2022 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part III
Welcome back to Part III of the 2022 Study Architecture Student Showcase. This week, we feature students from across the United States, specifically highlighting award-winning work. Each project represents a unique relationship between the built environment and the context within which the project is located. For more projects, please explore Part I and Part II.
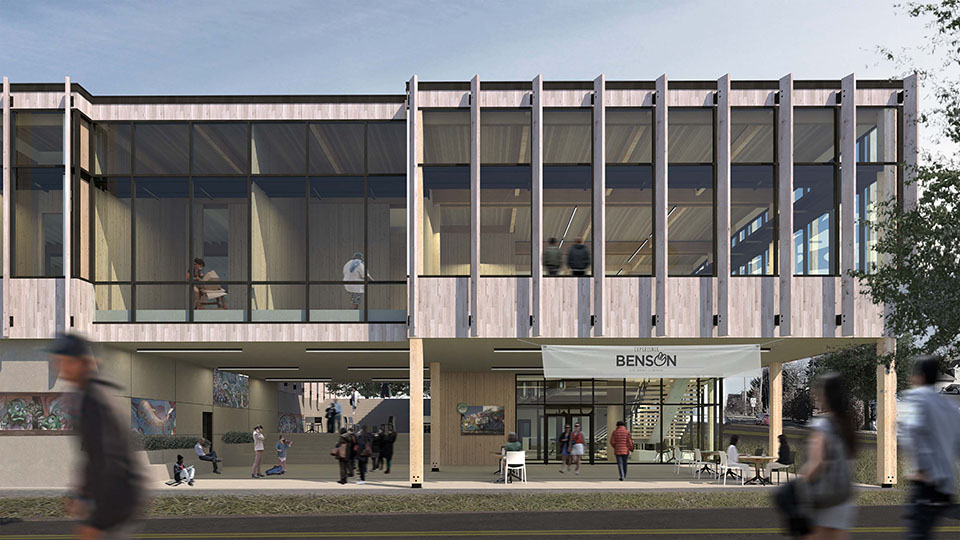
TEMPLE SCIENCE (Bio-Geometry and Sustainable Architecture) by Omar Ayache, B.Arch ’22
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Carla Aramouny
First Prize in Areen Projects Award for Excellence in Architecture & Dean’s Award for creative Achievement
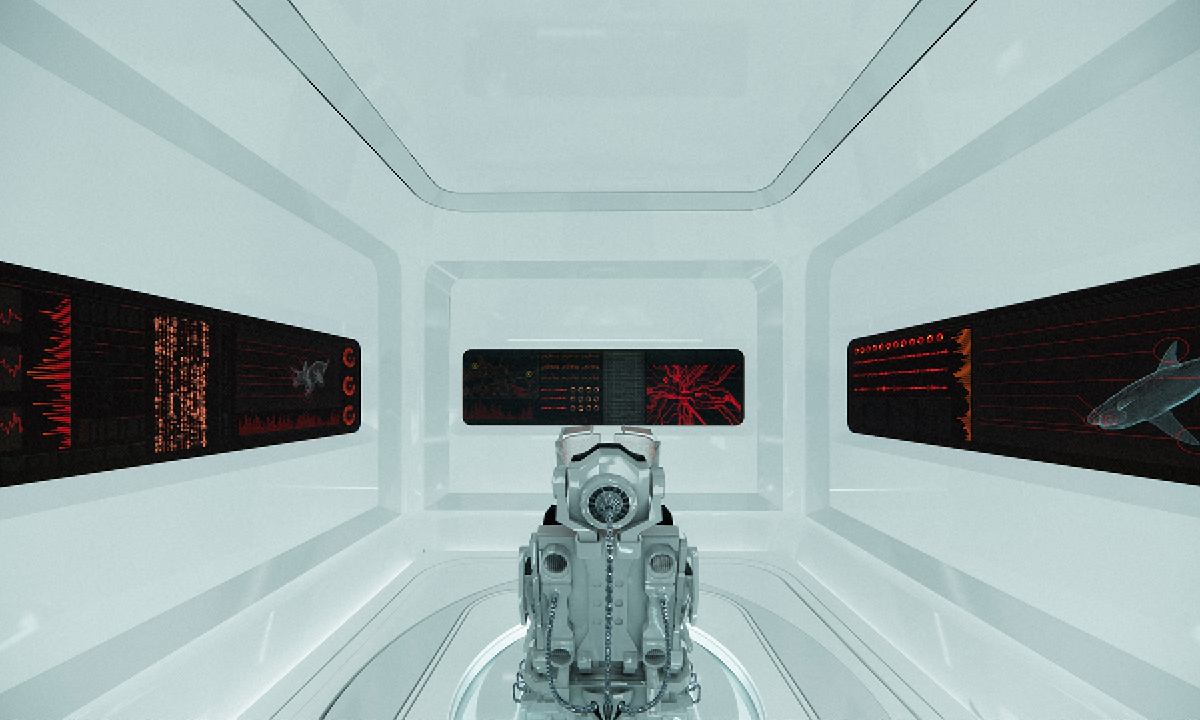
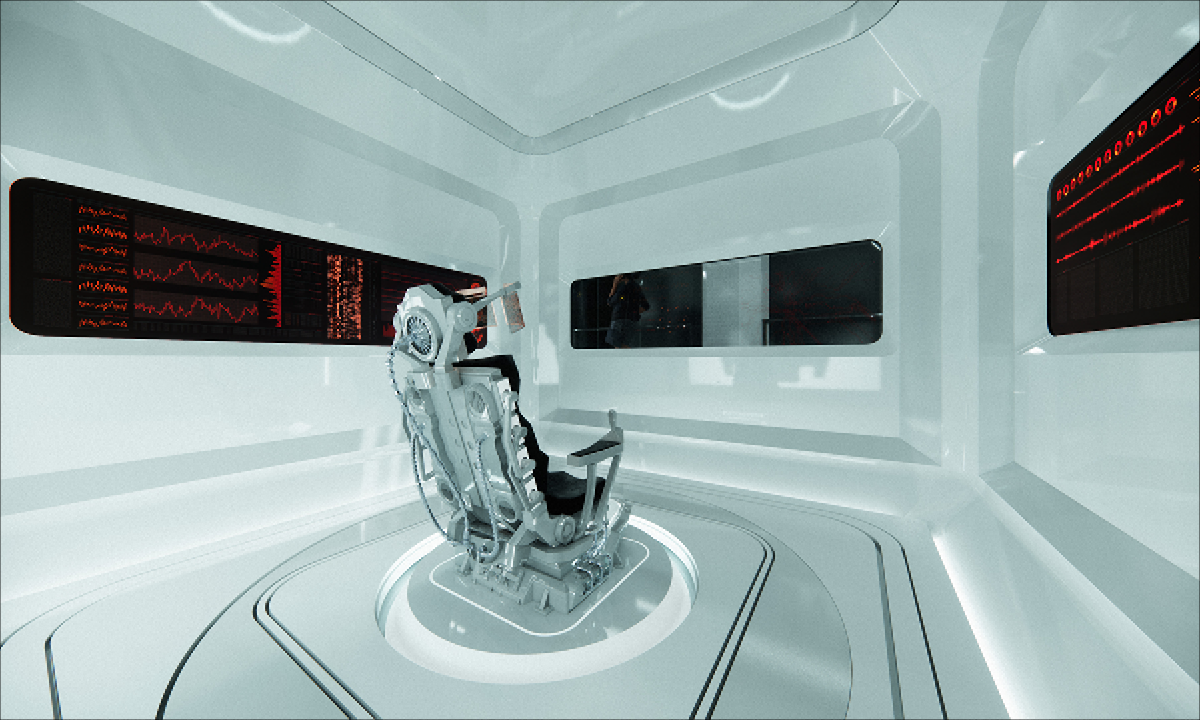
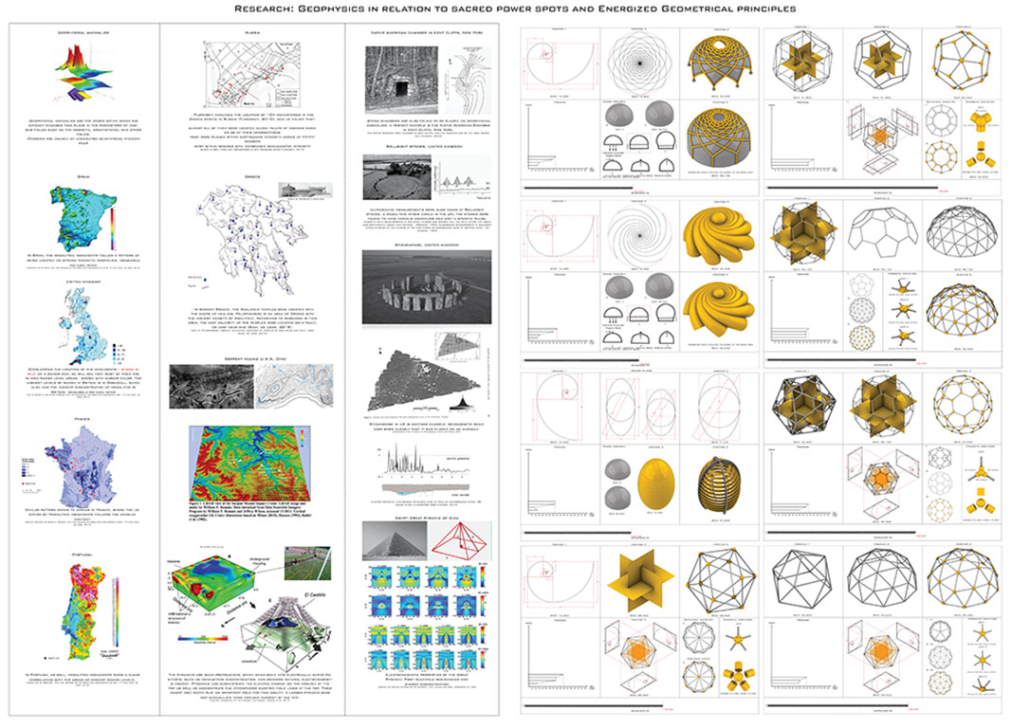
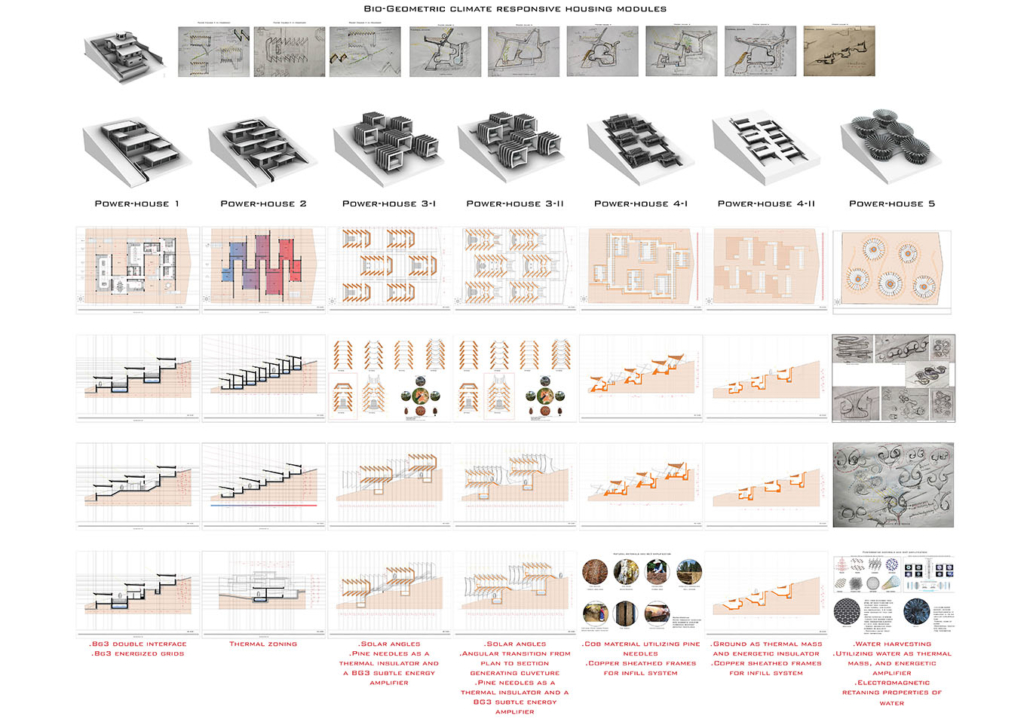
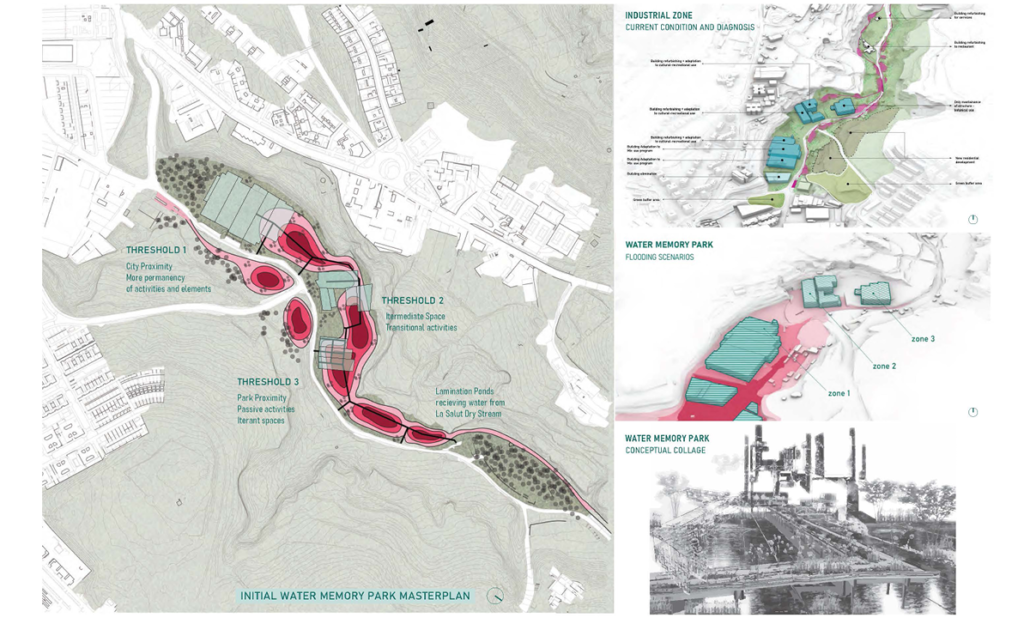
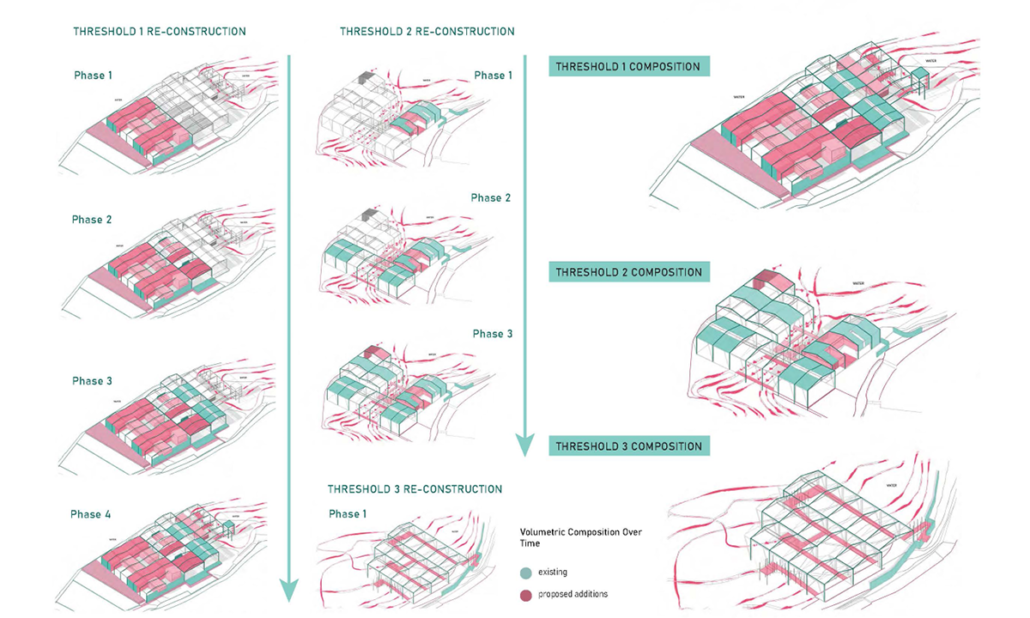
In the context of ambient threats such as environmental and electromagnetic pollution and global warming, this thesis explores the relationship between the human system’s geometric blueprint and the energetic structure of ancient temples. The purpose is to create responsible design with healing properties while addressing a pertinent Lebanese site in need of waste management and urban transformation. As such, a dual approach was applied with environmentally responsive design in addition to energetically aligned architecture.
This exploration aligns the geometric blueprints with those of the energetic planetary system as well as the physical correlates that emerge from them. After establishing the correlational relationship between geophysical anomalies (Sacred power spots) and their impact on the studied environments, I explore ancient design principles and their application in current contexts through the lens of a Geometrical Alchemy, Bio-geometry, at the individual, architectural, and urban scales, while illuminating the forgotten dimensions of environmentally responsive design. I initiated this thesis as a researcher taking foundation and advanced level courses in Biogeometry and a course at the Resonance Science Foundation on the sacred science of ancient temples. On the other hand, developed by Dr.Ibrahim Karim, Bio-Geometry is the science of detecting, amplifying, and reproducing the centering energy qualities found in sacred power spots and in the energetic centers of the human body, referred to as the BG3 energy quality, by using a design language, of shape, angles, colors, and proportions, that can be implemented in designs at any scale.
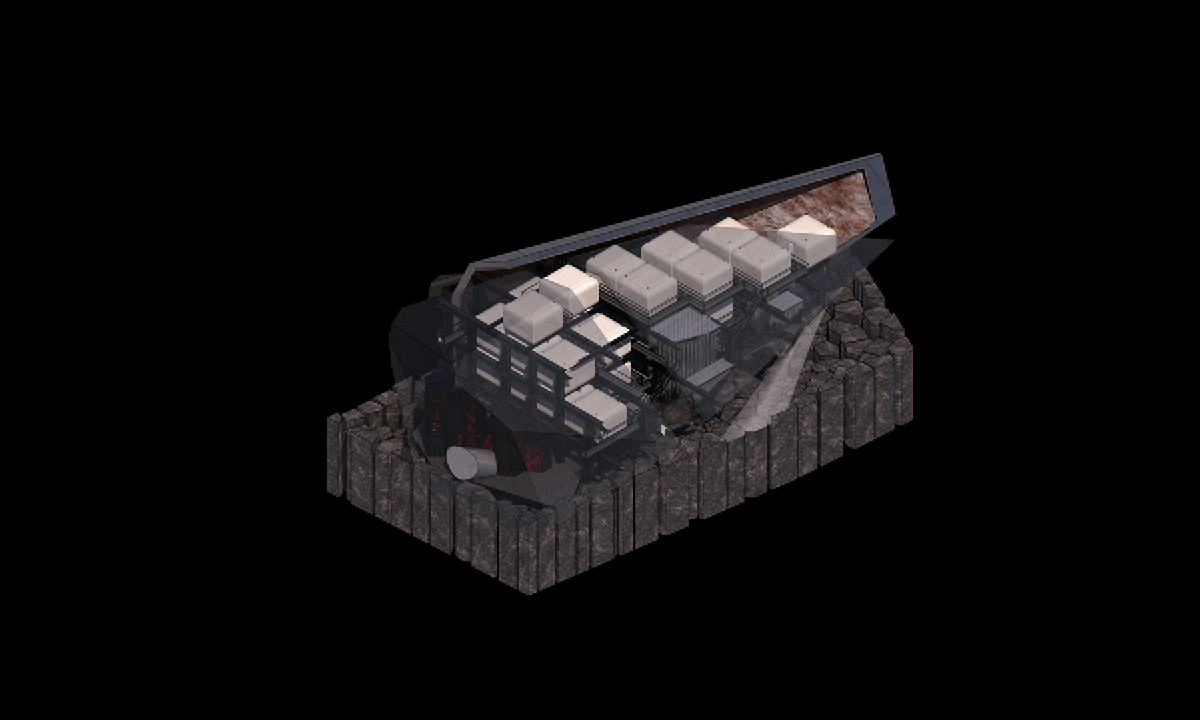
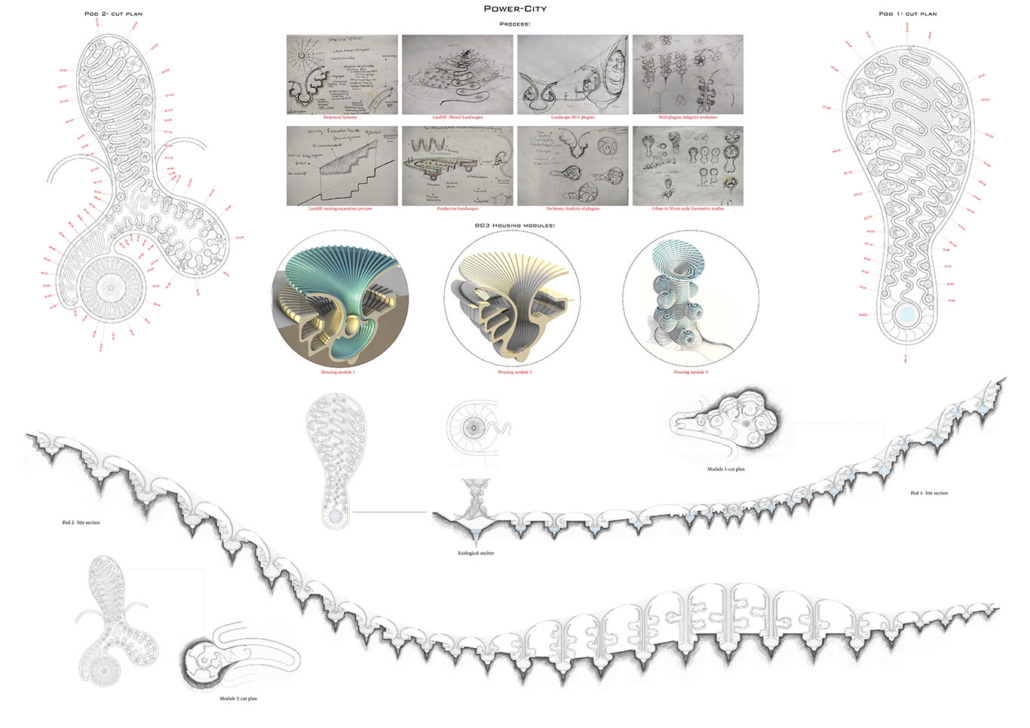
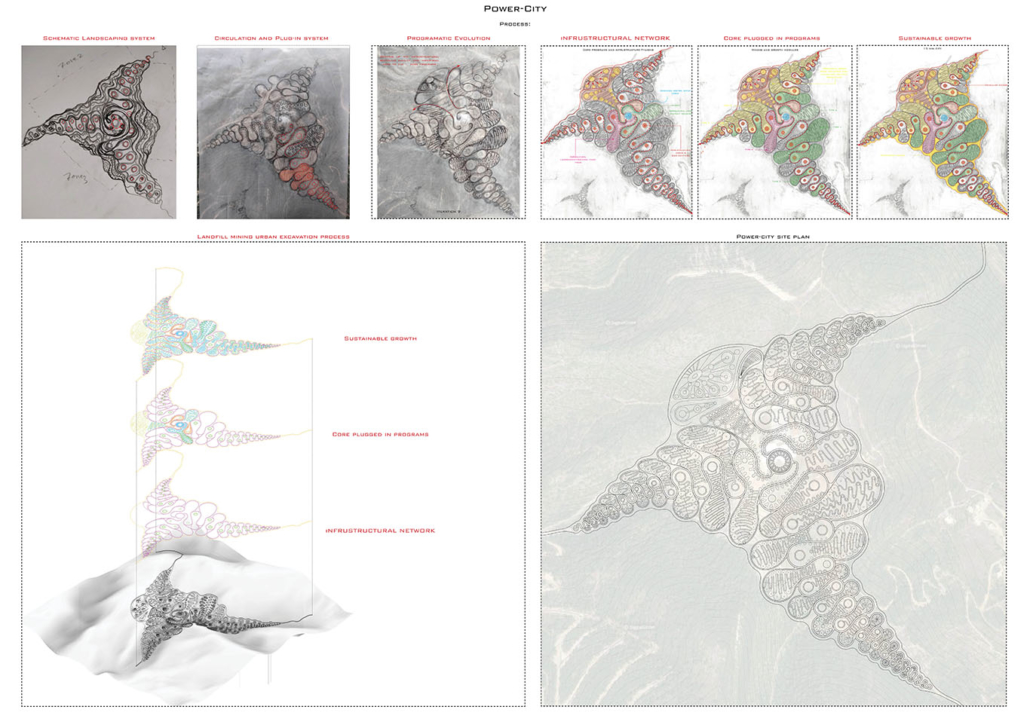
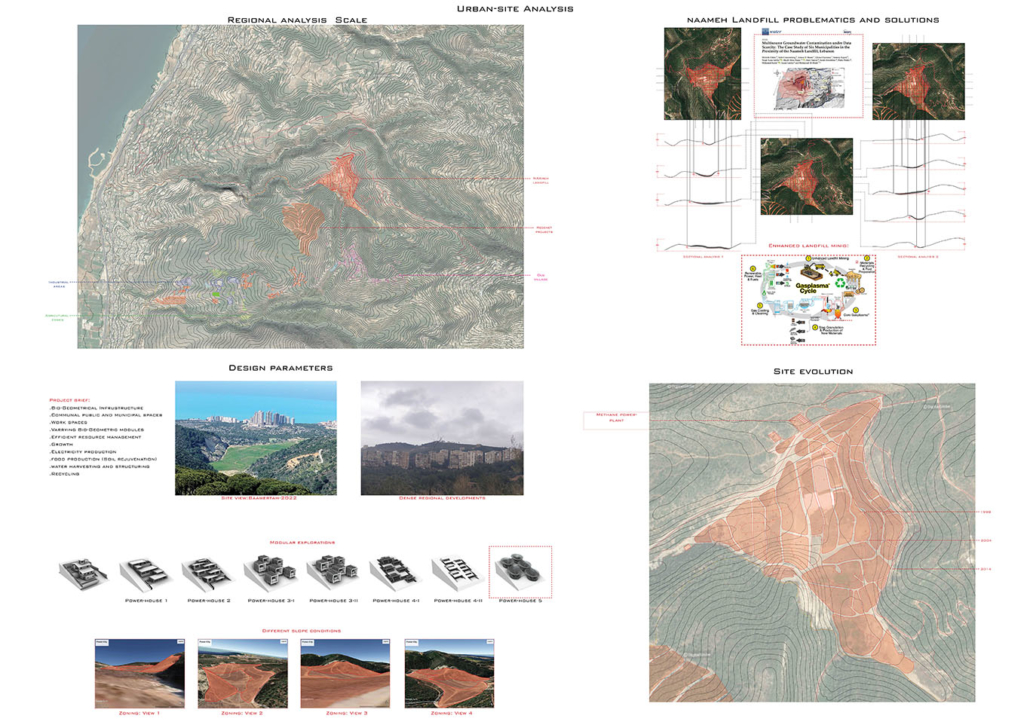
The variables generating habitable and functional architecture will be aligned with Biogeometrical science to integrate favorable energetic qualities while considering programmatic thermal zoning, climate-responsive geometry and naturally performative materials and building techniques at the architectural scale. At the urban scale, variables such as density, sustainable growth, resource management, and urban geometric infrastructure will be assessed taking the hazardous Naameh Landfill in Lebanon as a site of analysis and intervention through enhanced Landfill mining. An excavation process that would transform the landfill’s hazardous waste into Raw materials activating the local economy and revealing a Biogeometric climate responsive power-city in the process.
This project is a work in progress and would not have been possible without the guidance of Professor Rana Haddad, Professor Carla Aramouny, and Dr. Ibrahim Karim.
Instagram: @omaralayash01, @caramouny, @200grs, @ard_aub
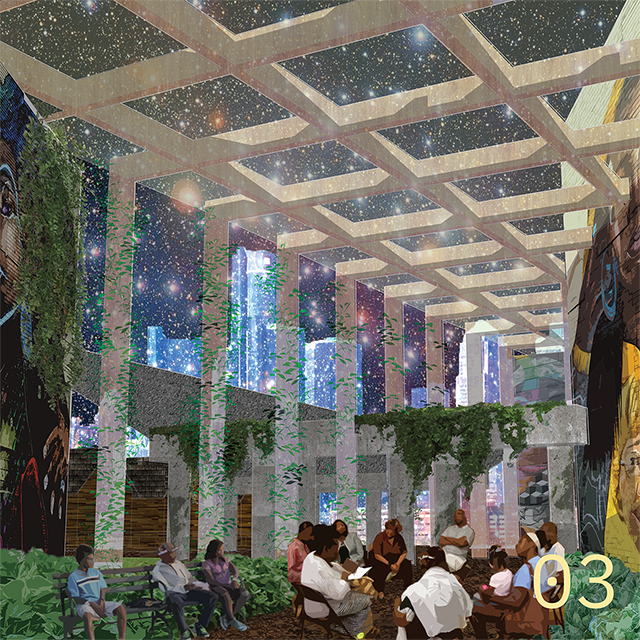
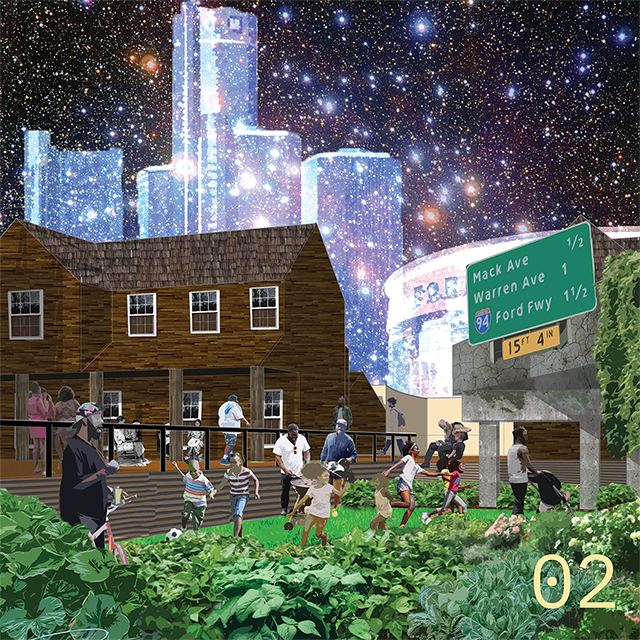
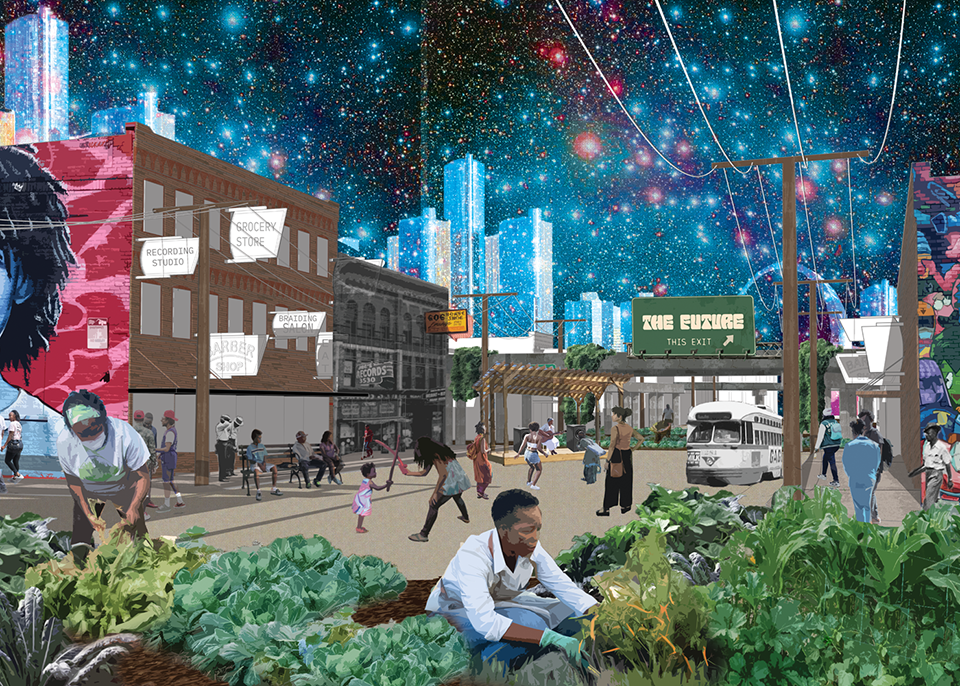
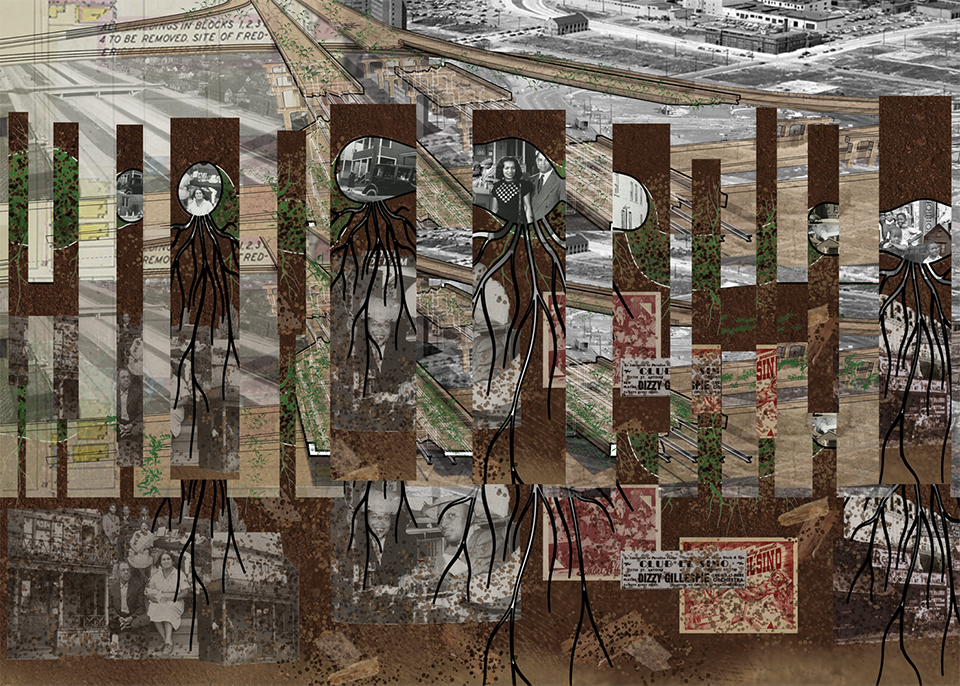
Invisible Realities of Future-Past by Cierra Francillon and Caleb-Joshua Spring, B.Arch ’22
Pratt Institute School of Architecture | Advisor: Gonzalo Jose Lopez Garrido and Daniela Fabricius
Degree Project Award ’22 Social Justice Prize
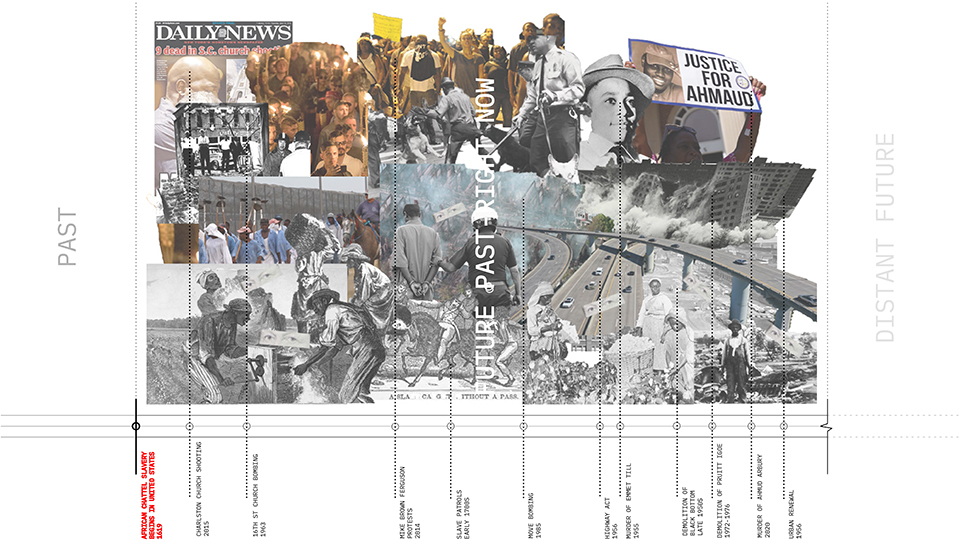
The neighboring communities of Black Bottom and Paradise Valley, located in Detroit, were once social and cultural meccas and symbolic centers of Black life. This place was one of the major destinations of the Great Migration of the twentieth century, the mass exodus of Black people fleeing the intense racism in the South in search of better opportunities. Black Bottom and Paradise Valley were razed by the city of Detroit and state of Michigan for urban renewal and the construction of the Chrysler Freeway (I- 375), displacing large numbers of Black people and creating “root shock”¹ in the Black community that has present day ramifications.
This project is rooted in exploring the dispossession and subsequent root shock caused by the American highway system and urban renewal. This project seeks to rectify the effects of root shock by imagining a parallel present where Paradise Valley and Black Bottom re-emerge and are allowed to grow without disruption from the effects of white supremacist policies. The goal is to speculate on a new way of black urban life, or a new Black Commons, by dissolving the highway system to return the commons to Black people, and accessing this parallel reality that is rooted in the legacies of Black Bottom and Paradise Valley. The domestic commons, the commons of sustenance, the commons of cultural production and leisure, and the space of the collective, are new typologies that lean on music, ritual, care, and agriculture to restore Paradise Valley and Black Bottom as cultural and social meccas in Detroit. We used an Afrosurrealist approach to encourage, support, and allow for a rhizome of personal relationships spanning across Africa and North America in order to reimagine and reform a Black Detroit in the crux of the interstate highway system and urban renewal. As the highway system crumbles into disrepair and is abandoned, a new Black Commons will emerge from the ruins of late stage capitalism and its anti-Black policies.
¹ Mindy T. Fullilove, Root Shock: How Tearing Up City Neighborhoods Hurts America, and What We Can Do About It (New York: One World/Ballantine Books, 2004).
Instagram: @cierra.png, @blkbencarson, @gjlg, @knitknot_architecture
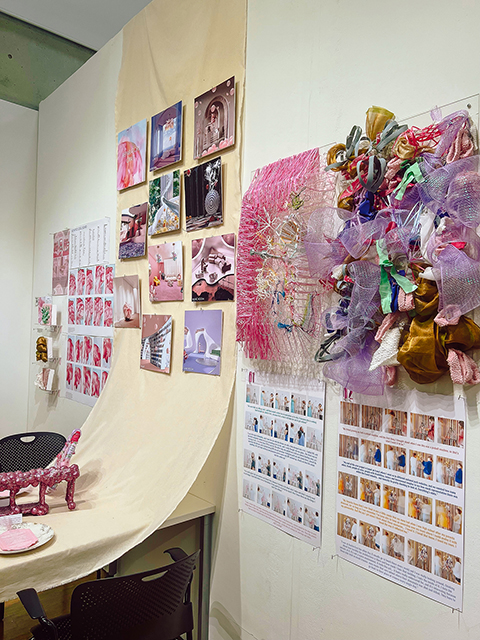
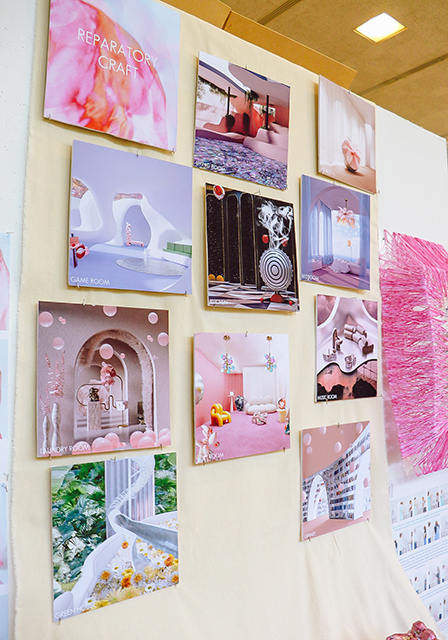
Reparatory Craft by Mary Margaret Williams, B.Arch ’22
University of Tennessee | Advisor: Jennifer Akerman
Tau Sigma Delta Bronze Medal, Distinguished Design Award, Third Place
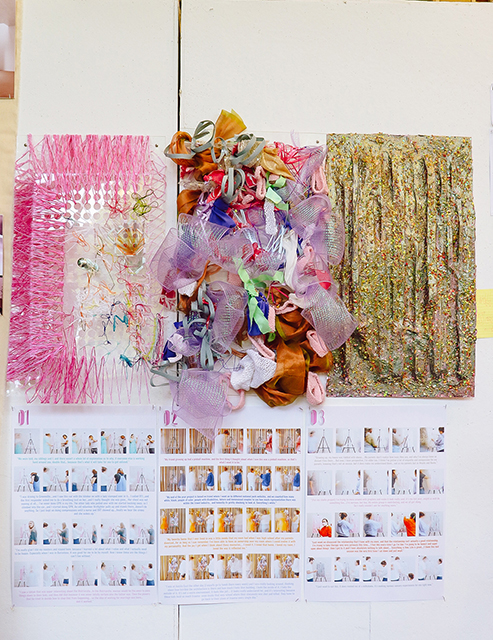
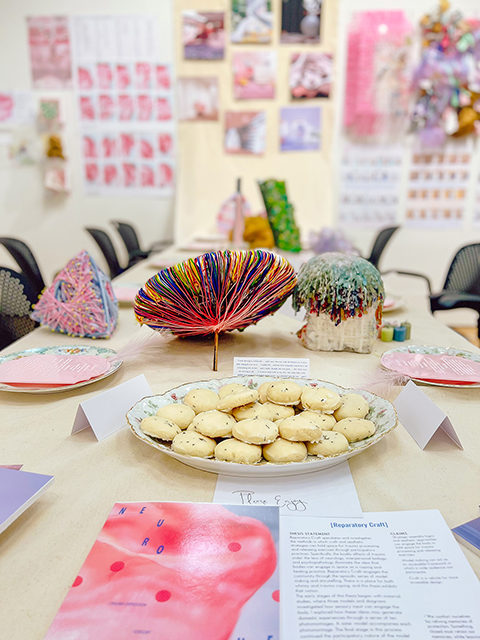
Reparatory Craft speculates and investigates the methods in which craft and aesthetic strategies can hold space for trauma processing and releasing exercises through participatory practices. Specifically, the bodily effects of trauma under the lens of neurology, interpersonal biology, and psychopathology illuminate the idea that bodies can engage in space as a coping and healing practice. Reparatory Craft engages the community through the episodic series of model making and storytelling. There is a place for both whimsy and trauma coping, and this thesis exhibits that notion.
The early stages of this thesis began with material studies, where three models and diagrams investigated how sensory input can engage the body. I explored how these ideas may generate domestic experiences through a series of ten photomontages. A sister model accompanies each photomontage. The final stage in this process continued the participatory nature of the model making through three wall assemblies with the engagement of twelve participants.
KEY QUESTIONS
-How can a multidisciplinary approach towards addressing trauma begin to shift the methodologies and conversations around design?
-What is architecture’s role in addressing trauma?
-What assembly strategies are productive in prompting dialogue?
-What sensory details are successful in engaging the body?
CLAIMS
-Strategic assembly logics and aesthetic approaches can engage the body to hold space for trauma processing and releasing exercises.
-Model making can act as an accessible framework in which a wide audience can participate.
-Craft is a vehicle for more accessible design.
“We comfort ourselves by reliving memories of protection. Something closed must retain our memories, while leaving them their original value as images. Memories of the outside world will never have the same tonality as those of home and, by recalling these memories, we add to our store of dreams; we are never real historians, but always near poets, and our emotion is perhaps nothing but an expression of a poetry that was lost.”
-Gaston Bachelard
Instagram: @marymargaretwilliams, @j_akerman
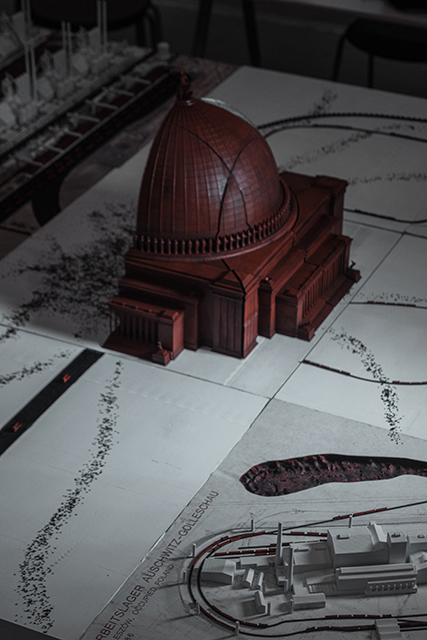
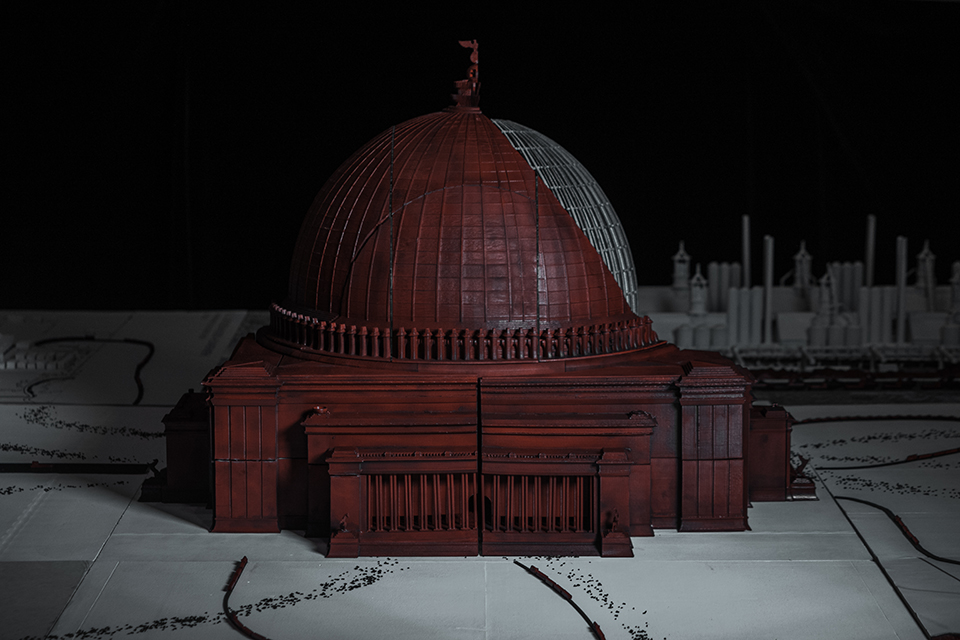
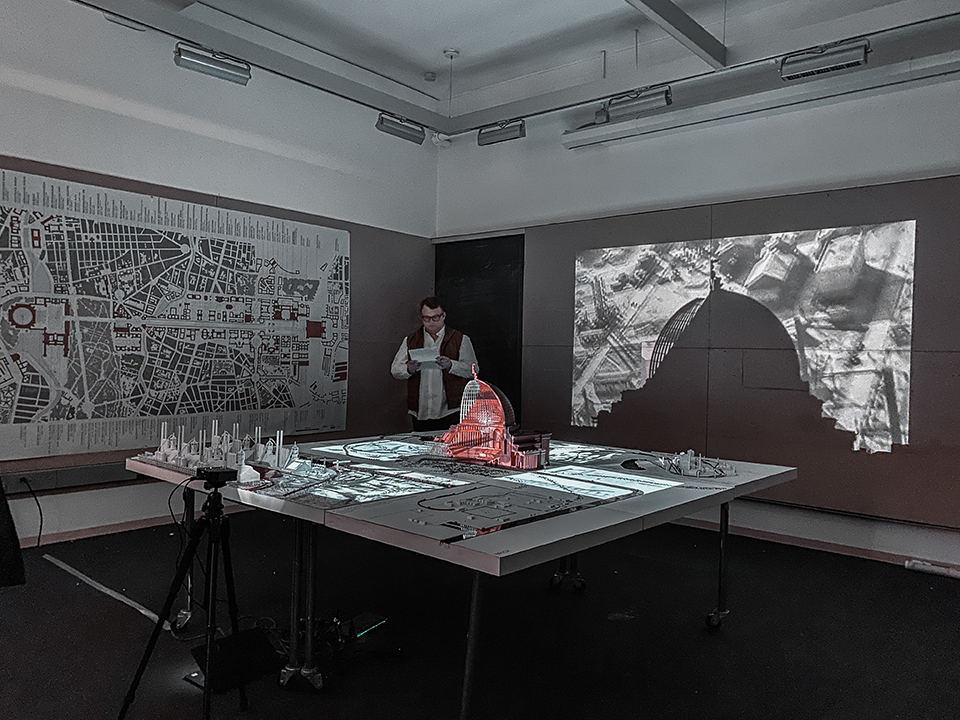
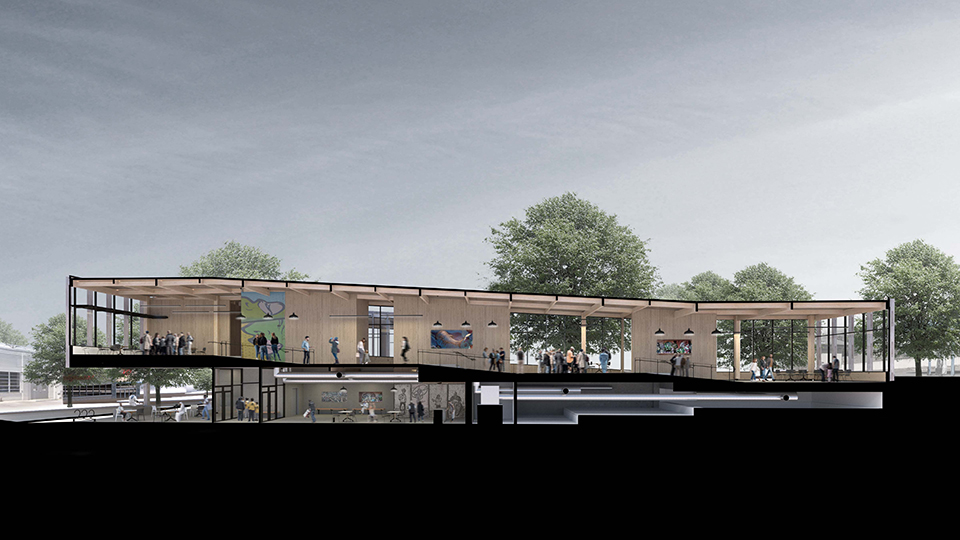
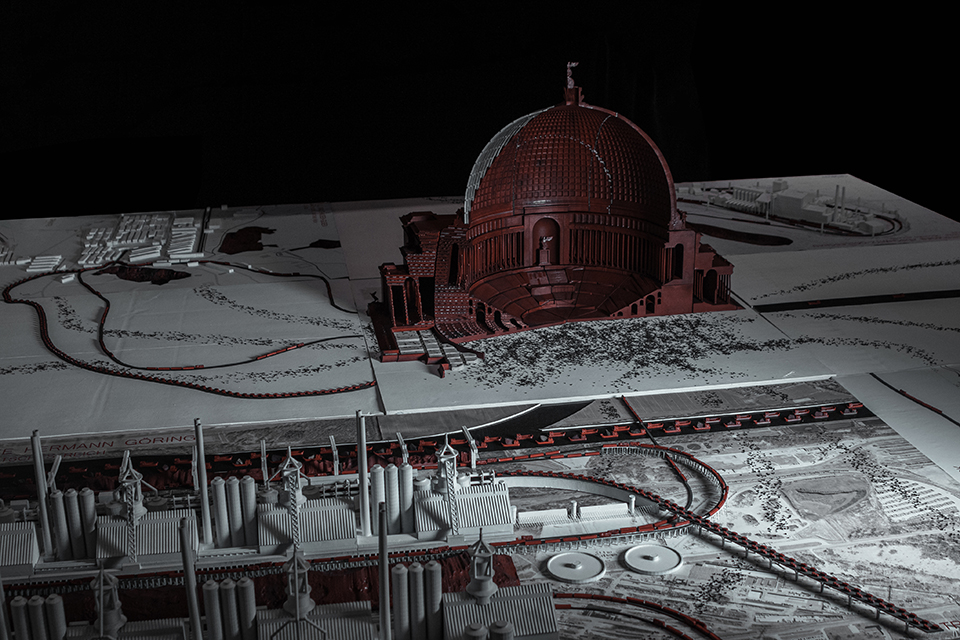
Ensanguined: Architecture, Militarism, and Slave Labor in the Nazi Monumental Building Program by Parker Klebahn, B.Arch ’22
Syracuse University | Advisor: Dr. Lawrence Chua
Dean’s Citations for Excellence in Thesis Design, Bernice Hogan Prize by the Department of History in the Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs
This project examines the monumental building practices and program of the Third Reich. By looking at the way monumental building was imbedded within the regimes policies of displacement, horrific and extractive labor, and genocide, this thesis establishes a critique of architecture and architects direct complicity and willing engagement with authoritarian regimes and atrocity. This project relies almost exclusively on original archival research and hopes to open a new line of discourse on the relationship between monumental architecture and labor practices in the Third Reich.
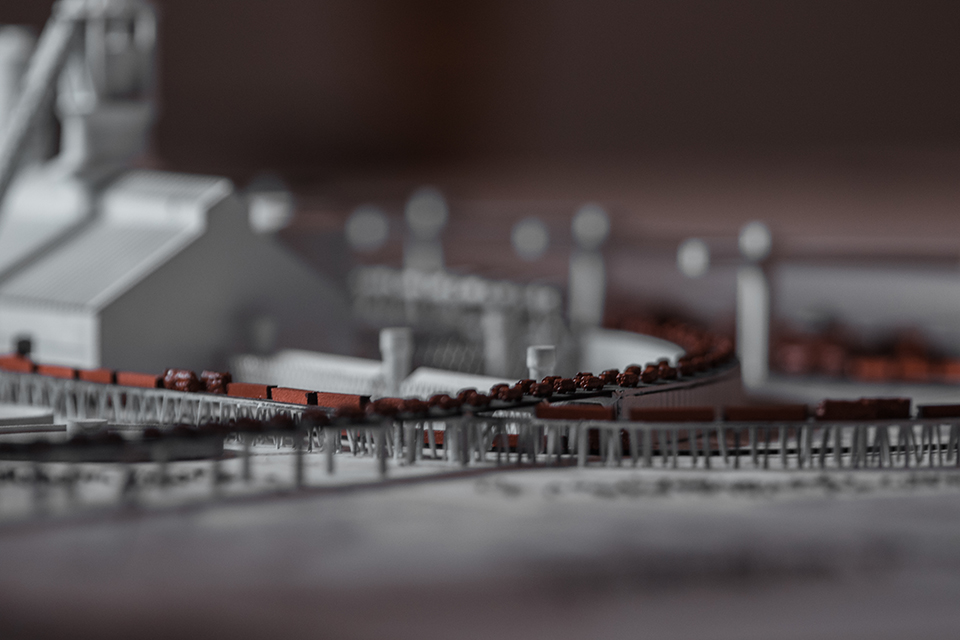
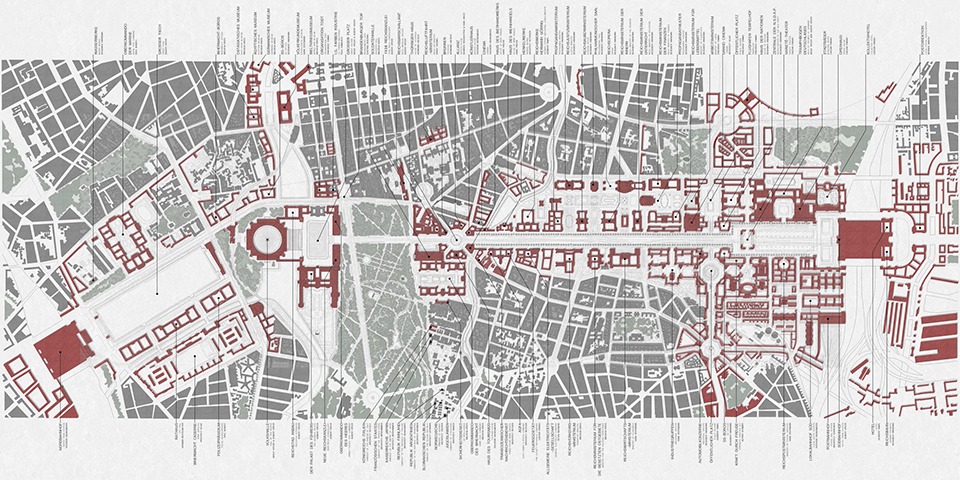
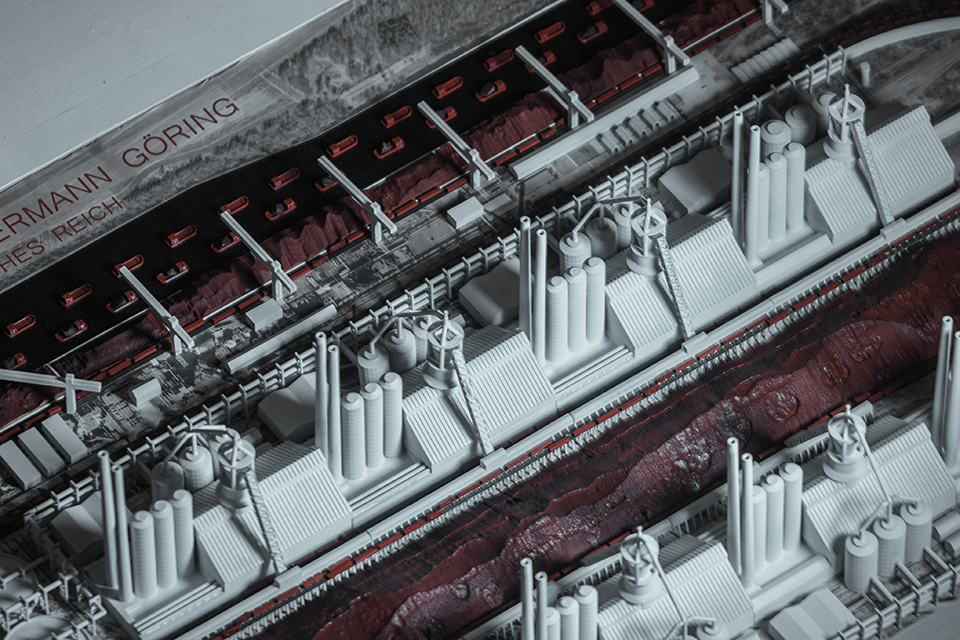
Architecture was an integral part of socio-cultural worldbuilding in Nazi Germany, the core of the Nazi’s architectural vision for Germany was Welthauptstadt Germania, a new masterplan for Berlin designed by Hitler, in conjunction with Albert Speer. At the center of Hitler’s new city was a massive domed hall that the Fuhrer had sketched years earlier while in prison writing Mein Kampf, it was to be called the Volkshalle, the hall of the people. Planning documents for The Volkshalle called for the largest slave labor force ever assembled, for 10 years of construction along with millions of tons of building materials. The Volkshalle, and all other Berlin reconstruction projects were to be built utilizing the massive systems of brutal oppression and slave labor that the Third Reich had created, often parts of it being purpose built for the monumental buildings themselves. This massive network of slave labor facilities, deportation centers, and extermination camps were the horrific reality of Hitler’s sketches and lofty architectural aspirations. Architects and Politicians in Nazi Germany had used monumental architecture directly in the pursuit of genocide.
This project takes shape in the form of a large model. At the center of the model sits the Volkshalle, but the Volkshalle has been Ensanguined, dirtied and is shown in a state of gross imperfection, the pieces of the model do not fit together properly. In the cutting of the mode, four primary building materials are shown. Adjacent to the Volkshalle are four of the real slave labor facilities that produced materials for the project, they are shown accurately, I offer no comment on their representation.
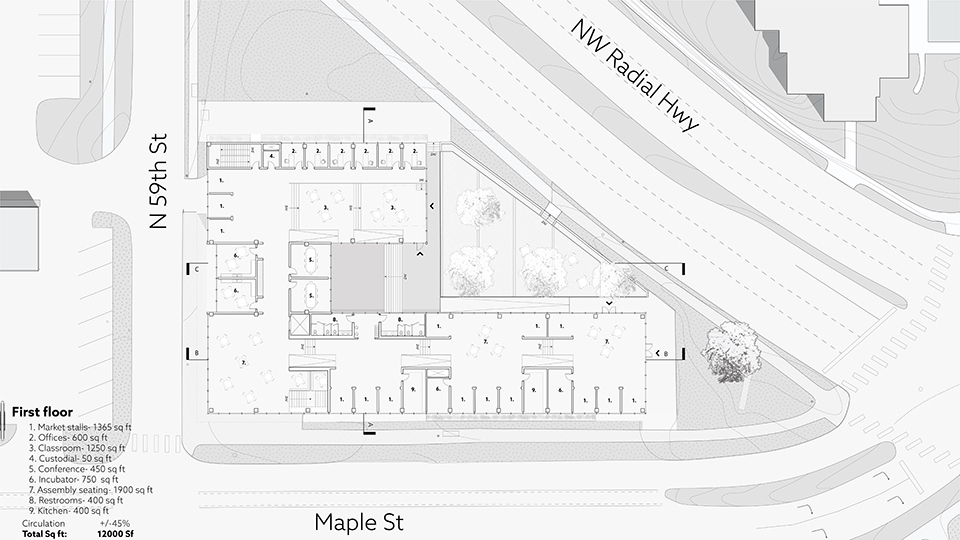
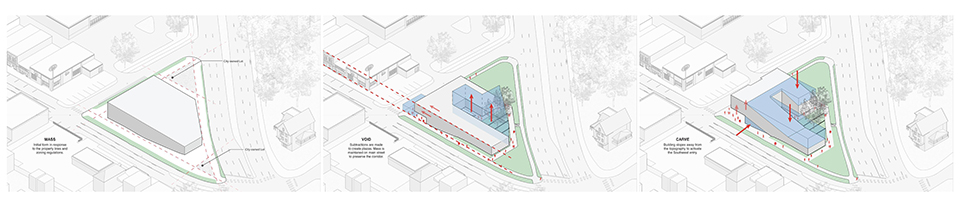
Community Crucible by Xander Parker and Austin Wahl, BSD Architecture
University of Nebraska | Advisor: Ashley Byars and Ryan Hier
SGH Concepts + Dri-Design Competition
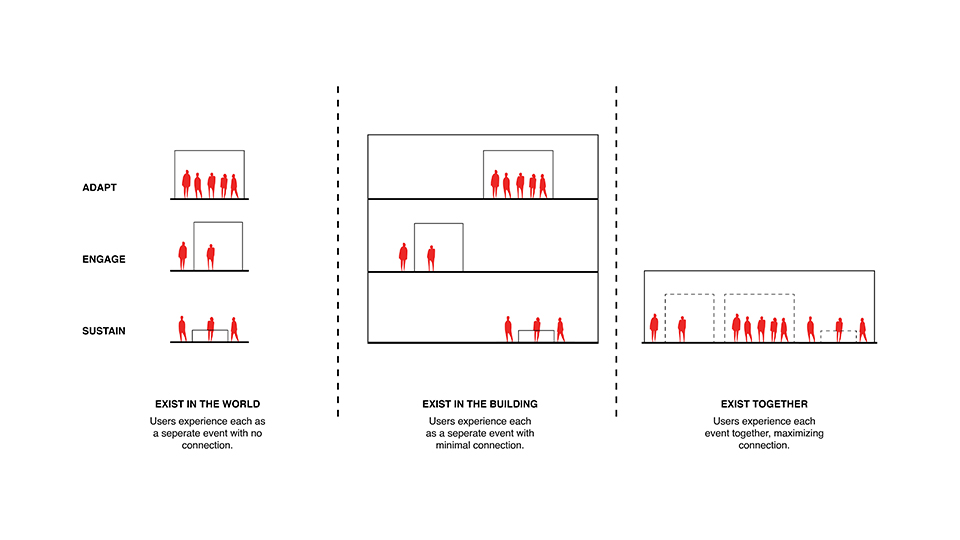
To provide a voice to the people, our project embraces the concept of Community Crucible. A place or situation in which concentrated forces interact to cause or influence change or development. To enact that change our proposal identifies three strategies to facilitate development; adapt, sustain, and engage.
Adapt refers to the flexible and loosely fitted program that sits within the project that is ever changing with community needs. Sustain invokes support through the physical preservation of the environment, while encouraging growth of the community. Likewise, engage refers to the intimate interactions that happen within transactional spaces. The community crucible having these strategies existing together allows a community to both grow and take authorship to preserve its culture.
Instagram: @austin_wahl15, @xanpar1, @ashley.k.byars, @ryanhier
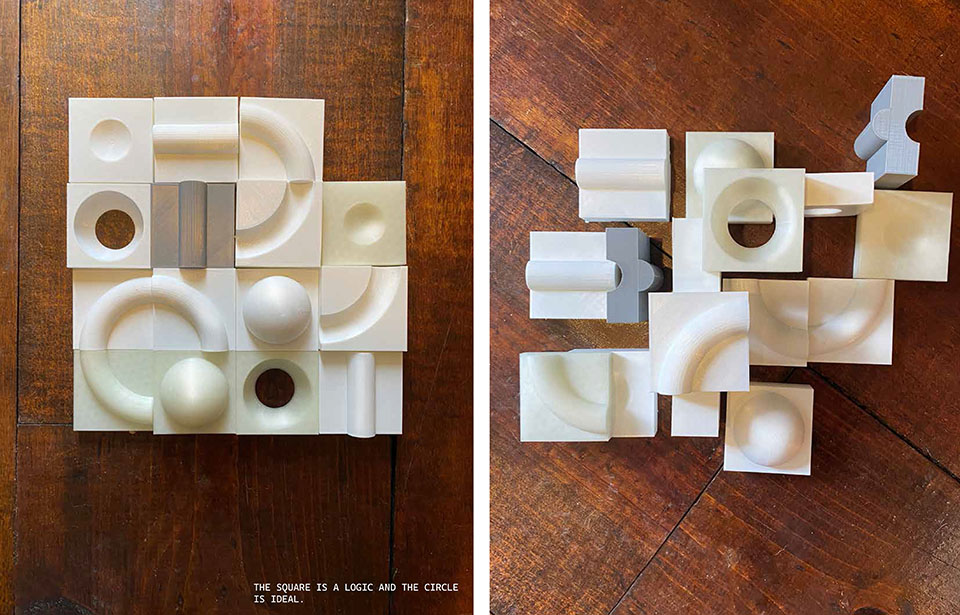
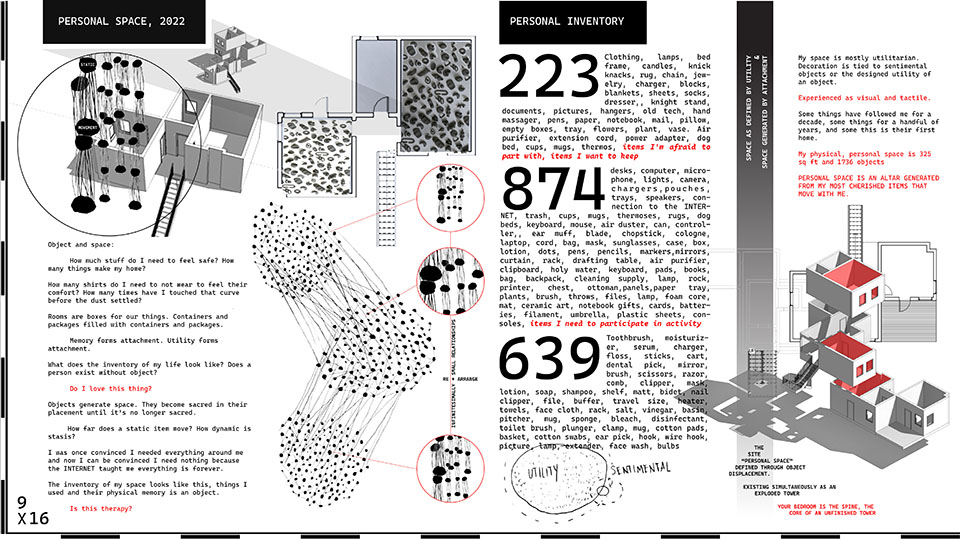
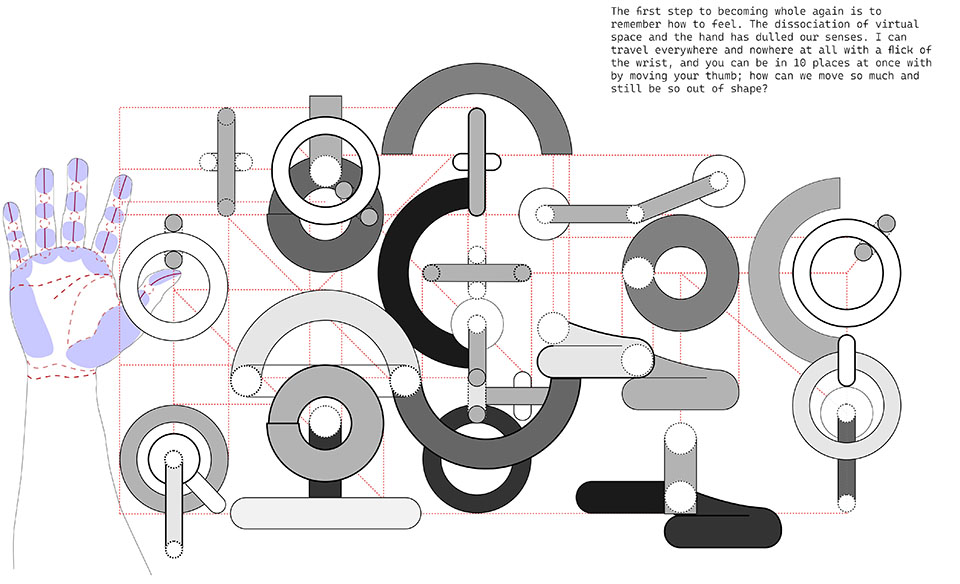
Objects & Affection by Andrew Tot Bui, M.Arch ’22
Morgan State University | Advisor: Coleman A. Jordan
Award for Best Thesis
Space is the accumulation of objects and artifacts of our daily lives. This project is a tactile exploration of form as a predetermination of virtual and real space.
We use our hands to navigate our real space and virtual space with limited feedback. This project is about the desk as personal space, the hand as the site, and object as architecture. Ergonomic designs are fractions of gestures and these derived forms are indeterminate fractals of gestures. Straight lines are logic tools and curves are corporal expressions starting from fingers and into the body.
The end result is a catalogue of forms, materials, and process that speak about void and figure as an object of personal reflection. These objects implore a user to navigate with their hands and arrange compositions to create space with grid and form by exploring the simplicity of shapes and wholeness.
Instagram: @andrew.bui.562, @studiocaje
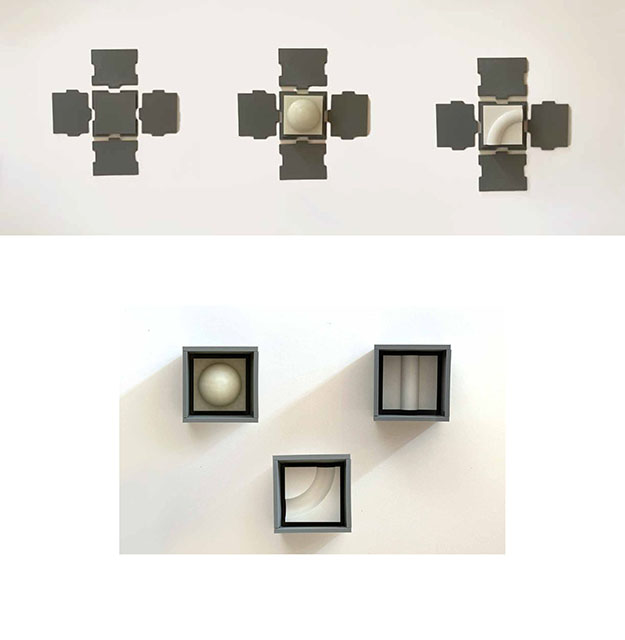
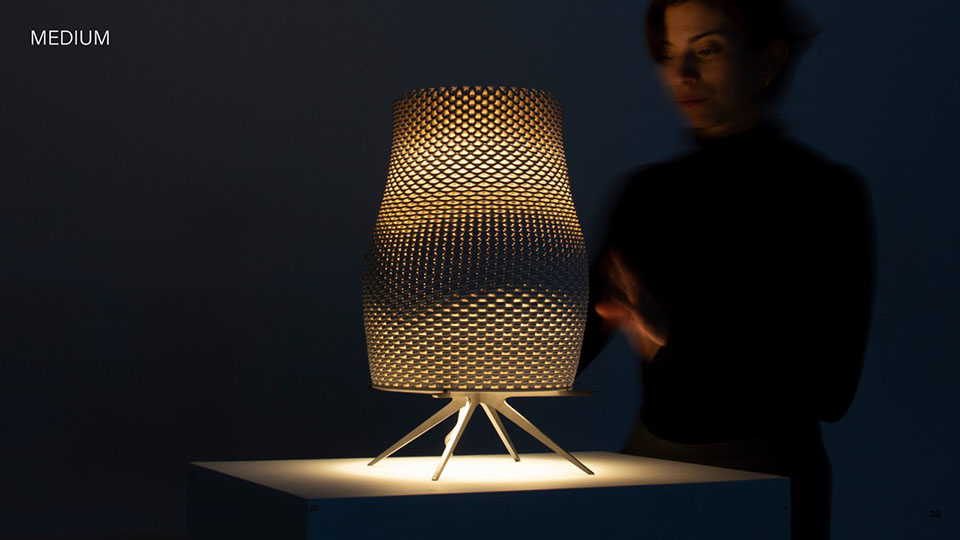
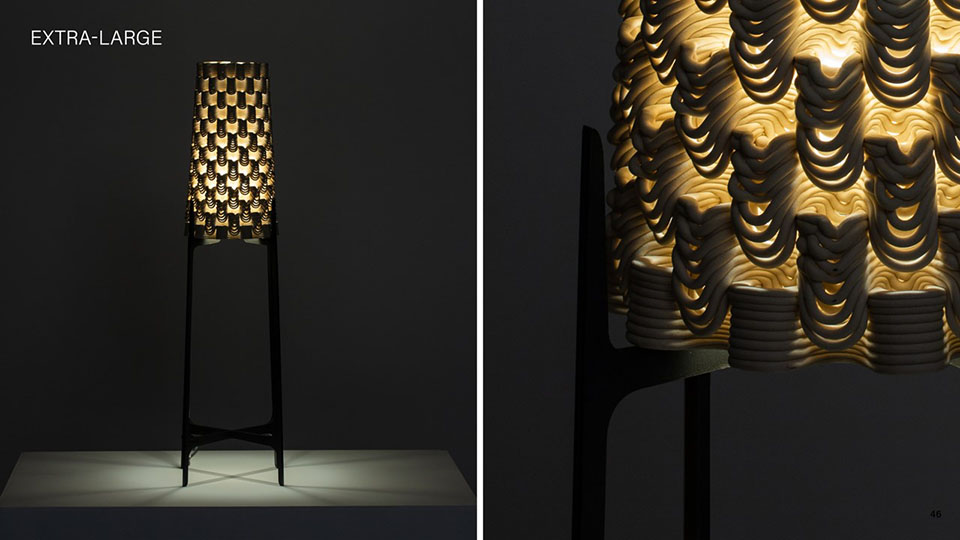
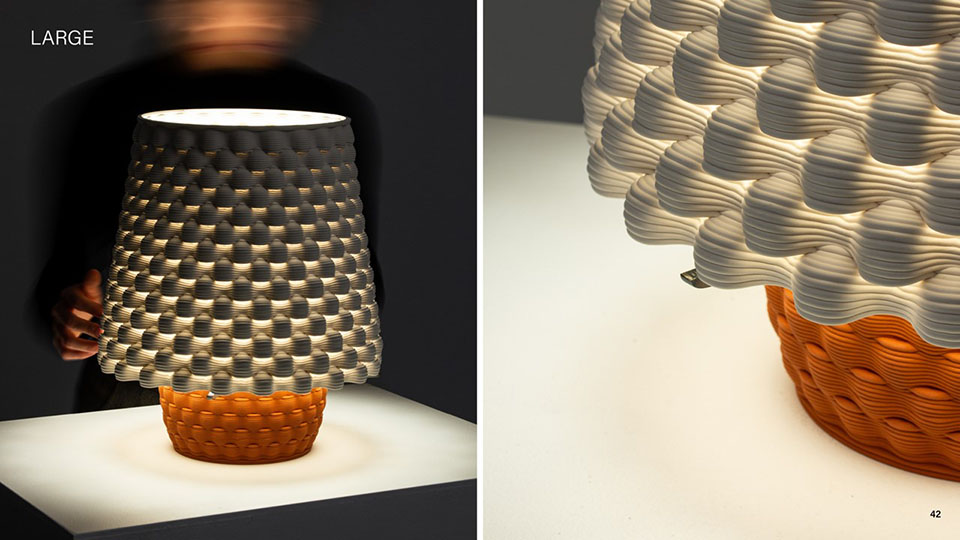
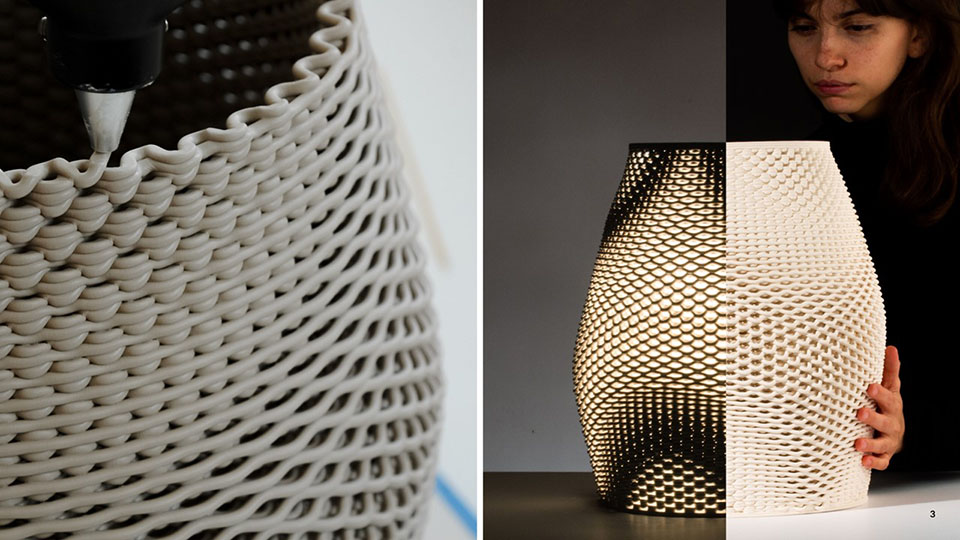
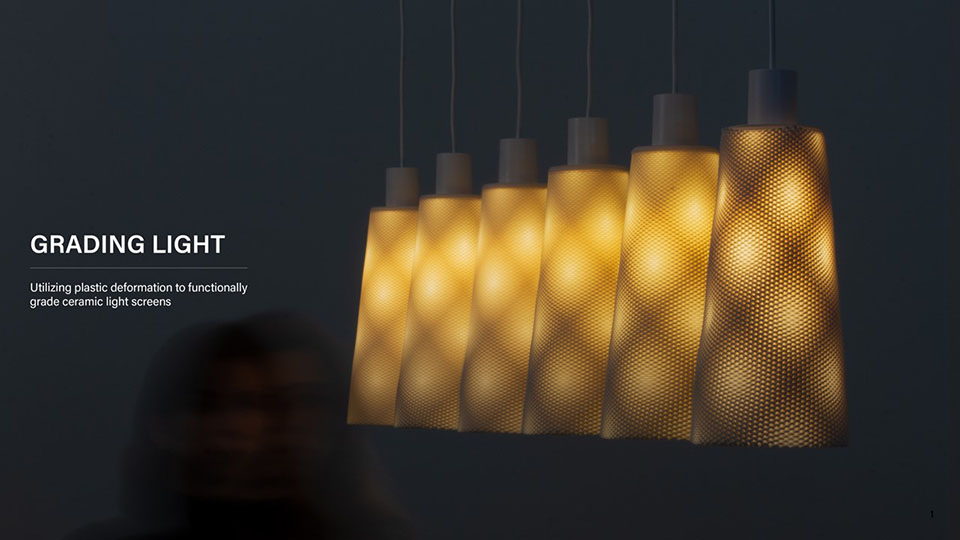
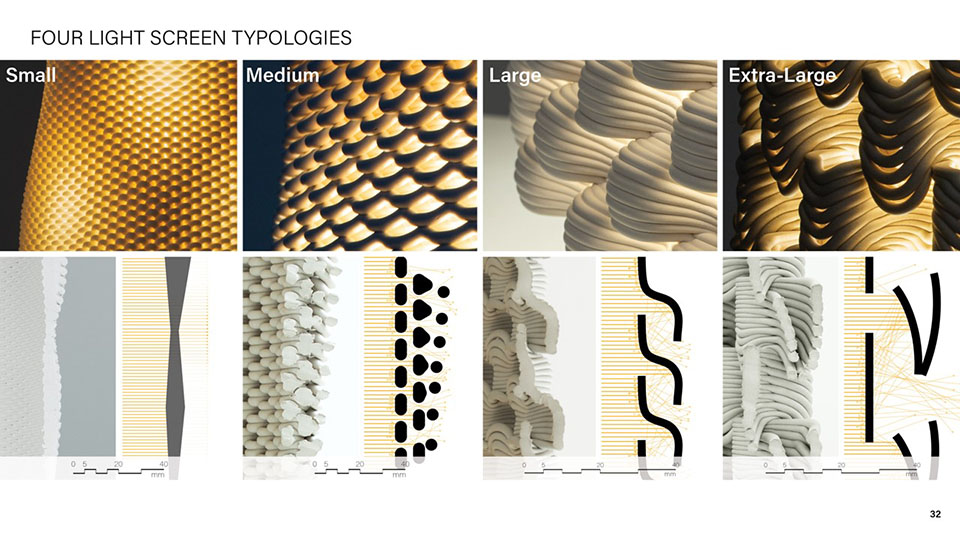
Grading Light by James Clark-Hicks and Isabel Ochoa, M.Arch ’22
University of Waterloo | Advisor: David Correa
When interacting with light, surface geometries and clay bodies can work together to heighten the perception of depth and alter illumination. This thesis investigates how clay 3D printing can generate materially responsive engagements between ceramics and light.
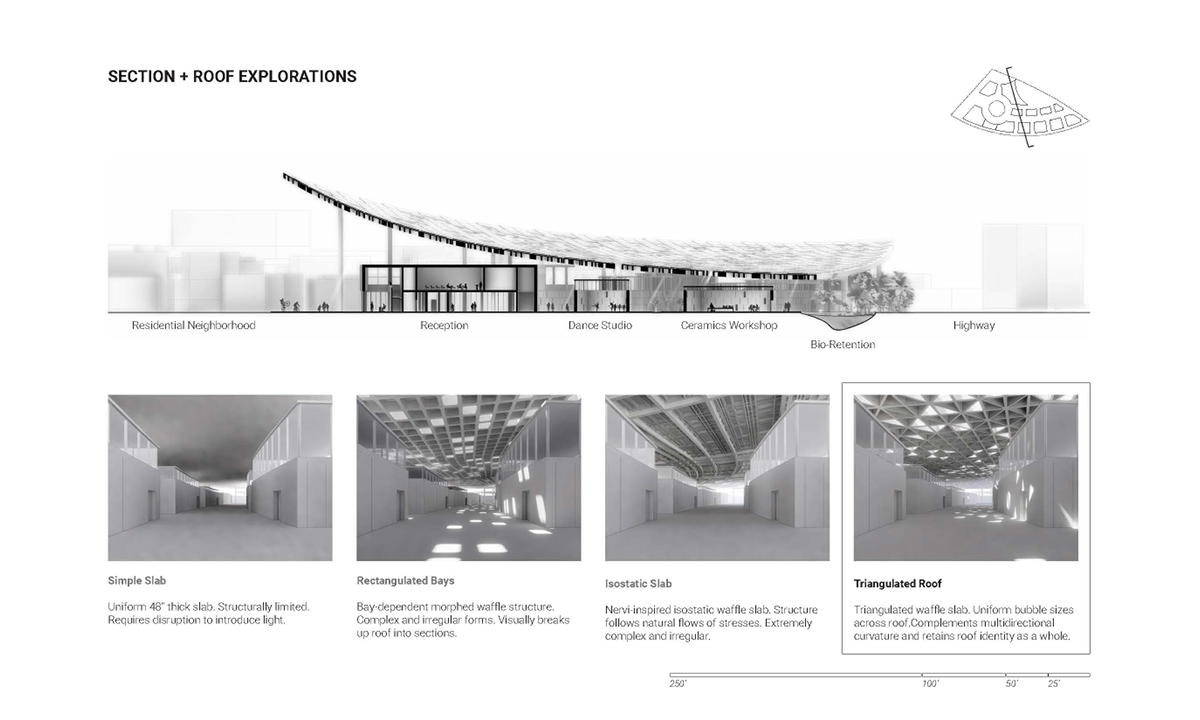
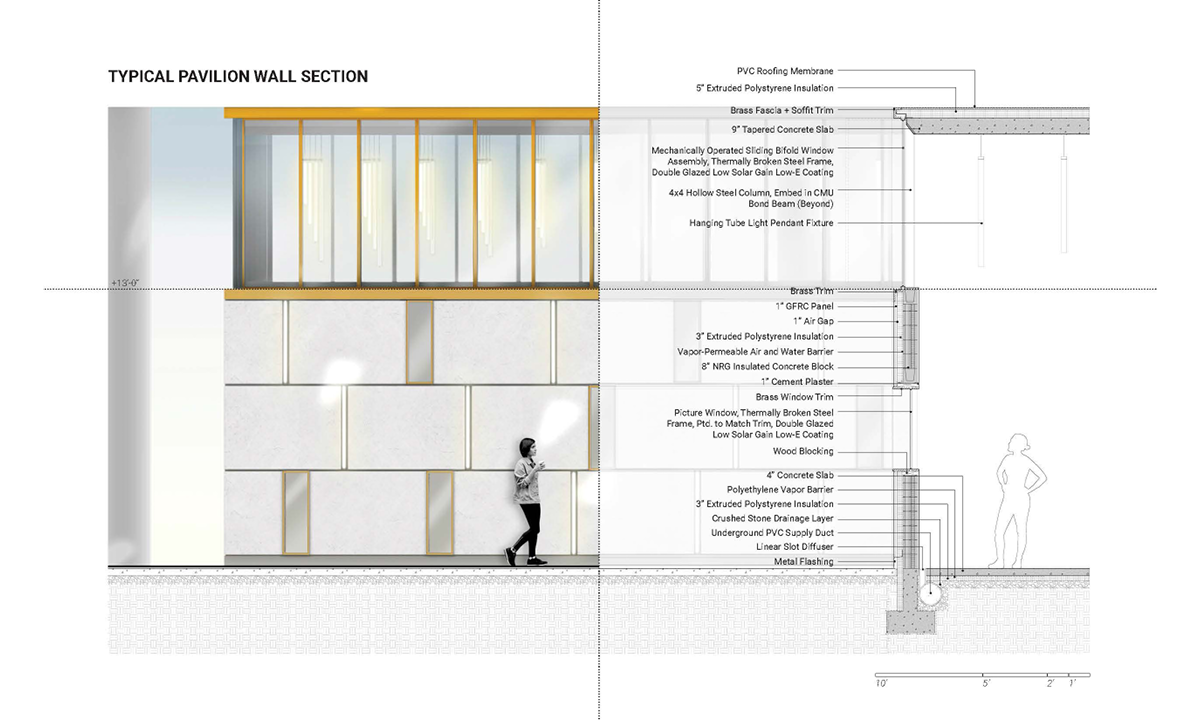
A computational methodology is developed to produce texture and sculptural relief in ceramic surfaces. Liquid Deposition Modeling is used to study the plastic deformation of clay during wet-processing. Most 3D printing technologies are currently conceived as end-stage production processes characterized by high-fidelity between digital models and physical outputs. Stoneware and porcelain have a wide variety of working properties and ceramic traits that demand new approaches to digital tooling. By making the study of material behaviour essential to the design process, clay 3D printing enables non-linear design-to-production systems. The research outputs are a series of stoneware and porcelain screens that vary in brightness and illumination based on how light may be obstructed, reflected or transmitted across their surfaces. Prototypes are developed at full scale to understand the relationship between sensory engagement and material properties.
The scope, context and research methods are divided into three parts: Light and Ceramic Material Performance– Explains stoneware and porcelain’s performance capabilities in the context of Functionally Graded Additive Manufacturing. Ceramics and Digital Fabrication– Explains the tools by which the research methods are produced in the context of how tool path design is being leveraged in the practice of digitally crafted ceramics. Methodology– Outlines the methods involved in making qualitative changes to alter light-scattering behaviour in 3D printed clay screens. The research is structured around a series of four light screen typologies. Each typology utilizes unique digital and physical tooling methods, harnesses plastic deformation, structural capabilities, and light scattering behaviour in porcelain and stoneware structures.
Instagram: @is_oc, @ochceramics, @materialsyntax
Check back next week for Part IV of the Study Architecture Student Showcase.