2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part IX
The projects featured in Part IX of the 2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase explore architecture’s role in supporting public health and wellness.
By addressing disparities in public health frameworks, the presented thesis work includes design interventions ranging from a mental health wellness resort for veterans to safe spaces for those addicted to opioids. With each design, there is an opportunity for rehabilitation, advocacy, and human-centered experiences.
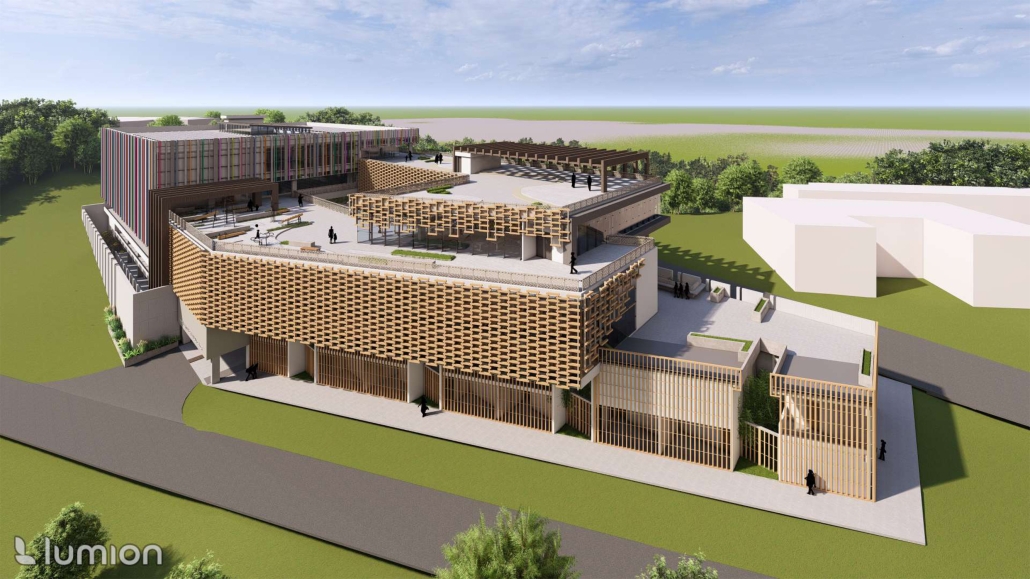
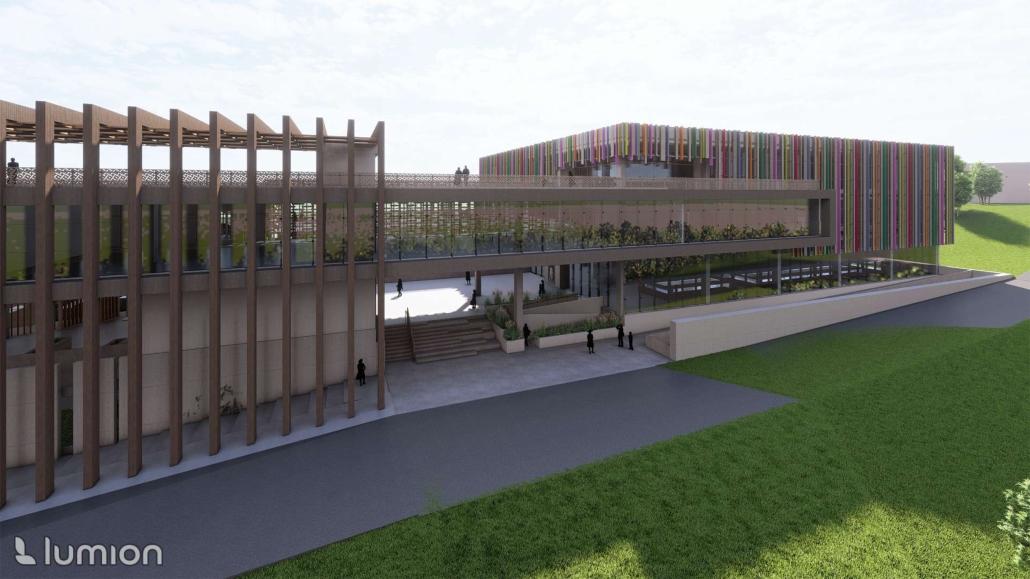
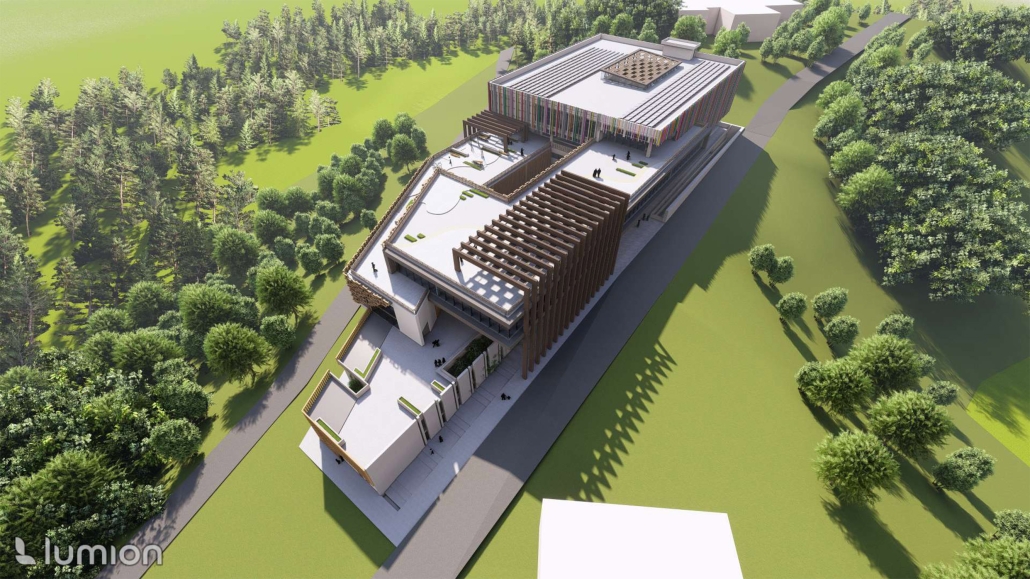
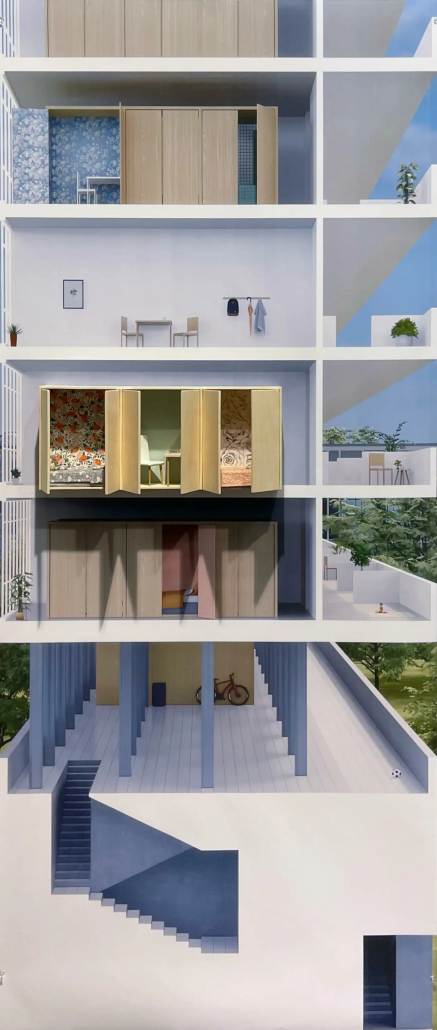
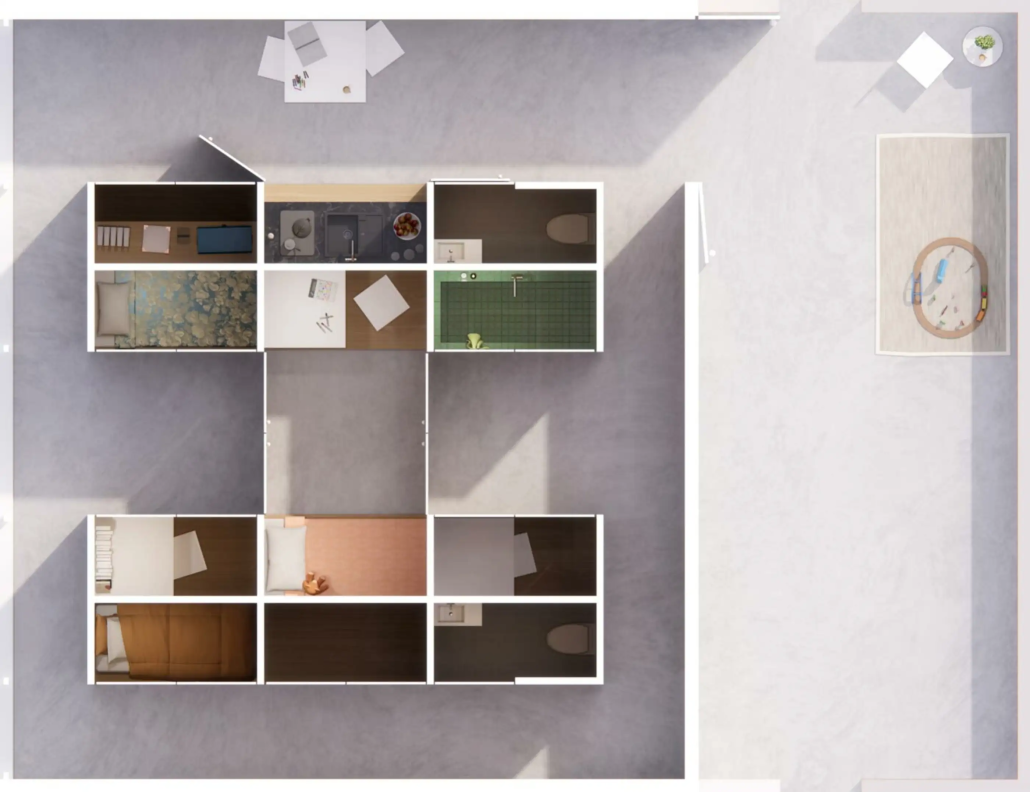
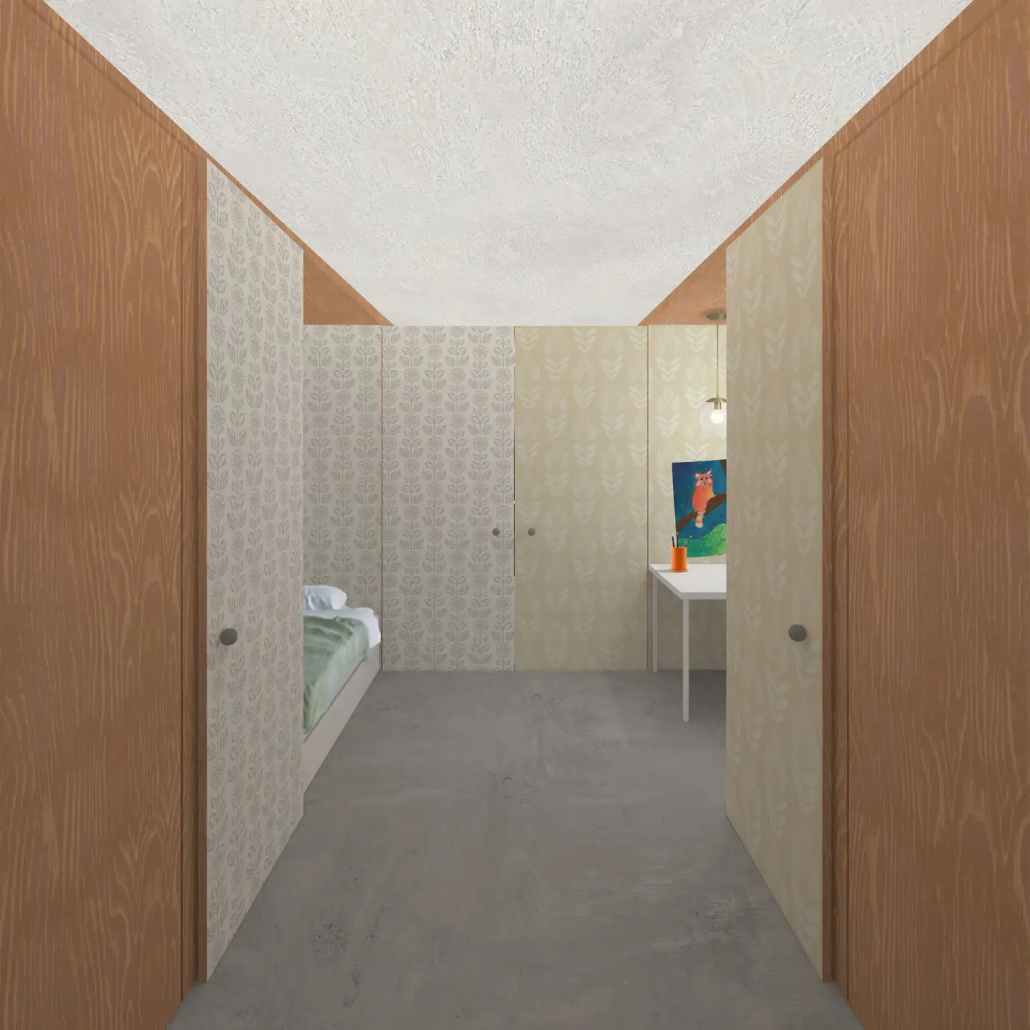
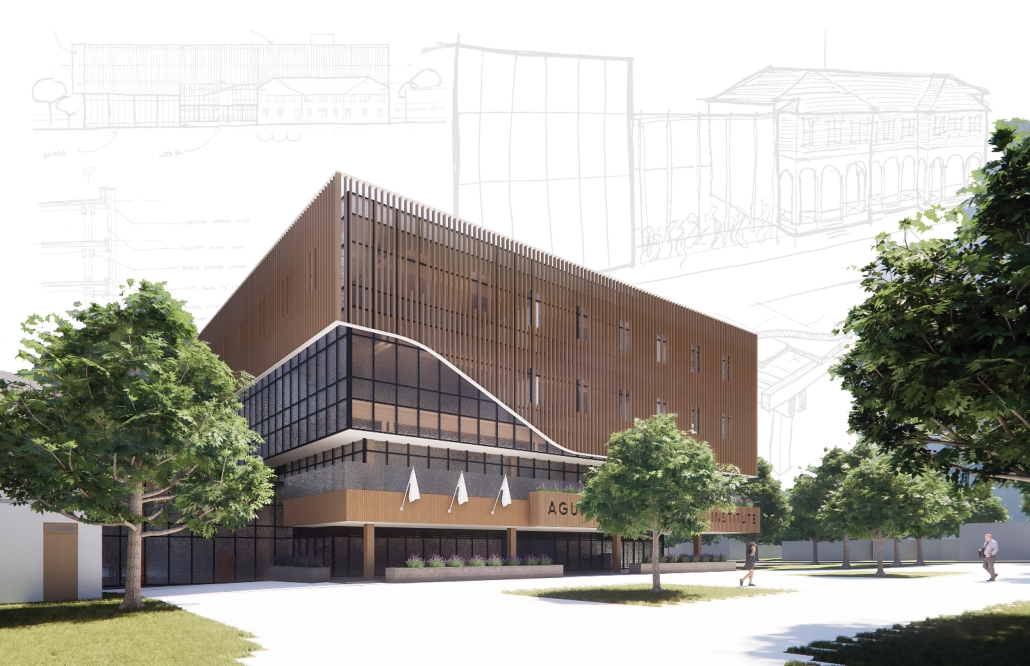
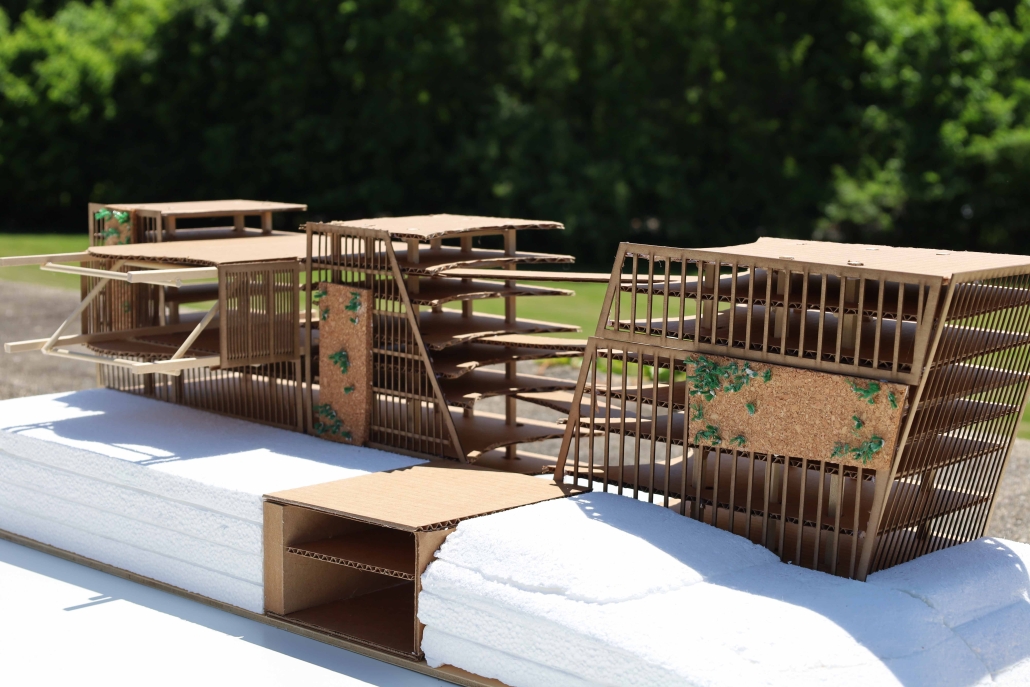
Return to Base: How Can Architecture Help Veterans Suffering from PTSD Reintegrate into Society through Therapy, Community and Routines by Leimar P. Acevedo-Santana, B. Arch ‘24
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisor: Pedro A. Rosario-Torres
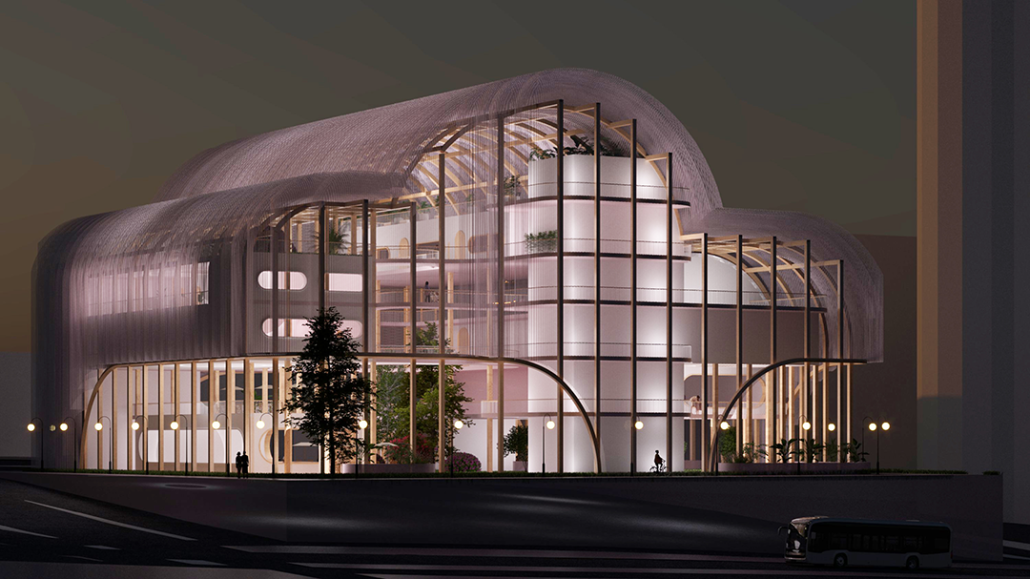
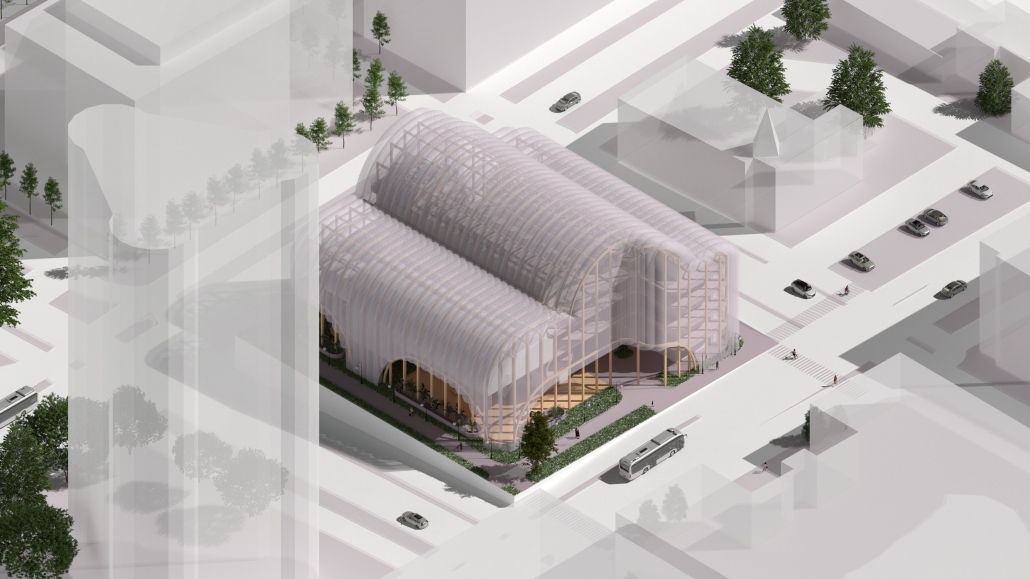
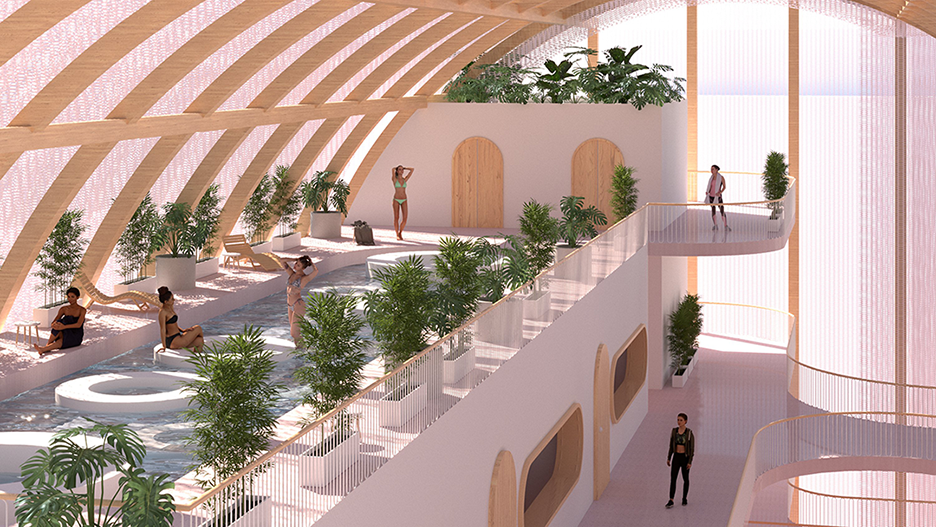
It is estimated that 30% of personnel deployed in Iraq and Afghanistan require some sort of mental health treatment; however, only half of them receive any. Many times, those who need treatment do not seek it due to stigma, accessibility issues like travel time, or because the facilities are oftentimes “not appealing or attractive”. By providing a place to tackle and heal mental health issues that is not a hospital or anything similar, the proposal hopes to attract and help those who need the help.
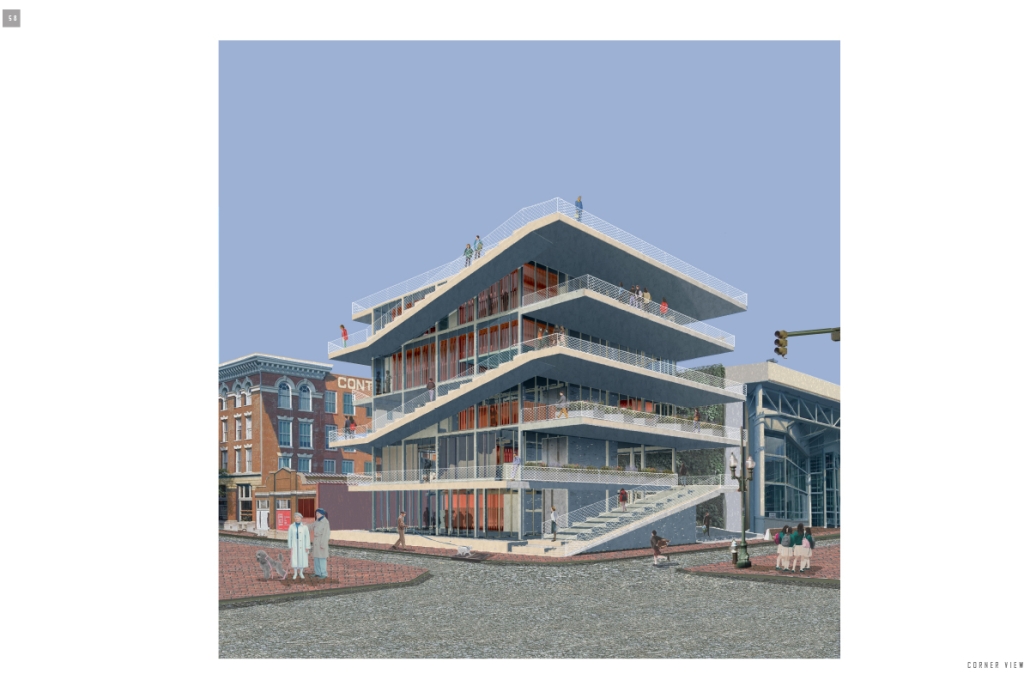
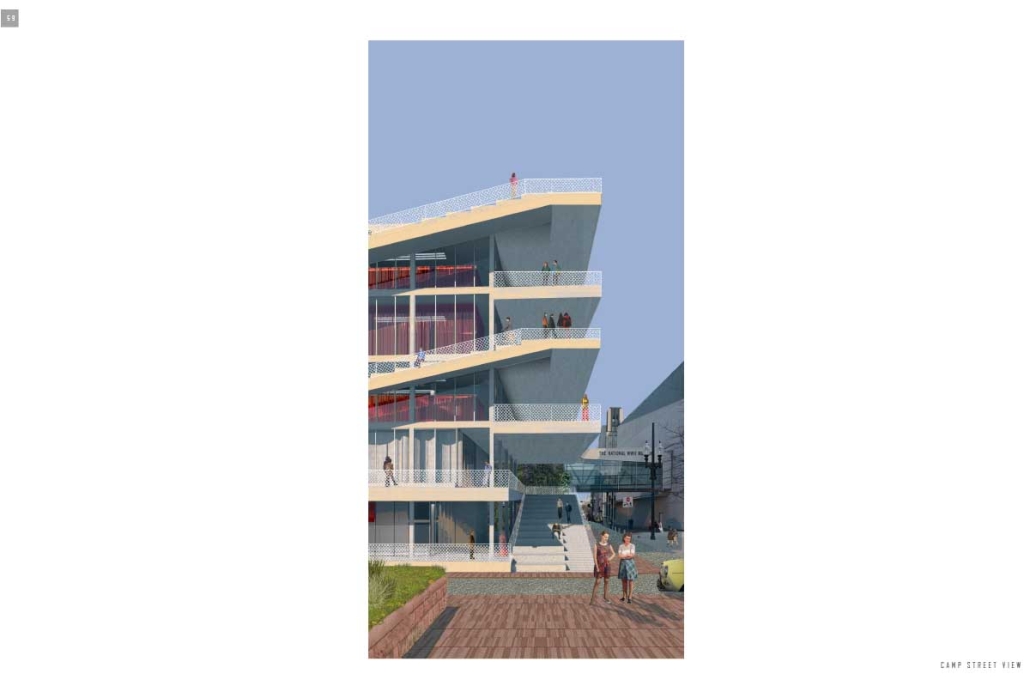
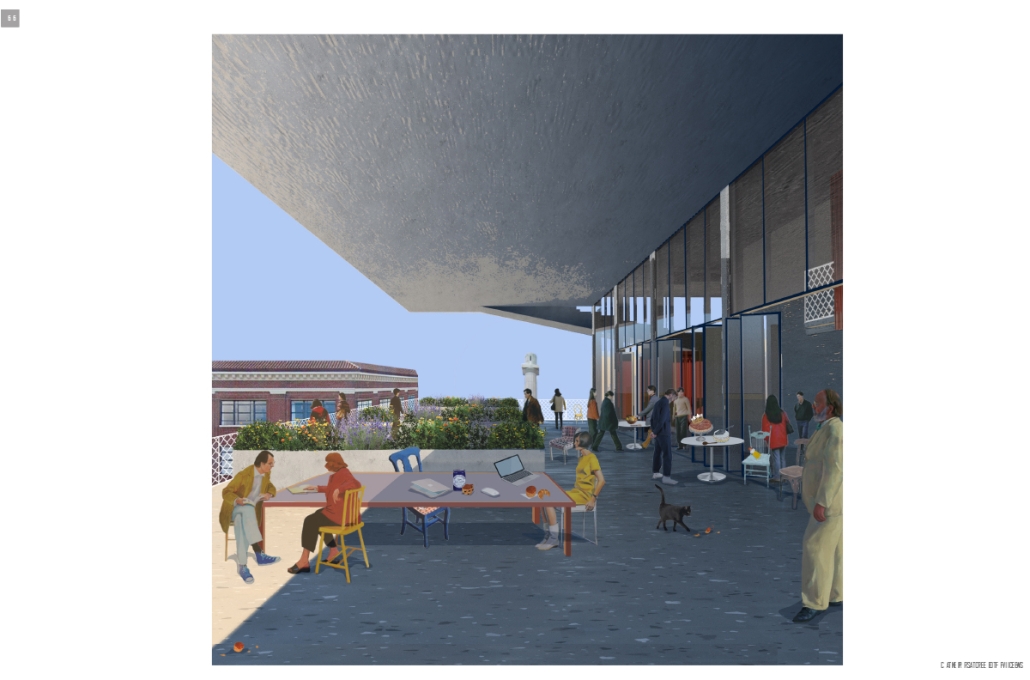
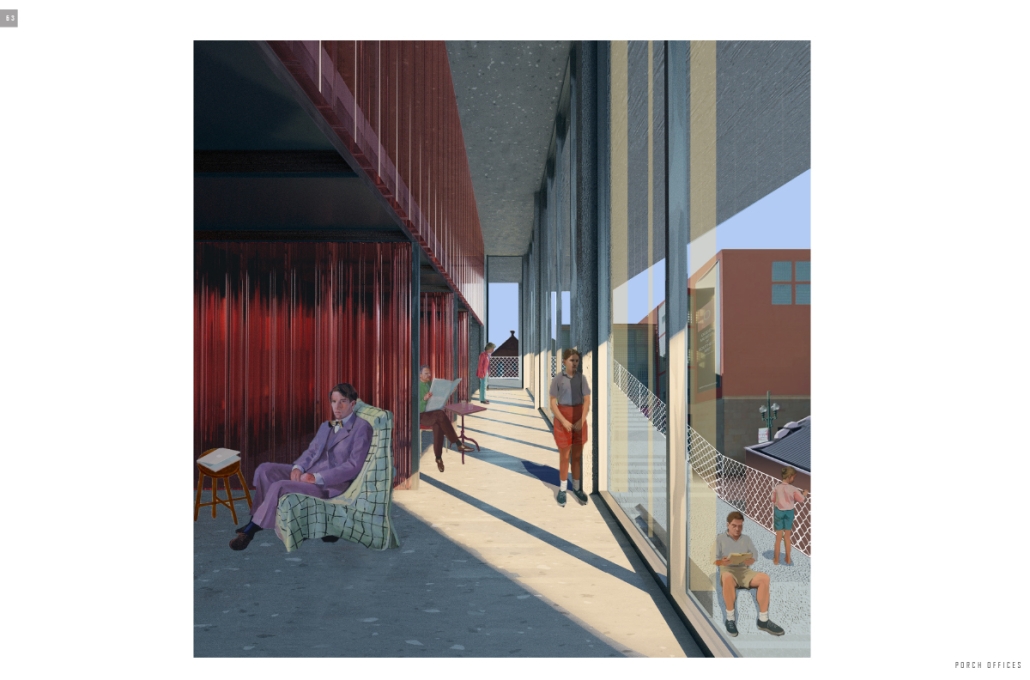
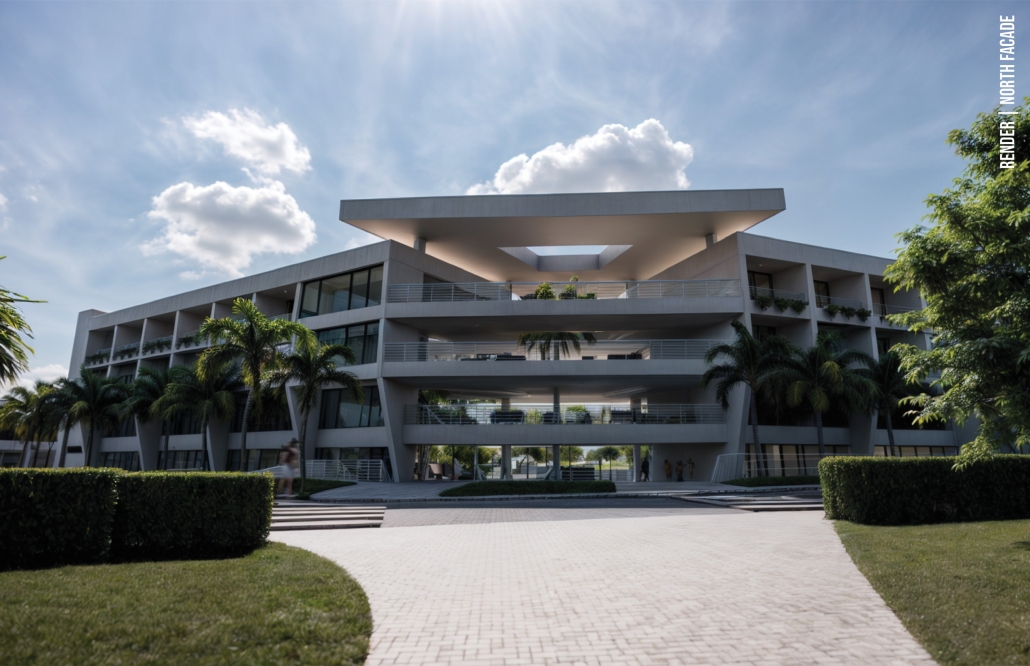
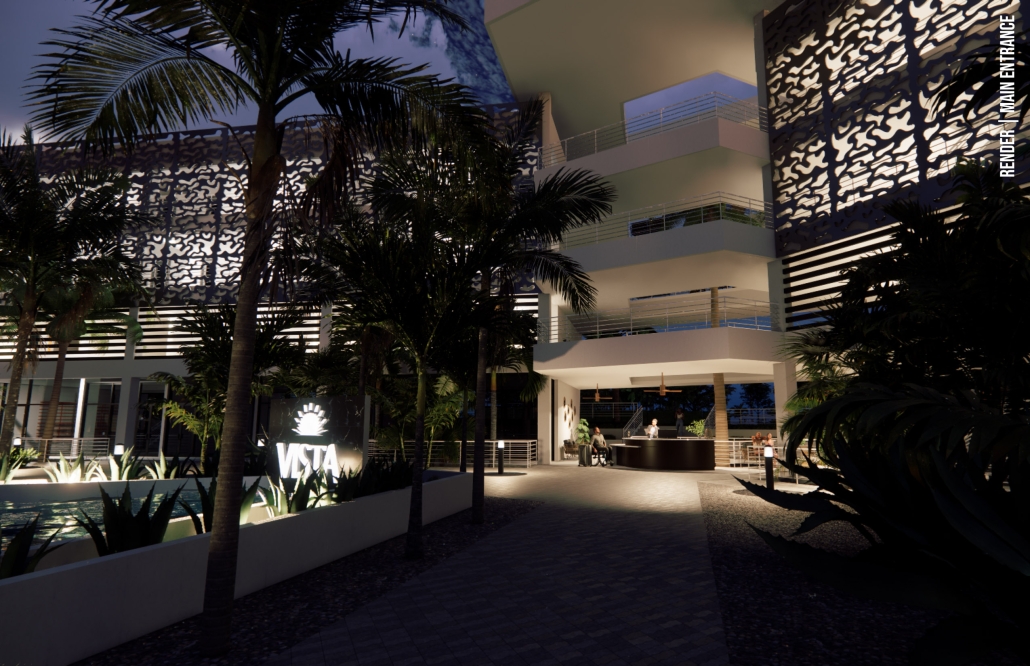
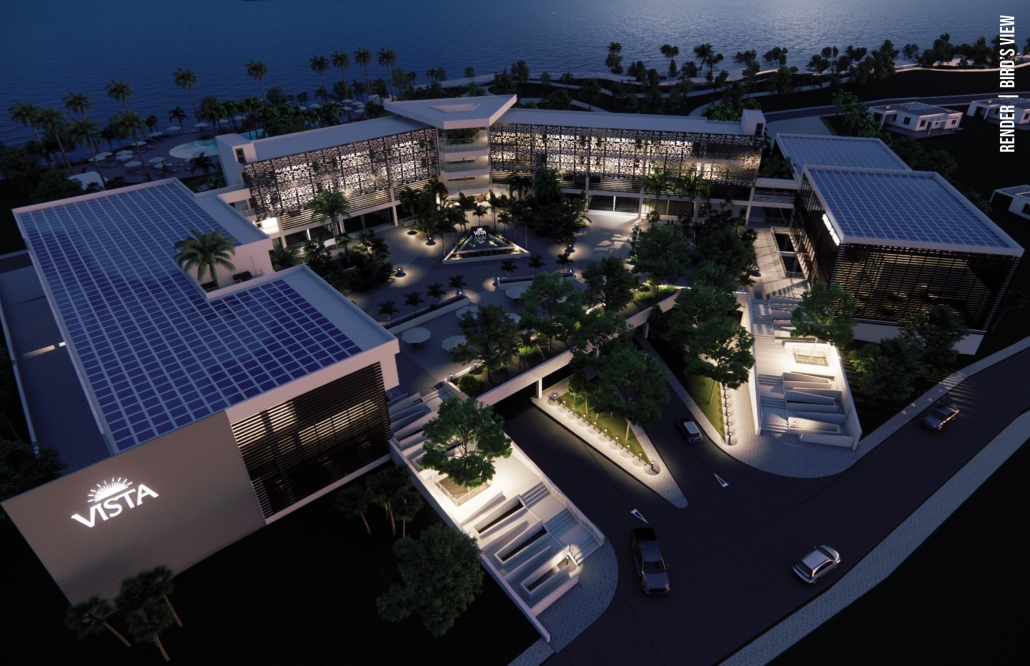
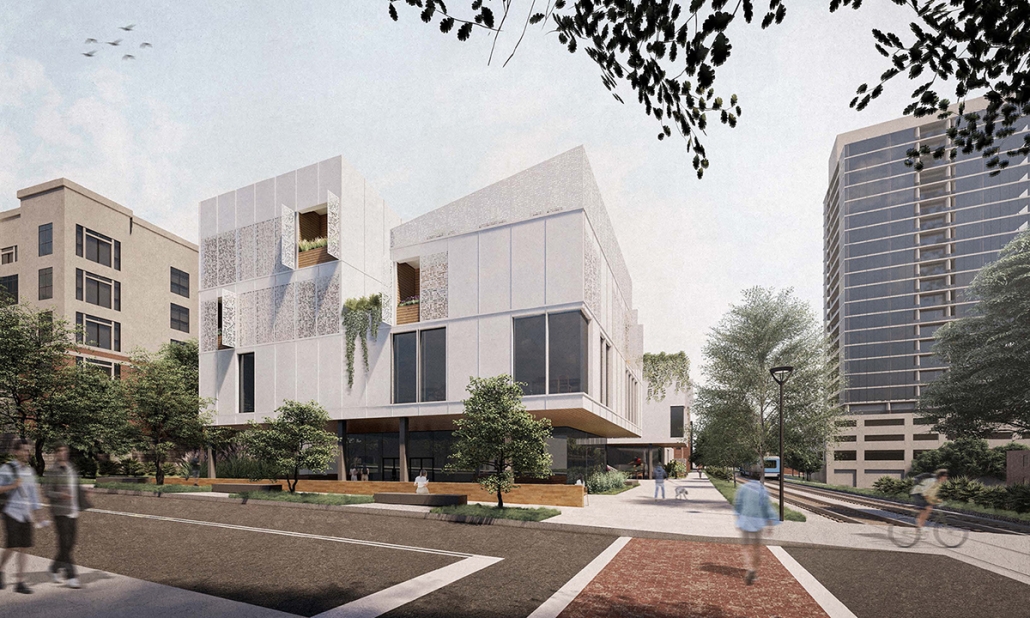
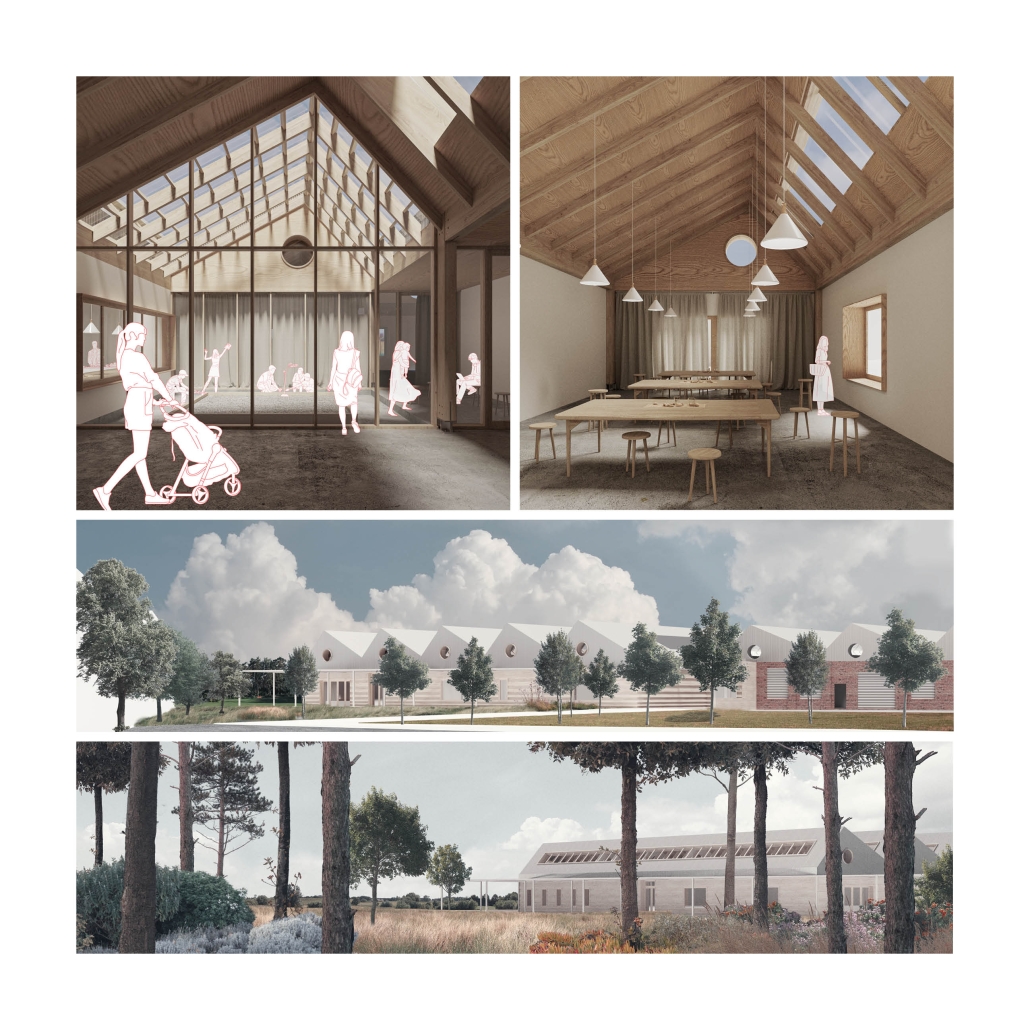
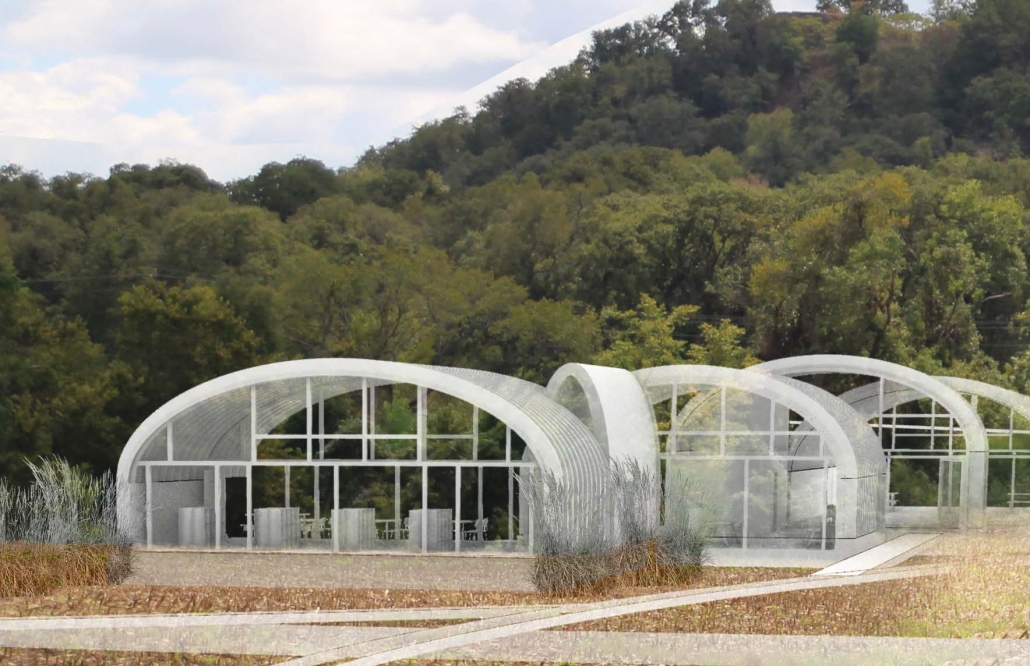
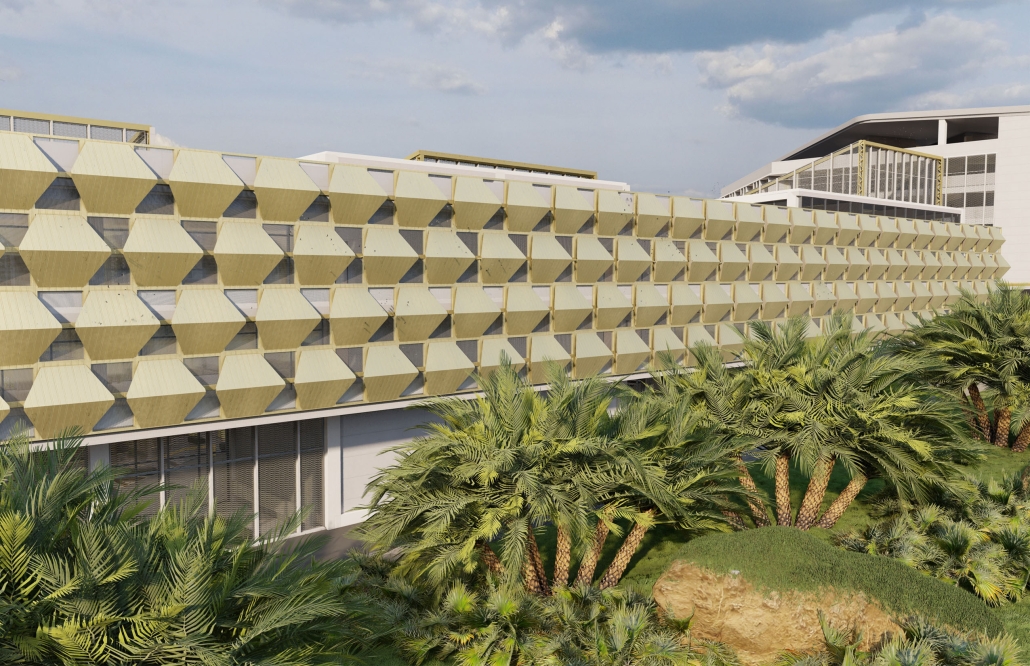
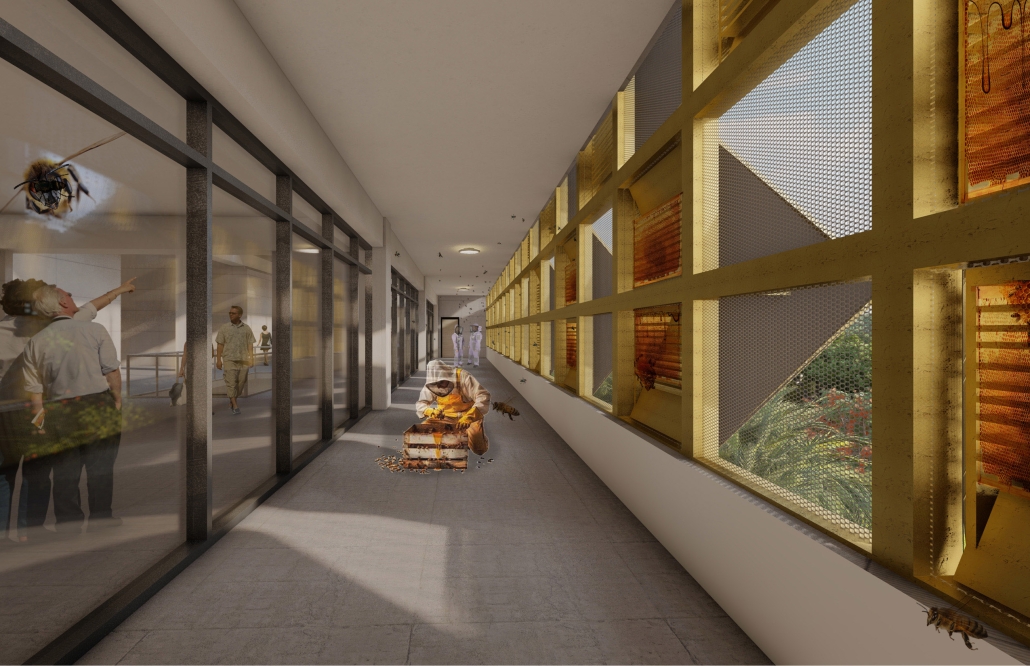
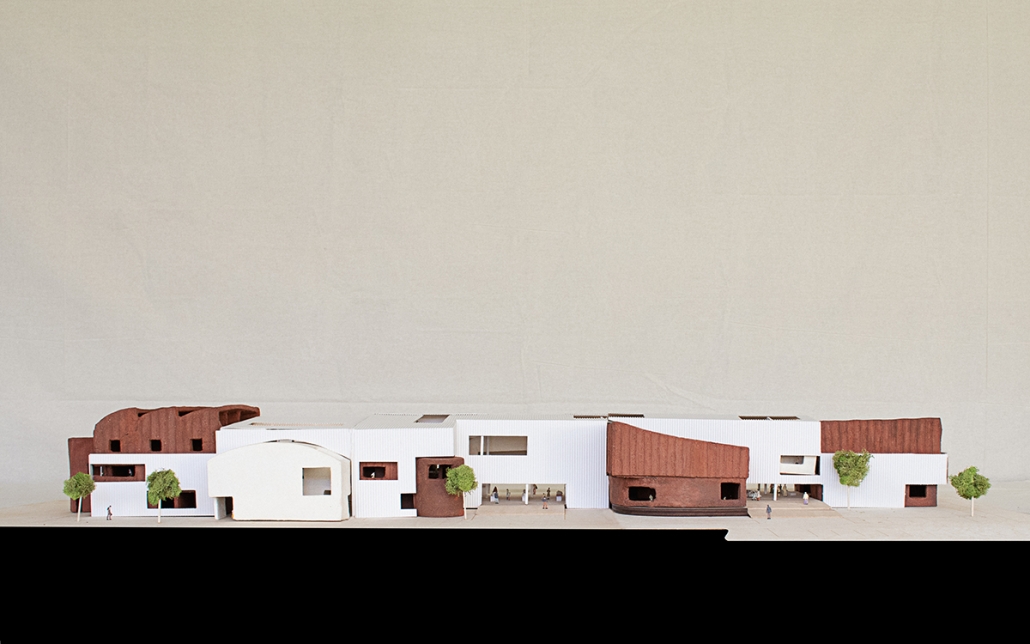
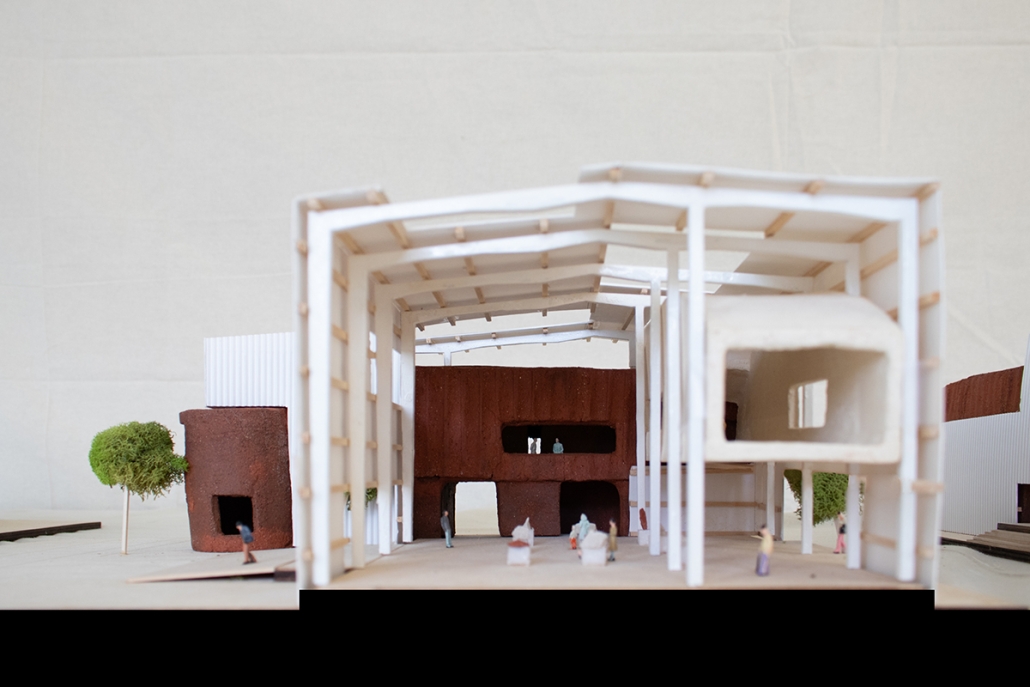
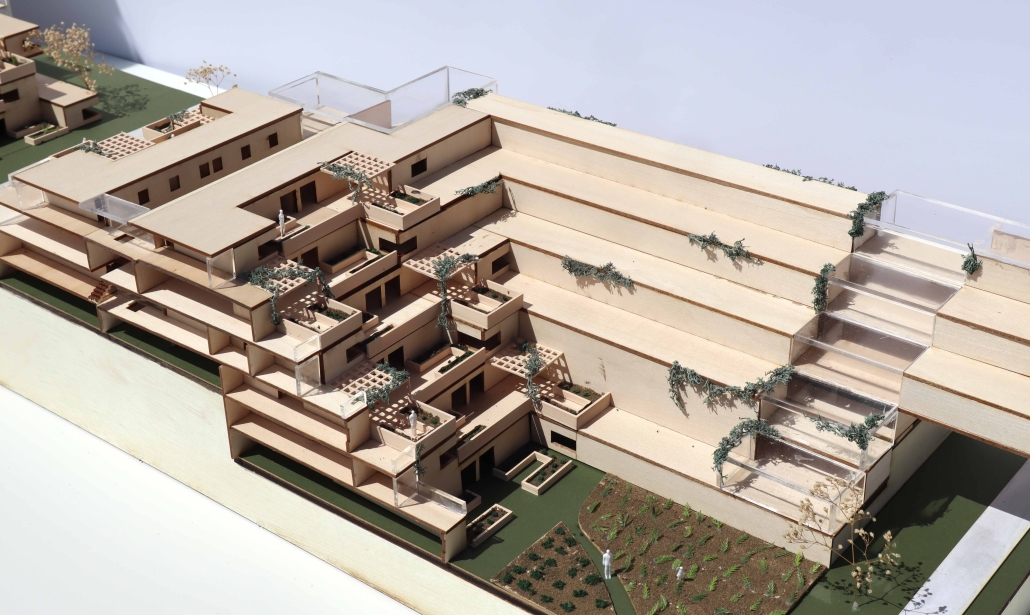
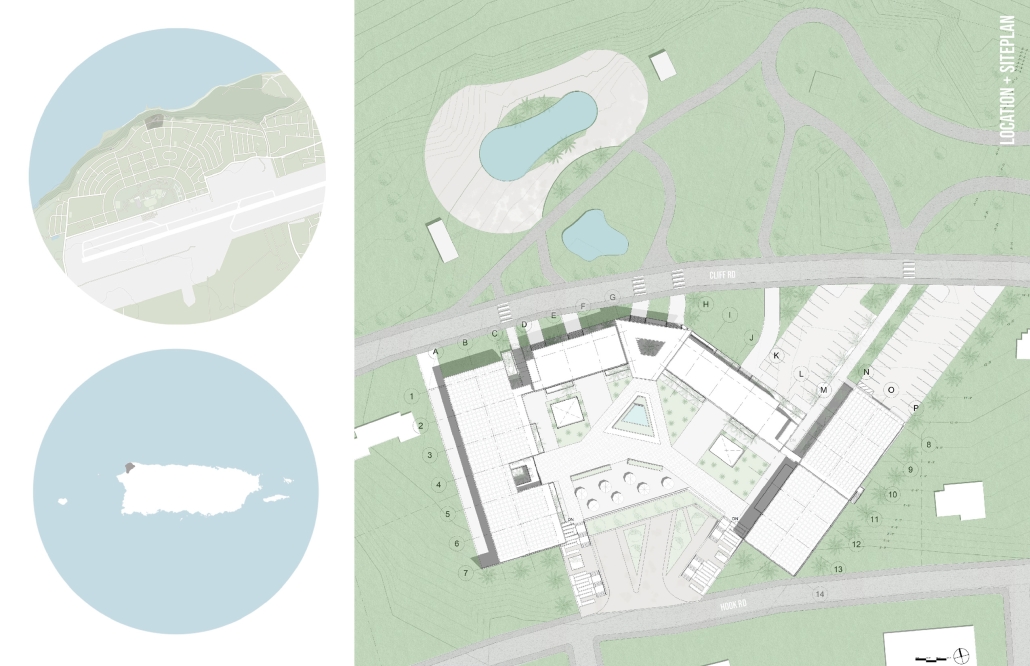
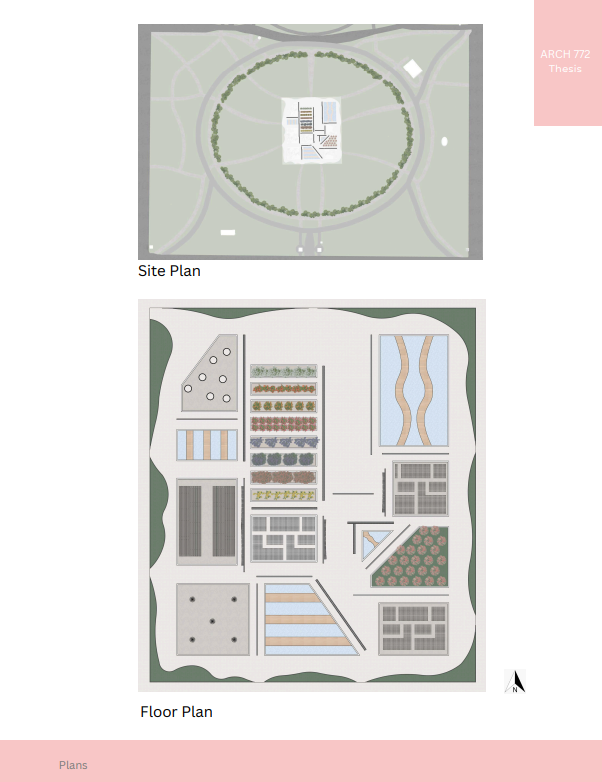
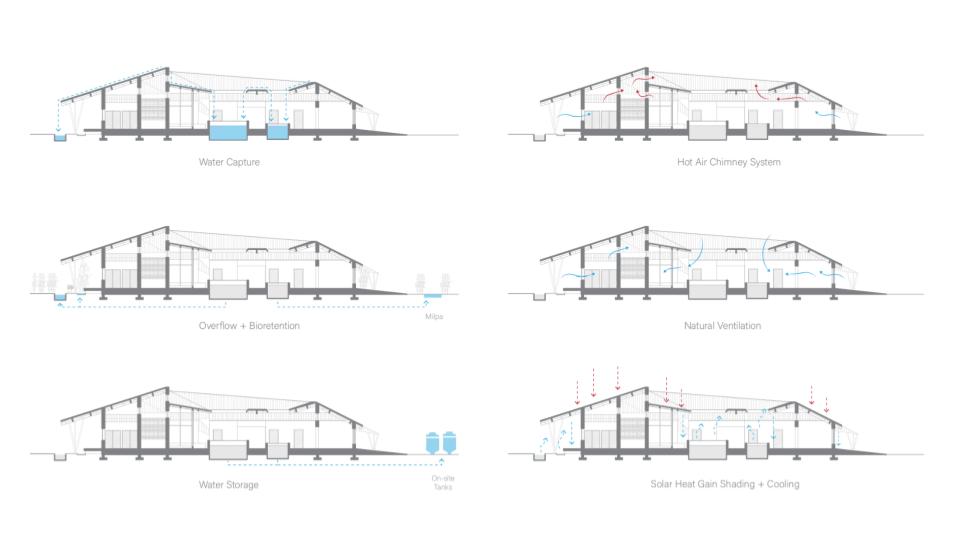
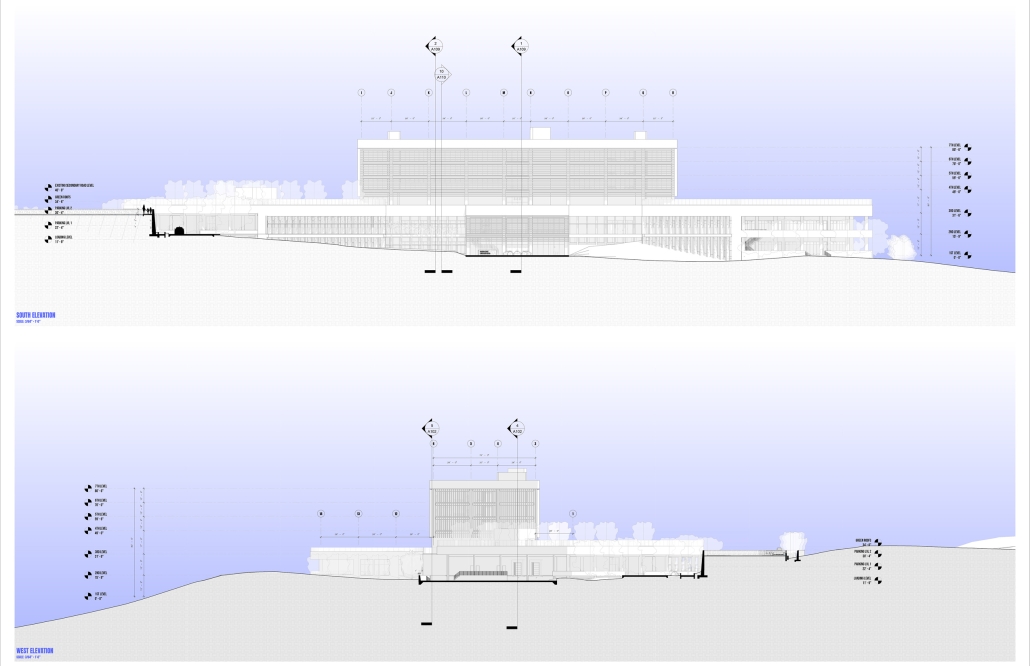
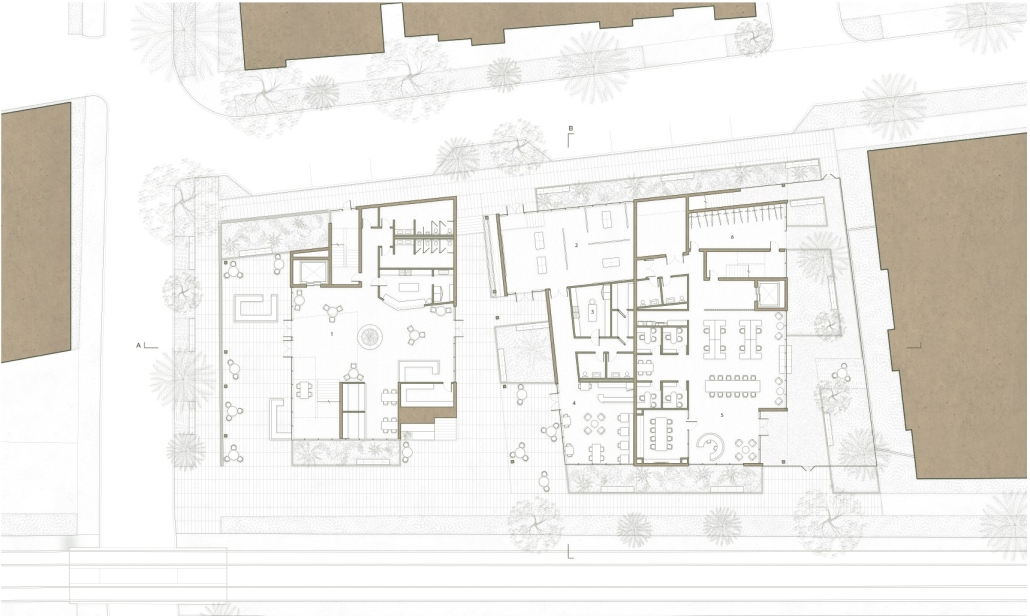
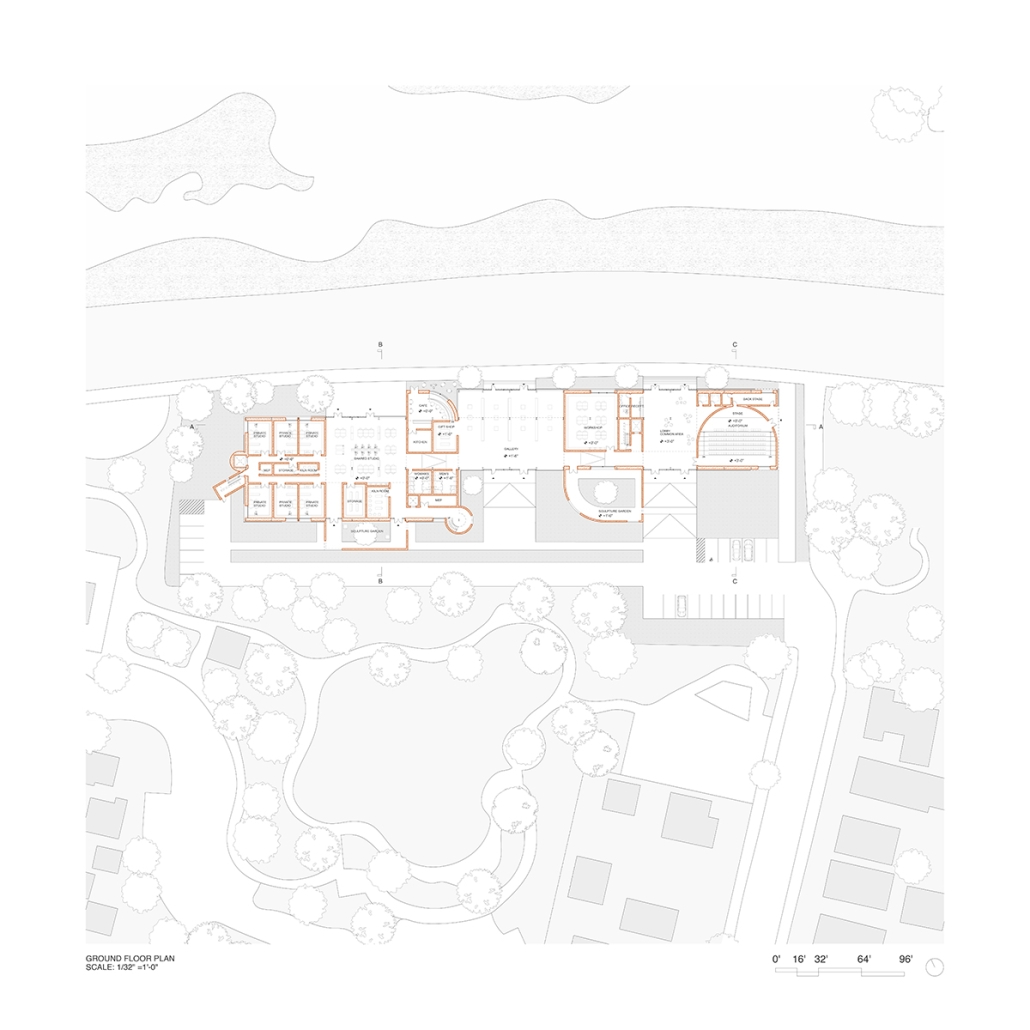
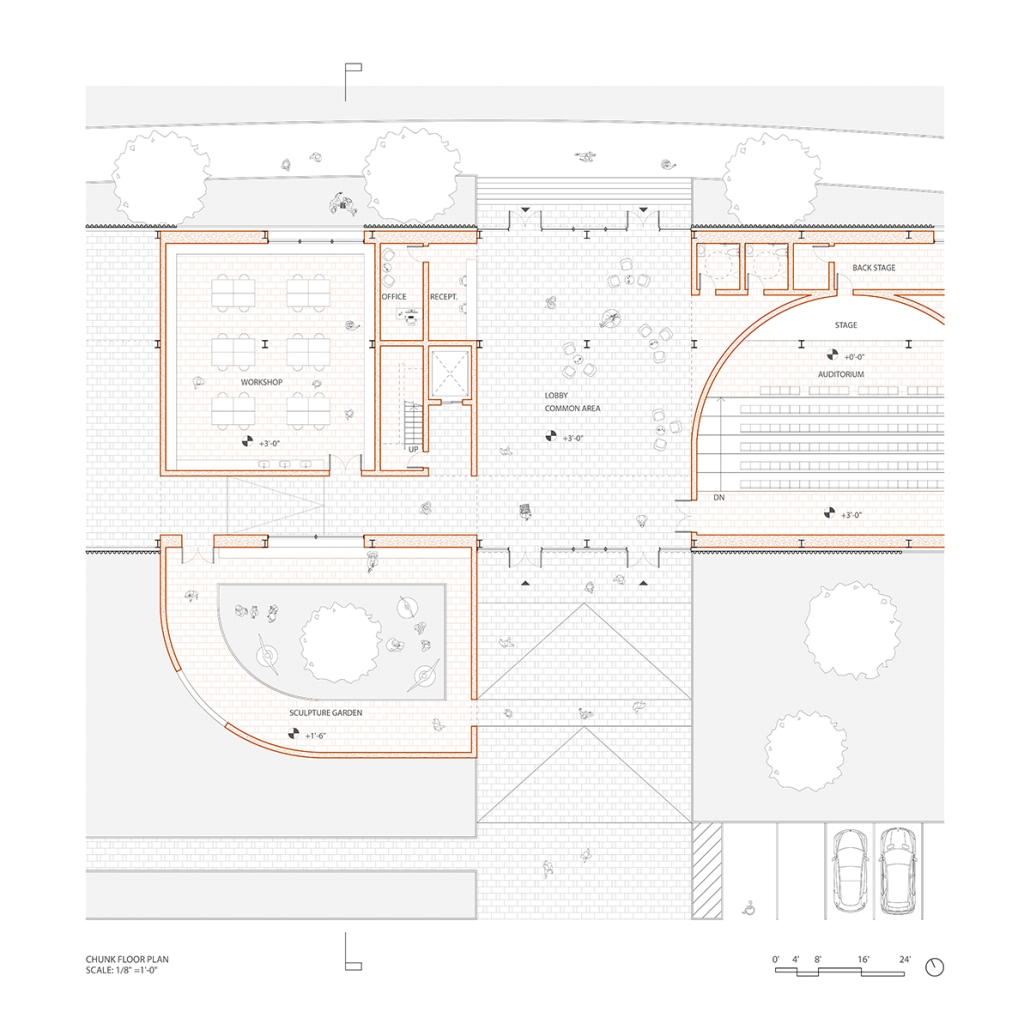
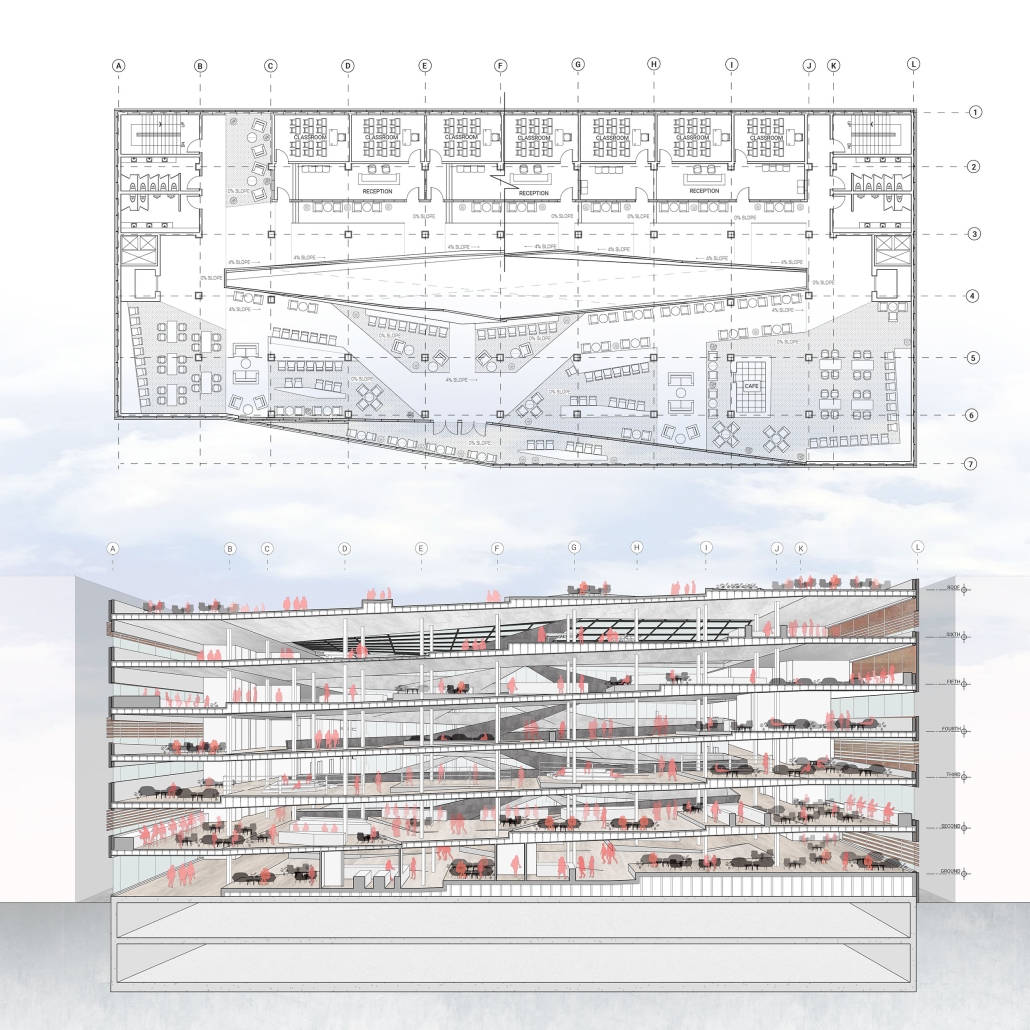
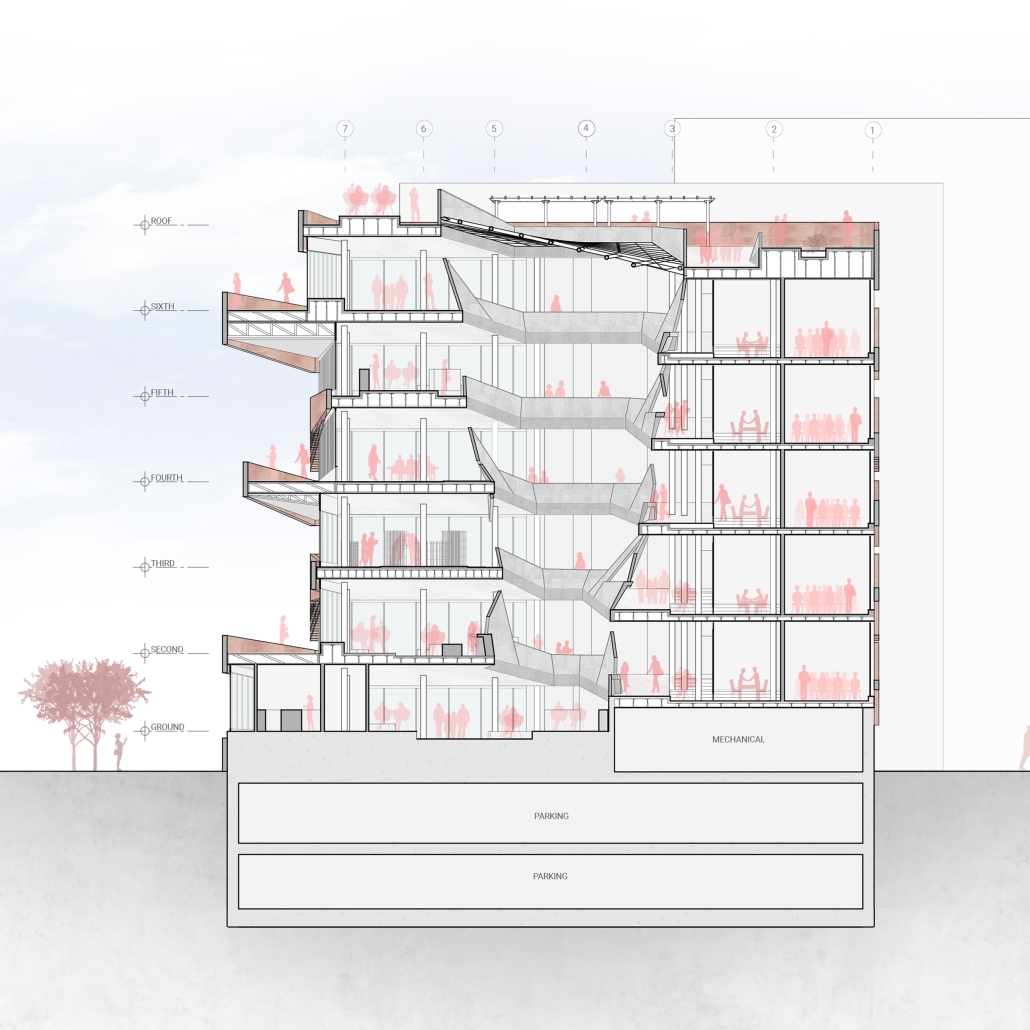
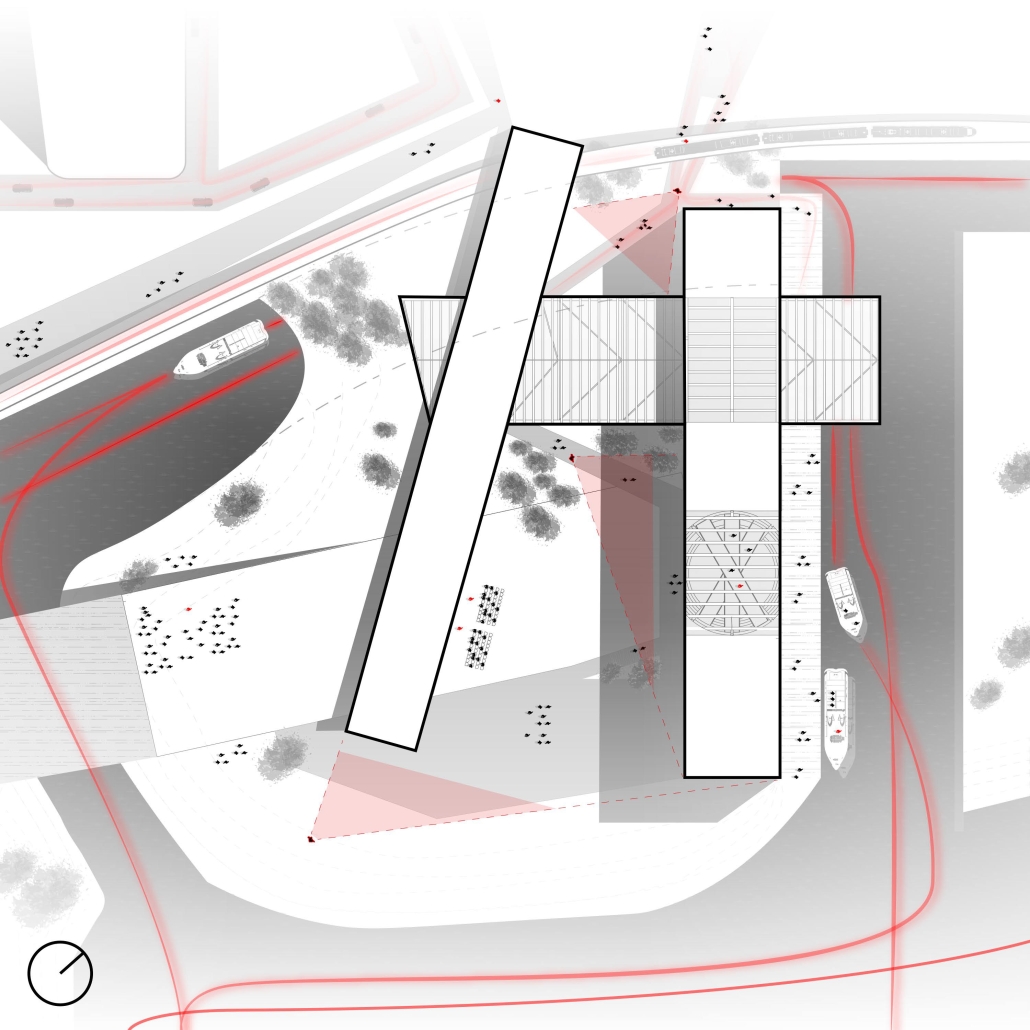
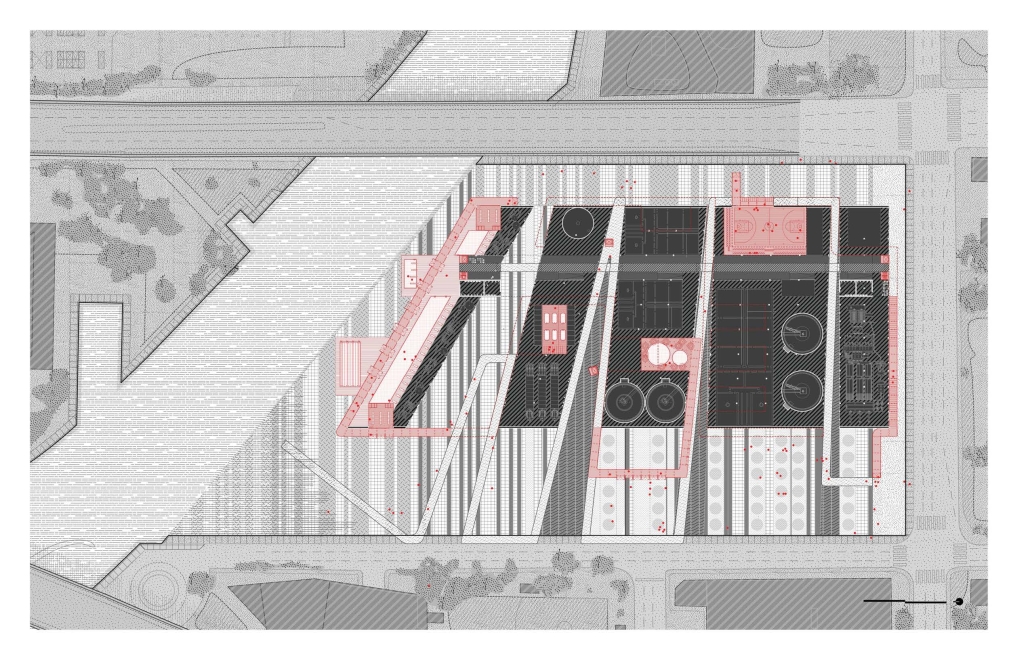
VISTA, Veteran’s Inn for Serenity, Tranquility & Ascendance, is a hotel located at the Ramey Base in Aguadilla, Puerto Rico. The proposal seeks to help veterans who suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) reintegrate into society by helping, not only with the psychological treatment they may need but also helping them transition into life as a civilian, by teaching them different social and life skills. The hotel, or “wellness resort”, offers wellness amenities to attract veterans, classrooms to teach veterans different social and life skills, and psychological and medical facilities at a smaller scale to offer treatment. Taking advantage of the topography onsite, the medical facilities are located at a semi-underground level which is only accessible from Hook Road, allowing those seeking treatment to arrive at a more private level rather than being “exposed” by arriving at the main lobby. By providing these medical services at a “hidden” level, the proposal, at first glance, appears to be an ordinary wellness resort. The proposal is located in a “guest community” in Ramey Base, allowing the hotel to not require any type of barrier and serve as a connector between the community, the new park, and the beach nearby.
Instagram: @lacevedosantana
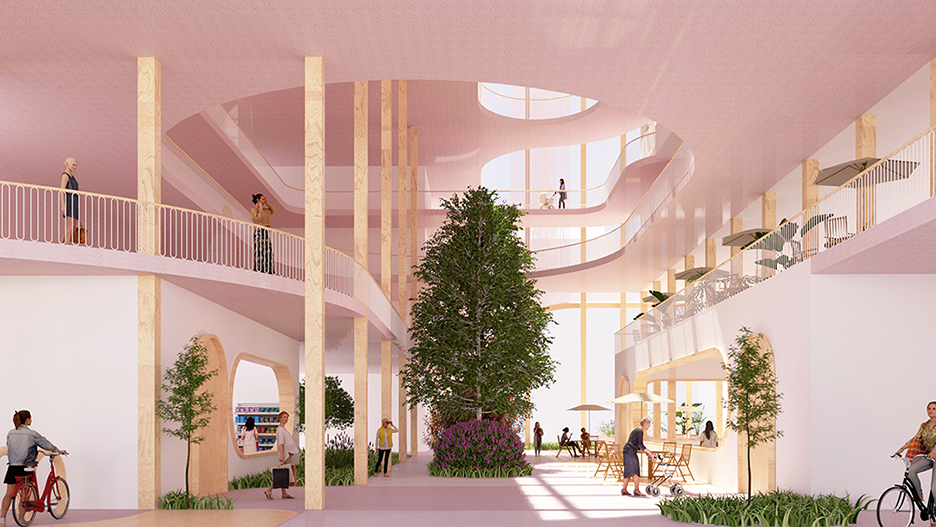
Heart House by Graziella Pilkington, M. Arch ’24
Boston Architectural College | Advisor: Russel Feldman, AIA
Thesis Statement:
This thesis explores how architecture can promote healing within inner-city populations affected by opioid addiction and homelessness. It investigates design interventions that alleviate social and health disparities, foster rehabilitation, and cultivate a sense of belonging and support.
Abstract:
Currently, our Nation is grappling with an epidemic—opioid abuse. This epidemic is by definition localized, and it often escapes our collective awareness. Yet, for individuals and communities whose lives are deeply entwined in the vicious cycle of addiction, it can feel as though they have nowhere to turn.
Architecture can serve as a powerful tool for cities to support people in overcoming addiction. Real change requires accessible, practical, and stigma-free resources and support.
This project provides a safe space where clients can access help when they are ready, on their terms, and use substances safely along the way to recovery.
Dignity is a sense of pride in oneself; self-respect.
How can architecture make someone feel this pride in themselves?
This building gives people the opportunity to feel worthy—worthy to walk into a beautiful building that is for them.
Self-worth is the first step in recovery.
Site:
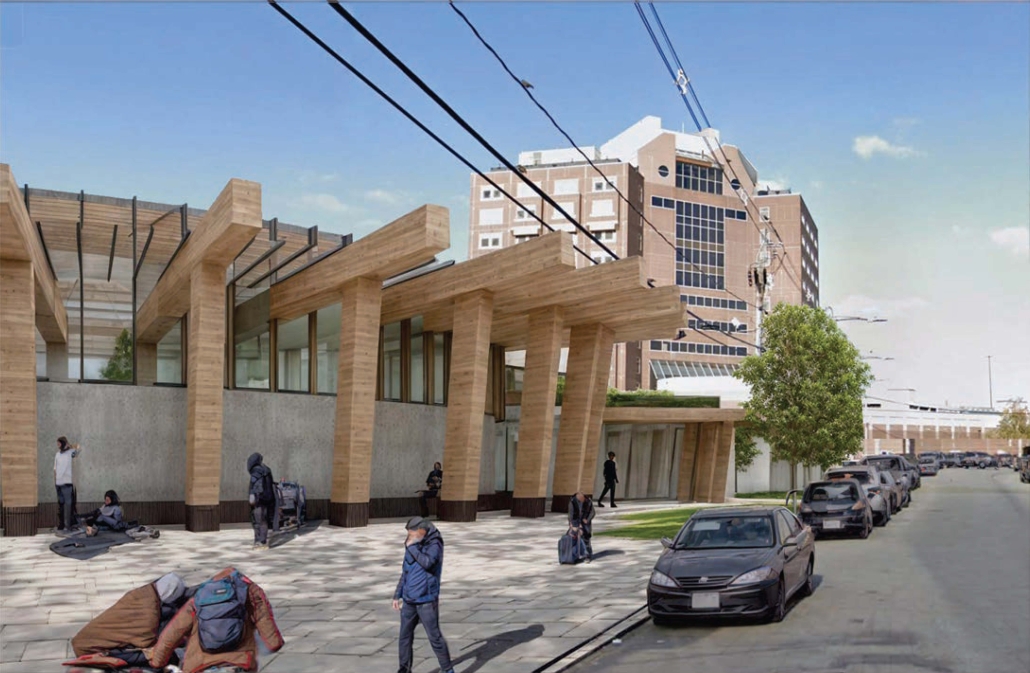
Located on Atkinson Street in Boston, Massachusetts, the site is a former industrial zone known as “Methadone Mile” or “Recovery Road.” This area is increasingly associated with homelessness, drug use, violence, crime, sex trafficking, and unsanitary conditions.
Program:
Heart House is designed to serve up to 250 clients per day, consistent with neighborhood needs according to the Mass/Cass Dashboard (2023).
The building features two main zones: the substance zone for safe self-administration and the recovery zone for rehabilitation resources. These zones do not intersect to prevent triggering clients in recovery. Staff travel between the substance and recovery zones. Secure outdoor space, which is lacking in the neighborhood, separates clients from the noise and distraction of the street, while providing a sense of nature in the city. The entry sequence safeguards clients’ privacy with a single secure entrance reducing stigma.
Heart House, the area’s pioneering drug consumption center, offers vital recovery services and prioritizes a dignified experience—an unprecedented offering for this demographic.
This project received an M. Arch Thesis Nomination for Commends
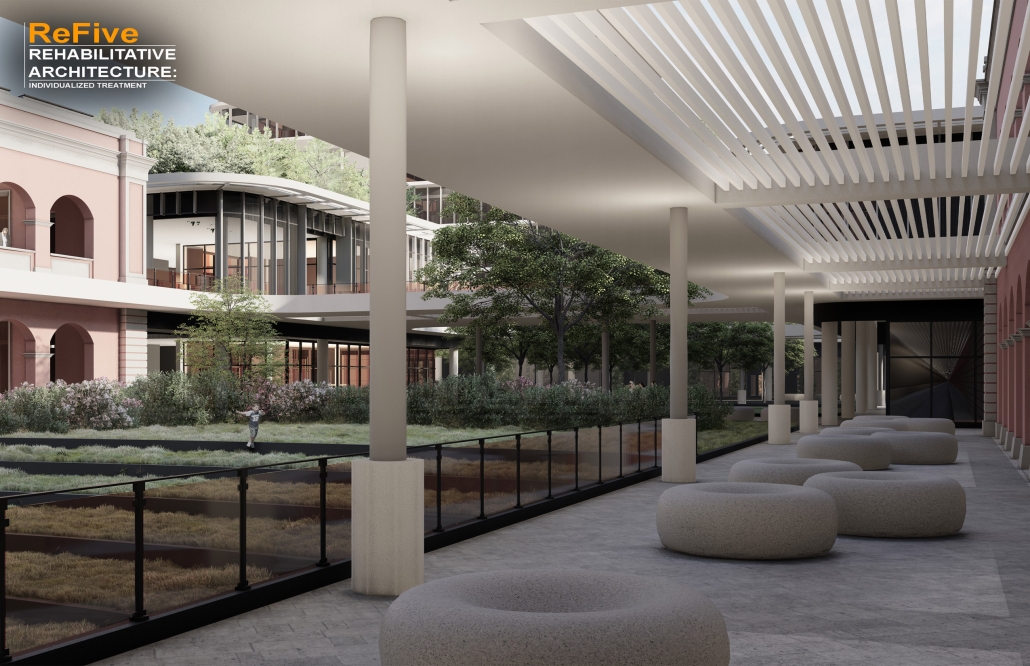
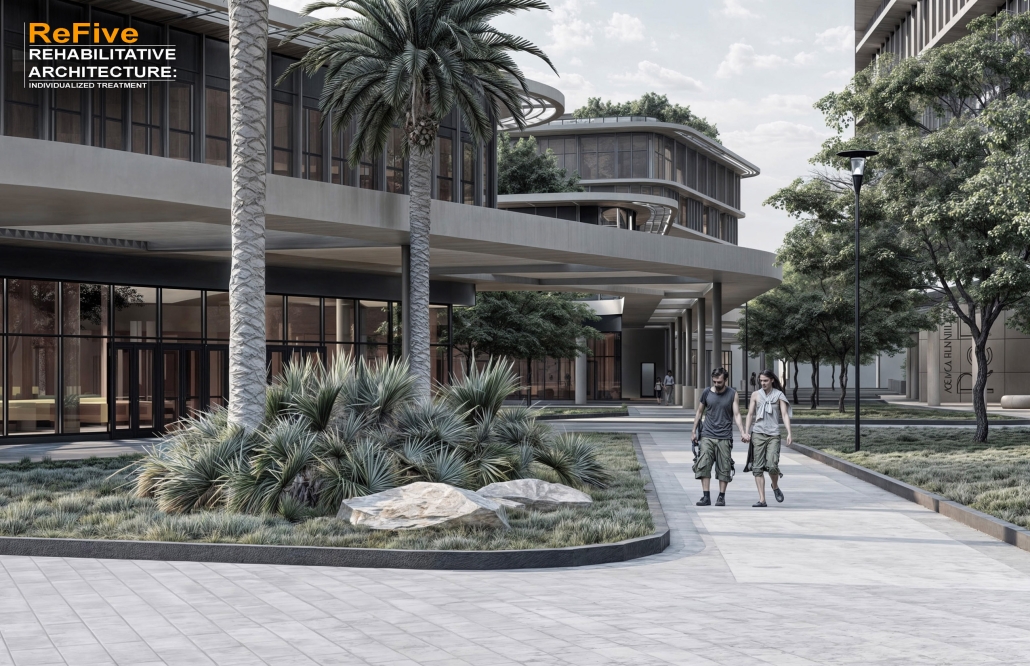
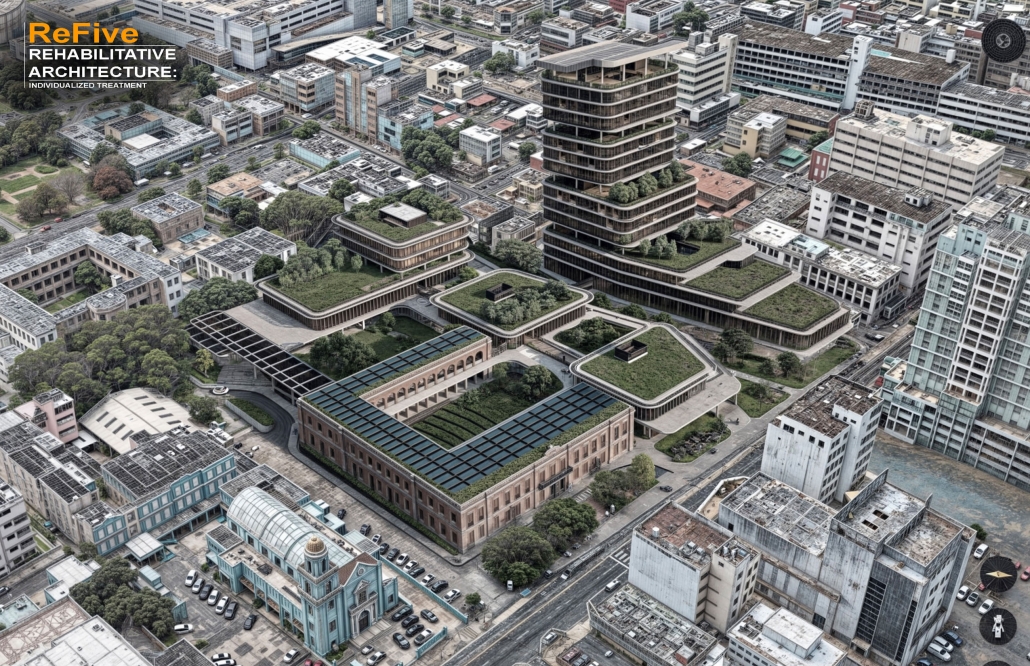
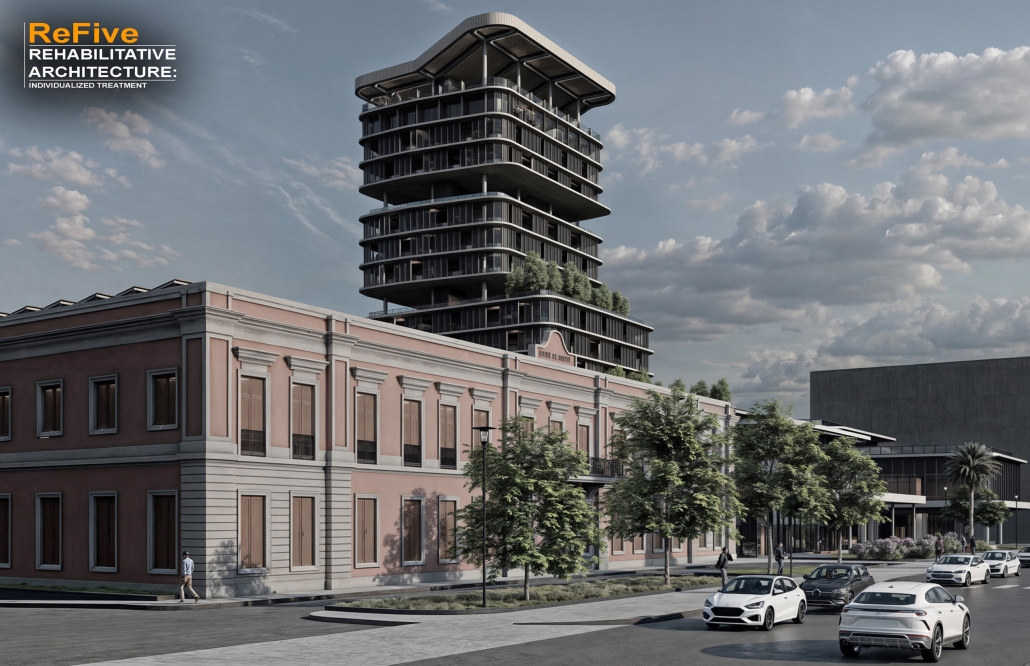
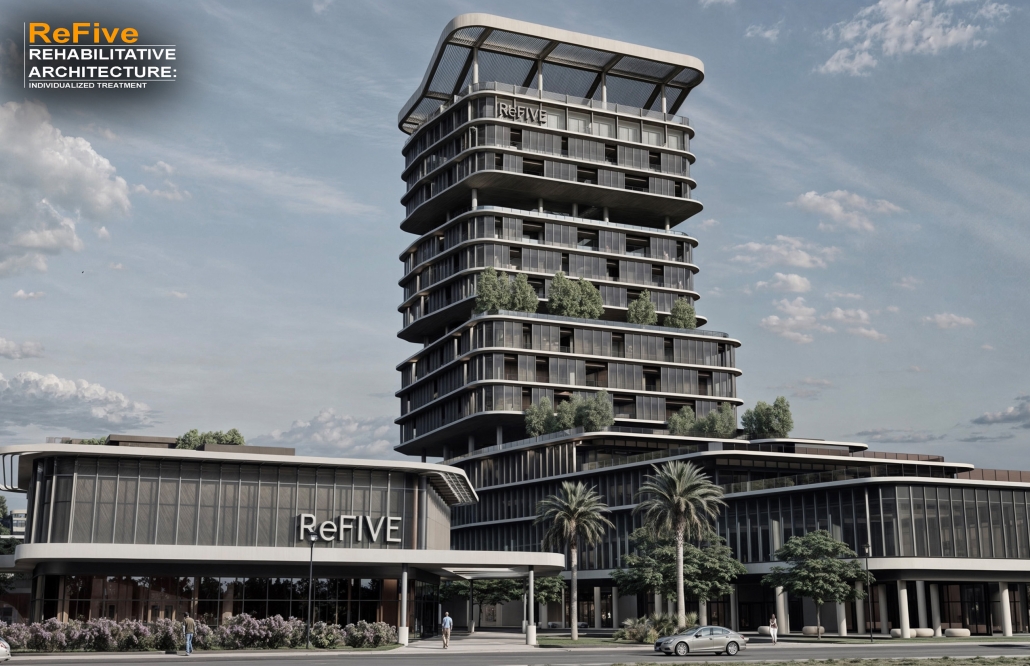
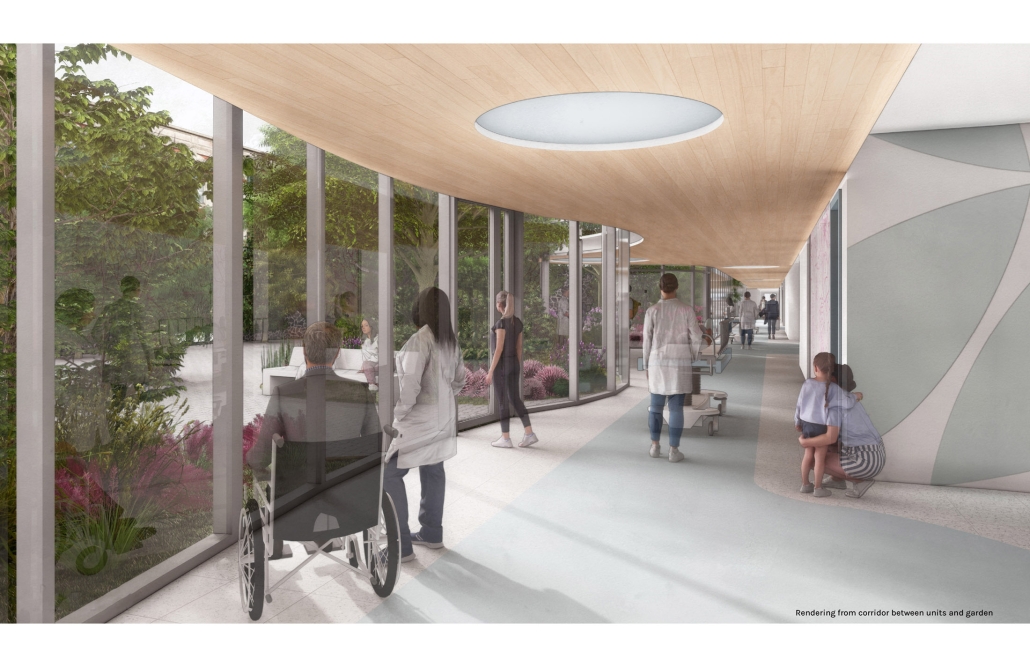
ReFive – Rehabilitative Architecture: Individualized Treatment by Sebastián A. Colón-López, B. Arch ‘24
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisor: Pedro A. Rosario-Torres
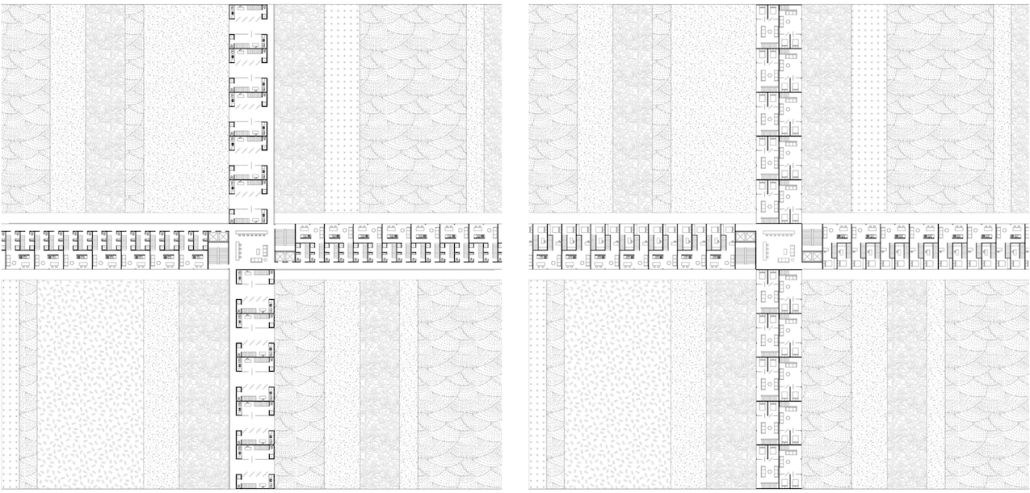
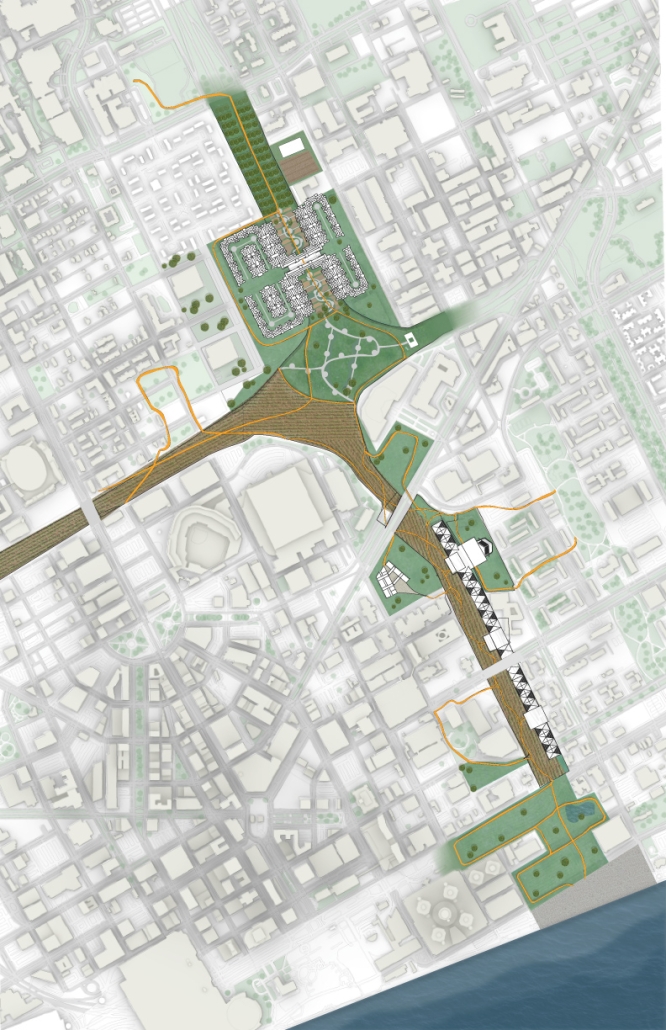
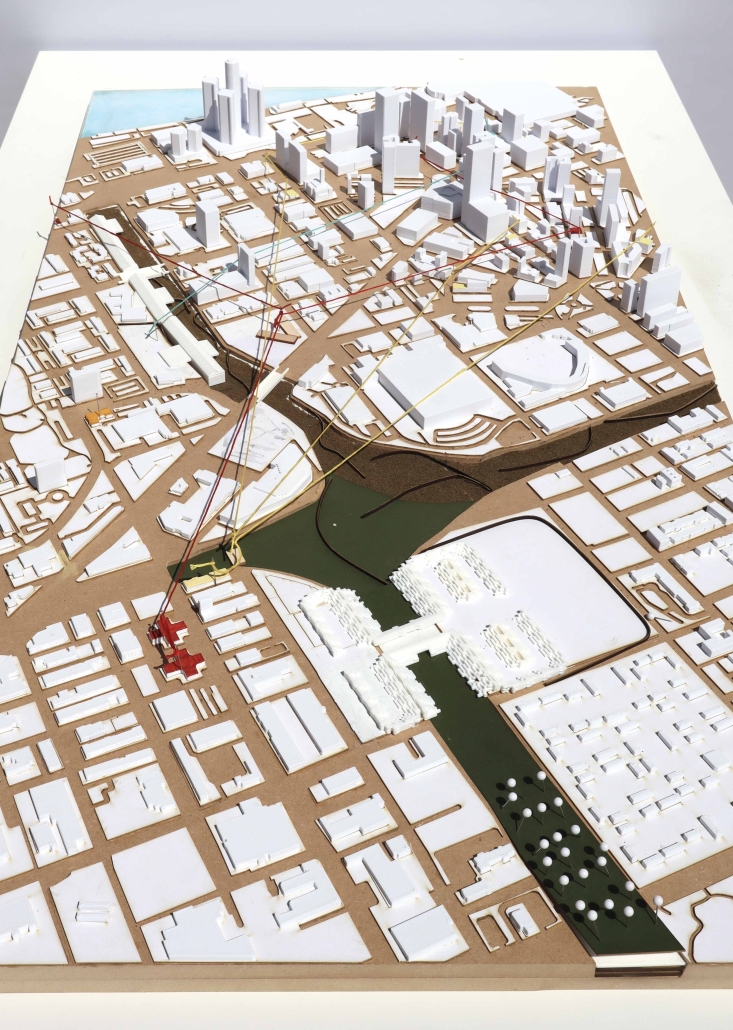
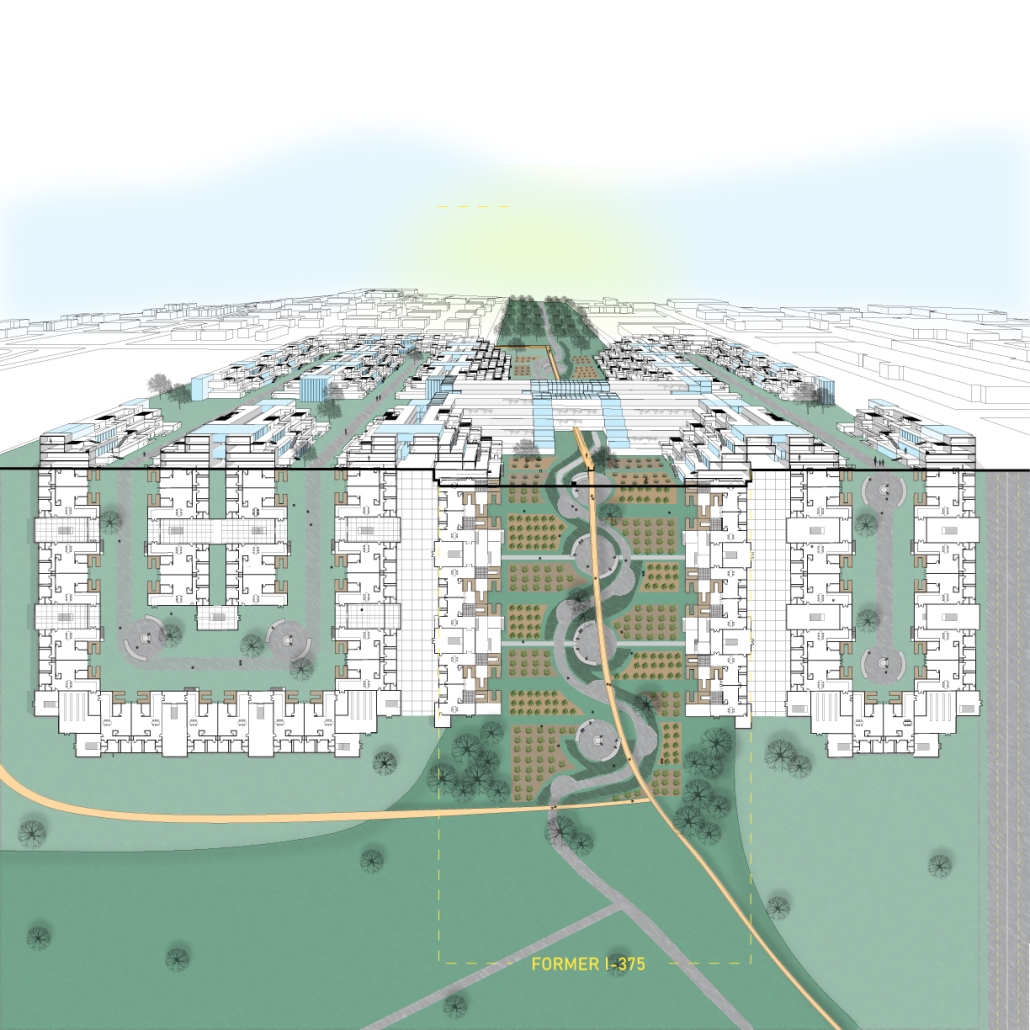
The “ReFive – Rehabilitative Architecture: Individualized Treatment” research offers a critique of Puerto Rico Law 67, which allows involuntary treatment of patients with drug addictions. This analysis underscores deficiencies in the island’s traditional methods, often based on religious beliefs and the use of inadequate facilities that were previously used for other purposes, rather than developing specialized spaces. The research highlights the need to adopt evidence-based treatments.
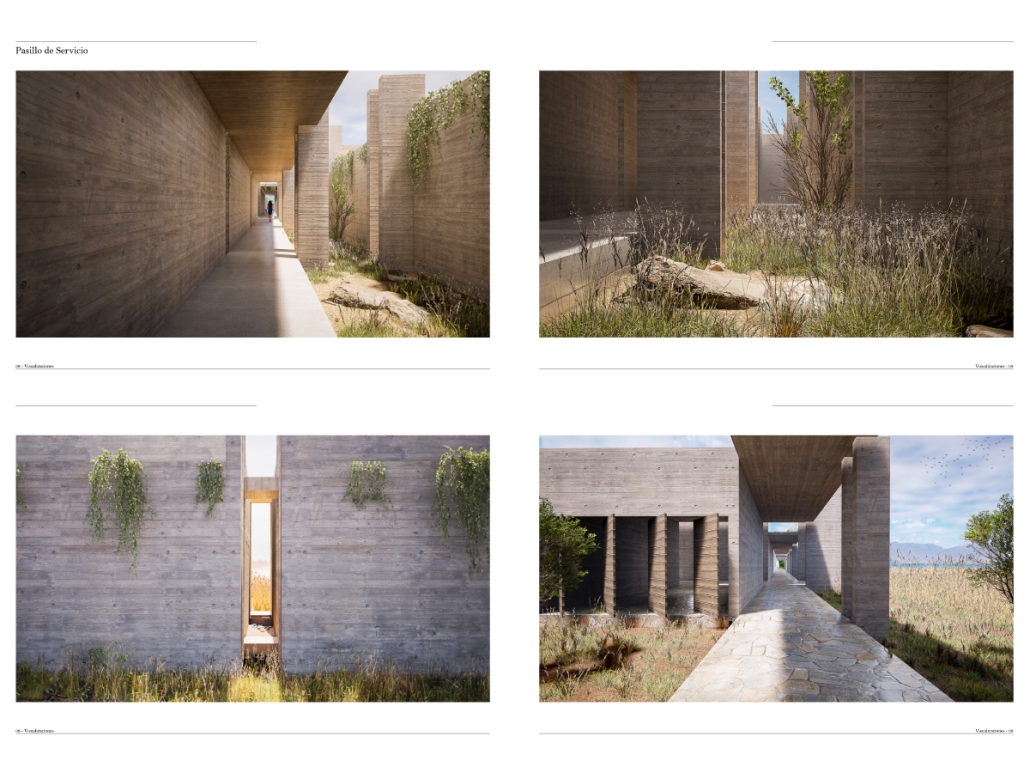
The conclusions of this research led to the creation of new infrastructures dedicated exclusively to rehabilitation, with environments that promote the recovery and well-being of patients. The project consists of five independent treatment phases and, therefore, five built volumes: detoxification (clinics), dishabituation (therapy), rehabilitation (education), reinsertion (temporary housing), and tracking (administration). These five phases are linearly arranged on-site to provide patients with a healing journey and, at the same time, assist in their orientation from arrival in critical conditions to reintegrating into society. Each phase is designed to meet the specific needs of patients at different stages of their recovery. Spaces include partially open areas with views to the outside, natural light, ventilation, and therapeutic gardens. These elements are essential for creating an environment that facilitates physical and mental recovery and promotes a sense of well-being among patients.
The project is located in Santurce, Puerto Rico because one of the main objectives is to reintegrate patients into society. Locating the building in a densified urban district provides better job opportunities and greater proximity to essential services, thus facilitating reintegration.
ReFive addresses ineffective and outdated methods in the treatment of substance use disorders in Puerto Rico through an innovative, evidence-based model. By critiquing current practices, it identifies shortcomings and presents a plan to transform the mental health care system to be centered on the patients and their specific needs.
This project was nominated for the Medal for Excellence in Design, Francisco Luis Porrata-Doria.
Instagram: @_sebaandrecl
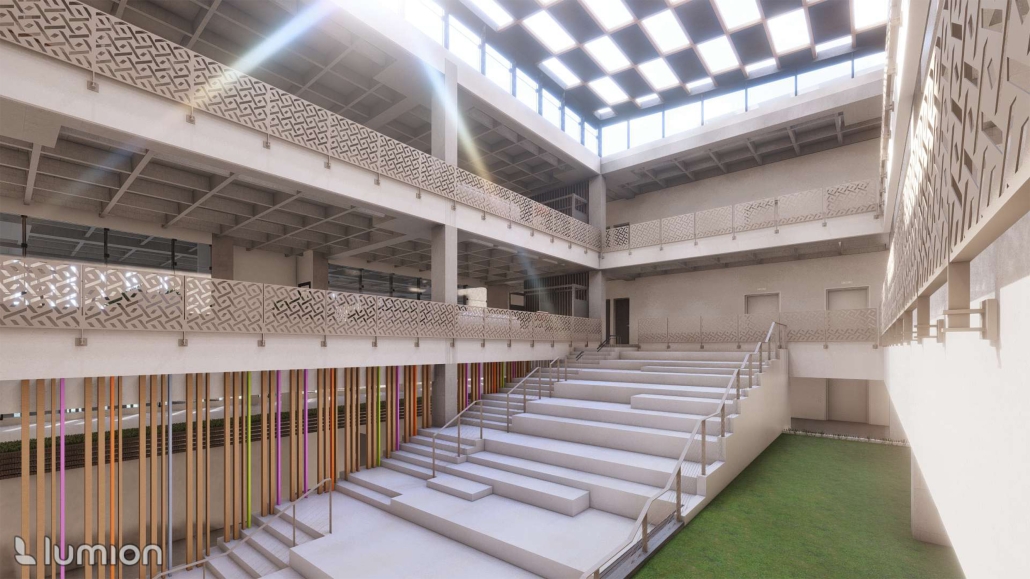
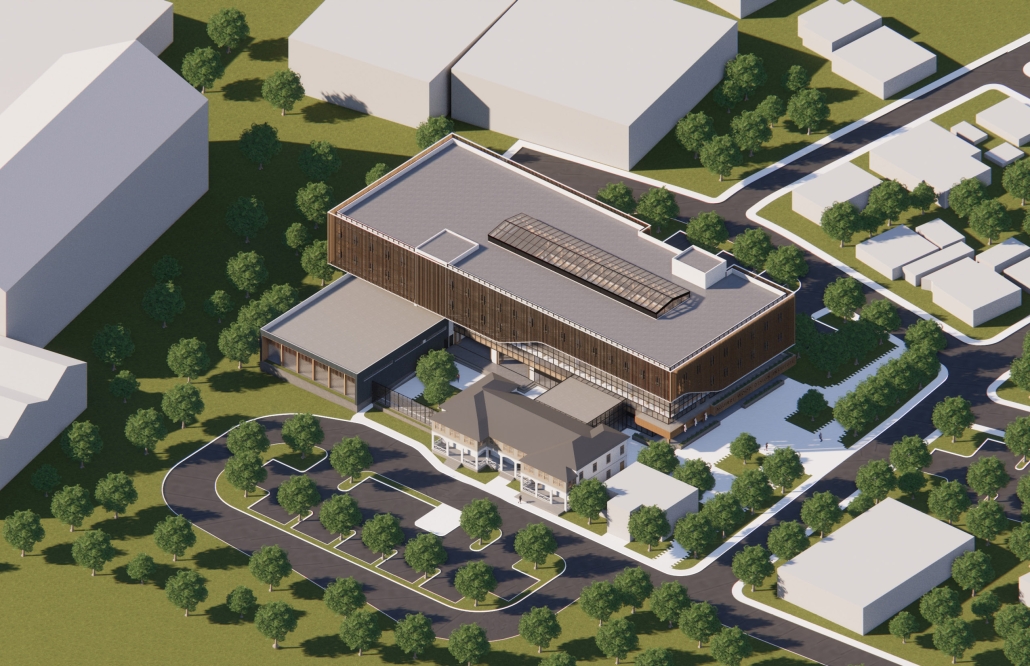
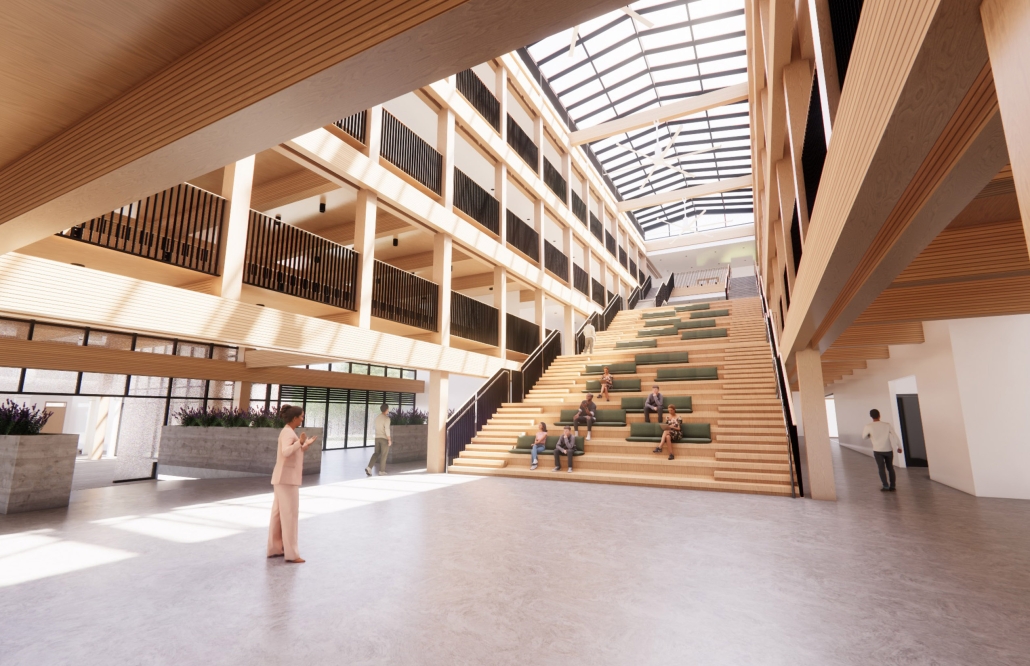
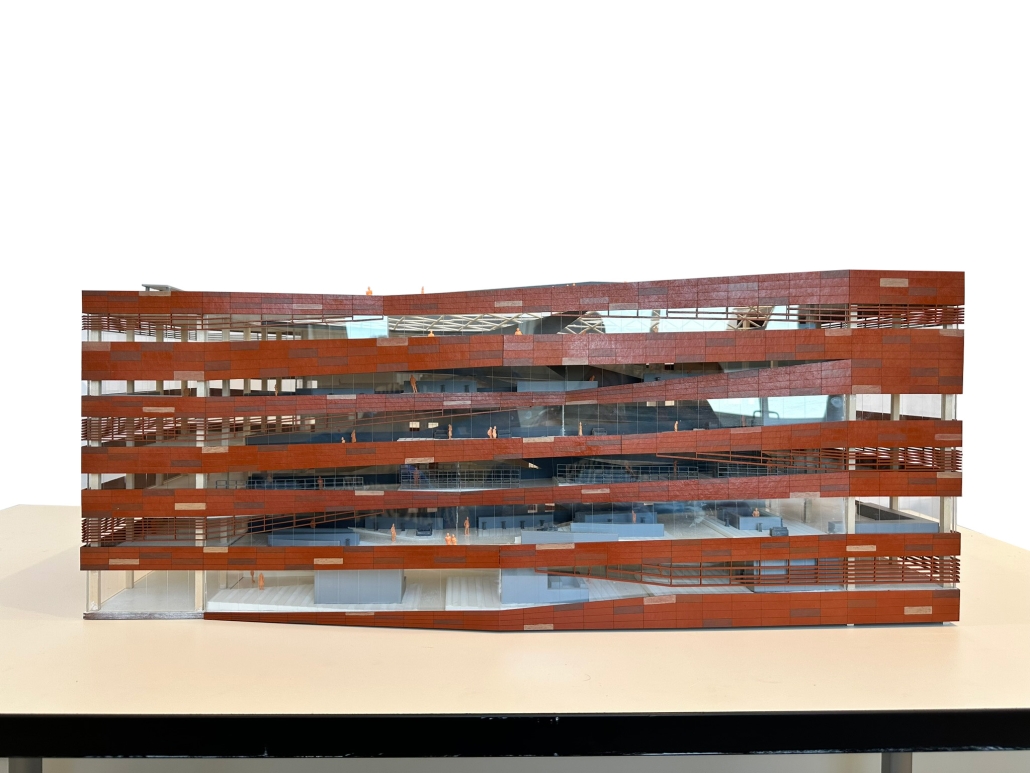
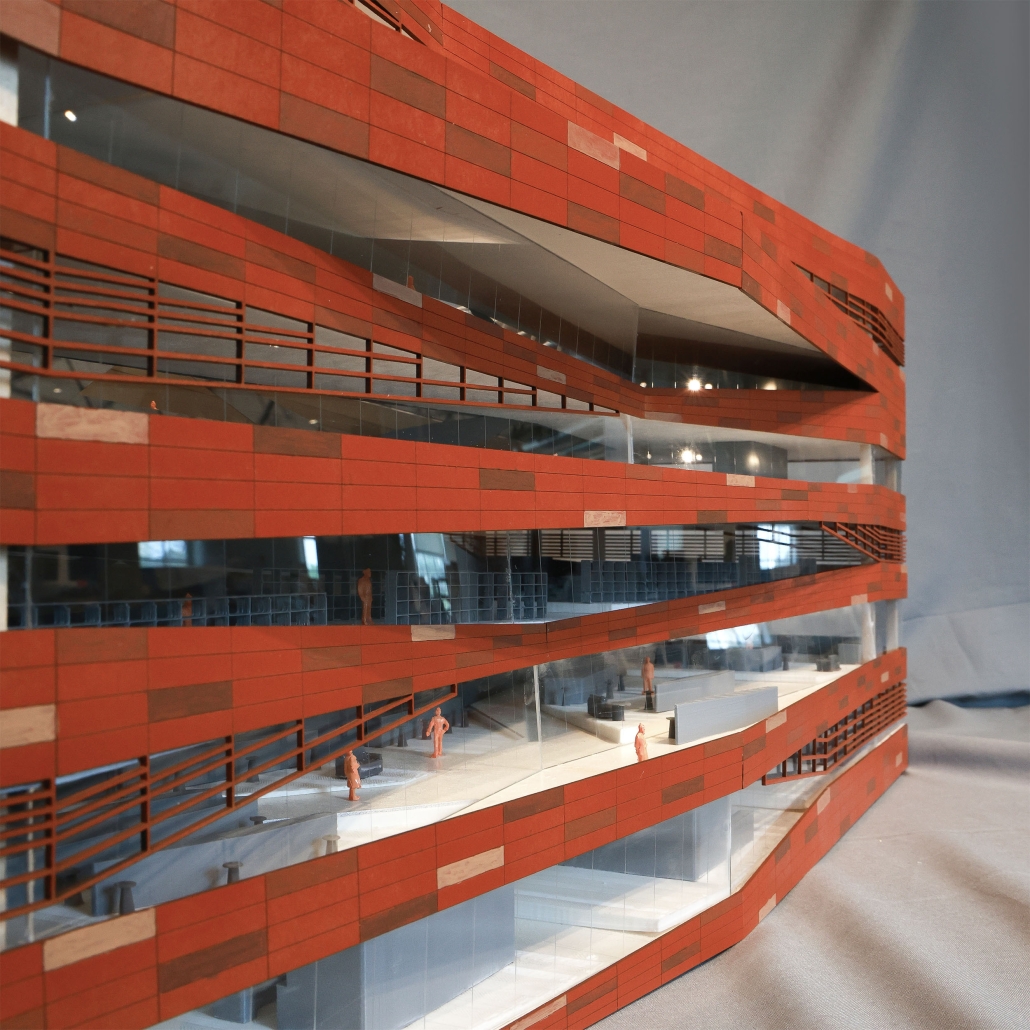
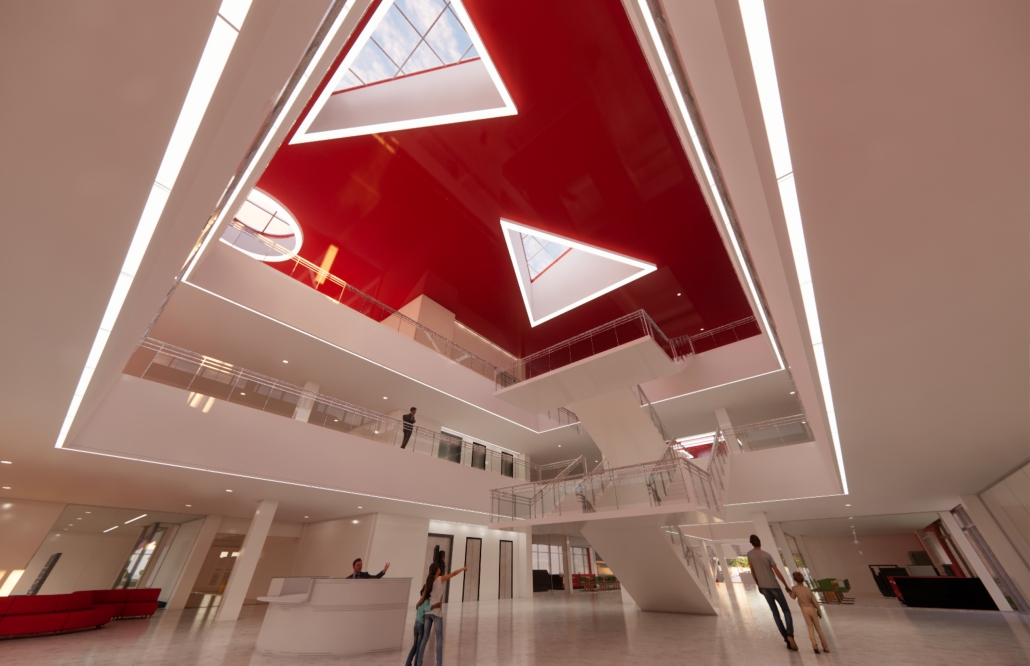
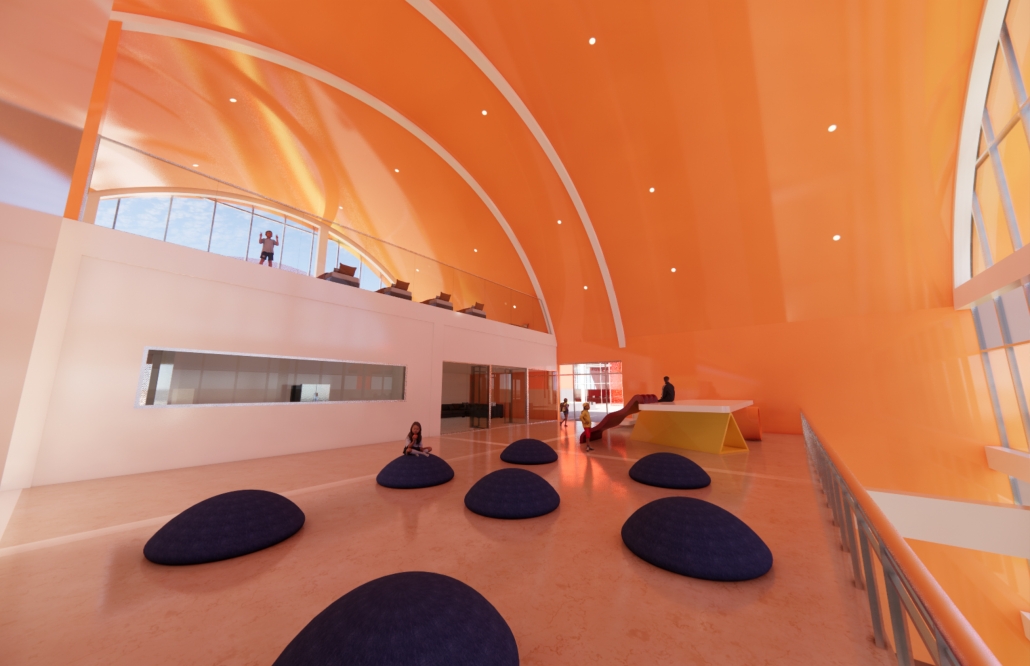
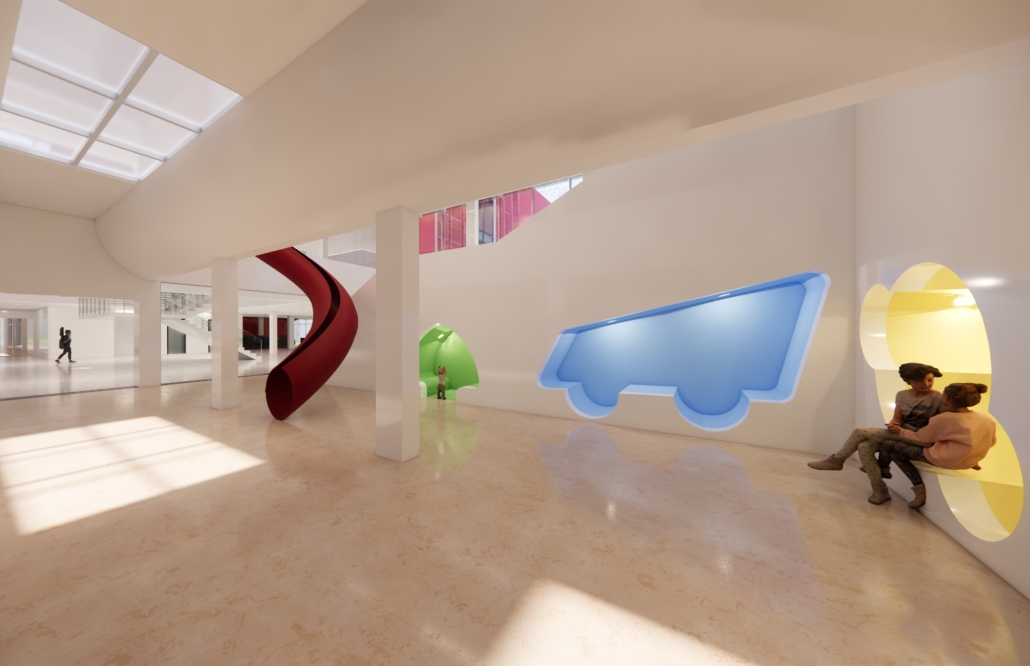
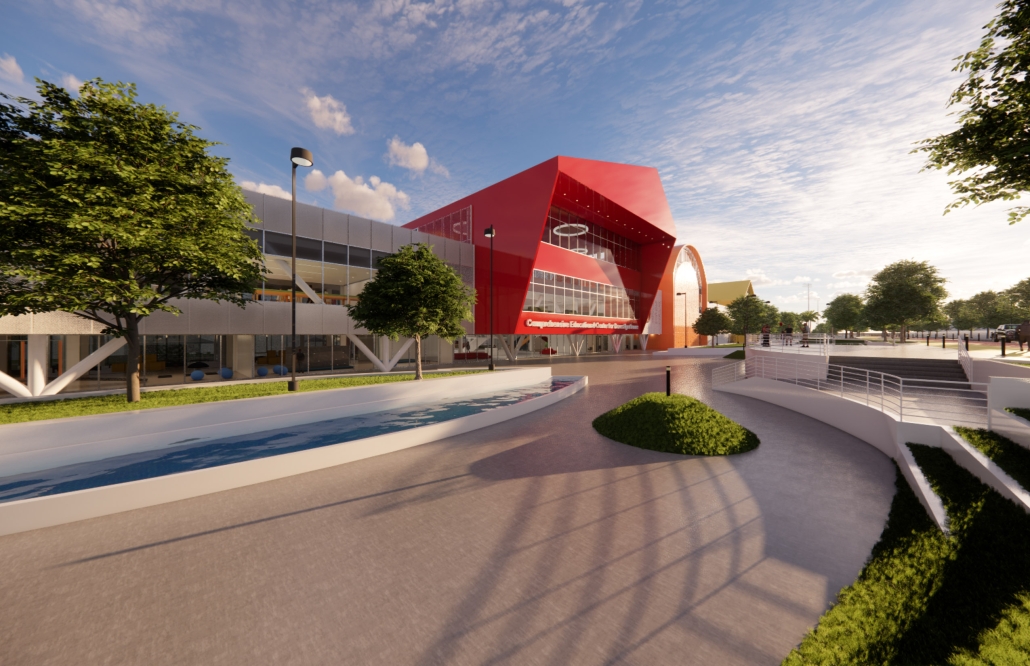
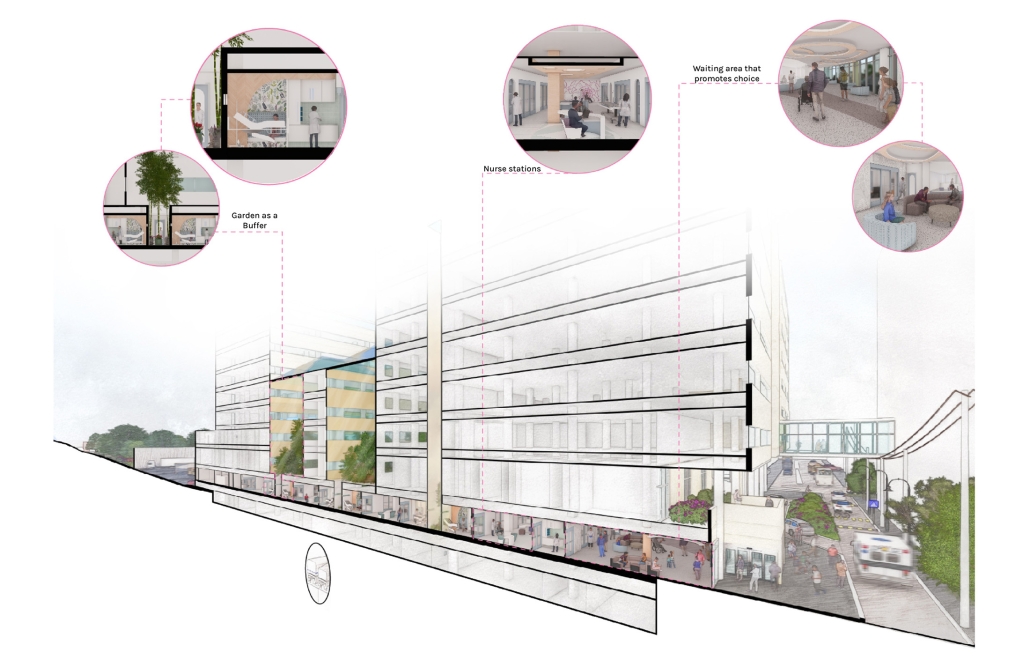
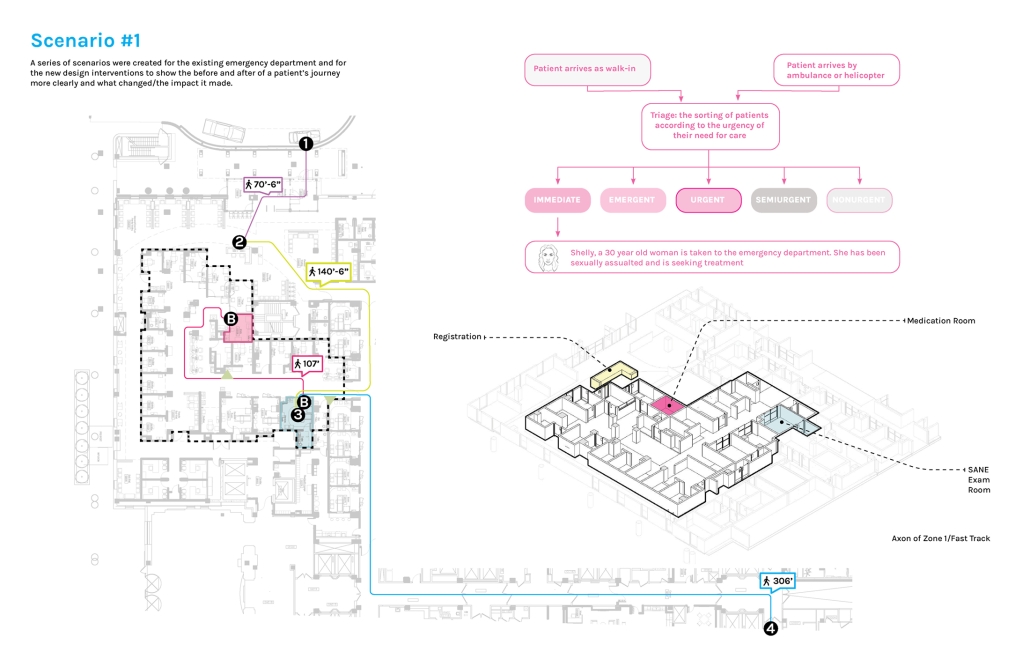
Architecture as a Form of Care: A Transdisciplinary Approach to the Integration of Human-centric Design in Grady Memorial Hospital’s Emergency Department by Sara Clement, B. Arch ’24
Kennesaw State University | Advisor: Pegah Zamani
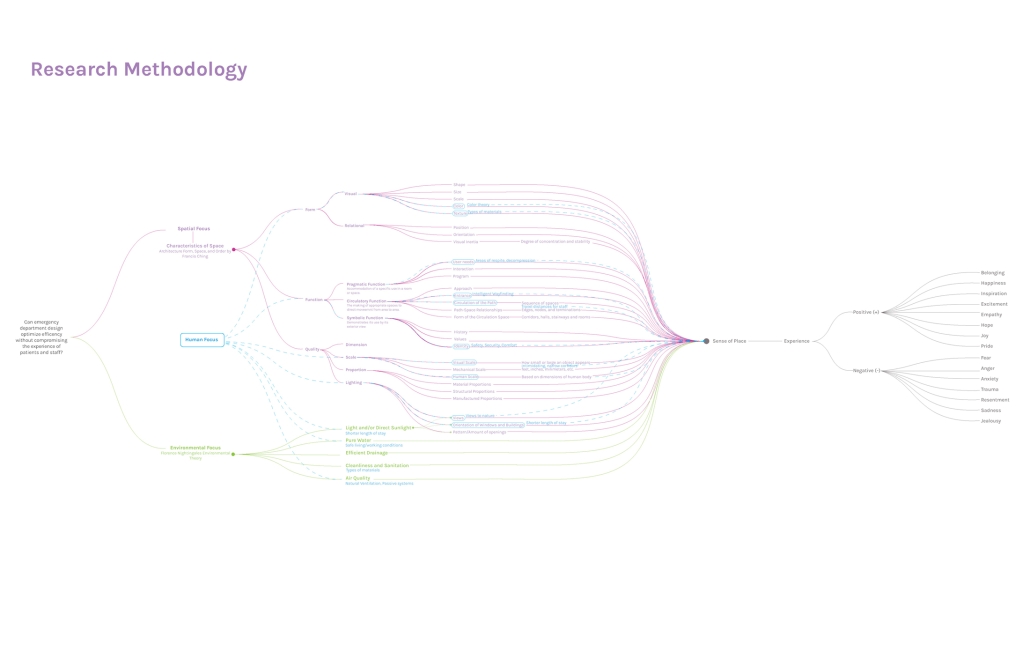
In what ways can the design of the built environment enhance spatial efficiency without compromising the spatial experience of its diverse occupants? This transdisciplinary research focuses on the possibilities of designing optimized built environments while advancing their inhabitants’ well-being. The study centers on a pivotal spatial setting: healthcare emergency facilities with a particular emphasis on Grady Memorial Hospital, a safety net hospital serving uninsured patients from marginalized communities. In the context of emergency care delivery, as a case, this thesis highlights the potential oversight of human-centered experience within the internalized and efficiency-driven nature of emergency departments (EDs) that impact inhabitants, especially in moments of extreme stress. I analyze visible and invisible, clinical and environmental factors. along with human-centered design interventions associated with efficient space planning that fosters connection between clinicians, patients, and visitors.
The research employs a multifaceted transdisciplinary methodology, incorporating an extensive literature review and case studies to identify innovative practices that improve the overall experience for aII stakeholders. The research utilizes evidence-based design as a catalyst to formulate a set of parameters for developing design strategies that aid in the patient’s healing process while responding to the needs of a diverse range of users as well as future needs. The research addresses the complexities of optimizing occupants’ well-being through design across a variety of built environment settings from the waiting area to the clinical spaces. By examining these critical spaces the goal is to identify ways in which designers can spearhead creating more effective sustainable, equitable, and healthier environments for diverse populations.
This project was awarded Second Place in the KSU Architecture Thesis Competition, 2024
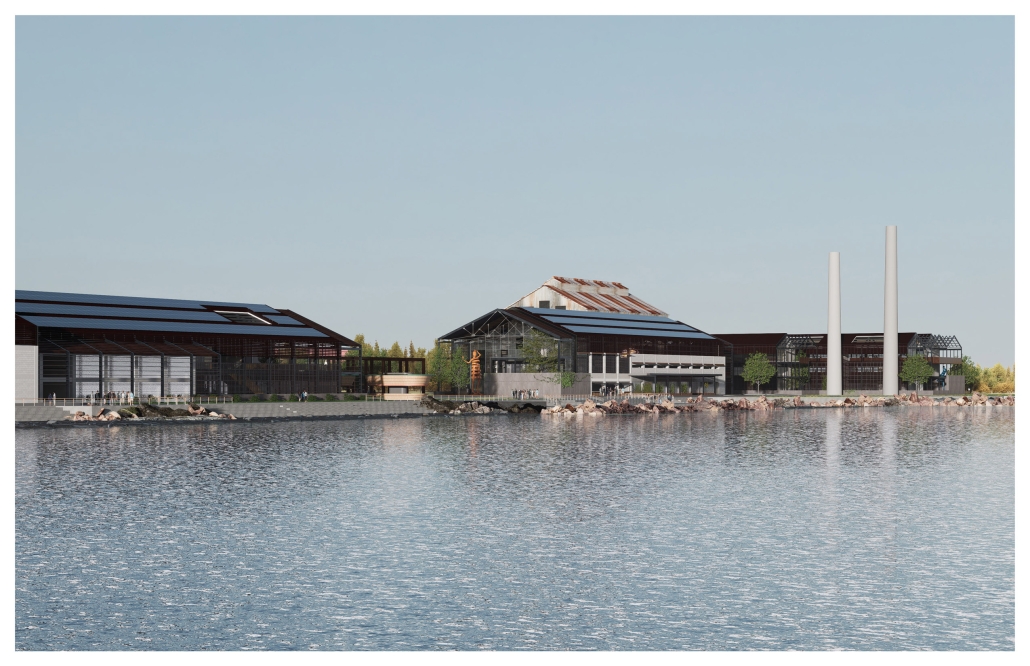
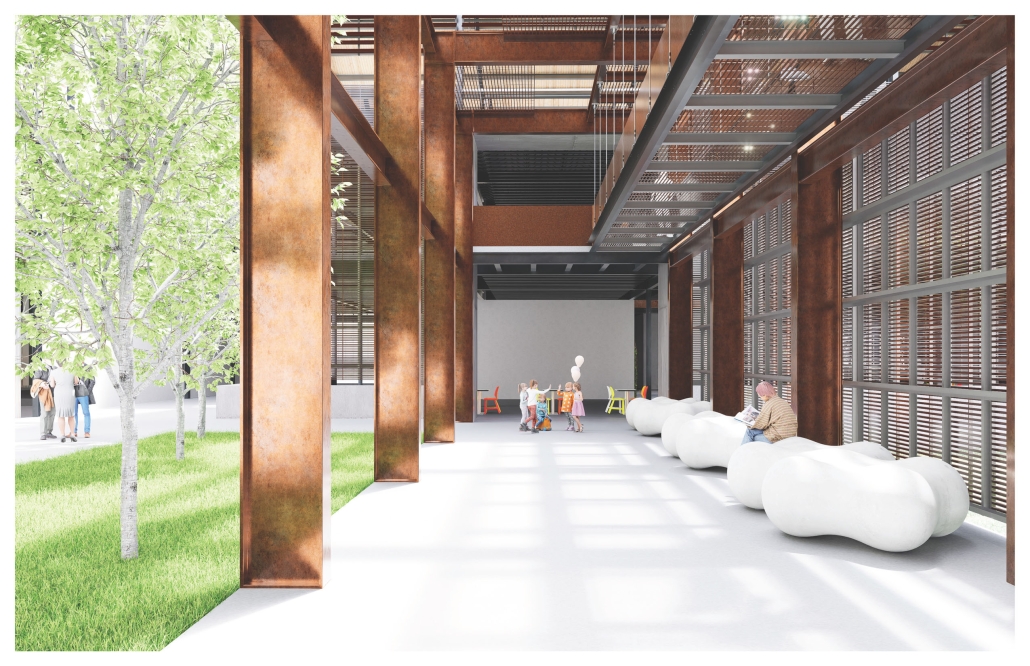
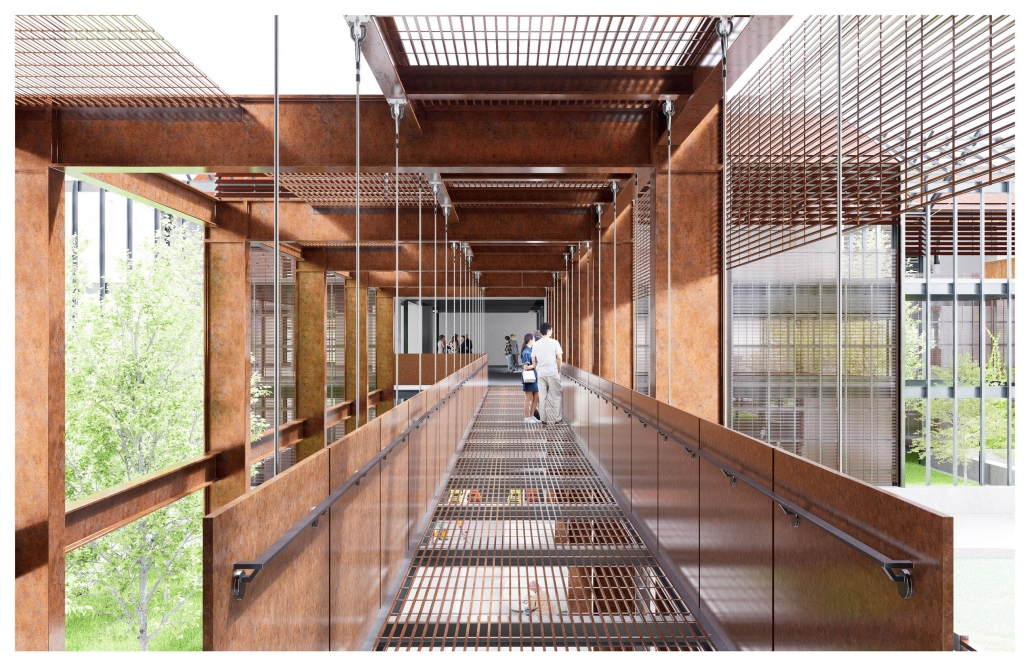
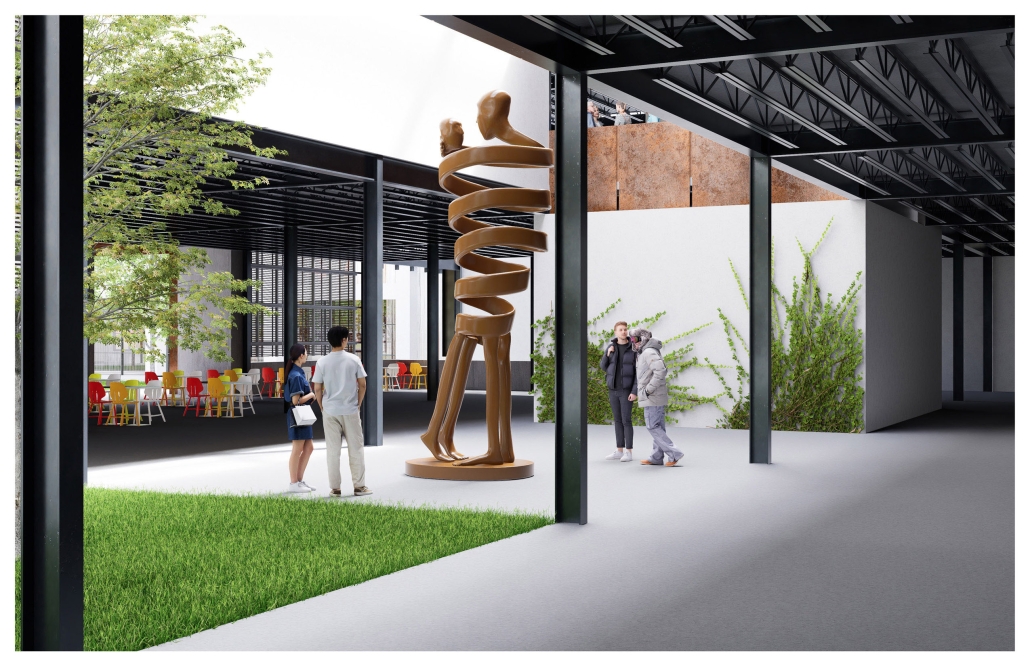
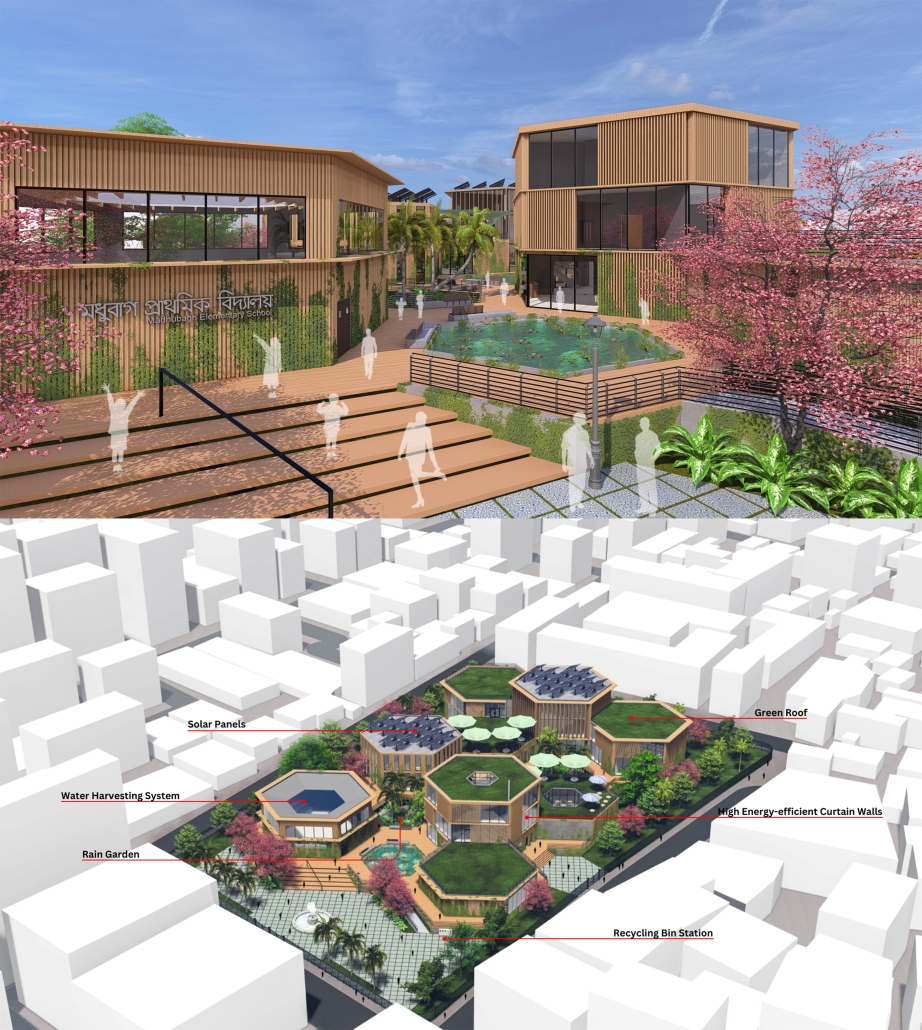
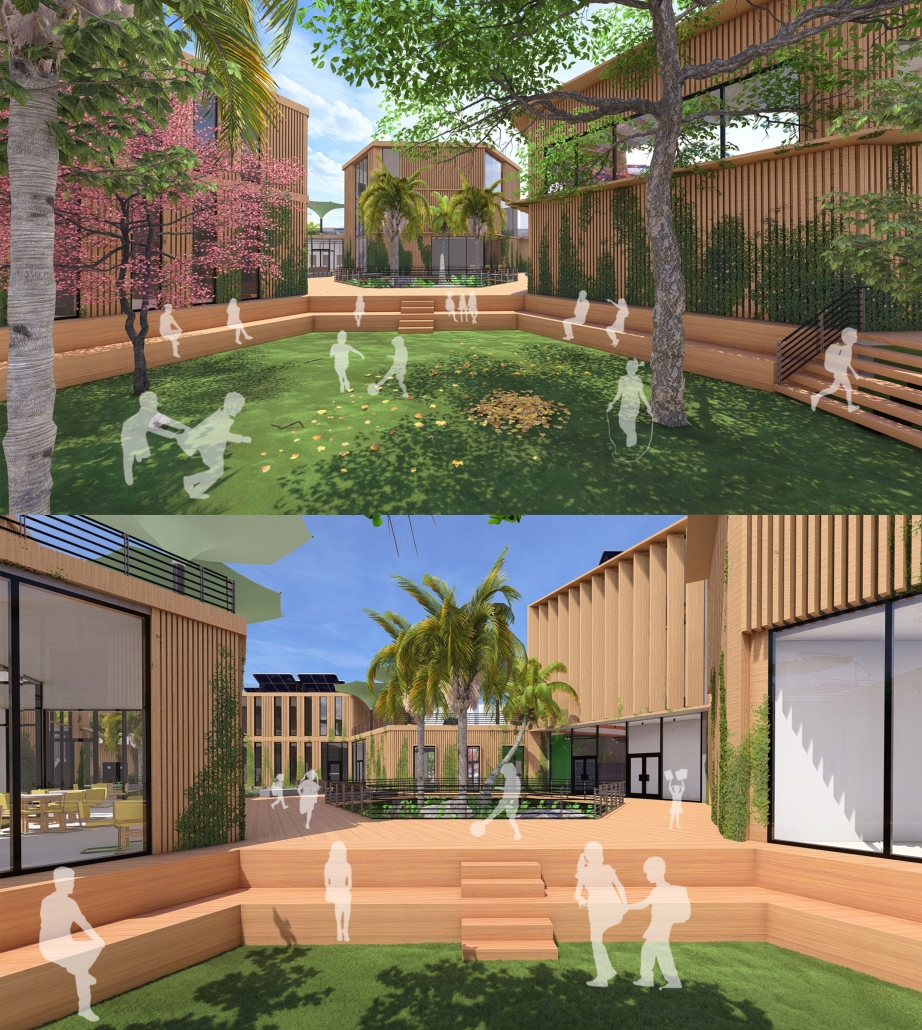
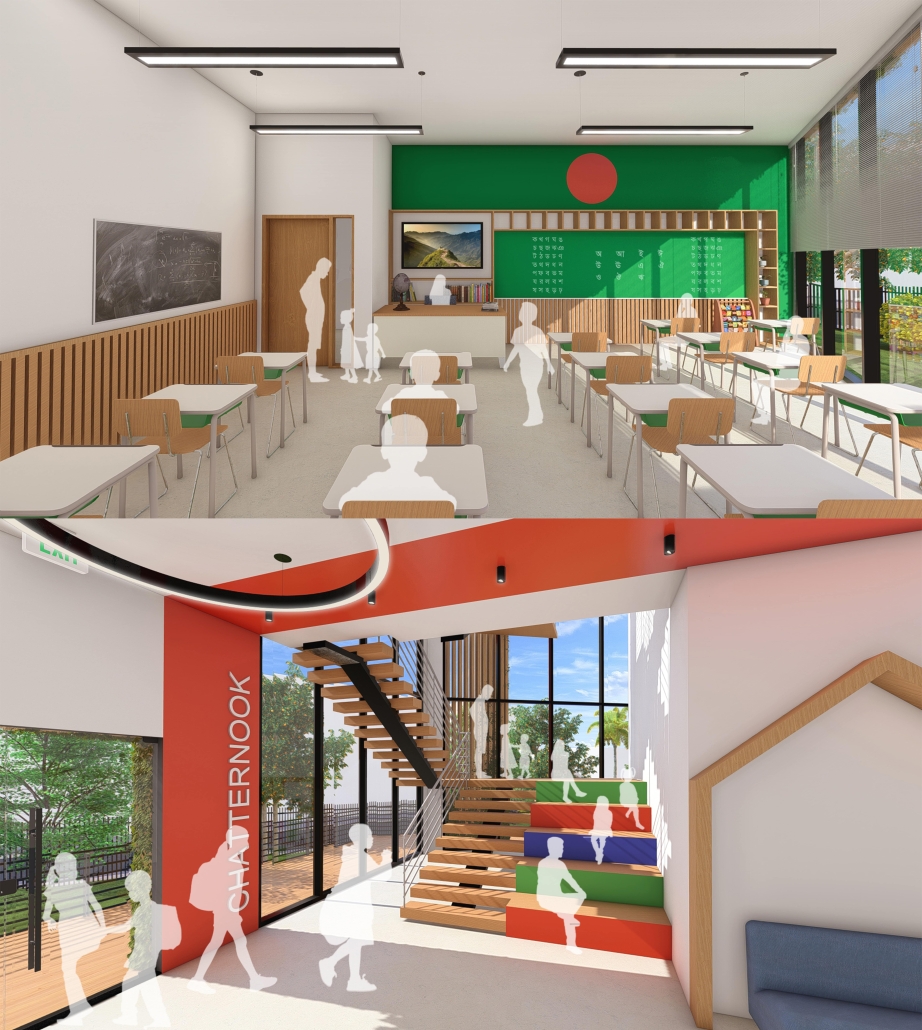
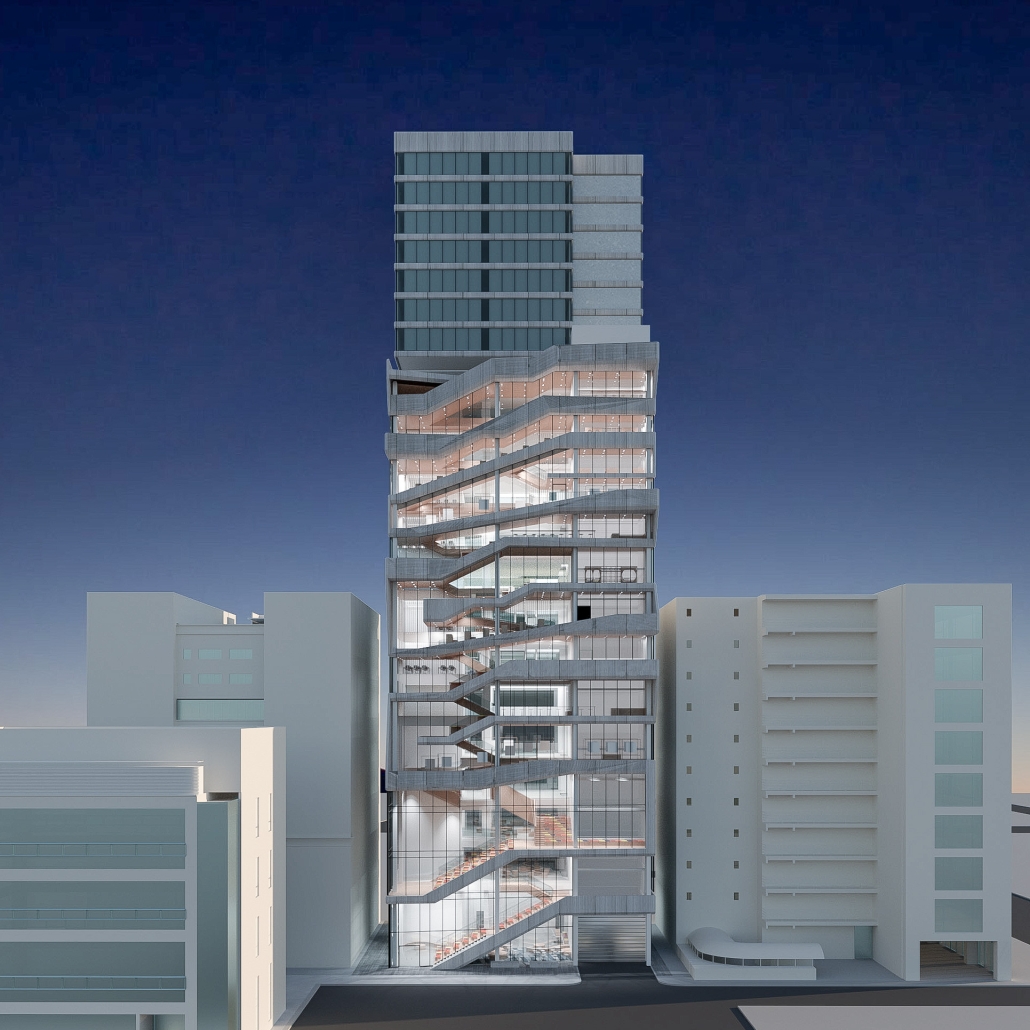
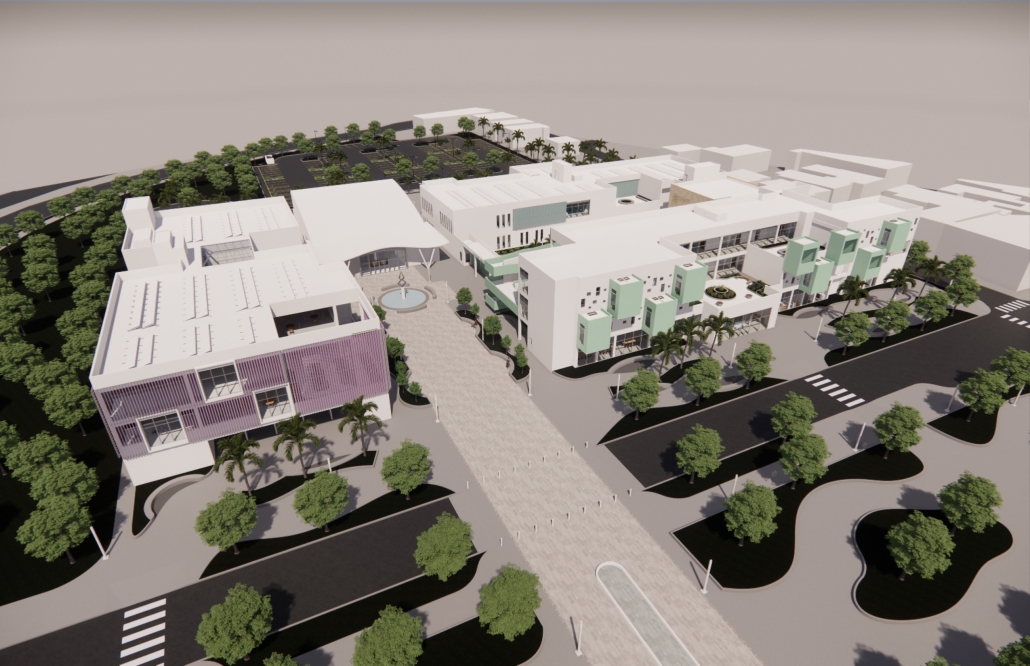
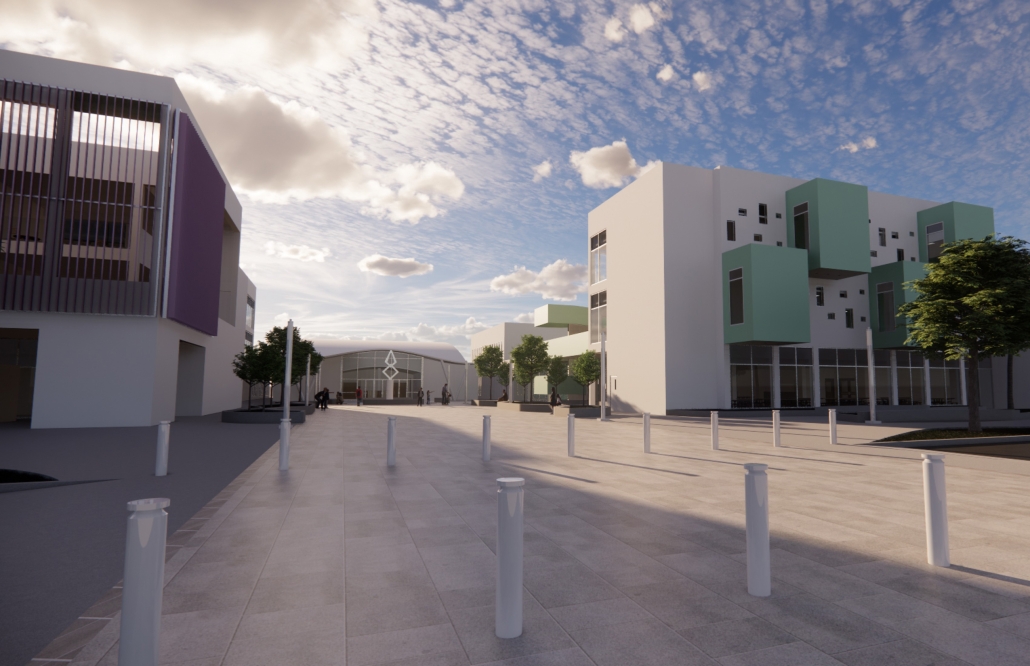
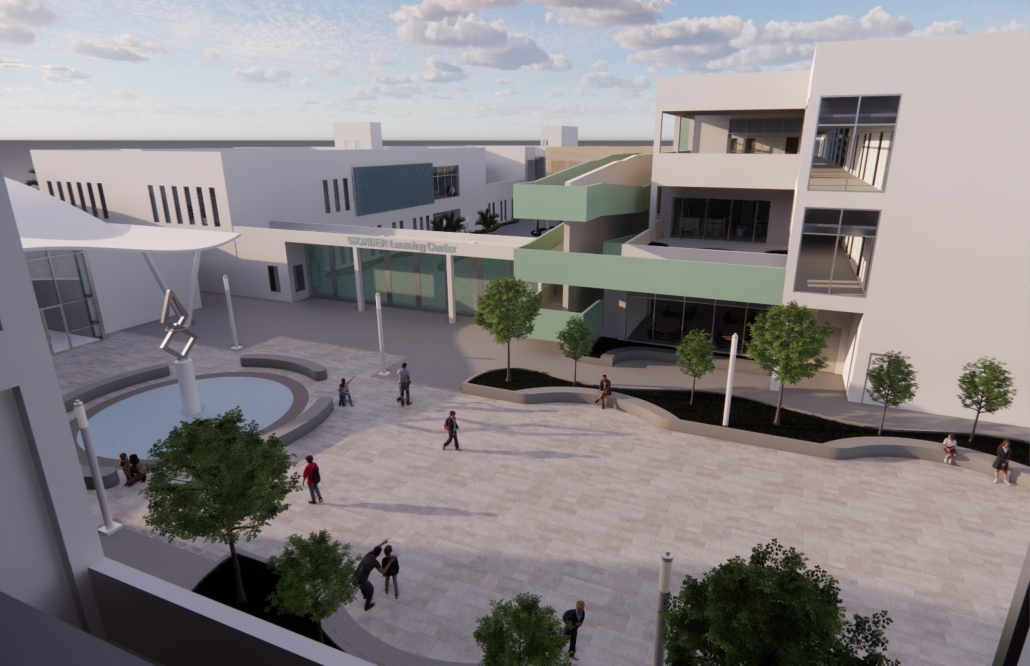
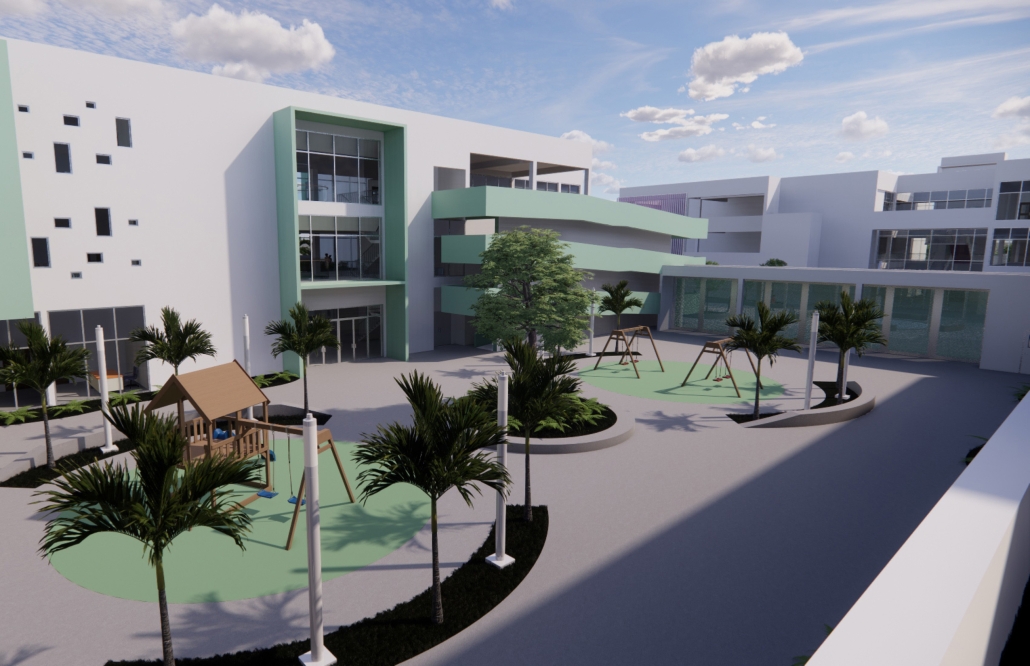
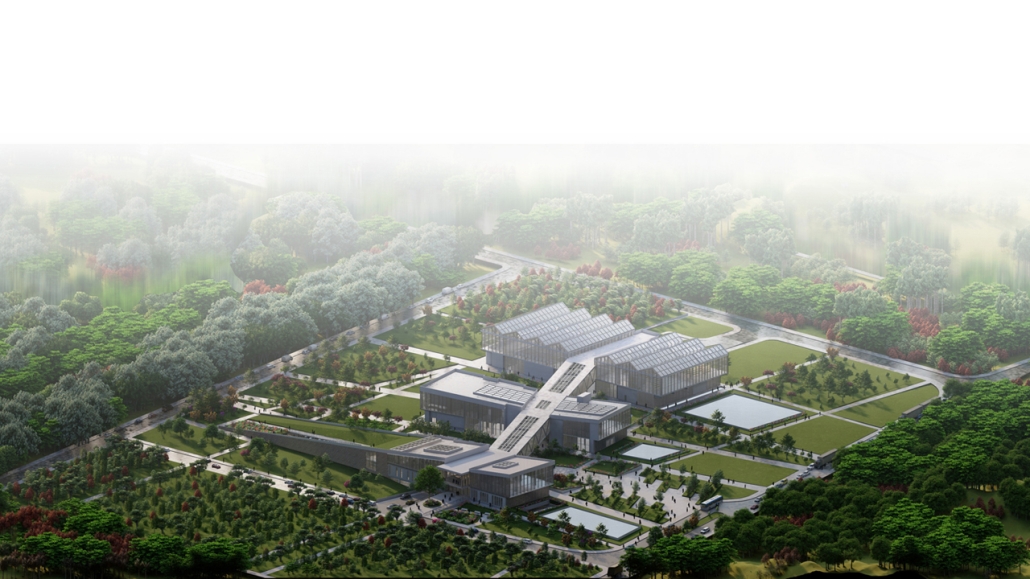
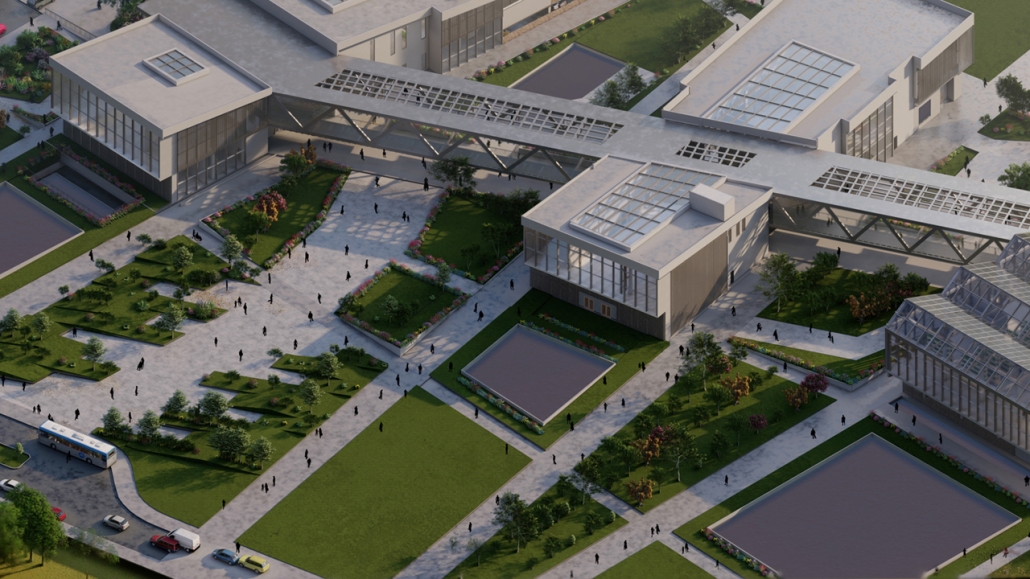
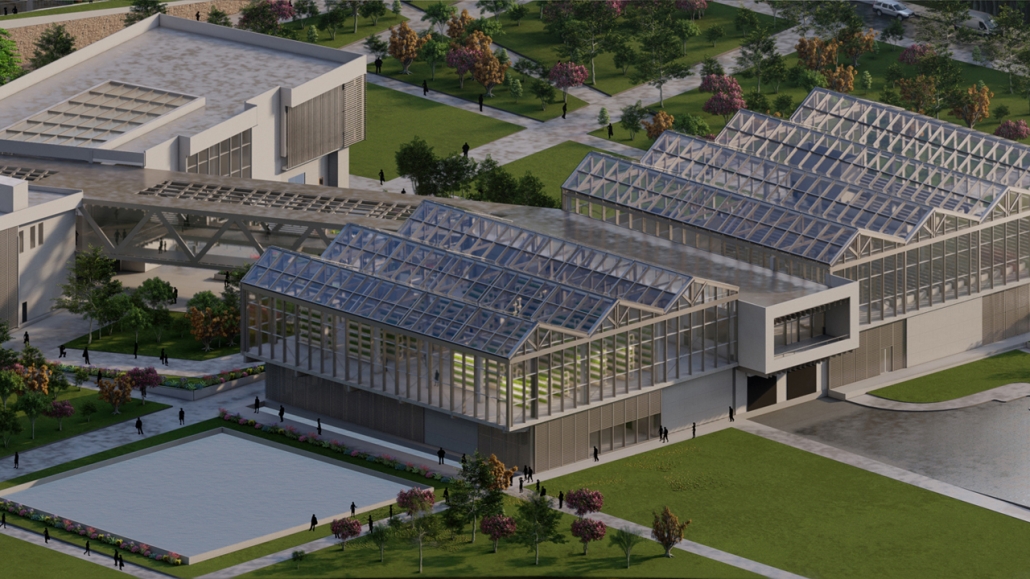
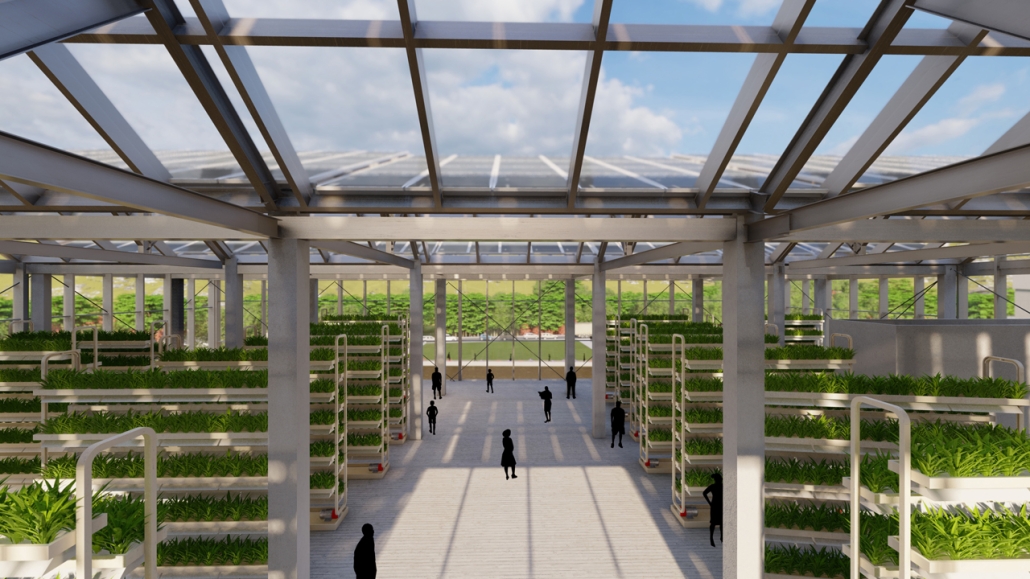
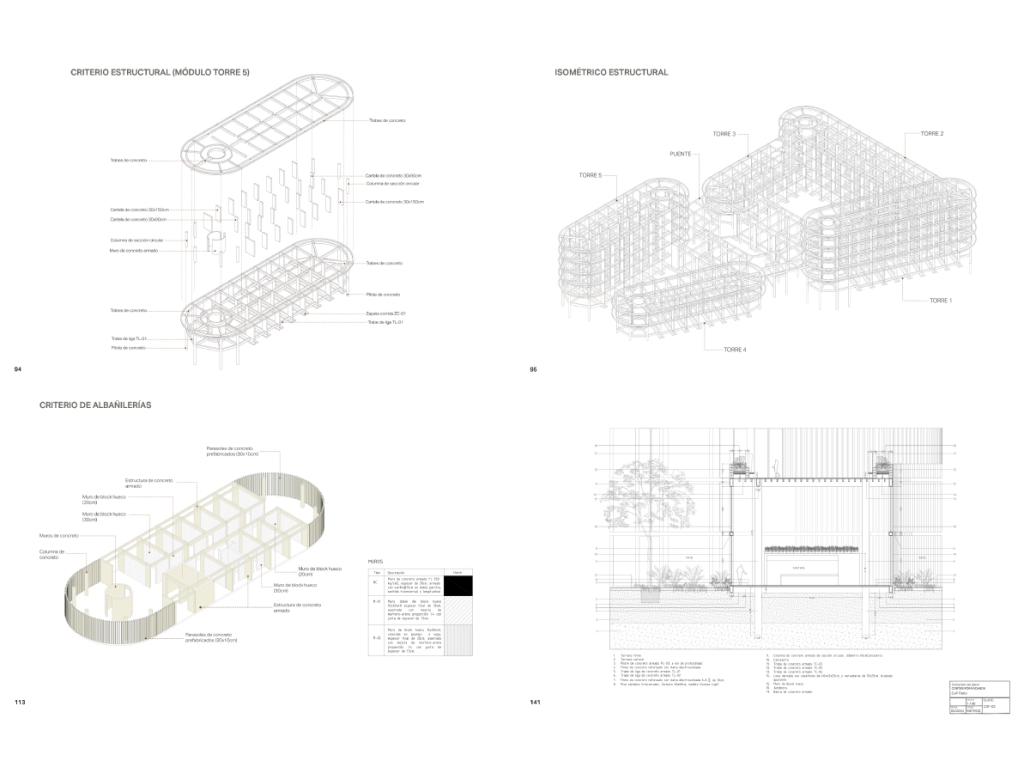
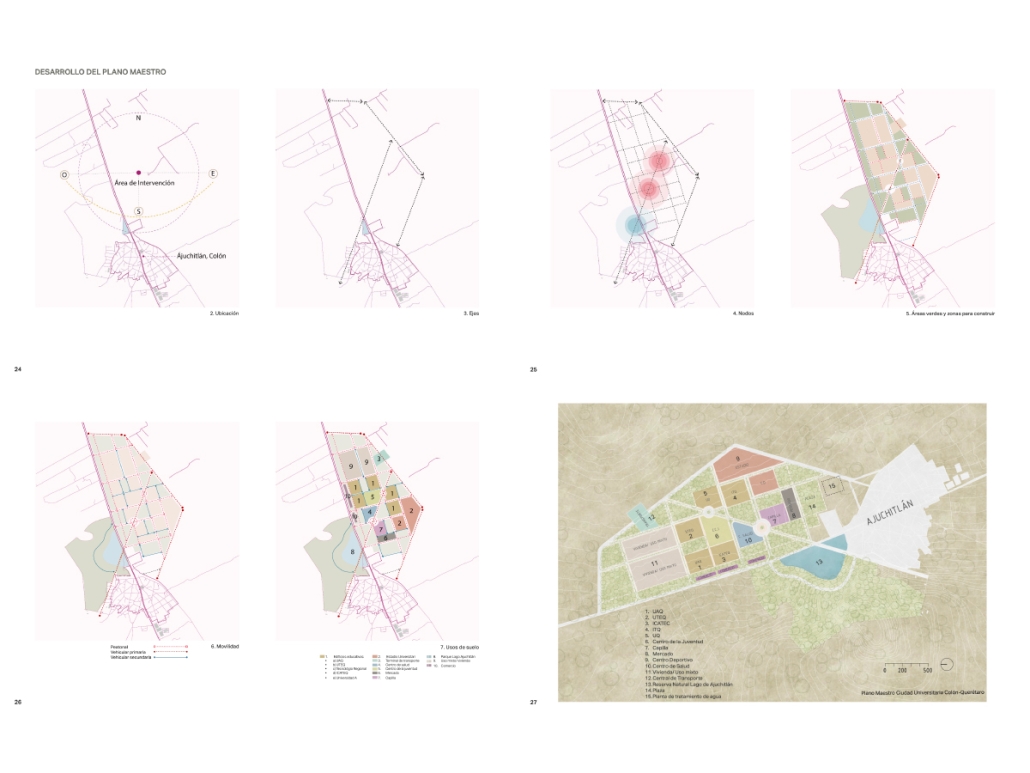
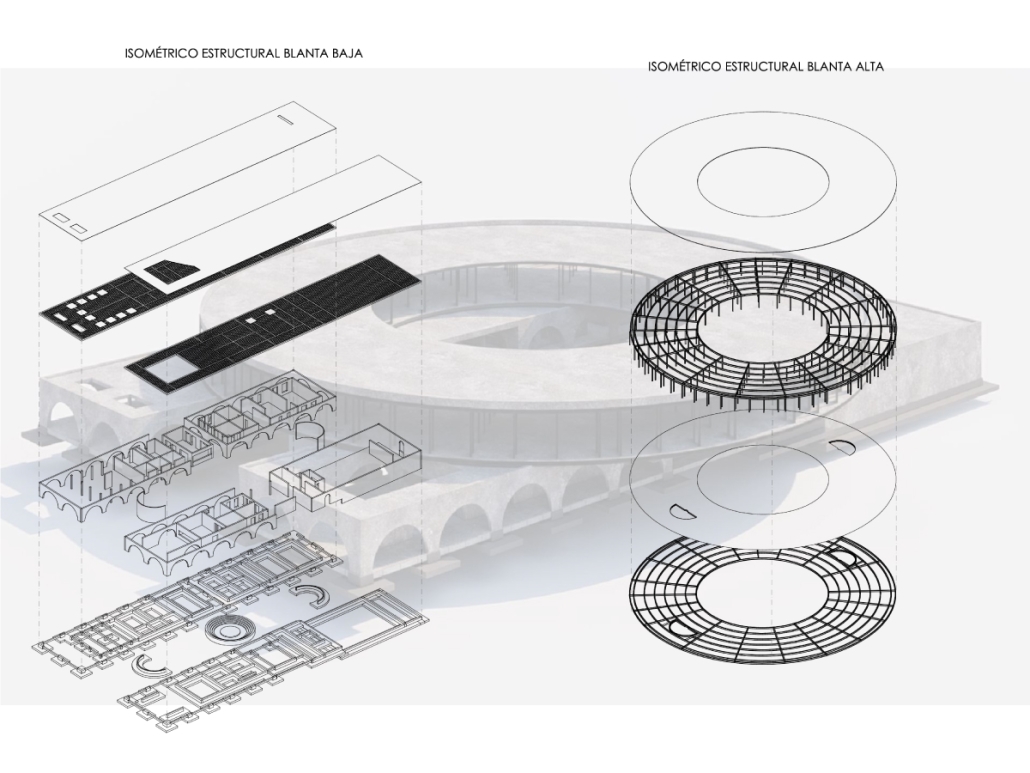
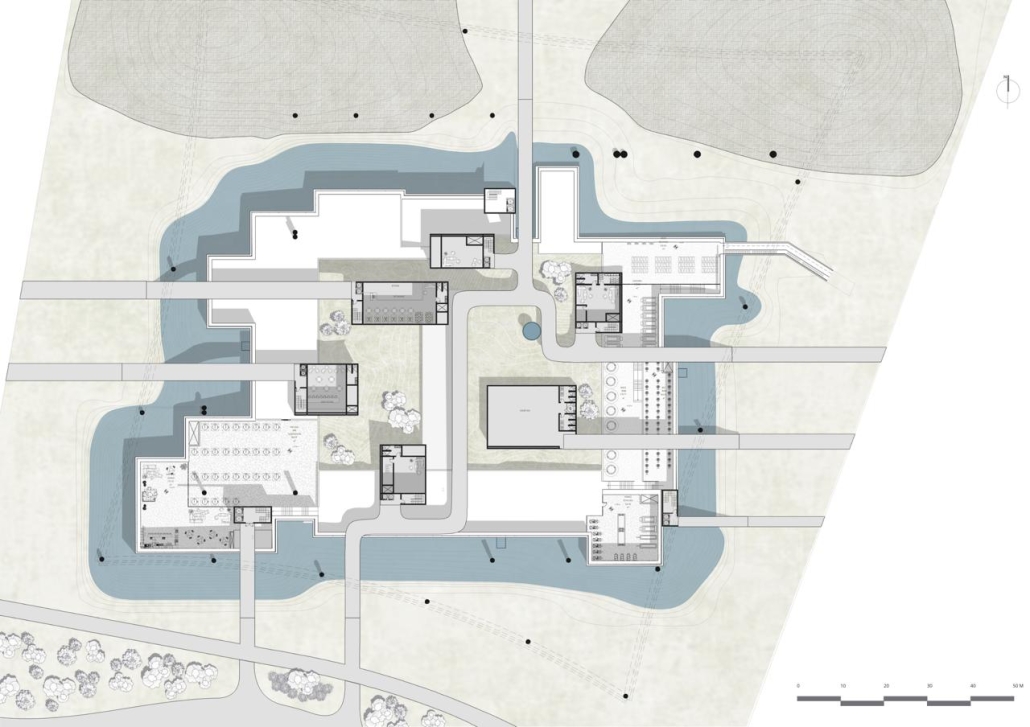
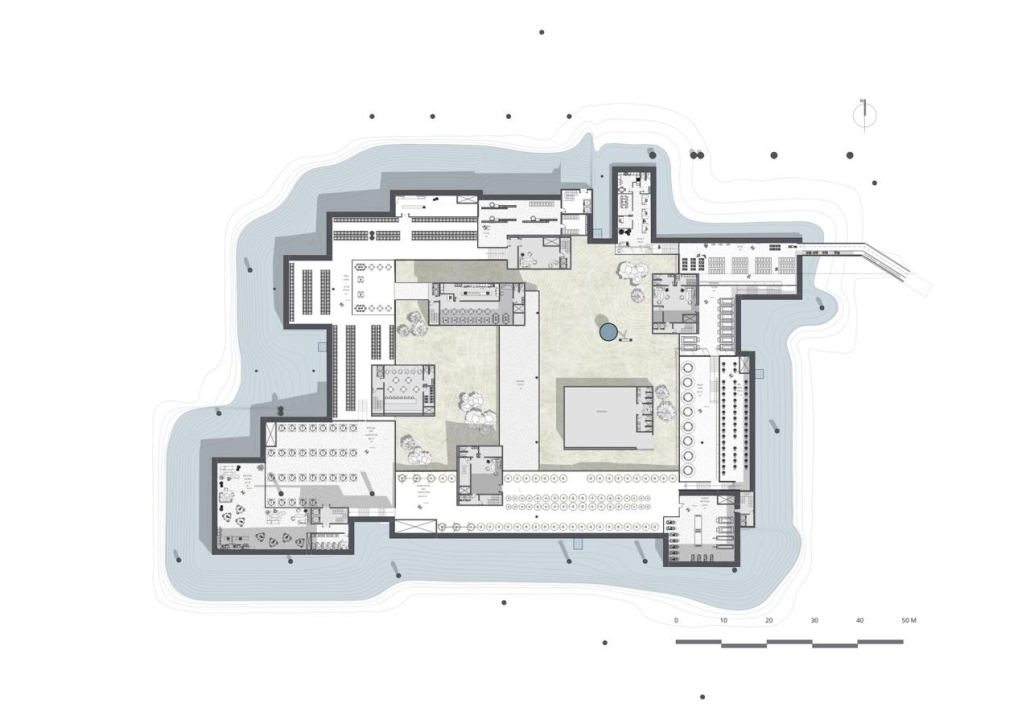
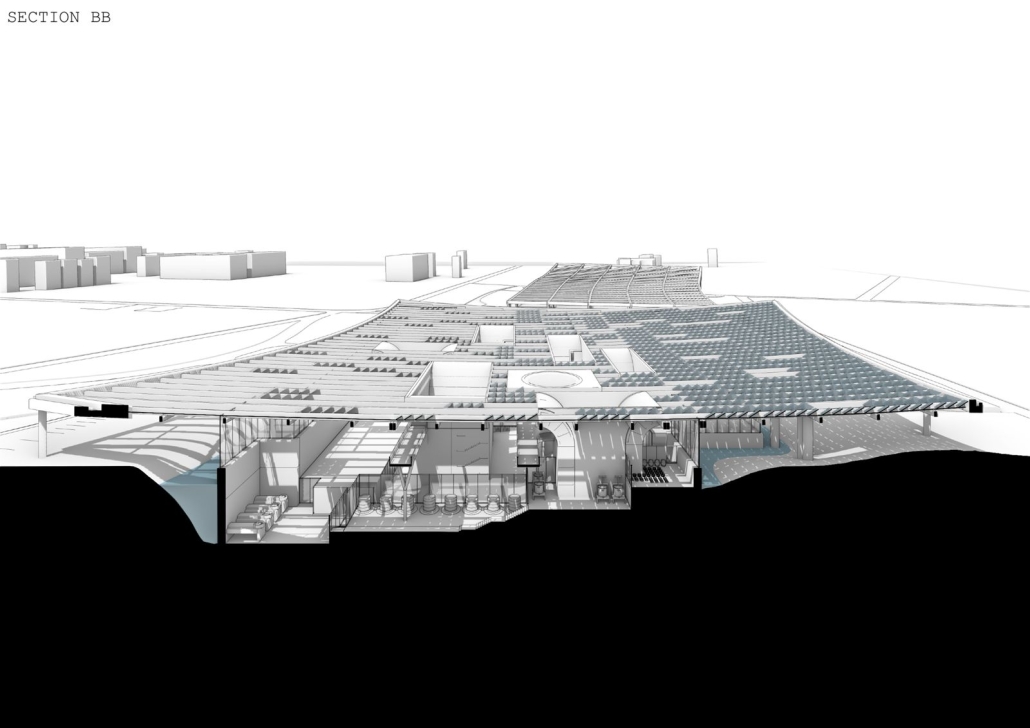
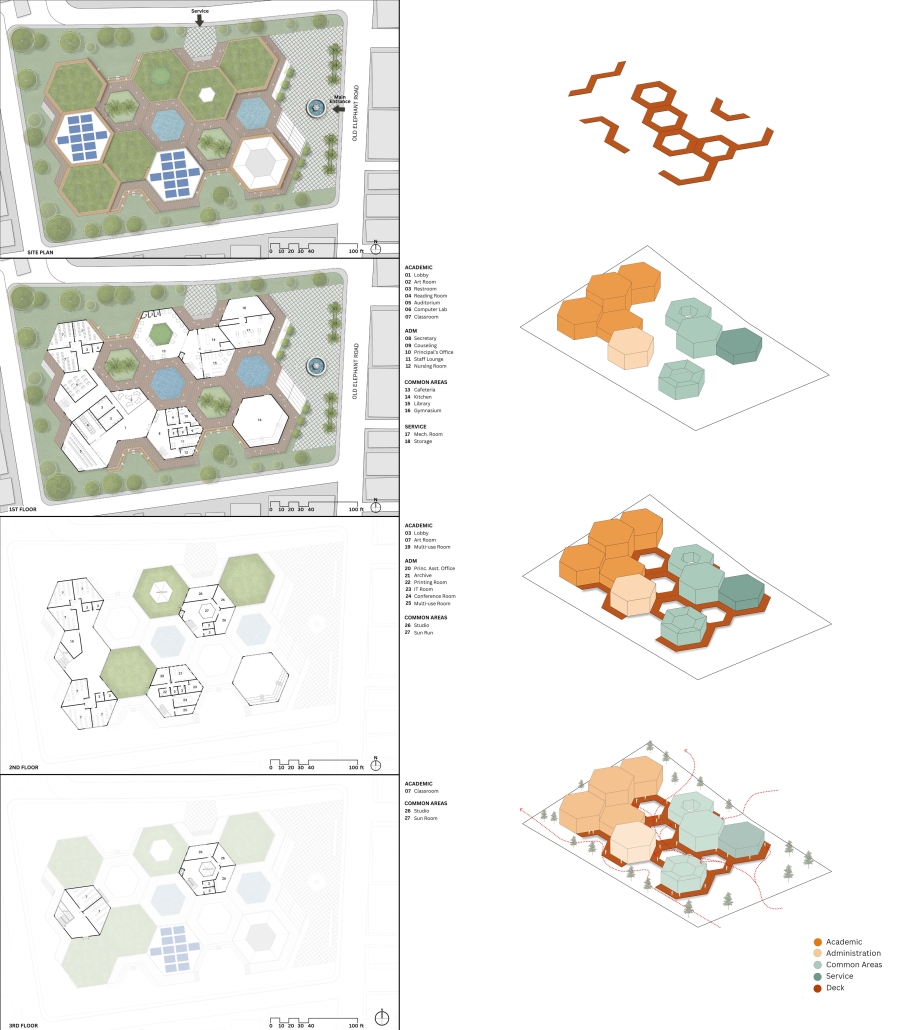
Centro de Salud Universitario by Jesús Gerardo Orduña Hurtado, B. Arch ’24
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Eduardo Herrera & Jorge Javier
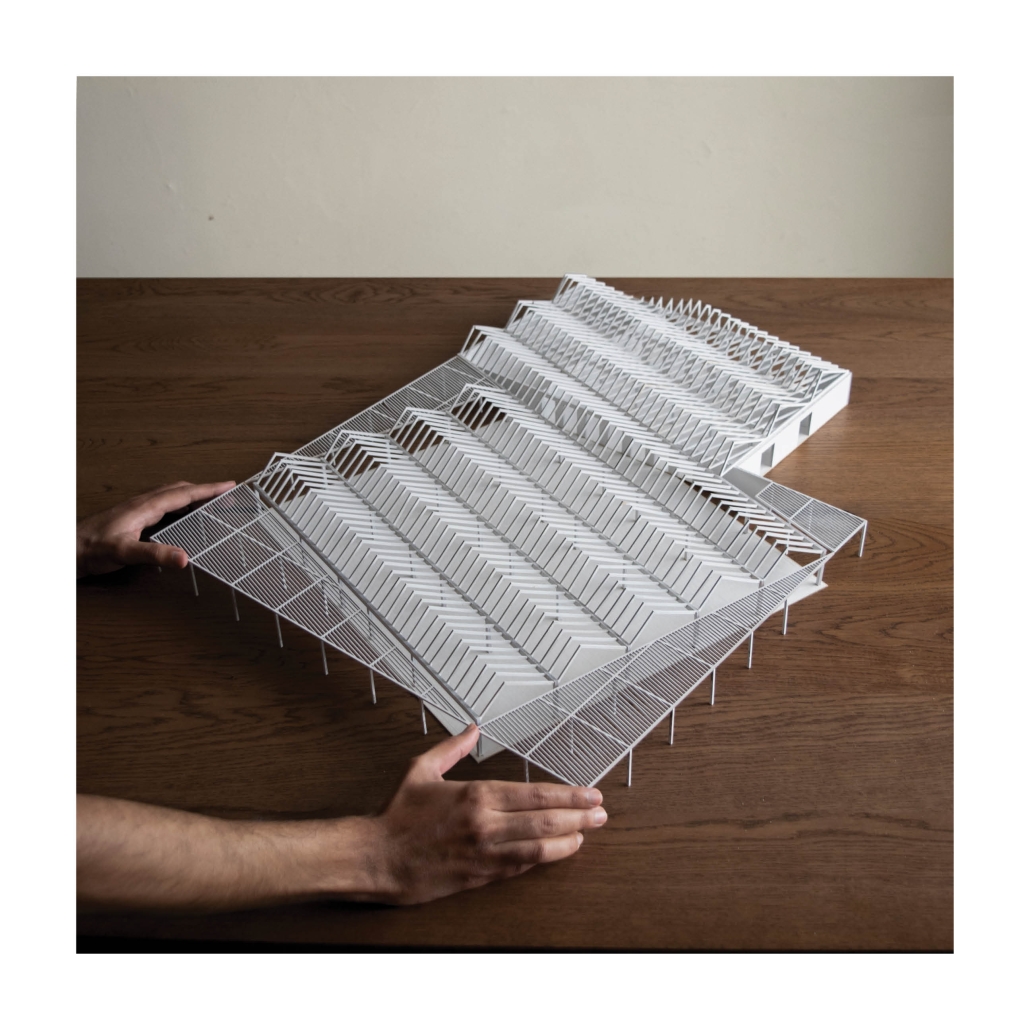
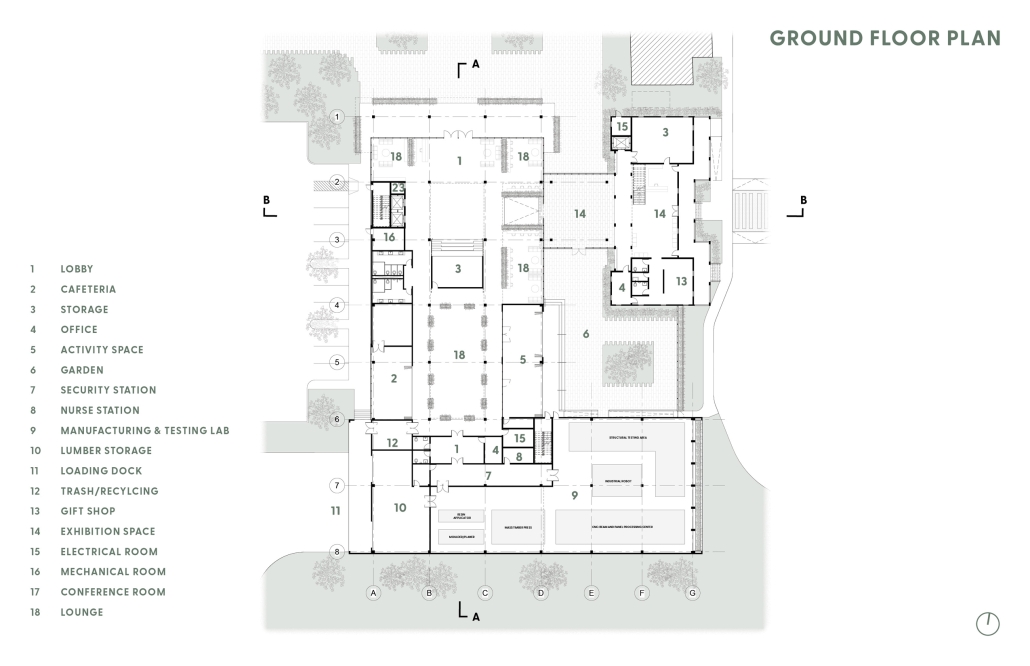
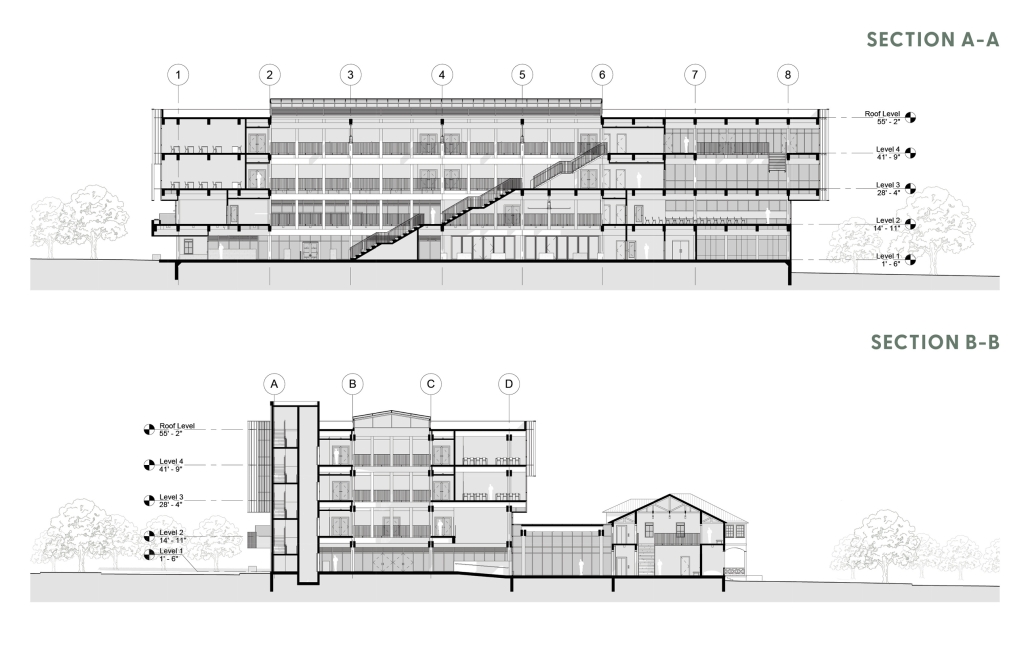
The project for the University Health Centre and the IMSS Family Medical Unit is born through different strategies that allow the land to be used to accommodate the diverse architectural programme. Formally, the building seeks to adapt to the geometry of the site through a grid that helps to modulate the floor plan.
The initial volume is fragmented into five blocks with curved corners and one central space to divide the different areas. The three interior courtyards help to generate voids that allow natural lighting and ventilation of the spaces. They also function as large terraces and open spaces that allow the user a direct connection with the natural landscape. The curved edges of the blocks make the building less aggressive despite its height, generating interesting views on all facades and orientations.
The curved spaces were used to generate four vertical circulation cores. These consist of a double spiral staircase, with the lift hub in the centre. In this way, the stairs become a geometrically attractive and not only functional space.
Instagram: @jgoh_arq, @arqwave, @arquitectura_anahuac
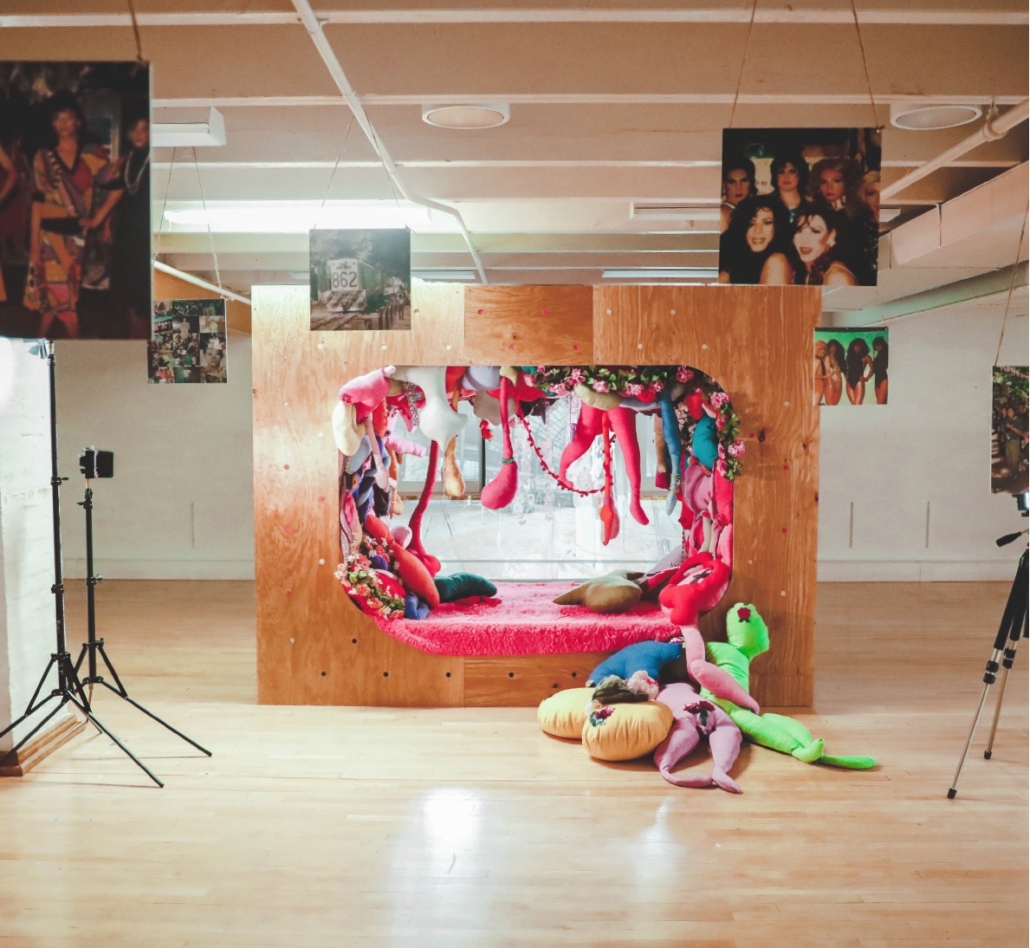
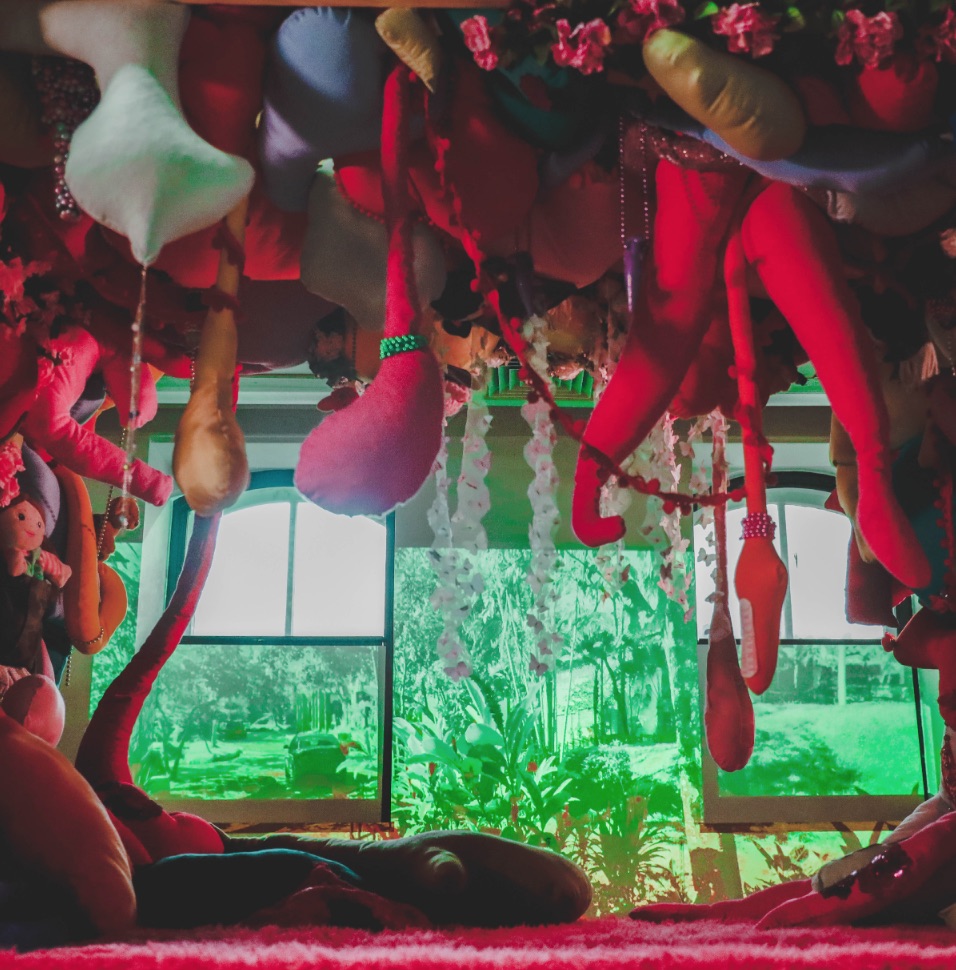
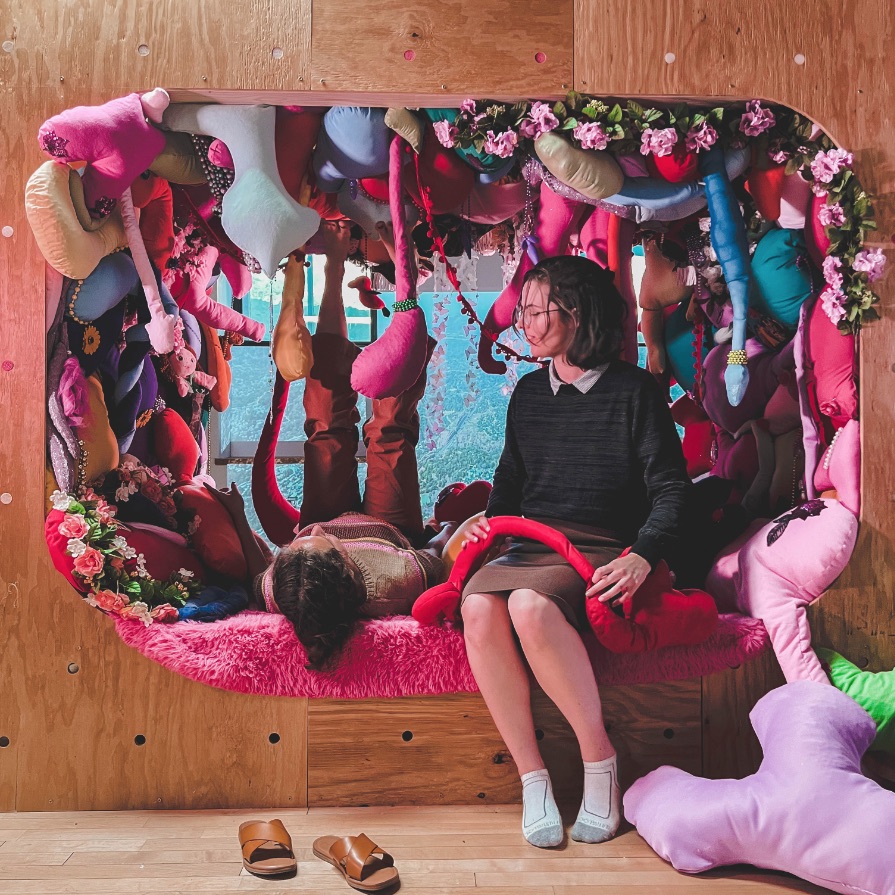
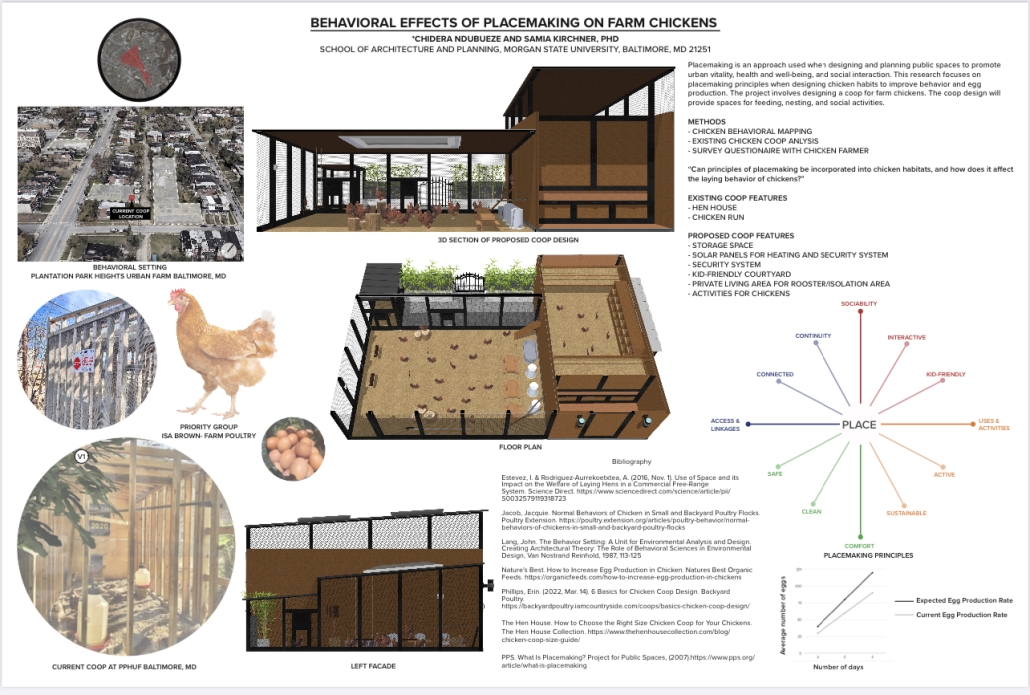
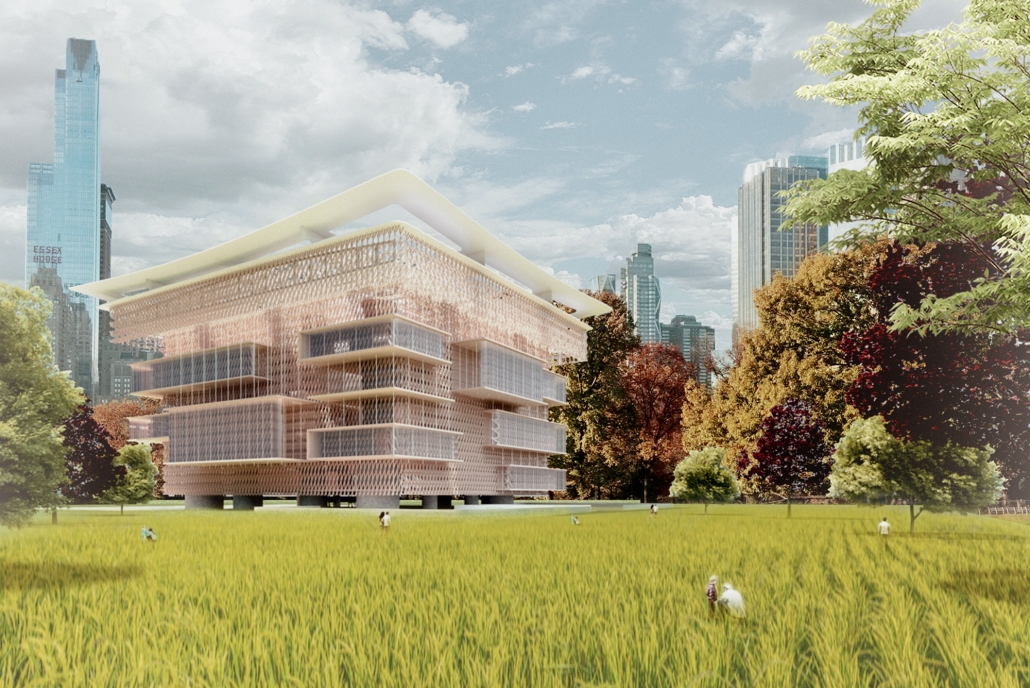
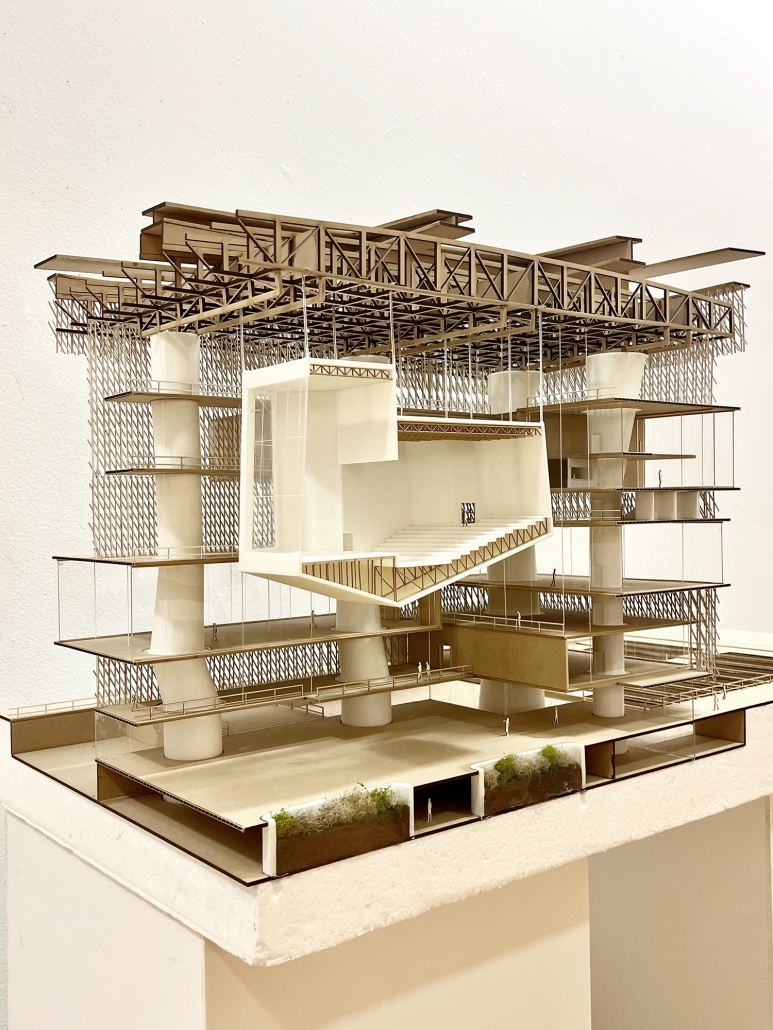
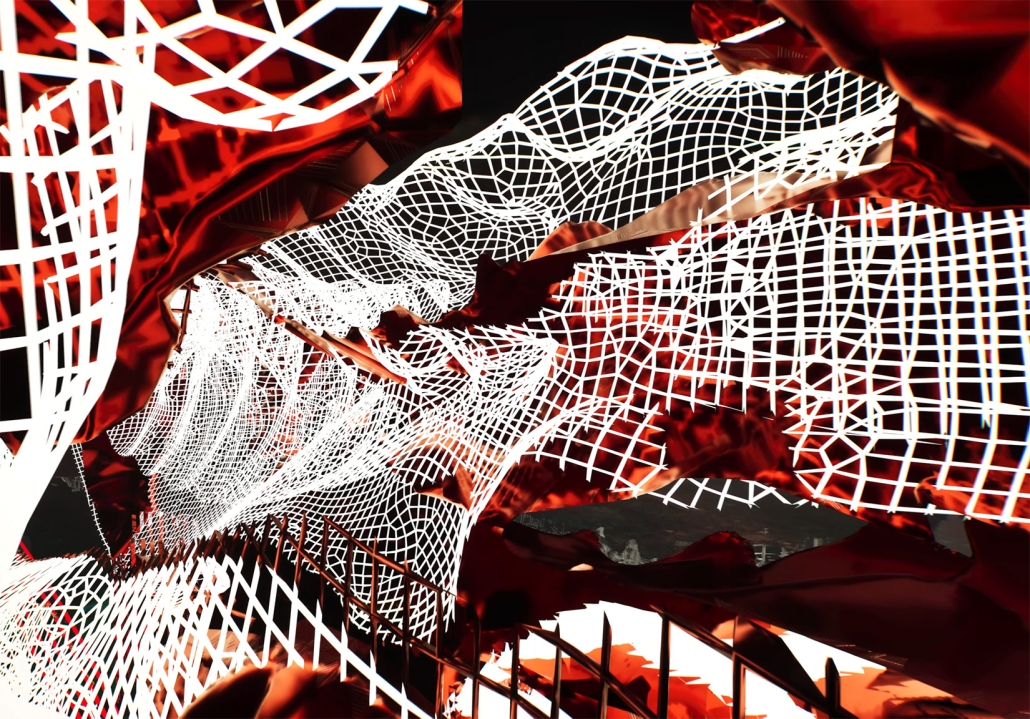
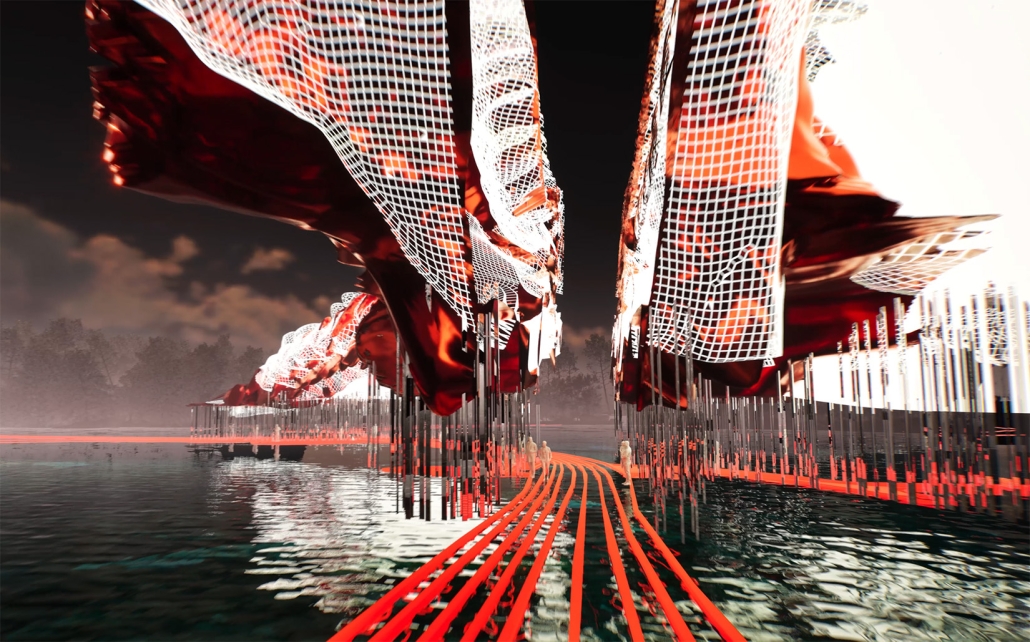
Architectural Decisions, Mental Health Outcomes by Naeemah Merchant, M. Arch ’24
Morgan State University | Advisor: Coleman A. Jordan
Introduction:
The Mental Maze Museum project investigates how space design influences psychological well-being. Rooted in the premise that spaces can significantly affect a person’s psychology, this project aims to demonstrate that intentional design can enhance mental health outcomes. The central research question is: What is psychology’s role in placemaking, and how can it improve mental health?
Research Objectives:
This project will explore how different sensory experiences within a space impact psychological states and contribute to mental well-being. The Mental Maze Museum will act as a live laboratory, focusing on the effects of touch, smell, sound, and sight on the brain’s perception of space and resulting emotional experiences.
Methodology:
Touch: The museum will feature various textures, weights, densities, and temperatures to study the impact of physical sensations on room perception and psychological state.
Smell: By incorporating distinct scents, the project will examine how olfactory stimuli capture and evoke memories, influencing emotional experiences.
Sound: Different acoustic properties will be used to explore how sound creates a three-dimensional atmosphere and its impact on mental health.
Sight: Visual stimuli will be employed to create new experiences, balancing the sense of freedom provided by open spaces with their potential to become overwhelming due to noise.
Expected Outcomes:
The Mental Maze Museum aims to provide insights into how intentional design can improve mental health. By understanding the brain’s analysis of space through sensory experiences, the project will offer evidence-based guidelines for creating therapeutic environments. These findings can inform architecture, urban planning, and mental health care, fostering spaces that promote psychological well-being.
Conclusion:
The project emphasizes the significant impact of space design on mental health. By exploring the relationship between psychology and placemaking, the Mental Maze Museum will contribute to the development of environments that support and enhance mental well-being.
This project received the Best Thesis Project for 2024 award.
Instagram: @studiocaje
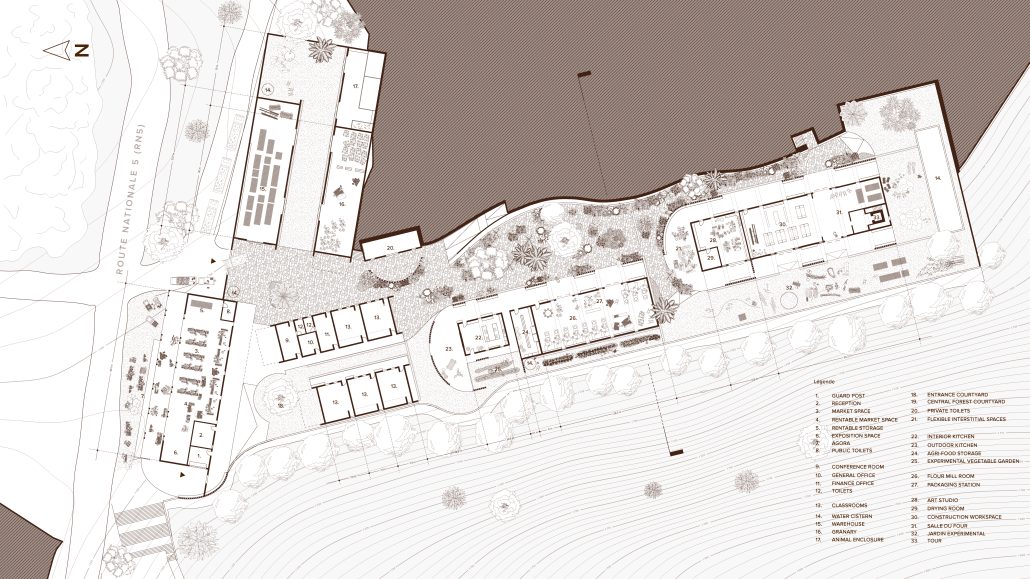
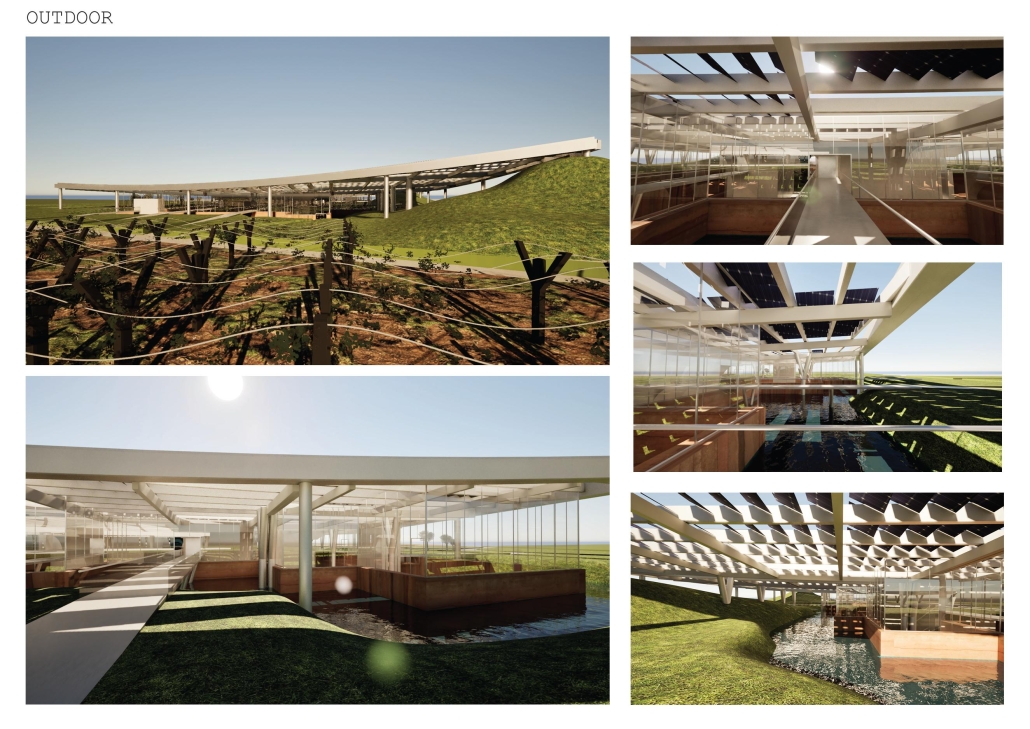
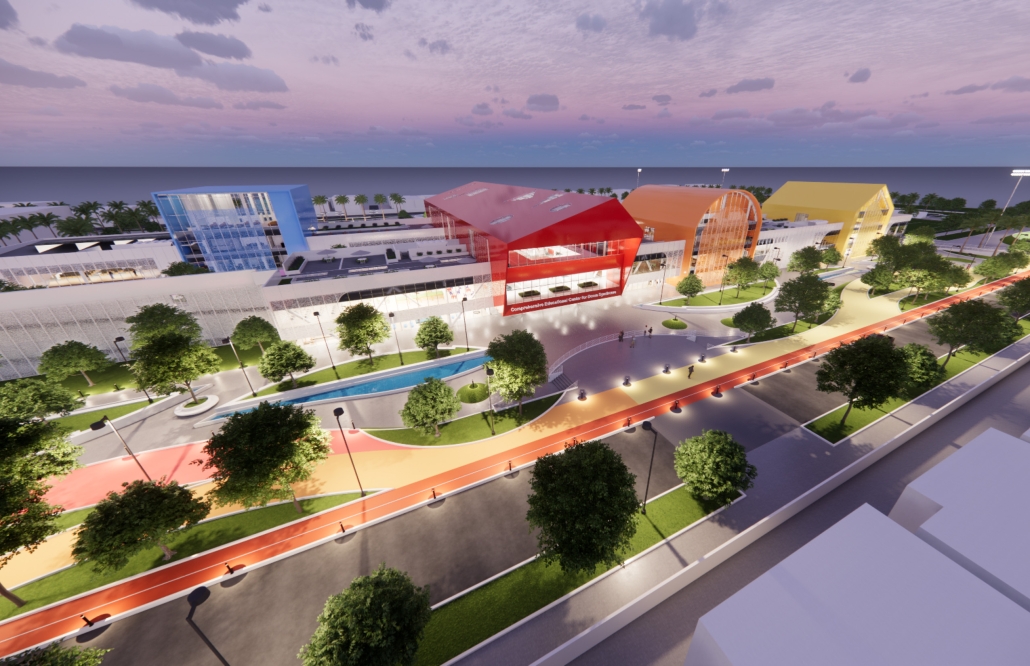
Nueva Reforma – Healthcare Design in Latin America by Madelene Dailey, M. Arch ’24
University of Southern California | Advisor: Andy Ku
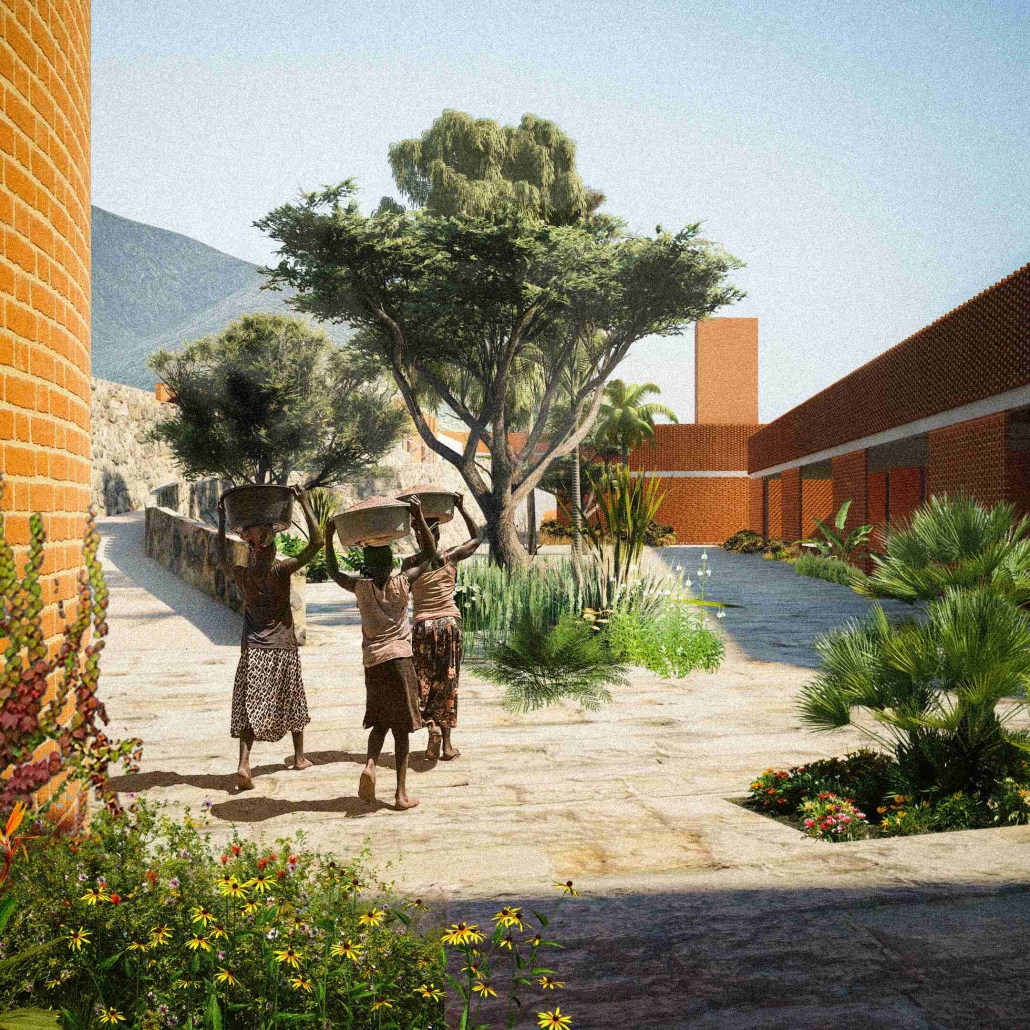
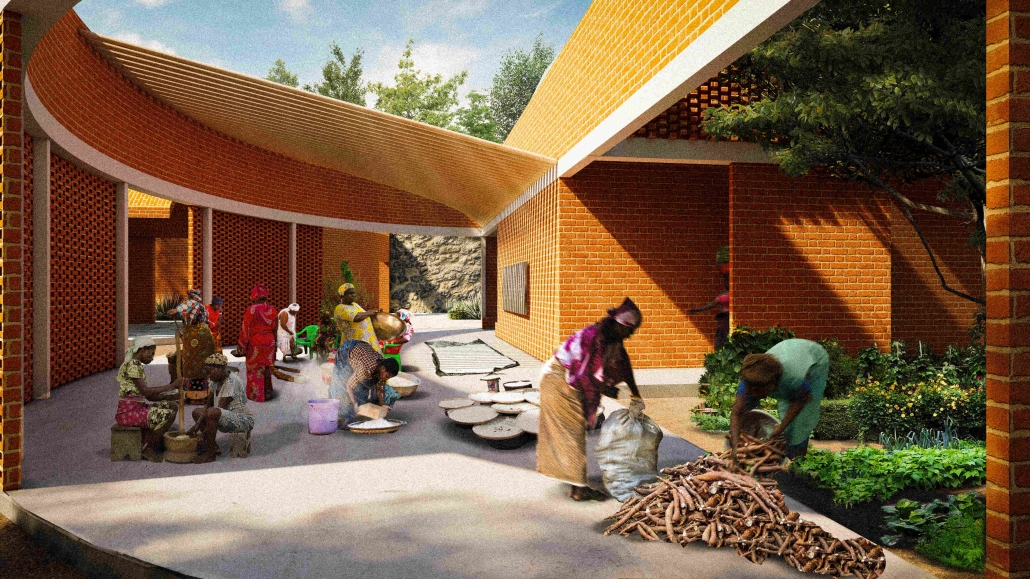
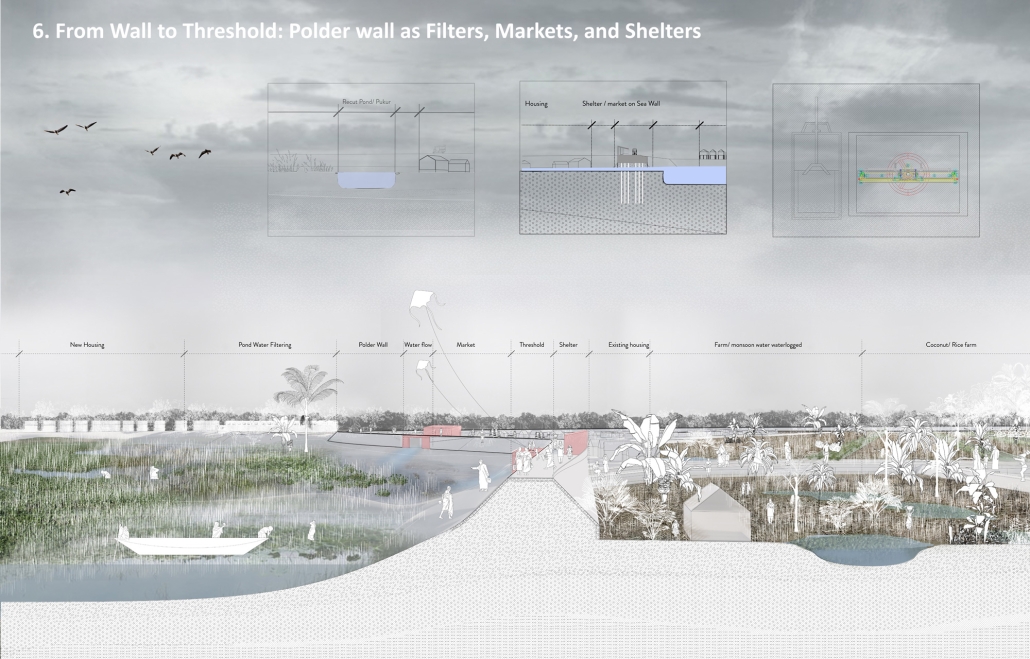
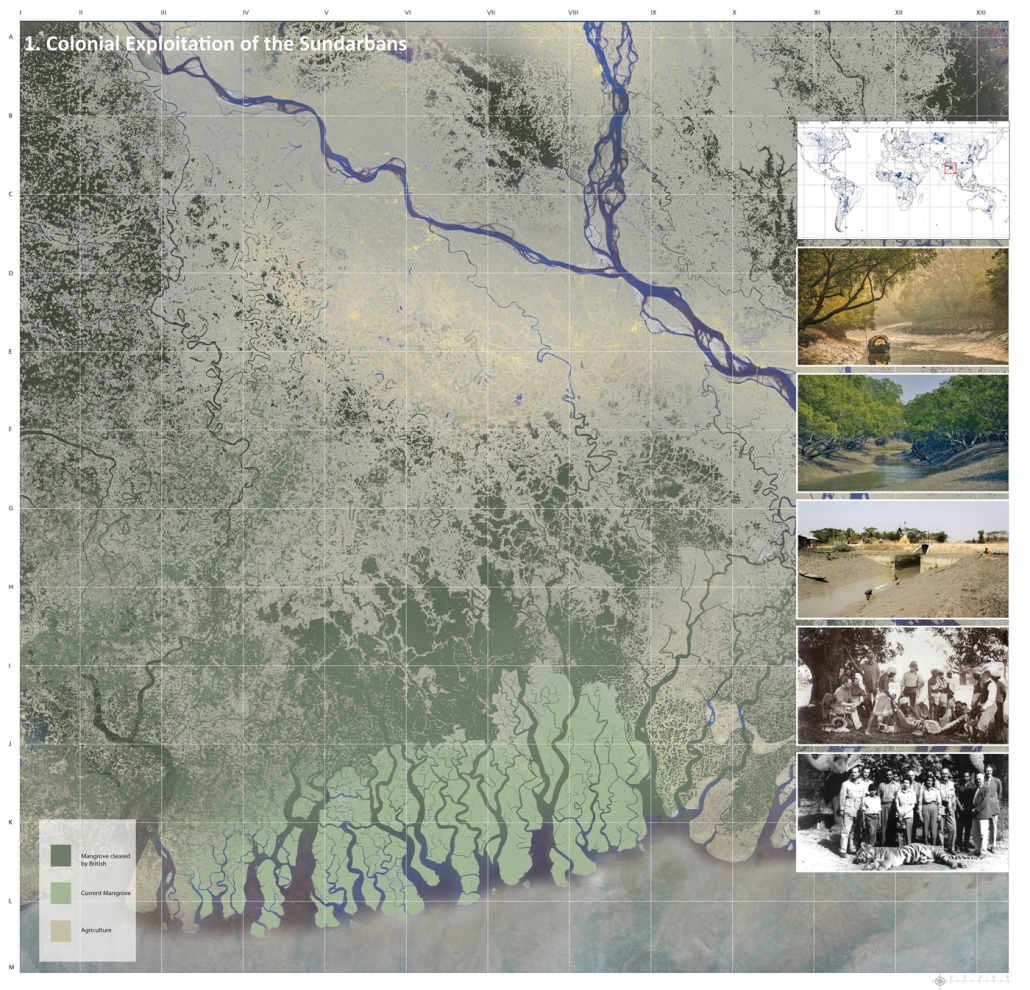
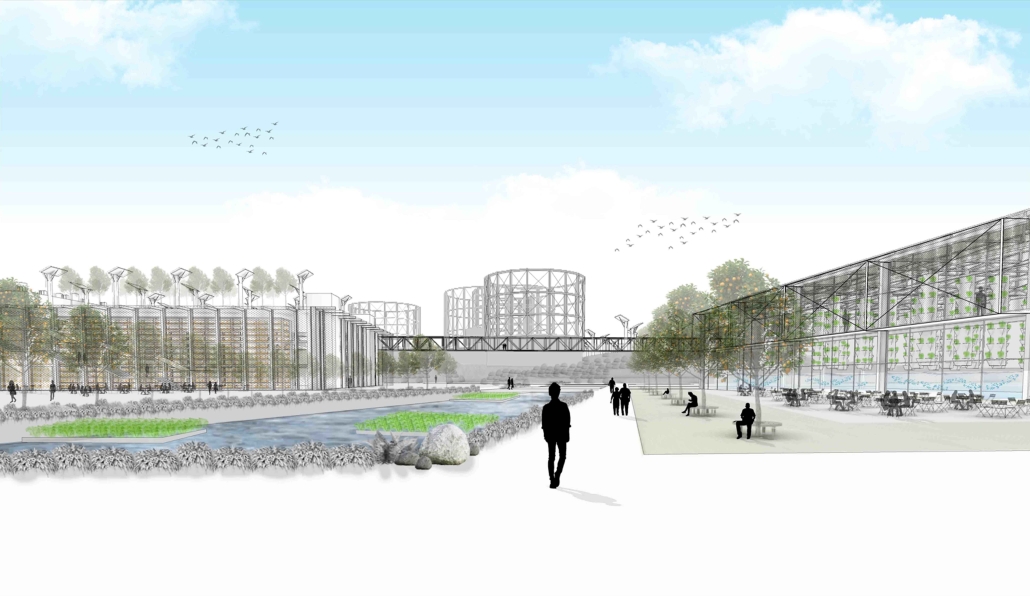
Widespread displacement and the inadequate distribution of resources caused by civil wars, social strife, and climate change are ongoing threats to the livelihoods of Latin America’s most vulnerable communities. The expansion of urban centers in Latin America has placed socioeconomic pressures on rural residents, forcing them to seek new resources and opportunities outside their native regions. As one of the most populous urban centers in Latin America, Guatemala also has one of the highest emigration rates in the region. The World Bank Group identified that U.S.-Guatemalan migrants have nearly tripled in the last two decades largely due to emigration from rural areas.
Roughly half of the country’s population lives in poverty and requires humanitarian aid, with numbers projected to increase by the end of 2024. Humanitarian efforts and research in response to this crisis are underway, but funding is limited, and aid is often unable to reach the areas that need it most. However, grassroots rural civic planning initiatives are facilitating opportunities that recenter investment in their communities. Merging culturally thoughtful practices with community-driven interdisciplinary approaches to sustainable rural planning, this project aims to investigate how architecture can be leveraged as a tool to support inclusive rural development frameworks that allow impacted communities to self-navigate crisis response efforts and achieve long-term stability through public healthcare design.
This project received the following awards and recognition:
2023 USC Gusendheit Fellowship Award
2024 USC Research Symposium – 1st place
2024 Distinction in Directed Design Research, USC School of Architecture
2024 Alpha Rho Chi Award, USC School of Architecture
2024 Award for Selected Professions Research, American Association of University Women
Instagram: @maddeedailey, @uscarchitecture
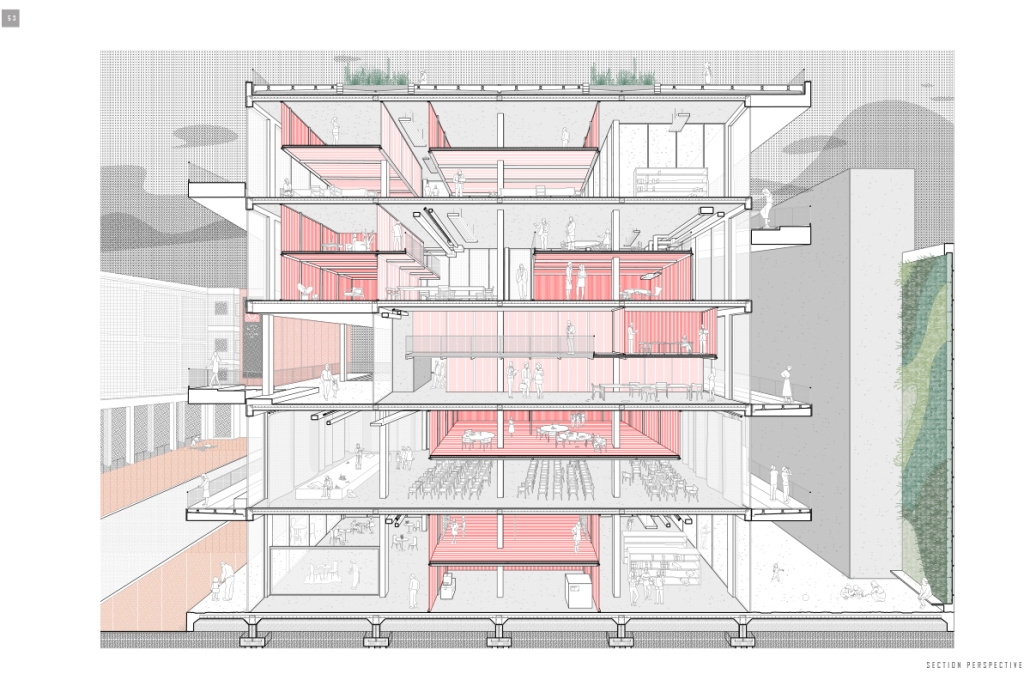
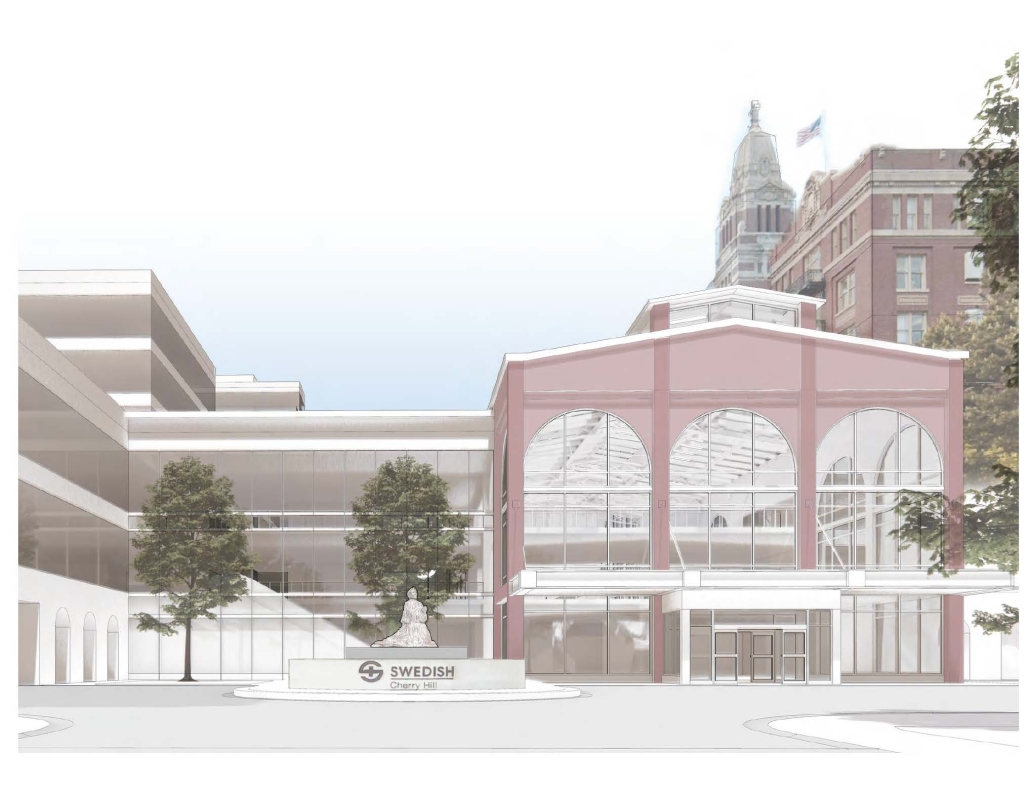
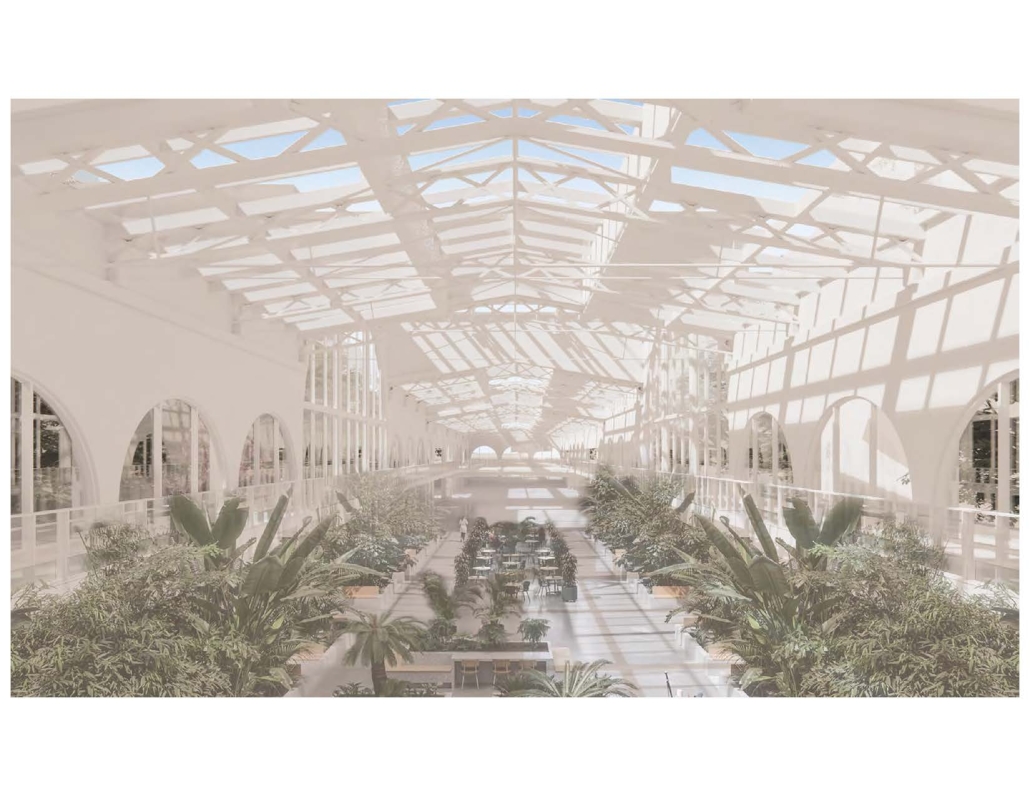
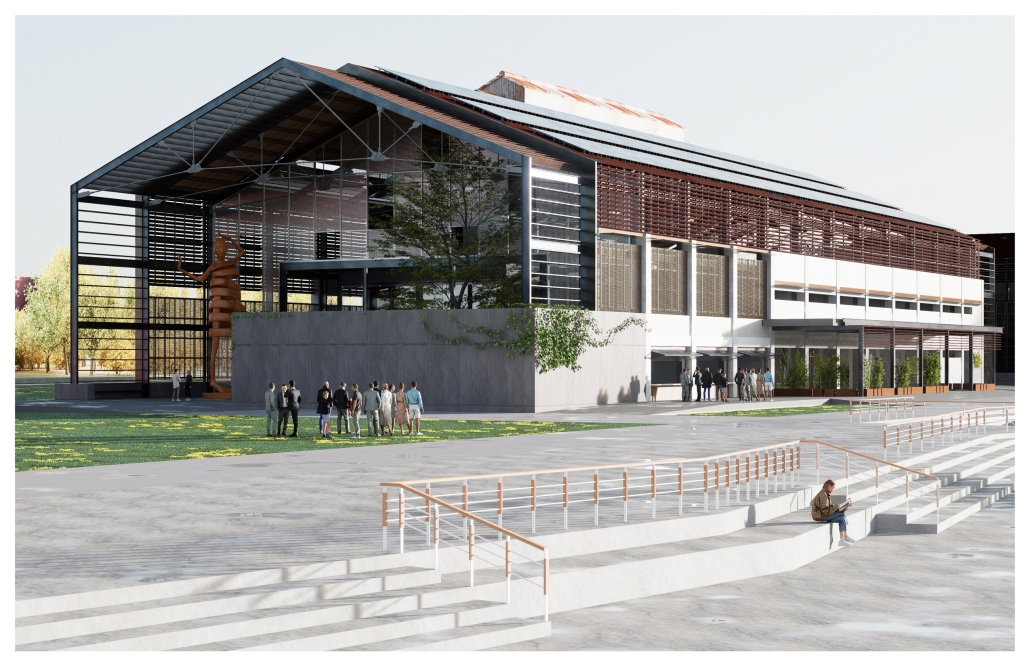
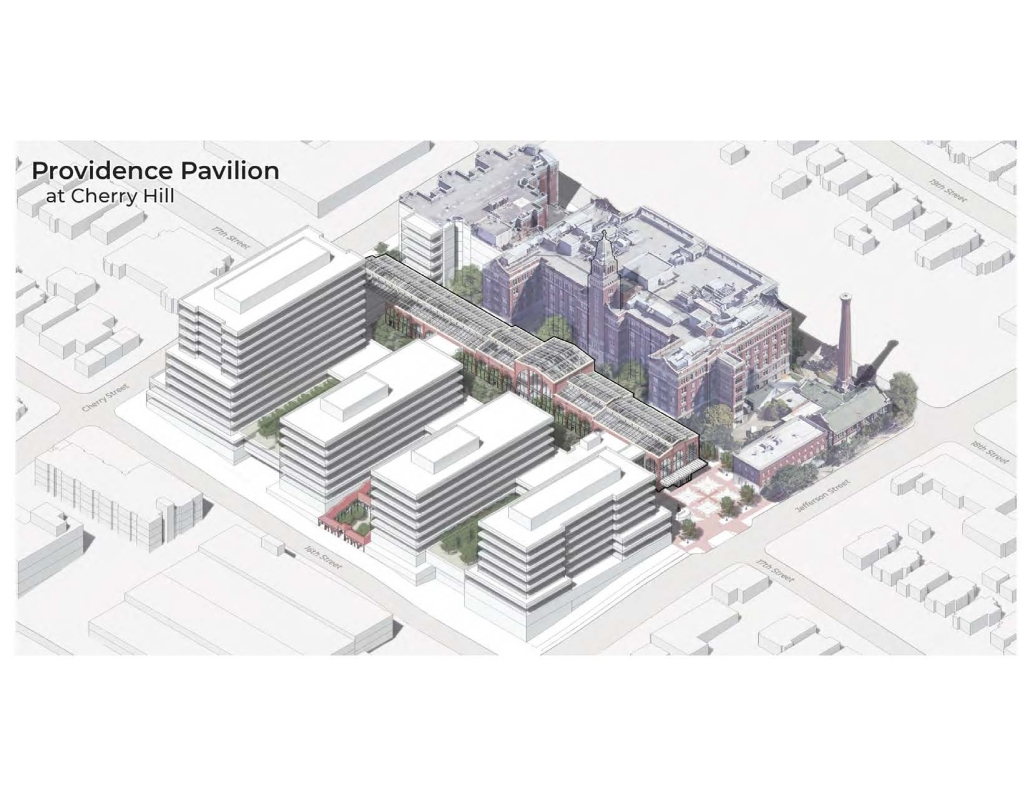
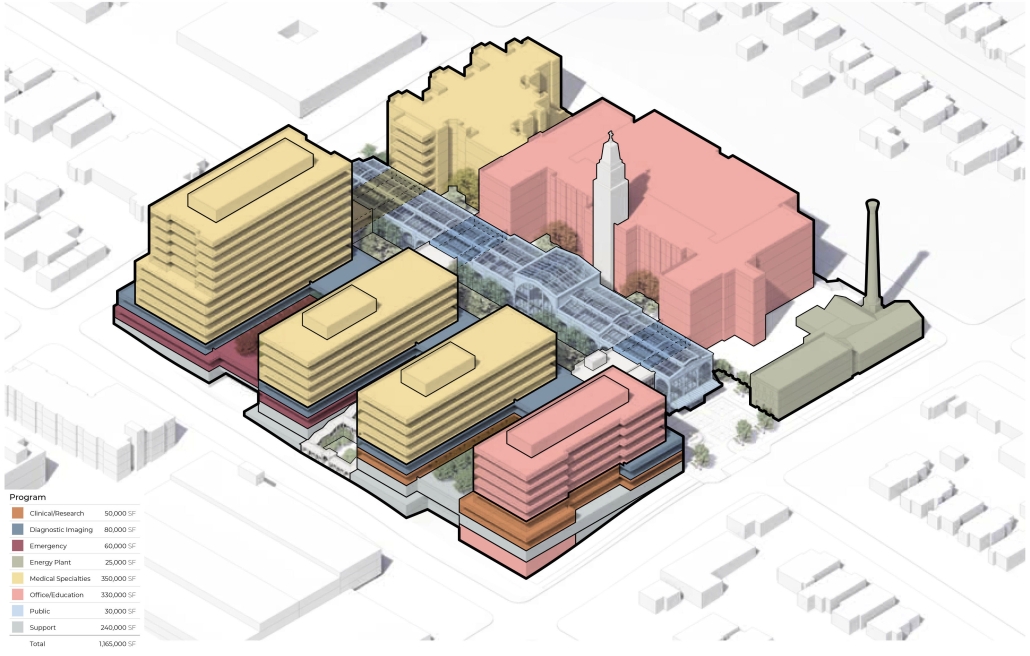
Seattle Health District: Providence Pavilion at Cherry Hill by John Edward Carlisle, M. Arch ’24
University of Miami | Advisors: Joanna Lombard, Veruska Vasconez & Elizabeth Plater-Zyberk
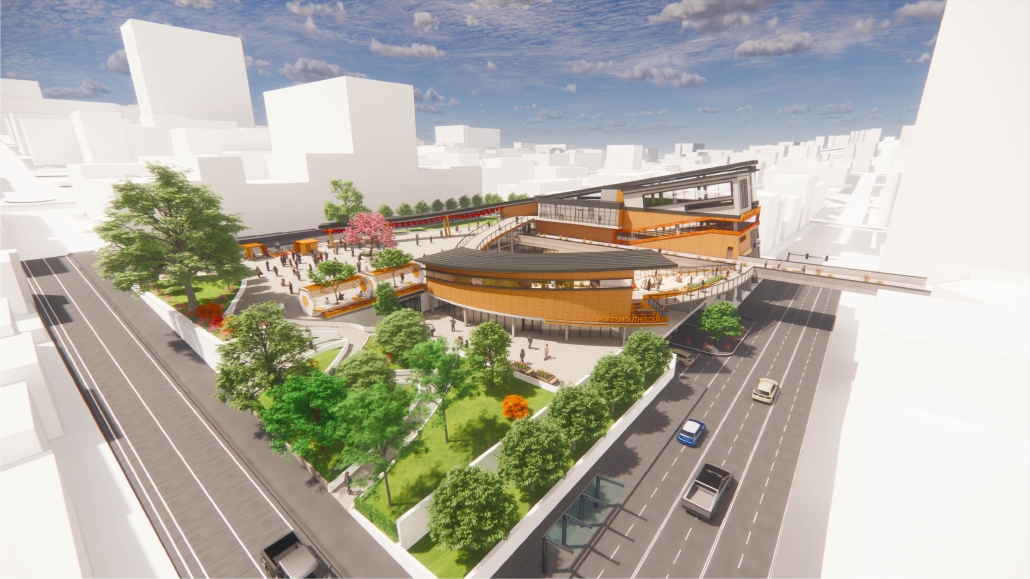
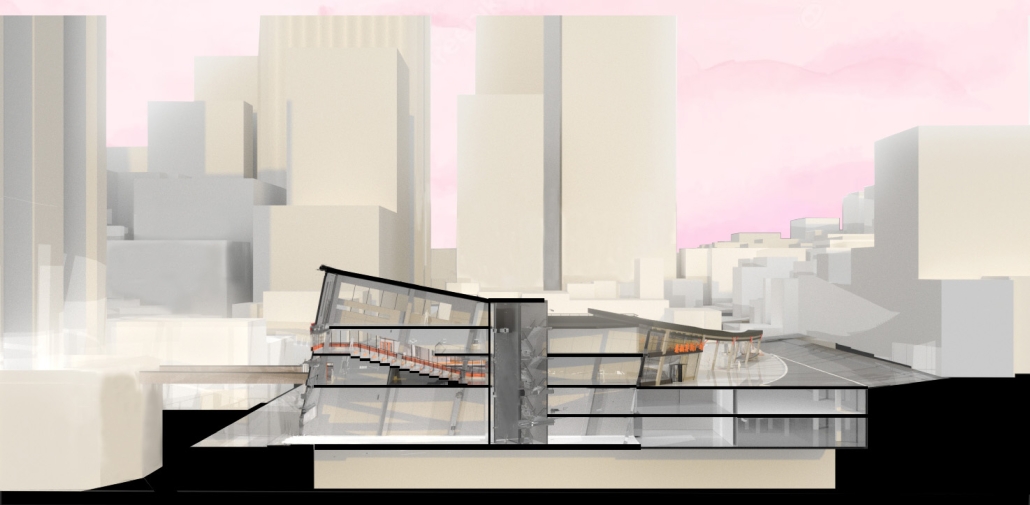
The role of Providence-Swedish in the First Hill and Cherry Hill neighborhoods represents a unique history as well as distinctive architectural, urban, and social characteristics. As the hospitals and academic institutions in these neighborhoods implement change, the present condition is poised between the past and the future. This offers a timely opportunity to imagine how each institution might draw on its own identity and aspirations to contribute to healthy urbanism as well as coalesce into a vibrant health district.
Each team explored the historic and current conditions of the neighborhoods as well as the Major Institution Master Plans (MIMP) approved by the City of Seattle for the academic and healthcare institutions within a ½ mile radius of one another. Each group then defined its primary objectives and developed a proposal for a Seattle Health District Masterplan that would provide key elements for neighborhood health and wellness—mixed use, connectivity, and greenness—and express both unique institutional and neighborhood character as well as distinctive identity as a Seattle destination Health District.
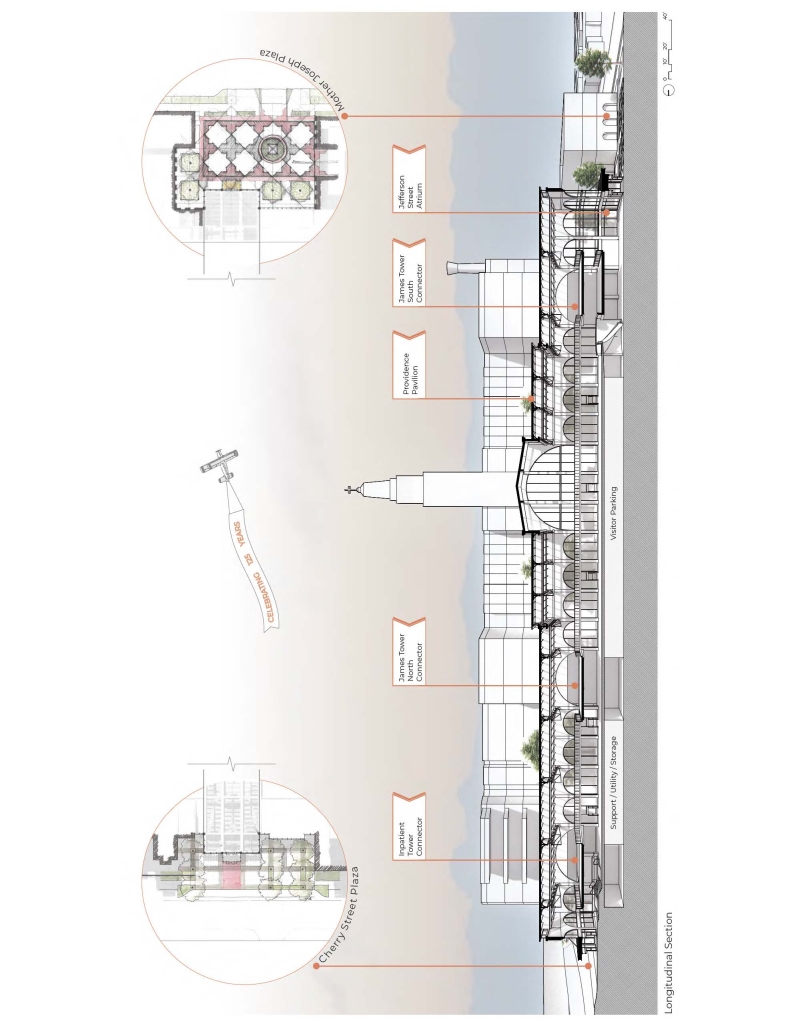
Each team member then developed a proposal for a project within their master plan. Carlisle’s proposal for the Providence Pavilion at Cherry Hill seeks to reestablish the prominence of the historic Providence Hospital (1911) through a new campus plan and to provide an imageable Health District destination through the addition of a new central gallery that supports a series of Medical Specialty Pavilions, gardens and plazas.
This project won the Urban Design Studio Award, Spring 2024
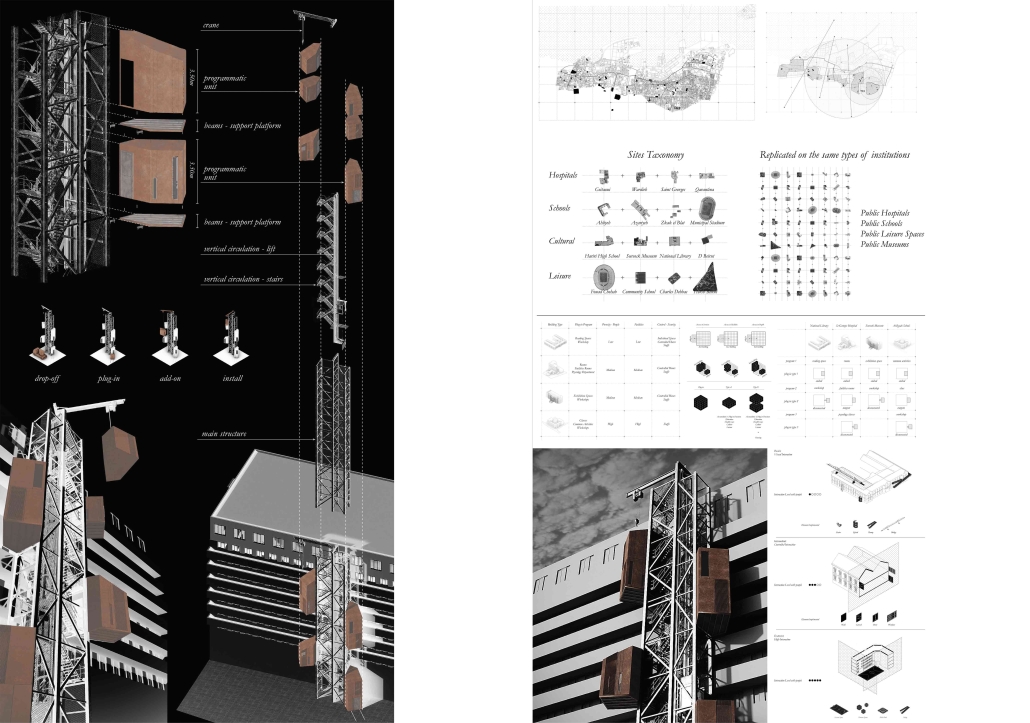
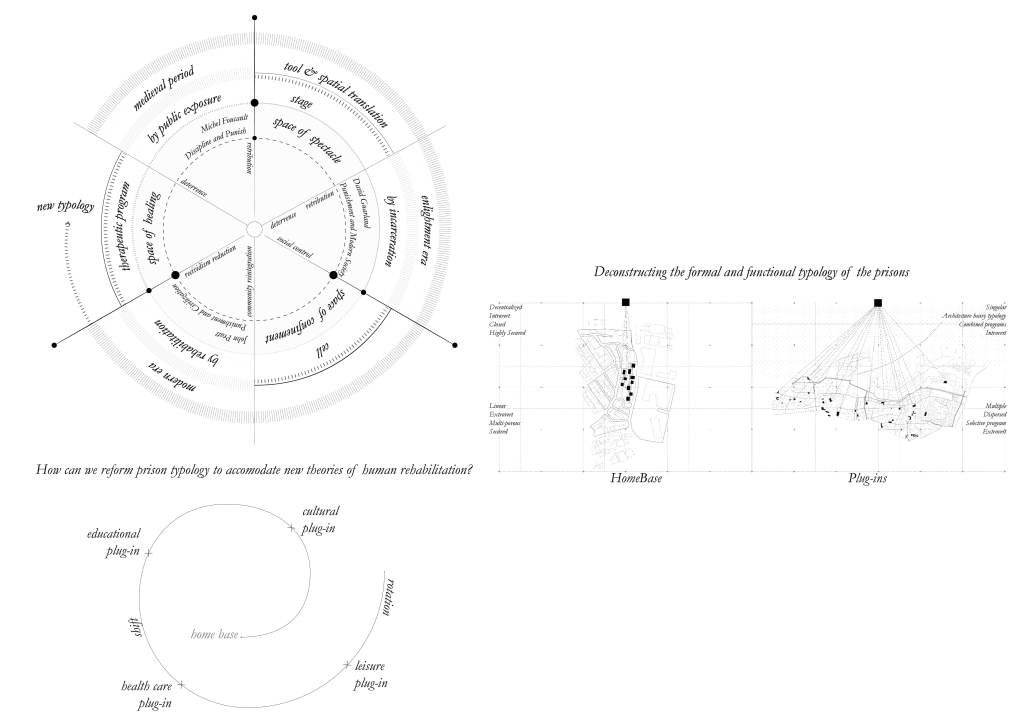
Adaptive PlugScapes: Rethinking Prisons as a Reformative Journey by Yasmine Tabet, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Dr. Howayda Al-Harithy
The evolution of punishment typologies from ancient civilizations to modern times has
seen a profound shift in ideologies and spatial translations. Historically, punishments were often embodied in public spectacles, with tools like the guillotine and the rack transforming public spaces into stages for retribution and deterrence. However, contemporary corrections systems have moved towards incarceration and rehabilitation, aiming to reform offenders.
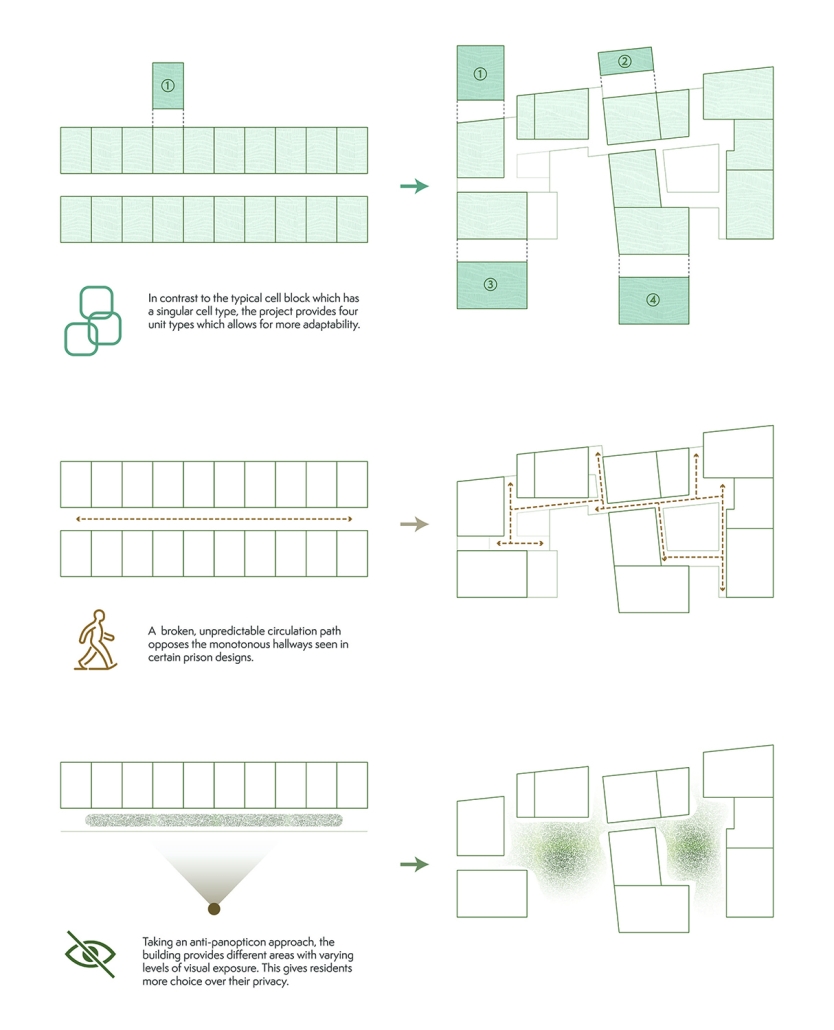
This thesis proposal delves into this historical trajectory, examining how spatial elements were designed to reinforce punitive ideologies. It highlights the persistence of existing typologies, though with some improvements, and underscores the need to transcend these traditional models.
To create a new typology aligned with contemporary theories of rehabilitation, the study draws inspiration from innovative design explorations. Case studies and emerging scientific trends, such as the Risk-Needs-Responsivity model and restorative justice, were used to conduct the study. By synthesizing these precedents and integrating emerging scientific trends, this proposal aims to forge a novel typology that reimagines the spatial dimensions of punishment. It envisions a future where architecture is harnessed as a tool for effective rehabilitation, fostering a more humane and socially beneficial corrections system.
This project was nominated for the Areen Projects Award for Excellence in Architecture
Instagram: @ard_aub
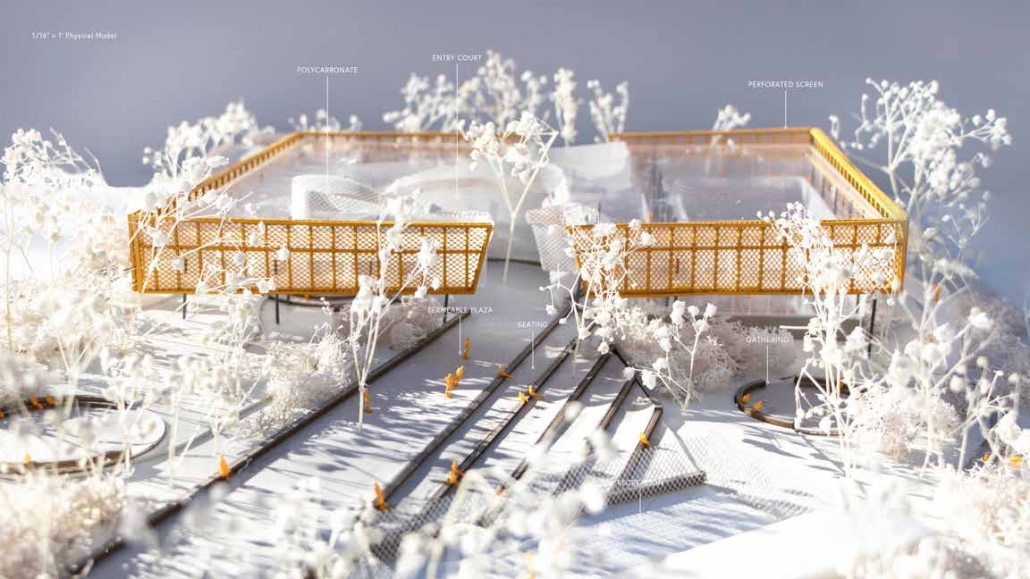
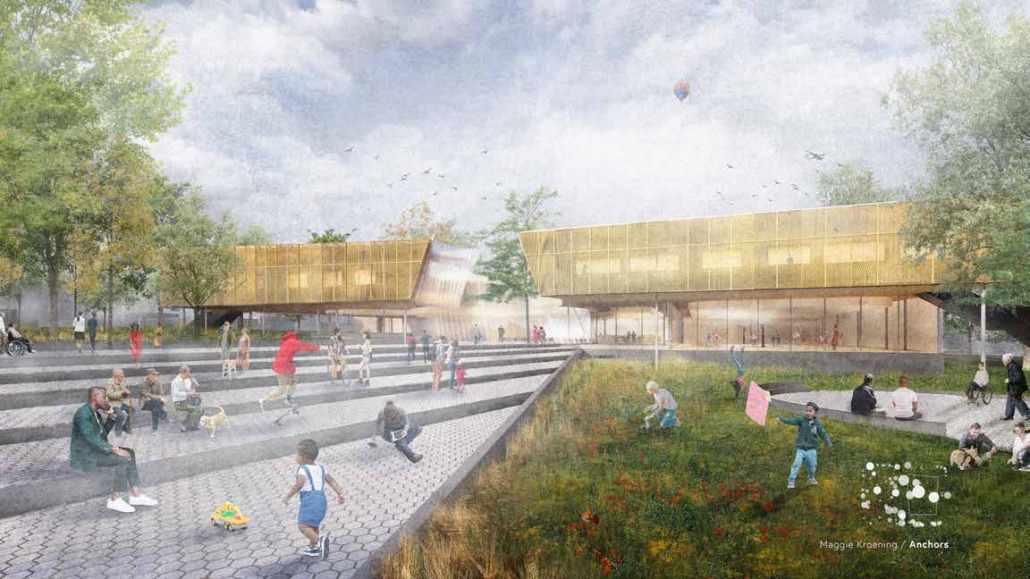
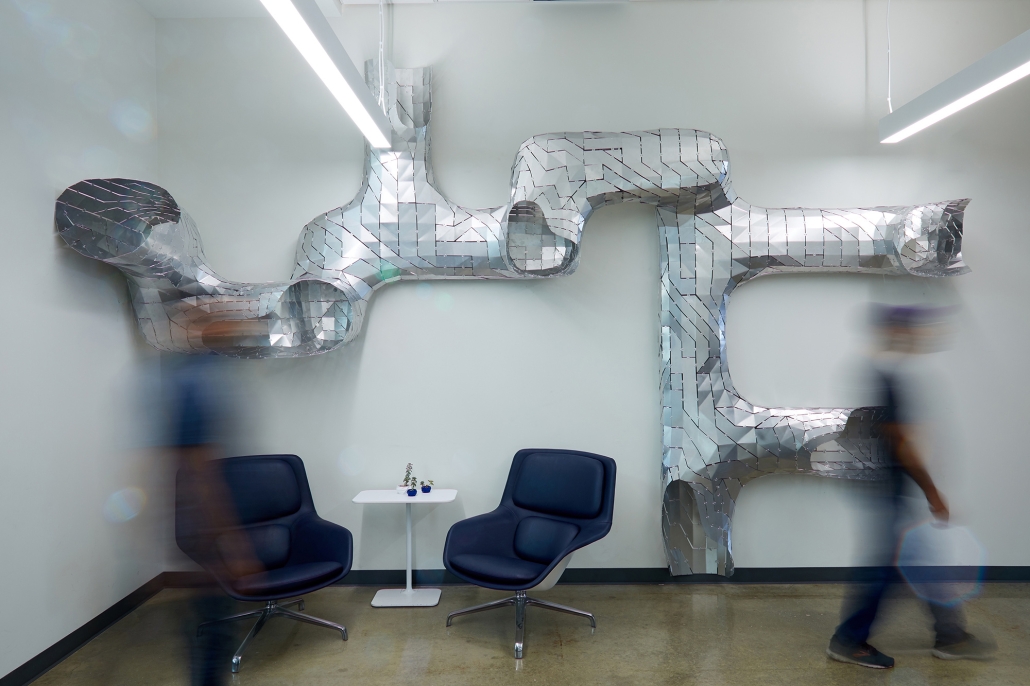
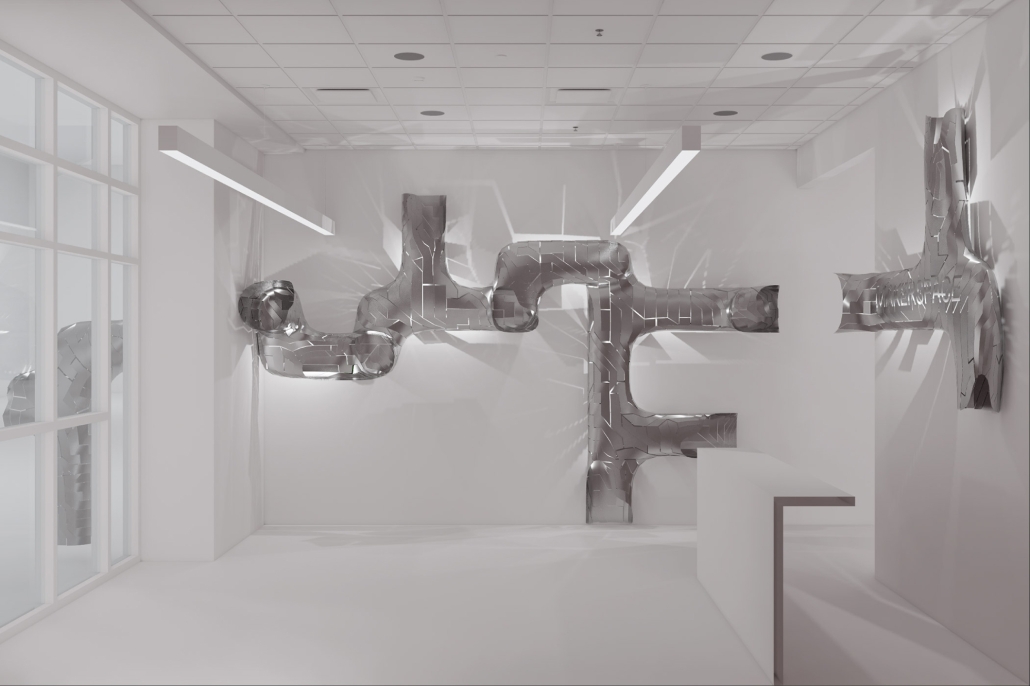
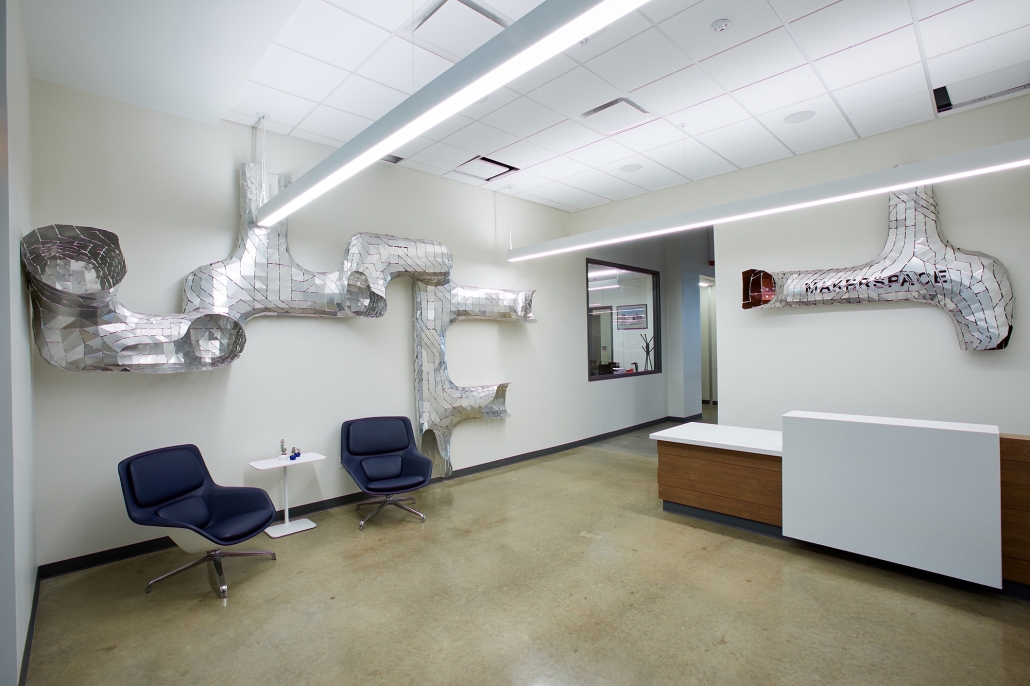
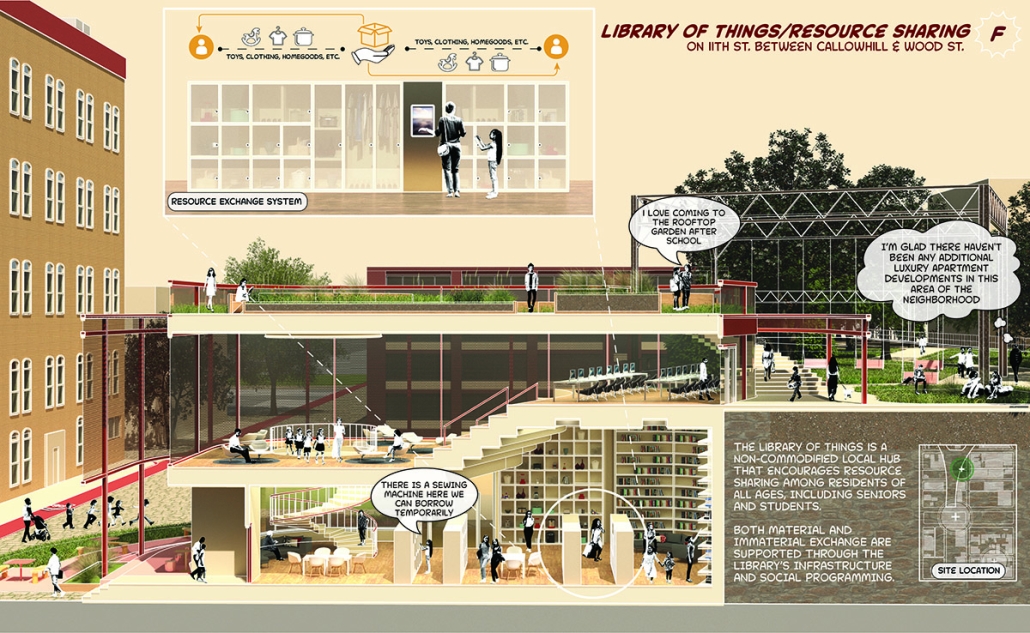
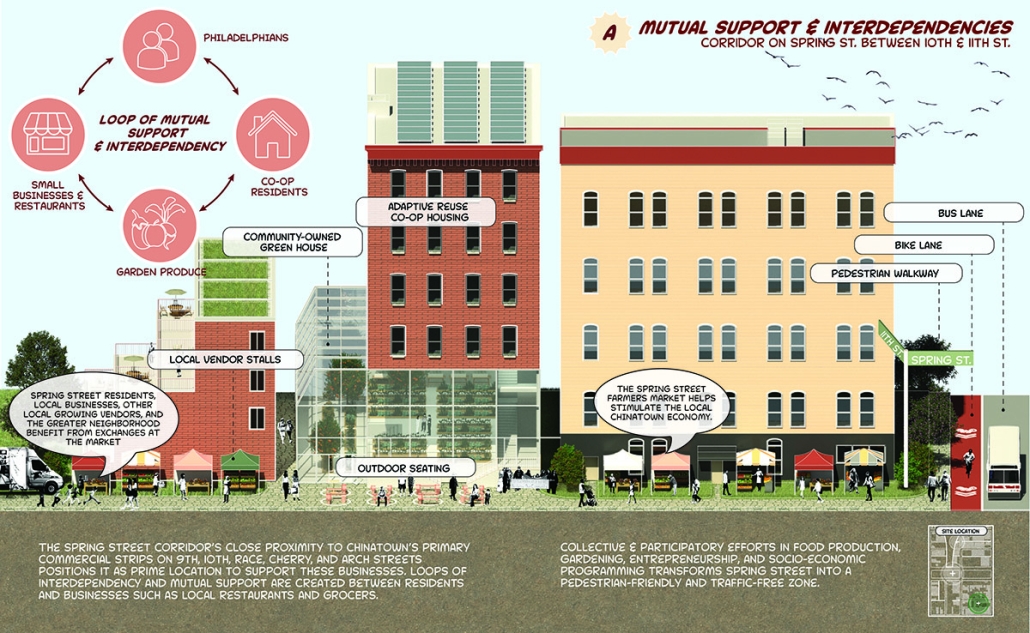
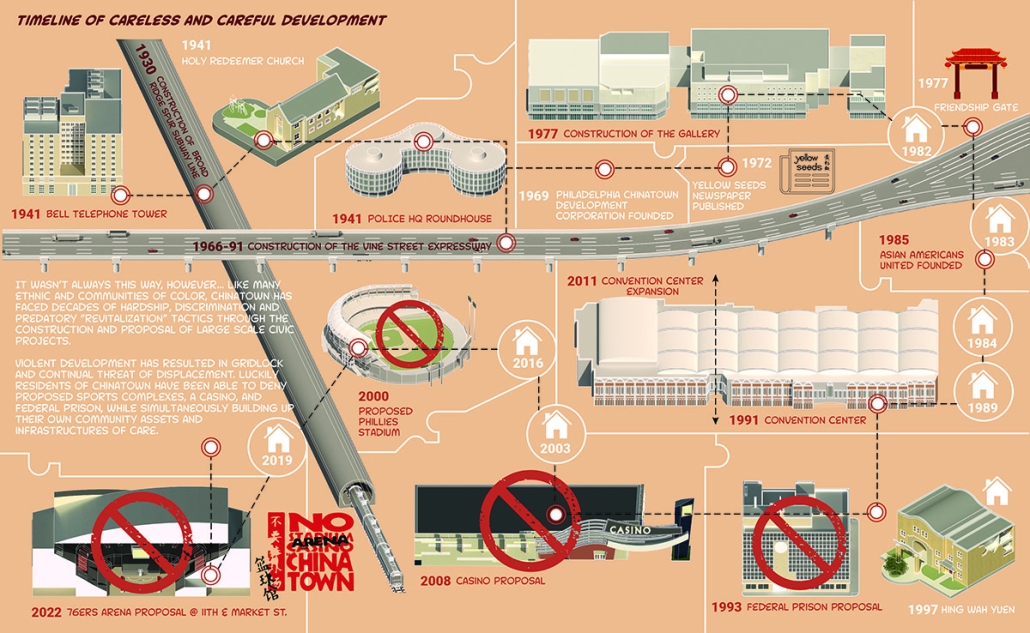
Infrastructures of Collective Care by Jessica Wong, M. Arch ’24
University of Pennsylvania | Advisors: Eduardo Rega Calvo & Rashida Ng
The concept of care is one explored by political theorist Joan Tronto, who writes about its potential to cultivate social cohesion and collective consciousness in urban environments. Tronto defines care as “a species activity that includes everything that we do to maintain, continue, and repair our ‘world’ so that we can live in it as well as possible.” Within this conceptual framework, five aspects of care can be identified: caring about, caring for, caregiving, care receiving, and caring with. Through these principles of care, this thesis explores ways to disrupt the ongoing structural violence and impositions faced by communities of color due to unjust and ignorant policies and urban development. The project also aims to shift the perception of care beyond domestic and traditional caregiving notions to promote the development of collective community infrastructures that are formed in solidarity with community input and existing development ambitions and visions for Philadelphia’s Chinatown.
As a result, a larger network of care interventions is identified and interpreted through a series of nodes seeking to amplify the already present social, economic, and cultural assets in Chinatown. The network consists of both future sites and existing resources that rely on adjacencies in the urban fabric of the neighborhood in the justification of their programming.
The overarching ambitions of Infrastructures of Collective Care aim to paint a holistic story of a community’s history of struggle, relentless perseverance, and future scenarios for community growth through a narrative and graphic novel-based approach. The graphic novel is a speculative document comprised of urban design strategies that represent the intersection of a yearlong process of research, analysis, and community engagement. Architectural and landscaping interventions reveal themselves in the graphic novel in hopes of projecting alternative Chinatown futures capable of resisting future institutional pressures of carelessness.
Instagram: @weitzman_arch
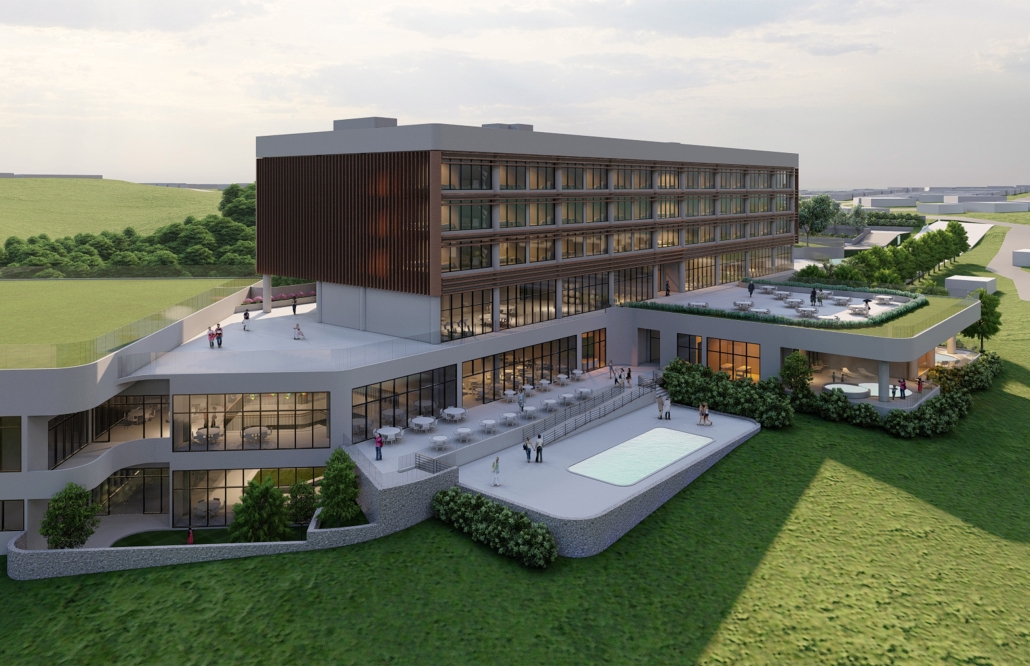
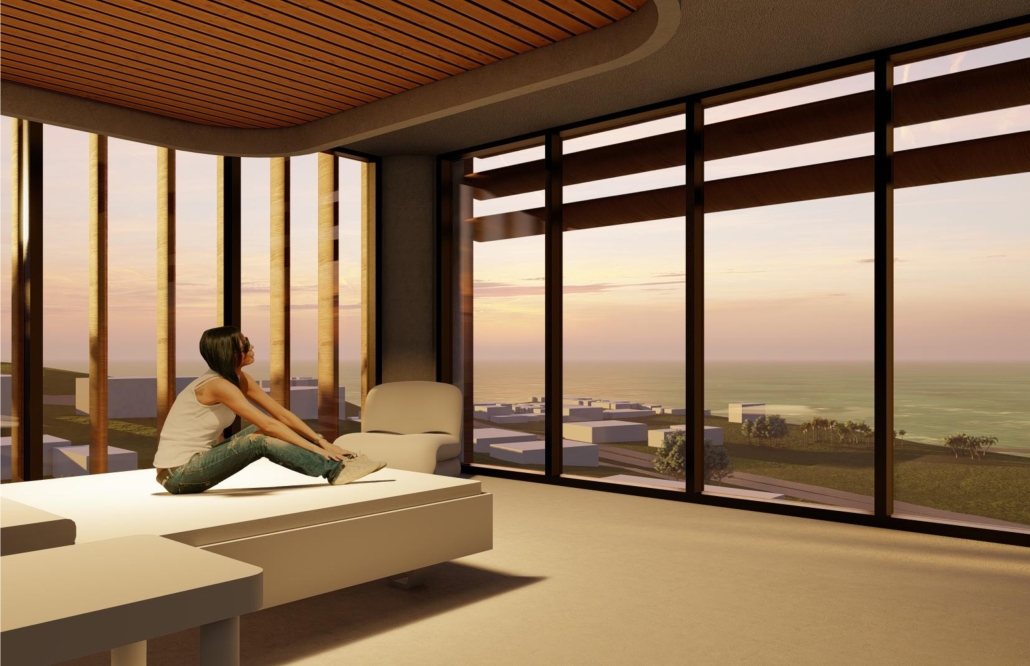
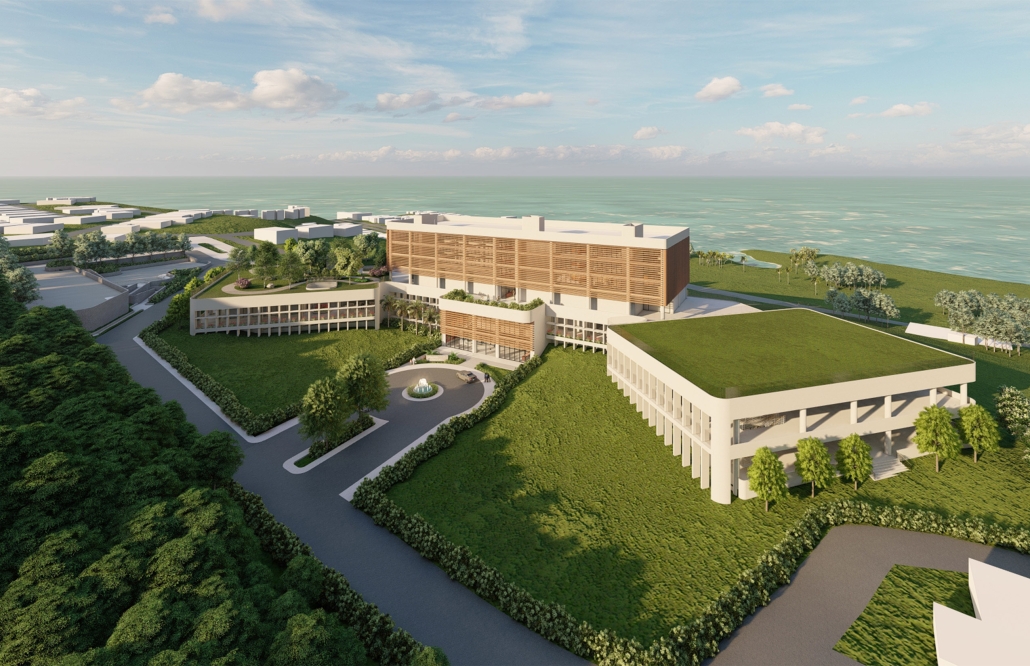
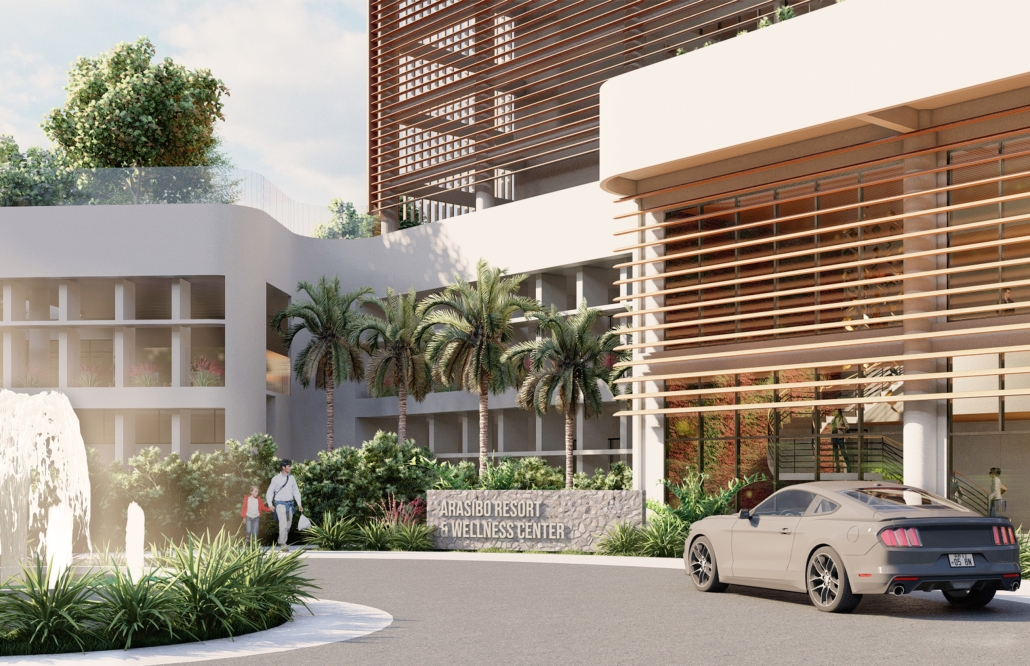
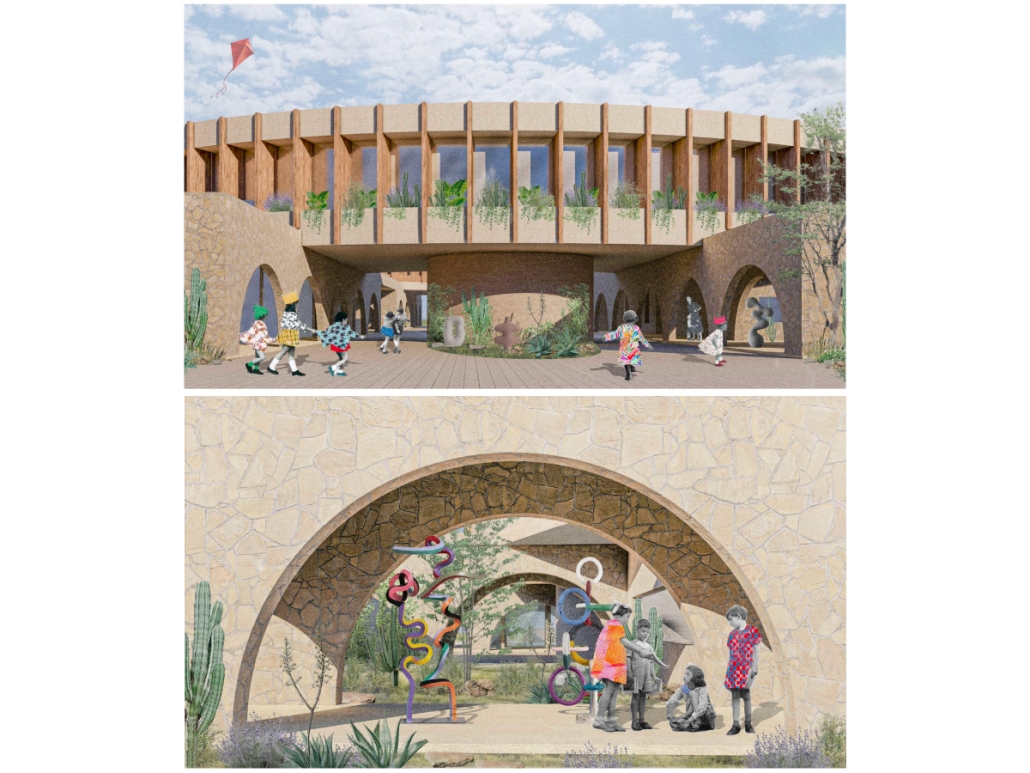
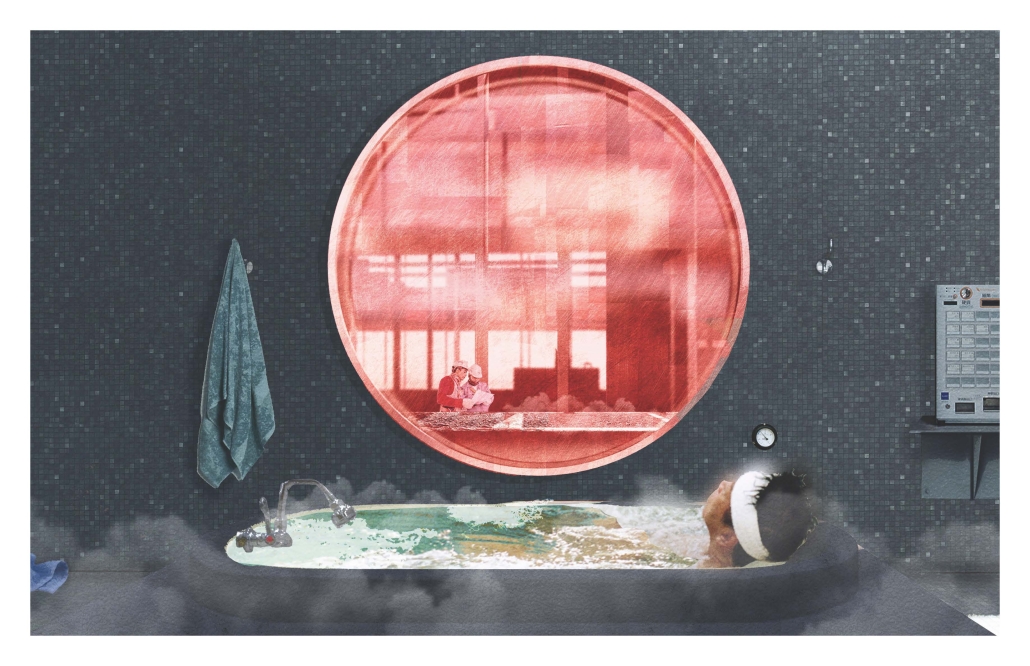
Designing for Well-Being: Preventive Architecture against Stress and Anxiety by Odalys Brugman-Santiago, B. Arch ’24
Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico | Advisors: Manuel De Lemos-Zuazaga & Pedro A. Rosario-Torres
According to specialists, in recent years there has been a notable increase in young adults suffering from diseases that generally used to occur in people over 45 years of age. Studies report that the appearance of many of these at an early age is due not only to genetic factors but also to the constant stress and anxiety that people experience in their daily lives. Although statistics show that women suffer the most from anxiety disorders, very few seek treatment compared to men. Of those who do attend, more than 70% report not having children or dependent children, which is why it is concluded that this is an important factor when deciding to take care of their mental and emotional health.
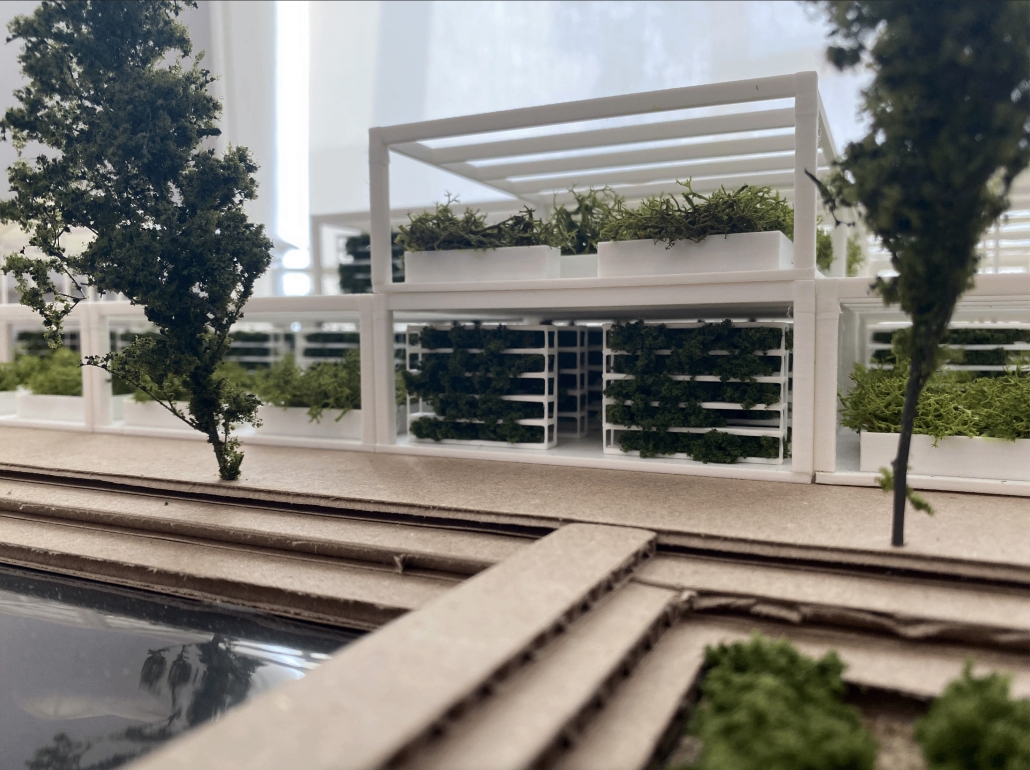
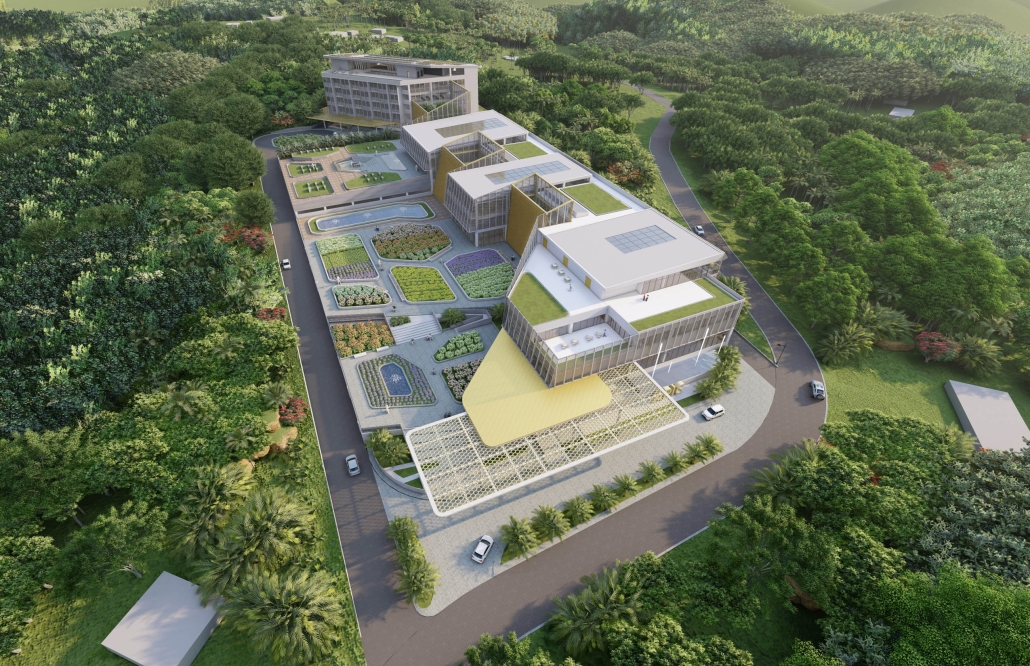
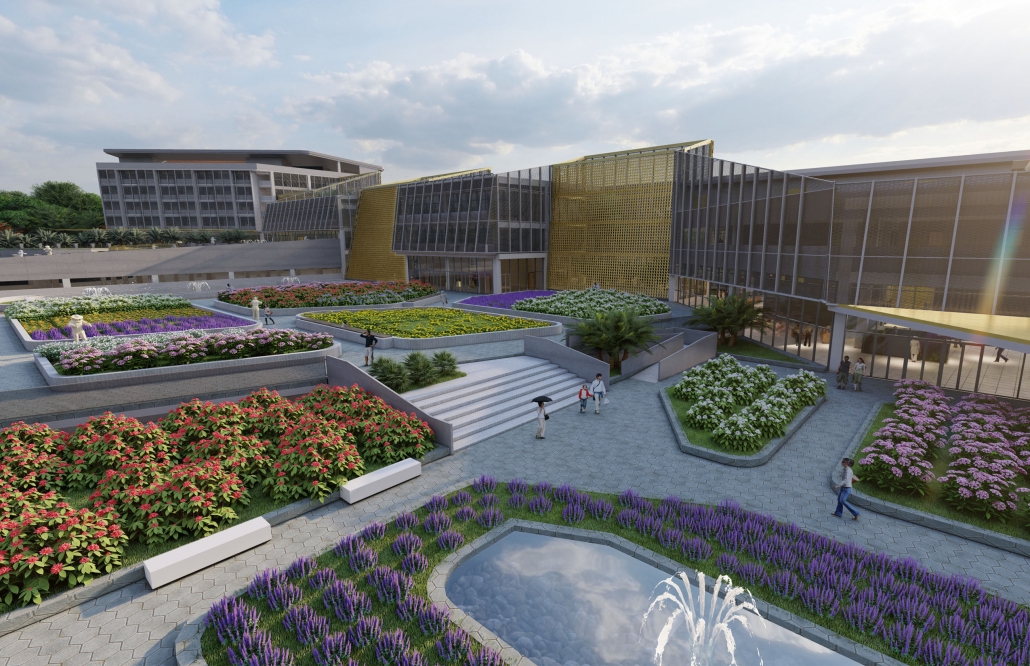
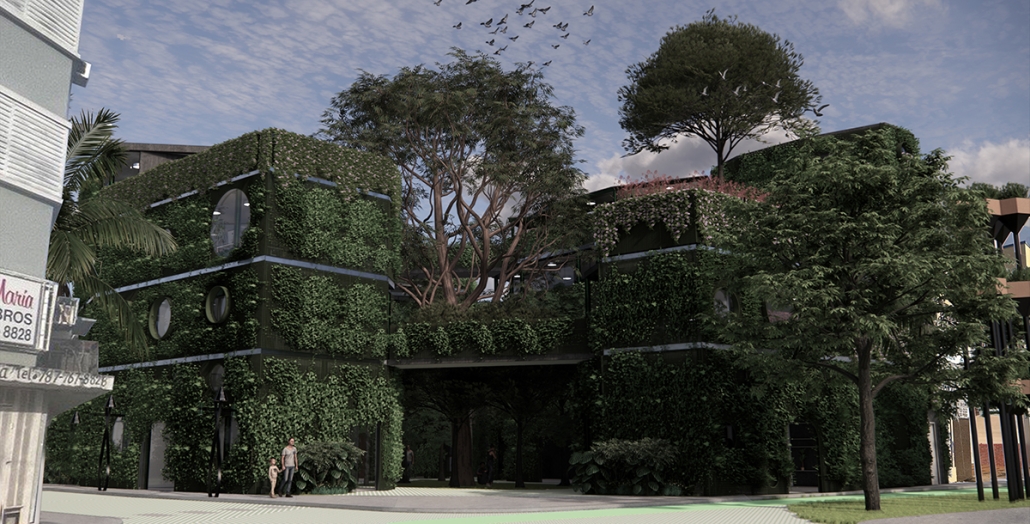
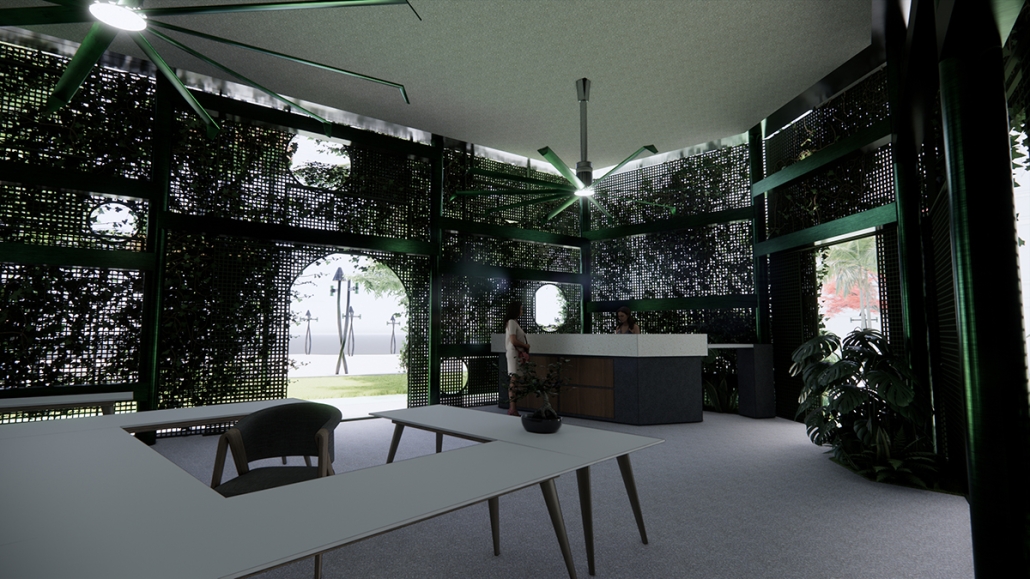
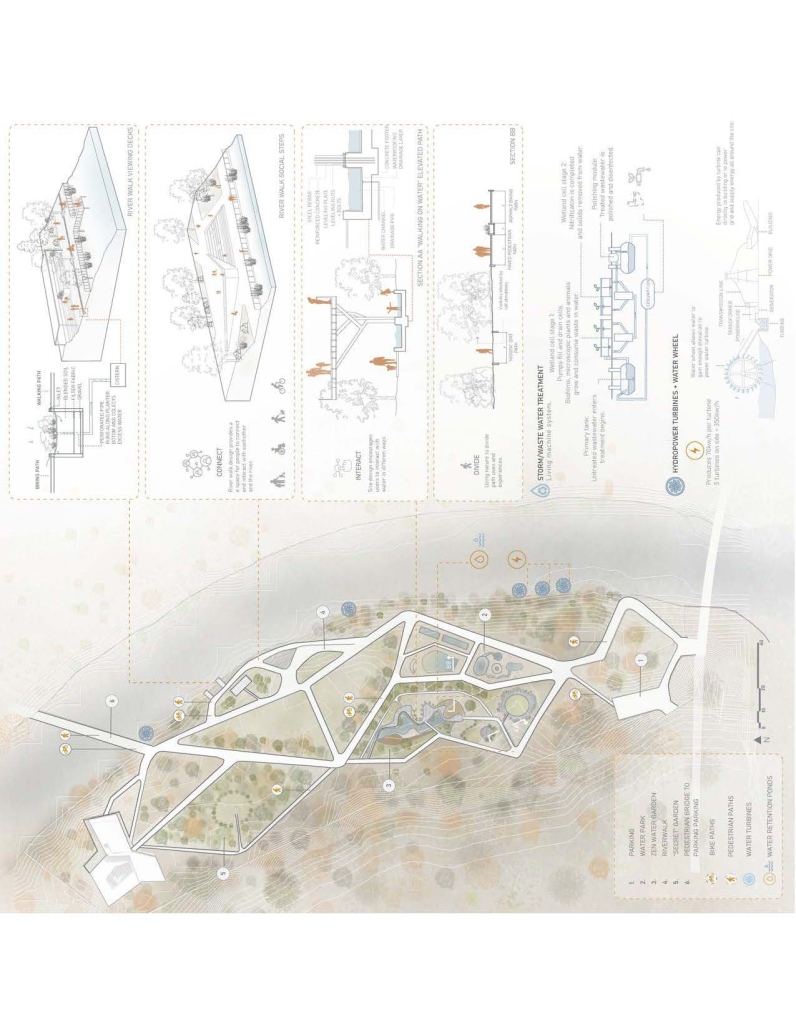
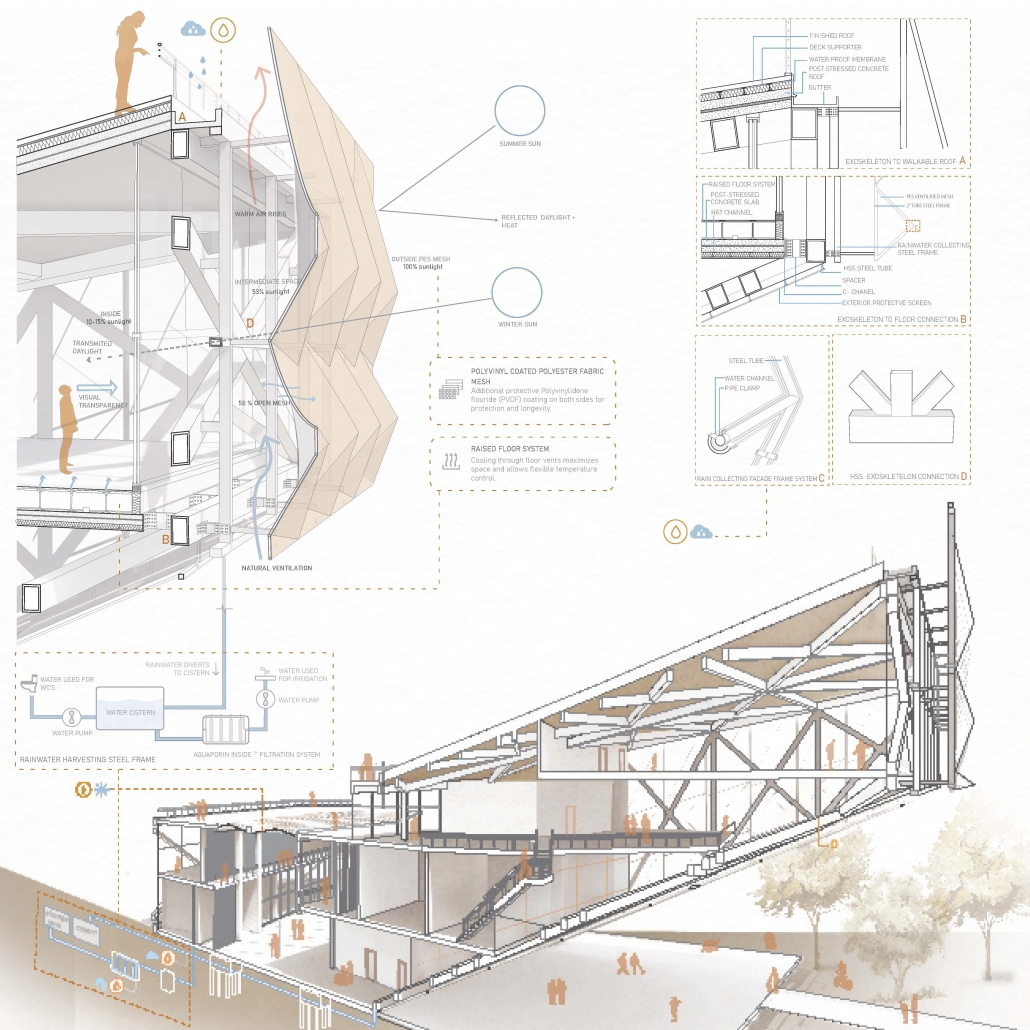
The proposal for the Arasibo Resort & Wellness Center seeks to create a welcoming space where women and children can come to receive services to take care of their mental and emotional health in order to prevent the development or exacerbation of diseases due to constant exposure to situations of stress and anxiety. Its strategic location near the northern coast of Puerto Rico, specifically in the municipality of Arecibo, provides the user with pleasant views of the sea and other natural environments from any of the spaces. In addition, the project provides areas of encounter with nature for both outpatients and inpatients.
The main spatial programs in this project are: mental health service areas, a child daycare center, hotel-type rooms for inpatient treatment, an art and recreation area, commercial spaces for rent, a pharmacy, cafeteria, restaurant, and spa, among others. Every design decision is mainly based on strategies resulting from extensive research. For this, the following theories were cautiously studied: Psychosocial Stress, Chronic Stress, Neuroarchitecture, Architecture through the Senses and Phenomenology of Architecture.
Instagram: @obrvg
Reforming Re-entry: Creating Healing Transition Spaces For The Formerly Incarcerated by Leonard Jefferson, B. Arch ’24
Auburn University | Advisor: David Shanks
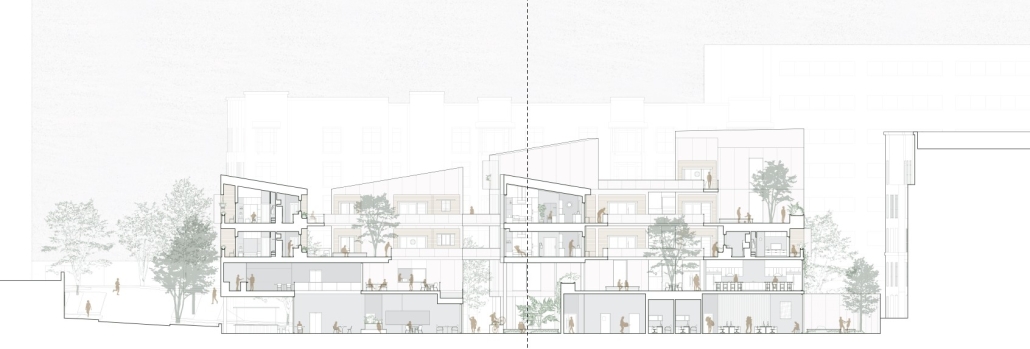
This thesis proposal seeks to address the issue of life post-incarceration for former prisoners. After their release, these individuals inevitably cross paths with the many barriers to reentry into society. One reason these barriers exist is due to the time spent within the American prison system itself. In general, this system is built to dehumanize the incarcerated by stripping them of their freedoms. Prisoners are consistently exposed to psychologically traumatizing environments, leaving a negative impact on their mental fortitude. Once released, ex-prisoners face the second barrier of stigmatization from society. Prejudged due to their criminal background, they often have trouble finding stable housing and jobs due to a lack of trust. Based on this realization, the following design proposal creates a transition space that combines housing, education, and employment opportunities under one roof. There are two primary ideals tested in this proposal: (1) Providing opportunities on multiple scales for residents to choose the level of privacy they desire; and (2) embracing the interpersonal contact theory, by creating ample space where residents can interact more often with the public. All in all, if we aim to help the formerly incarcerated, we must provide an architectural typology equipped with the fundamental resources they need to better themselves and fulfill their desire for a second chance.
Instagram: @leo.dj_, @davidrshanks
Stay tuned for Part X!
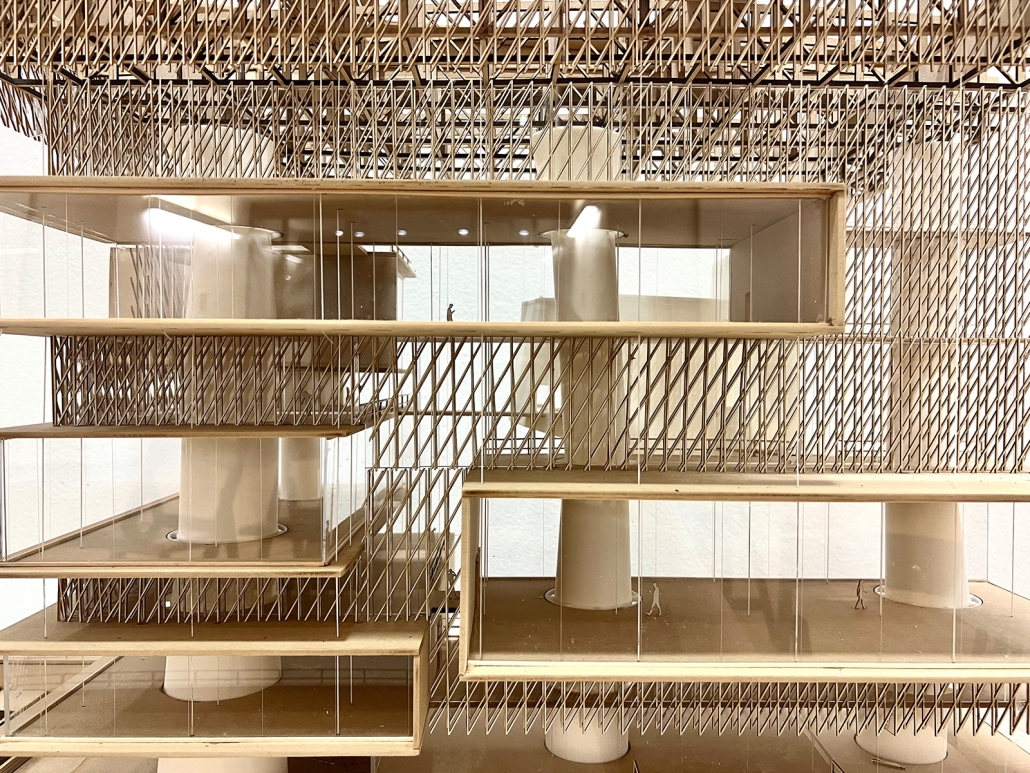
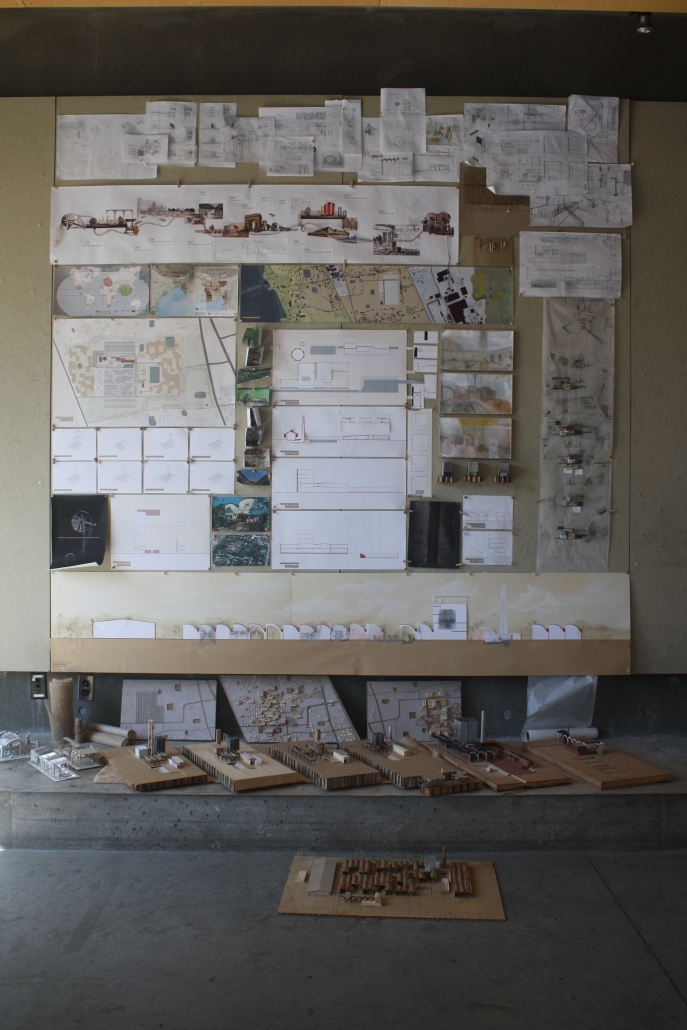
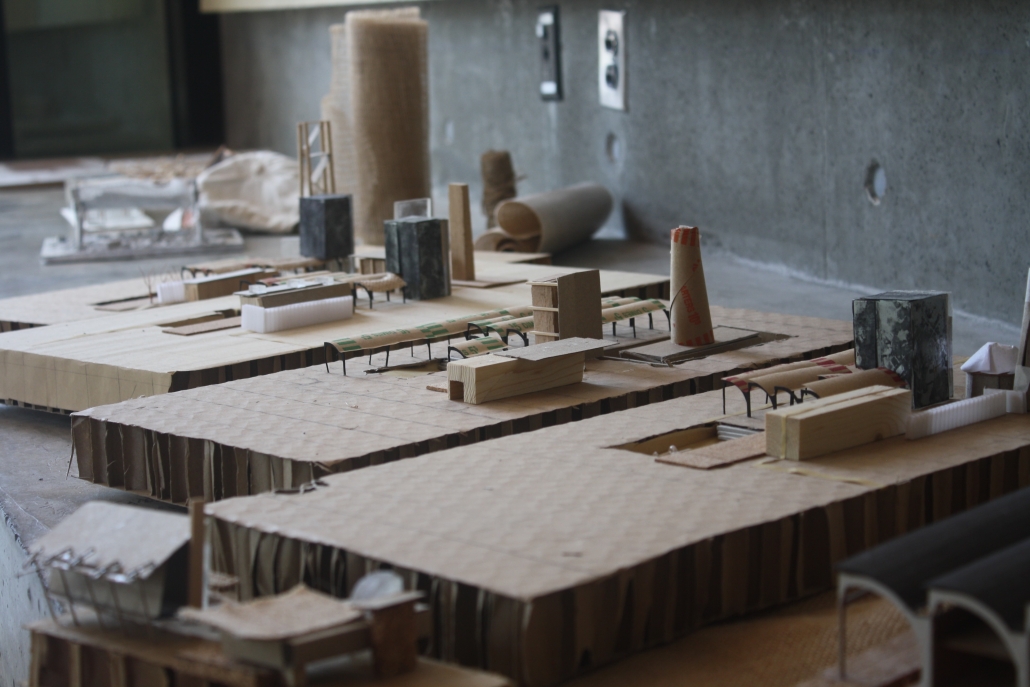
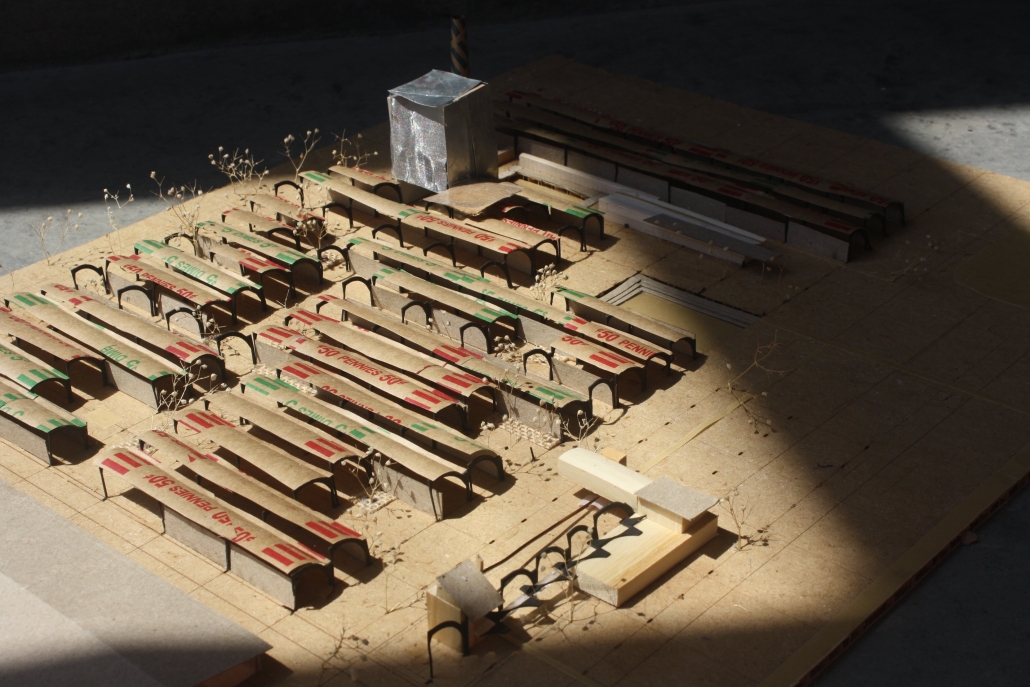

















































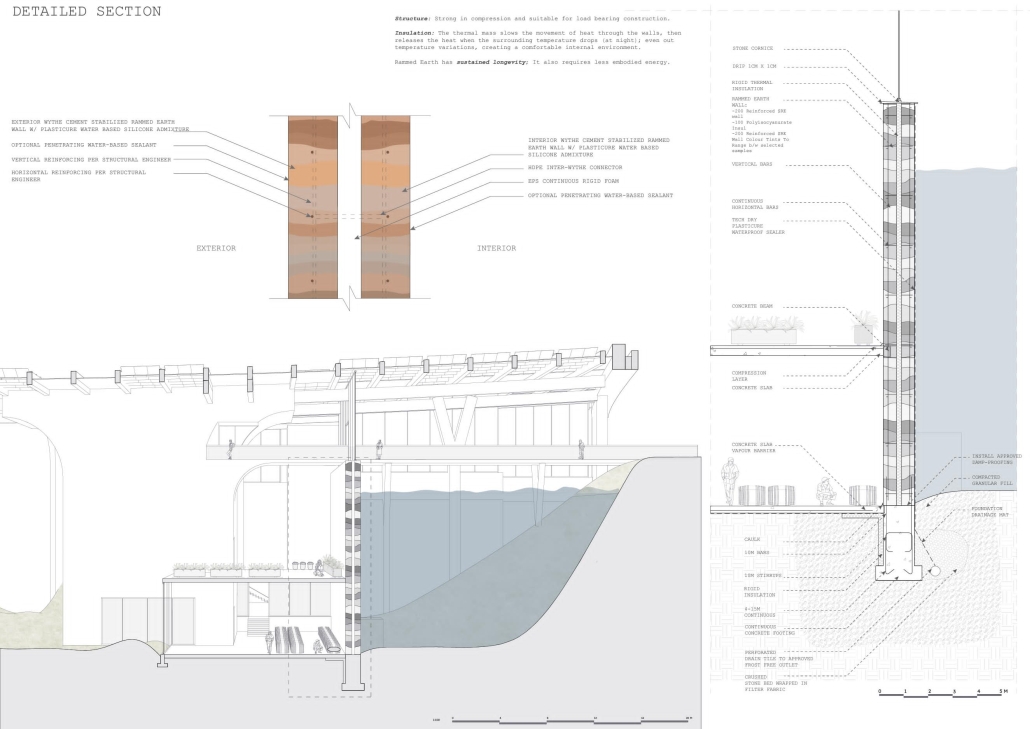

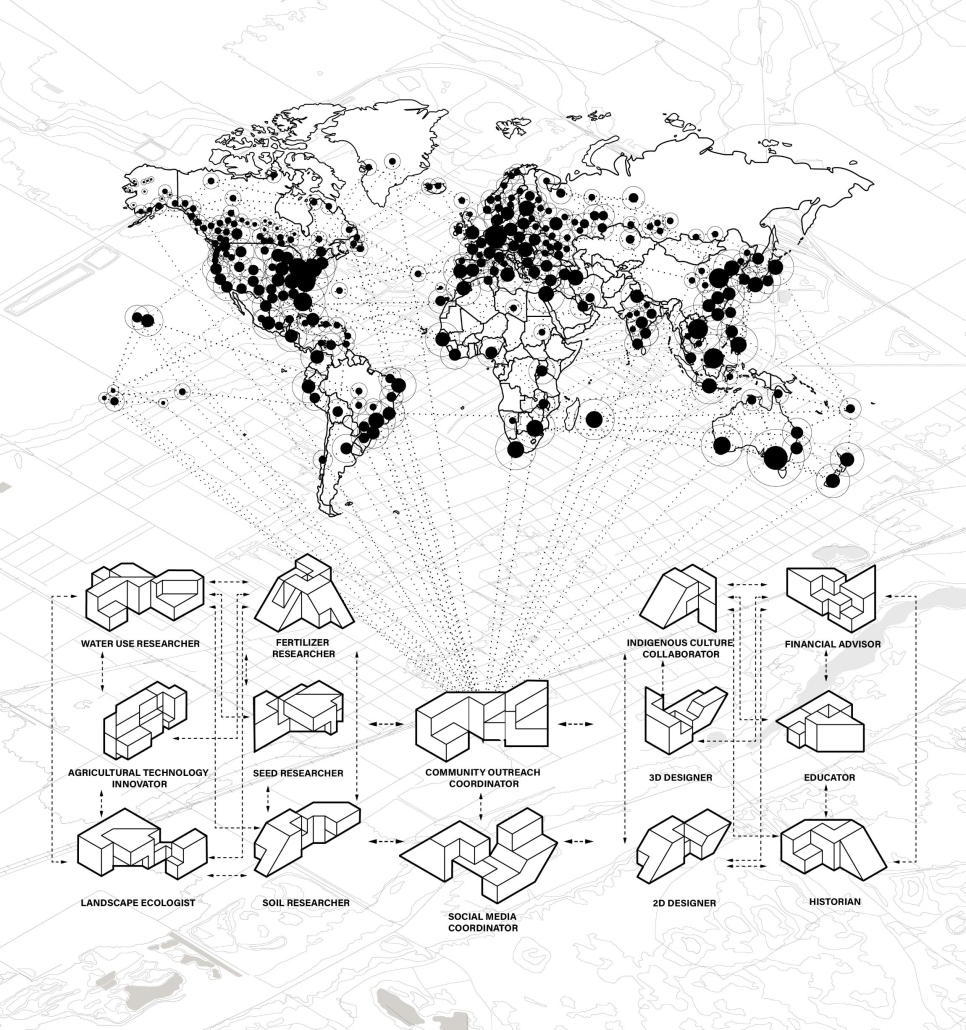
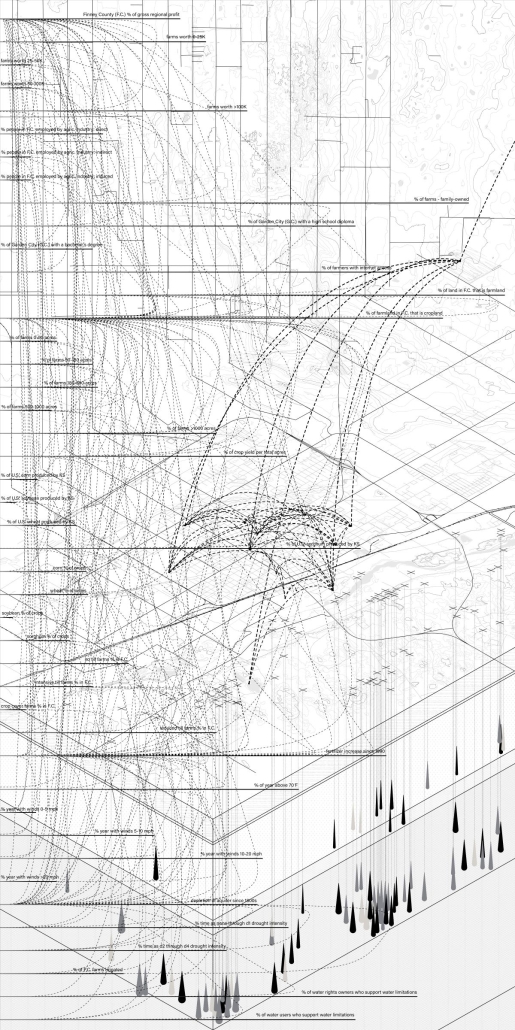

























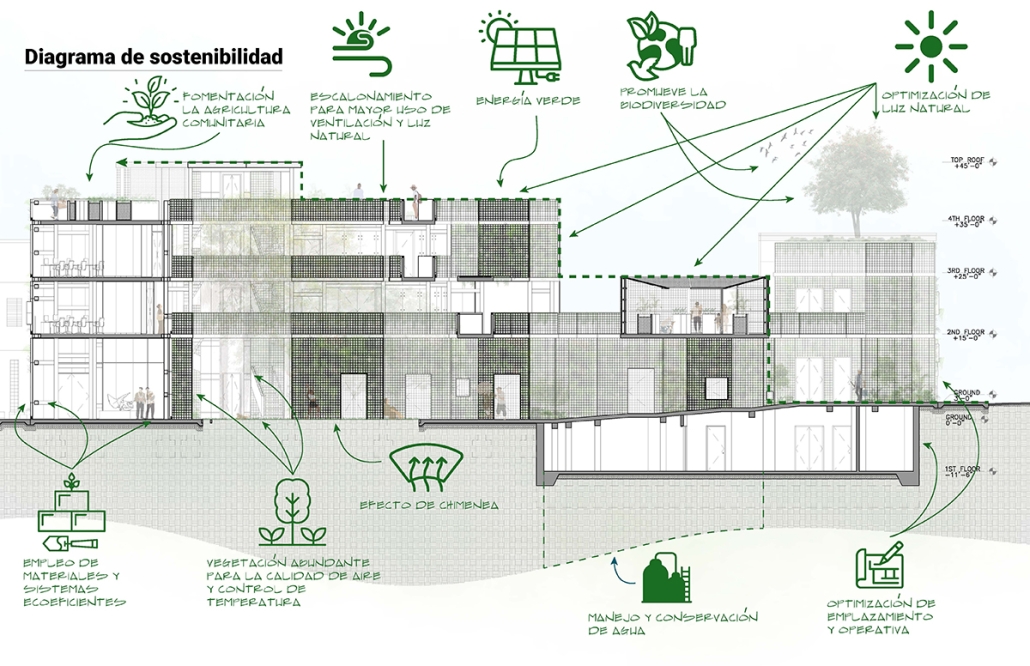


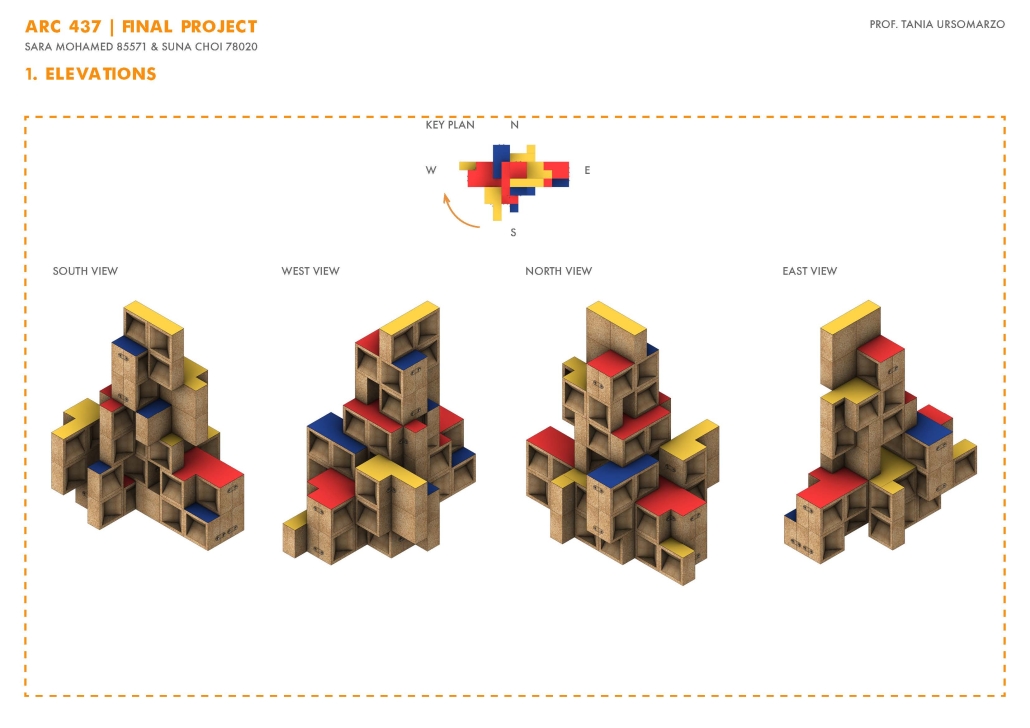
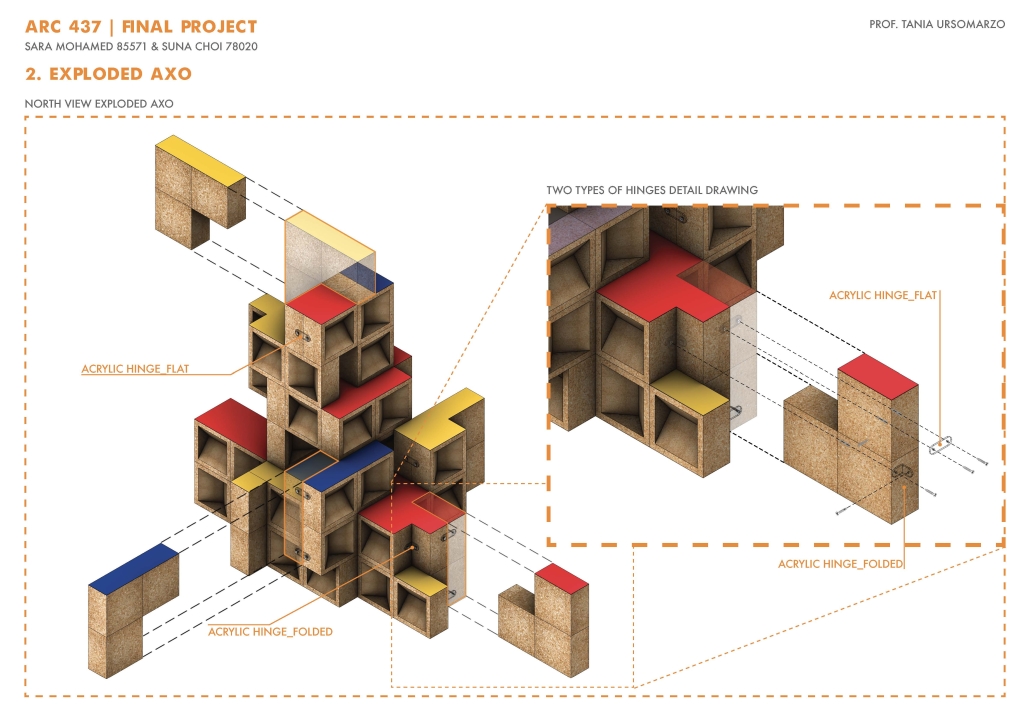
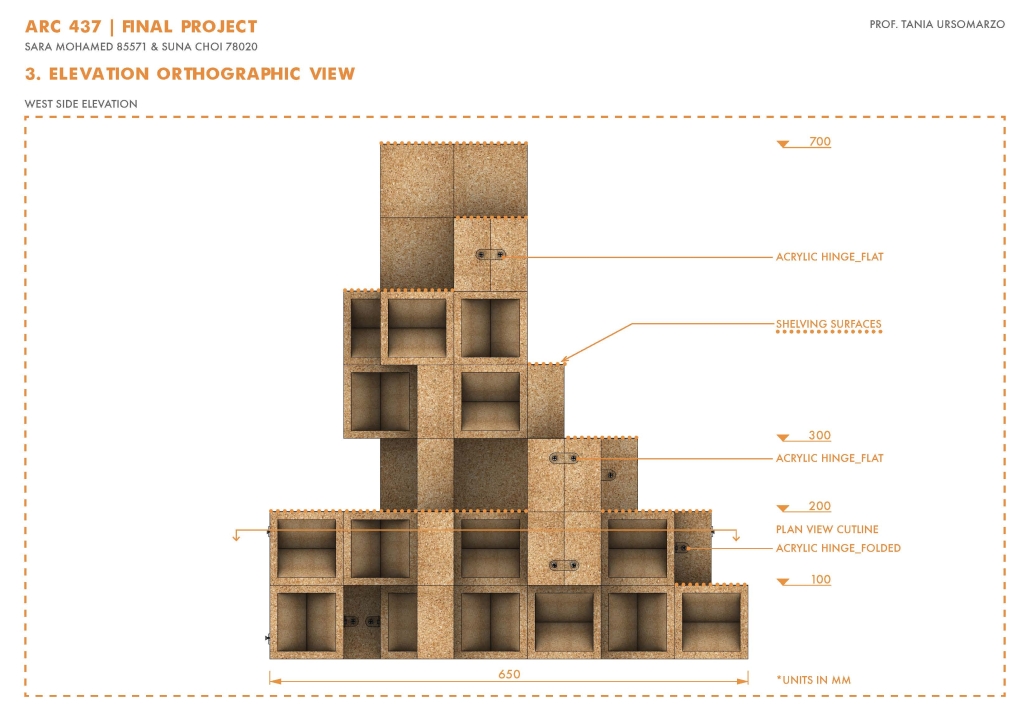






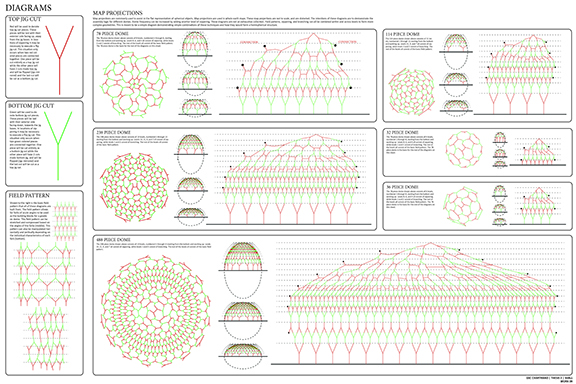
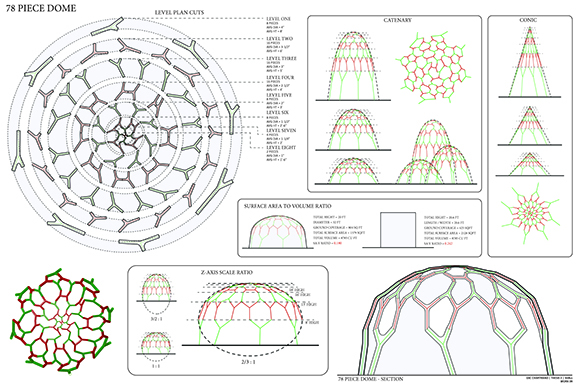
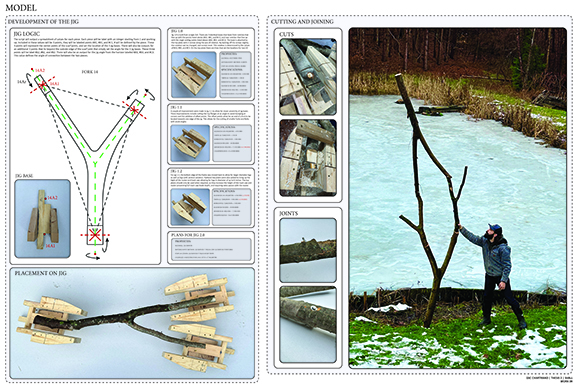
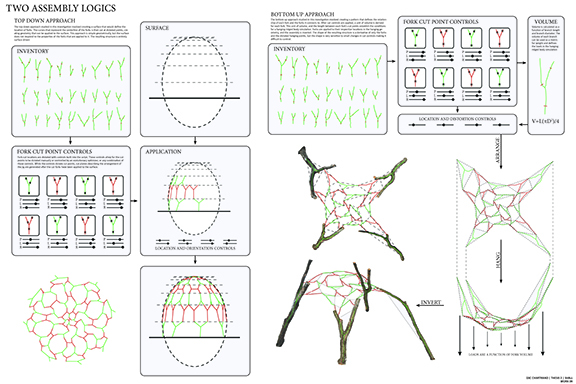
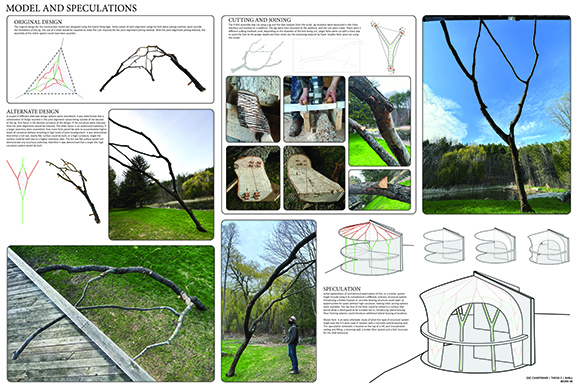

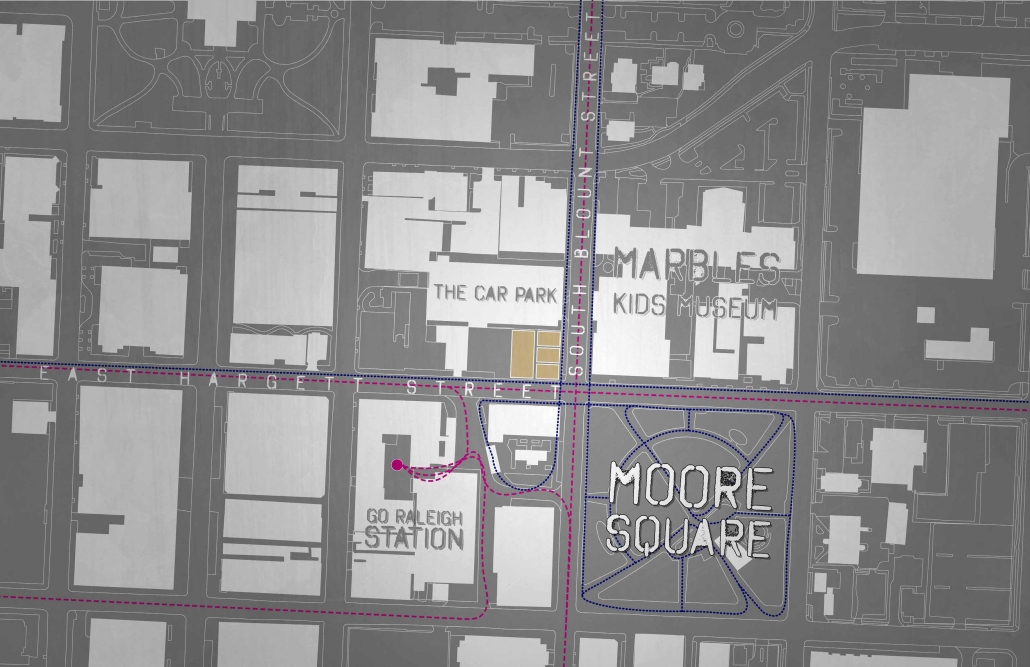

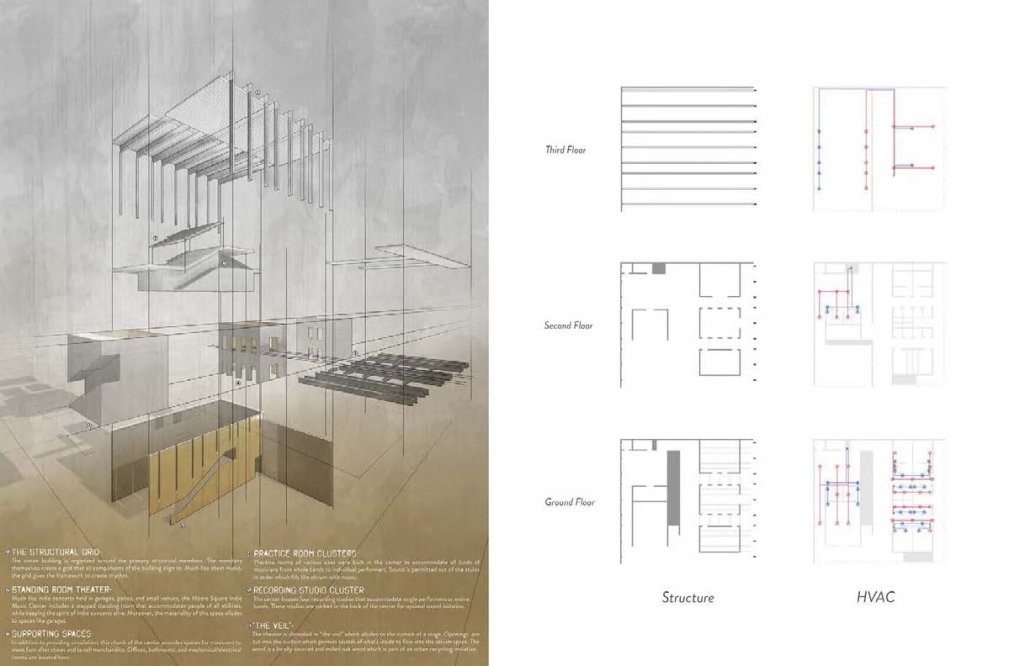
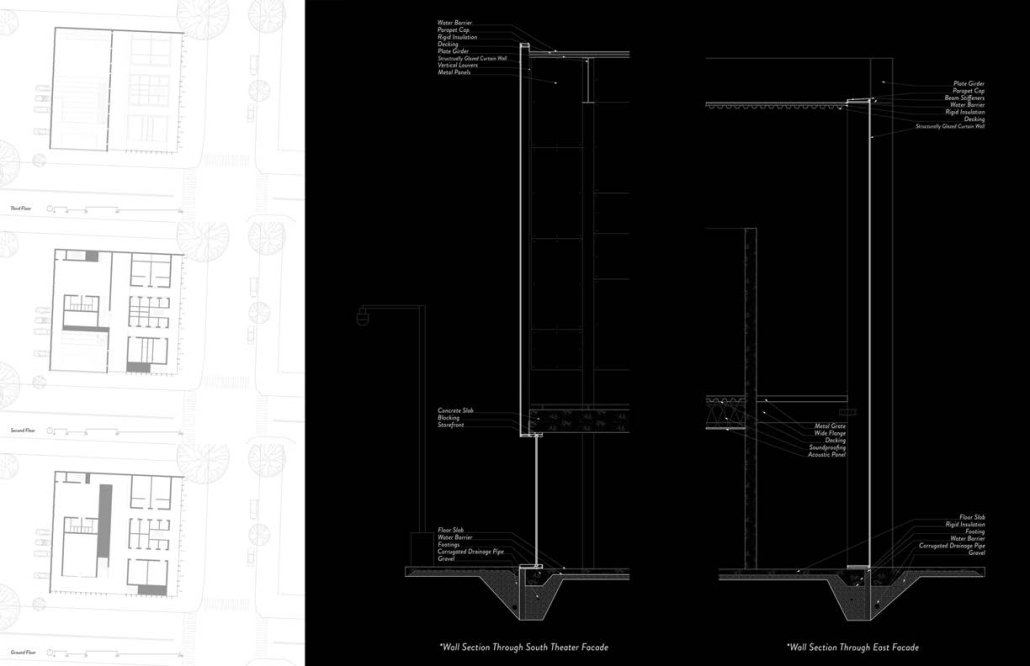





























































































![music room [Converted]](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/musicRoom-copy-2-Maggie-McMickle-1030x1004.jpg)