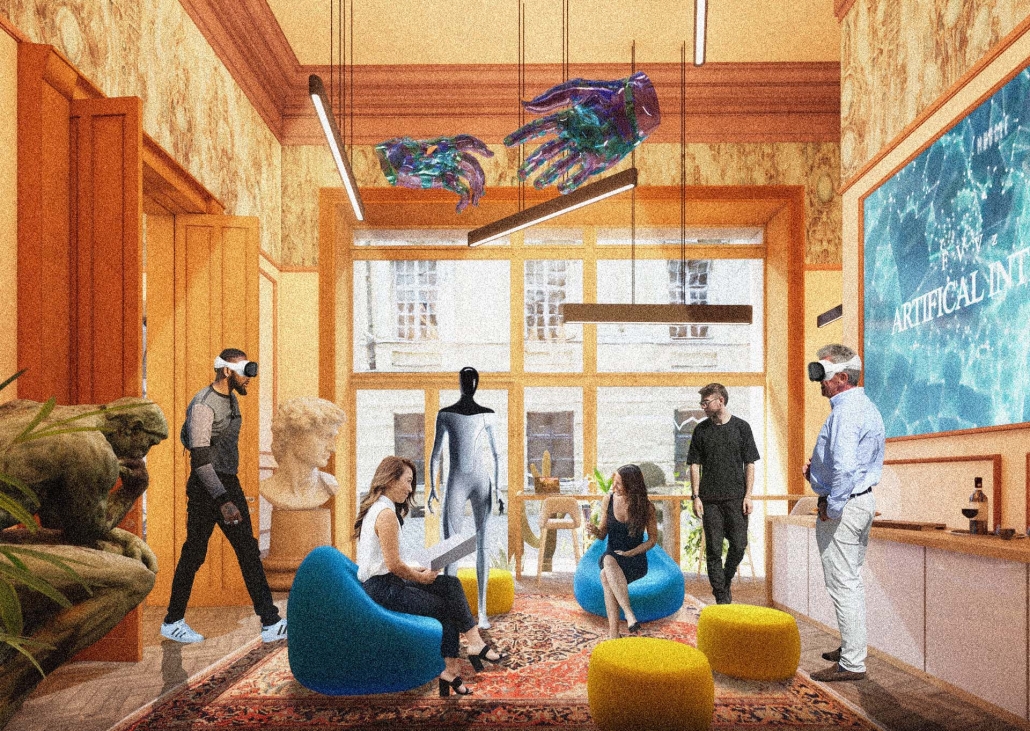
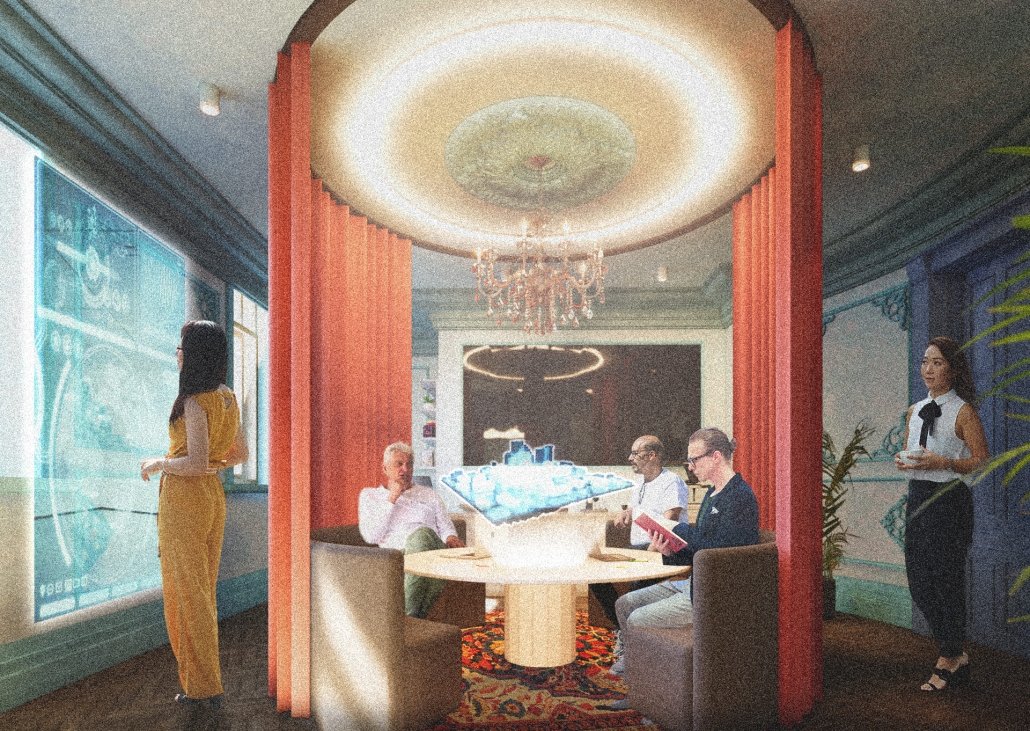
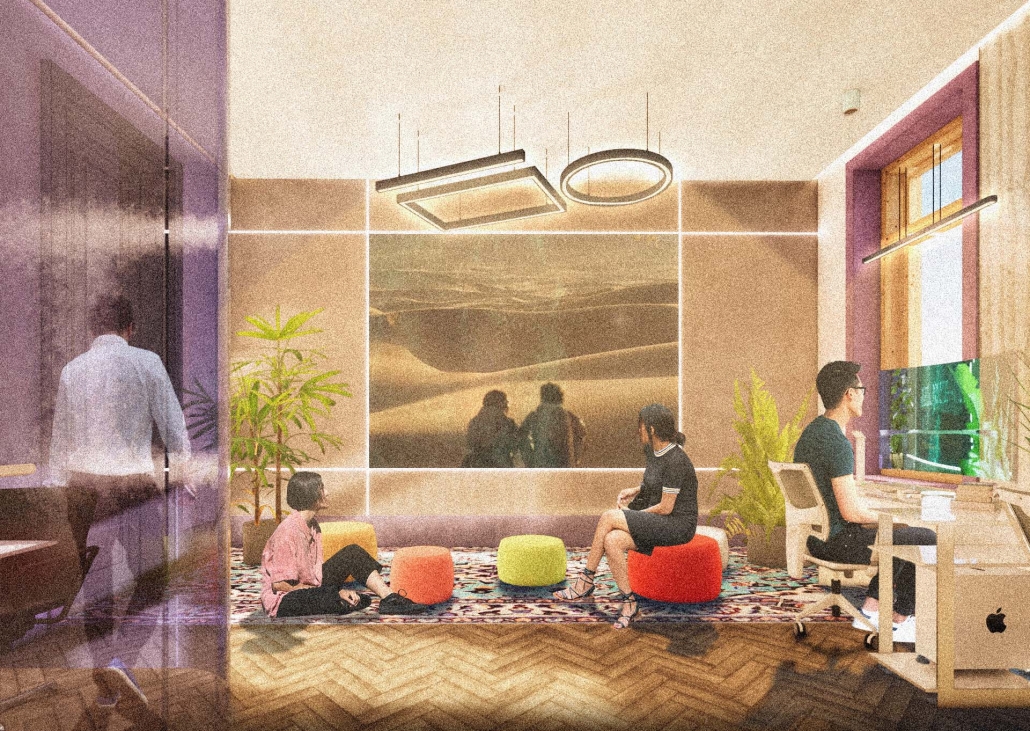
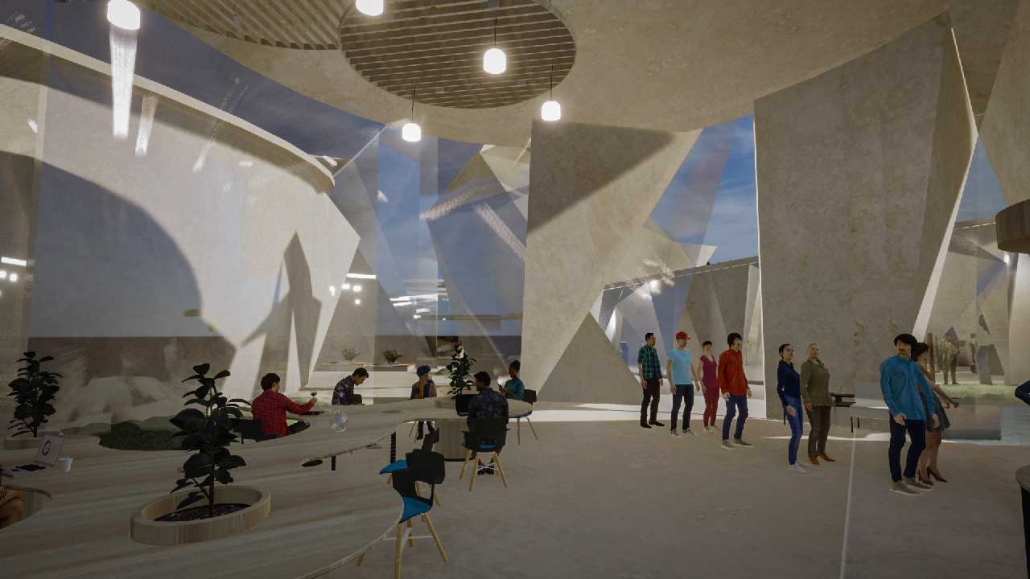
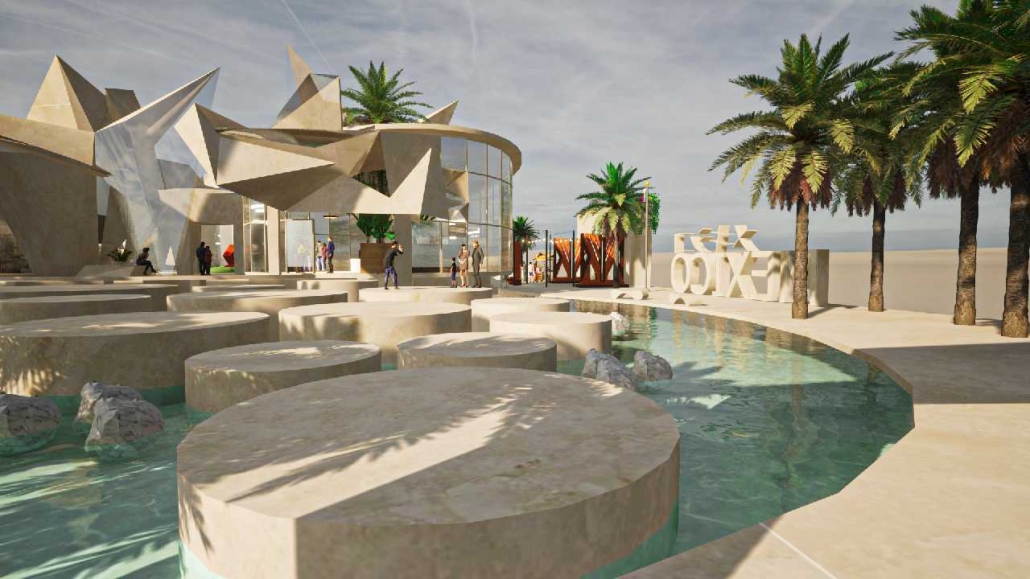
Global Educational Center for IT Specialists and Migrants in Istanbul by Anatolii Savoskin, Diploma in Strategic Interior Design / Private Master Degree ’24
IE University | Advisor: Elvira Munoz
For my graduate project, I tackled the challenges faced by skilled migrants, drawing from my own experience and that of friends worldwide. Using design tools, I aimed to provide solutions by identifying a real client in crisis and repurposing an underused building. Researching the client’s needs and challenges was pivotal in shaping our design strategy. We chose a historic building in central European Istanbul, strategically located near public amenities and transportation hubs to cater to our target audience: migrants with IT backgrounds. Detailed user mapping helped to understand their expectations and needs. My design concept focused on four key elements: an Al educational center, a rebranding campaign for Blackberry, integration of multicultural design elements reflecting migrants’ cultures, and a transition from classical to modern styles throughout the building’s floors.
Instagram: @iearchdesign, @anatolii_savoskin
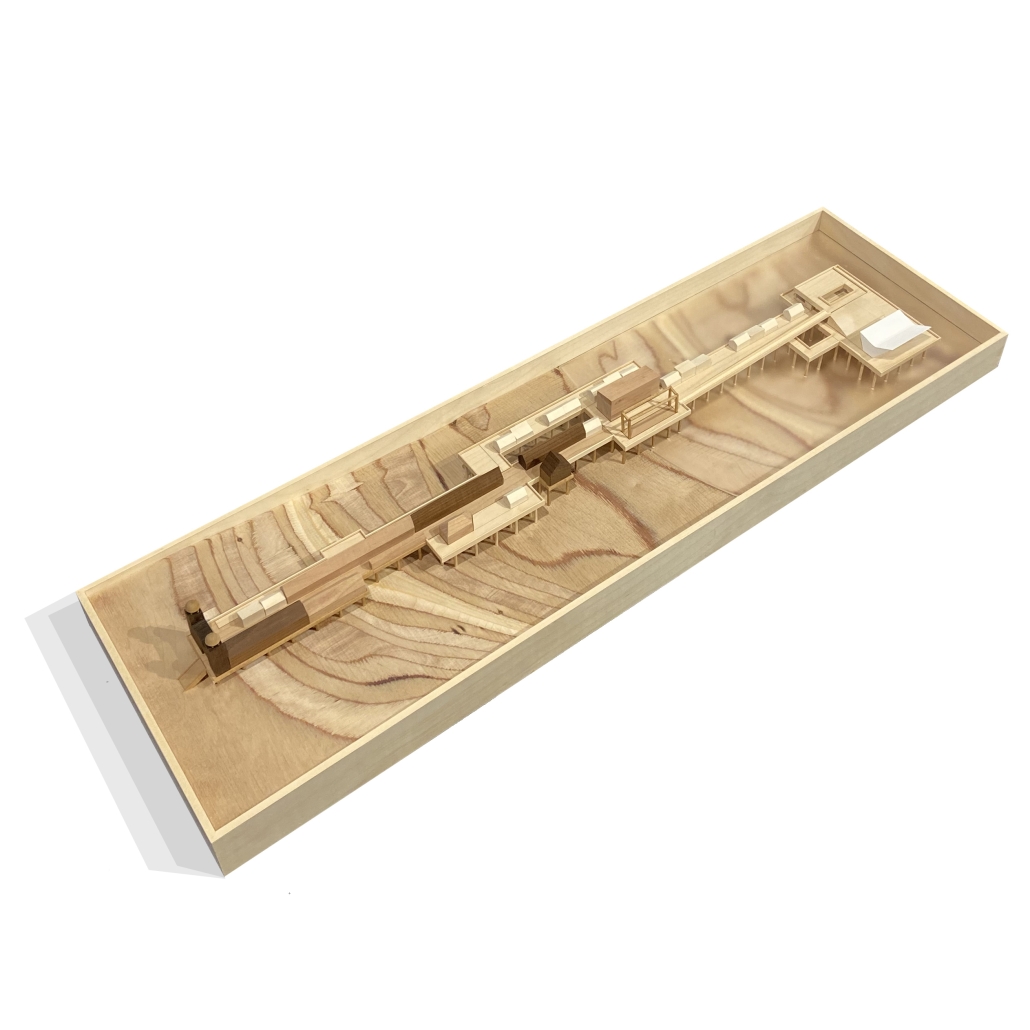
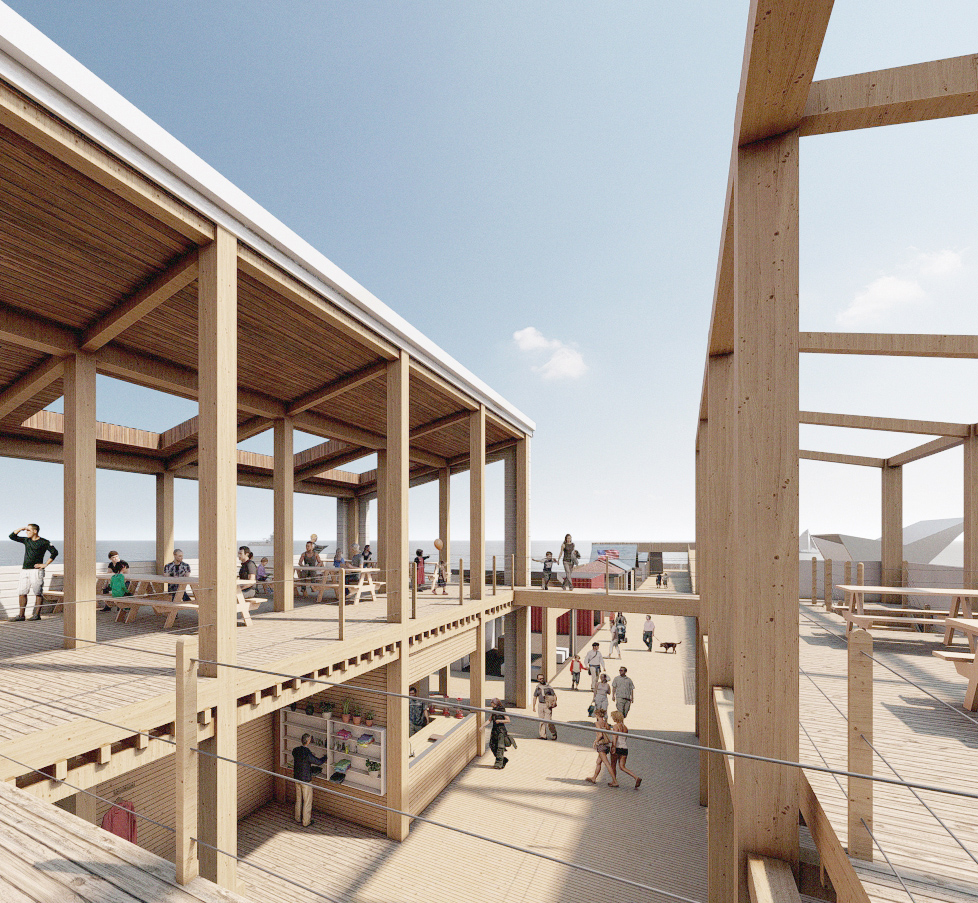
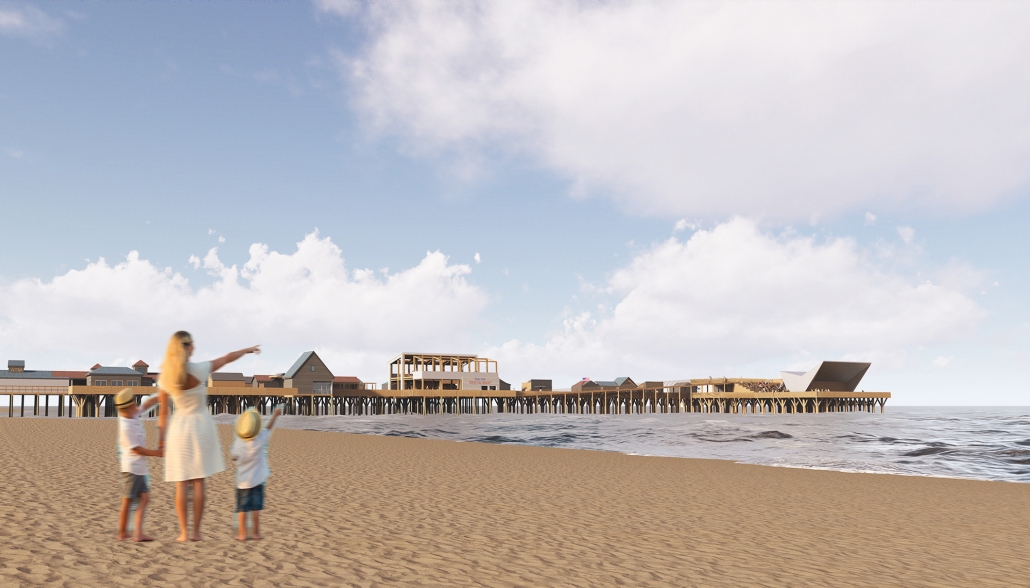
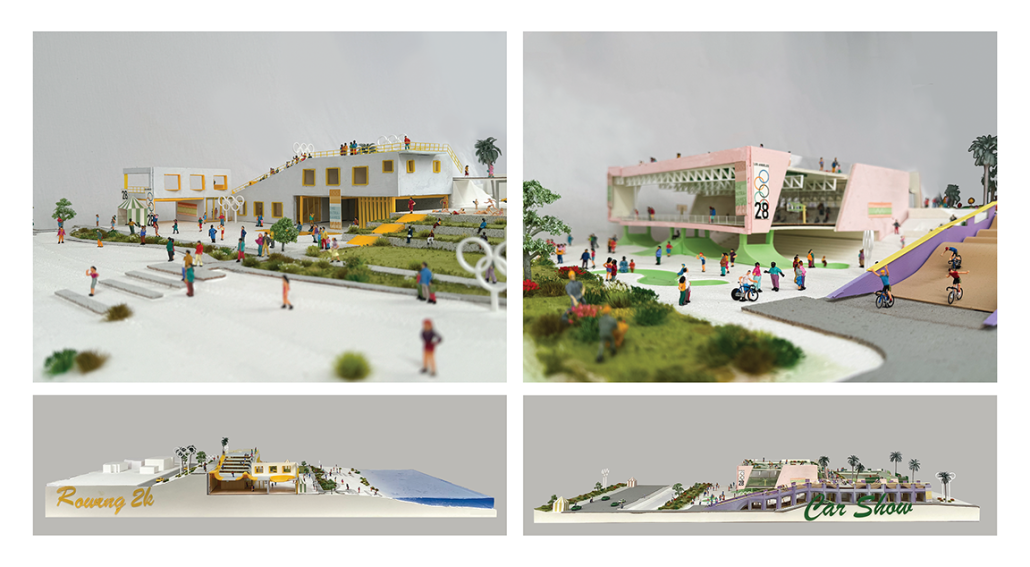
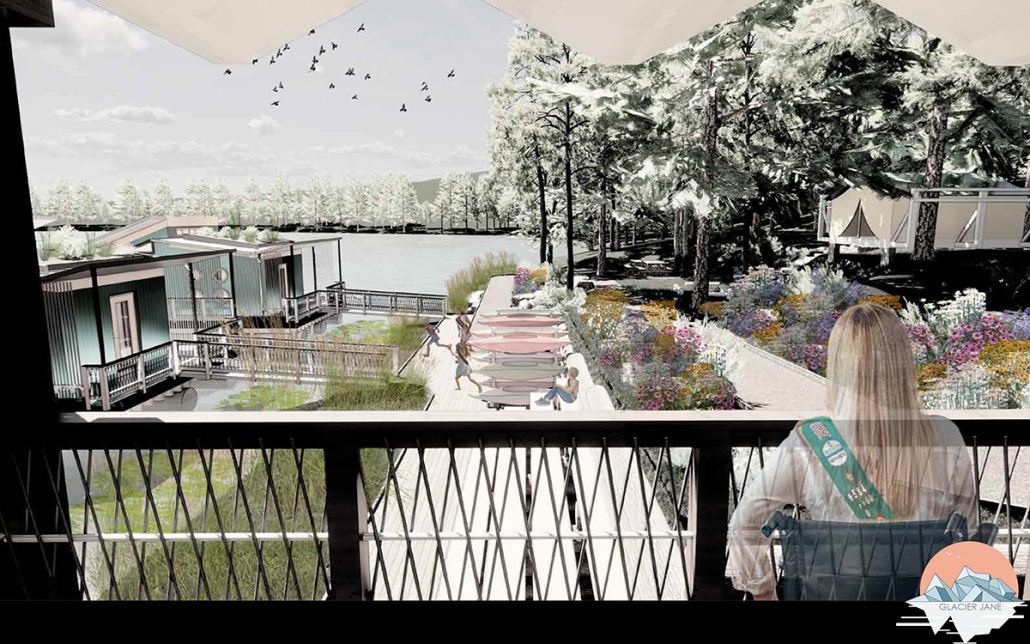
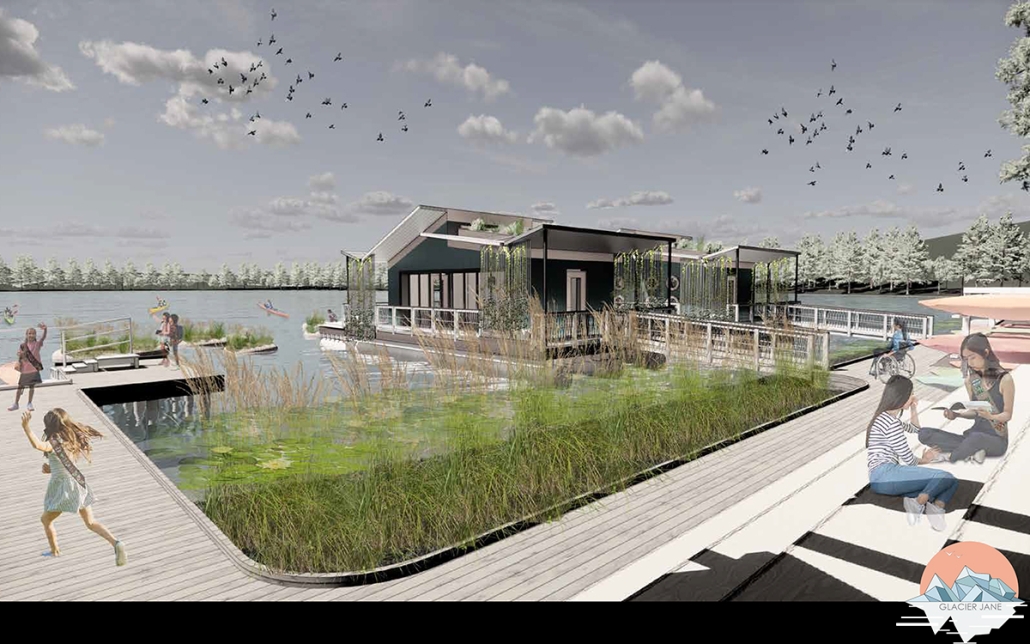
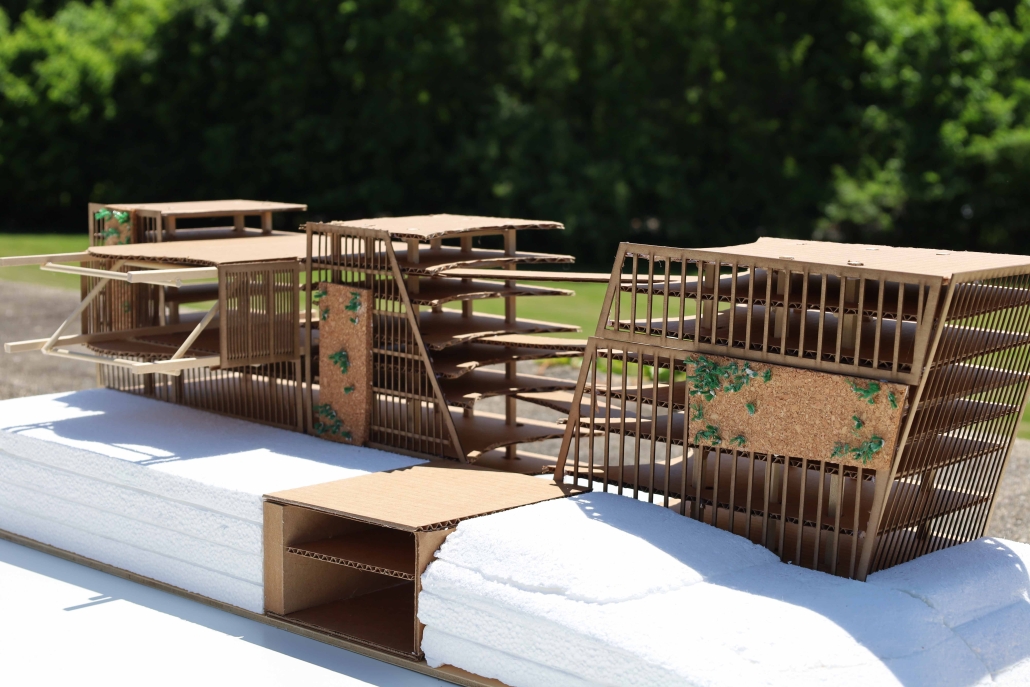
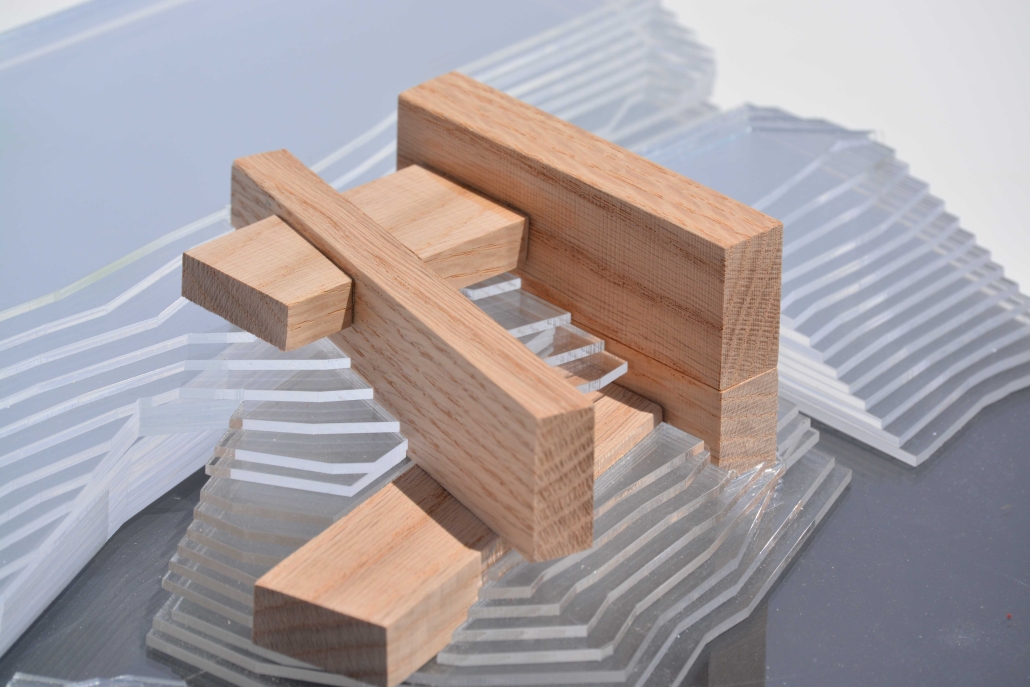
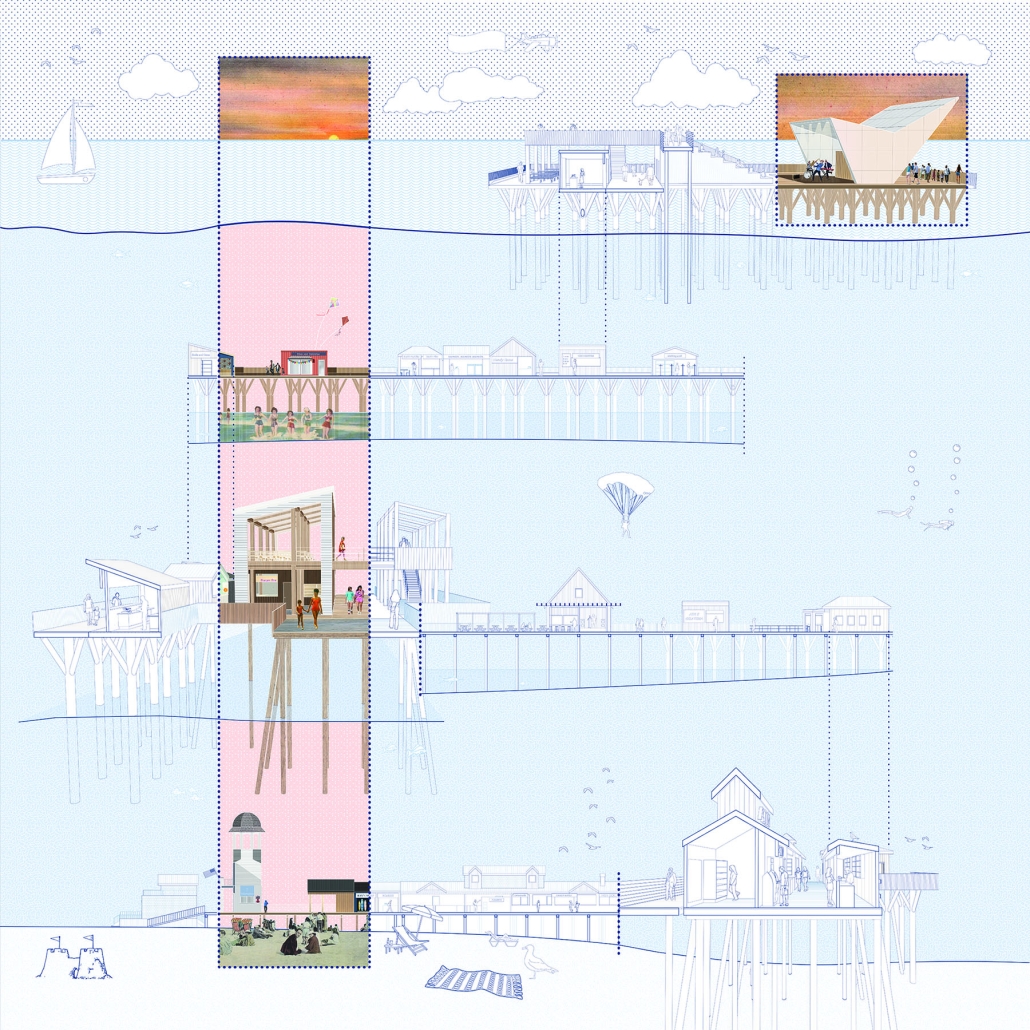
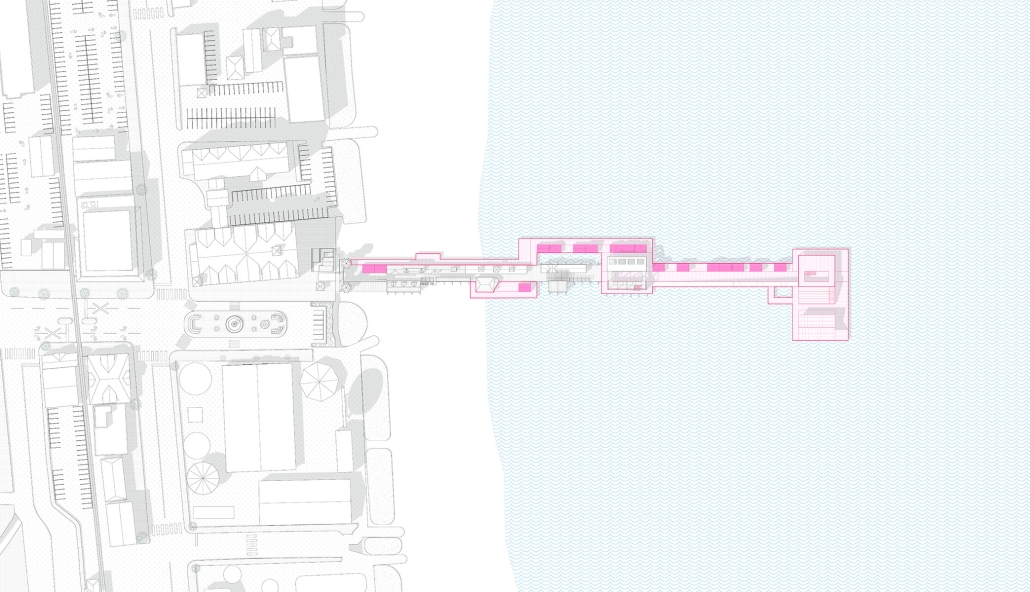
Extending The Patchwork | The Pier by Jillian Sproul & Olivia Nunn, M. Arch ’24
Toronto Metropolitan University | Advisors: Joey Giaimo & Julia Jamrozik
Located in Old Orchard Beach, Maine, a tourist beach town, the project proposes an extension of the current pier providing opportunities for vendor expansion. The new pier proposal is achieved through the implementation of subtractive and additive heritage strategies. It provides locals with the agency to expand their business onto the structural modules that will aggregate as needed based on future growth, extending the existing vendor and architectural patchwork. The existing main pavilion has been opened up as a midpoint for resting and [eating]. The newly designed end pavilion embraces the past entertainment values of the site, showcasing live performances and expansive views out to the water. The form of the performance structure is shifted to align with the main street of the town, inviting visitors to adventure through the entirety of the pier, especially during sunset, when sun rays reflect off of the metallic panels. The two-storey performance pavilion is accessible with the feature ramp leading tourists on a journey separated from the busy vendor stalls. The total pier addition allows the current architectural and vendor patchwork to be valued as a key component to the pier’s long-standing success since 1899.
The physical model utilizes three types of wood to visualize the architectural patchwork of the current pier and the proposed extension. The burnt maple represents existing components of the pier, while the cherry represents existing components that have undergone renovations. This is contrasted with the basswood that represents the proposed patchwork extension.
Instagram: @jilliansproul, @olivianunn14
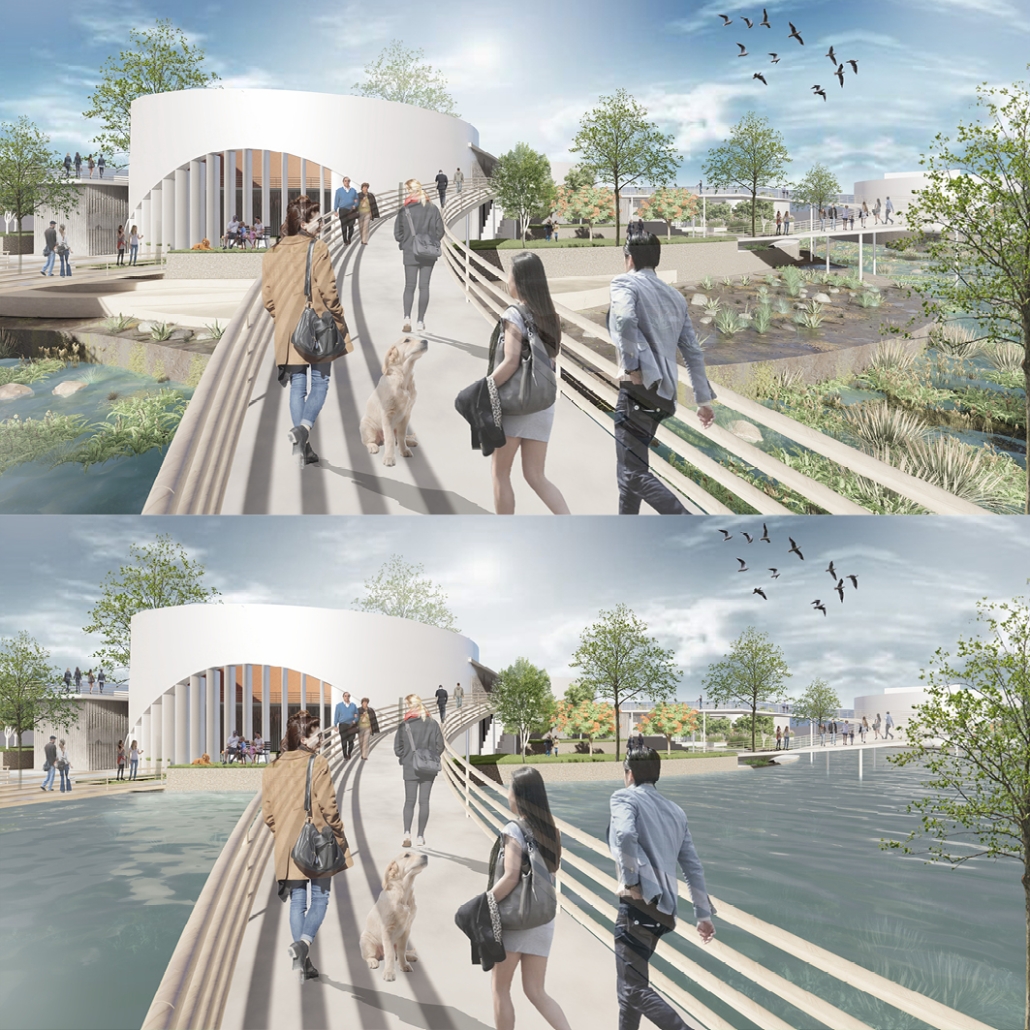
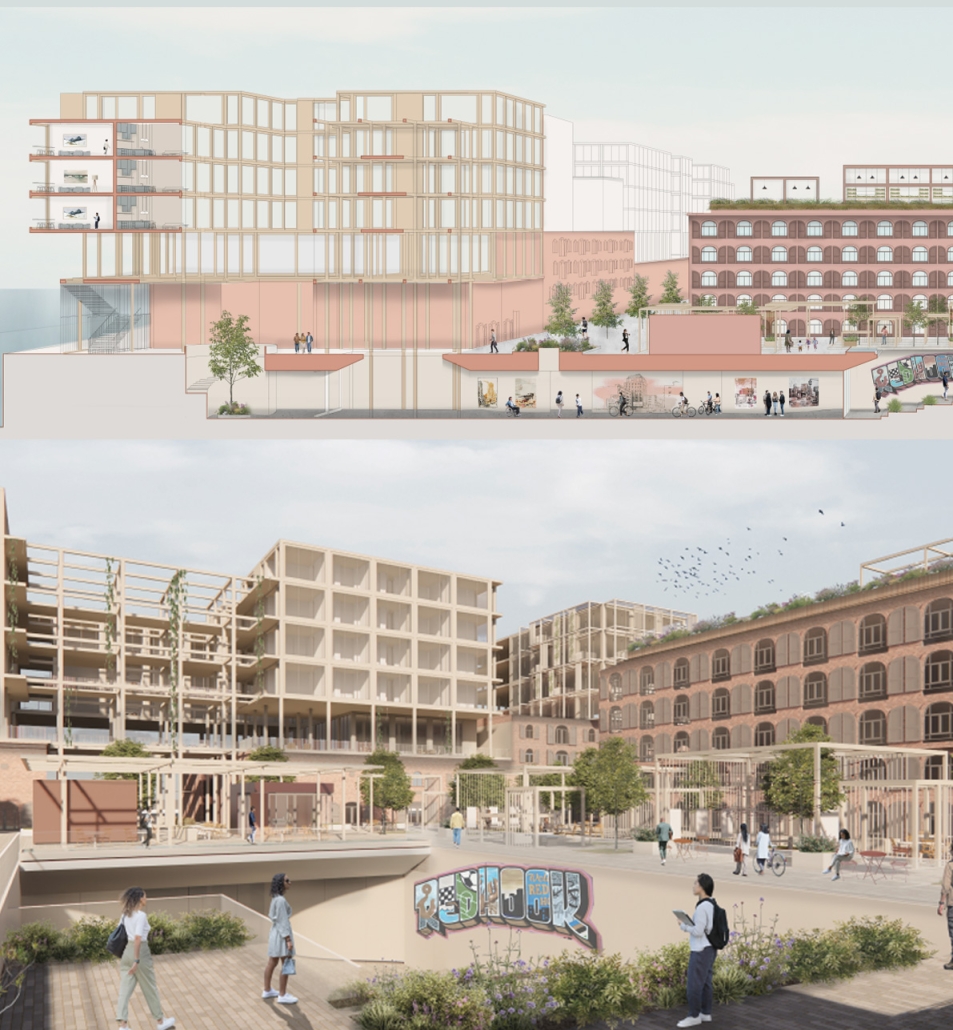
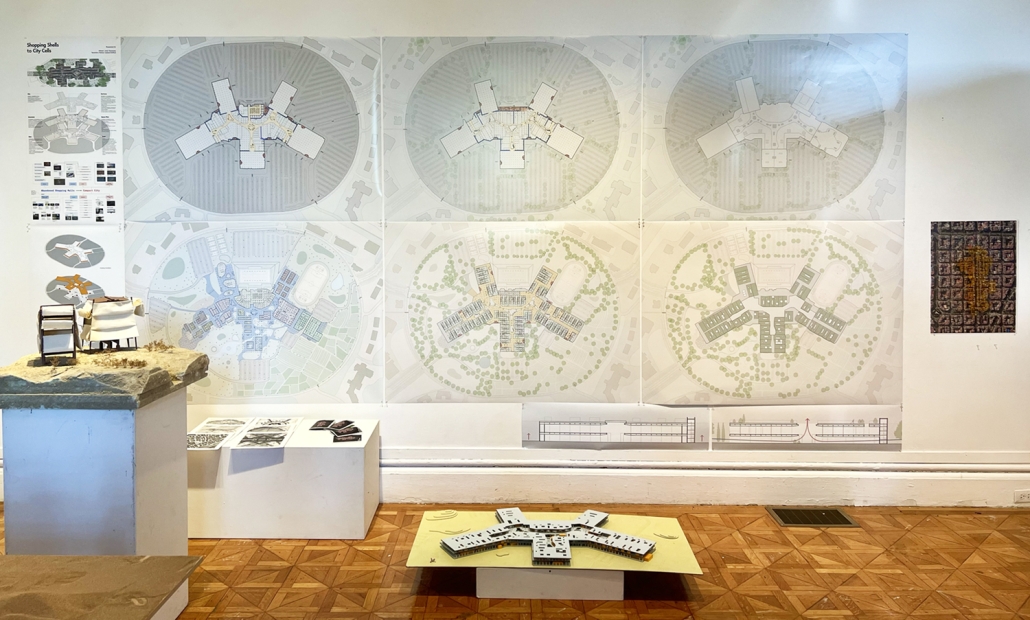
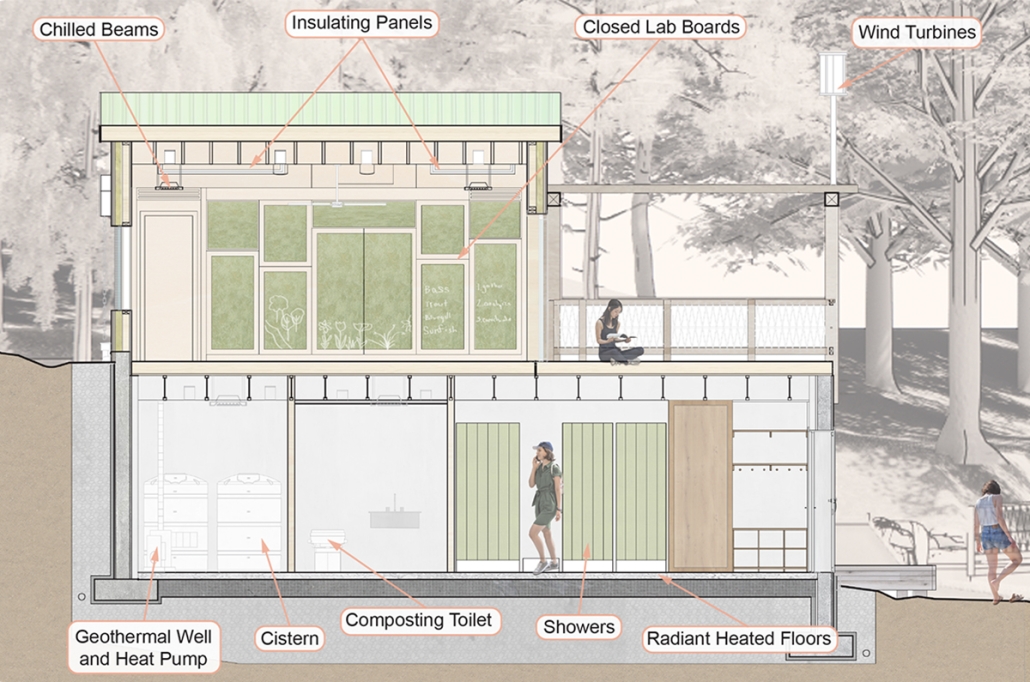
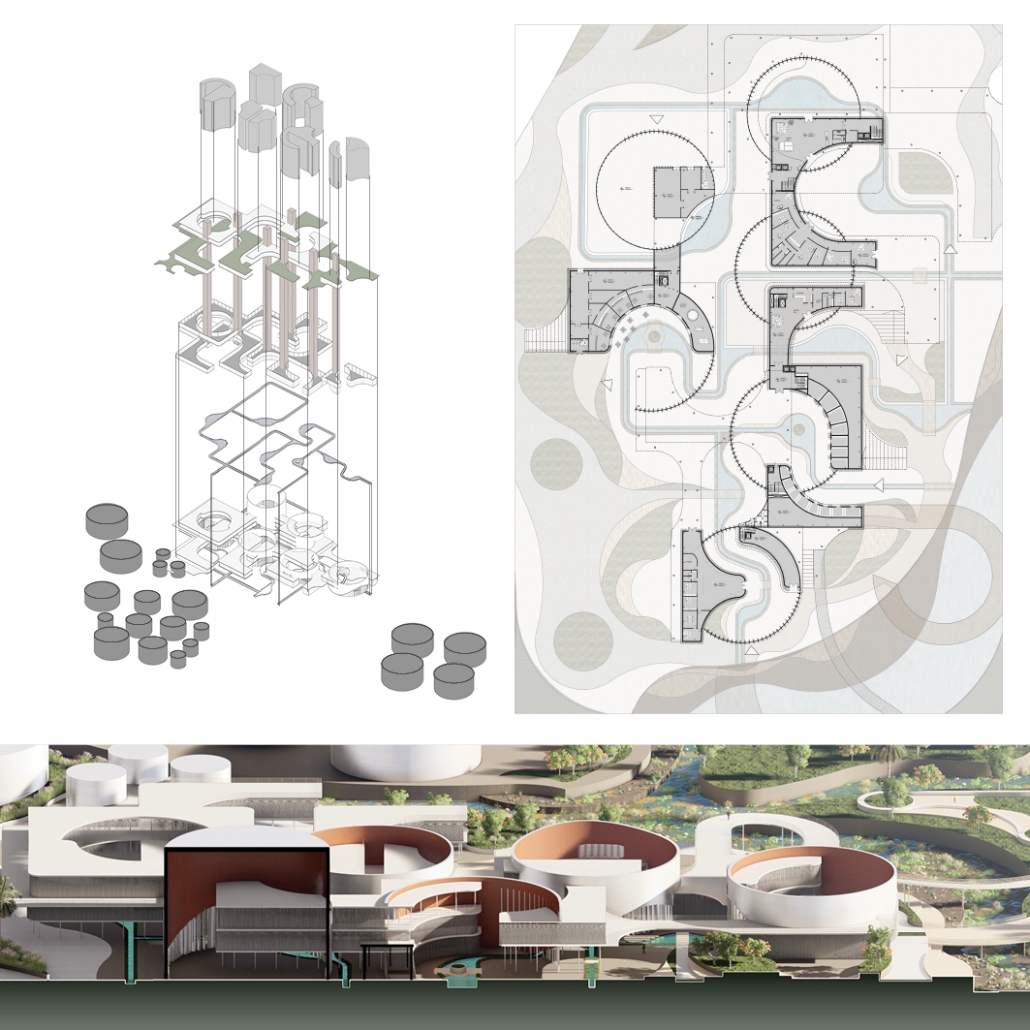
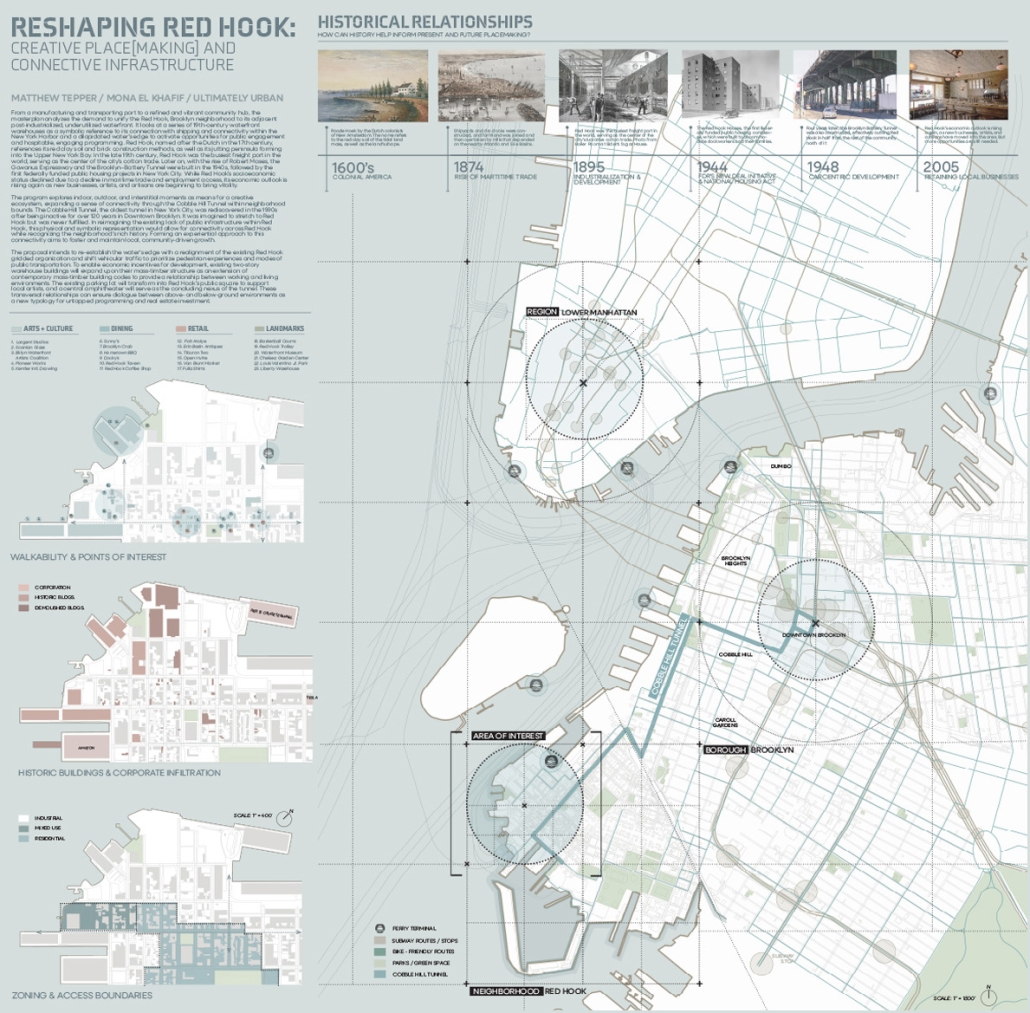
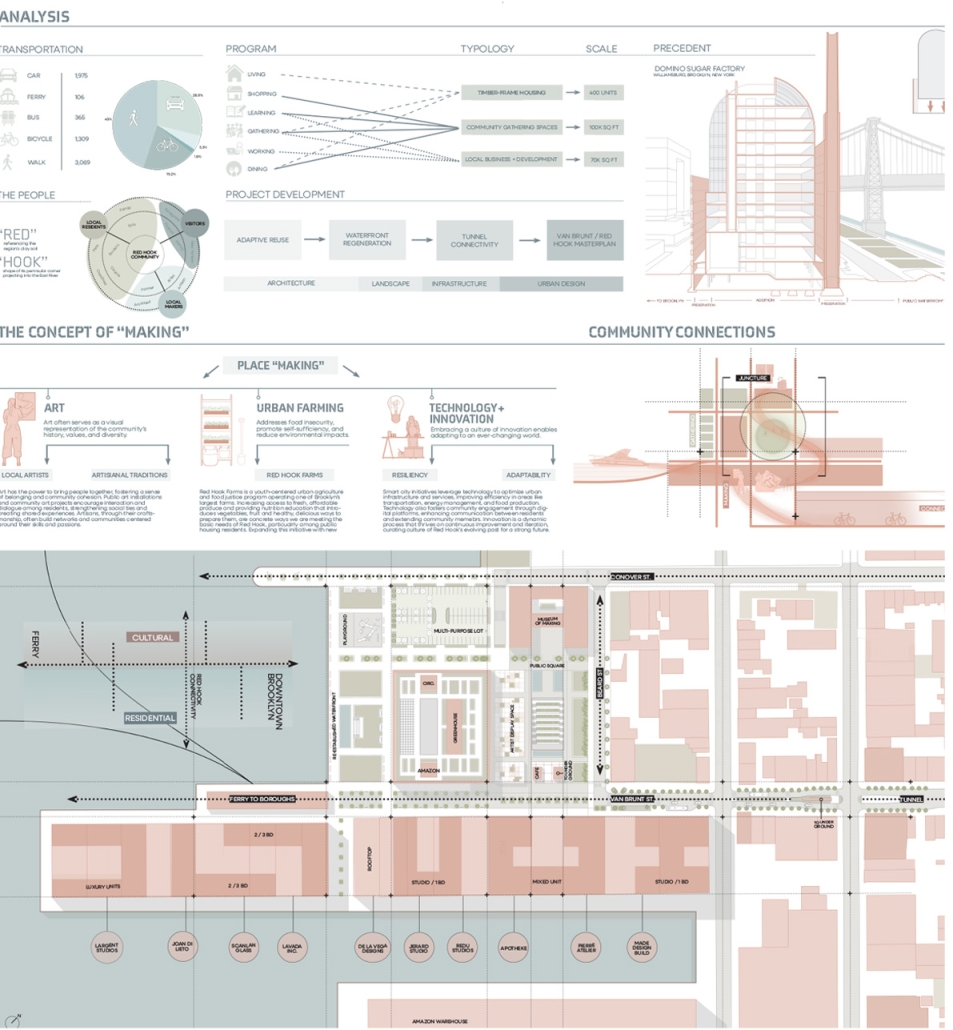
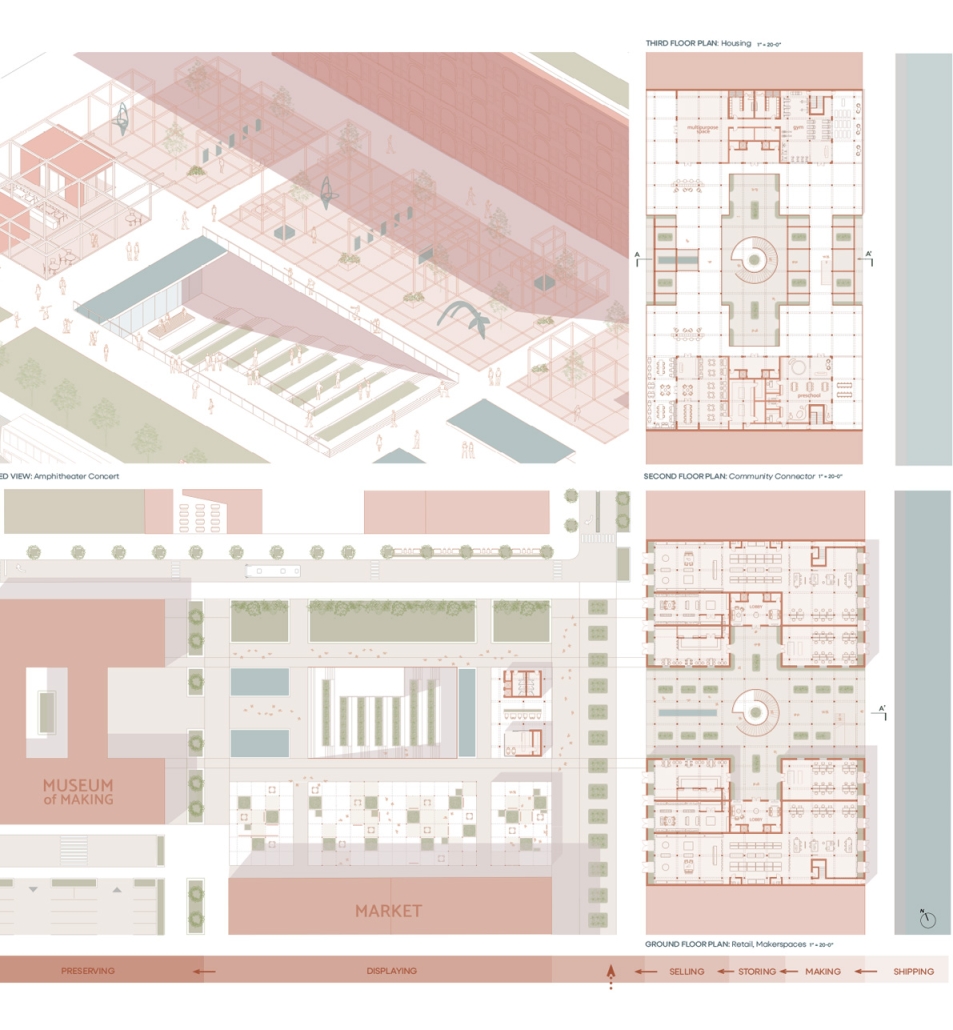
Reshaping Red Hook: Creative Placemaking and Connective Infrastructure. by Matthew Tepper, B.S. Architecture ’24
University of Virginia | Advisor: Mona El Khafif
From a manufacturing and transporting port to a refined and vibrant community hub, the masterplan analyzes the demand to unify the Red Hook, Brooklyn neighborhood to its adjacent post-industrialized, underutilized waterfront. It looks at a series of 19th-century waterfront warehouses as a symbolic reference to its connection with shipping and connectivity within the New York Harbor and a dilapidated water’s edge to activate opportunities for public engagement and hospitable, engaging programming.
Red Hook, named by the Dutch in the 17th century, references its red clay soil and brick construction methods, as well as its jutting peninsula forming into the Upper New York Bay. In the late 19th century, Red Hook was the busiest freight port in the world, serving as the center of the city’s cotton trade. Later on, with the rise of Robert Moses, the Gowanus Expressway and the Brooklyn–Battery Tunnel were built in the 1940s, followed by the first federally funded public housing projects in New York City. While Red Hook’s socioeconomic status declined due to a decline in maritime trade and employment access, its economic outlook is rising again as new businesses, artists, and artisans are beginning to bring vitality.
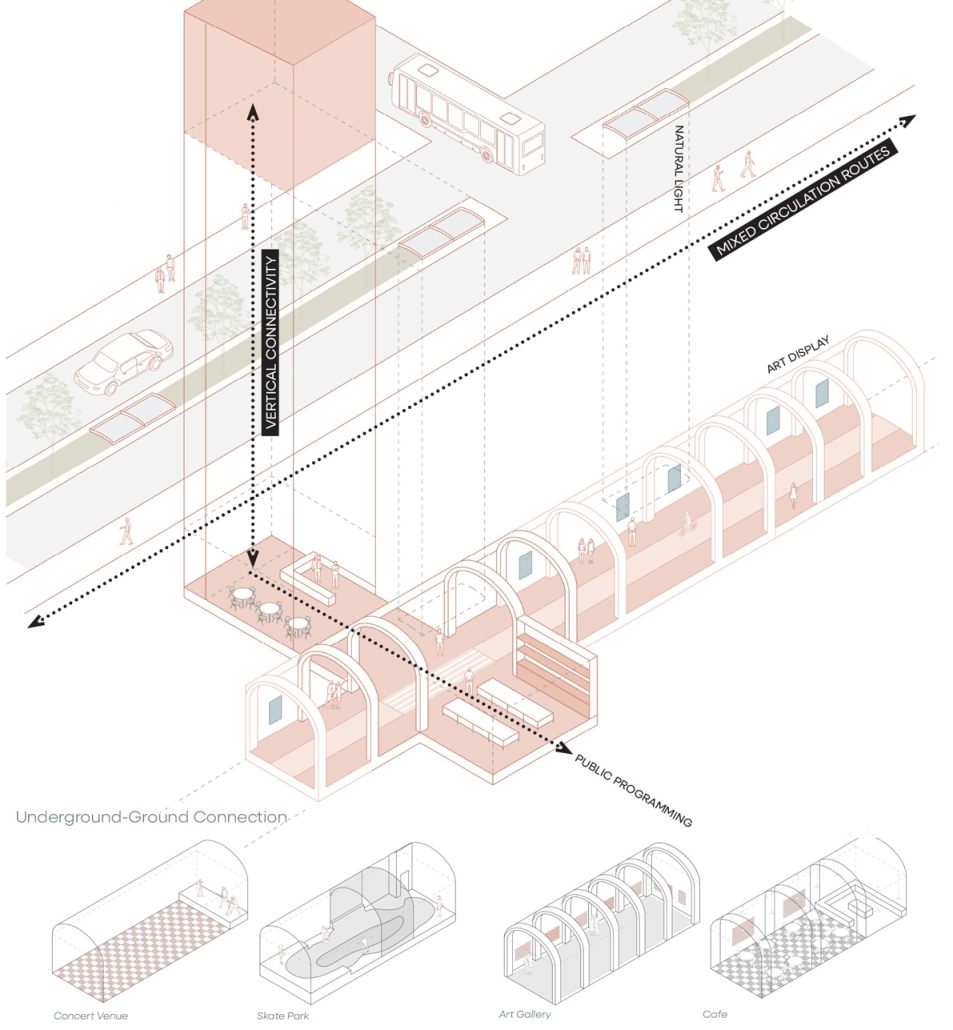
The program explores indoor, outdoor, and interstitial moments as means for a creative ecosystem, expanding a sense of connectivity through the Cobble Hill Tunnel within neighborhood bounds. The Cobble Hill Tunnel, the oldest tunnel in New York City, was rediscovered in the 1990s after being inactive for over 120 years in Downtown Brooklyn. It was imagined to stretch to Red Hook but was never fulfilled. In reimagining the existing lack of public infrastructure within Red Hook, this physical and symbolic representation would allow for connectivity across Red Hook while recognizing the neighborhood’s rich history.
Forming an experiential approach to this connectivity aims to foster and maintain local, community-driven growth. The proposal intends to re-establish the water’s edge with a realignment of the existing Red Hook gridded organization and shift vehicular traffic to prioritize pedestrian experiences and modes of public transportation. To enable economic incentives for development, existing two-story warehouse buildings will expand upon their mass-timber structure as an extension of contemporary mass-timber building codes to provide a relationship between working and living environments. The existing parking lot will transform into Red Hook’s public square to support local artists, and a central amphitheater will serve as the concluding nexus of the tunnel. These transversal relationships can ensure dialogue between above- and below-ground environments as a new typology for untapped programming and real estate investment.
Instagram: @mattportfolio, @aschool_uva
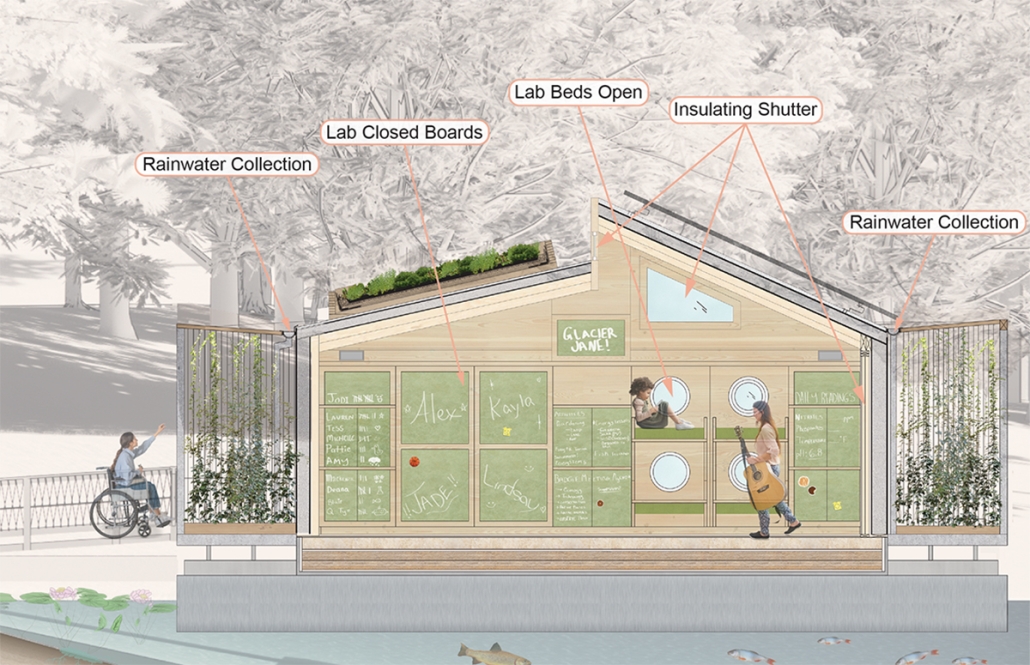
Fluid Landscape: A Speculation on Edge by Marla Stephens, M. Arch ’24
University of Florida | Advisors: Charlie Hailey & Jeff Carney
Architecture for a Fluid Landscape: A Speculation on Edge, addresses the ephemeral nature of dwelling on Florida’s coastal edge. This project aims to unearth Florida’s fluid strata to resurface a forgotten timeline of architectural ruins and stories lost at sea and to reinterpret future coastal habitation for an accreting landscape. Using Wilbur-by-the-Sea and Cape Canaveral, Florida as stations for witnessing and recording the evolution of an edge, this project will begin to negotiate the nature of impermanence and symbiosis of architecture along the shore.
As time passes, layers of stories, artifacts, ecologies, and technologies are embedded within the anthropogenic landscape. Is time as fluid as the littoral edge? Is there a way to work between the layers, to establish a permanent marker of change, to record the unfolding of time on an uncertain edge? Time moves quicker and shorter here, each day is a different coast. On the edge, change is felt at a more alarming rate. Here we bear witness to the ecological impact we have made; impacts which are felt slowly, suddenly, or all at once. Can architecture make us notice more? Notice the imprint of a seashell along the shore, and the fluttering of the saturated sand made by a sand flea hiding beneath the surface; to the detrimental effects of toxic runoff which tarnishes the shore with a nauseating green film, and the infrastructural damage inflicted by hurricanes and rising tides. We must notice more, to slow down time once again and decelerate our current path towards exponential degradation, to restore Mother Nature’s natural procession.
This project will collect and unearth objects and stories found along the fluid landscape while using the Florida Houses of Refuge as a generative part for testing markers on the coast. The Houses of Refuge were ten stations along the east coast of Florida constructed for the sole purpose of saving the lives of shipwrecked persons, yet they evolved into much more. This project uses the forgotten coast of Chester Shoal as a proving ground for ever-evolving iterations of stations that witness the transformations of an ephemeral landscape.
Instagram: @charlie.hailey, @marla.stephens
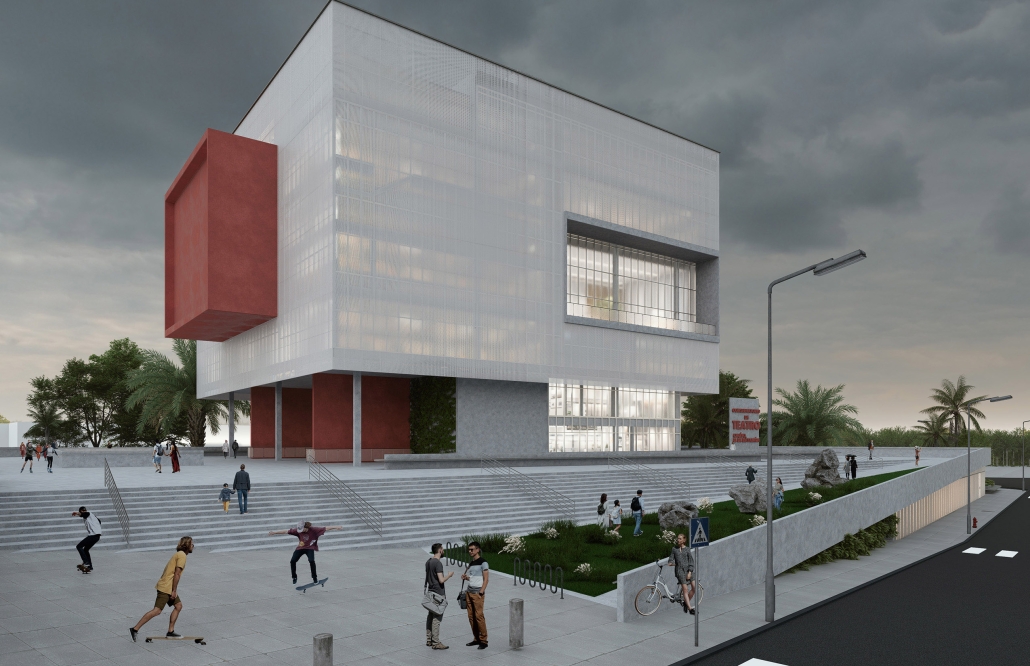
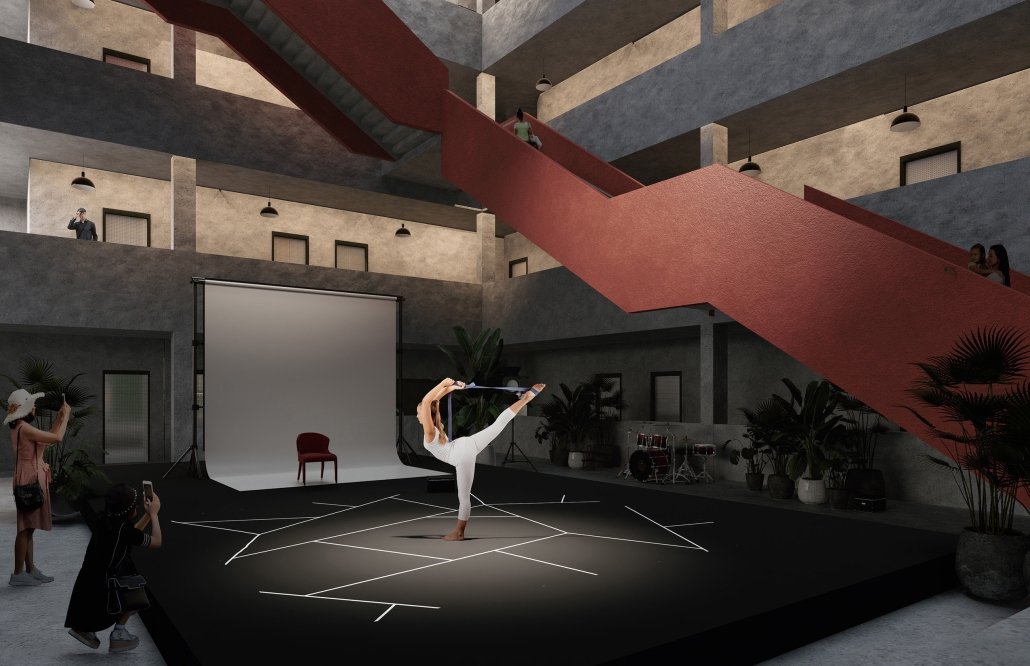
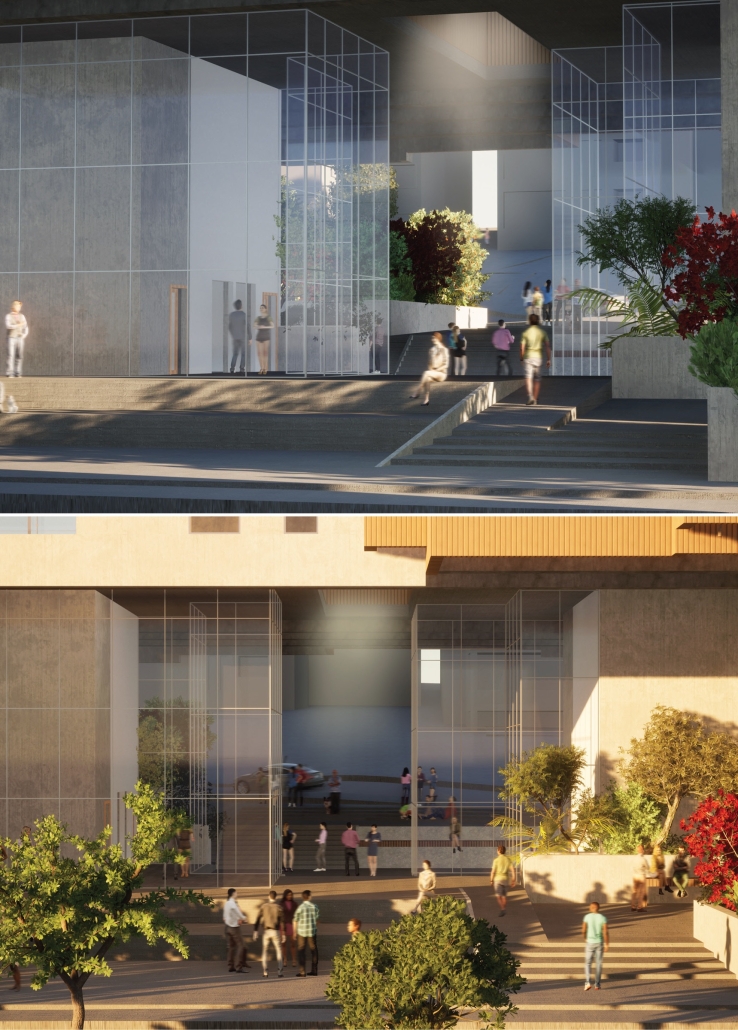
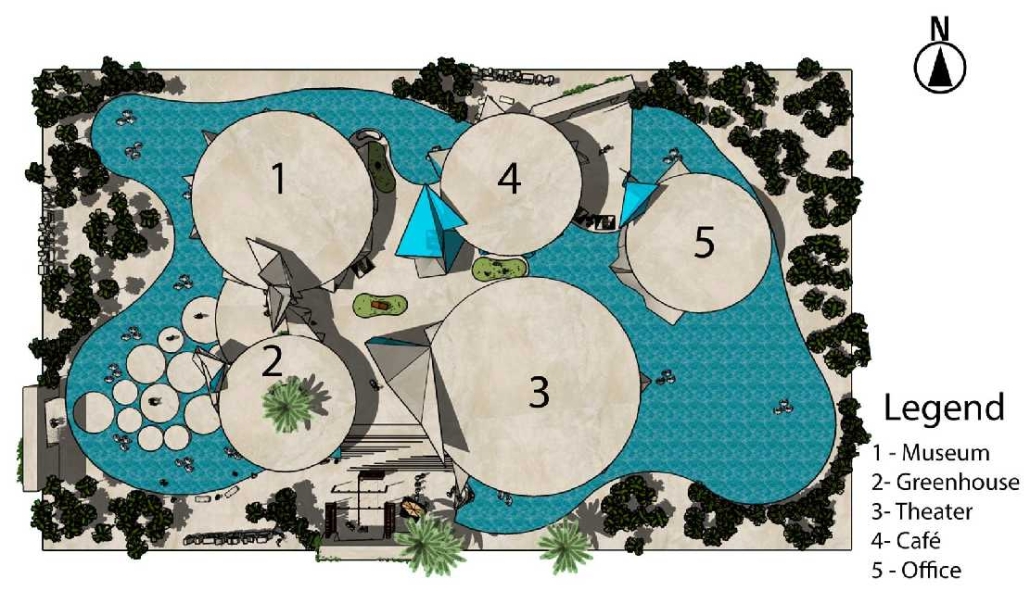
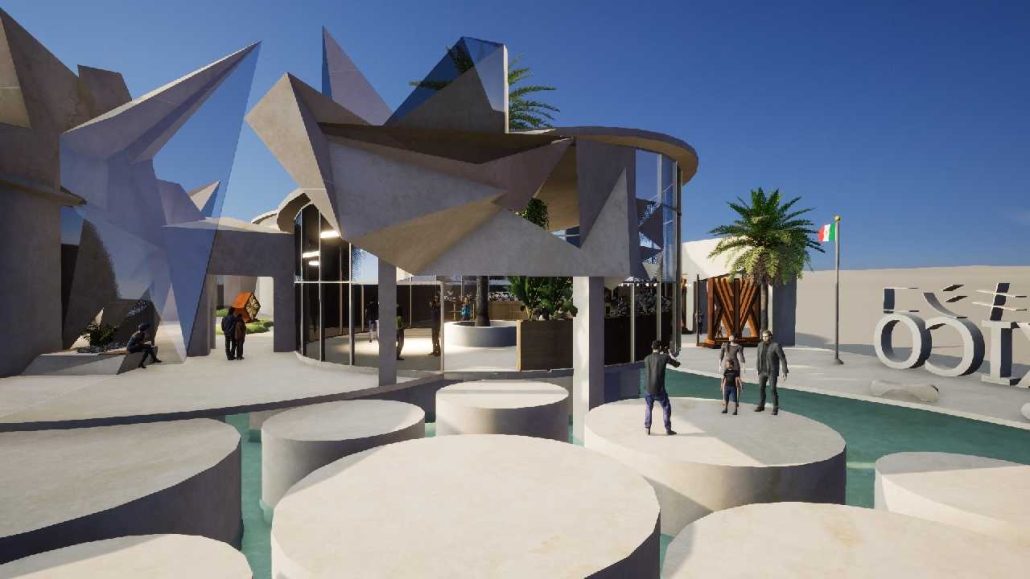
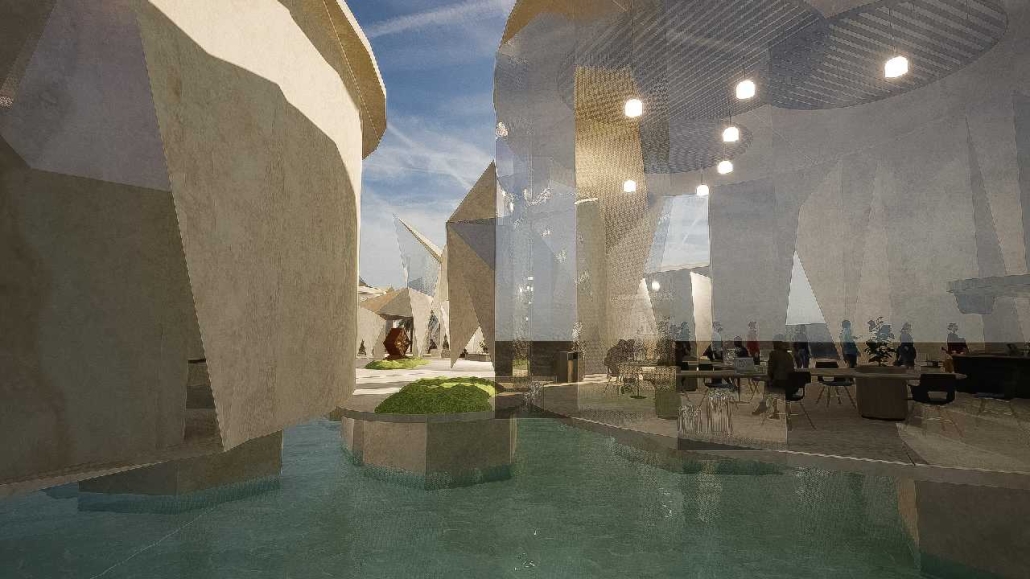
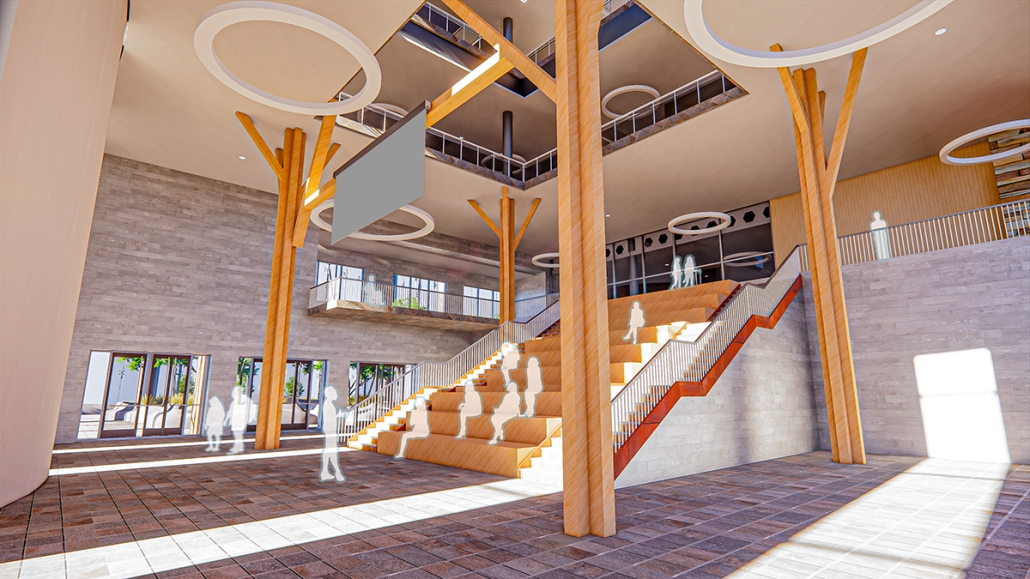
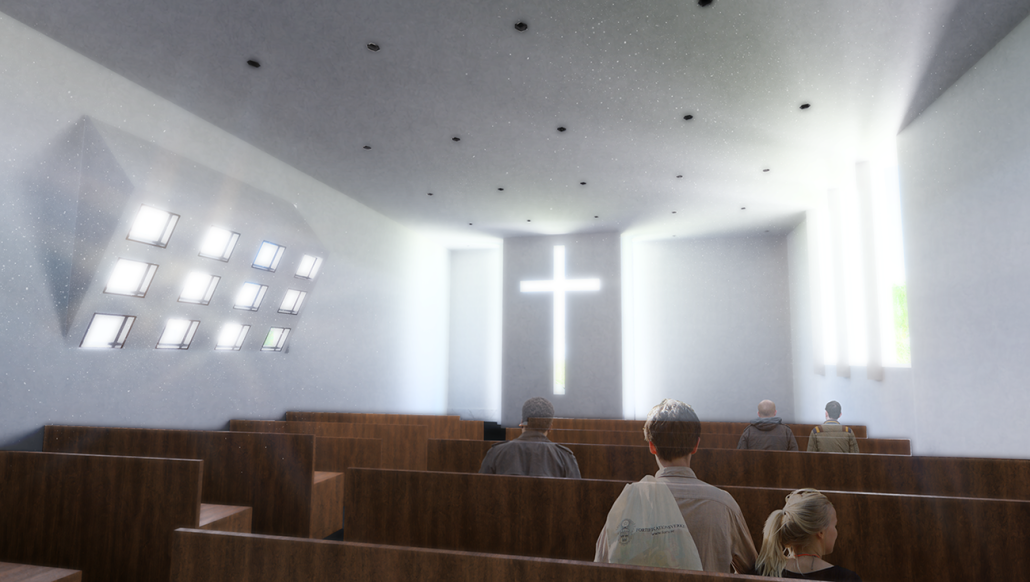
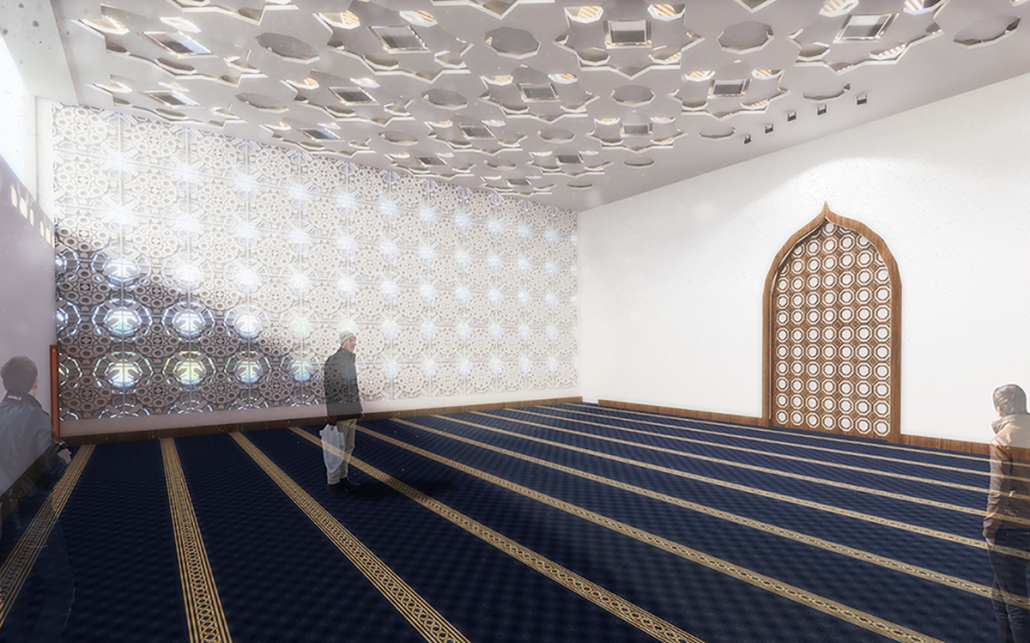
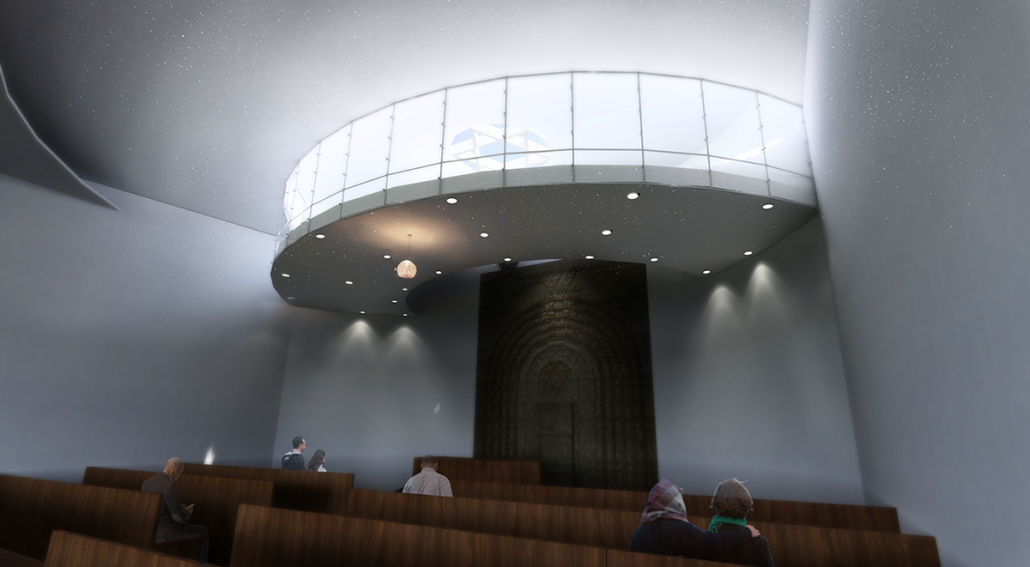
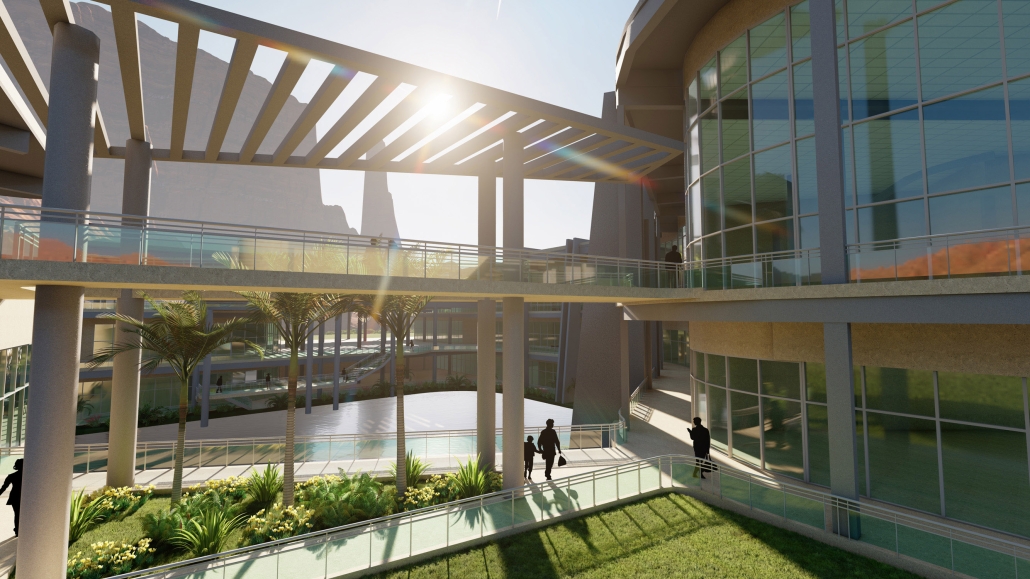
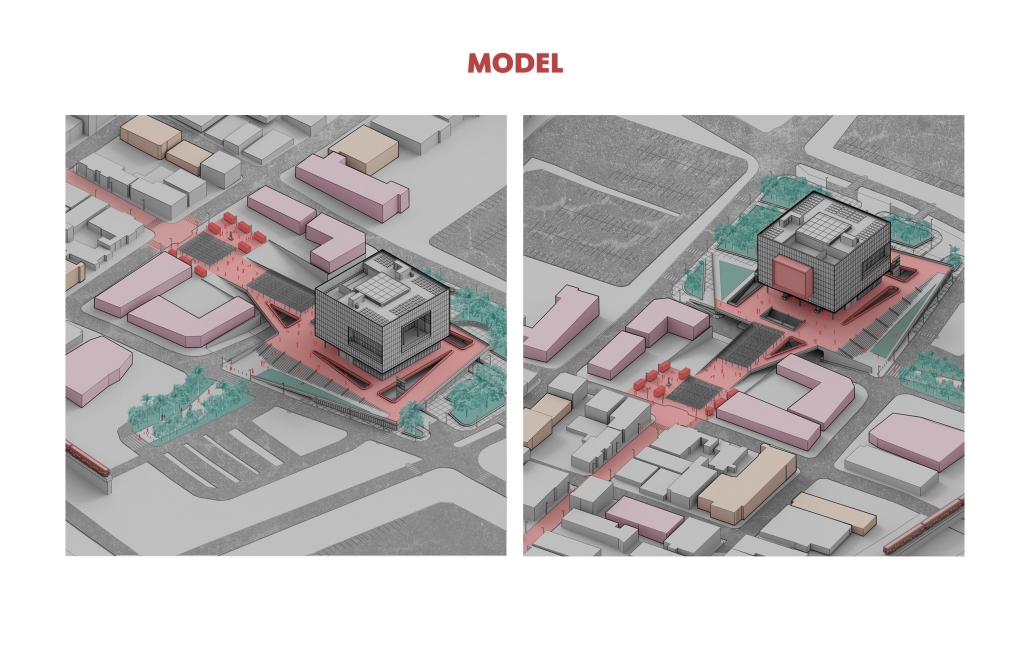
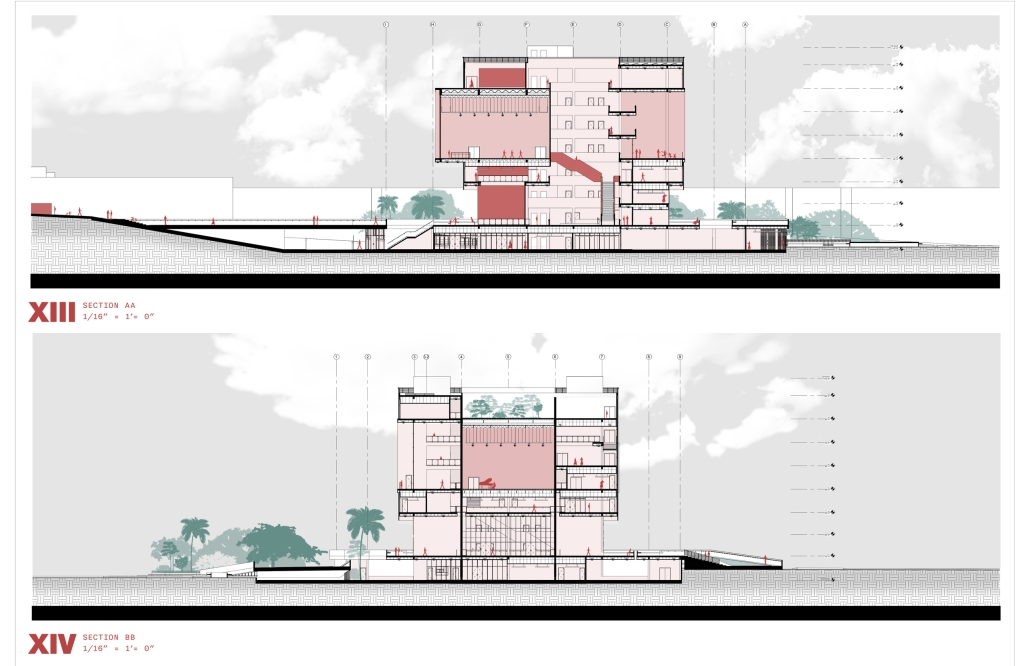
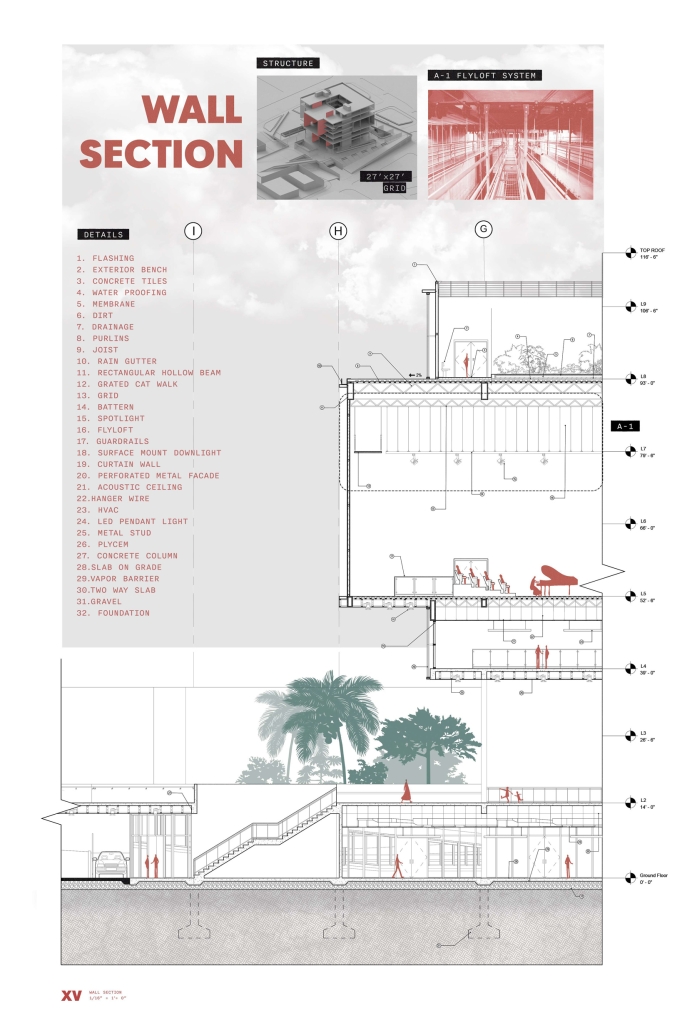
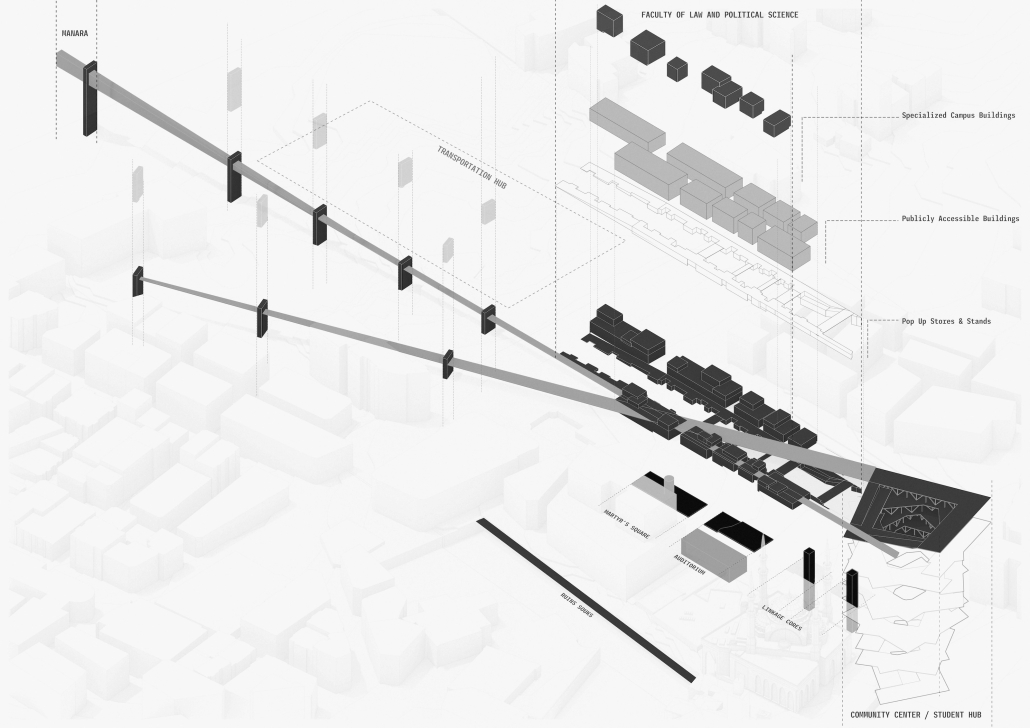
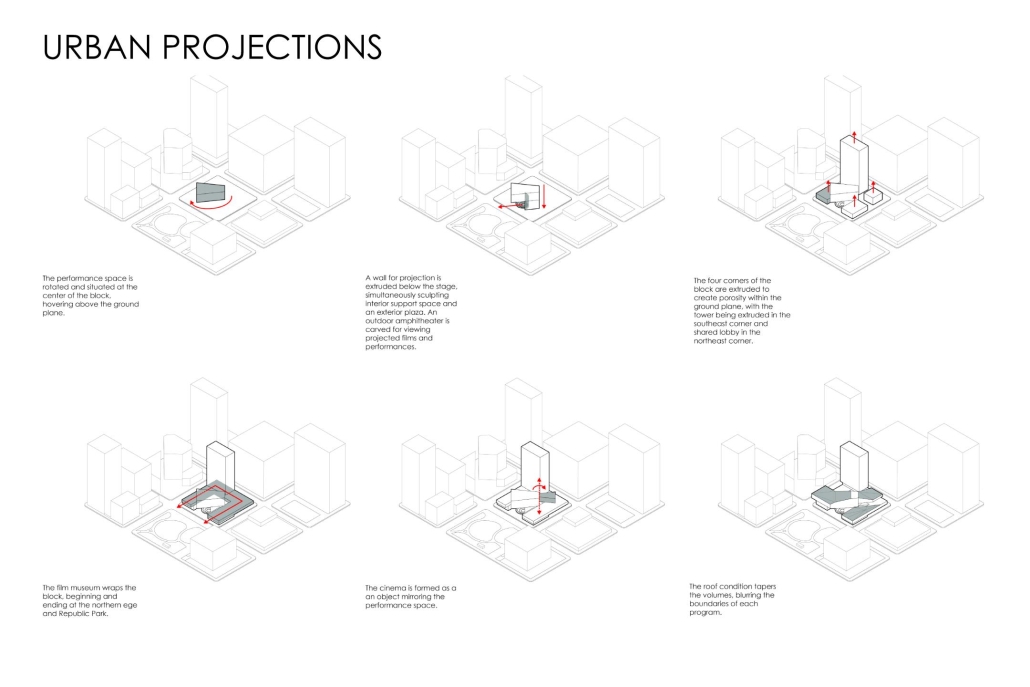
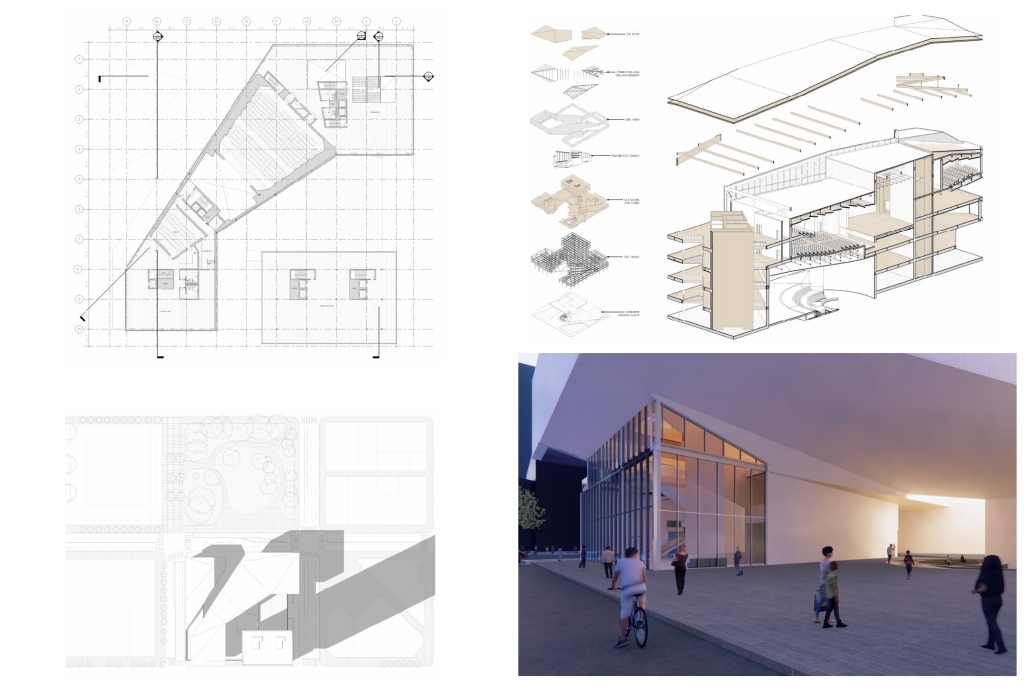
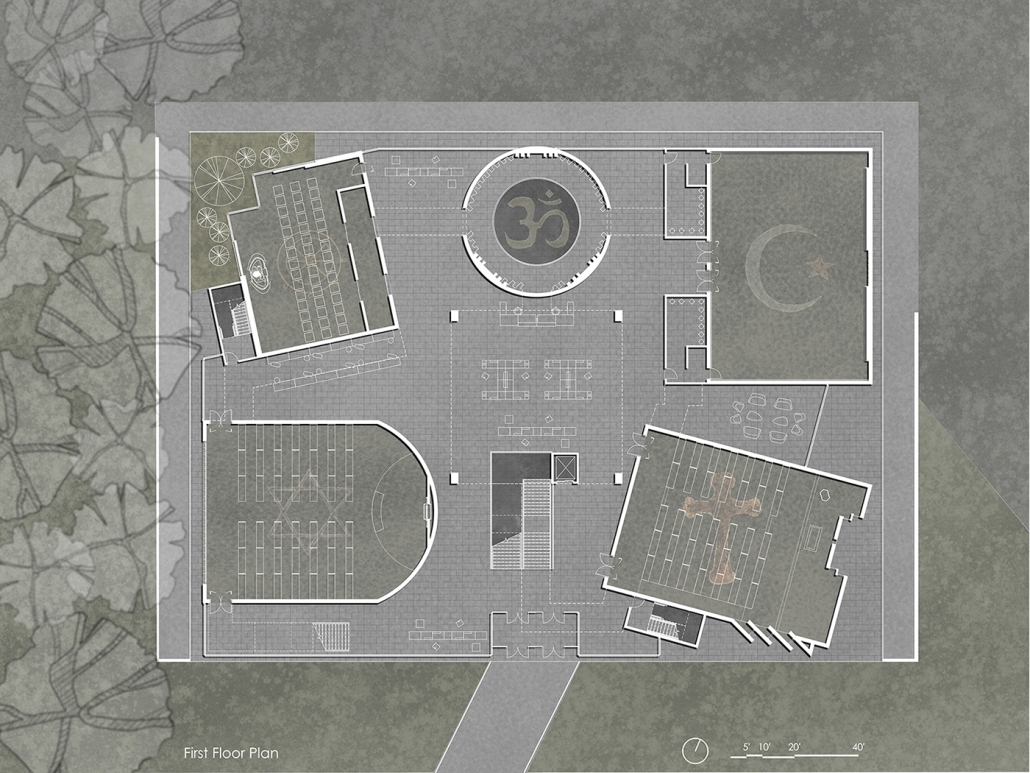
Conservatory of Theater: A Spot Light in the User by John M. Campis-Bobe, B. Arch ’24
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisor: Pedro A. Rosario-Torres
The decline of performing arts in contemporary culture can be attributed to a lack of cultural identity. Historically, theater served as a platform for societal reflection and discussion of political and sociocultural issues. Today, this art form has lost its prominence in many countries, necessitating a revival to inspire a new generation. To address this, the project employs the concept of a perfect prism to contrast its surroundings, highlighting the performance space as a vital expression of cultural identity.
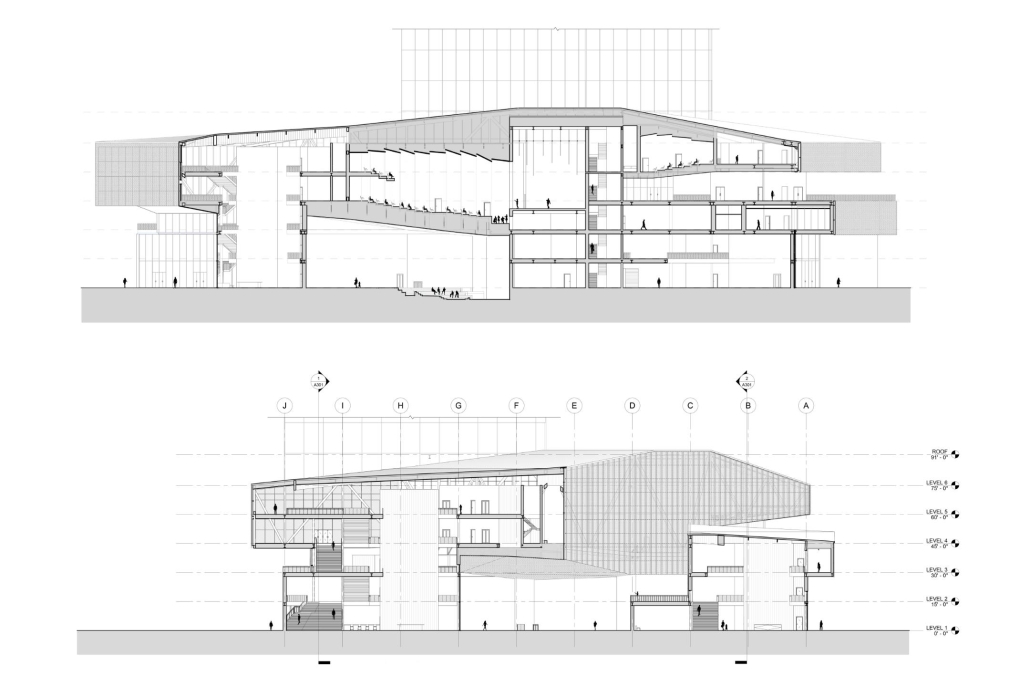
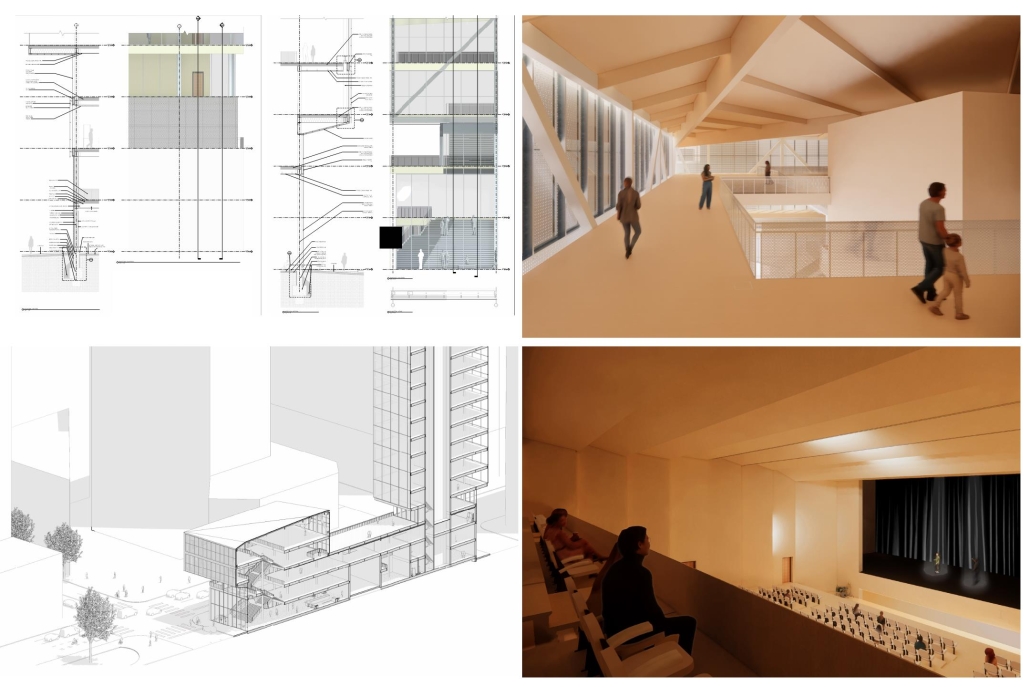
Located in Bayamón, Puerto Rico, near the urban train’s last station, the project identifies existing entities and highlights those proposed for improvement. By linking the urban core, it establishes a new theatrical district with an axis running from the town hall through Marti Street to the Theater Conservatory. The conservatory’s design incorporates six strategies from modern theater culture, seamlessly integrated into the urban context, emphasizing both external and internal engagement. Its purpose is to create a series of encounters between performances and spectators, inviting exploration and contemplation throughout the city. For example, urban niches carve fenestration within each façade, showcasing rehearsal rooms, foyers, and terraces to residents and visitors passing by. The black box theater is cantilevered from the building façade, marking the culmination of the theatrical district axis. Inside, there are adaptable spaces for various scenarios that aren’t restricted by a fixed arrangement. This expands on the versatility to reconfigure to the constant changes in our contemporary culture. To improve the user experience and accessibility, an elevated urban plaza is created, bridging the conservatory with the surrounding urban fabric and inviting community interaction. Due to the tropical climate, sustainable features include natural ventilation on all floors, permeable pavement, solar panels, and an underground cistern for water storage.
The final model reveals the axis that unifies the new theatrical district and an alternative route from the train station, designed to enhance pedestrian access. By integrating urban connectivity, cultural engagement, and sustainable design elements, the conservatory sets a new standard for functionality and environmental stewardship, marking a transformative icon for new cultural expression.
Instagram: @johncampiss
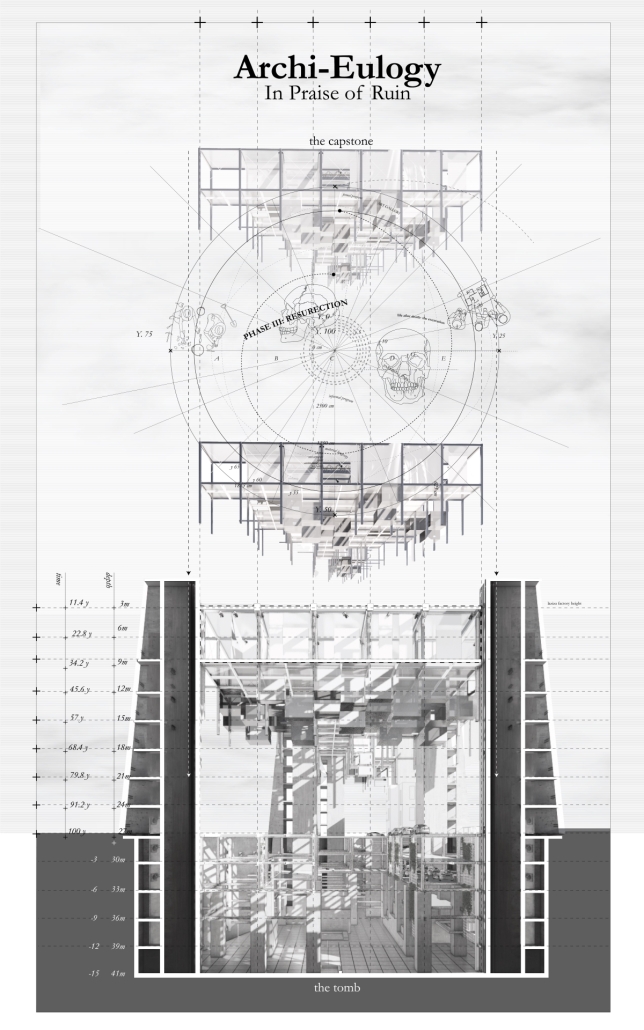
Archi-eulogy: Negotiating Ruination in the Urban Void by Glory Nasr, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Sinan Hassan
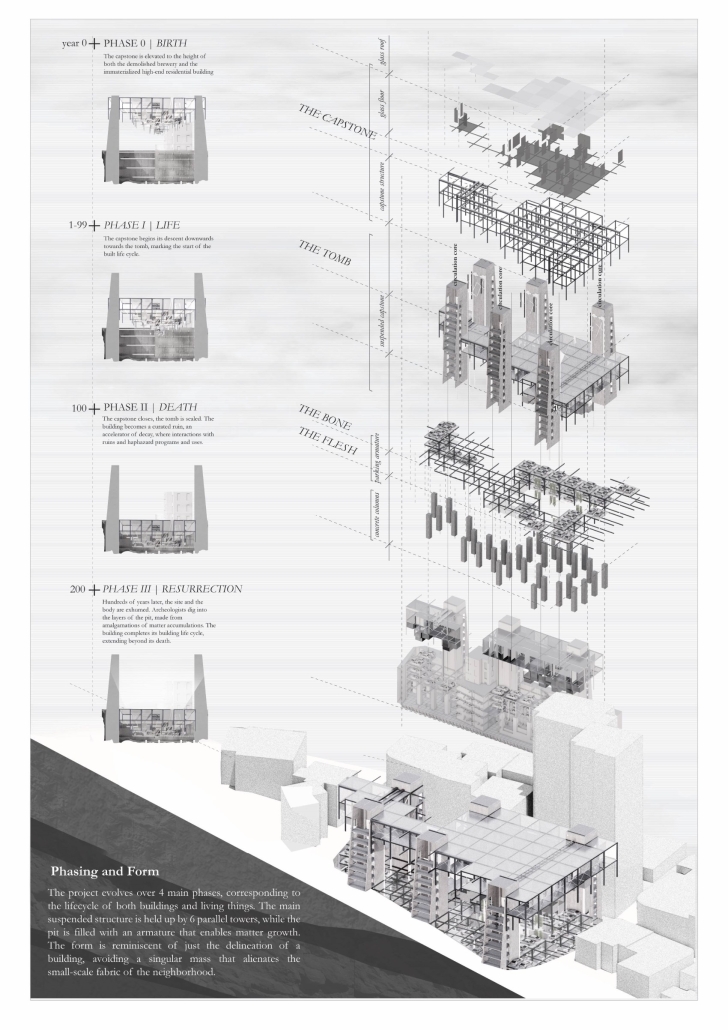
In a dense alleyway of a residential suburb of Beirut, Lebanon, lies a neighbourhood-sized construction site, halted at the excavation stage. Where once stood the Laziza Factory, the first brewery in the Levant that was demolished in 2017, remains a 20-meter-deep manufactured chasm, vestiges of the unfinished construction of a high-end, Starchitect-made residential project. The chasm resembles a tomb with no capstone, a tomb for the demolished brewery and the immaterialized lofts, but more importantly for the notion of architecture as a practice above the human realms of economic crisis. The result is an absurd condition caught between architecture, geology, and ruin.
With this urban condition as the site of the project, Archi-eulogy stands as a manifesto
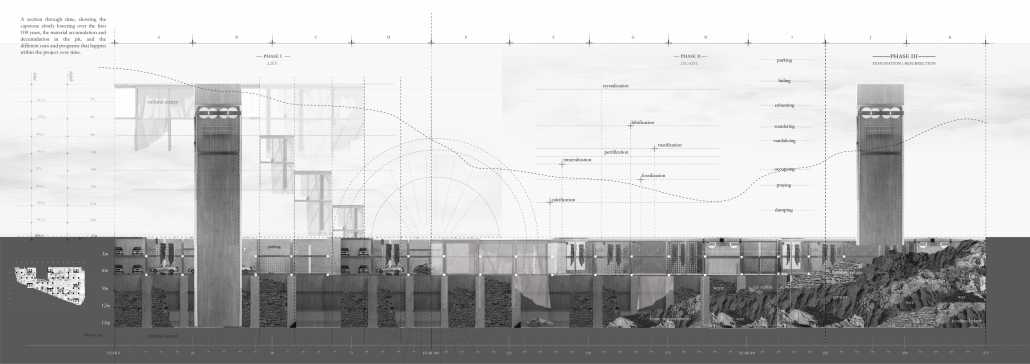
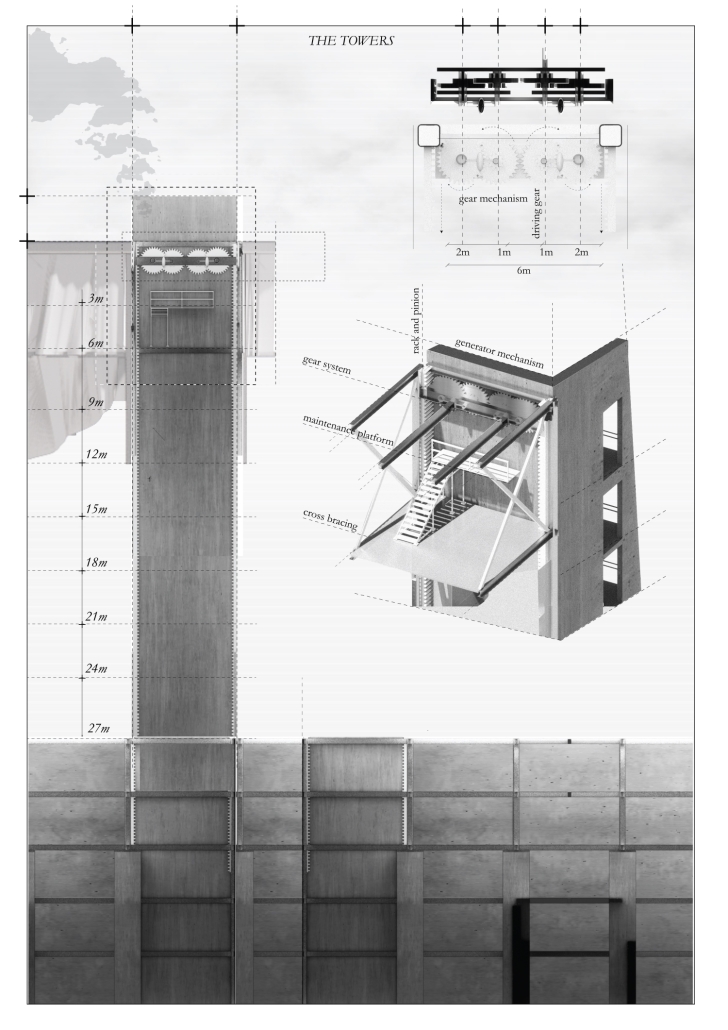
critiquing the method with which we build, developing an architecture that is inherently one of nonarchitecture. Building on the image of the site as an urban tomb, Archi-Eulogy proposes the acceptance of death through a lowering of a literal and metaphorical capstone onto the construction site over a 100-year cycle, corresponding to the average lifespan of a building. The capstone houses an art gallery and archival space, preserving the memory of the original brewery. Each height above the street level corresponds to a year, creating a geological stratification of the building height. As the capstone descends 0.5 cm a week
for a century, matter accumulates and decumulates in the pit. The pit houses a parking space on the upper two floors, while the bottom three floors are left as public space for the residents of the neighbourhood. Once the capstone closes and the excavation is remediated, the project enters its second phase, becoming a curated ruin-scape, allowing for informal uses of the public park. Finally, hundreds of years into the future, archaeologists descend into the pit through its towers, exhuming the archaeological body buried in the tomb. By literally and metaphorically closing the urban tomb, the project aims to remediate the violence the unfinished construction inflicted on the neighborhood.
This project was the 2nd Prize Winner of the Areen Projects Award for Excellence in Architecture and won the Dean’s Award for Creative Achievement.
Instagram: @ard_aub
Stay tuned for Part XV!