2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XII
Part XII of the 2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase features exemplary projects that explore housing-related topics and address challenges ranging from gentrification to high costs. These award-winning designs demonstrate how architecture can promote inclusive housing models rooted in local community, cultural heritage, equity, and affordability.
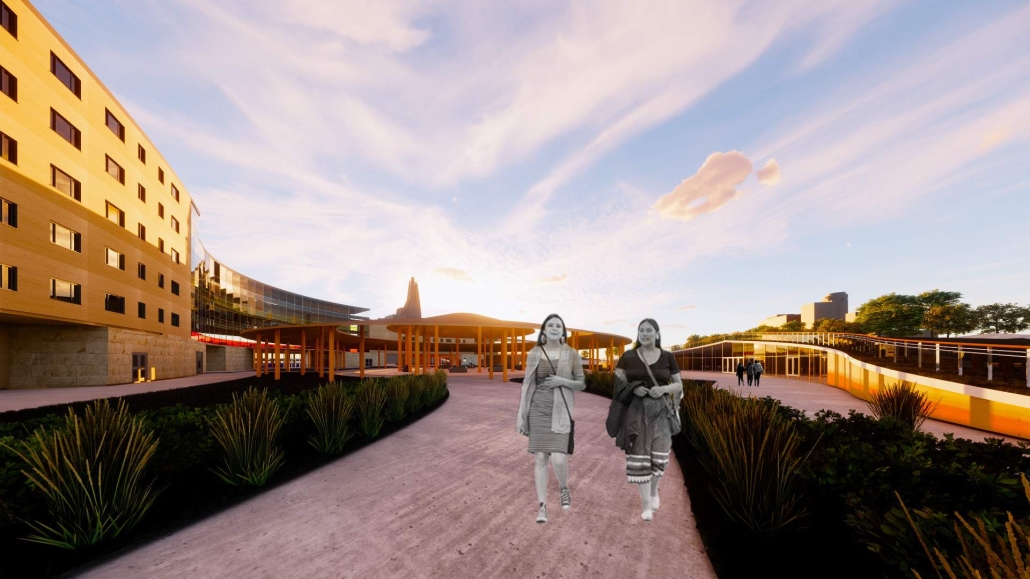
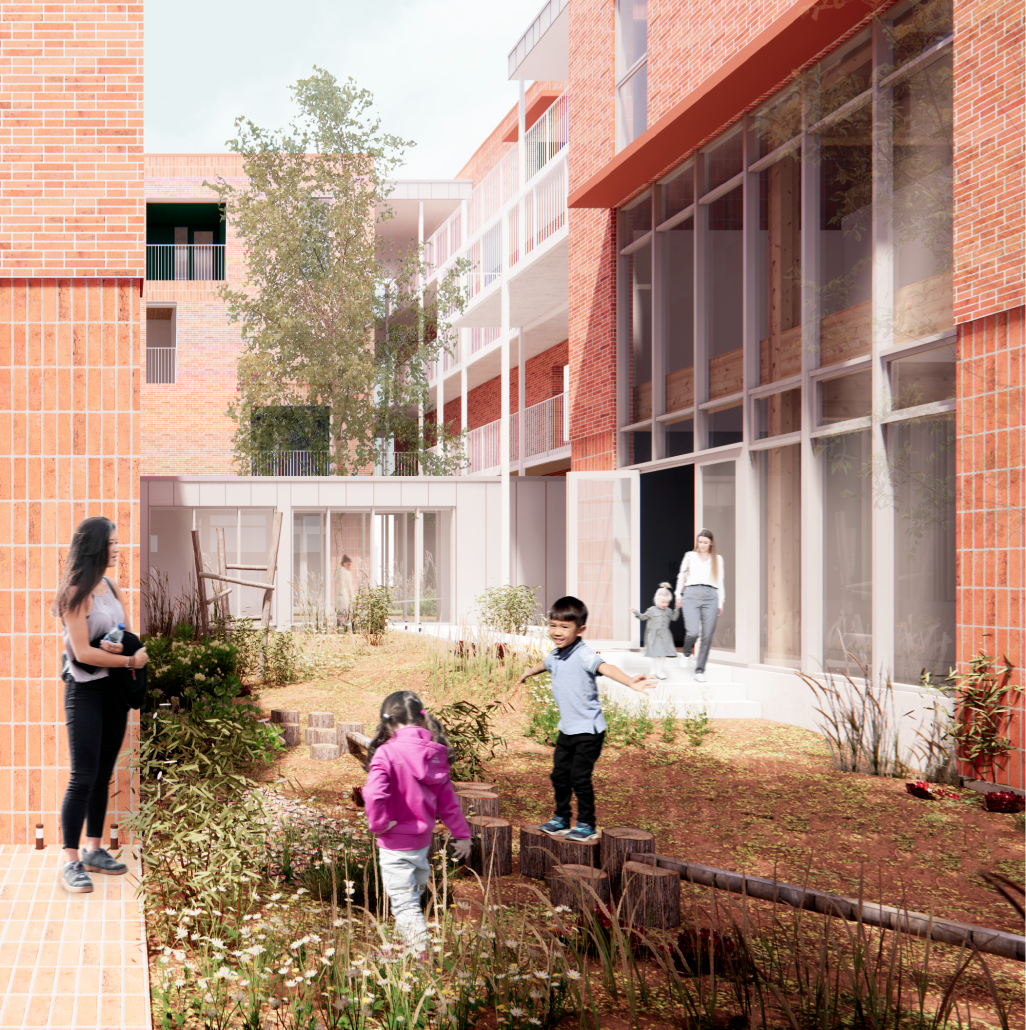
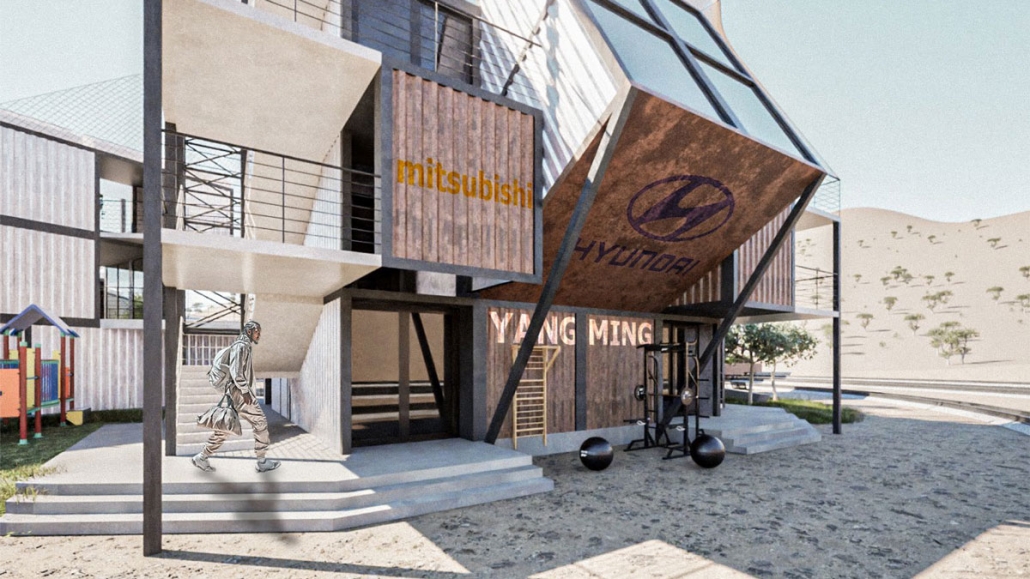
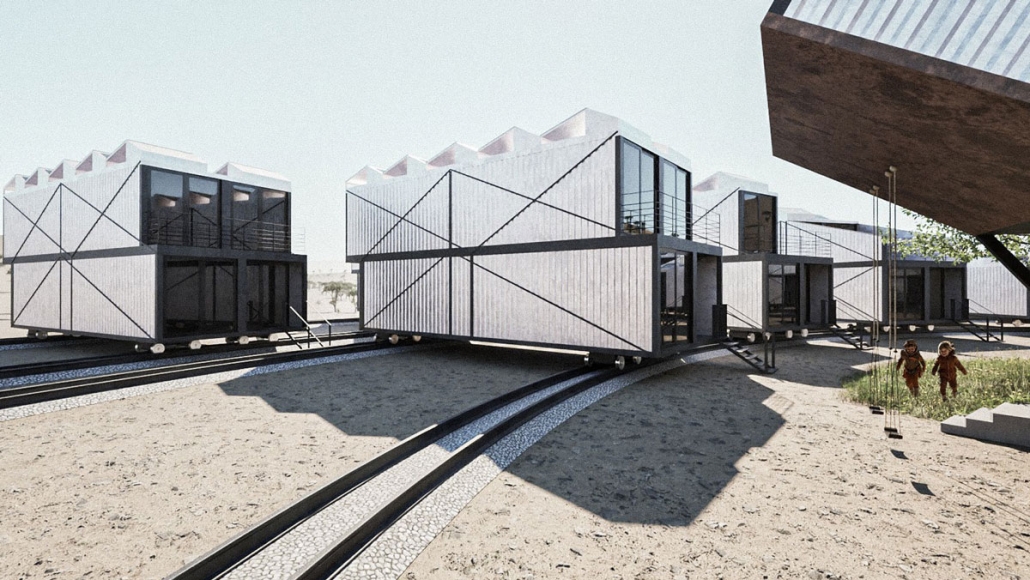
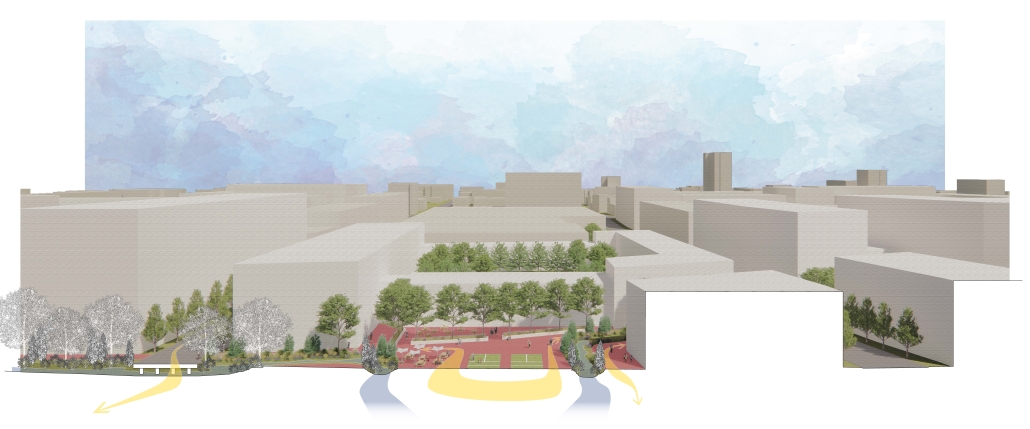
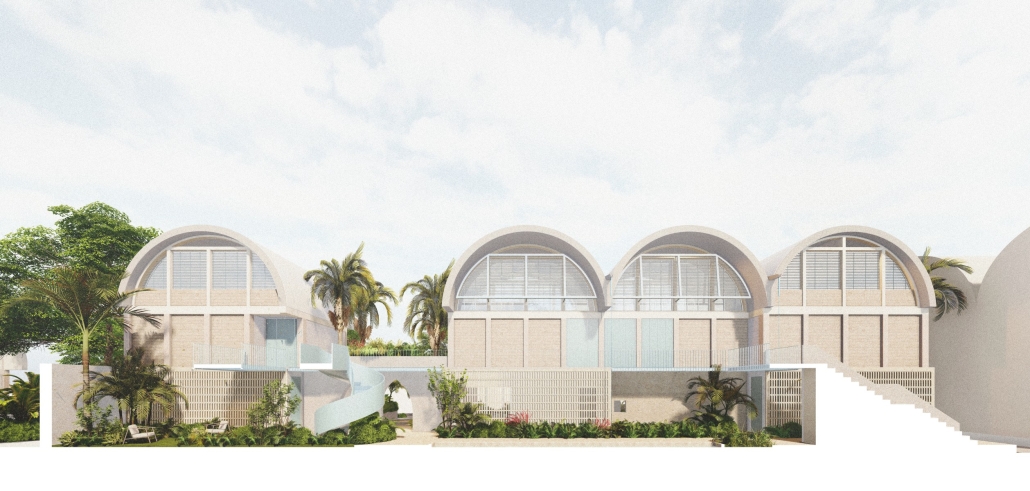
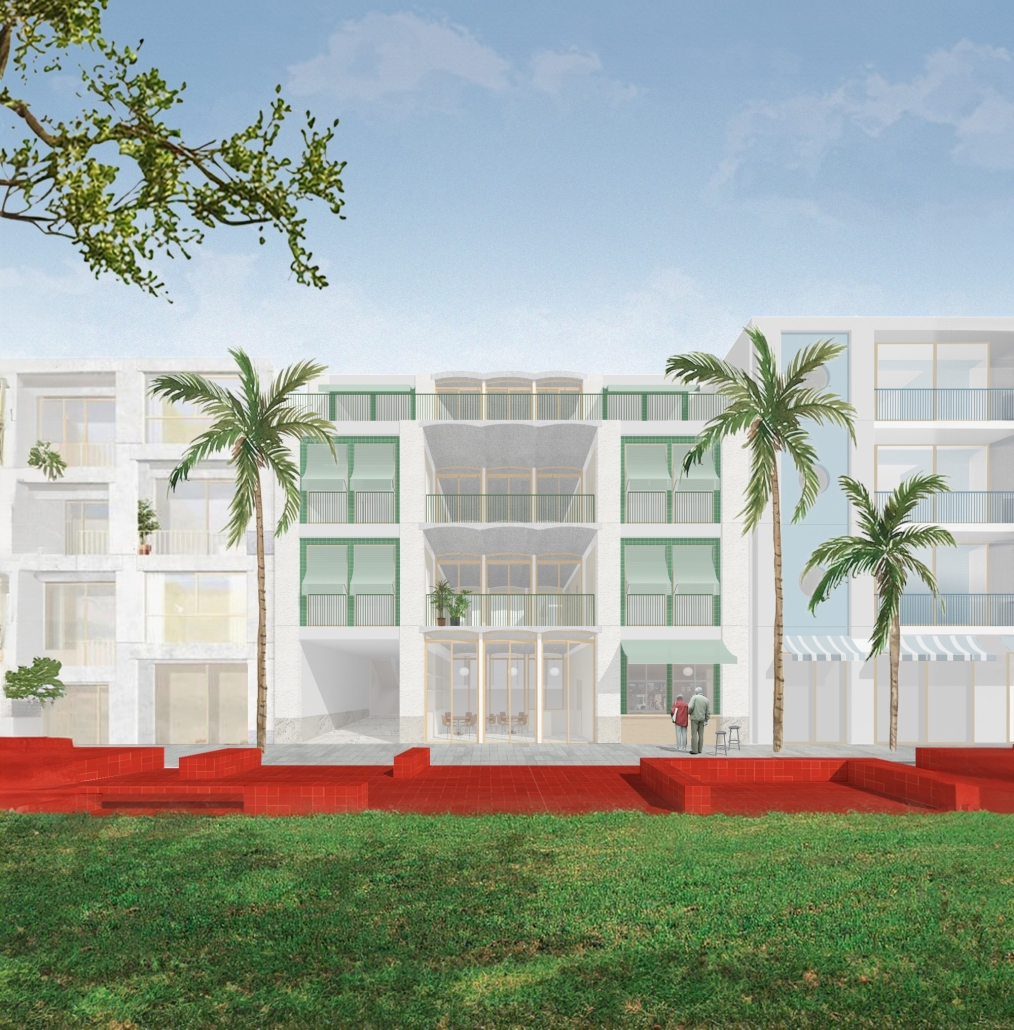
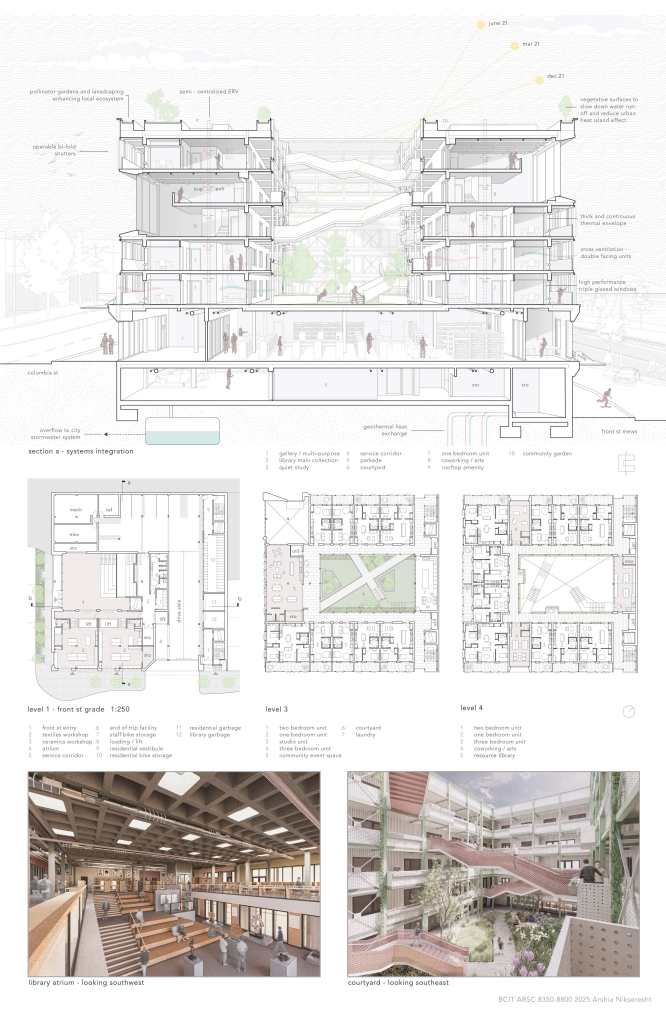
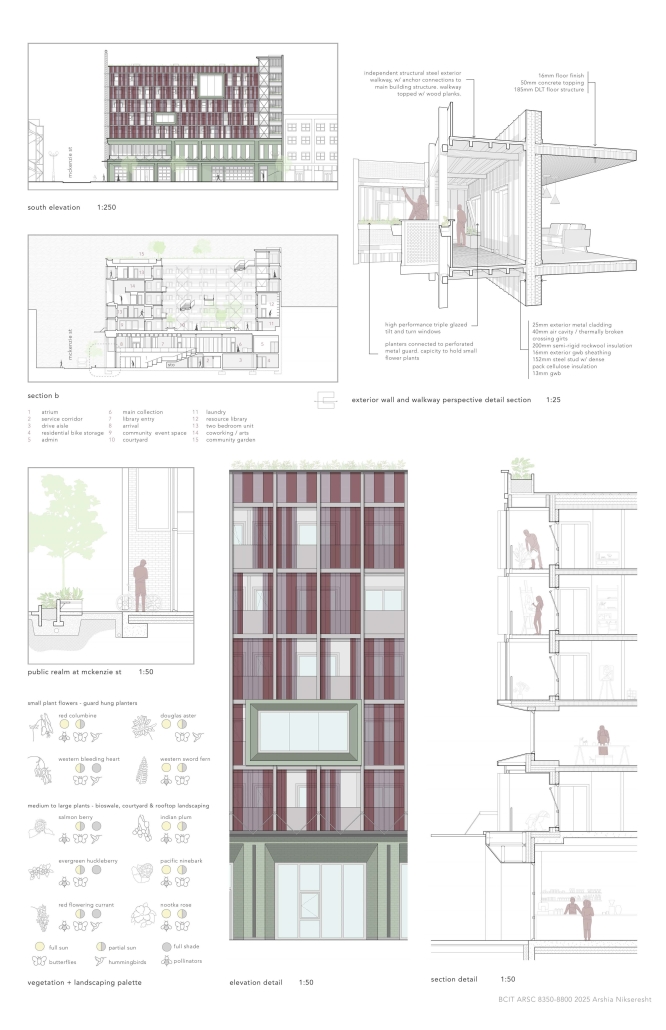
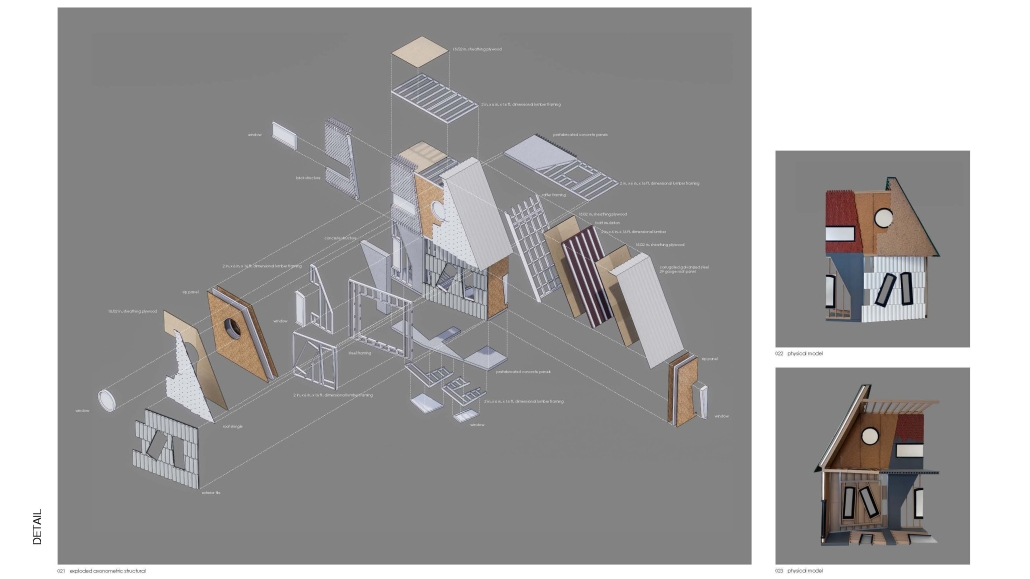
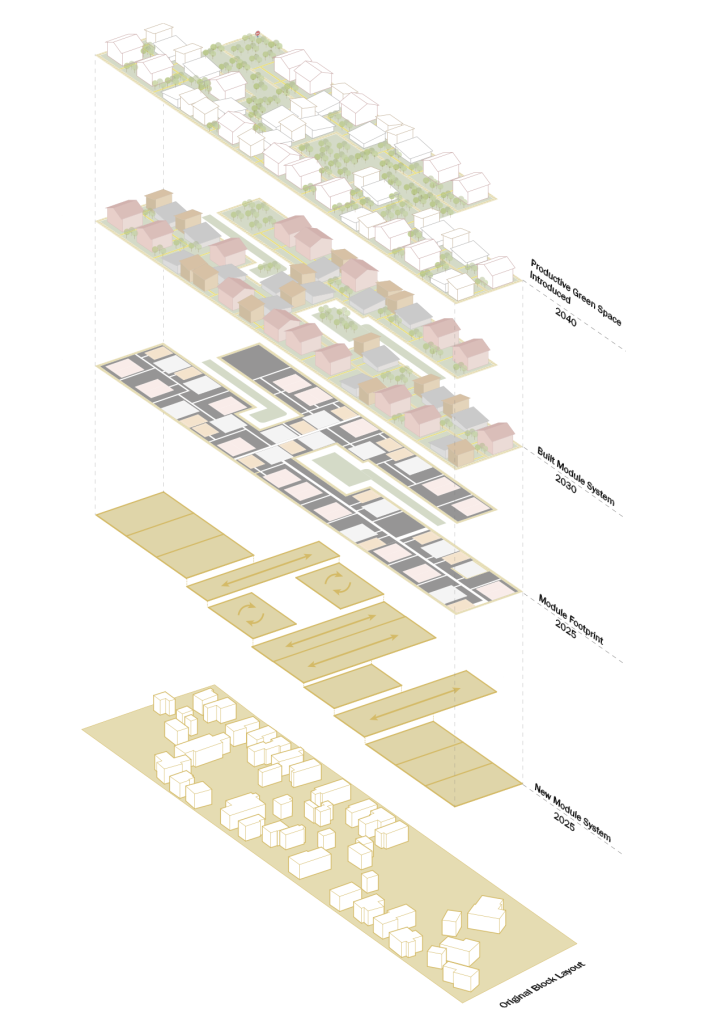
stacks + studios by Arshia Nikseresht-Ahaki, B.ArchSci ’25
British Columbia Institute of Technology | Advisors: Jody Patterson & Michel Labrie
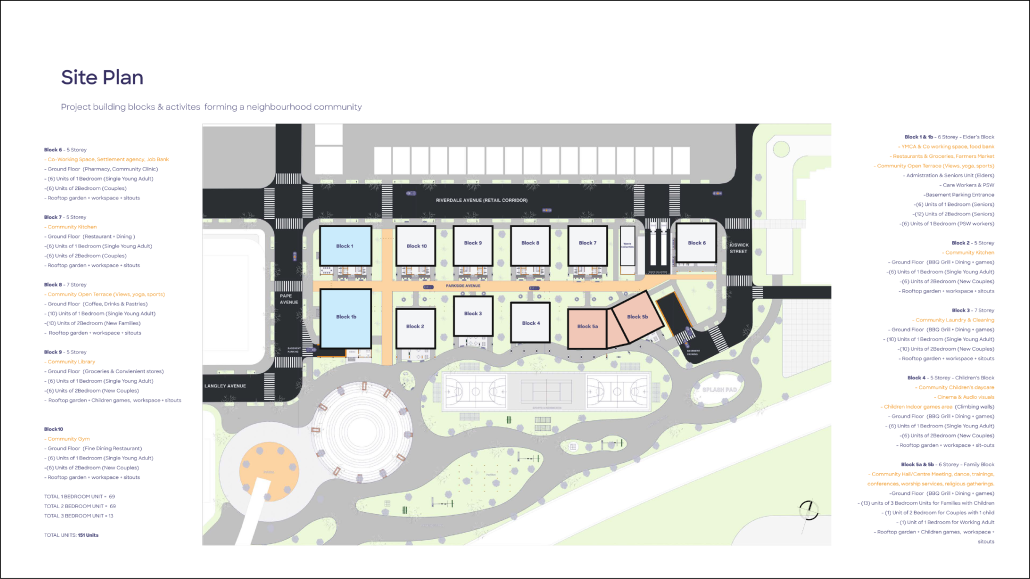
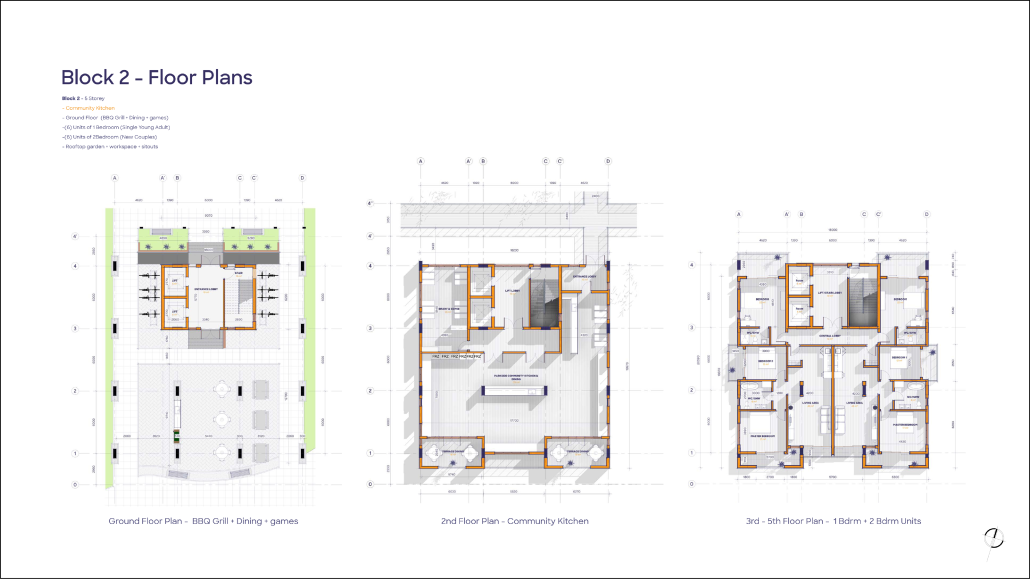
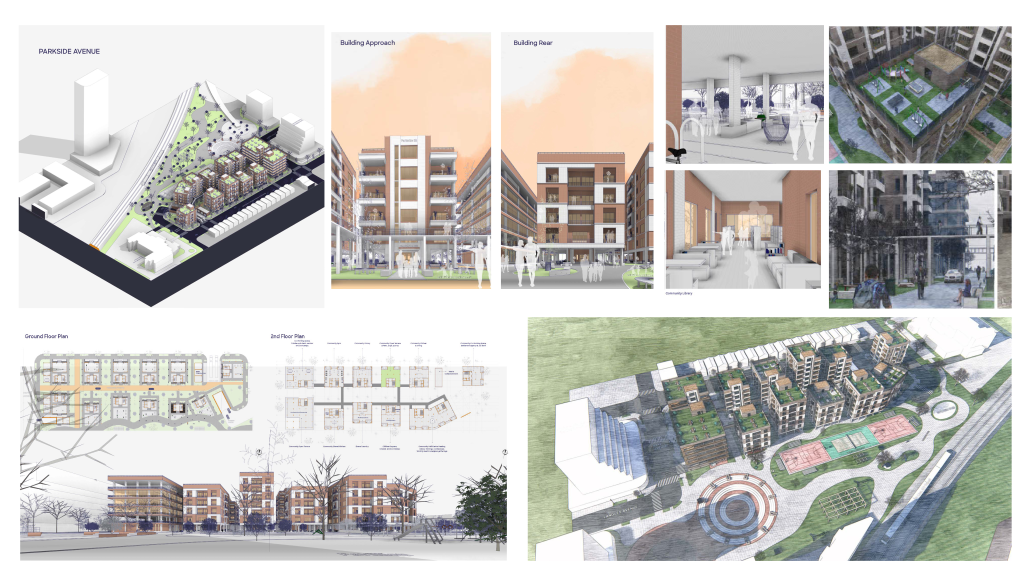
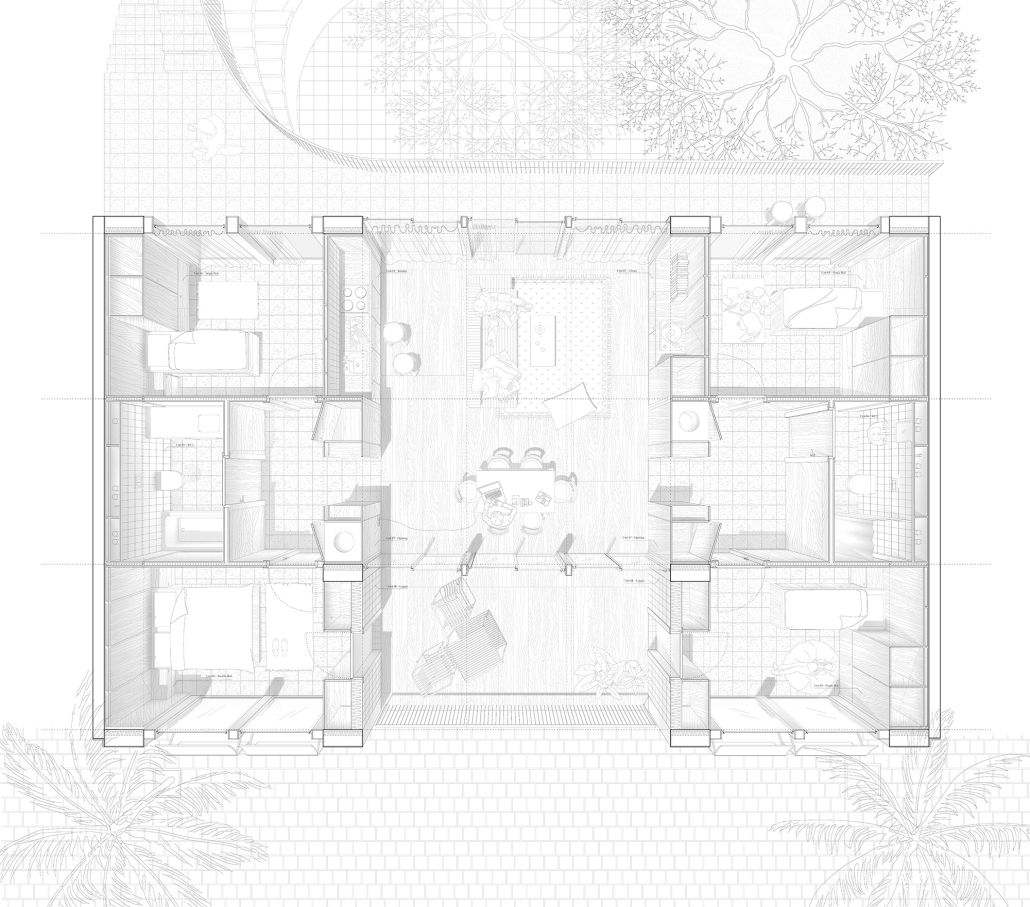
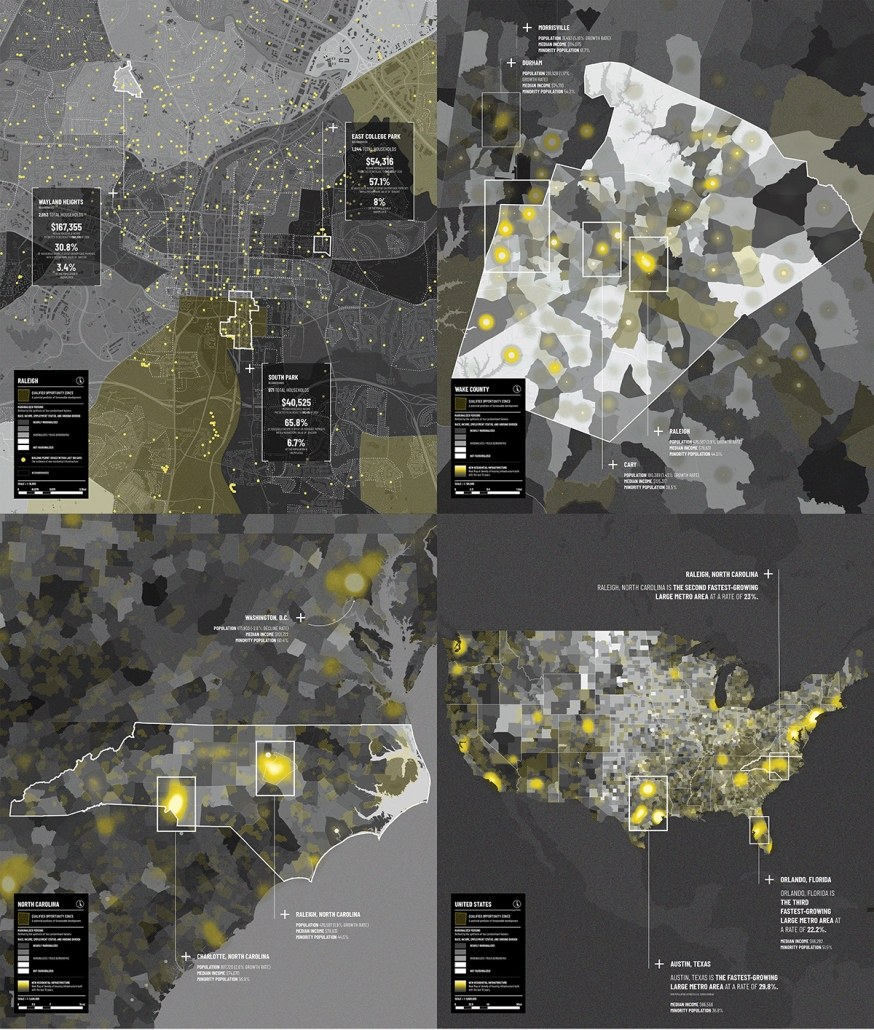
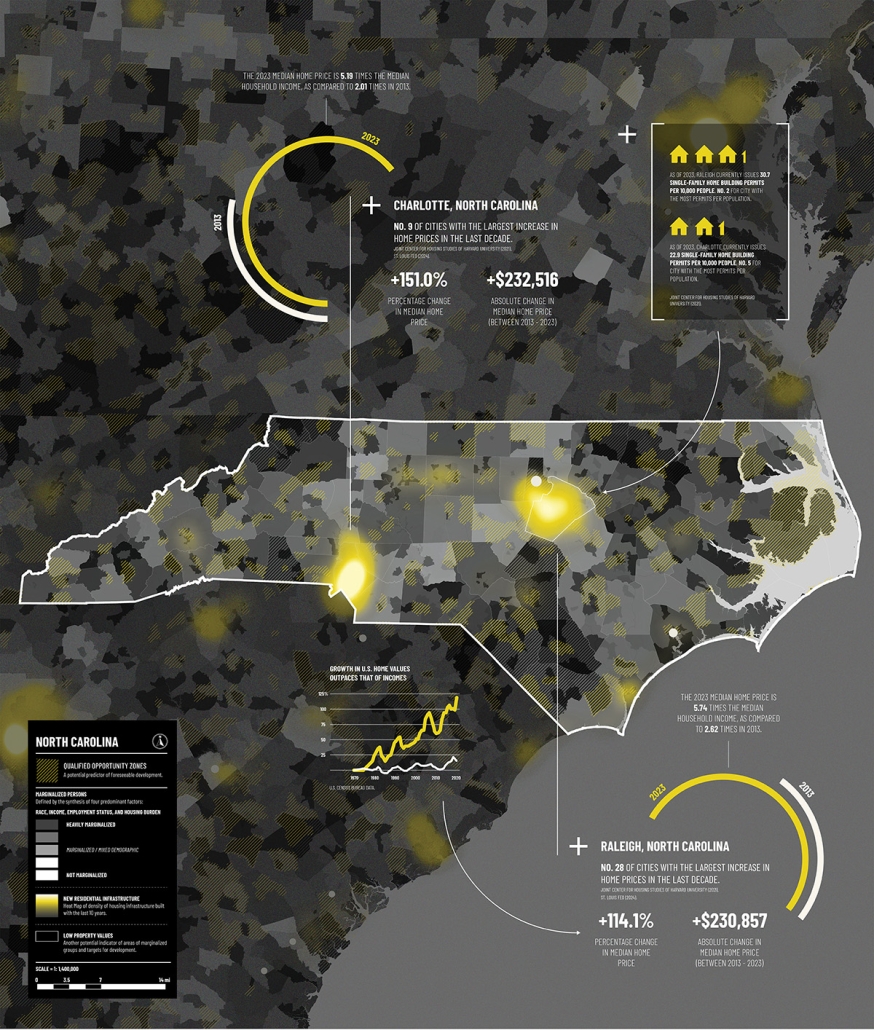
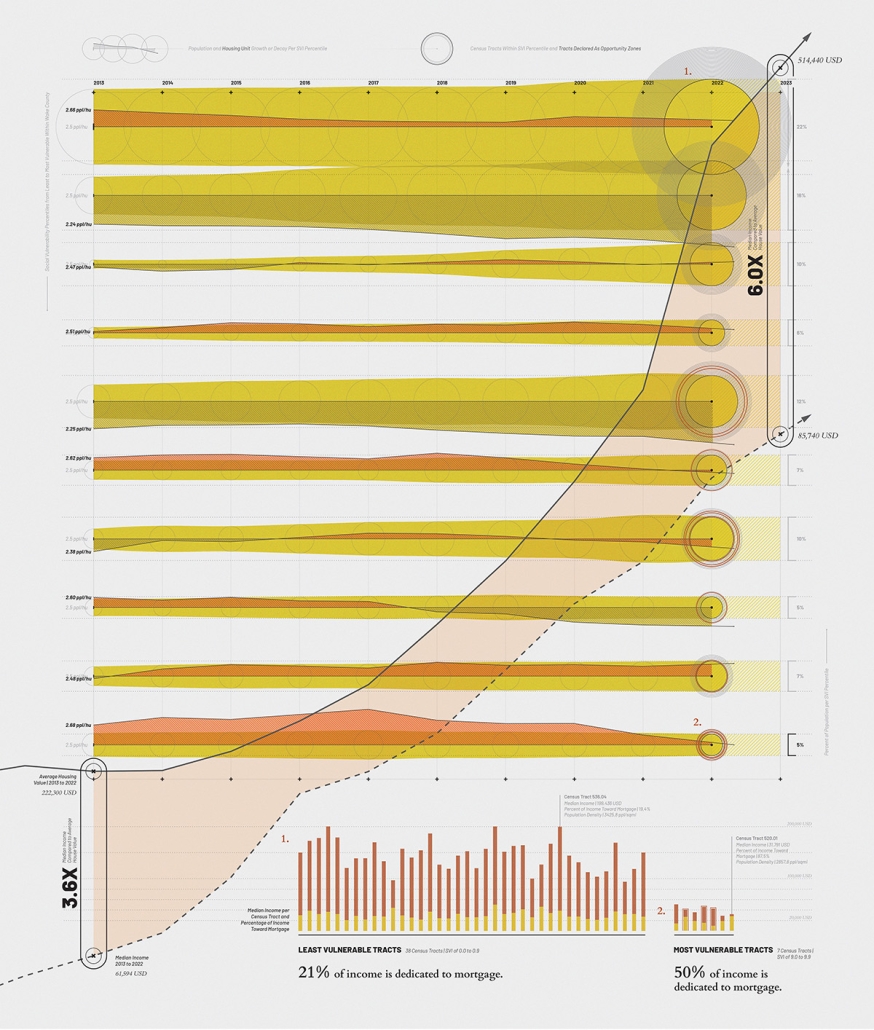
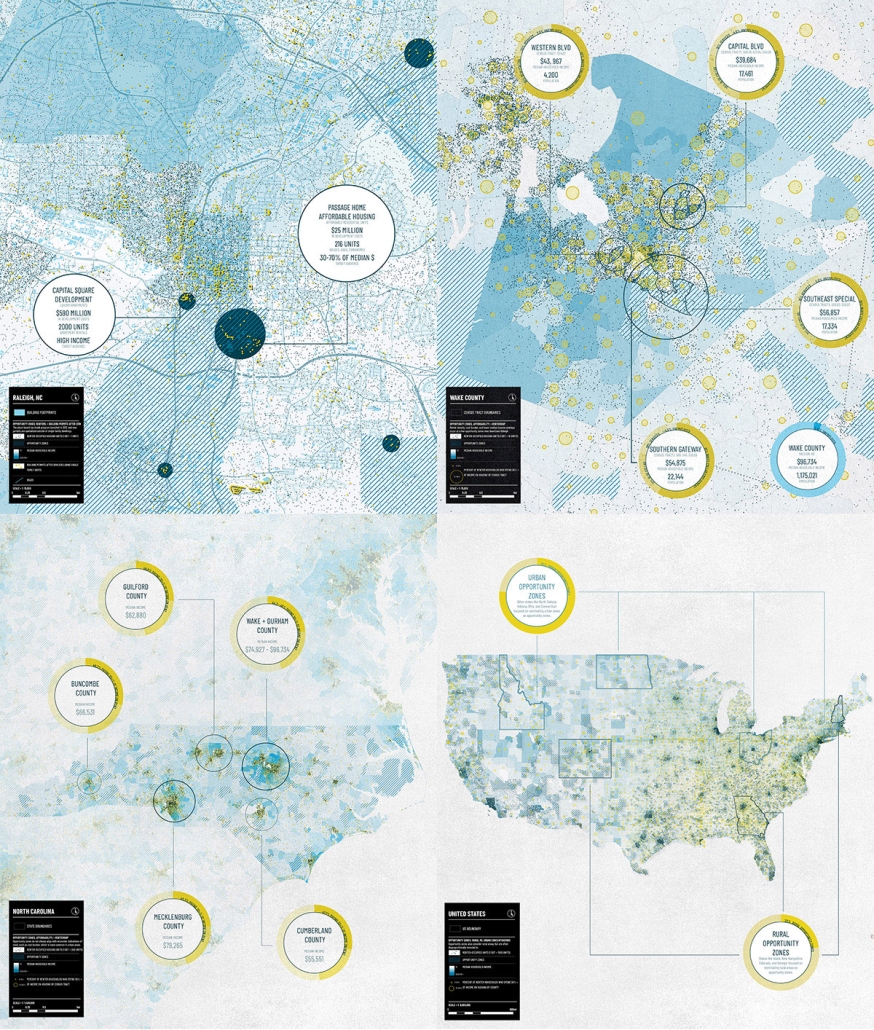
The City of New Westminster, BC, faces a number of current urban challenges. Housing affordability concerns have caused many local residents to experience housing alienation, while the rising cost of commercial properties and redevelopment pressures are increasing the cost of renting or maintaining creative spaces, pushing artists out of the area. These issues are early signs of gentrification – especially within the historic downtown – threatening local culture and identity. New Westminster is one of several historic downtowns in the Greater Vancouver Area forecast to become “a city without art” in the near future.
This project addresses four key problem areas:
- Rising housing costs
- Renovations and redevelopment
- Shift in housing stock
- Changing demographics and community identity by proposing an affordable housing project on a vacant lot, with a public library and artist studio/maker spaces at grade.
With the city of New Westminster emphasizing the importance of preserving the local community identity alongside its culture and heritage, this proposal aims to maintain and enhance this vision. Library and art facilities at grade engage with the greater public and create a vibrant community hub, while residents form a tight-knit network with one another through shared spaces. The project aims to foster interaction and a vibrant community between users who experience social, environmental, and creative alienation, while preserving and enhancing New Westminster’s arts identity.
To further revitalize this urban fabric, the project aims to increase biodiversity within the building by incorporating green spaces, gardens, and native plant species. These features enhance natural habitat, support local ecosystems, and contribute to a healthier environment, promoting both ecological balance and the well-being of residents and the public.
New Familiar by Negin Sabouhi, M.Arch ‘25
University of Southern California | Advisor: Ryan Tyler Martinez
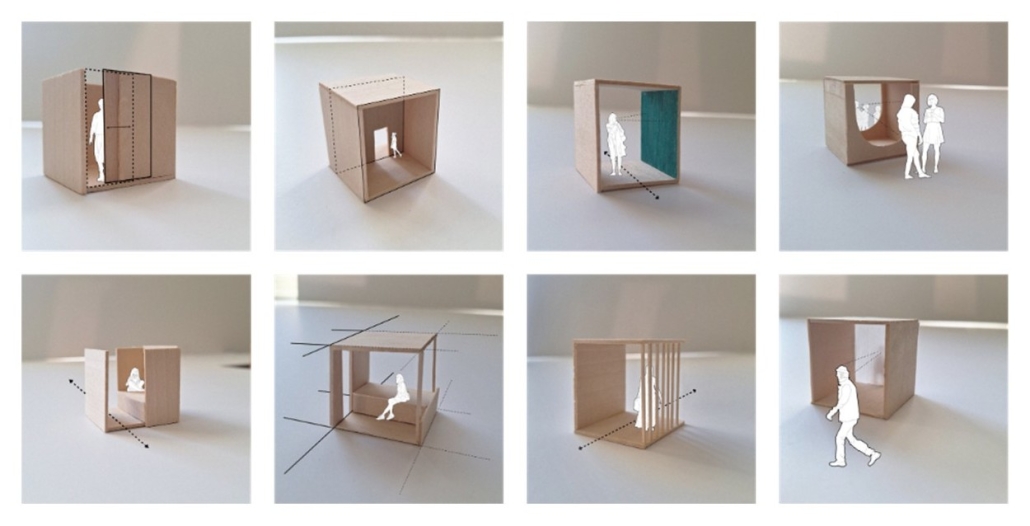
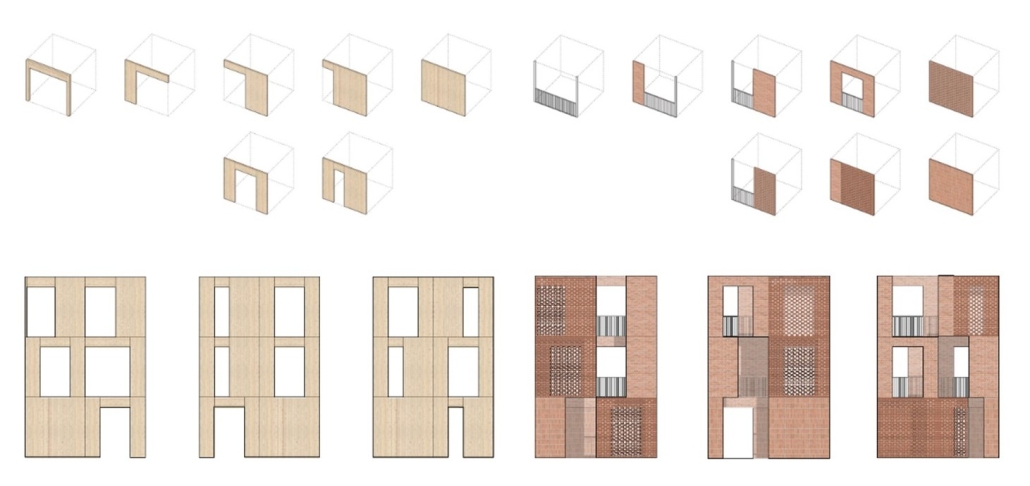
This thesis explores a speculative design methodology that recontextualizes both architectural typologies and everyday building materials through a game-like system inspired by the mechanics of a Rubik’s Cube. The project investigates the potential of ready-to-buy hardware store materials and modular housing forms to challenge conventional construction practices and spatial expectations.
By reorienting and juxtaposing iconic Los Angeles housing typologies—rotating, combining, and transforming them through a semi-cube modular system—the design generates hybrid typologies that address contemporary urban conditions with adaptability and creativity. This modular framework enables a range of spatial outcomes, where each unit is distinct yet formally related, expanding the possibilities of housing through combinatory logic.
Simultaneously, the use of off-the-shelf materials in unconventional roles—structural, non-structural, and purely spatial—problematizes the ordinary and opens new aesthetic and tectonic dialogues. Through acts of reconfiguration and reapplication, this thesis questions: What is the 21st-century version of recontextualizing everyday materials in architecture? How can reorienting common elements redefine their architectural agency?
The interactive game, featured in the “Ready to Build” section of the website, demonstrates this novel framework in action—showing how a single system can yield multiple, speculative housing proposals. In doing so, the project proposes a new design approach that is both accessible and generative, redefining how we might engage with material, form, and typology in the built environment.
This project was awarded a Distinction in Directed Design Research from the University of Southern California.
Instagram: @Negin.sabouhi, @ryantylermartinez
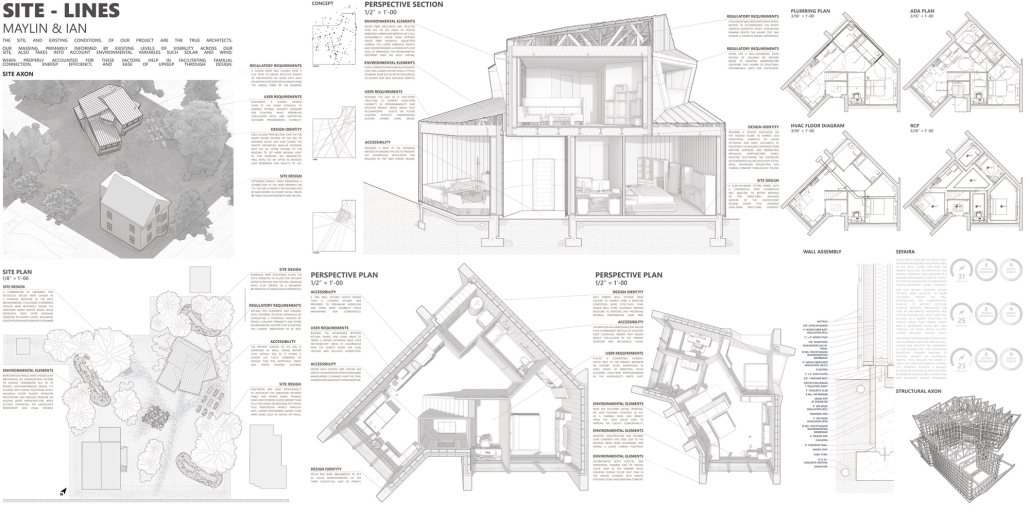
SITE-LINES by Maylin Rosales Martinez & Ian Rivera, B.Arch ’25
The City College of New York | Advisor: Damon Bolhassani
The site and its existing conditions are the true architects of our project. Our massing is primarily informed by the natural sightlines and levels of visibility across the site, while also carefully considering environmental factors such as sunlight and wind patterns. When thoughtfully integrated, these elements not only enhance family connections but also promote energy efficiency and simplify long-term maintenance through design construction practices.
This project won the Faculty Award for Academic Excellence in B.Arch Core, 3rd Year.
Instagram: @spitzerschool_ccny, @damon_bol
33/45: Mixed-Use and Architectural Recycling in Querétaro’s Historic Center by Daniela Rivera Ruiz, B.Arch ’25
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Guillermo Márquez, Patricia Cutiño, Jorge Javier
“33/45” is a mixed-use architectural recycling project located in the historic center of Querétaro, México. It addresses two urgent urban issues: the lack of affordable housing and the increasing gentrification of the area. In recent years, working-class residents have been pushed out due to rent prices up to six times higher than the average monthly income in the city.
This project proposes an alternative: a dignified, inclusive housing model rooted in cultural heritage and community resilience. The property is owned by the government, allowing for rent regulation and fair, affordable prices. This strategic intervention offers high-quality living spaces that help stabilize and counterbalance the rising costs in the area, making it possible for local people to remain and thrive, restores five abandoned historic houses—protected by the INAH (National Institute of Anthropology and History)—and transforms them into 14 housing units and 20 commercial spaces. These ground-level homes and businesses aim to rebuild the urban fabric while ensuring affordability and accessibility for the local community.
Built with traditional Mexican construction techniques, such as brick vaults and modular layouts, the design honors its architectural heritage while remaining efficient and replicable. The materials—warm, familiar, and deeply rooted in Querétaro’s identity—create inviting, cozy spaces that feel like home. Every detail was considered to enhance comfort, daylight, and ventilation, crafting spaces where people can live with dignity. The ground floor becomes a shared threshold between public and private, offering patios and semi-open areas that invite connection and community. The layout draws from urban theories like in-between and rich order to create spatial richness and intimacy within a compact footprint.
“33/45” is more than a housing project—it is a social statement. It challenges speculative urban development and defends the right to stay, belong, and build a future in the place one calls home.
Instagram: @arqui_en_progreso, @dani_riverar, @arquitectura_anahuac, @arqwave
MUTUA collective housing by Jimena Borbón de la Torre, B.Arch ’25
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Guillermo Márquez, Patricia Cutiño, Jorge Javier
This project presents a cooperative housing model in the heart of Querétaro, designed to adapt to the changing needs of its residents over time. The homes are built with the possibility of expansion, allowing families to grow and modify their spaces as their needs evolve. A key aspect of this model is the active participation of residents in the construction process. By working directly with materials such as wood, participants not only build their homes but also acquire valuable construction skills, opening up opportunities for self-sustainability through this new trade.
At the heart of the design are the shared spaces, which foster a sense of community and connection. These common areas promote interaction, mutual support, and shared responsibility among neighbors, creating a vibrant and inclusive environment. This project goes beyond housing—it’s about building community, empowering residents, and creating a space where everyone feels a part of it.
Mútua is aimed at all those living in Querétaro who have limited financial resources, own no other property, face difficulties accessing housing in the traditional market, and are willing to join a cooperative. The target audience is people between 20 and 40 years old, interested in living in a strategic urban environment like downtown Querétaro, with immediate access to services, transportation, and commerce. People are willing to commute without a car and use alternative means of transportation.
The project is aimed at those seeking a compact and flexible first home, who are willing to share common areas such as the kitchen, living room, laundry room, and workspaces.
Instagram: @jb_arq_, @arquitectura_anahuac, @arqwave
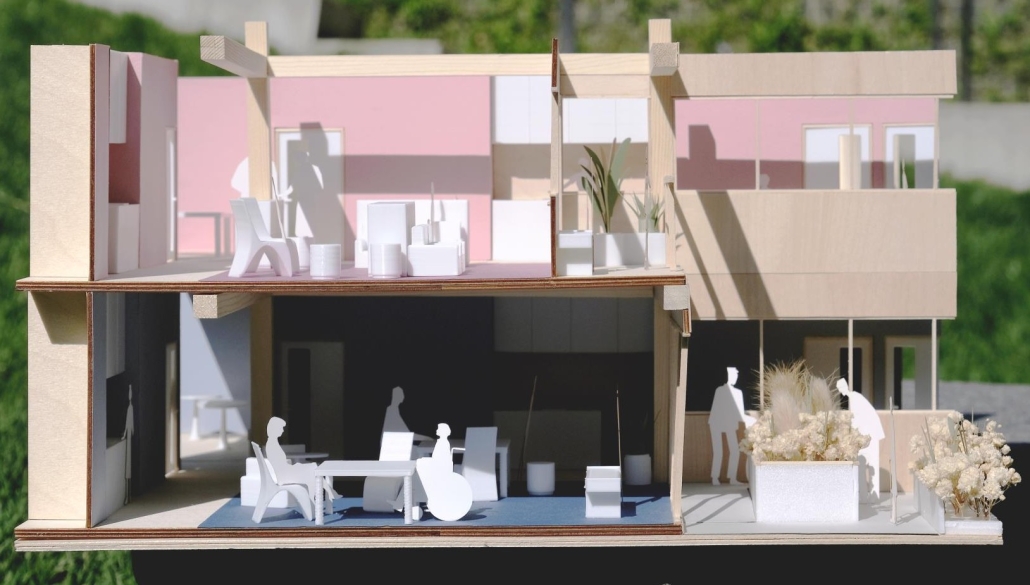
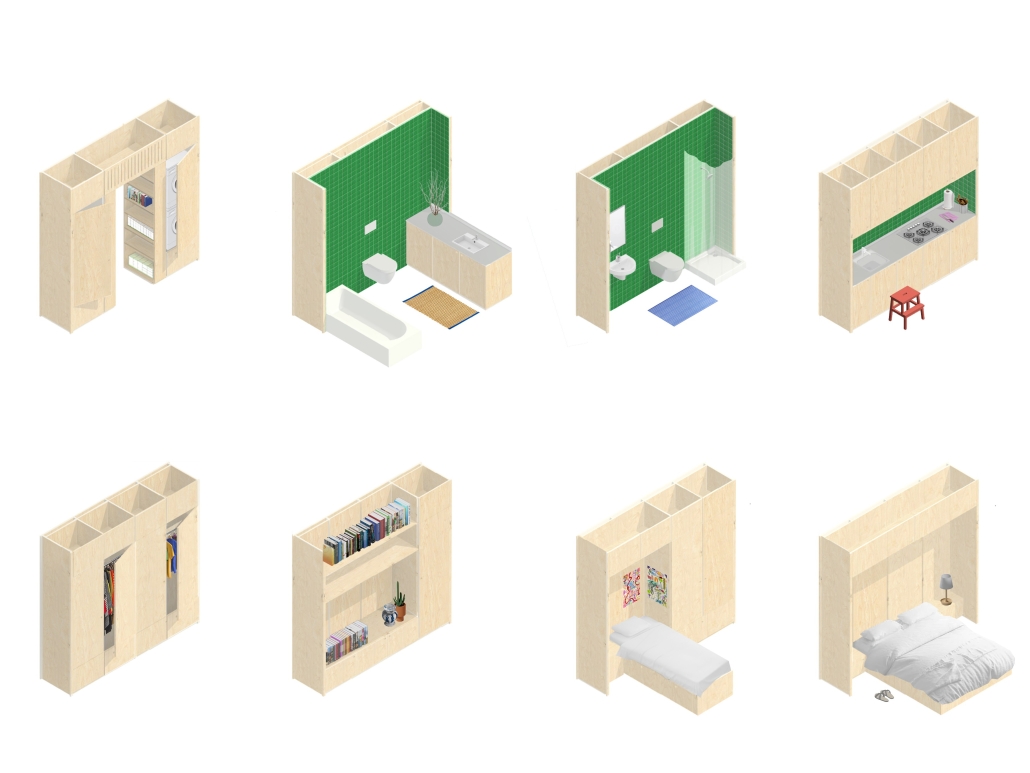
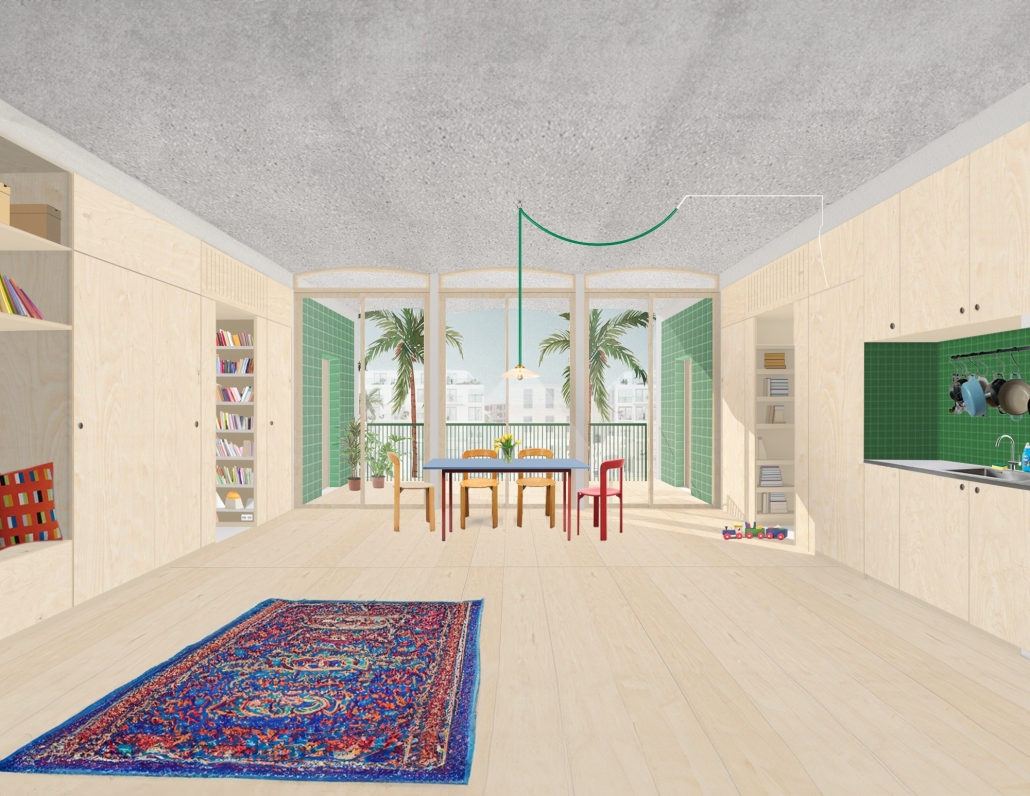
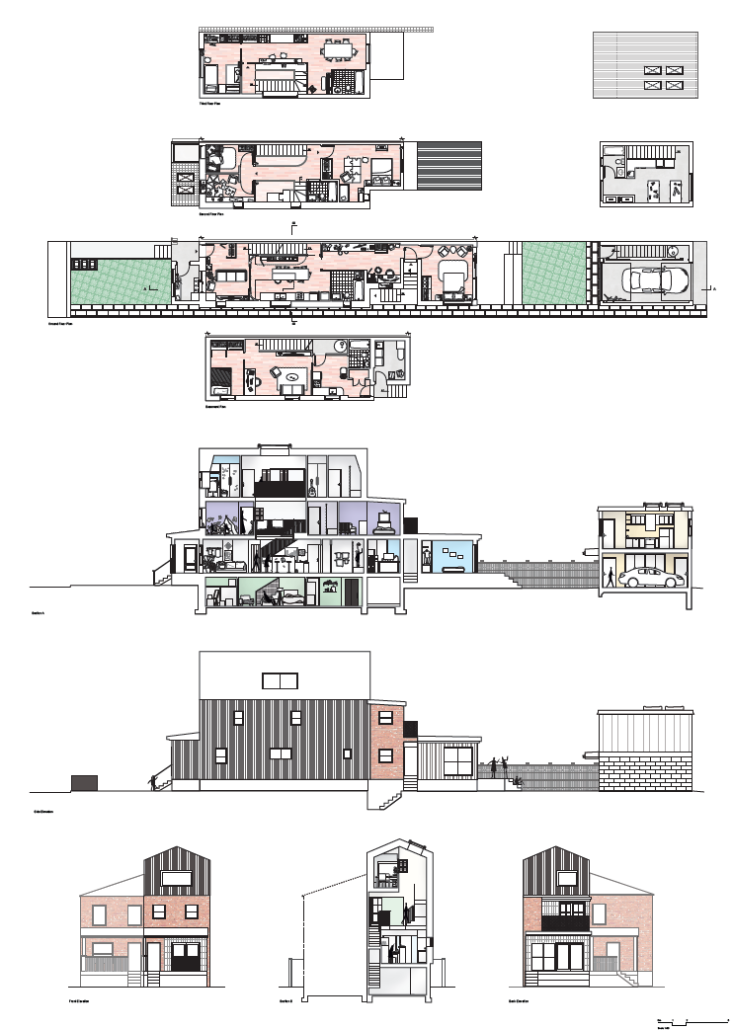
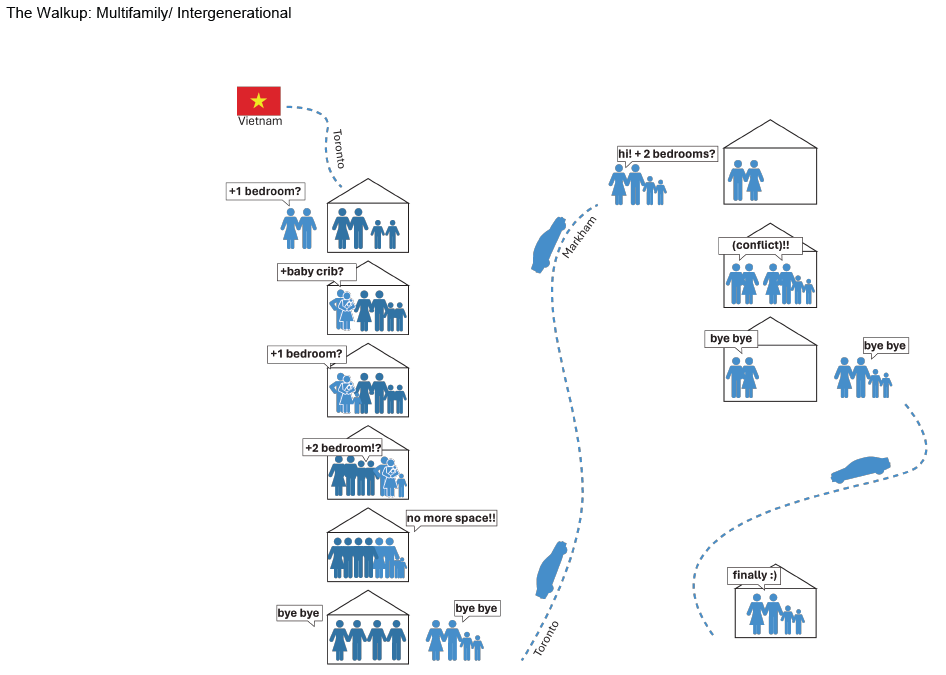
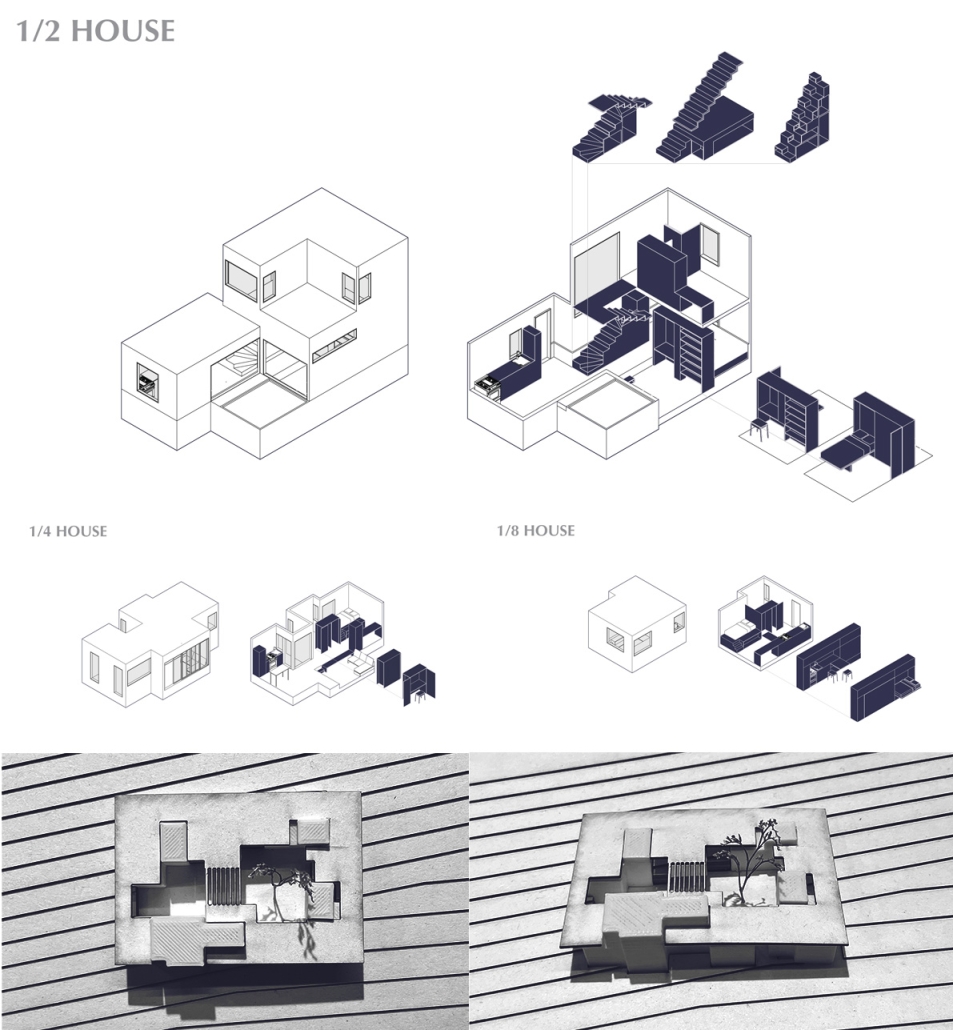
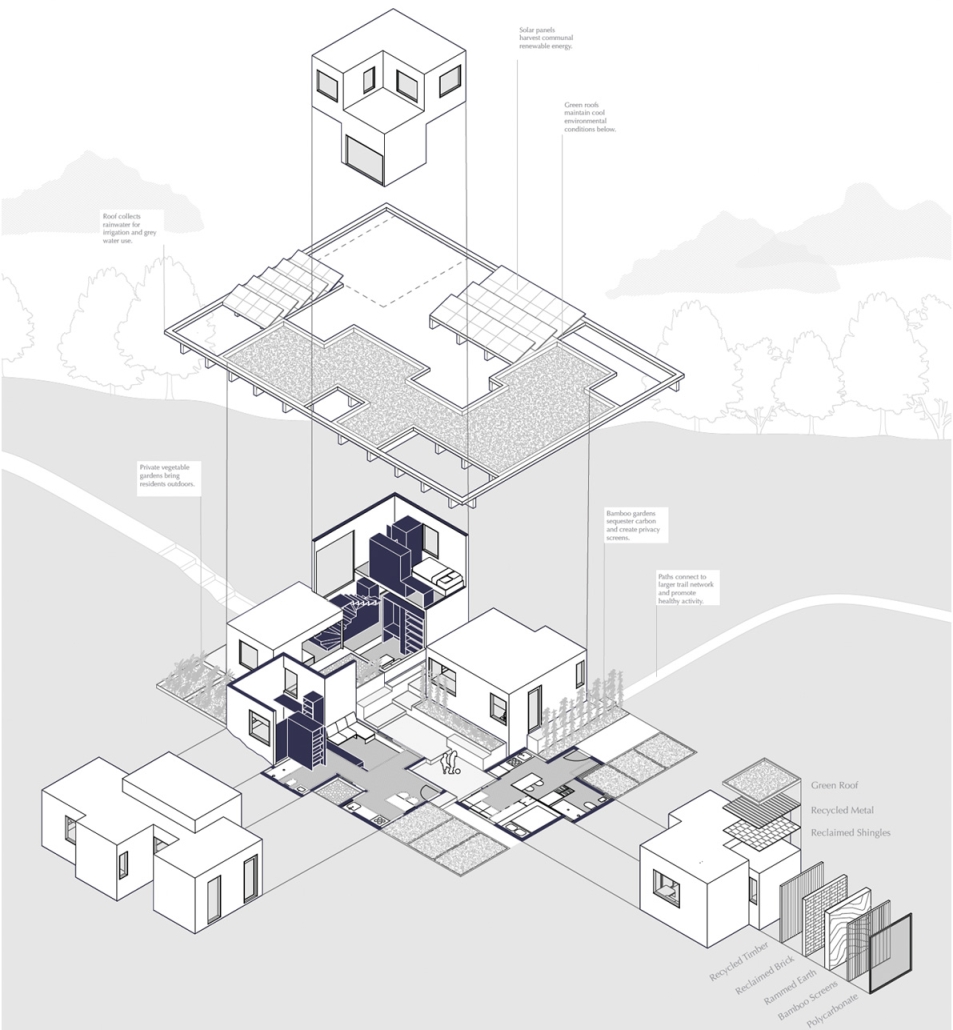
Home in Flux: Reclaiming Homes for Co-Living by Jennifer Nguyen, M.Arch ’25
University of Toronto | Advisor: Karen Kubey
The single-family home is dying; but the single detached home is ready to be reborn. “Home in Flux” reclaims Toronto’s detached homes as adaptable spaces for intergenerational, multigenerational, and collective living, supporting contemporary and future ways of life. Where Toronto’s housing stock once met resident needs, it is now financially unattainable and spatially inadequate.
Housing is a human right, and homes must evolve with their households. Disrupting conventional spatial patterns, the project inserts flexible spaces into existing housing stock to adapt to shifting families, cultures, and needs. “Home in Flux” provides residents with agency and belonging.
Instagram: @kjenn.n, @karenkubey
Tucson Hope Factory Micro Shelter Project by Yasmina Dashti, Caro Durazo, Souhayla Farag, Ashlea Hume, Graciela Keymolent, Christian MacKay, Daniela Navarro, Olivia Nelson, Chloe O’Hail, Alberto Ramirez, Berenice Ramos Pena, Alondra Rodriguez, Mariana Rodriguez, Josh Russell, Jordan West & Connor Worley, B.Arch ’25
University of Arizona | Advisors: Teresa Rosano & Greg Veitch
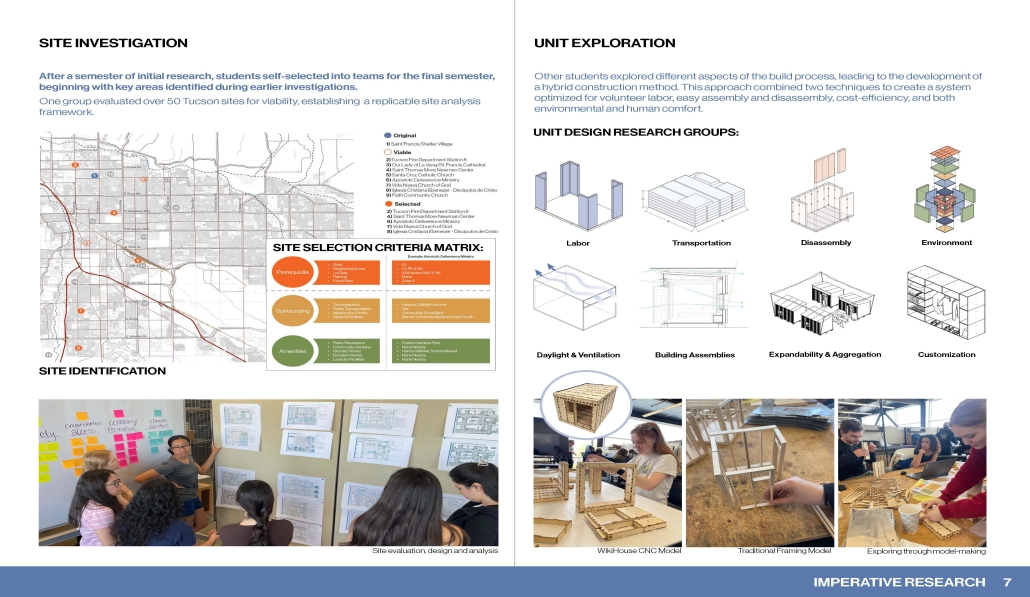
The Community Design & Action Capstone Studio engaged 16 fifth-year architecture students from the University of Arizona in designing transitional micro-shelter villages, in collaboration with Tucson Hope Factory and the Drachman Institute. Rooted in trauma-informed and community-based design, the studio addressed housing insecurity through inclusive, service-learning pedagogy.
Across two semesters, students investigated root causes of homelessness, conducted site analyses, and proposed scalable solutions for villages of 10–40 units. They evaluated over 50 Tucson sites, ultimately producing master plans for five viable locations and developing a replicable framework for future implementation. A modular micro-shelter prototype emphasized climate responsiveness, cost-efficiency, and ease of volunteer-led assembly.
Centering lived experience, students engaged directly with unhoused individuals—including veterans and women—as well as nonprofits, service providers, and faith-based partners. A pivotal trip to Seattle included collaboration with Sound Foundations NW (which reports a 63% success rate transitioning residents to permanent housing) and hands-on construction of a tiny home. Students also drew insights from the University of Washington’s Design-Build Studio and Habitat for Humanity’s CHUCK Center.
Throughout the process, students crafted detailed construction guides and prototyped a full-scale shelter to test environmental performance and feasibility. The design prioritizes privacy, safety, and community—balancing individual dignity with collective support.
As one student reflected, “I really appreciated the community aspect of this project, having a real client and really feeling like there was a real project that is making a difference.” A community member echoed: “This is a beautiful project coming to life. I am very proud of the University for being part of this. I am thankful that many lives are being impacted!”
Exemplifying the power of inclusive, community-driven design, the initiative has garnered media attention, secured grant funding, and positioned itself as a scalable model and catalyst for zoning reform in Tucson and beyond.
Instagram: @_carood21, @souhayla_farag, @oliviatnelson, @bere.ramoss, @alondra_rodriguez_j, @mmariandreaa, @jrussell_tm, @jordaan.west, @cj_the_prodigist, @teresarosano
Parametric Housing Aggregation Model – PHAM by Hunter Wells, D.Arch ’25
University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa | Advisor: Karla Sierralta
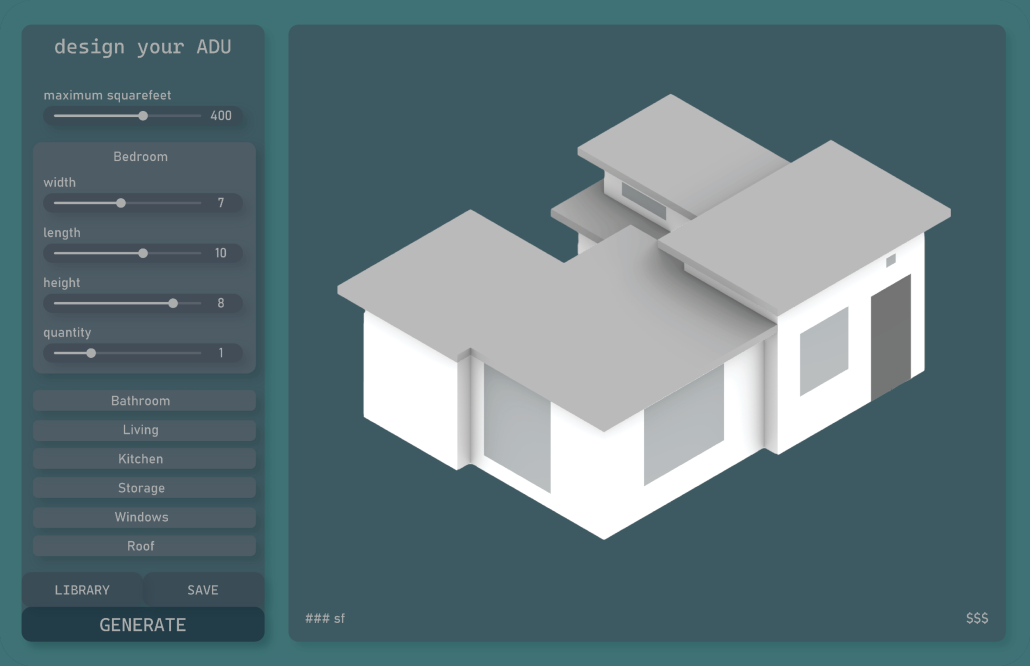
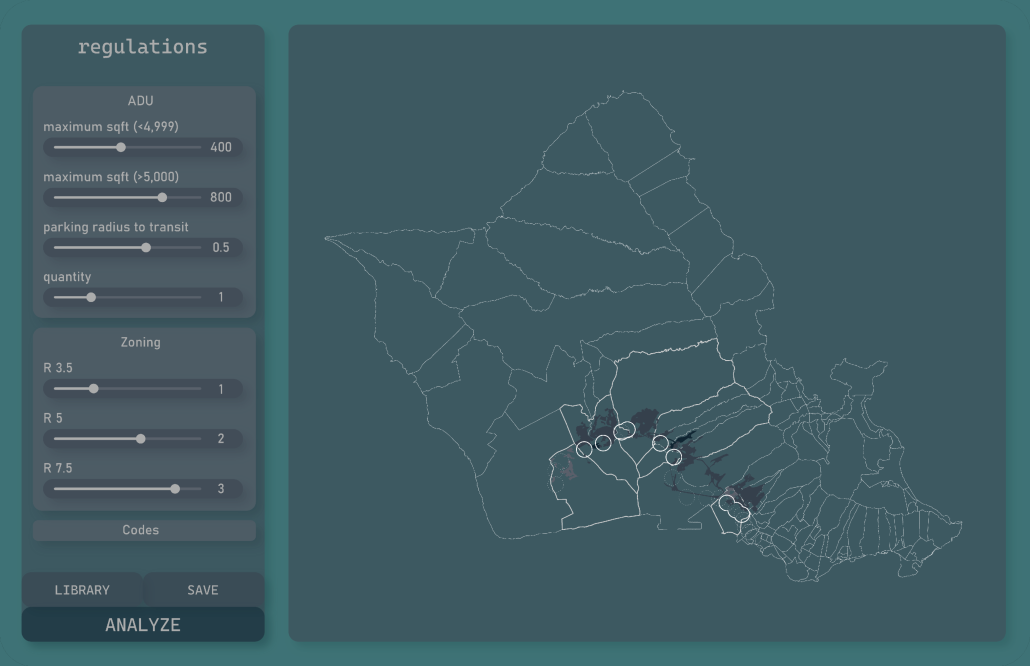
This project reimagines how we design housing in Hawai‘i, starting with one of the most promising solutions: the Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU). In response to the state’s ongoing housing crisis, the Parametric Housing Aggregation Model (PHAM) is a digital tool that helps homeowners, designers, and policymakers rapidly generate ADU designs that are affordable, space-efficient, and culturally grounded.
At its core, PHAM transforms zoning codes, lot dimensions, and programmatic needs into a flexible design language. Using parametric modeling software and modular components such as bedrooms, kitchens, and bathrooms, the system can generate hundreds of unique ADU configurations based on user inputs like room dimensions, site location, and layout adjacencies. Each option is evaluated in real time for spatial efficiency and estimated construction cost, grounded in localized data from Hawai‘i’s building market.
To bridge technical design with architectural character, the model also integrates AI visualization tools that help communities and designers visualize how ADUs might blend with the island’s built and natural environments. This creates a dialogue between form, culture, and cost, allowing for design solutions that are not only efficient, but place-based and aspirational.
The tool also includes a planning interface where policymakers can explore how changes in zoning or proximity to transit might affect where and how ADUs can be deployed. Ultimately, PHAM functions as both a generative engine and a decision-support platform, empowering homeowners, designers, and city officials to work together toward more resilient and equitable housing futures in Hawai‘i.
This project received the 2025 ARCC King Student Medal – For Excellence in Architectural + Environmental Research.
Instagram: @thewellsdesign, @ksierralta
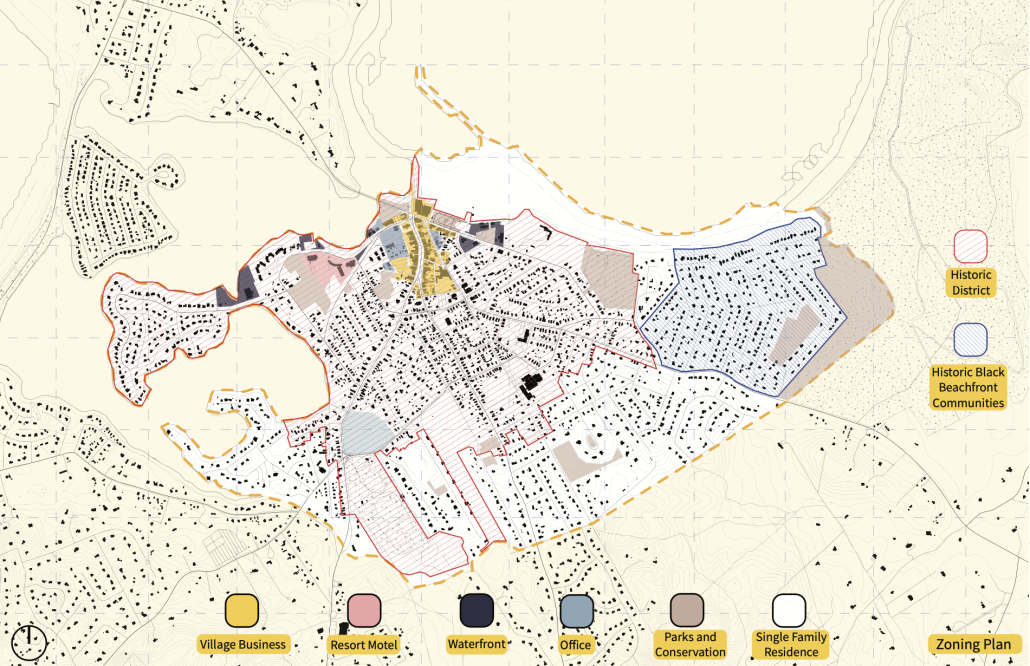
Pathways to Sustainability: Densifying Sag Harbor by Maxamillion Foley & Samie Zia, B.Arch ’25
New York Institute of Technology | Advisor: Dongsei Kim
Sag Harbor, a scenic East End village on Long Island, has become increasingly unaffordable due to unsustainable zoning and development practices. Current regulations require minimum lot sizes of over 20,000 square feet, but only 25% of each lot can be developed, which raises housing costs and results in land being underutilized.
Although there are 2,100 housing units, only half are occupied year-round, and many local families face rising costs for housing, energy, and transportation. Large-lot zoning has also displaced small businesses and increased reliance on private cars, which has contributed to population decline, especially among younger residents who often do not return after college due to a lack of affordable options.
Our proposal introduces zoning reforms to support denser, more affordable housing without displacing current residents. By reducing maximum lot sizes to 10,000 square feet and targeting underused parcels, we outline three infill strategies to double or triple housing density while preserving the village’s character. These homes will be designed with environmental considerations in mind, including solar orientation, flood risks, and energy-efficient materials.
We also suggest expanding public transportation by adding four new bus stops and a local shuttle system to decrease car reliance and connect residents to jobs and services. Stops will feature bike storage, solar collection, and small amenity spaces. These changes aim to lower financial burdens, enhance accessibility, and create a replicable model for sustainable growth across the East End.
This project won the Faculty Thesis Award.
Instagram: @dongsei.kim
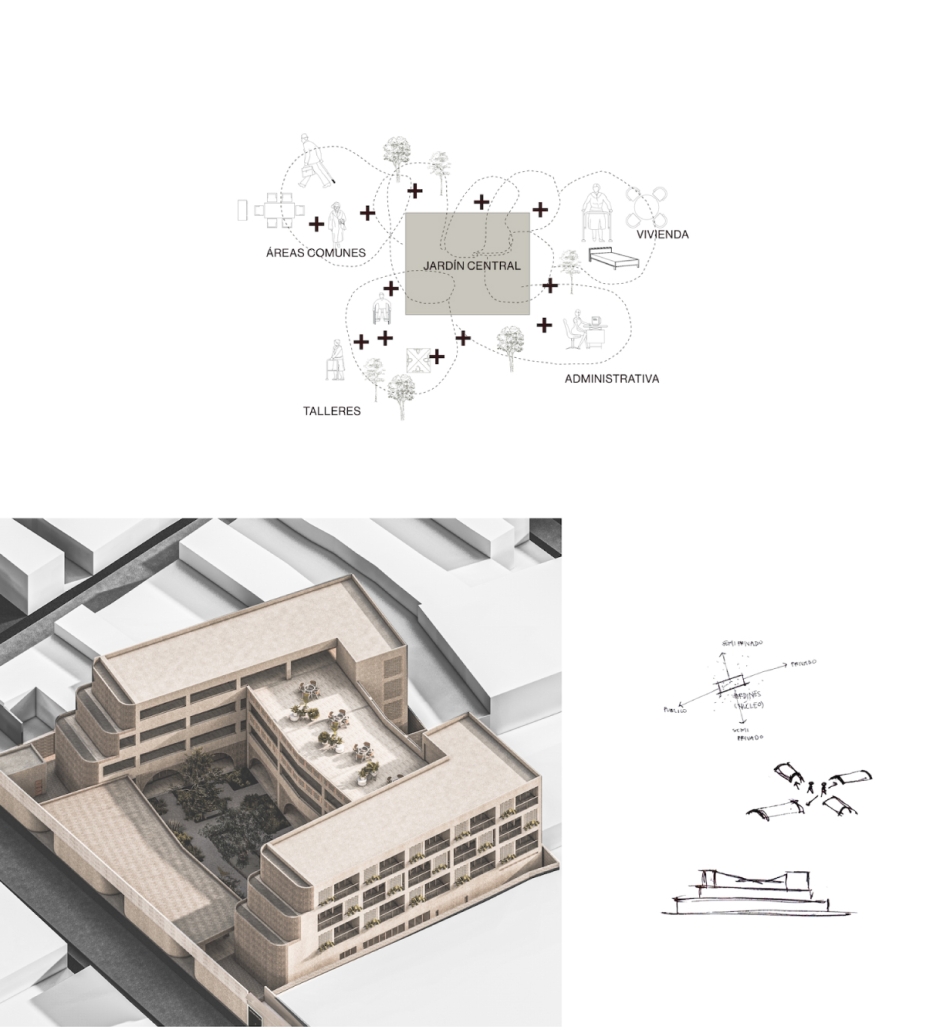
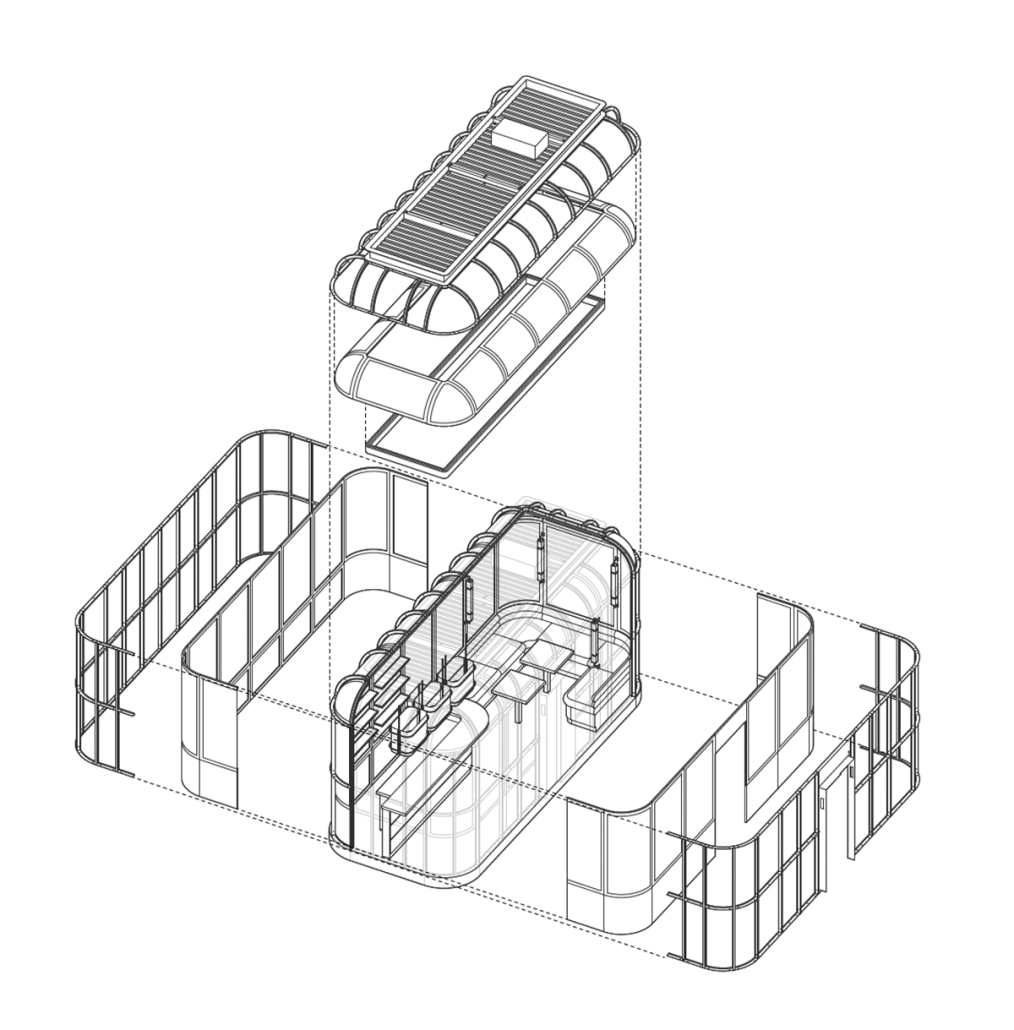
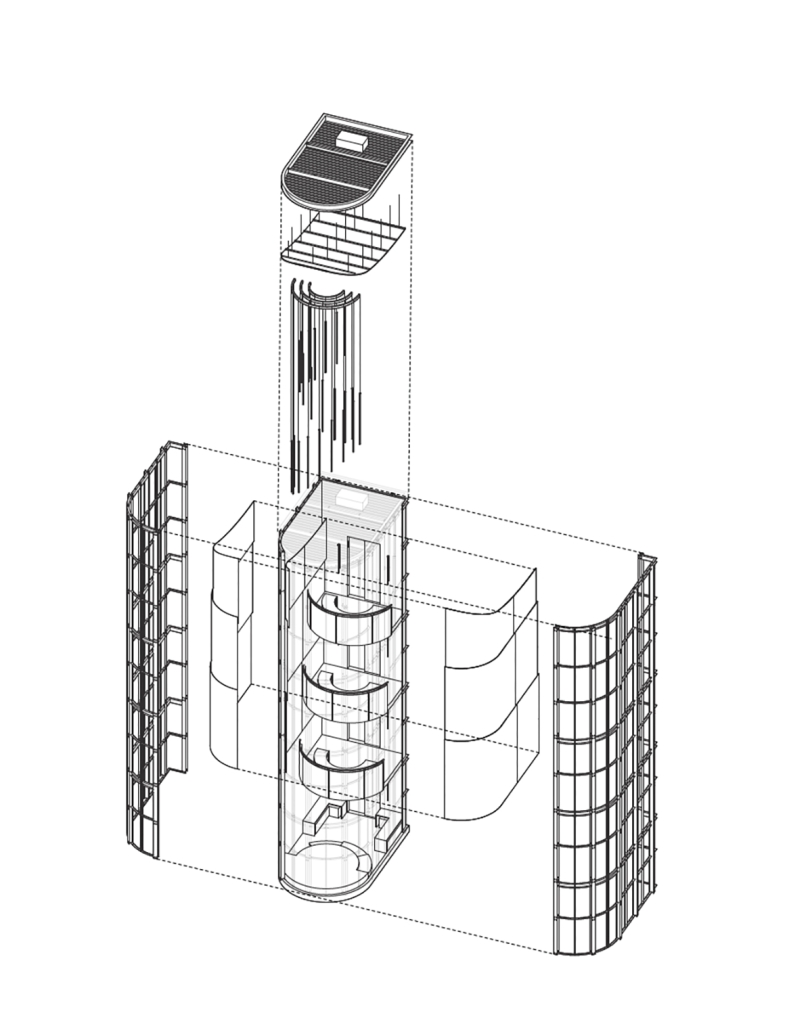
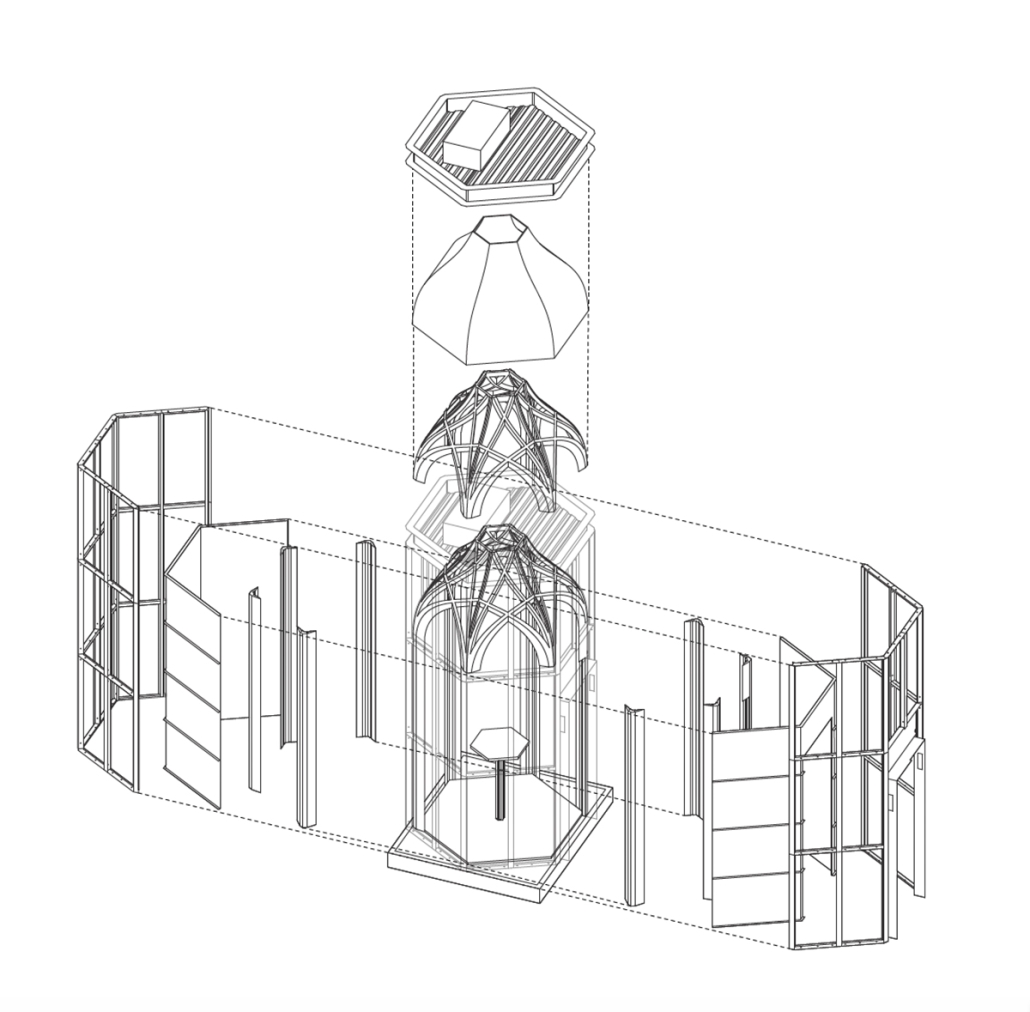
Fädi, House for the Elderly by María José Castaños Murillo, B.Arch ’25
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Guillermo Márquez, Patricia Cutiño & Jorge Javier
The Fädi House concept symbolizes the stages of life through a play and intersection of architectural volumes, each representing a different phase of our lives. The design is conceived as a habitable sculptural piece, where transitions between spaces reflect the passage of time and personal evolution.
We spend every year of our lives trying to live longer and have more retirement years, but we don’t think deeply about how we’ll make those years truly worthwhile, where we will spend those final years.
At the heart of the project, the central gardens act as the symbolic core, representing the purpose and roots of life, while a conceptual bridge links nature with the living spaces, promoting a harmonious integration between humans and their environment.
The arches, inspired by Querétaro’s historic centre, act as portals that link to the interior spaces with nature, evoking the city’s colonial architecture and reinforcing a sense of cultural belonging. By crossing these arches, residents not only connect with the architecture of the project, but also with the history and identity of Querétaro, feeling that they are part of a heritage that transcends generations. The design of patios, gardens, terraces, and other green areas in spaces designated for older adults offers a valuable opportunity to promote social gatherings, participation in group activities, and the creation of spaces for social interaction. These areas seek to minimize feelings of loneliness while promoting well-being and strengthening social interaction in harmony with nature.
Instagram: @mariajoseecm, @archbymj, @arquitectura_anahuac, @arqwave
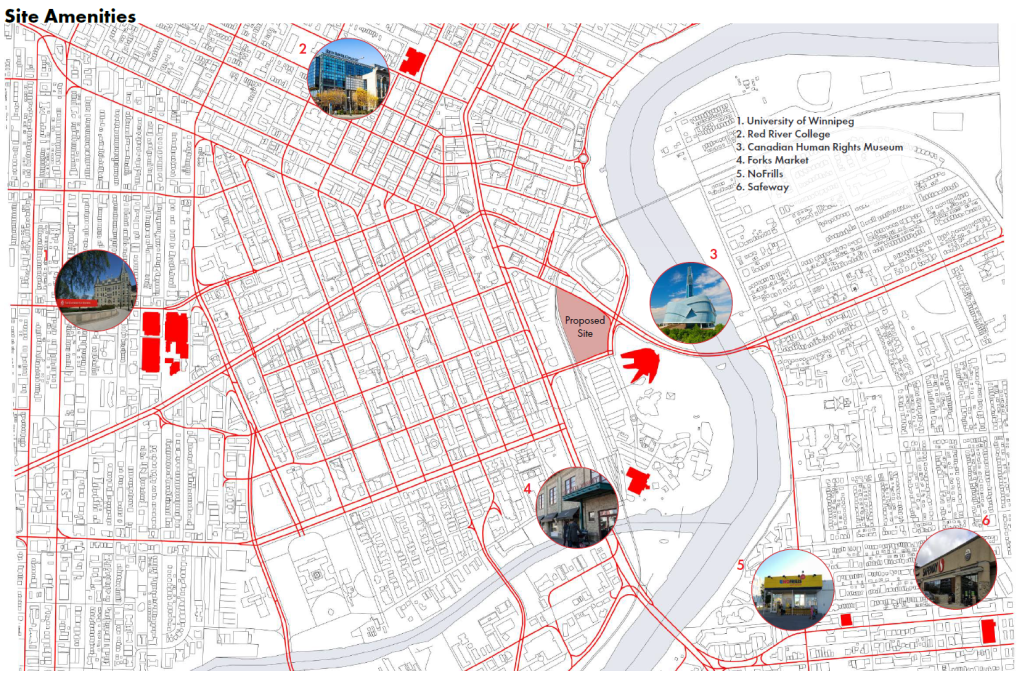
A Journey Towards Home: A Holistic Approach to Indigenous Youth Homelessness in Winnipeg, Manitoba by Jordan McKay, M.Arch ’25
University of Toronto | Advisor: Karen Kubey
Winnipeg, Manitoba, is home to the highest population of Indigenous people in Canada. Unfortunately, Indigenous youth make up 84% of all Winnipeg youth experiencing homelessness. Utilizing an Indigenous-led approach, “The Journey Towards Home” creates an intentional and purposeful housing space that challenges the colonialist definition of homelessness and alleviates its impact on our youth.
The space fosters an environment for reconnection to land, culture, community, ceremony, and growth within the urban fabric. Emulating the path of the Red River, this multi-use mid-rise residential project promotes growth and healing by creating culturally adequate spaces for learning, connecting, and ceremony within the built form and the landscape. The project houses youth, live-in mentors, and elders and provides built-in services, programs, and amenities.
Instagram: @jmckay43, @karenkubey
Harbor: A Safe Haven that Fosters Growth and Creativity by Mayowa Odunjo & Brenda Meloto De Oliveira, B.Arch ’25
Kennesaw State University | Advisor: Robin Puttock
“Harbor” creates a safe haven that fosters growth and creativity. The design aims to bring people in and create exciting and engaging spaces.
Instagram: @mayze.o, @brendameloto, @robinzputtock
Re-Itera, Collective Housing by Sebastián Mercado Zaldivar, M.Arch ’25
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Guillermo Márquez, Patricia Cutiño & Jorge Javier
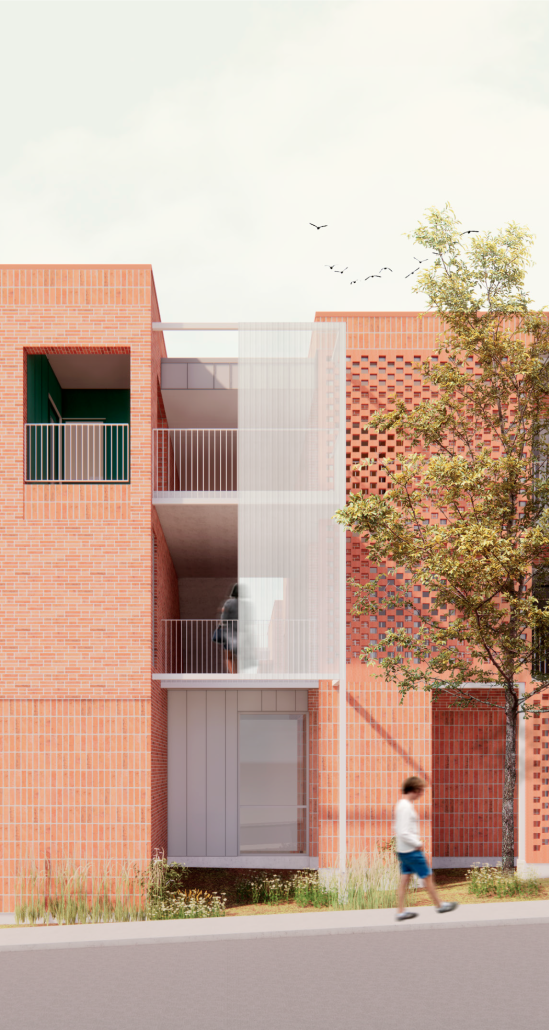
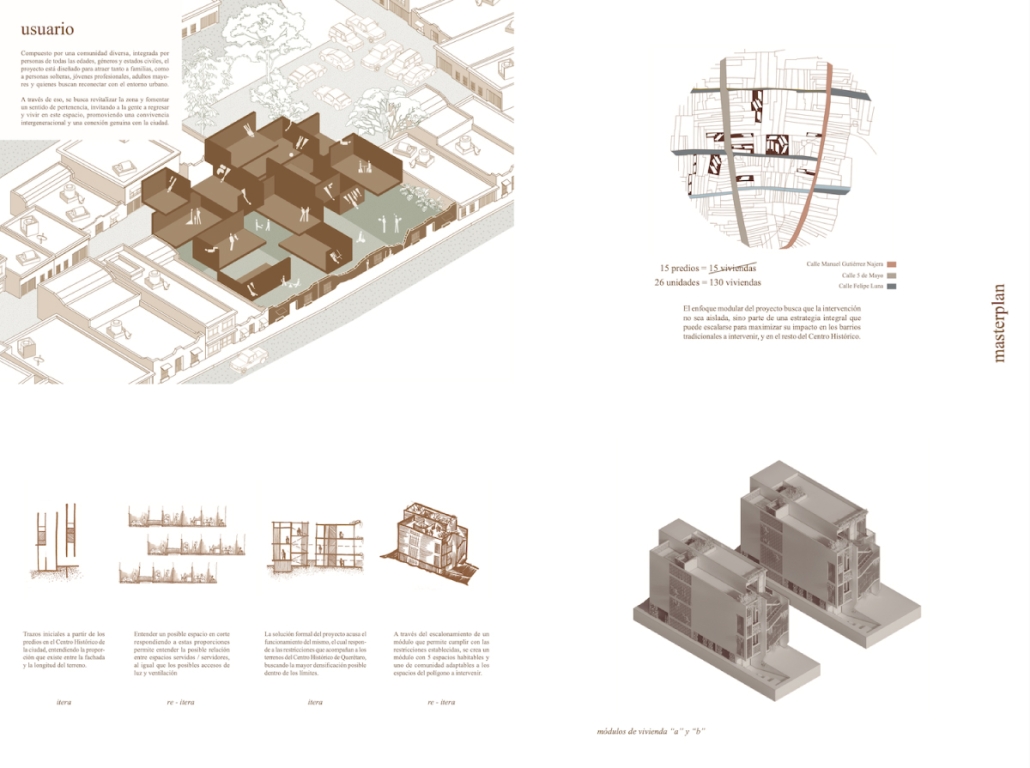
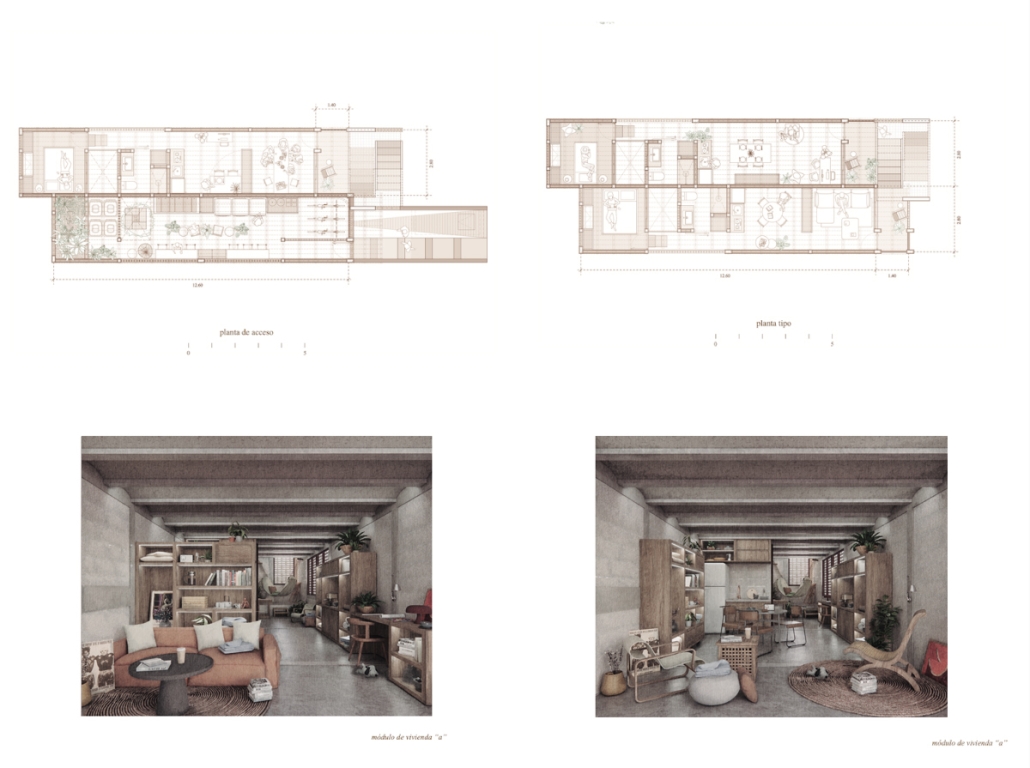
The reuse of abandoned lots within the Historic Center of Querétaro is the starting point of an urban strategy aimed at reversing the physical and social deterioration of the area. “Re-itera” proposes an affordable, flexible, and site-specific collective housing typology, capable of adapting to the specific conditions of each lot and the transformations of the inhabited environment. The project introduces a replicable, adaptable housing module designed to respond to the physical, historical, and regulatory constraints of the site while enhancing the built environment.
Each module is configured linearly and comes in two typologies: Type A, which consists of three meters in width and forty square meters, and Type B, of 4.5 meters in width and sixty square meters. Both maintain a depth of fourteen meters and distribute five dwellings along with communal spaces on the semi-basement and rooftop levels. A system of staggered half-levels enables vertical compactness, allowing for compliance with the 7.5-meter height limit imposed by local heritage authorities. The layout centralizes kitchens and bathrooms to optimize infrastructure, while a longitudinal void ensures cross ventilation and natural lighting in every unit.
The structure is based on a rigid frame system composed of reinforced concrete columns and beams. The floor system uses joist and vault construction, with precast concrete dovetail-shaped vaults, reducing construction time and cost, embracing a material honesty that aligns with sustainability goals.
The ensemble located on Felipe Luna Norte #22 demonstrates the system’s potential: an underused lot is transformed into 35 new housing units across seven modules—where only four existed before—while preserving historic facades and reinforcing the neighborhood’s character. Shared spaces, including dual-purpose parking and recreational areas, encourage community interaction.
Rather than imposing new urban forms, Re-itera integrates sensitively into the existing fabric. Its modular logic allows it to densify responsibly, adapt to irregular lots, and preserve architectural heritage. More than a housing solution, it offers a scalable model for urban regeneration—revitalizing neglected areas, fostering inclusivity, and enhancing quality of life through contextual and sustainable design.
Instagram: @elarquitonto, @arquitectura_anahuac, @arqwave
Co-Care Lodge: Community-Focused, Cohousing Care Homes in Toronto by Ho Yeung Miu, M.Arch ’25
University of Toronto | Advisor: Karen Kubey
“Co-Care Lodge” responds to the urgent need for tailored, affordable housing solutions for Toronto’s aging population. Since COVID-19, many city-operated elderly care facilities have become under-maintained, with some facing demolition. The project offers a new intergenerational, care-based cohousing model that reimagines the relationship between older adults, caregivers, and their families.
Through unlocking infill opportunities in established neighborhoods and integrating shared indoor and outdoor spaces, the Lodge integrates new care residences without extensive land acquisition and reduces costs while fostering stronger community ties across roles and generations. Co-Care Lodge embraces a sustainable and replicable building approach that prioritizes economical, durable dwellings that promote long-term community integration while challenging the outdated “warehousing” of seniors.
This project won the University of Toronto Daniels Faculty Design Prize.
Instagram: @o.en.mo._, @karenkubey
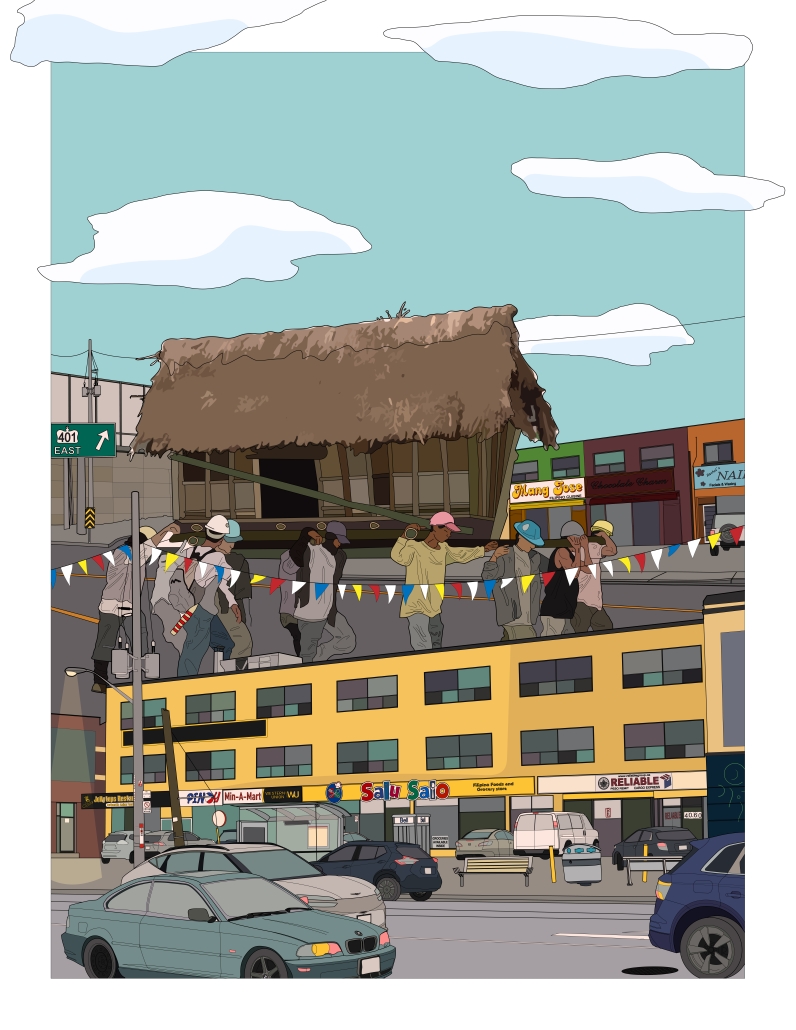
Balikbayan: Creating a Sense of Place through Housing by Julia Buli-e, M.Arch ’25
University of Toronto | Advisor: Karen Kubey
“Balikbayan” housing celebrates Filipino cultural identity and fosters community in Toronto’s Little Manila. Facing unaffordable housing and limited flexible spaces, Filipino immigrants have created a vibrant hub. This proposal reimagines balikbayan – Tagalog for “return home” – by adapting traditional Filipino residential typologies, like the “compound,” to a high-density Canadian setting.
A mid-rise building incorporates familiar design elements to enhance belonging. Using a limited-equity cooperative model, Balikbayan promotes multigenerational living, stability, and inclusivity. The project balances cultural heritage with contemporary urban needs, offering affordable, accessible housing that strengthens community ties. Incorporating live-work and “compound” housing units, Balikbayan is informed by interviews with Filipino Torontonians.
This project won the Irving Grossman Prize.
Instagram: @buli.e, @karenkubey
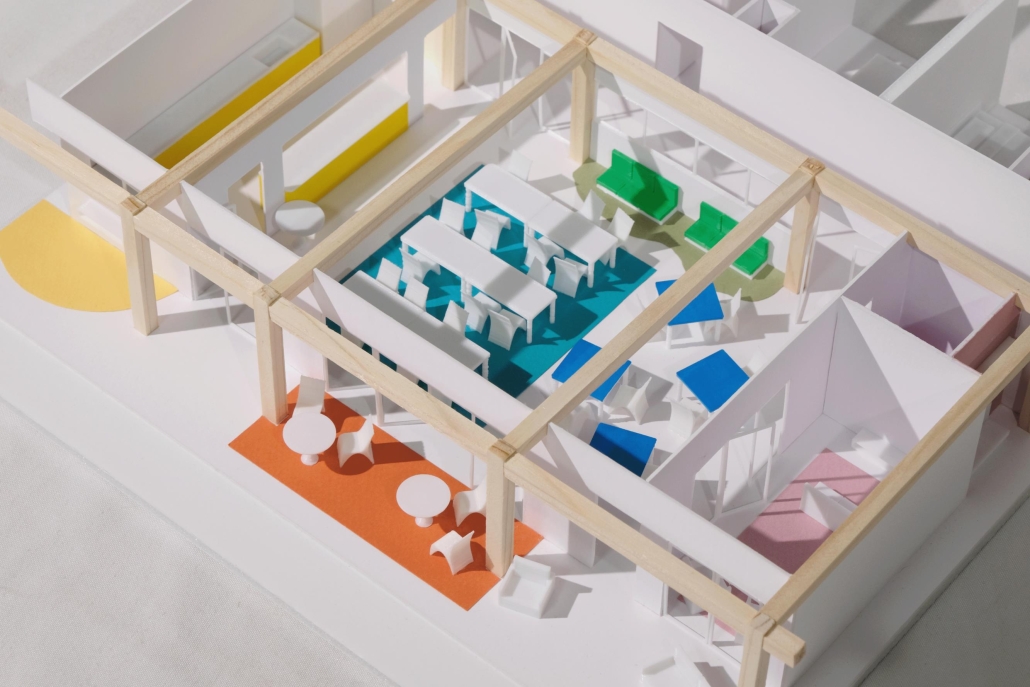
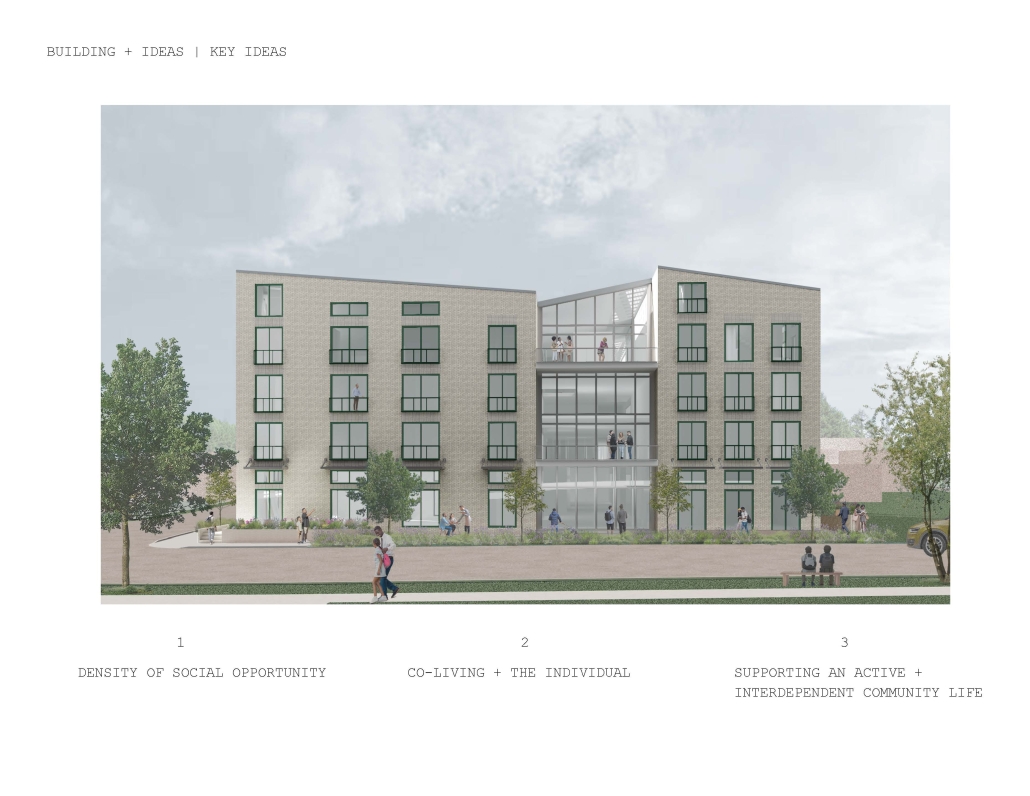
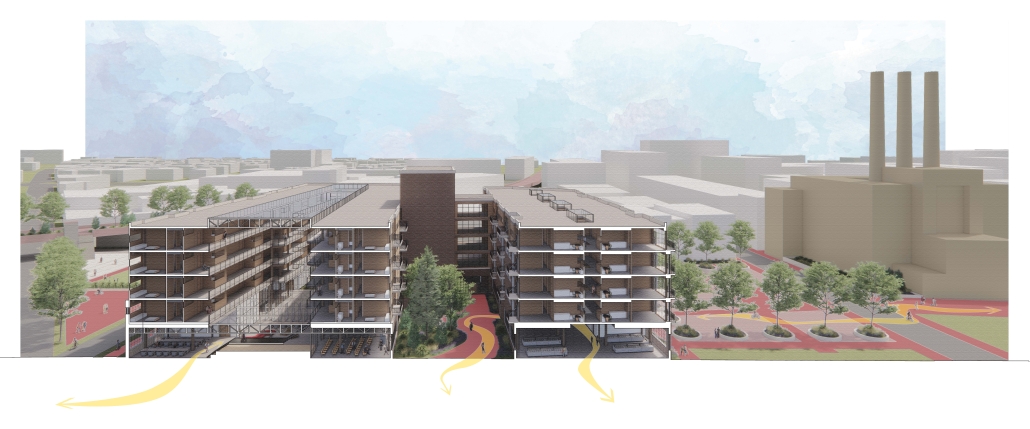
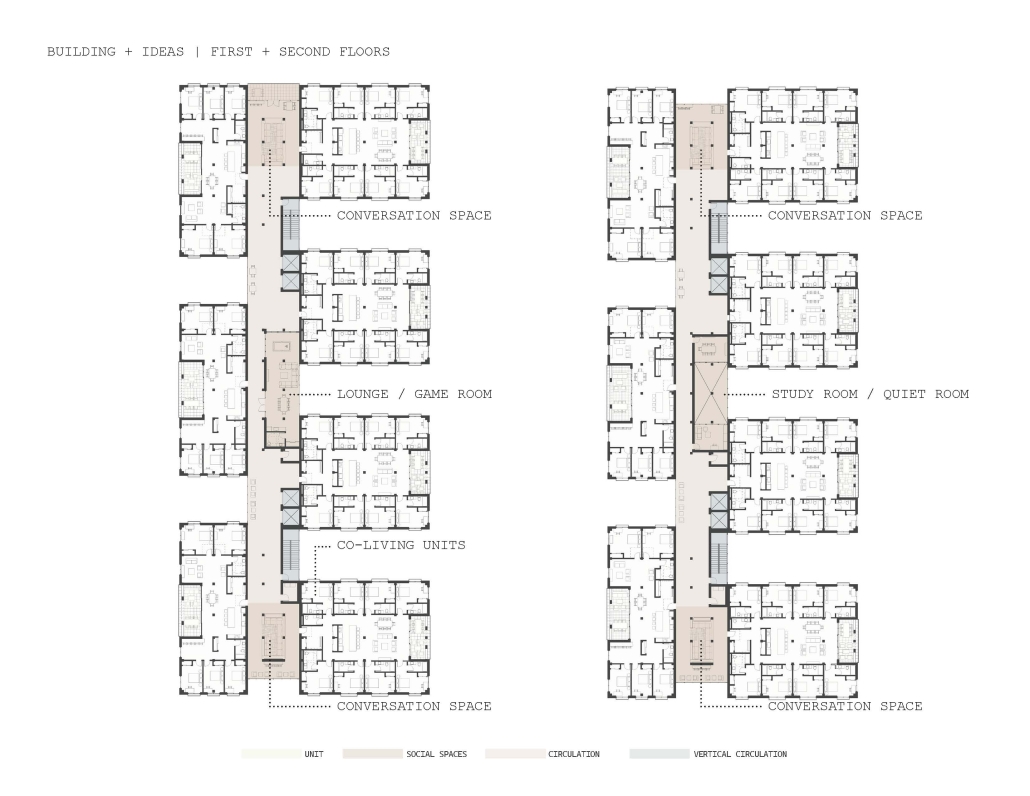
The Rainier Collective by Marianne Radillas, M.Arch ’25
University of Washington | Advisor: Dawn Bushnaq
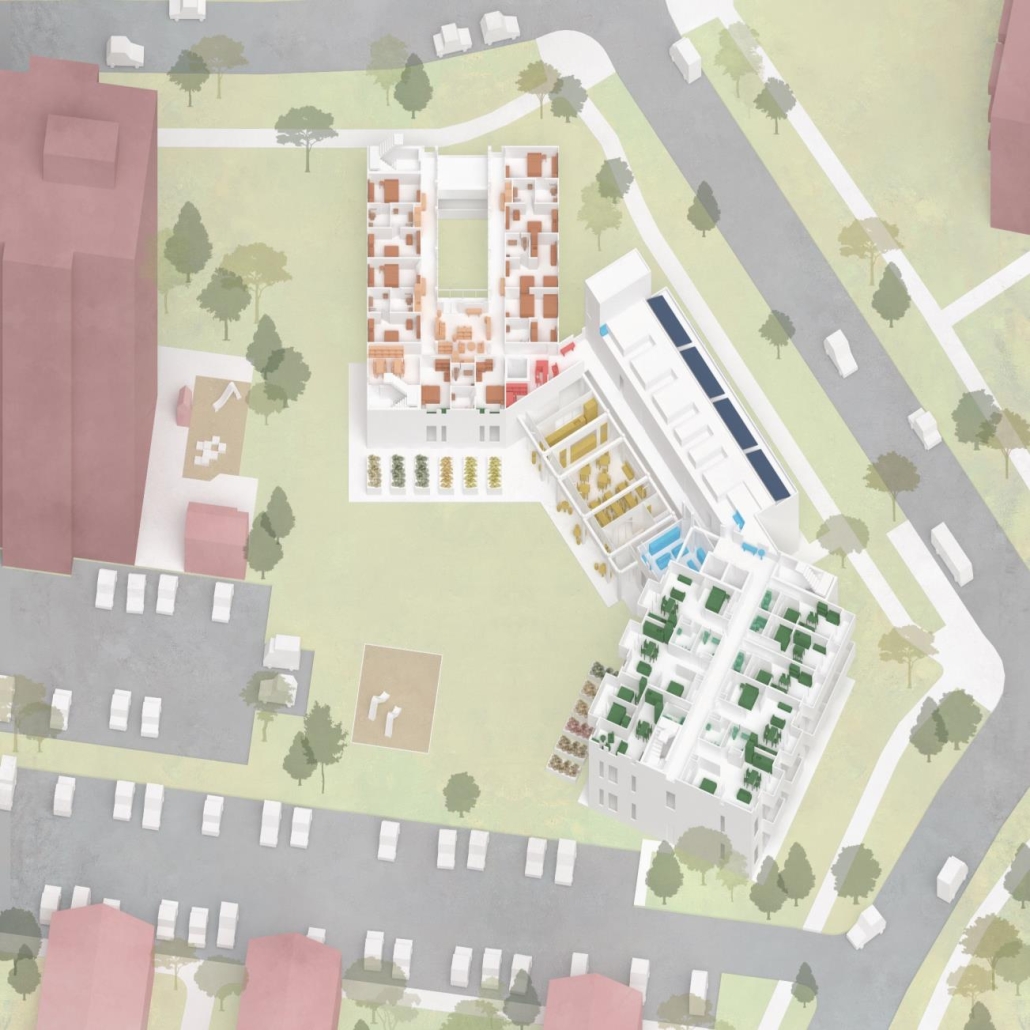
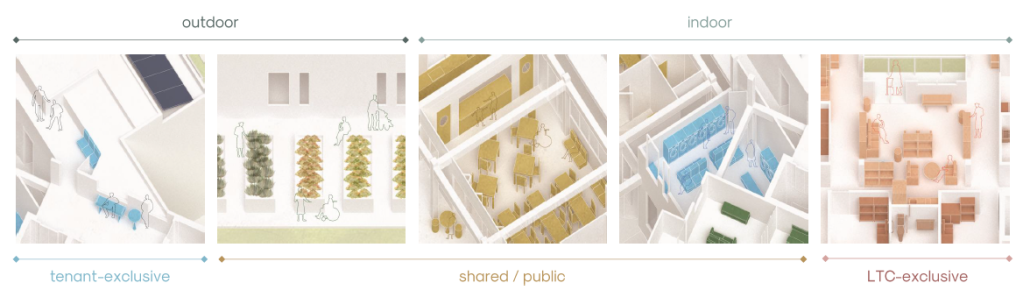
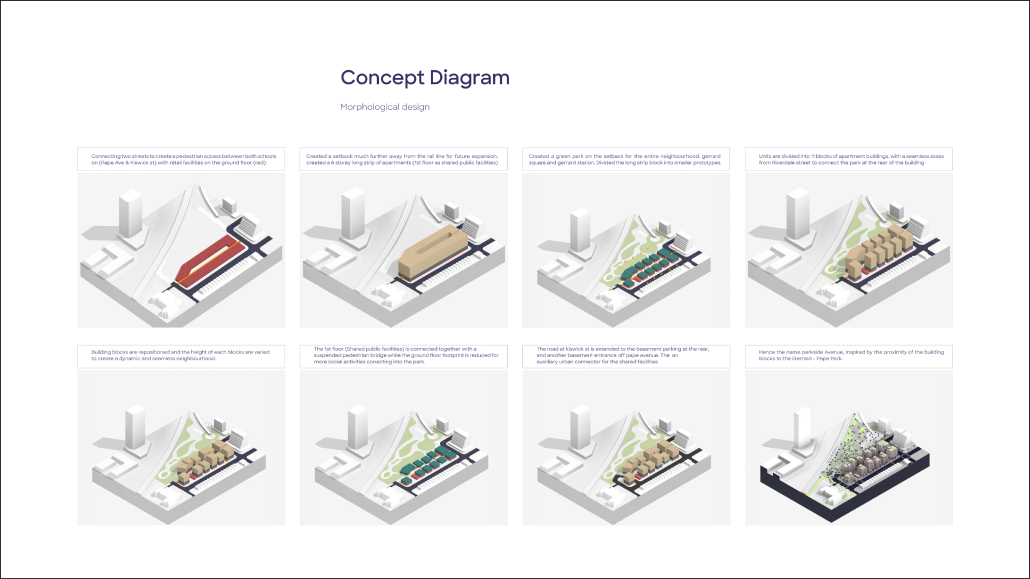
The project is from the required ARCH 503 design studio, which focuses on mixed-use, multi-family housing in Seattle’s Rainier Beach neighborhood. Seattle is facing a crippling housing affordability crisis and the studio tasks students with addressing this crisis at scale while responding to neighborhood concerns, creating a vibrant urban environment, and fostering community within the building. The Rainier Collective provides a density of social opportunity, co-living and the individual, and supports an active and interdependent community life. The project consists of 116 co-living units and ground-floor uses, including a bakery, maker space, food bank, and dining hall. The building is configured as a series of discrete blocks with full-height courtyards between them to reduce the scale of the building on the street, provide ample light and ventilation to the units and foster community. Each block houses a discrete co-living community with a central shared kitchen/dining/living space and terrace. A central “street” connects the blocks while providing amenities for the building as a whole, including lounges, game rooms, conversation spaces, and quiet work spaces. The building is clad in an understated gray brick to put the emphasis on the courtyard gardens and the community within.
This project received commends.
Instagram: @mariannered
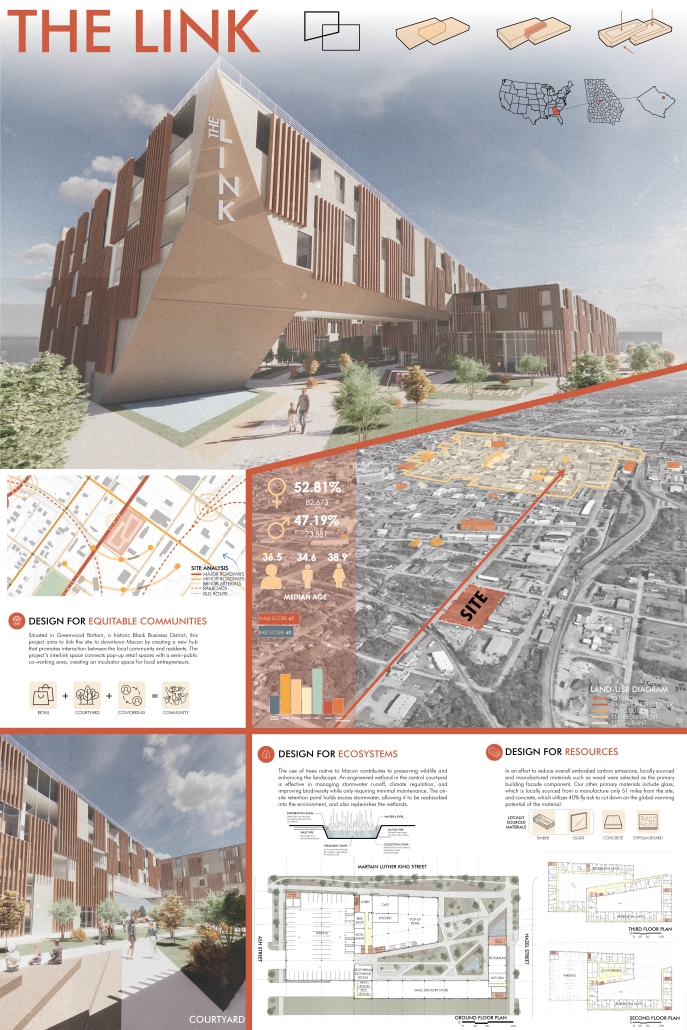
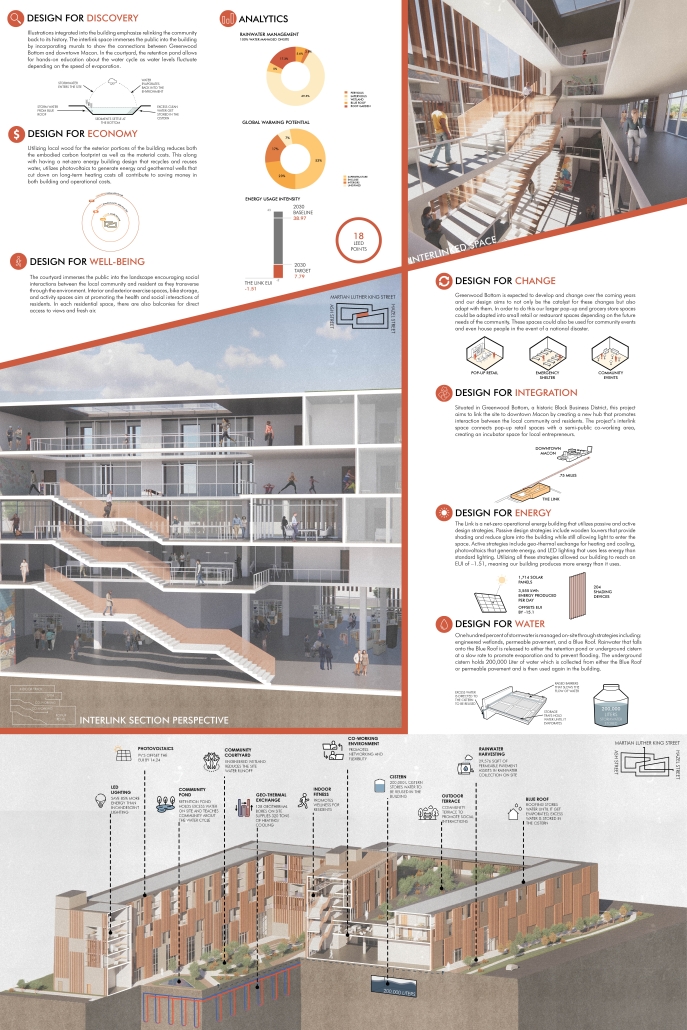
The Link by Emmaline Payne & Kevin Toudeka, B.Arch ’25
Kennesaw State University | Advisor: Robin Puttock
Situated in Greenwood Bottom, a historic Black Business District, this project aims to link the site to downtown Macon by creating a new hub that promotes interaction between the local community and residents. The project’s interlink space connects pop-up retail spaces with a semi-public co-working area, creating an incubator space for local entrepreneurs.
The use of trees native to Macon contributes to preserving wildlife and enhancing the landscape. An engineered wetland in the central courtyard is effective in managing stormwater runoff, climate regulation, and improving biodiversity while only requiring minimal maintenance. The onsite retention pond holds excess storm water, allowing it to be reabsorbed into the environment, and also replenishes the wetlands.
In an effort to reduce overall embodied carbon emissions, locally sourced and manufactured materials such as wood were selected as the primary building facade component. Our other primary materials include glass, which is locally sourced from a manufacturer only 51 miles from the site.
Instagram: @emmalinepayne, @robinzputtock
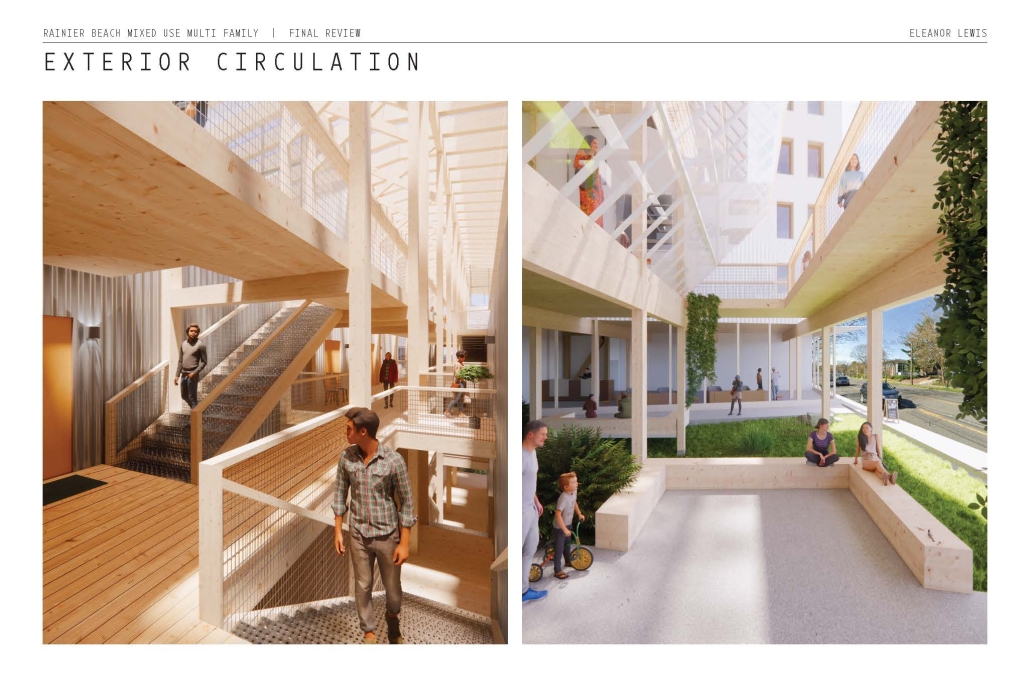
The Understory by Eleanor Lewis, M.Arch ’25
University of Washington | Advisor: Jack Chaffin
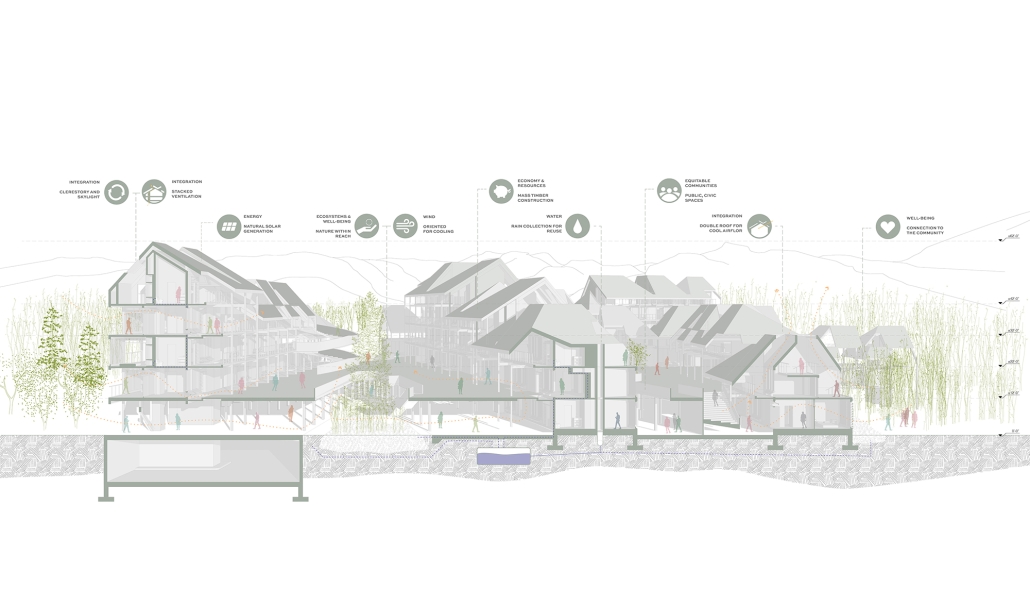
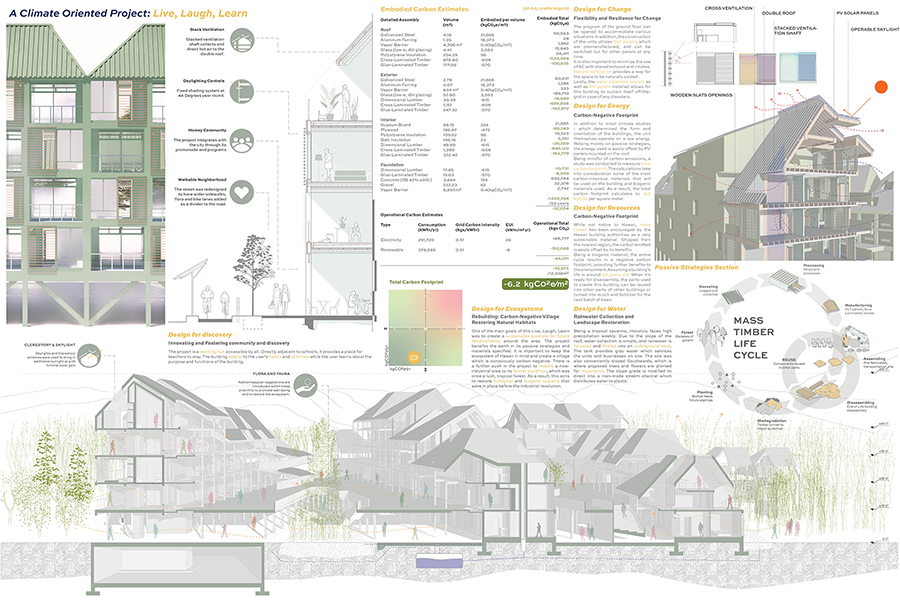
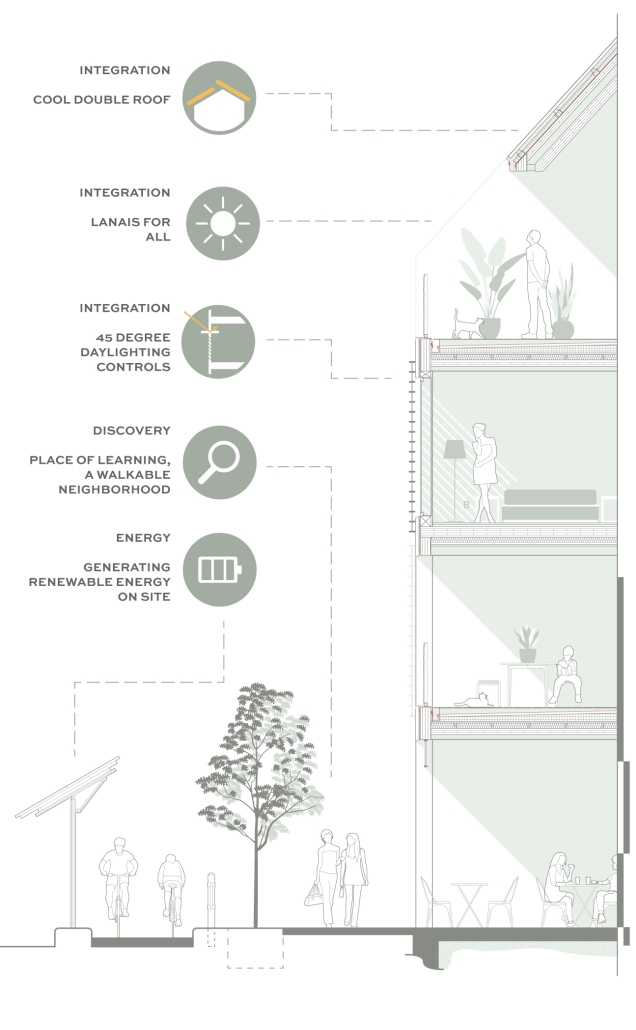
The project is from the required ARCH 503 design studio, which focuses on a mixed-use multi-family housing project in Seattle’s Rainier Beach neighborhood. Seattle is facing a crippling housing affordability crisis and this studio introduces all M. Arch students to the challenge of providing much-needed housing at scale while addressing neighborhood concerns, creating vibrant urban spaces, and fostering community within the building. “The Understory” provides 80 units of cohousing along a central residential “street” with an array of community-focused amenity spaces, including lounges, maker spaces, library, art gallery, and community garden. The building is conceived as a series of discrete boxes organized beneath a single, low-slope gable roof. The informal arrangement of the boxes juxtaposed with the continuous roof creates a variety of interstitial spaces that provide ample opportunity for community gathering and the fostering of relationships. The primary structural system is mass timber and the porosity of the building provides ample opportunity for passive heating, cooling, and ventilation in Seattle’s temperate climate.
This project received commends.
Instagram: @l.n.r, @jchaffin32
The Hive by Justin Monzon & Soreya Ganda, B.Arch ’25
Kennesaw State University | Advisor: Robin Puttock
Eco-conscious design for resilient, inclusive, and efficient workforce housing. Inspired by Macon’s historic Tybee community, “The Hive” honors the legacy of Greenhood Bottom, once home to a close-knit Black community known for its flourishing small businesses and cultural vitality. Located on the same site where Tybee residents were displaced by a never realized urban renewal plan, this five-story mixed-use project is designed to bring back the vibrancy and resilience of a once-thriving “Black Wall Street.”
The HIVE combines residential and commercial uses within a community-centric environment. The design prioritizes a lively ground floor with diverse retail options, a community center, a grocery store, and an open courtyard to foster daily interaction and access for Macon residents. Strategically, the project emphasizes reconnection, aiming to seamlessly integrate the Greenhood Bottom neighborhood with downtown Macon through a pedestrian- and bike-friendly environment.
The HIVE is divided into smaller, interlinked structures scaled to reflect Macon’s urban fabric, creating a strong sense of continuity and accessibility. Connection is central to The Hive’s design approach. Drawing inspiration from the Charles Douglass Theatre’s chain symbol, bridges link each building to provide both circulation and community gathering spaces. These public bridges, symbolic of strength and unity, house resident amenities and foster communal interactions, while rooftop gardens contribute to environmental sustainability and urban agriculture. The Hive is both a tribute to Greenhood Bottom’s rich cultural history and a beacon of future resilience, offering Macon a vibrant, integrated, and sustainable community space that connects people and place in meaningful ways.
Instagram: @justin_at_life, @___sosso___, @robinzputtock
Make & Mend by Madeleine Cordray, M.Arch ’25
Washington University in St. Louis | Advisor: Donald N. Koster
“Make & Mend” is a response to the self-initiated research and design proposal fulfilling the degree project requirements for the first-professional Master’s degree program in the Graduate School of Architecture & Urban Design at Washington University in St. Louis. Work in this studio is the architectural response to the intentional, programmatic, and situational project brief developed through in-depth research into a specific transect of the St. Louis Region conducted during the prior semester.
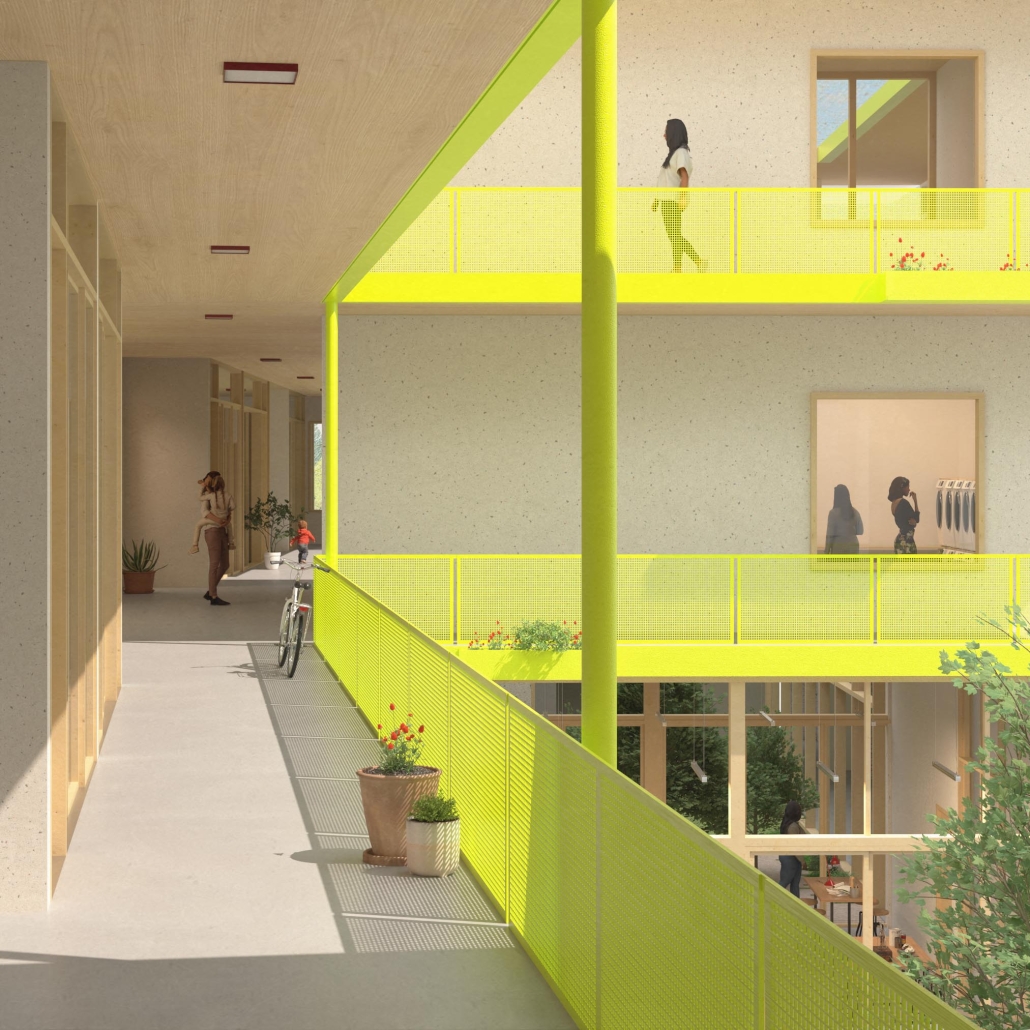
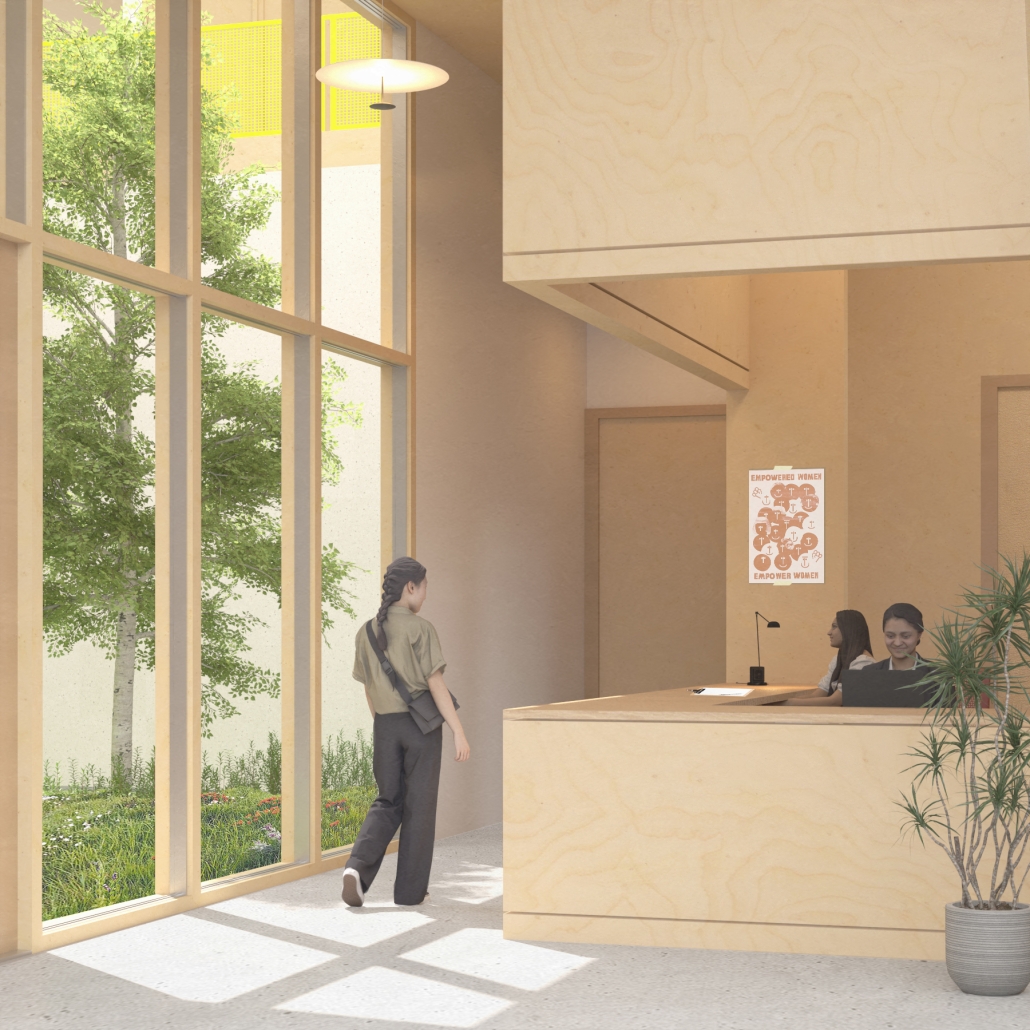
In North St. Louis, rates of violence against women are considerably higher than the national averages, with the State of Missouri ranked seventh in the country for reported domestic abuse. In crisis, women need more than immediate shelter; they need a safe space that can foster healing, skill-building, and strength. Given the high number of assault cases within the researched transect, the lack of resources to combat violence against women, and a need for economic stability, this proposed safe space for female-identifying individuals and their loved ones takes a unique approach, combining a makerspace to empower women not only as survivors of hardship but also as creators and professionals.
Designed with both privacy and community in mind, the shelter offers a safe, dignified environment while inviting women to engage with the transformative potential of hands-on skills. In the makerspace, residents can explore trades such as woodworking, sewing, and digital design—skills that support pathways to employment and financial autonomy. This architectural intervention is more than just a building; it is a holistic response to the unique needs of survivors. Local artisans and volunteers will host workshops, fostering an environment of shared learning and support, enabling women to rebuild confidence and community connections.
By aligning thoughtful architectural design with critical social services, this safe house and shelter aims to disrupt cycles of violence and poverty, creating a lasting impact. Here, residents find not only refuge but also a resource-rich environment tailored to foster self-sufficiency and future opportunity in a way that strengthens the entire North St. Louis community.
Instagram: @mad.cord, @donkoster
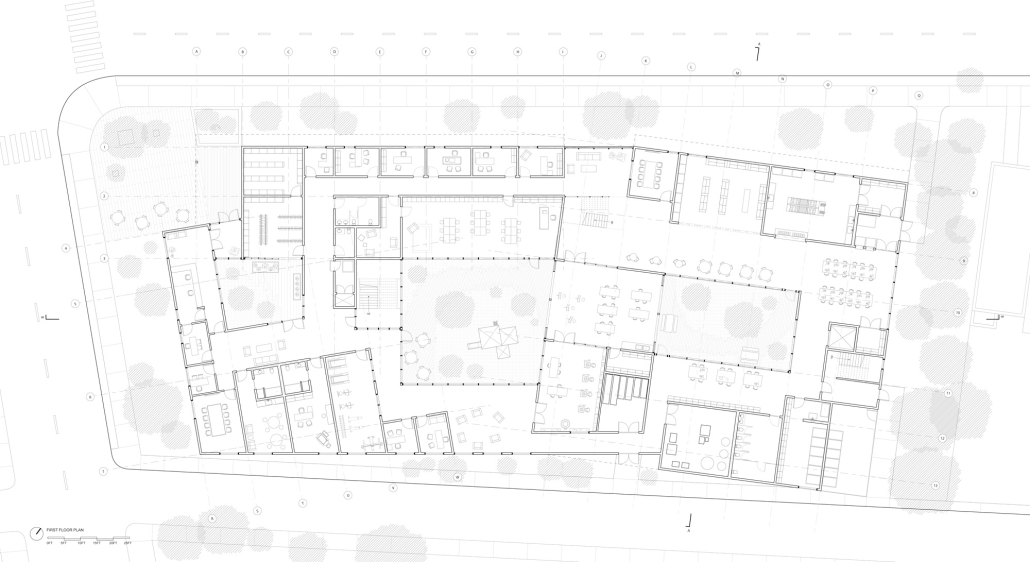
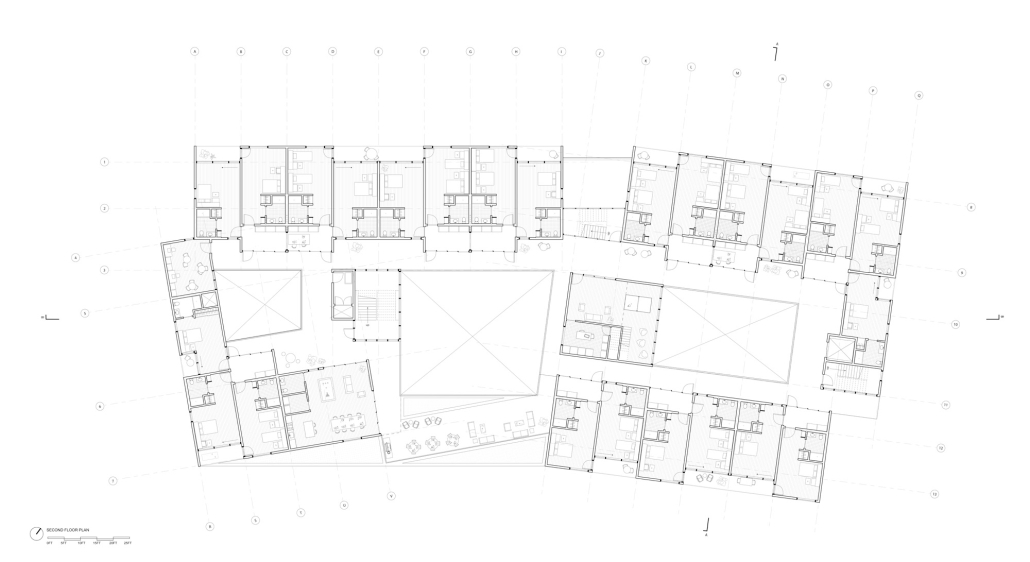
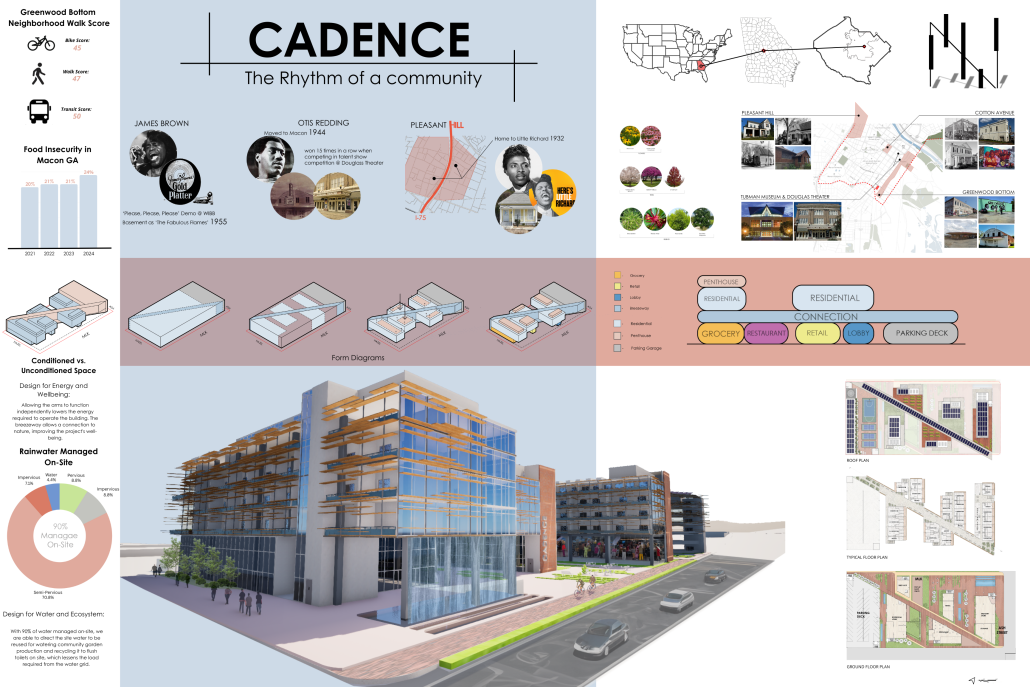
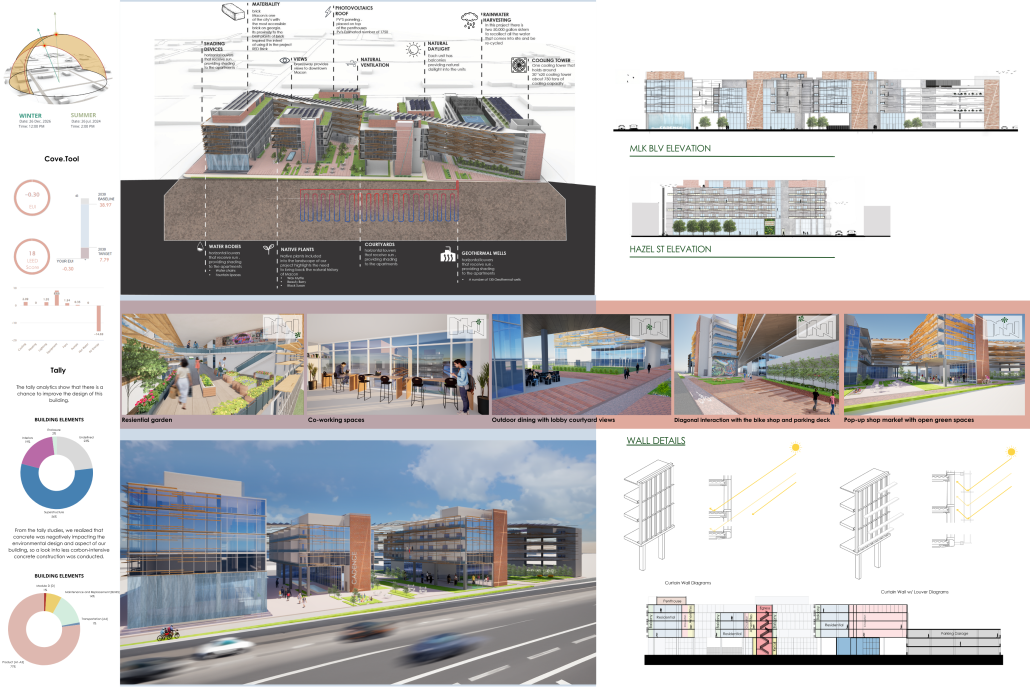
Cadence: The Rhythm of a Community by Marianna Sanchez, Nicholas Stile & Sofia Gomez, B.Arch ’25
Kennesaw State University | Advisor: Robin Puttock
“Cadence” is a sustainable, multi-use building inspired by Macon’s musical heritage. It connects downtown with the site through native landscaping, solar-responsive elements, and local red brick. Featuring photovoltaics, rainwater harvesting, natural ventilation, and geothermal wells, it offers an energy-efficient, community-friendly space blending public and private areas.
Instagram: @msg2002, @nicholas._.stile, @gomez.sofia1, @robinzputtock
Legacy: A Visual Timeline that Honors Macon’s Past, Embraces its Present and Advocates for its Future by Caroline Puckett & Alejandra Montalvo-Mendez, B.Arch ’25
Kennesaw State University | Advisor: Robin Puttock
As time goes on, it’s easy to forget what got something to where it is today, especially when some of those things are not considered to be highlights in history. However, the worst thing that can happen is forgetting or trying to erase that history. While some moments in time are moments less than ideal, it’s important to acknowledge and understand that without the moments that came before, one cannot move forward. Macon is a city that was shown just that; it acknowledges that its history and origin are filled with the suffering of slaves and other grim moments, but it’s not afraid to show that they have grown from what they once were.
Their urban landscape is a visual look into the past of Macon and everything they’ve done to create a better city today. Yet, not only does Macon embrace their past in their present, but they are looking to the future for their current and new residents looking to make a home there. Macon is currently looking to create a community where people are not afraid for their future generations and can rest easy knowing that the environment they are in is nurturing and caring for them. One way they’re doing this is by designing a space where people can settle and create their own legacy. This space not only mirrors Macon as a whole in embracing the rich past but also displays where Macon has grown to in this day, while pushing toward the future Macon wants to create for its residents.
Instagram: @thatoneazian, @alejandra_montal, @robinzputtock
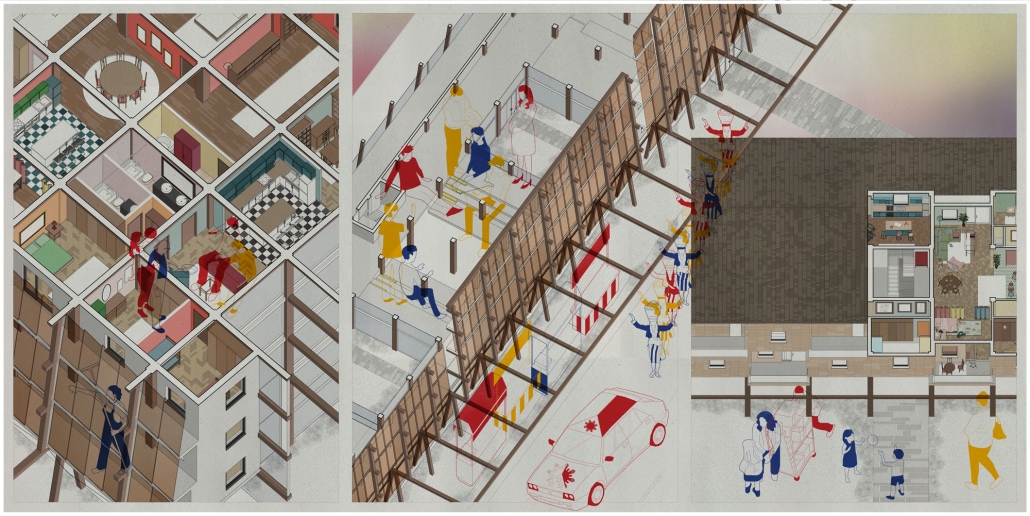
Reconnect with Home : A Long-Term Shelter for Women Who Have Experienced Domestic Violence by Roxanne Boulet, M.Arch ’25
Université Laval | Advisor: Maria Del Carmen Espegel
It is acknowledged that a home should be a place of refuge — a space where one feels safe and free to express intimacy. However, the experience of domestic violence goes against these fundamental needs associated with the notion of “home.”
Although it is commonly believed that domestic violence occurs during the relationship, the violence that happens after separation is often overlooked. Long-term shelters are recognized for offering specialized services in post-separation domestic violence. Through transitional housing, they support women in becoming aware of the violence they have endured and in reorganizing their lives. It is therefore important to consider what design strategies can support women in their process of regaining control over their lives and reconnecting with their homes. More specifically, this project seeks to answer the following question: How can the built environment contribute to the empowerment of women who have experienced domestic violence?
This housing project explores how spatial qualities can help rebuild the bond of trust between survivors and their living space. It examines how the built environment can support the idea of reconnecting with one’s home — the home as a safe, secure, and intimate place — as well as reconnecting with oneself — the home as a space of self-appropriation and self-affirmation.
Instagram: @roxanne.boulet, @eaul.architecture
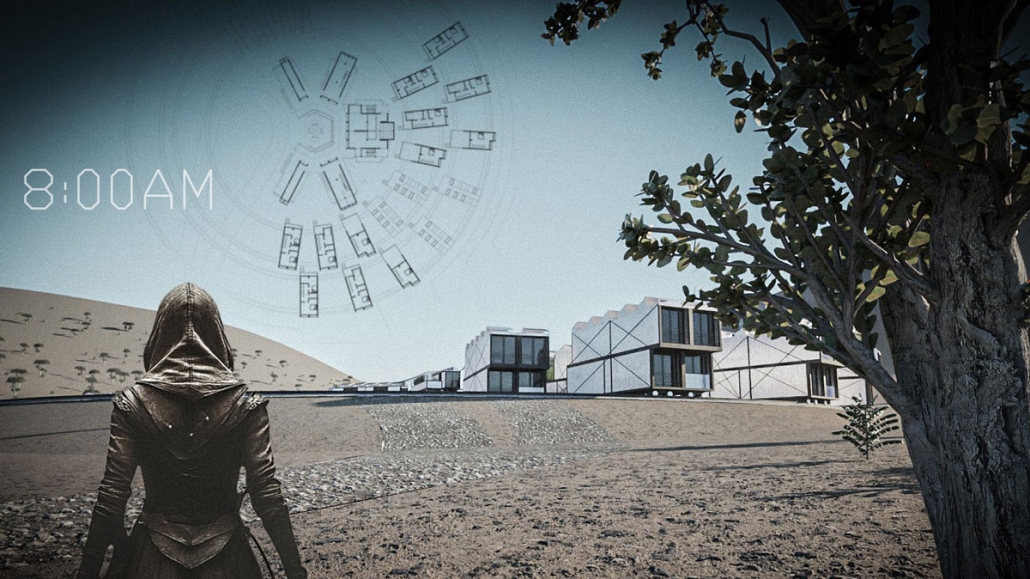
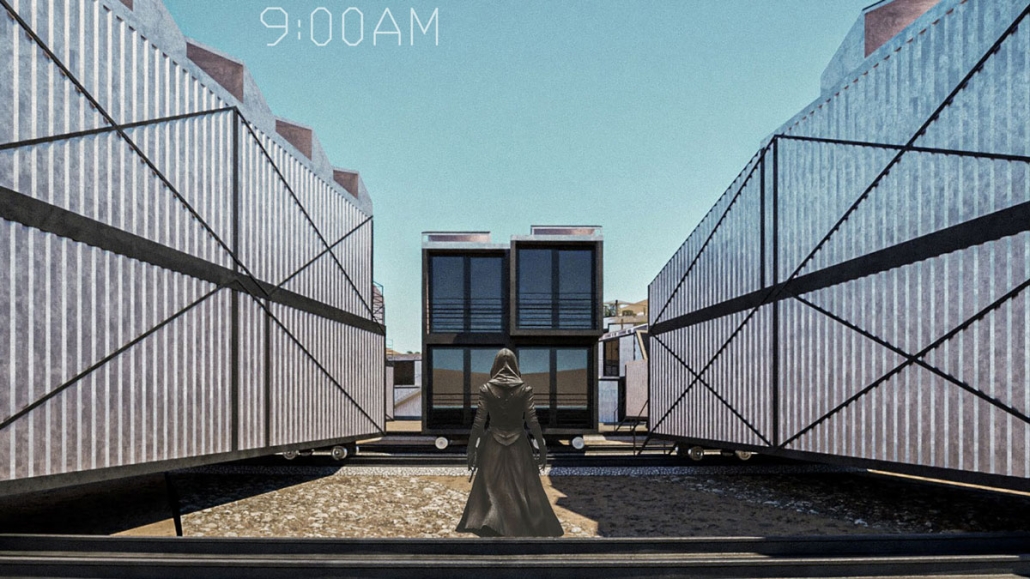
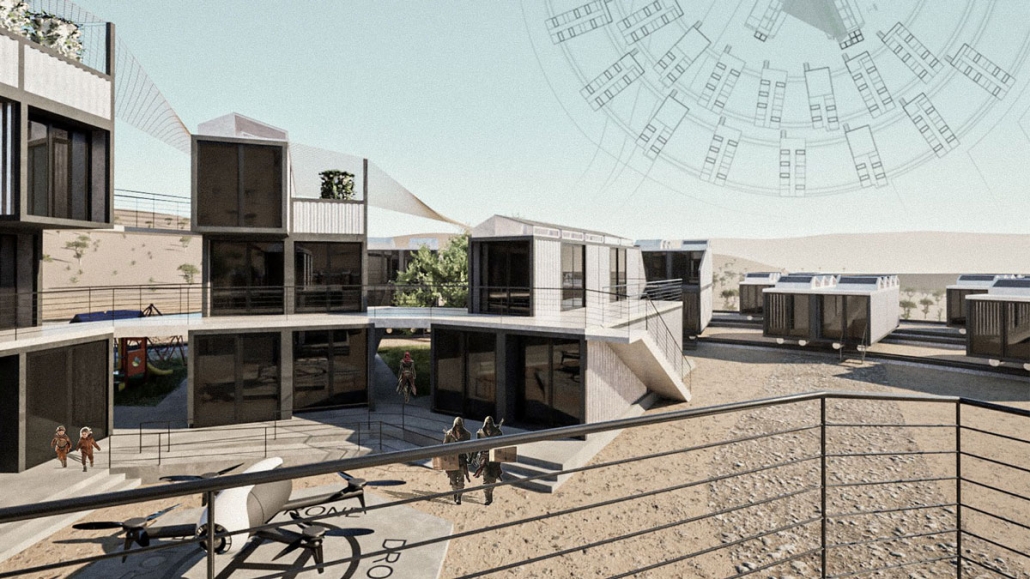
Project Nomad: Modern Solution to Adaptable Desert Living by Nick Pshegodskyy, B.Arch ’25
Academy of Art University | Advisor: Jason Austin
This project is positioned as a UTOPIAN vision that speculates its DYSTOPIAN realities. The temperatures on planet Earth have reached triple digits. The record-breaking temperatures are making uninhabitable large cities with vast surfaces covered with asphalt and concrete. This project assumes that, as a consequence, some people will move away from large urban centers to remote locations such as the Joshua Tree Desert. Open landscape, climate adaptation, and renewable energy production provide a safe haven for the newly transplanted residents. The architecture provides cool breezes, fresh air, and beautiful views of the site. The implementation of the latest technology provides a continuation of services like the internet and deliveries in this remote location. But as we all know, life doesn’t always work as it is described, thus the DYSTOPIAN aspect becomes a central part of the project. The project’s DYSTOPIAN elements draw from social community prototypes based on sci-fi movies, video games, and historical precedents. Life in the desert will not be easy. While project NOMAD provides residents with some conveniences, there is no way to ignore that, beyond the project boundaries, the emptiness of the desert is enormous and hostile to life. This project imagines how humanity might adapt to such a setting.
This project won the Design Excellence Award.
Instagram: @godsky_design, @aus.mer
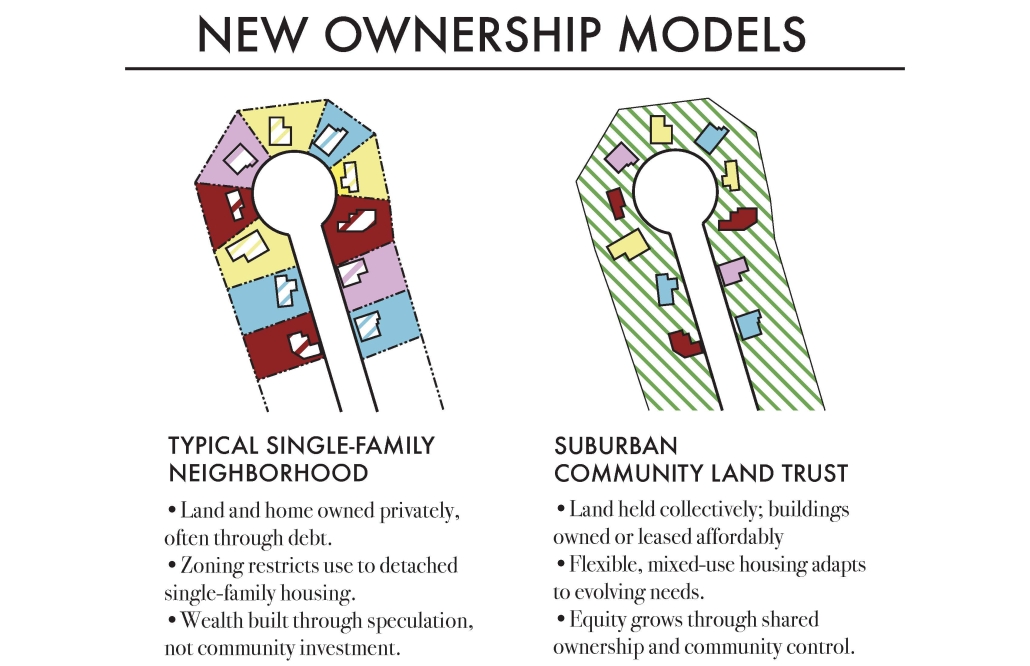
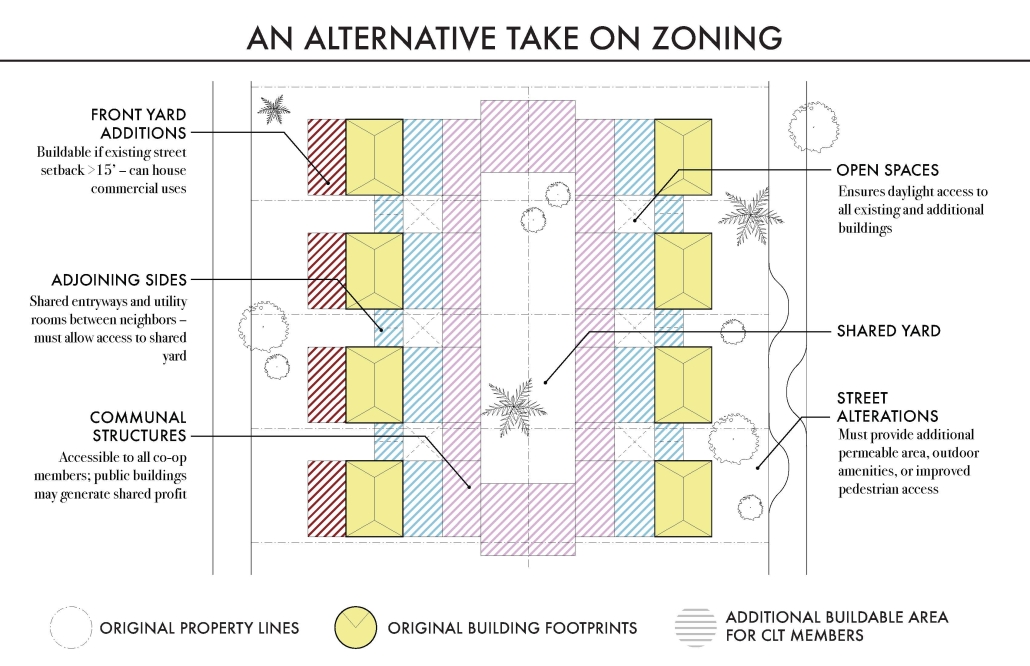
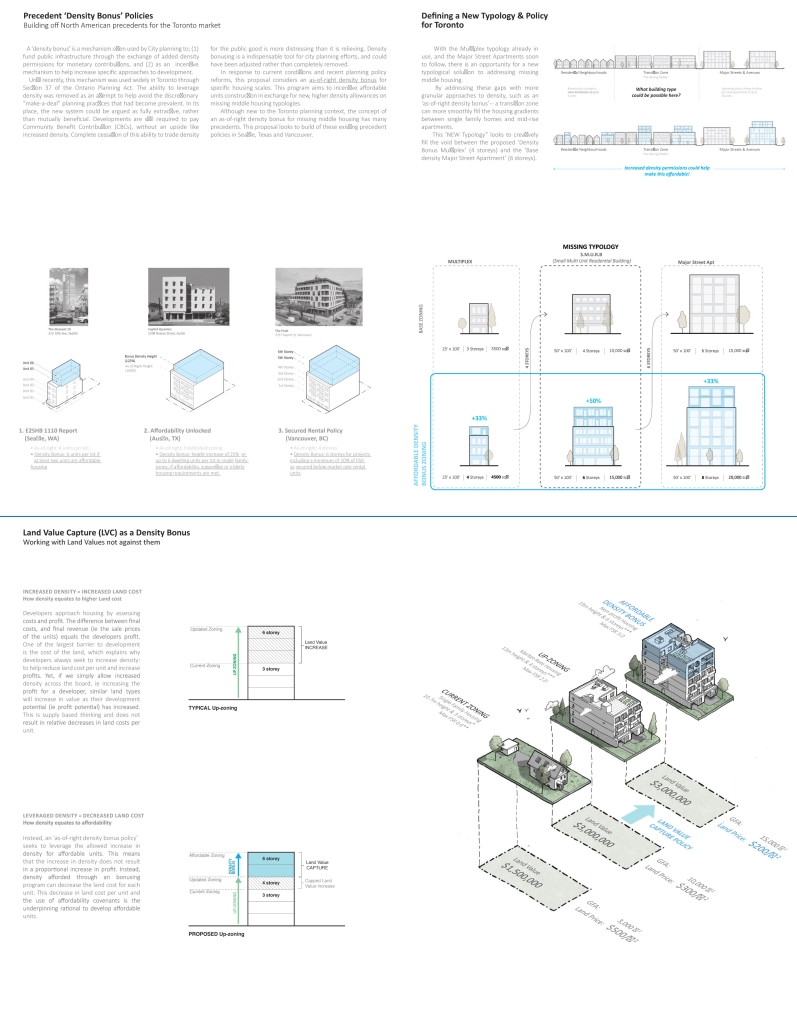
Subversive Suburbs – Join the Altadena Land Trust Alliance by Charles Lafon, M.Arch ’25
University of Southern California | Advisor: Sascha Delz
The typical residential subdivisions that define much of the housing supply in the U.S. have drawn persistent criticism from architects and planners. Suburban sprawl has contributed to car dependency, social atomization, and an affordability crisis fueled by land speculation and debt. While urban co-ops and rural utopian communities have attempted to address some of these structural issues, “suburbia” remains deeply tied to conventional forms of ownership, use, and consumption. Subversive Suburbs argues for the adaptation of suburbs into sites that resist, rather than reinforce, these socioeconomic norms. Using post-wildfire Altadena as a case study, this proposal for a Community Land Trust (CLT) and affiliated incentives retains the area’s suburban character while supporting more resilient, collective lifestyles. The envisioned Altadena Land Trust Alliance (ALTA) offers residents who lost their homes the opportunity to convert their land titles into shares in a new housing cooperative that gradually but efficiently redevelops the neighborhood. ALTA incentivizes collectivization by allowing members to build under a new zoning framework, adding a variety of shared infrastructure and amenities without sacrificing affordability. The project thus subverts both the formal and economic logic of suburban development, creating an alternative vision for the future of this contested typology.
Instagram: @coop_urbanism
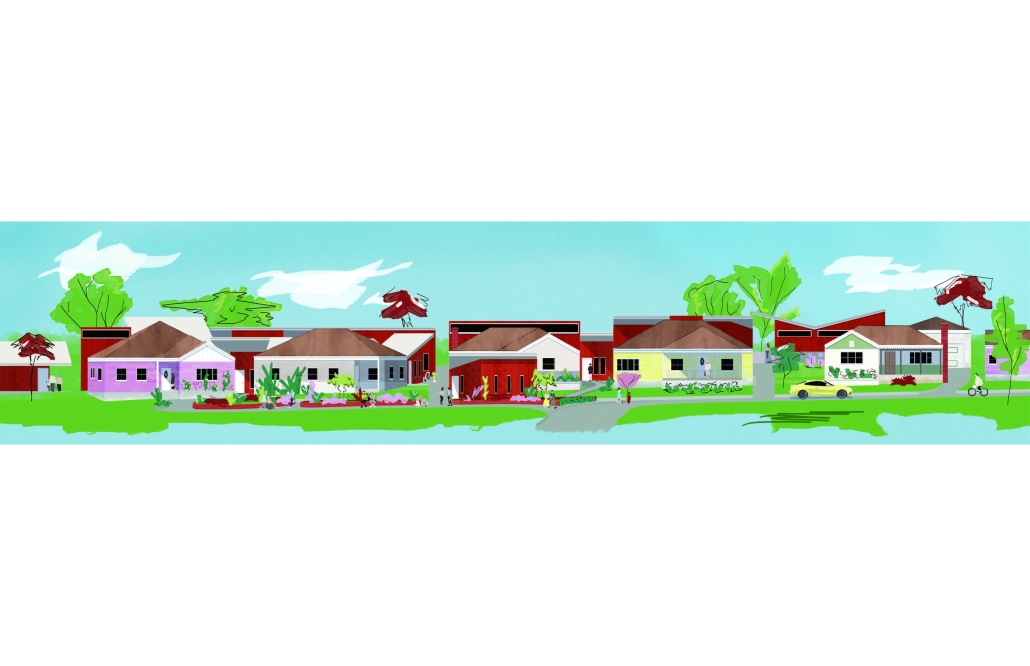
COOPERATIVE AGING: REIMAGINING MULTIGENERATIONAL HOUSING TO SUPPORT AGING IN PLACE by Reilly O’Grady, M.Arch ’25
University of Maryland | Advisor: Ken Filler
Multi-generational housing is an ancient solution to a modern problem. The idea of living in a home with others to share in the workload, responsibilities, and security of the whole has been around since humans first constructed shelters. In modern times, however, we have lost this sense of community and resulting support. A majority of the population is facing elderly age and changing physical and mental requirements. The world is not prepared to care for and house such a large group of elders, especially the United States. Many people, young and old, are forced to move and seek assistance outside of their known and grown homes. Aging in place is the ability to remain in your home or community safely, independently, and comfortably, regardless of age, income, or ability level. Multi-generational housing proposes a solution where adaptive unit design, focus on shared spaces, and slow circulation can create a community that grows and changes with its residents. By creating social engagement in an age of isolation, future growth and connection can be inspired in the greater community.
Instagram: @_rjogrady_, @kenfiller
Stay tuned for Part XIII!