2022 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part II
We are back with week two of the 2022 Student Thesis Showcase featuring six more projects from schools across the US and Canada! This week’s projects explore the intersection of architecture and feminism as well as gender. If you missed it, make sure to check out Part I of this series.
We will be sharing these projects on Instagram at @studyarchitecture and @imadethat_ so let us know what you think there.
WINDS OF CHANGE by Leila Ghasemi, M.Arch ’22
Southern California Institute of Architecture | Advisor: Elena Manferdini
Do we have the capacity as architects to influence politics and bring social changes?
Does architecture still have a utopian agency to shape our future societies?
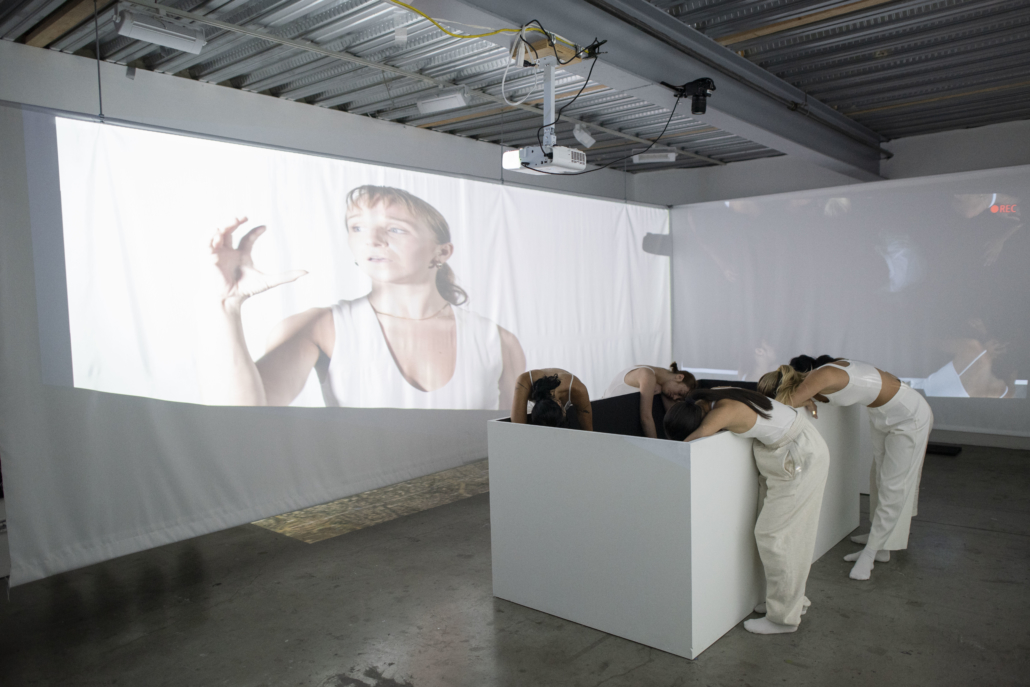
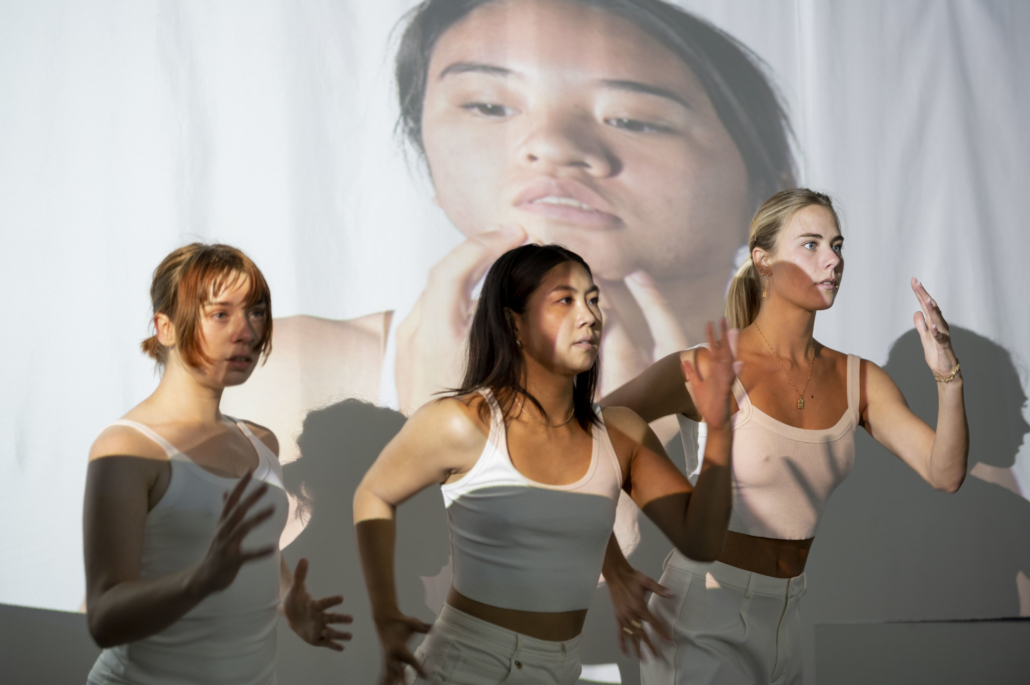
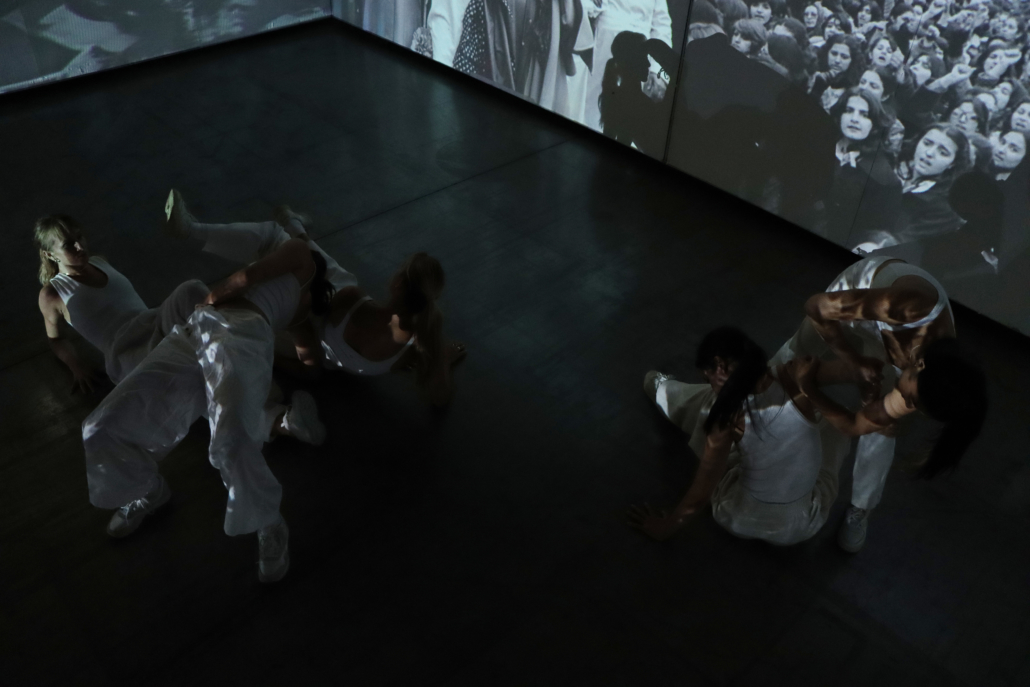
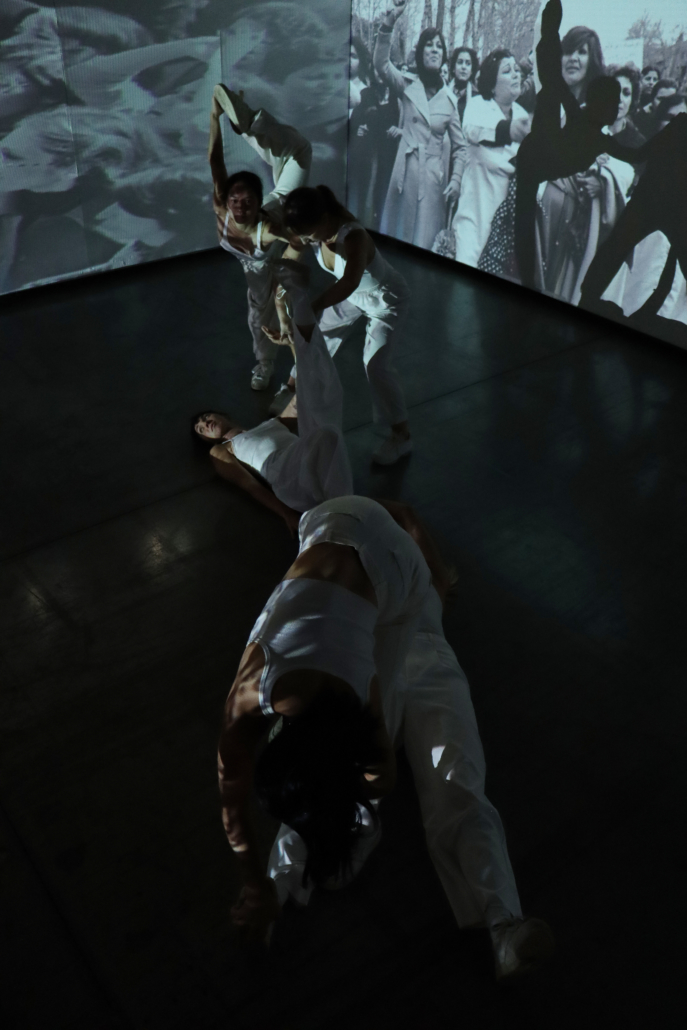
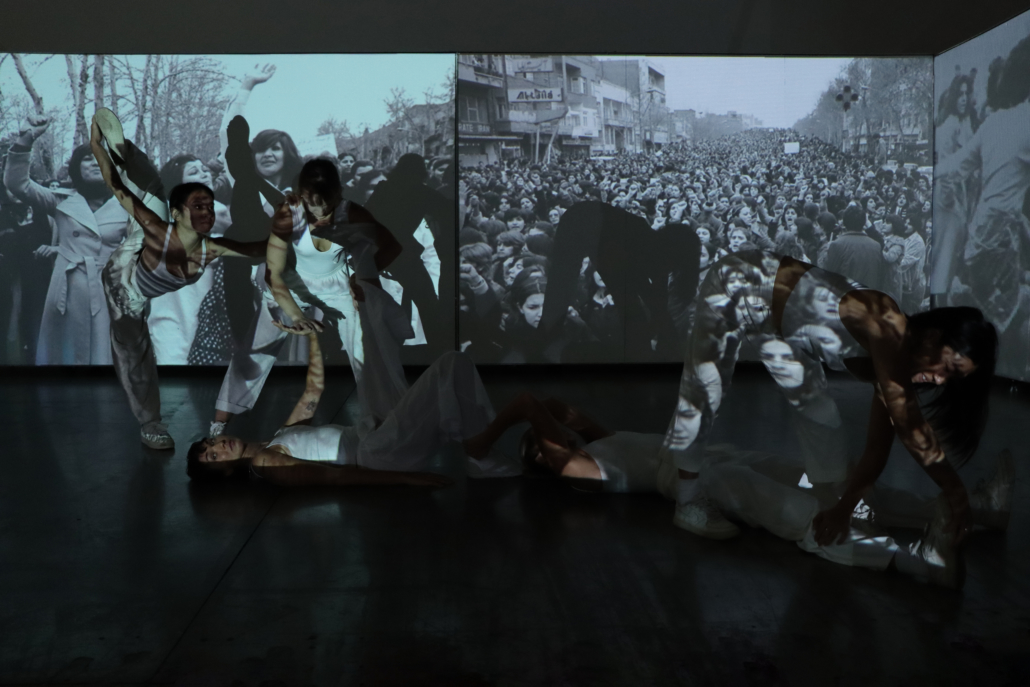
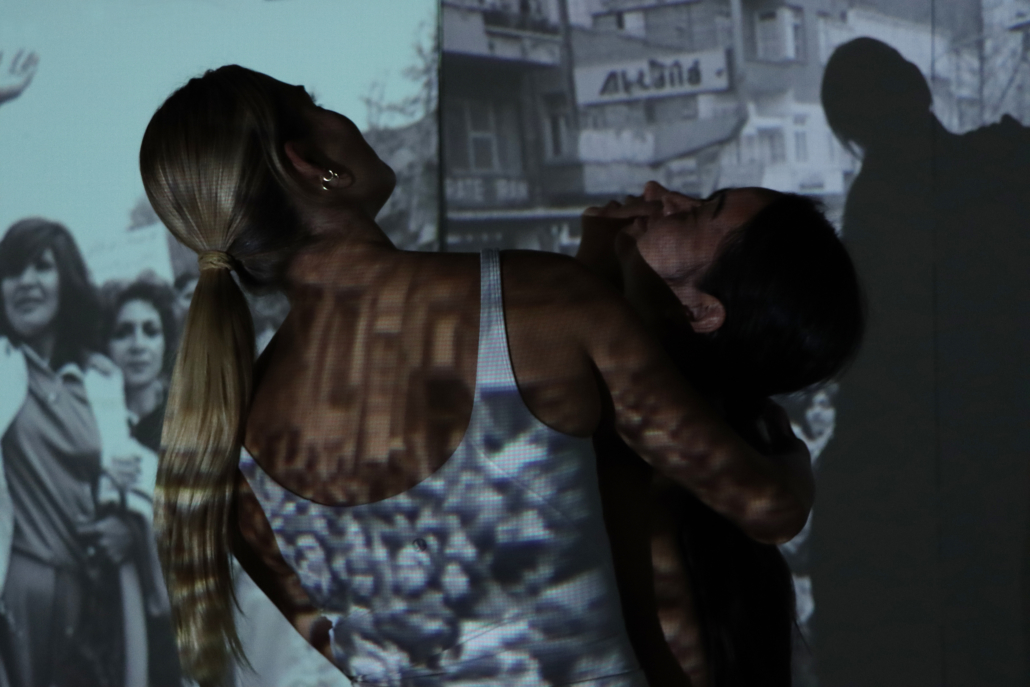
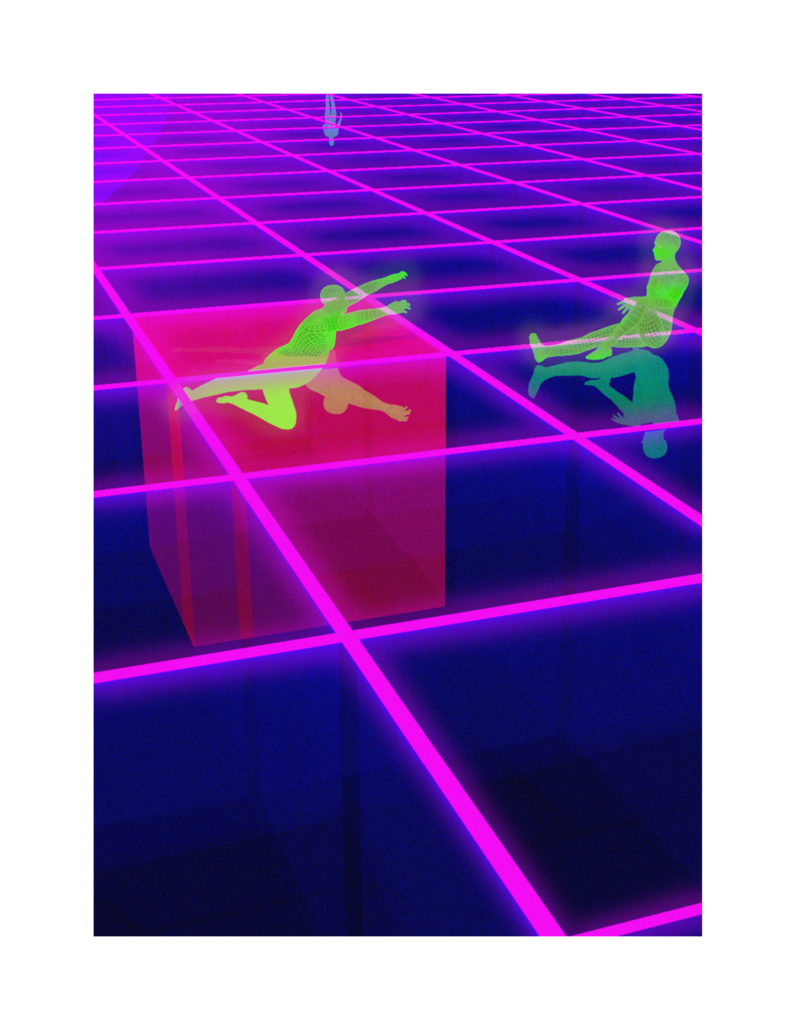
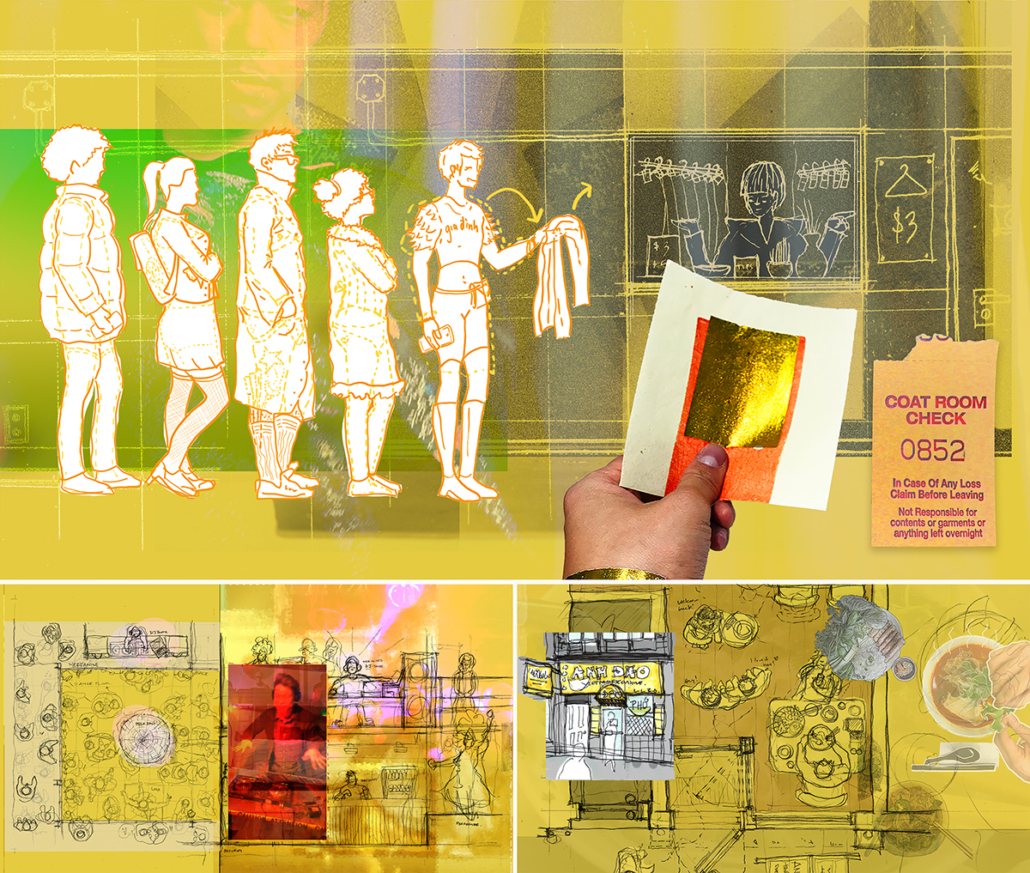
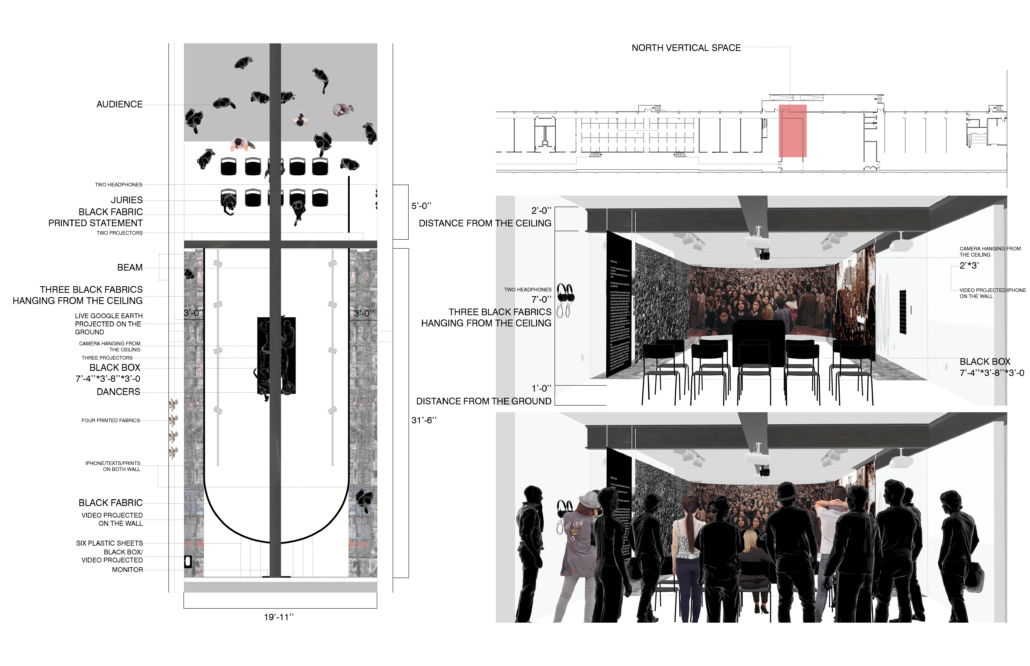
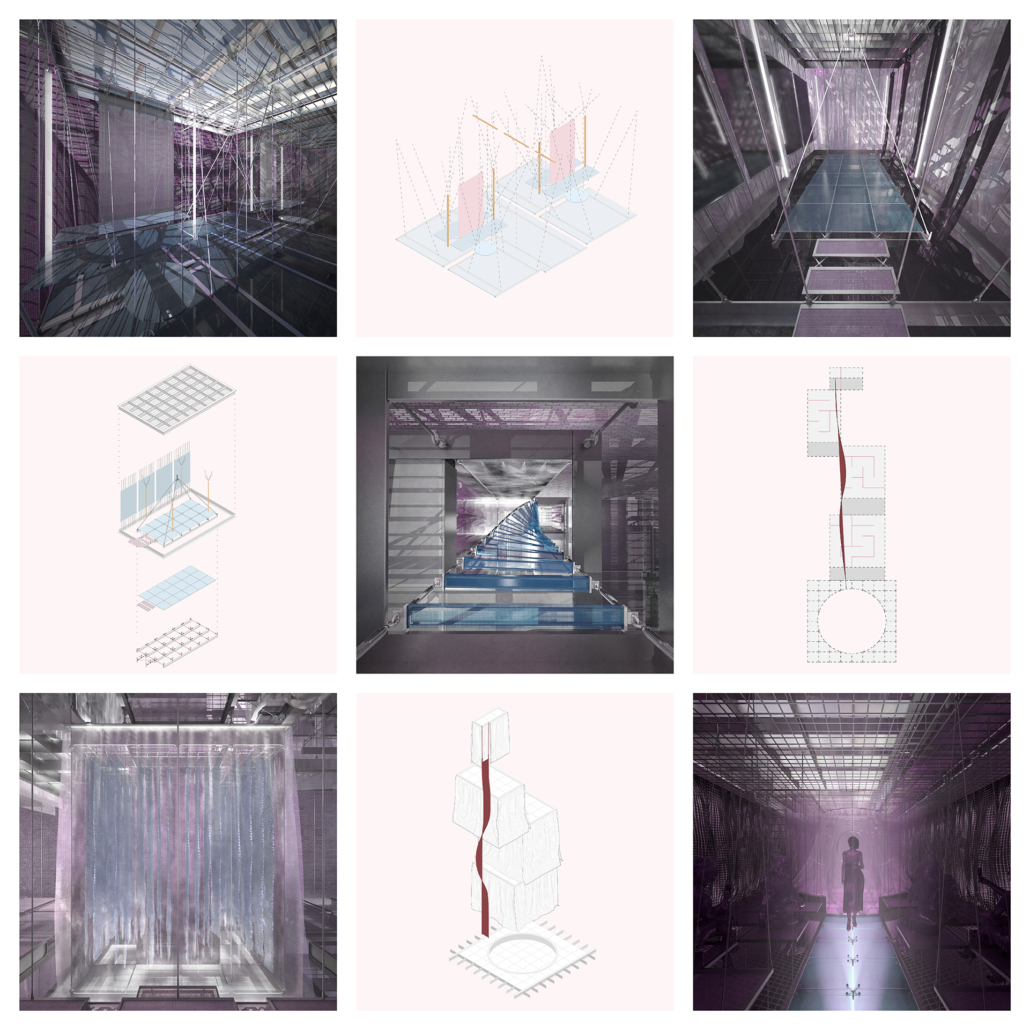
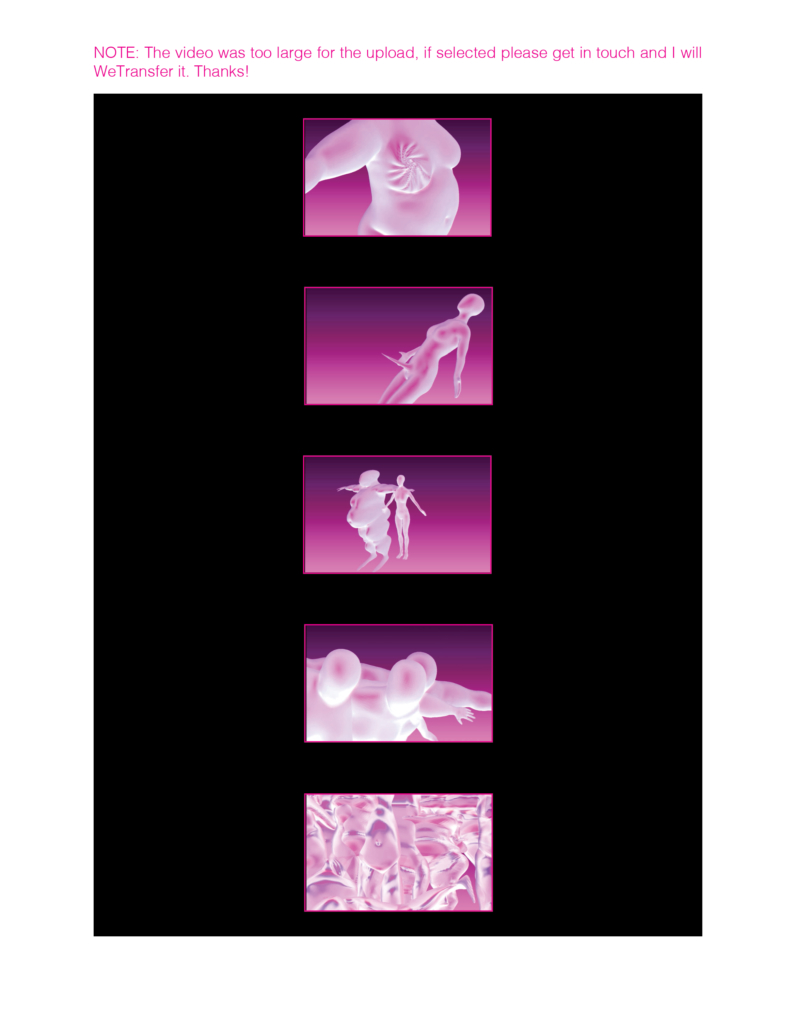
This thesis addresses Iran’s current situation, particularly the social injustice against women, by using architecture’s tools and analytical strategies through space, objects, videos, sounds, lights, materials, projection mapping, and the medium of dance to explore the role of new spaces of protests in social activism. Since Iran’s 1979 Revolution, Women have long faced legal, political, economic, and social challenges in Iran. Women are not allowed to work specific jobs, polygamy has become legal, and women have lost the right to divorce. For 43 years, Iranian women have not been allowed to express themselves through their bodies. The Islamic Republic mandated wearing a head covering, or hijab, in public. All females are required to cover their hair and dress modestly from puberty. Women cannot take off their compulsory hijab, cannot sing solo, cannot ride a bike, cannot dance.
Women have no place to protest and defend their human rights and make their voices heard against this cruelty. This thesis tries to create an opportunity to express dissent away from government surveillance or the immediate threat of police action. This thesis establishes a platform for activism and self-expression through the human body and tests the capacity of utopia (Hypothetical utopias) and activism in space. The platform for activism is an installation that includes an open inner space as a raised stage surrounded by an outer corridor, which together portrays and enacts women’s activism and government. The outer corridor is dark and narrow enough that people must enter it one at a time. There is a path with live google earth mapping of Azadi street in Iran where projected on the ground and pictures and videos of the 1979 Iran revolution on the wall that show we should move beyond this history. The inner space includes black fabrics offset from walls to create a dark area with a black box in the center where dancers perform. A camera hangs above the box to film dancers performing as live broadcasts are projected on the three black screens, and simultaneously, their expression through the camera is broadcast live to the whole world.
Iran’s government forbids all forms of activism (social, political, environmental). This multidisciplinary approach uses tools from architecture and dance to do more than each can do in isolation; it connects spatial strategies of architecture and the critical capacities of dance. This project will enact and empower the Iranian women protesting the mandatory hijab. The thesis creates a utopia, a fantasy reality, a truth that is not true, an act of optimism that shows something does not exist yet but could exist if we wanted it. This project will enact a piece of good news in this impossible situation in Iran through women’s choreographers to present the reality of the current situation in Iran and create a desire for the change we need to build. This is a revolution, through architecture and women’s body expression, to create a platform to protest for Iranian women’s activists, which could be developed everywhere, and people worldwide could see and hear them.
Watch Leila’s thesis presentation
Instagram: @leilaghasemi.la, @sciarc_manferdini
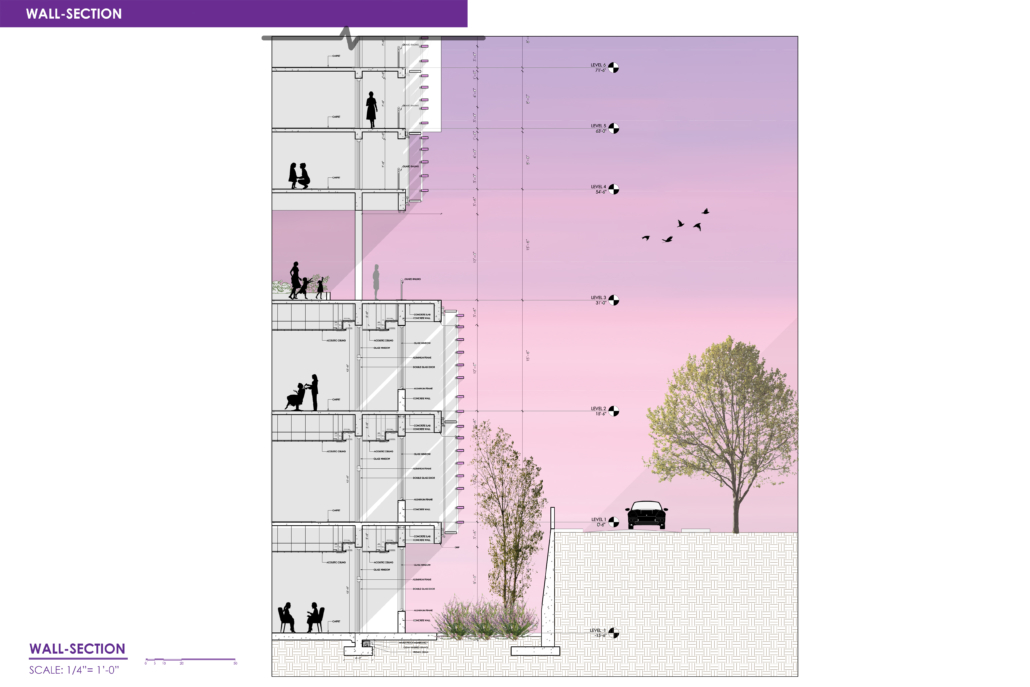
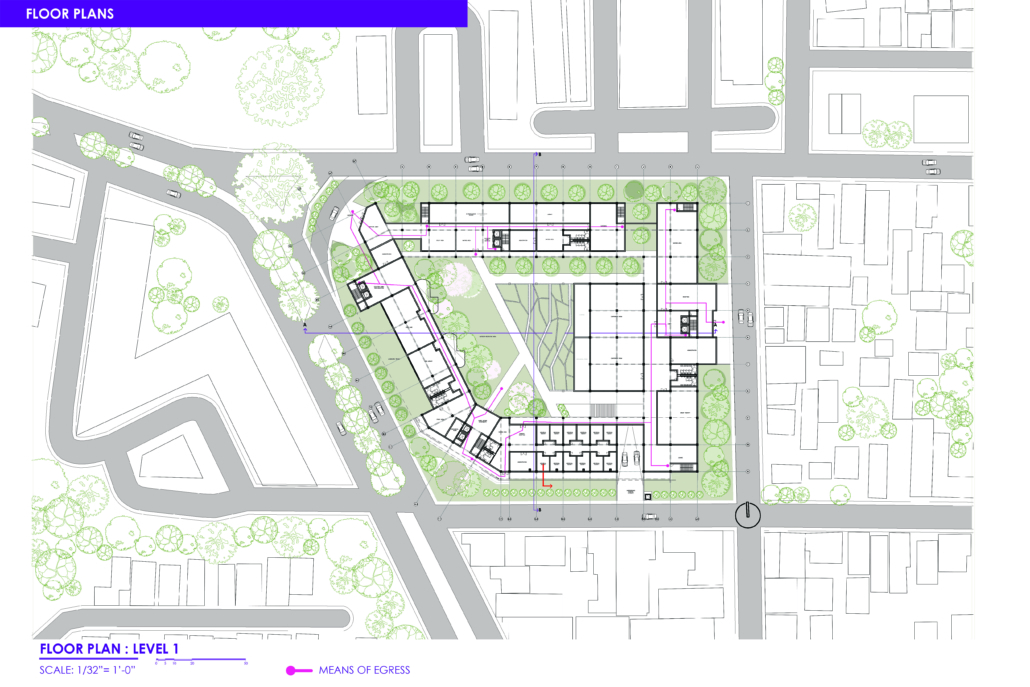
Architectural Design Strategies in Reentry Facilities: Post-Incarceration by Carly Chavez, M.Arch ’22
University of Florida | Advisor: Lisa Huang
The U.S. has one of the highest recidivism rates in the world. The population of women in prisons is rapidly increasing and thus creating gender-specific problems. Addressing these problems is often difficult because attention is focused on male inmates representing the majority prison population. All individuals, post-incarceration require housing, education, and work opportunity; however, research shows that women have a higher need for reintegration with the community and regaining custody of their children. Research also shows that the application of gender-informed policies is effective in reducing the recidivism rate. This acknowledges that men and women have different needs, and policy should address and respond to those differences. This project examines the conditions for women before, during, and after incarceration. The objective is to understand the gender-specific needs of women, what problems are being addressed, and how. Then, develop design strategies for women’s reentry facilities after incarceration. Ultimately, the research intends to contribute to the effort of reducing the number of women returning to prison, and to define the prominent external forces impacting women released from prison. This project focused on understanding these forces and the problems created to identify which issues can be translated into a solution in the built environment. This research proposes a multi-faceted women’s transitional facility as a building typology to support the effort to reduce recidivism.
There is an abrupt transition for incarcerated women as they finish their prison sentence, ultimately contributing to a higher likelihood to repeat offenses. Generally, this is the result of a lack of support for helping women transition into “normal” life. This project establishes that the architecture of transitional programs should reflect the specific needs of women to create an environment conducive to successful reentry into society. How does the architecture of transitional facilities change when children, community, and skill development are incorporated as part of the solution? This research advocates for a gradual reuniting of women with their children that parallels other efforts necessary to reintegrate women into the community. The architecture to support this program must establish the facility as a connection to the community with a focus on developing relationships between women, their children, and the community.
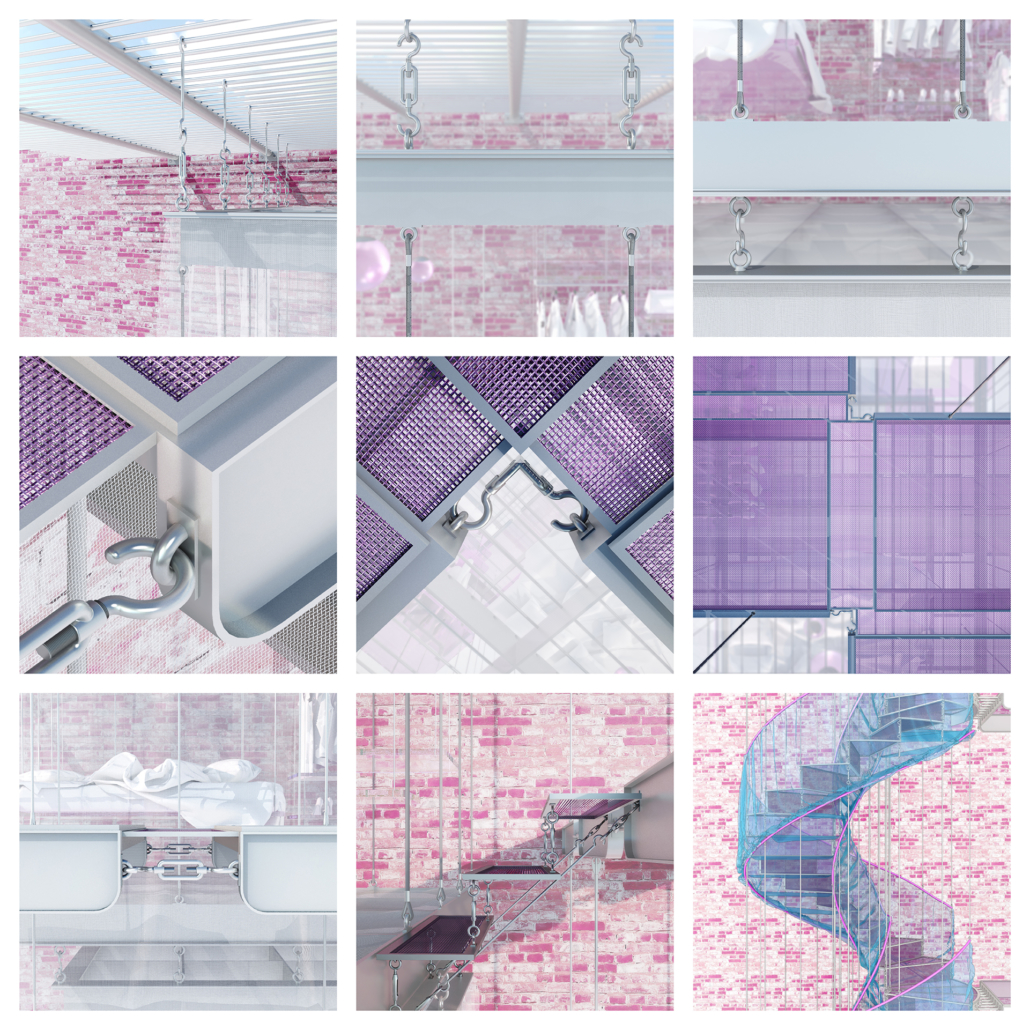
Architecture in Drag by Michael Evola, M.Arch ’22
Toronto Metropolitan University | Advisor: Marco Polo
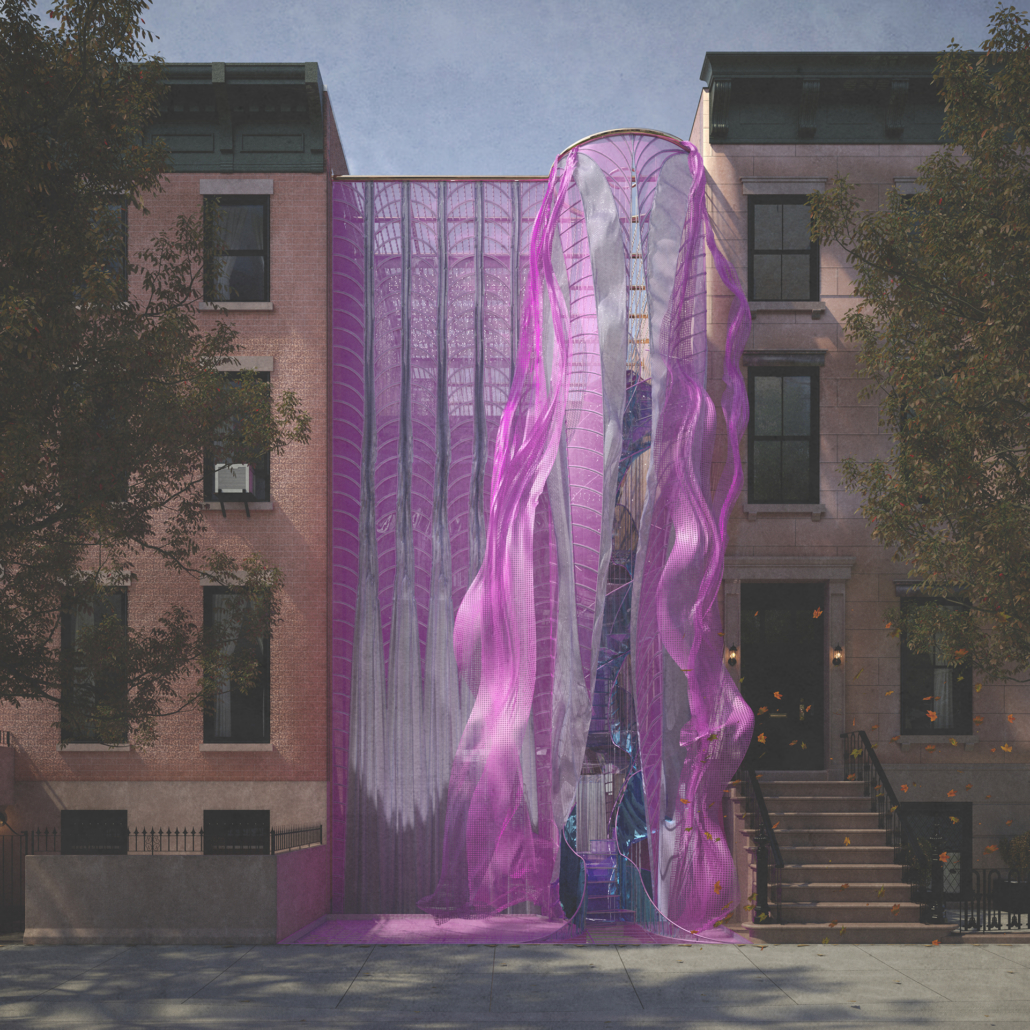
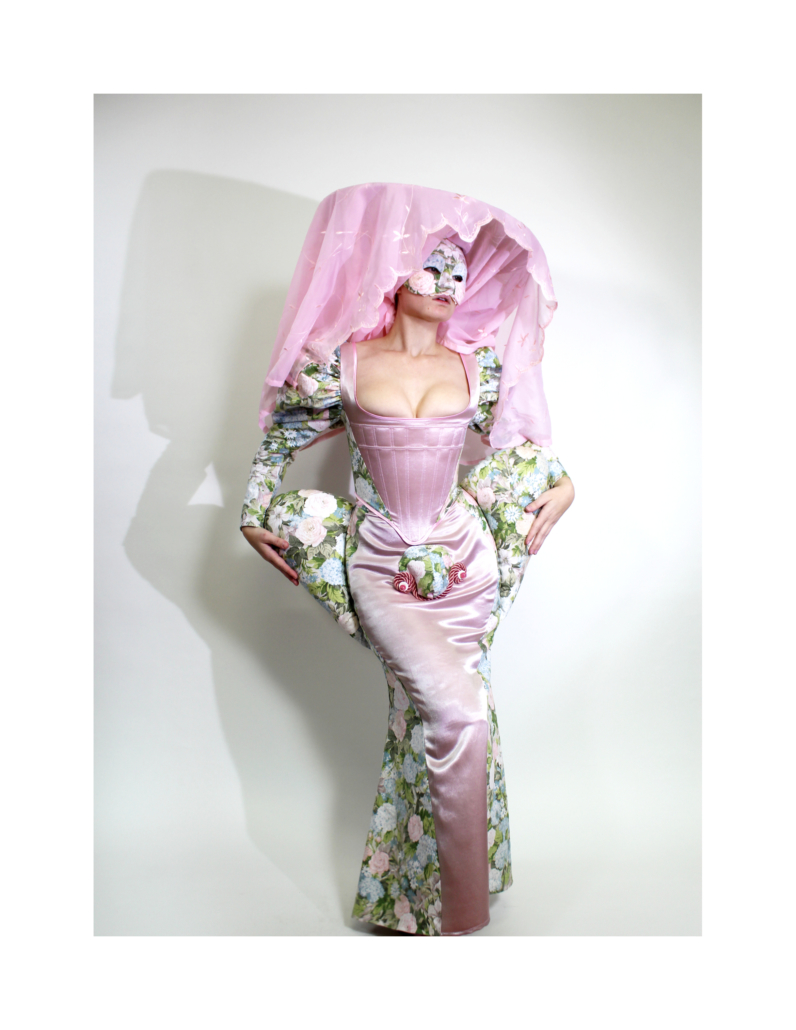
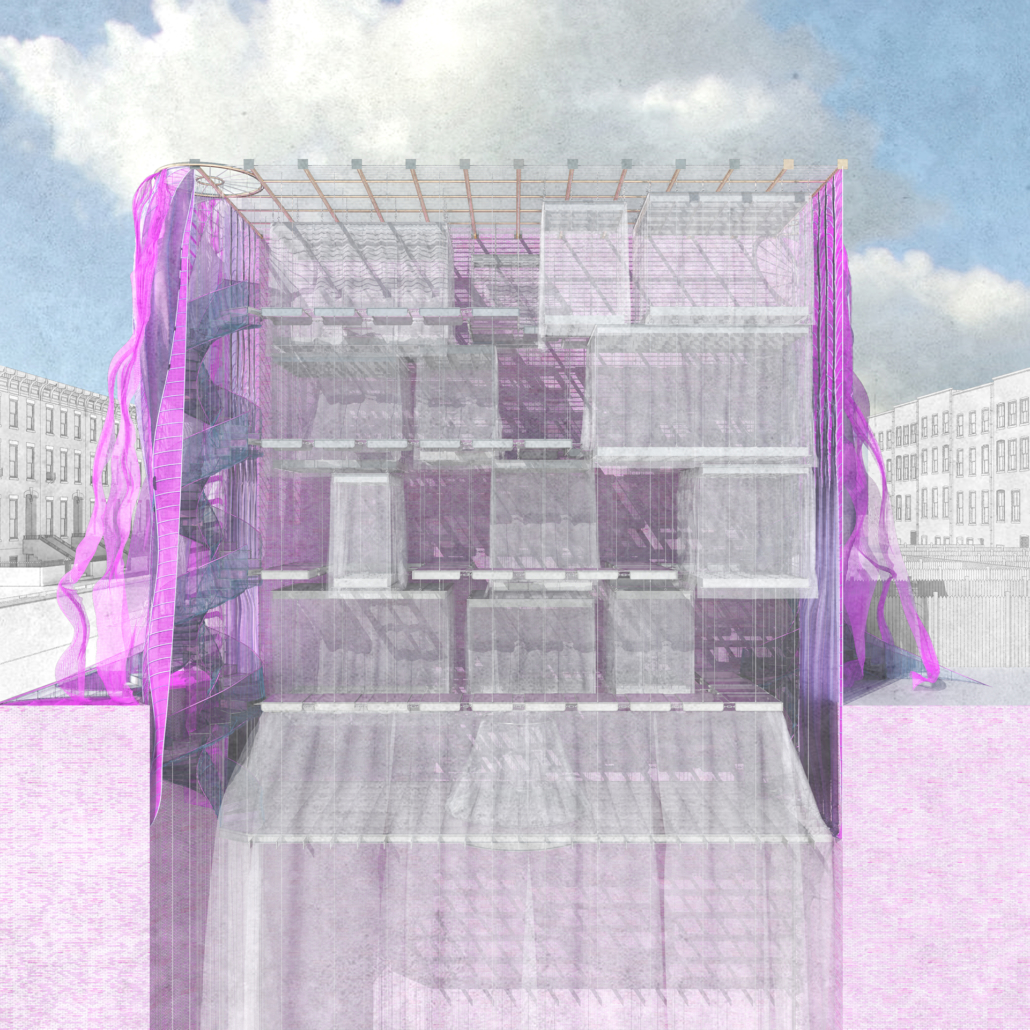
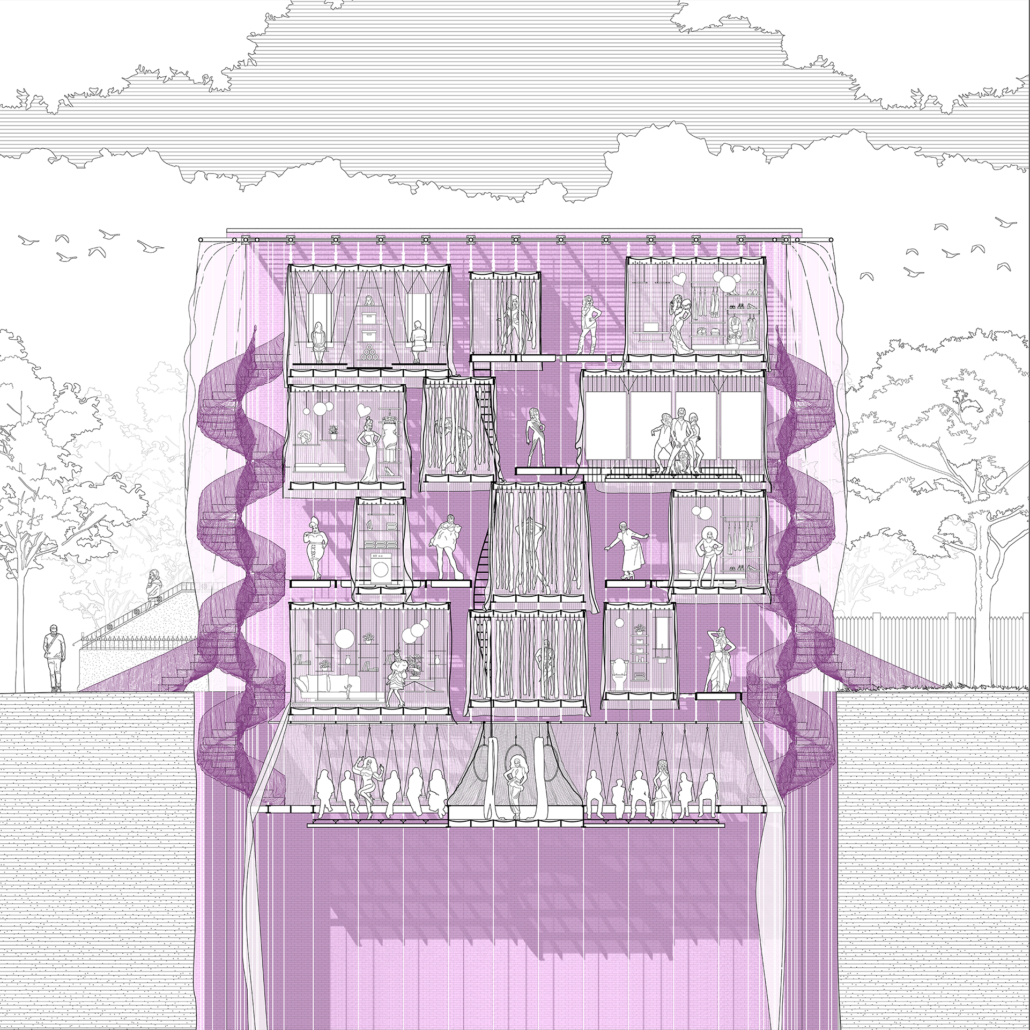
Through imitation and parody, Architecture in Drag challenges architecture’s identity. “/” is an imitation of a building, a ballroom and a home. Situated in New York City, the birthplace of modern drag culture, / begins by separating and interconnecting two rowhouses through a horizontal structural grid. From the grid, all of its characters (program and circulation), are hung and interconnected through fluid architectonics. By hanging its characters, / removes the ground on which architecture rests upon. In its place, a series of fluid spaces affect the other. In this manner, space is boundless, inviting and encompassing. Similarly, / invites its audiences to customize it. Although its characters are organized within a grid, this, like the power of the grid within architecture is a false truth. Thanks to its semi-fixed industrial characters, all of /’s characters are free to be moved and be re-arranged Thereby, / has exactly half a plan. The industrial connections enabling this feature are appropriated from their intended use, like the appropriated fixtures drag performers utilize to re-arrange their identities. No material should be off-limit in the construction of architectural ideas. Moreover, no idea should be considered non-architectural. Architecture in Drag challenges the ground defining truths within abstractions such as architecture and gender. / is the byproduct of this challenge, it is a performance of architectural ‘truths’ parodied as fluid.
Instagram: @mikeevola
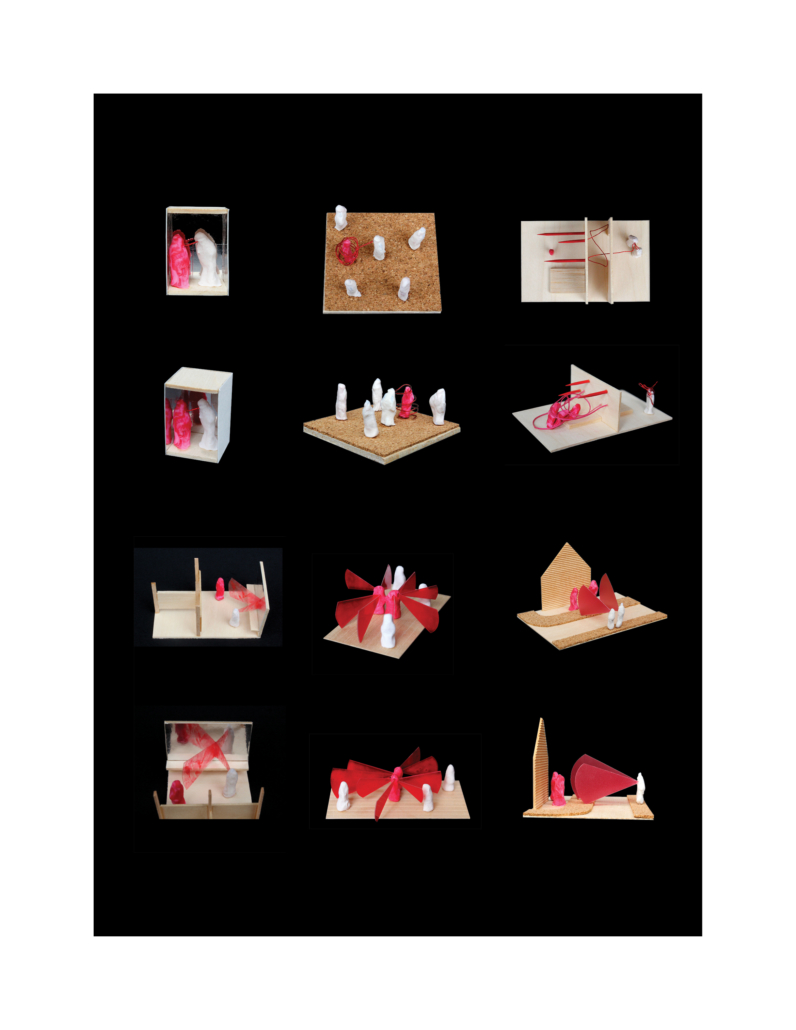
A Gender-Based Violence Architecture: Protection and Empowerment of Women by Isamar Collazo, B.Arch ’22
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisor: Pedro A. Rosario
Currently, there is a lack of places to protect female victims of domestic violence, focusing on self-help programs to assist them in becoming independent and reintegrating into society. The existing shelters isolate women from their environment, which makes the transition process difficult during reintegration into their context. Therefore, this project aims to protect female victims by promoting their independence through therapies, workshops, housing, and recreational activities so that they may have the necessary tools to return to the outside world. Also, most of the women that report the most cases are mothers of two or more children.
This project will allow the mother to be with her children by providing safe spaces for education and play areas for the kids. Creating a space close to their context will enable them to reduce the sense of isolation they experience while receiving the help they may need. Some of the site selection criteria were: to locate the project in densely populated areas, locate where there are more reported cases and where there is a lack of nearby shelters. The project is located in El Salvador due to the fact that it has the highest number of femicides (female-focused homicides) per capita among Latin American countries. Research shows 6.8 per 100,000 women, which represents 435 femicides per year. Most of these incidents have been reported in the capital city, Santa Tecla, San Salvador.
Dismantling the Architecture of Othering: Queer Reclamations of Space by Minette Murphy, M.Arch ’22
Carleton University | Advisor: Piper Bernbaum
This thesis positions itself around the opposing forces of architectural normativity and queer spatial production. It investigates heteronormativity and its spatial manifestations, in order to engage in the practice of queering space as an act of resistance. By researching the heteronormative order, and typologies such as the public toilet and the private home, it seeks to demonstrate architecture’s complicity in the process of othering queer bodies. Applying a norm-critical perspective to spatial phenomena, it encourages architects to divest from contributing to this form of spatial violence.
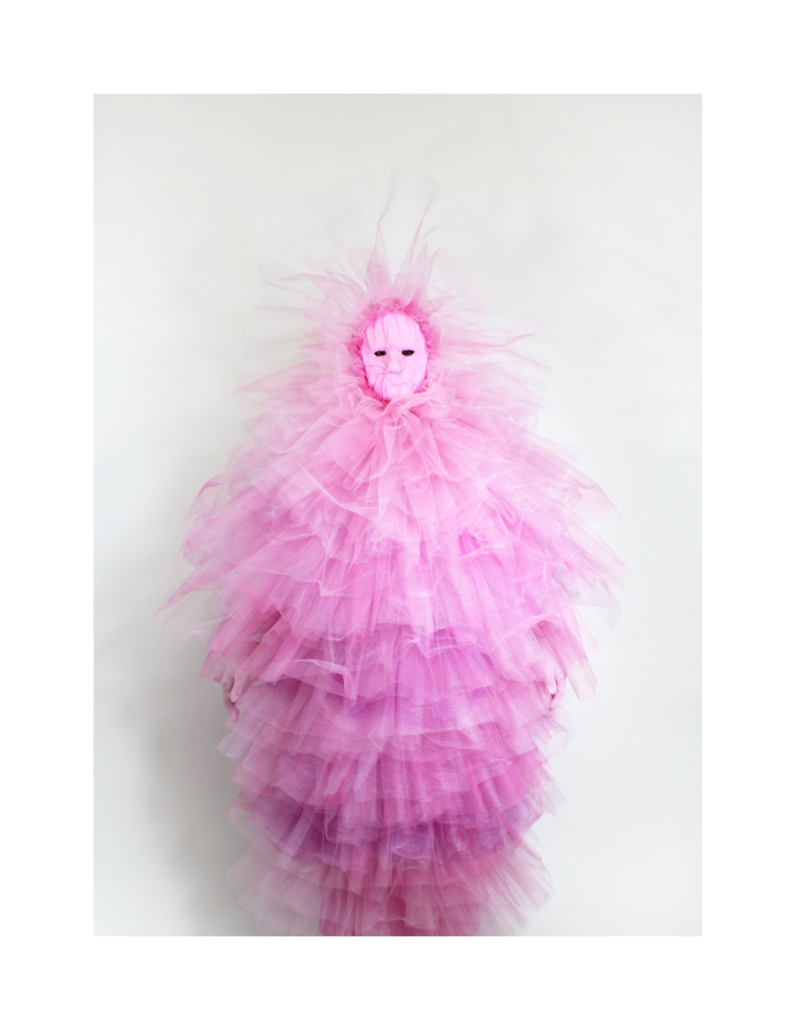
Next, it explores the act of queering as a contestation of the normative order through design. Continuing to dismantle various facets of heteronormative spatial production, six design explorations consider the body through a multi-scalar approach. As the site where queerness is initially produced, the body is where all contestations must begin. The first question ‘what is the body?’ deconstructs the normative body which forms the basis of all architectural standards in order to explore the concept of a fluid and relational body. The second ‘what is the layered body?’ analyzes the heteronormative imposition of meaning on clothing and the spatial implications of layer, while subverting both through costume. The third ‘what is the shared body?’ questions the privatization of the body and its various functions, and proposes opening private spaces up to new experiences. The fourth ‘what is the protected body?’ investigates spatial conditions that limit the safety of queer people, and mobilizes mechanisms innovated by the heteronormative order against itself. The fifth ‘what is the worshipped body?’ reflects on the abjection of queerness and implants queer rituals of joy into places that prohibited them. Finally, the sixth ‘what is the transcendent body?’ recounts moment of queer world building, and engages in open-ended experimentations of queer futurity. Throughout the whole document, this thesis seeks to question, reveal, subvert, and transform. Ultimately it will conclude that there is no one way to ‘queer.’ In all its forms, ‘queering’ is a practice of resisting normativity that should be embedded in the architectural practice of all.
Instagram: @minetteyo, @piperb
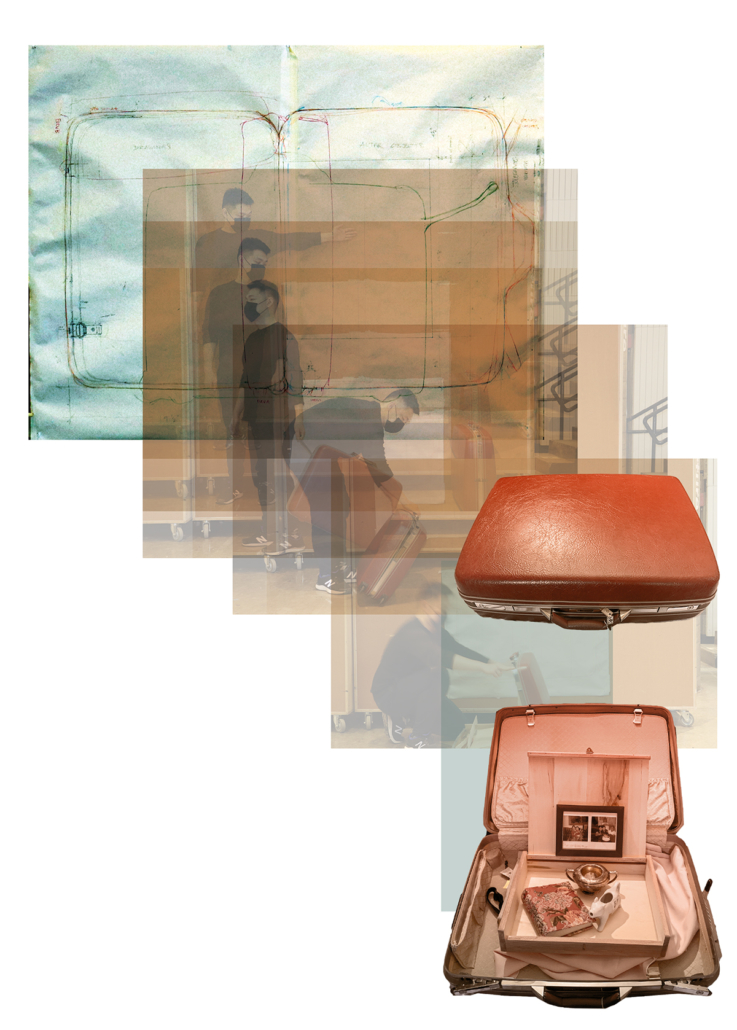
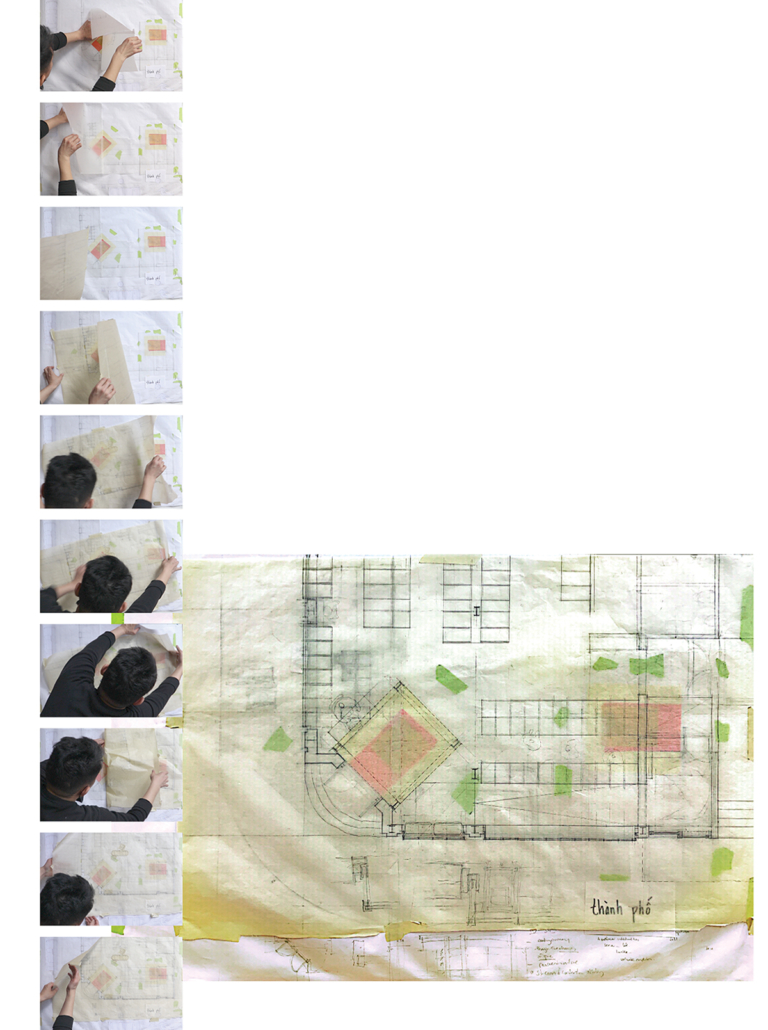
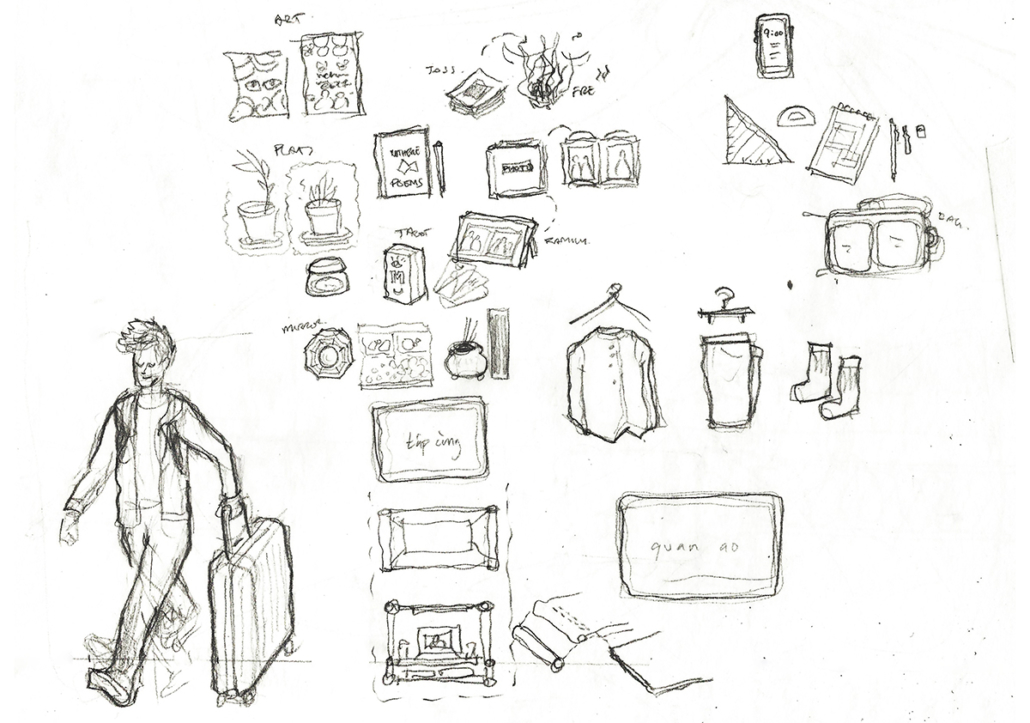
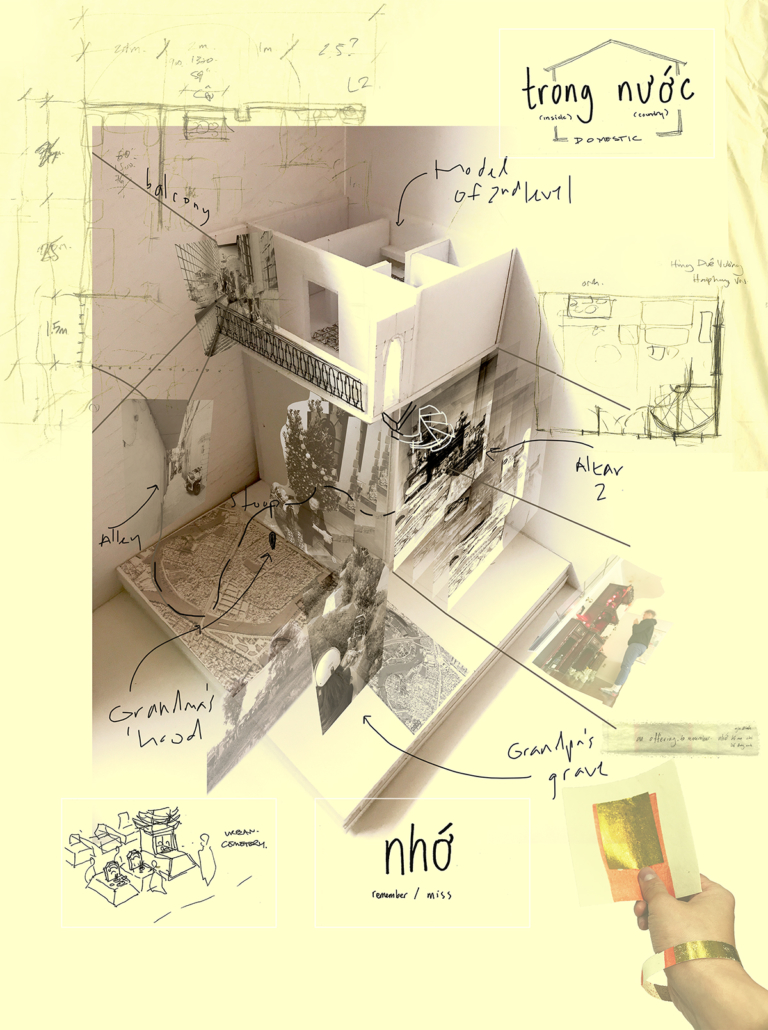
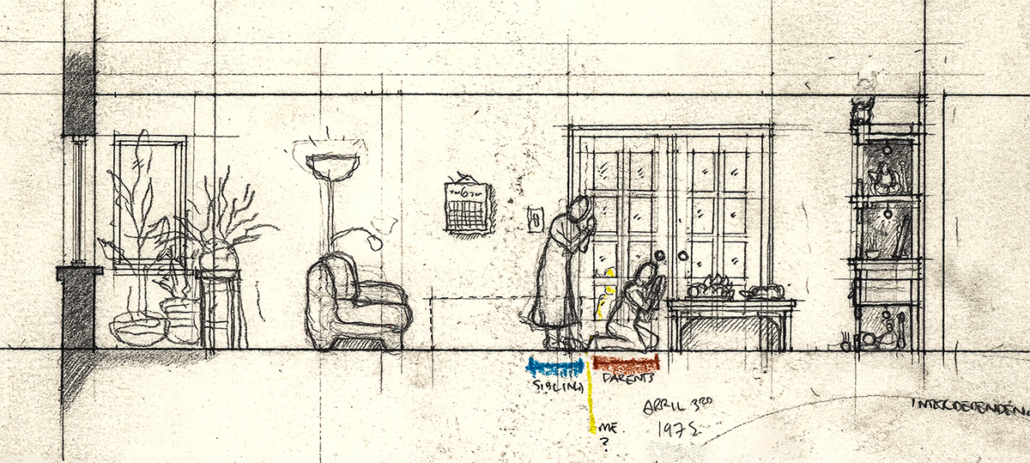
Offerings and Inheritances: Reconstructing Altars for Queer Vietnamese Kin by Thompson Cong Nguyen, M.Arch ’22
Carleton University | Advisor: Piper Bernbaum
How do we offer our selves – as diasporic, queer, Vietnamese families in settler-colonial Canada – to honour our ancestral kinship ties while creating space for new, authentic rituals and traditions? ‘Offerings and Inheritances for Queer Vietnamese Kin’, my architectural thesis at the Azrieli School of Architecture and Urbanism at Carleton University, Ottawa, investigates how practices of ancestral worship are performed in everyday sites scaled to the body, the street and the nightclub. This involved multi-modal and multi-scalar artistic explorations of offerings and identities which prompted the design of three new altars fitted to a suitcase, an urban storefront and a queer clubbing event. Each altar offers new fields of inquiry that embrace the mess of queer diasporic identities and affect how space is conventionally created through architectural design. This process invites designers, scholars, and queer, diasporic kinfolk to collectively reconstruct new practices of belonging for our ancestors, kin and our multi-adjectival selves.
Instagram: @thompydraws, @piperb
Check back next week for Part III of the Study Architecture Student Showcase.