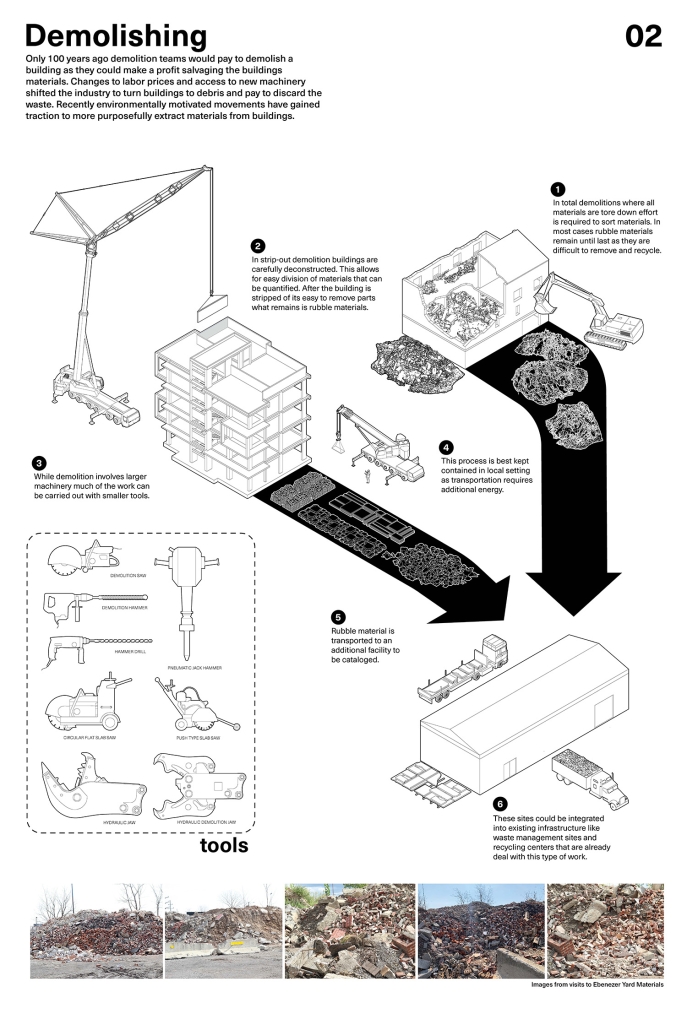
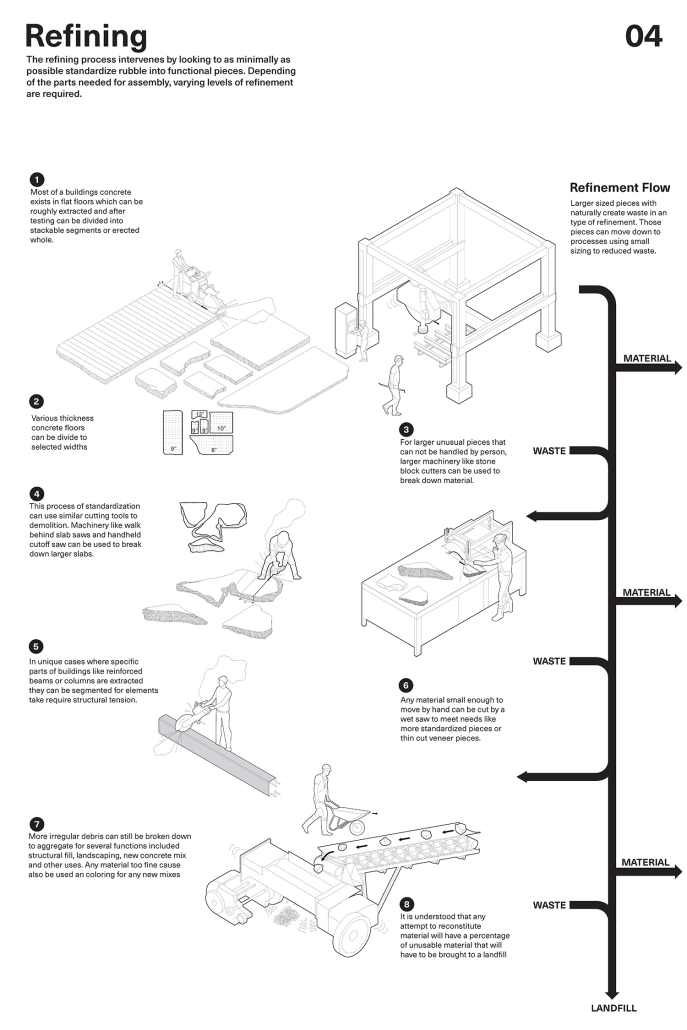
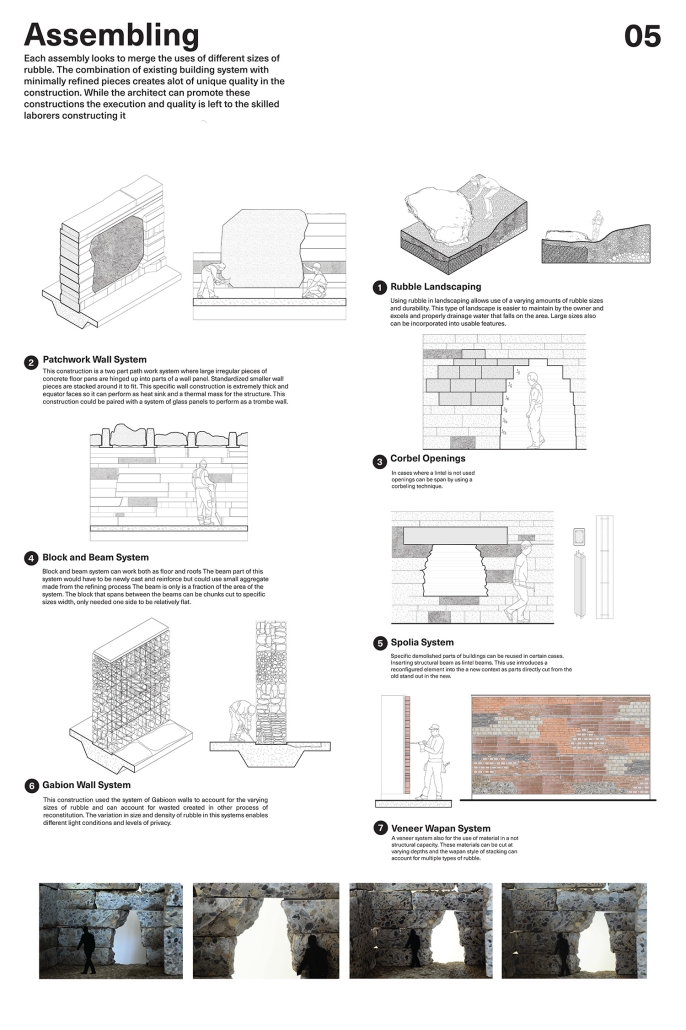
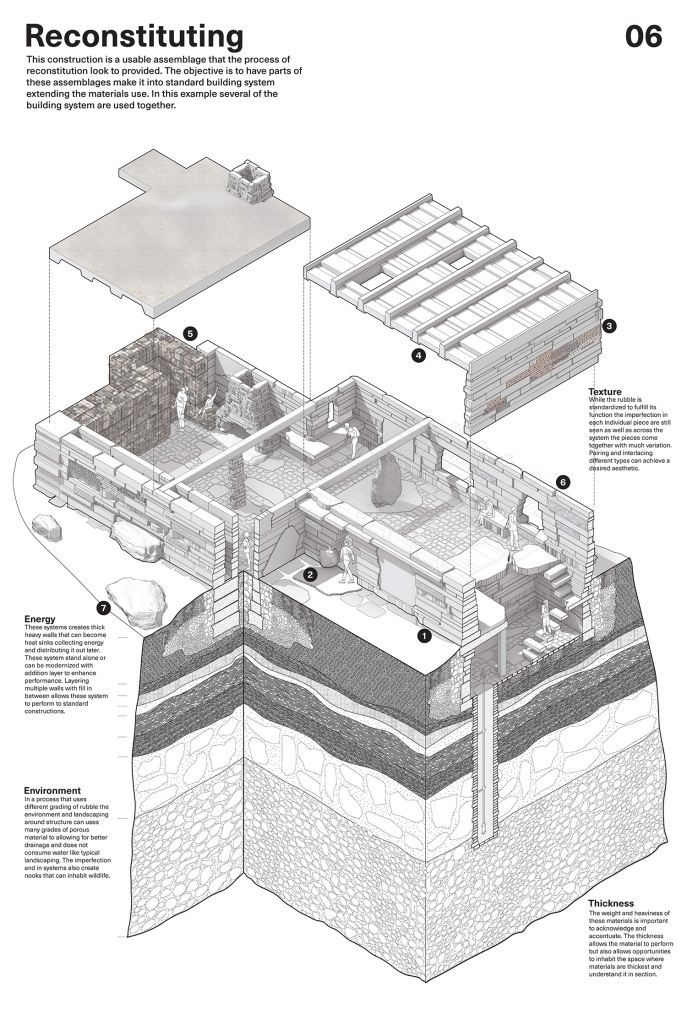
2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XXIX
How can architecture and design bridge the gap between tradition and modern-day practices? In Part XXIX the Study Architecture Student Showcase, we take a look at student work that recontextualizes funerary architecture to incorporate contemporary cityscapes and technology.
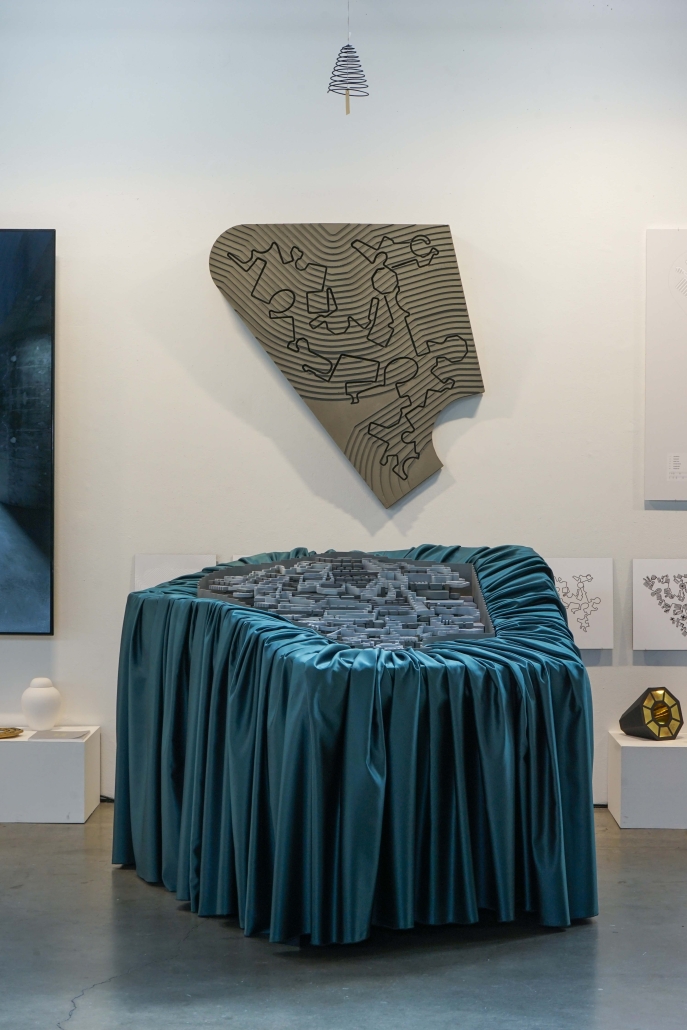
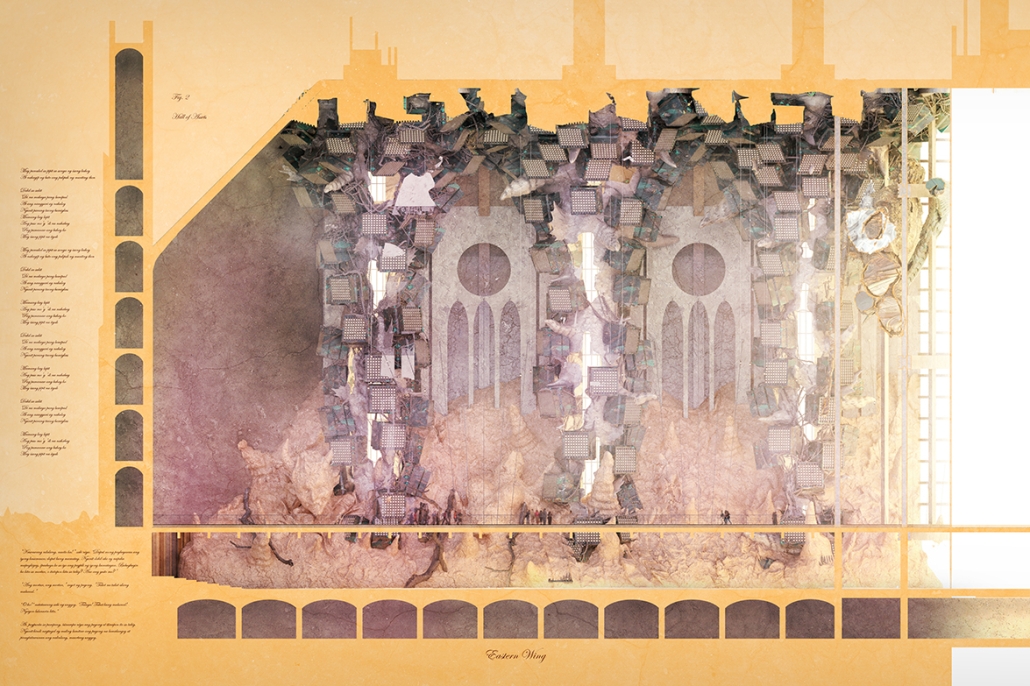
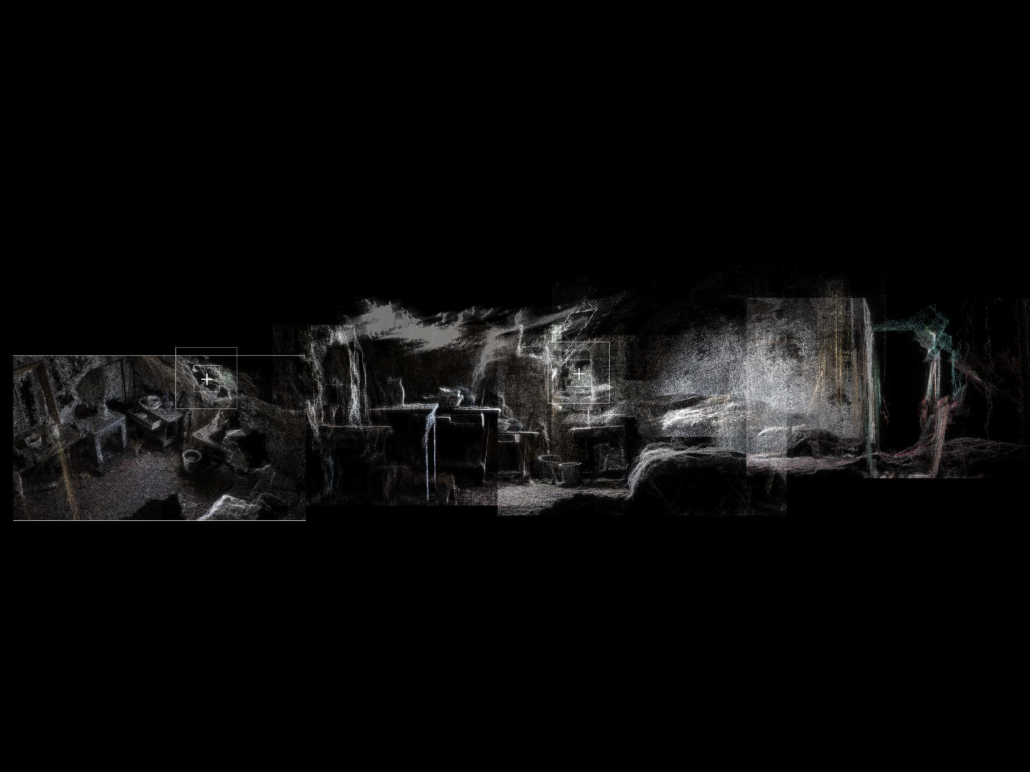
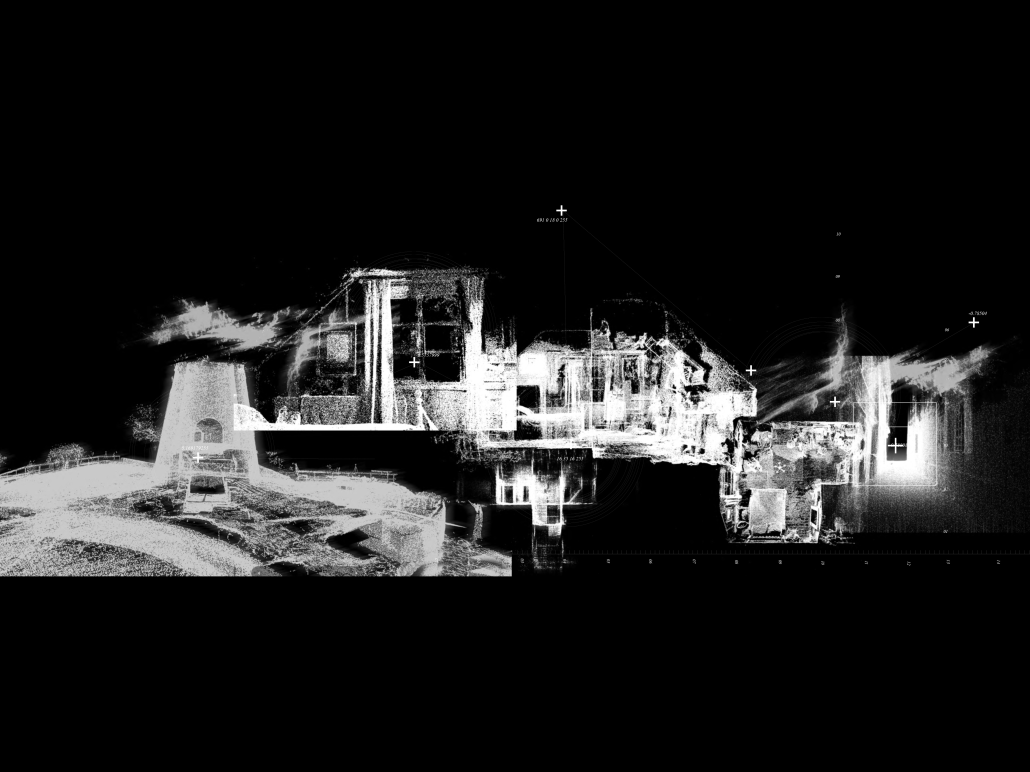
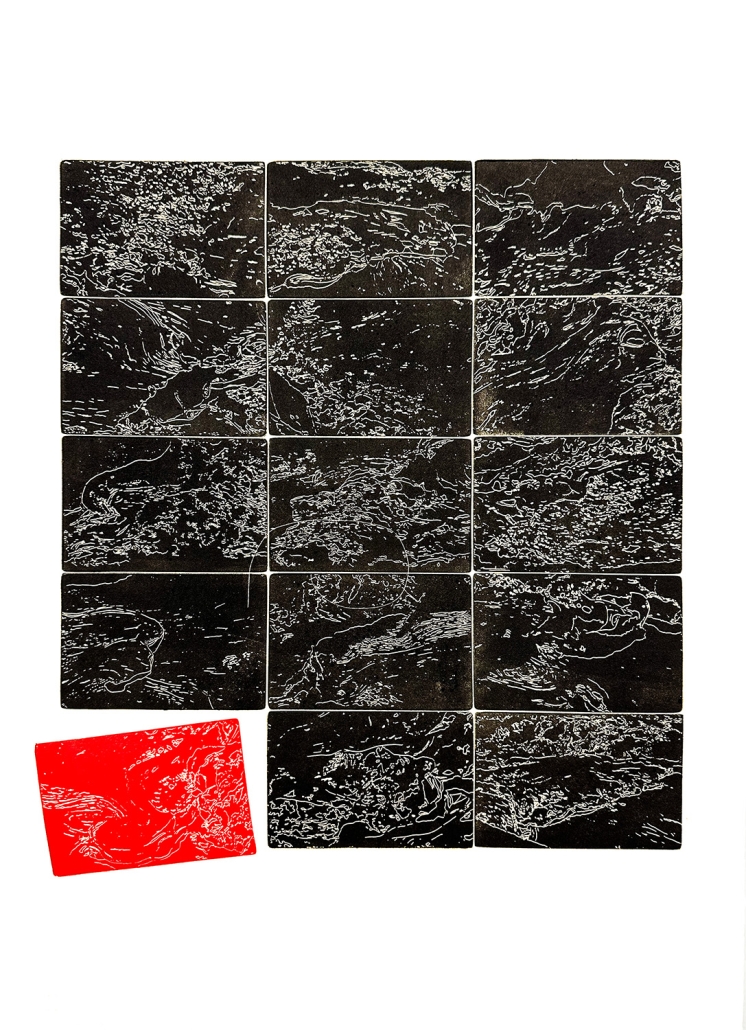
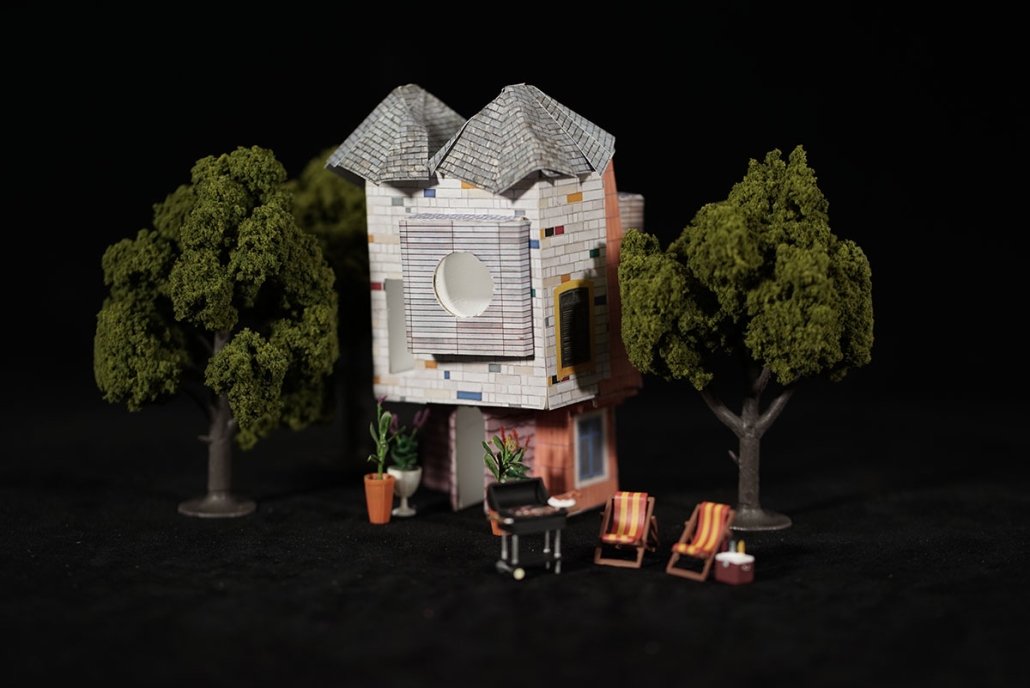
Earthly Passage by Si Ian Wong & Sue Choi, M.Arch ‘23
Southern California Institute of Architecture | Advisor: David Eskenazi
The traditional Cantonese funeral procession calls for a public performance of mourning. However, this tradition is no longer common practice today. Though there are still public ceremonial grieving practices, grievers in contemporary culture prefer experiences that are isolated from the distractions of the city, and for many, in solitude.
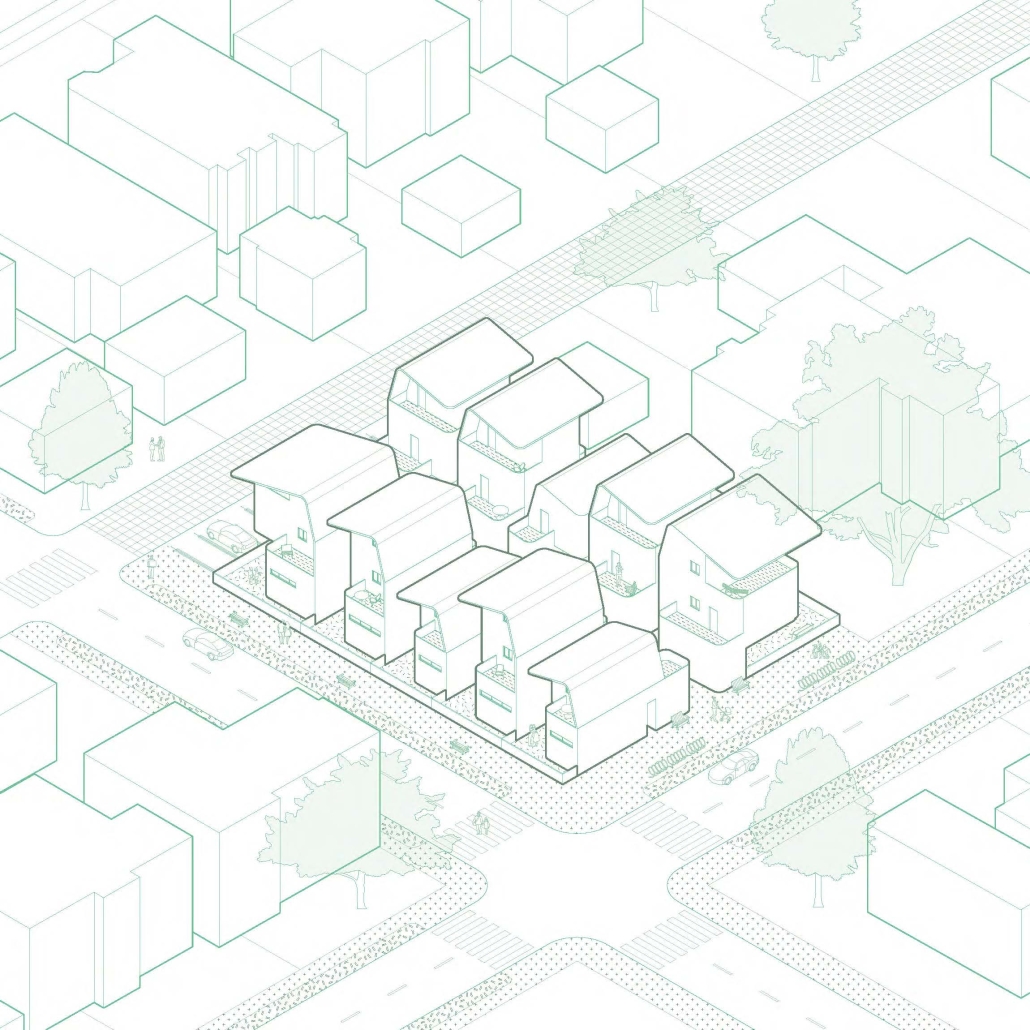
But in a city like Hong Kong, where spaces of seclusion are rare, mourners are forced to amble against the chaos of urban life to traverse between the various sites of the funeral – from the funeral home to the hillside cemetery, and back to an ancestral hall/temple/church – all of which are dispersed throughout the city in conformance to the traditional model of the processional funeral.
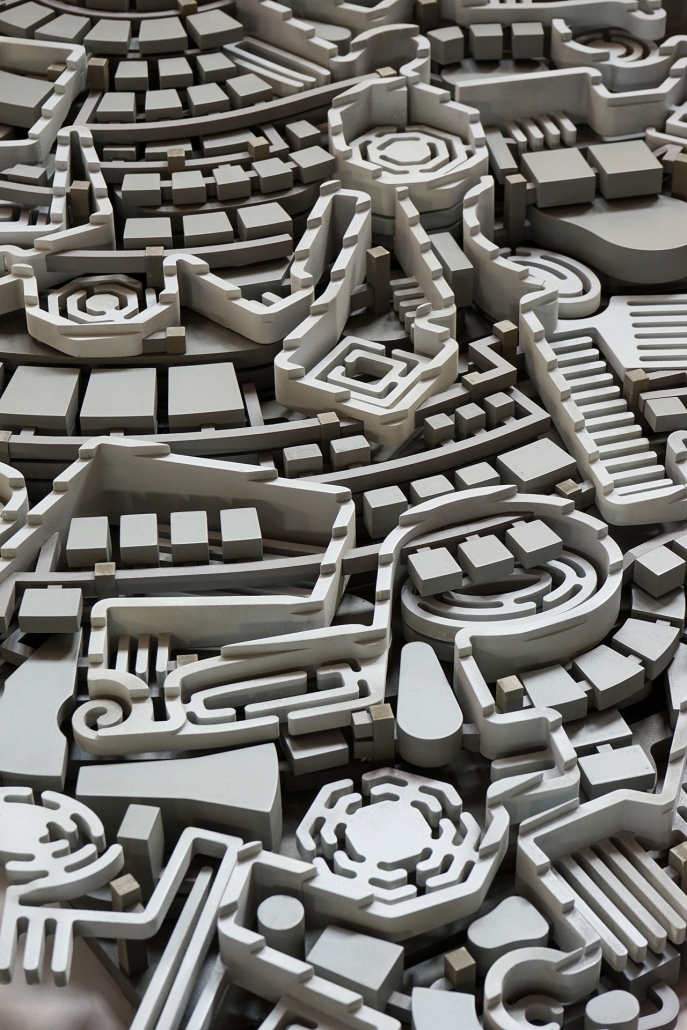
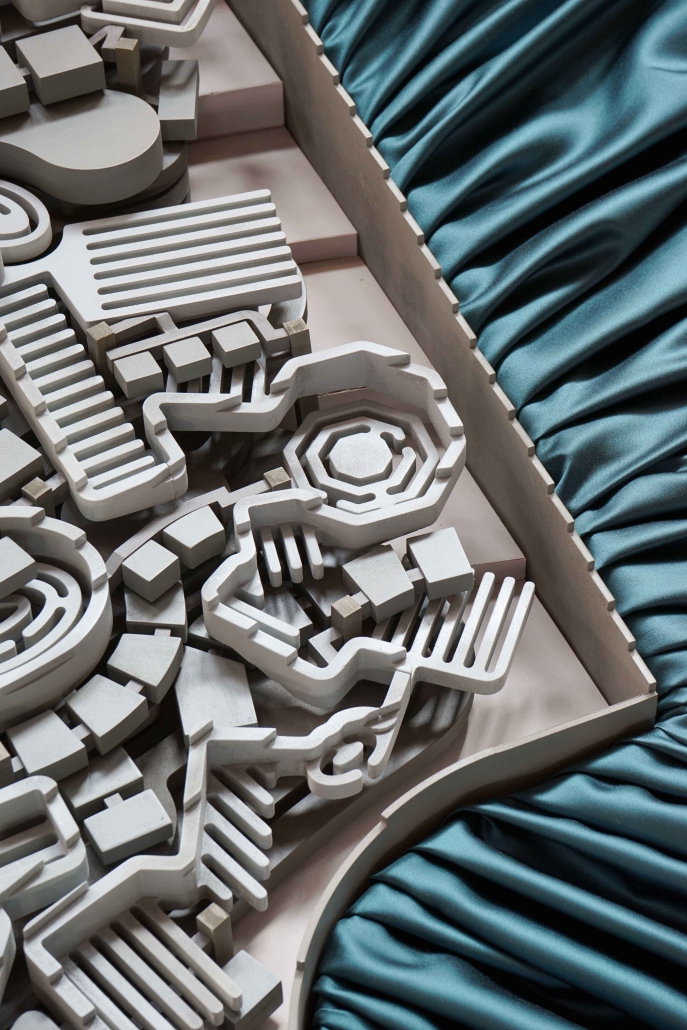
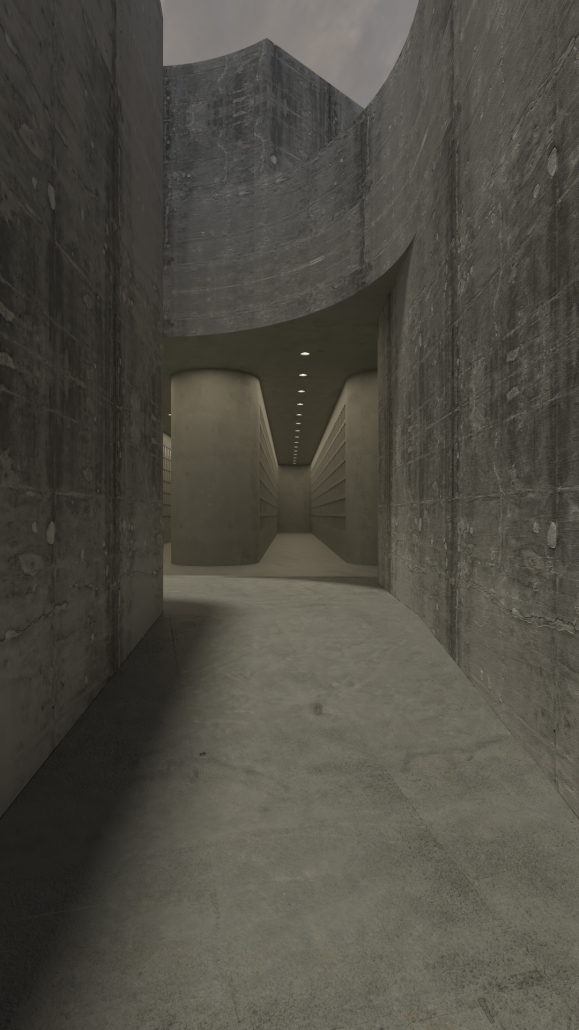
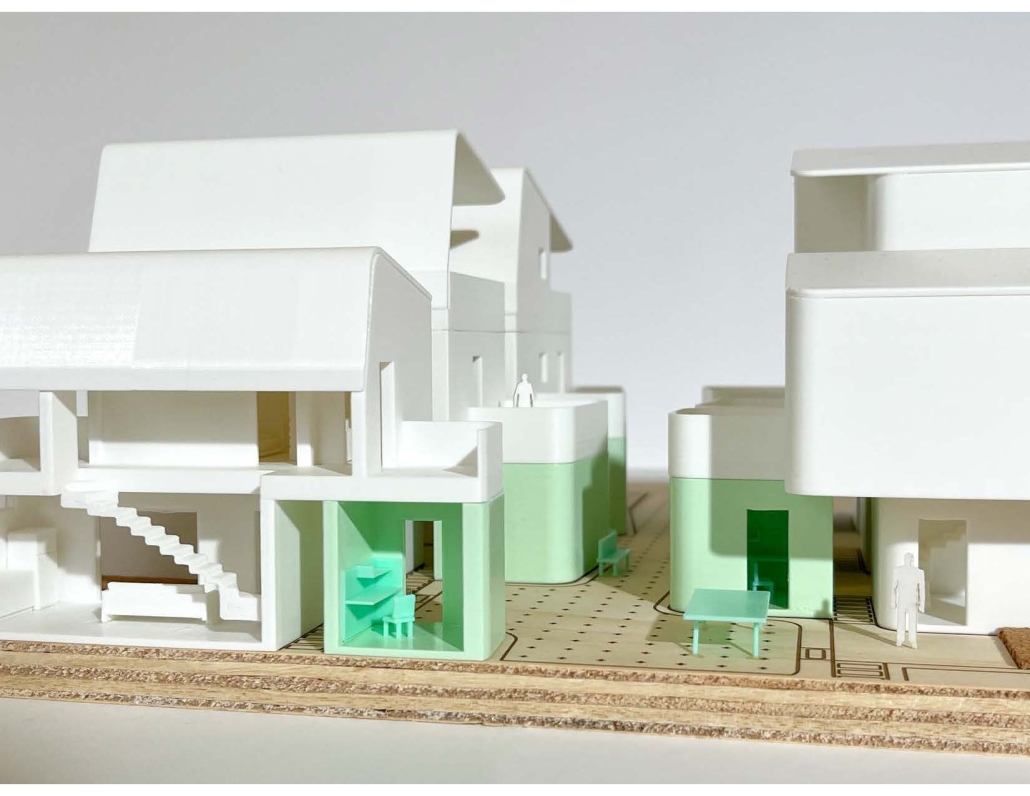
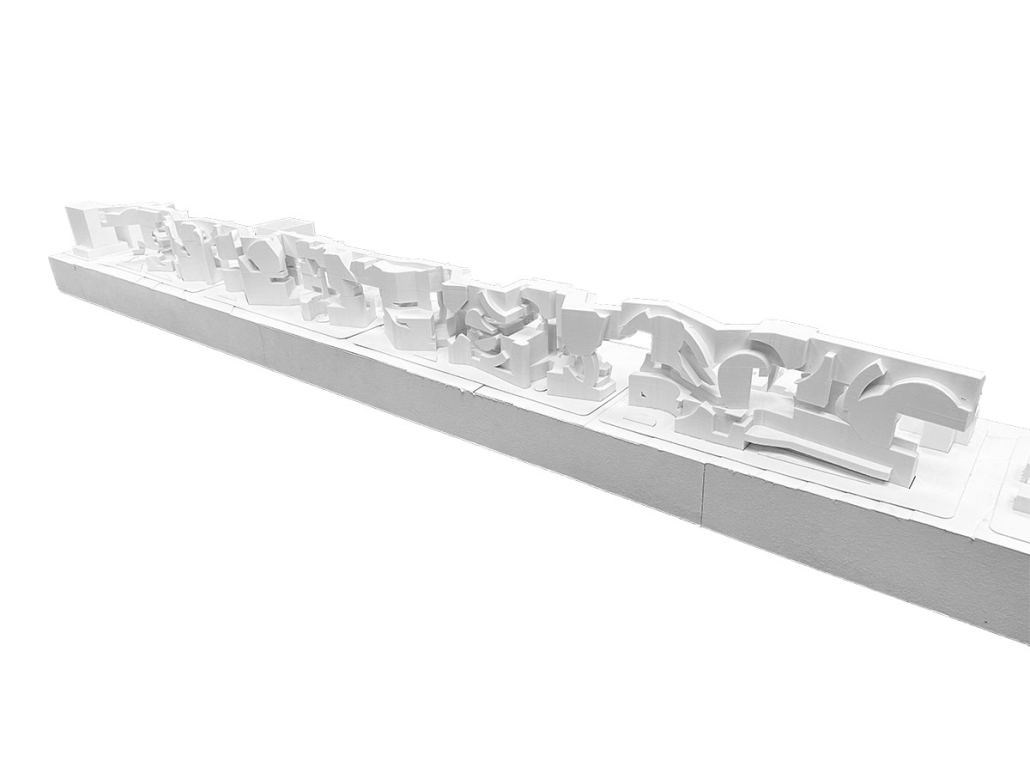
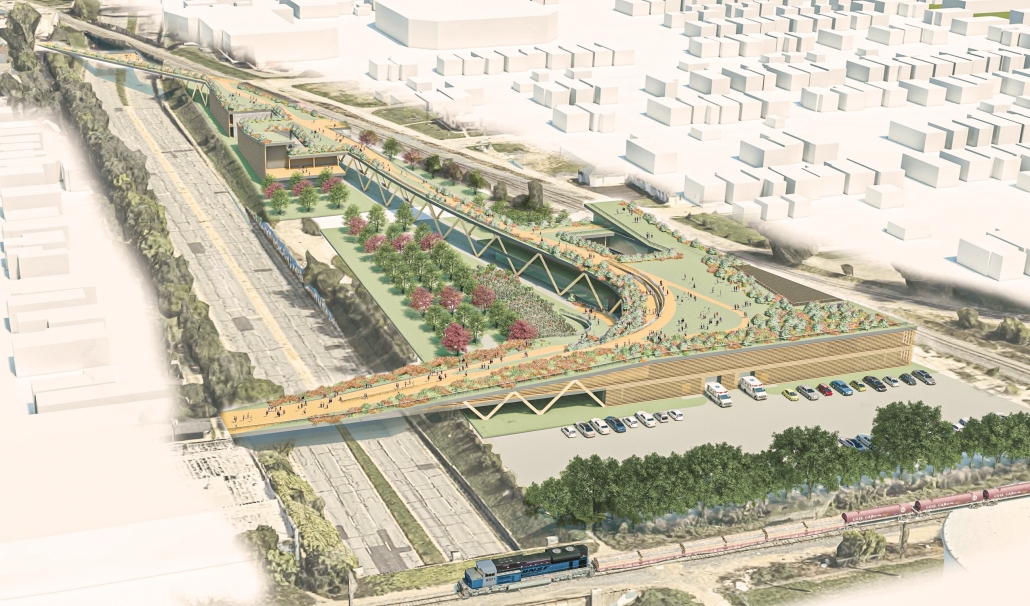
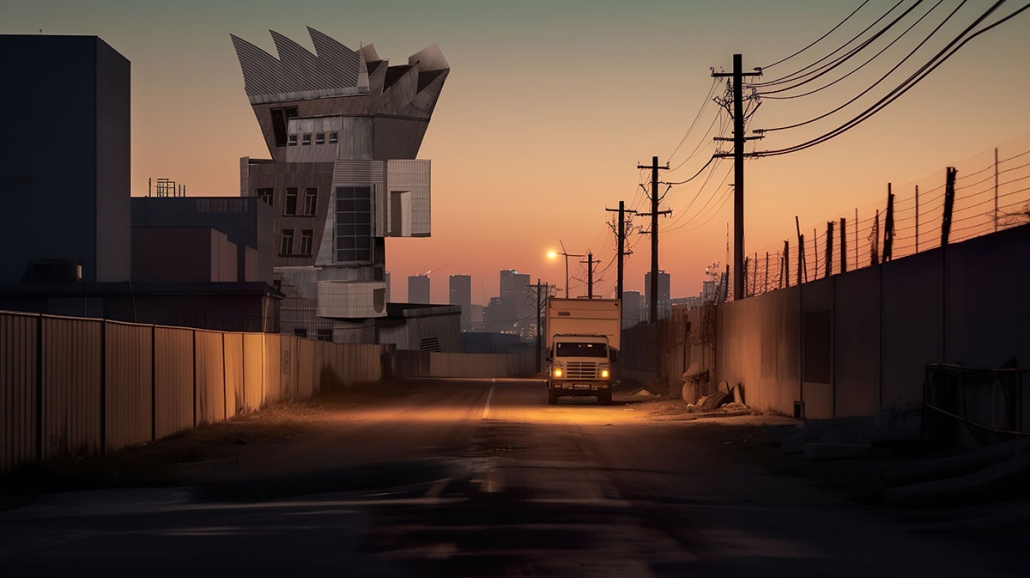
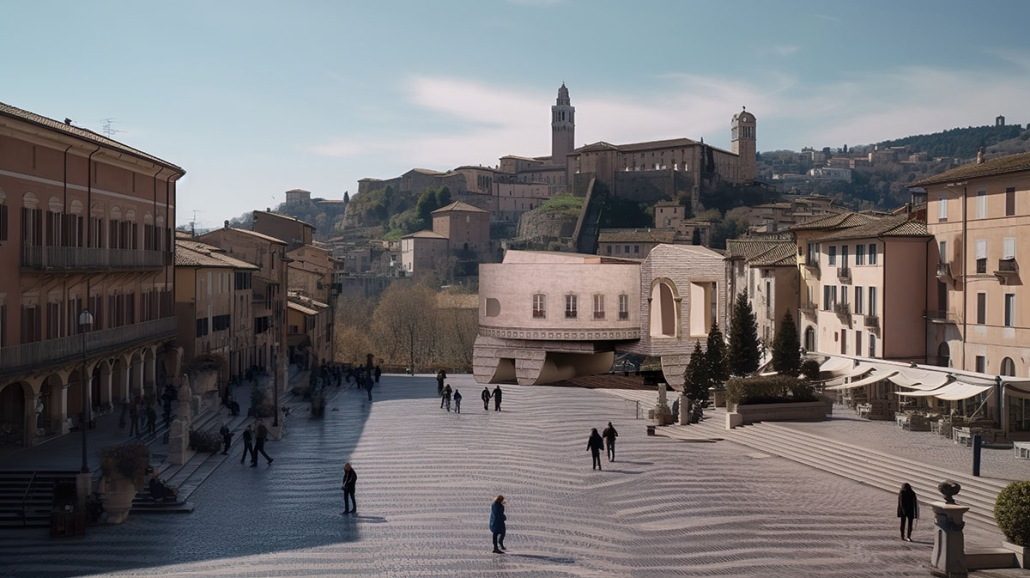
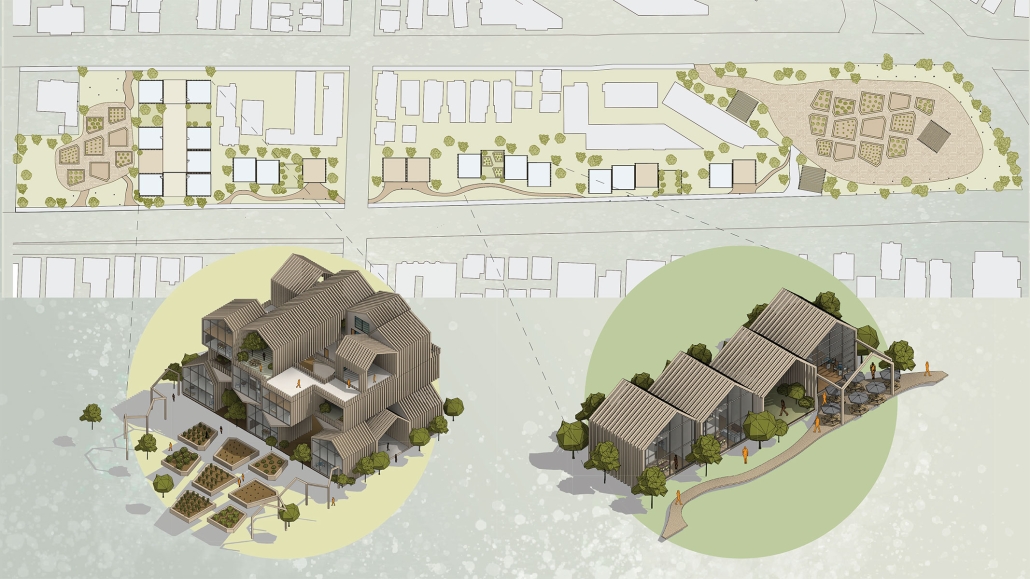
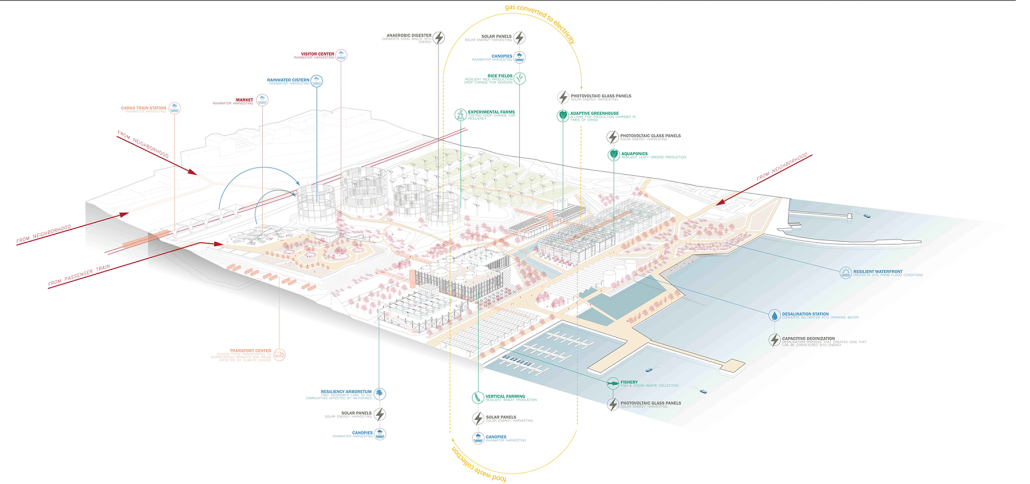
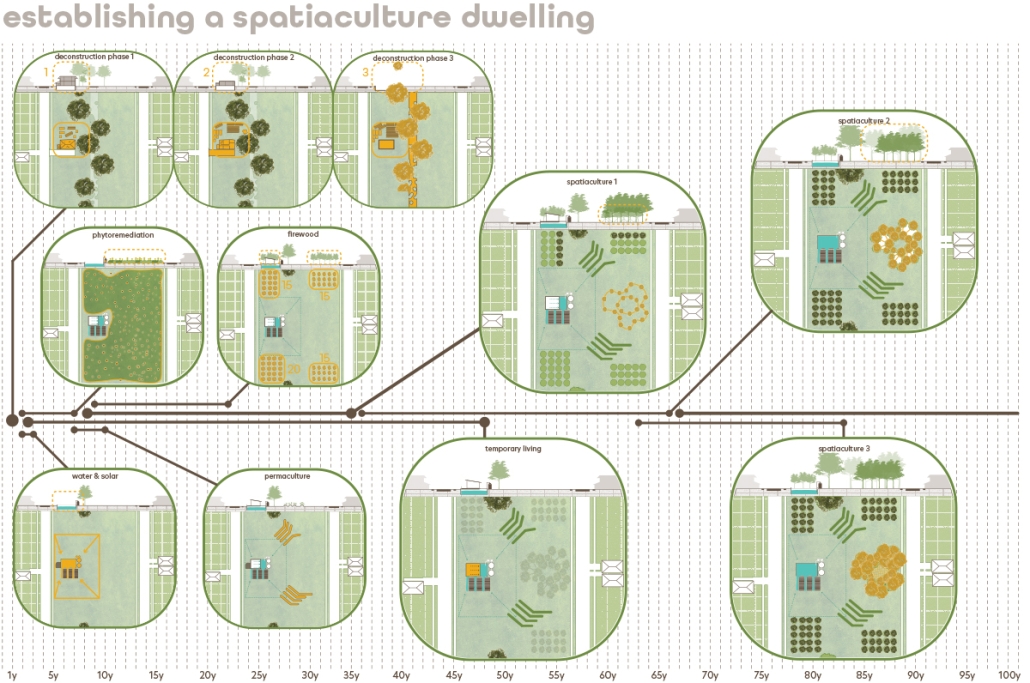
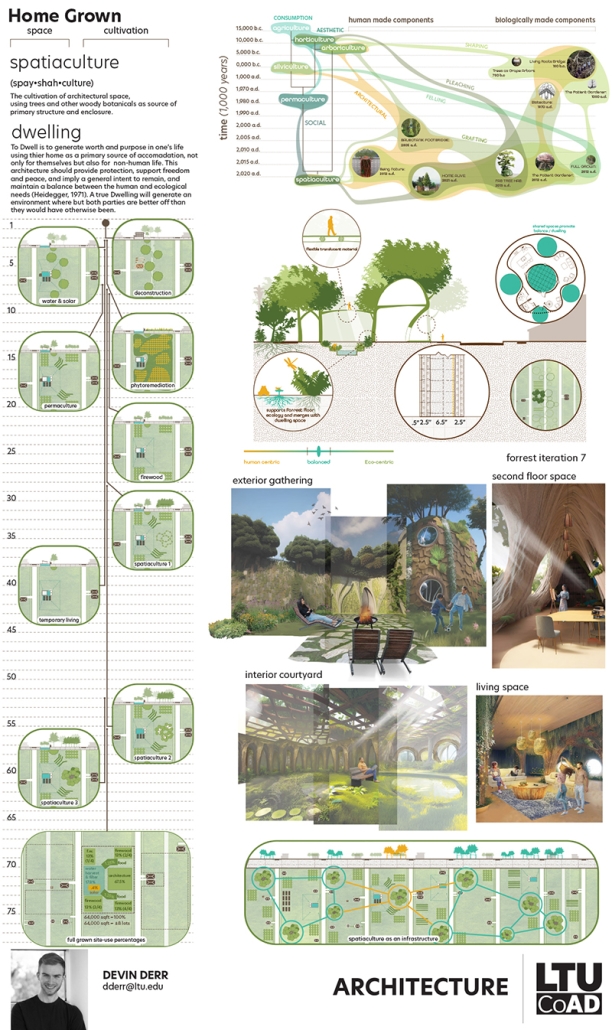
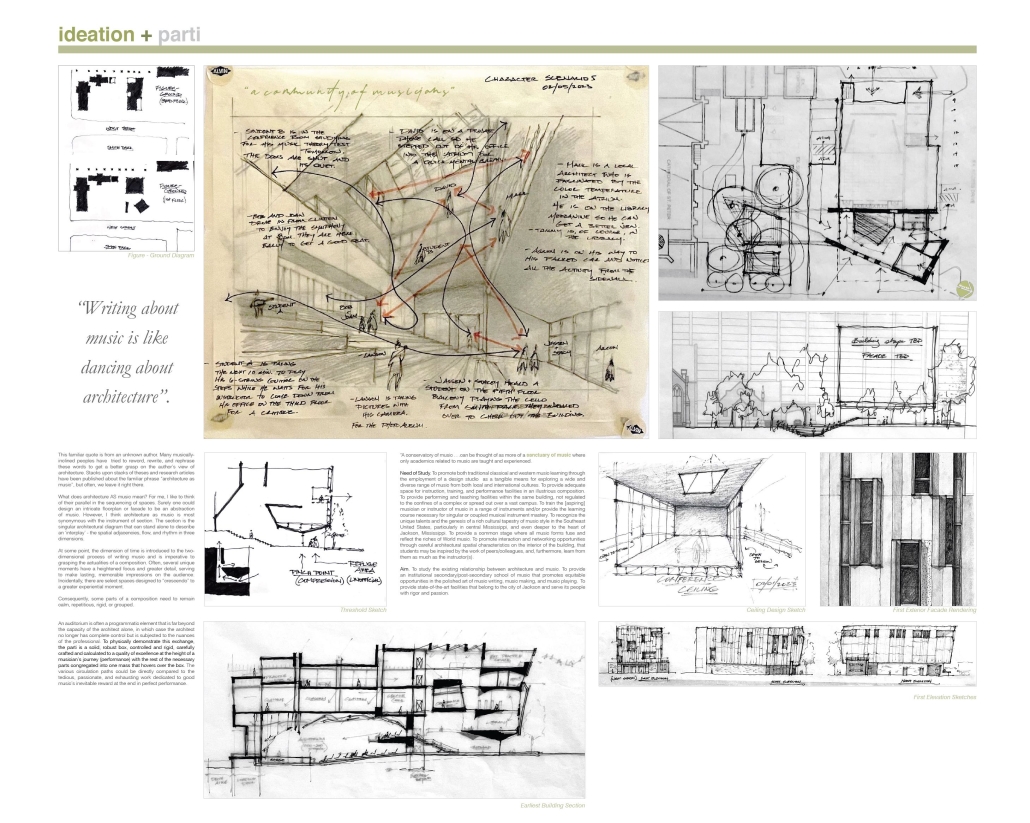
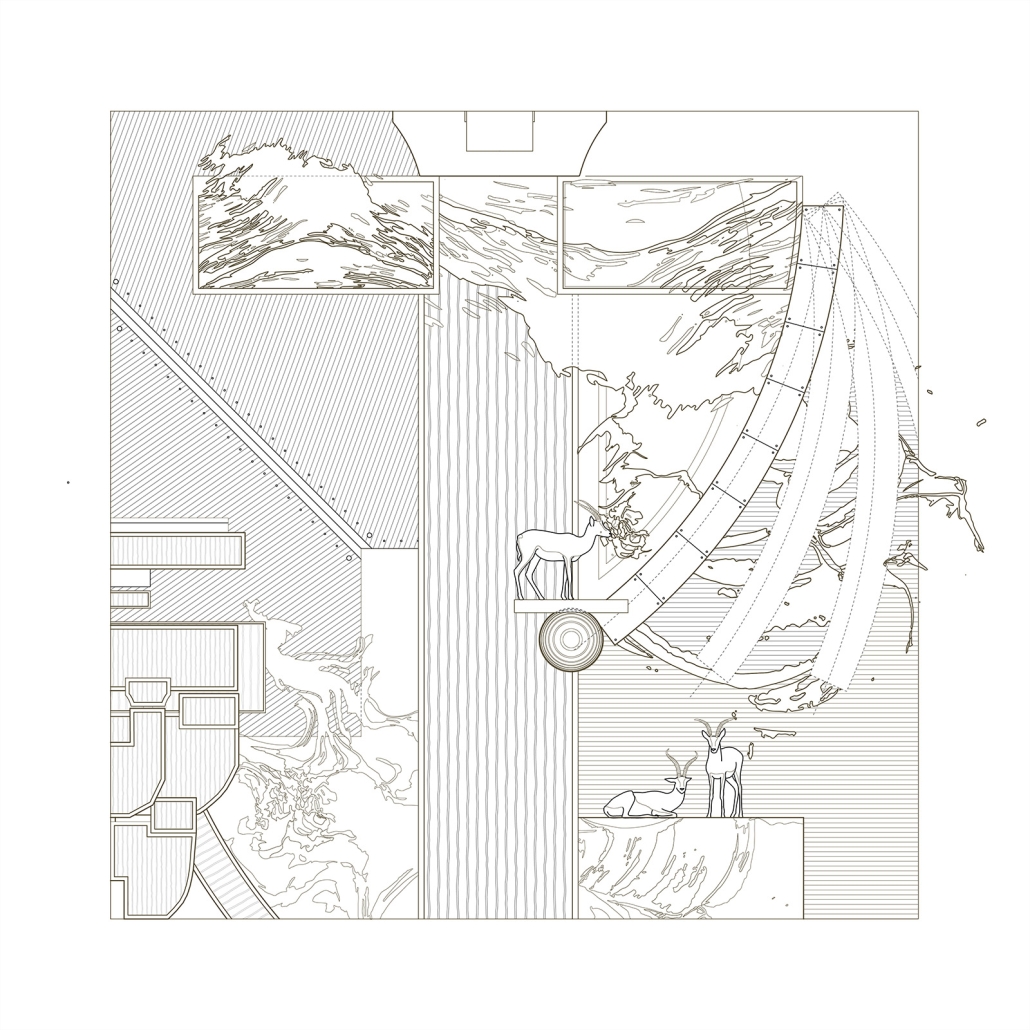
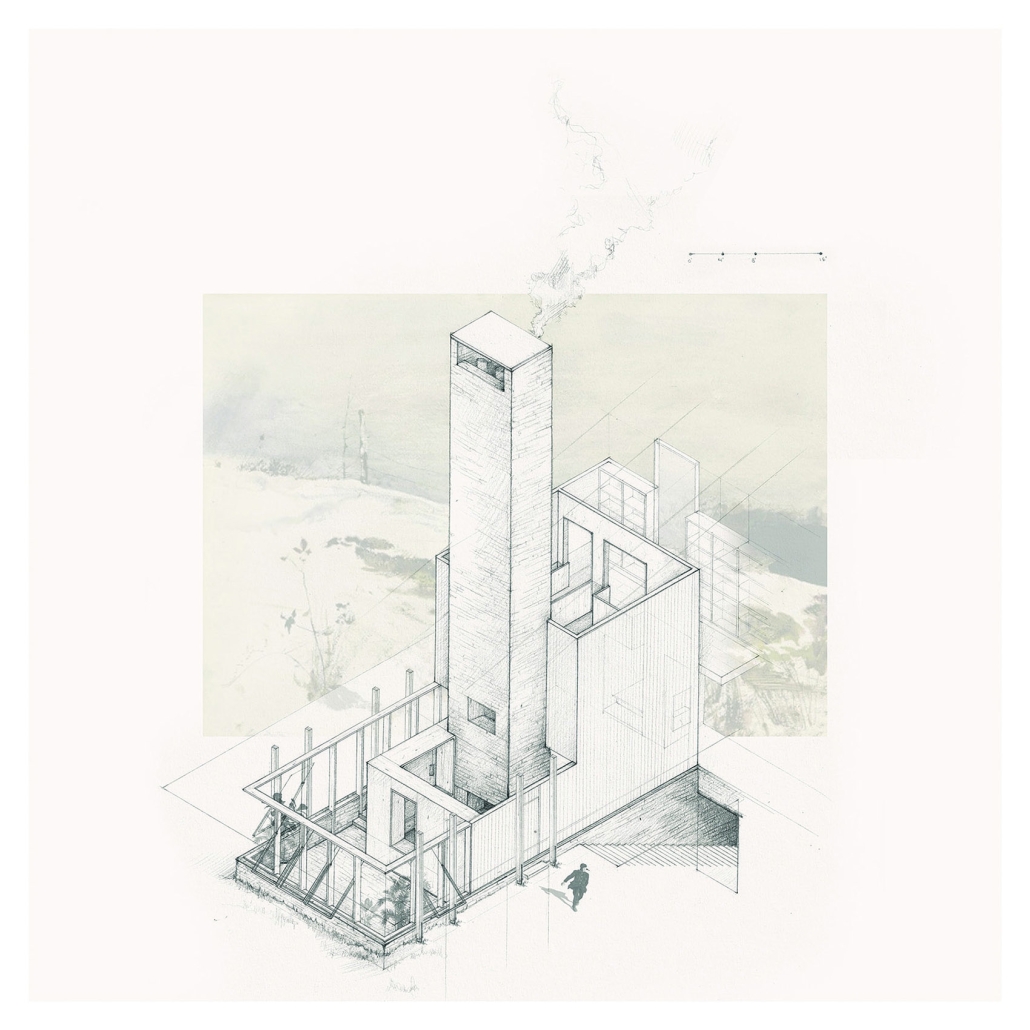
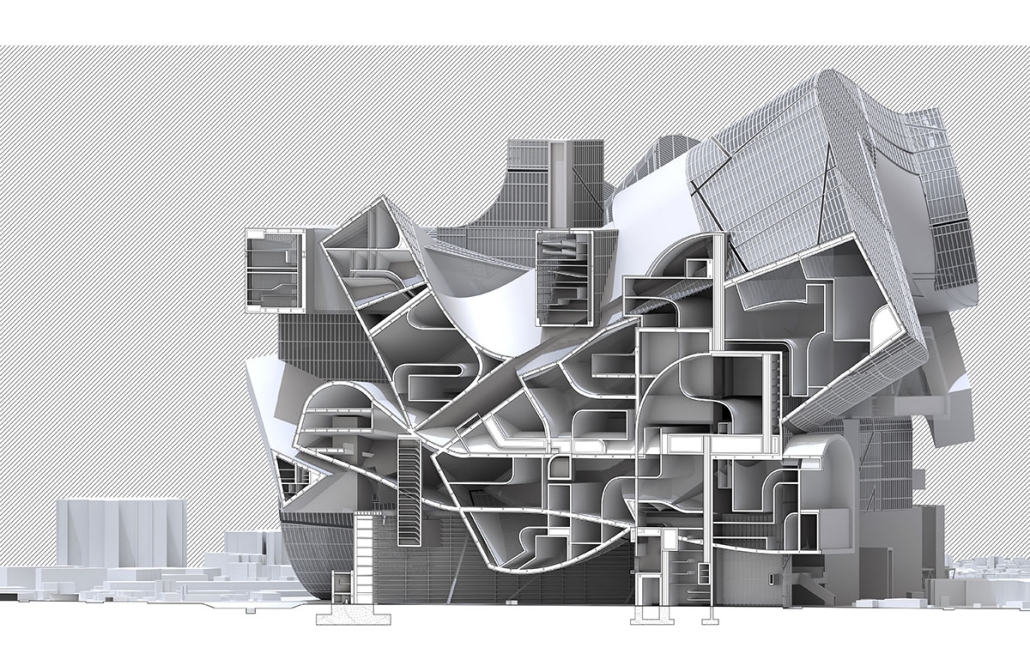
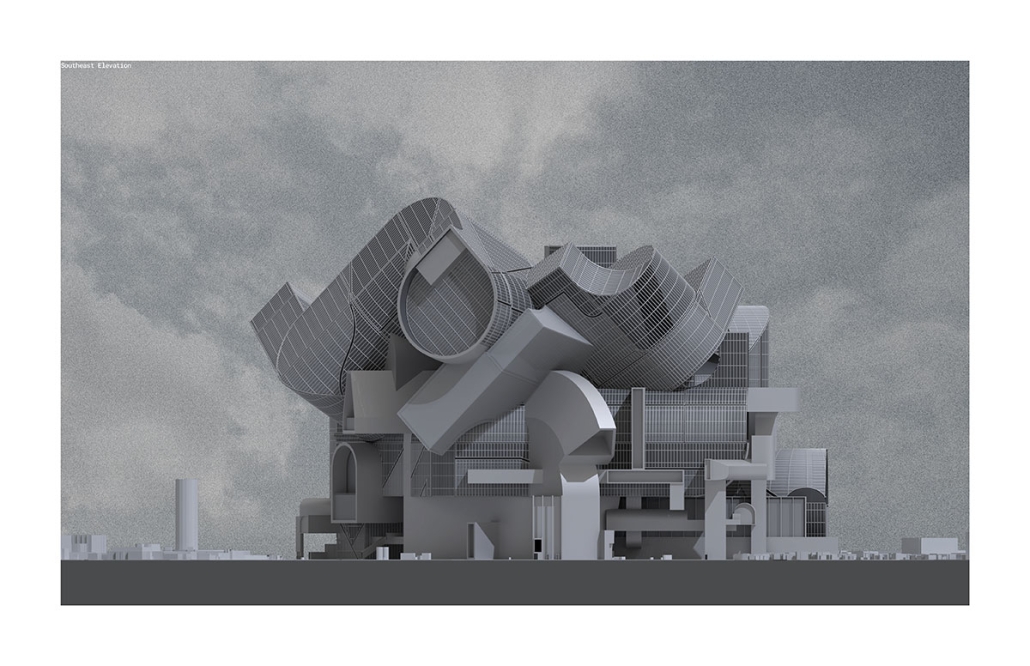
Earthly Passage is a new model of funerary architecture: a cemetery in Hong Kong that centralizes funerary sites whilst memorializing and refining the bygone funerary traditions and architecture of Hong Kong. It commemorates the canonical terraced landform cemeteries of the 19th century and upholds the tradition of the funerary procession. Where the processional path was once a result of logistic necessity, this path is purposeful, intentional, figural, and defined; a clear passage through the various sites of the funeral, but condensed into an abstraction of Hong Kong that evokes a procession through the city with all the distractions filtered out.
This project won the SCI-Arc Gehry Prize.
Instagram: @sometimesarchitecture, @suechhh, @d.esk
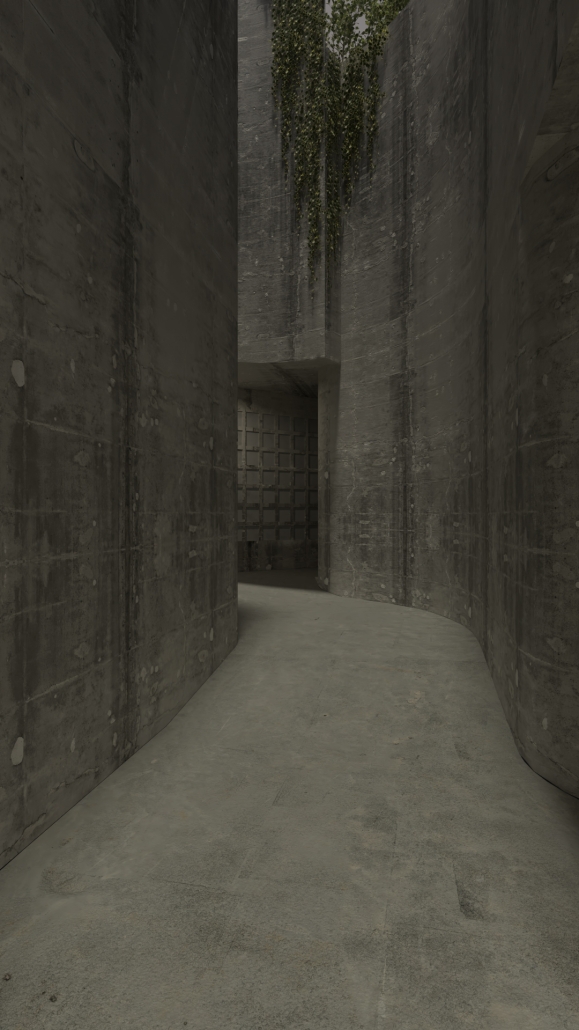
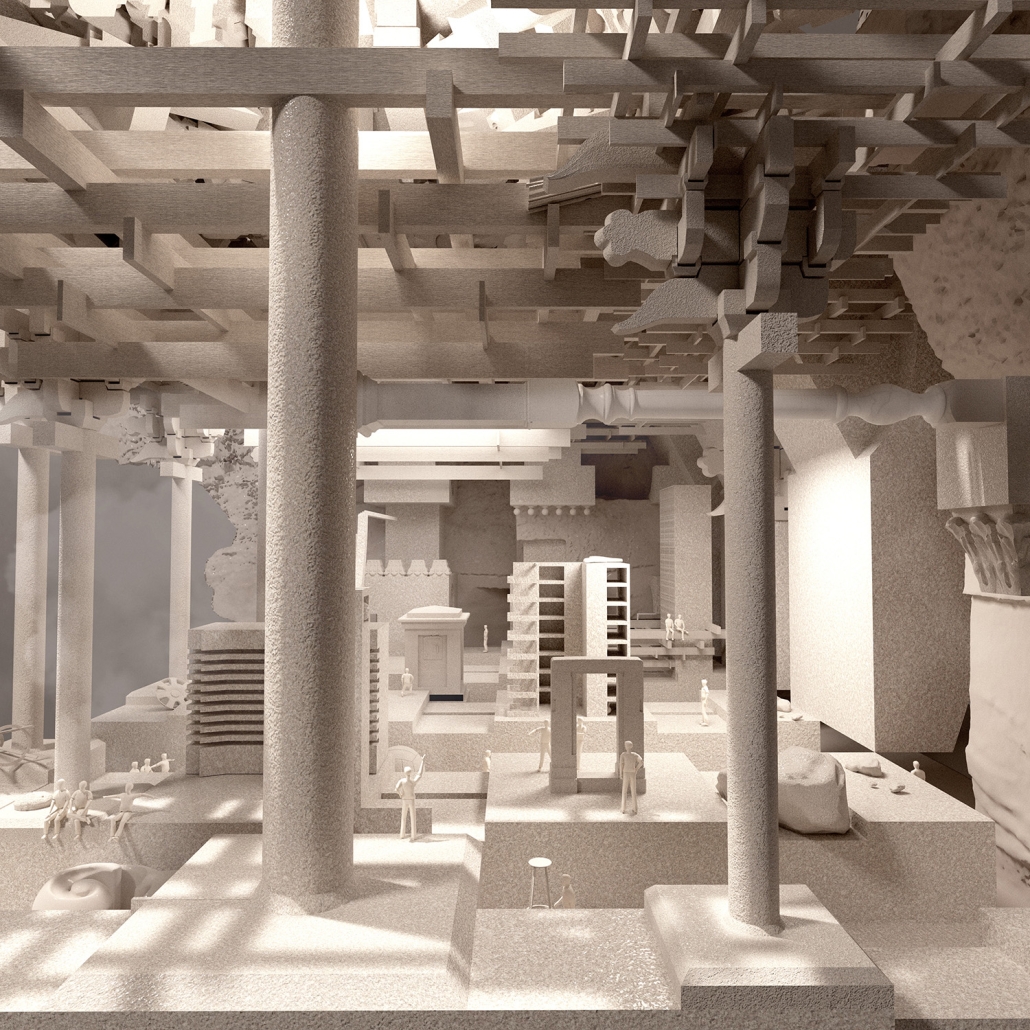
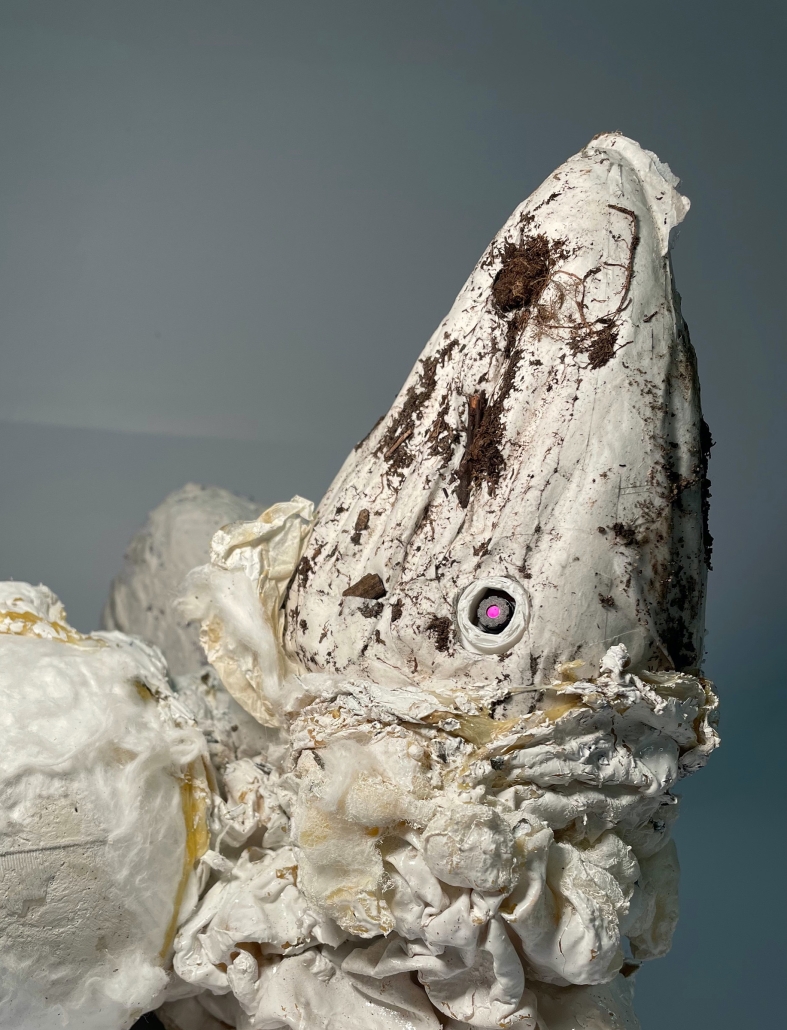
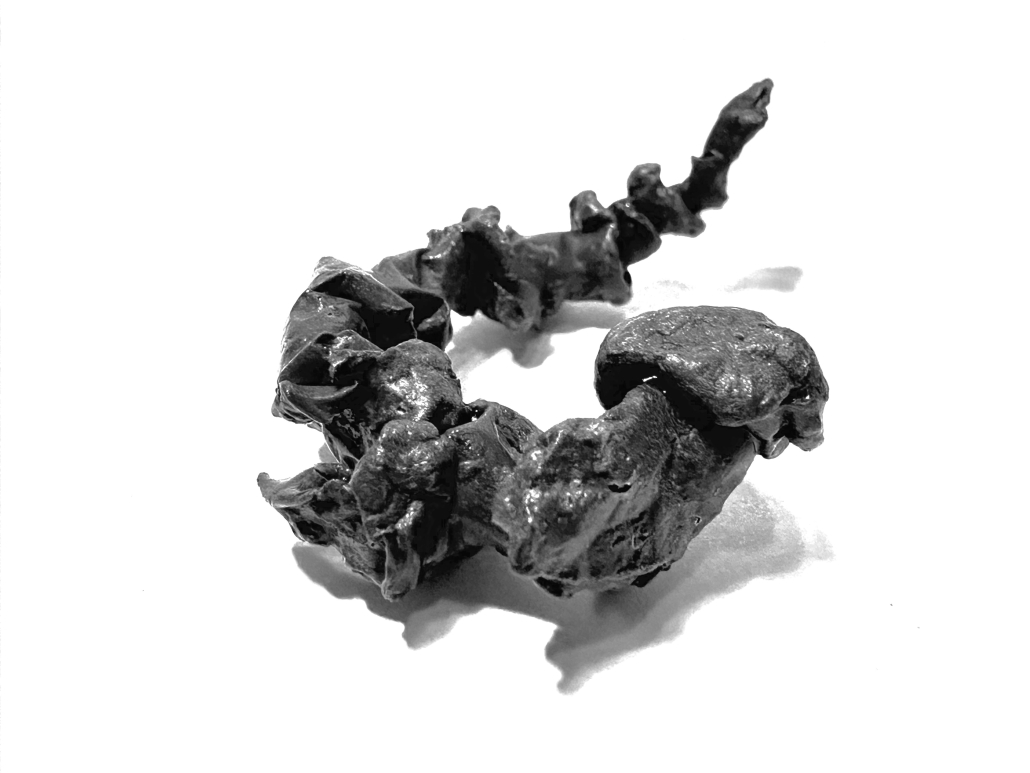
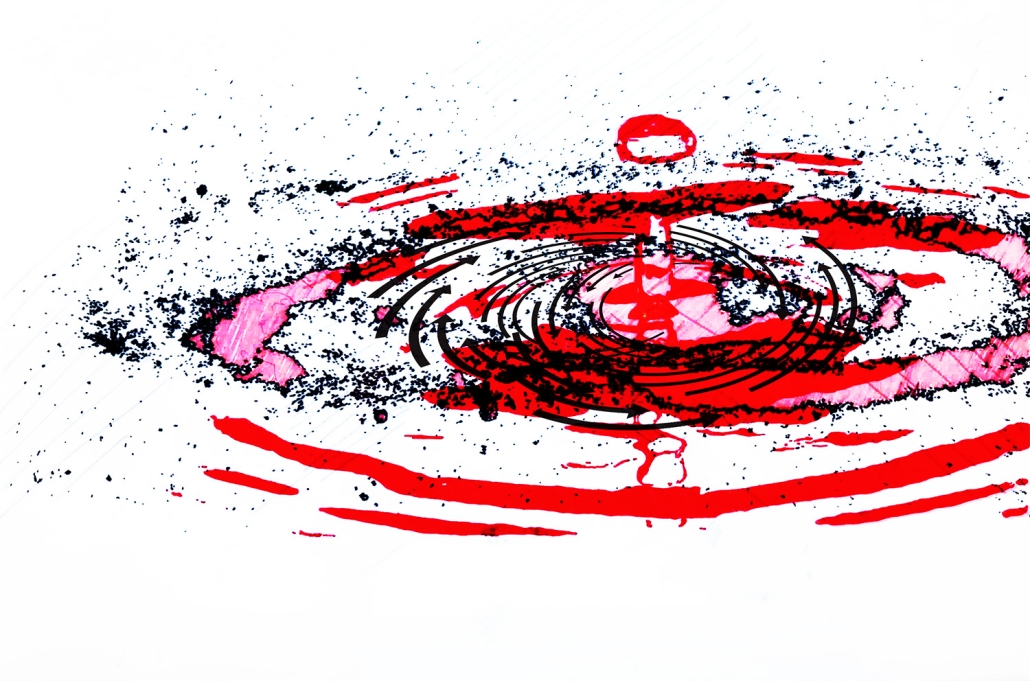
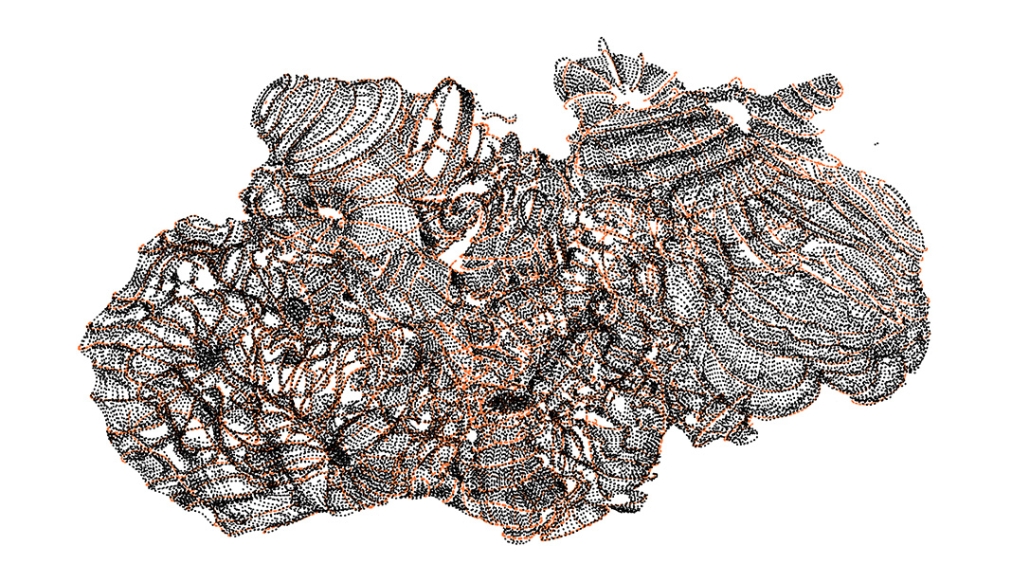
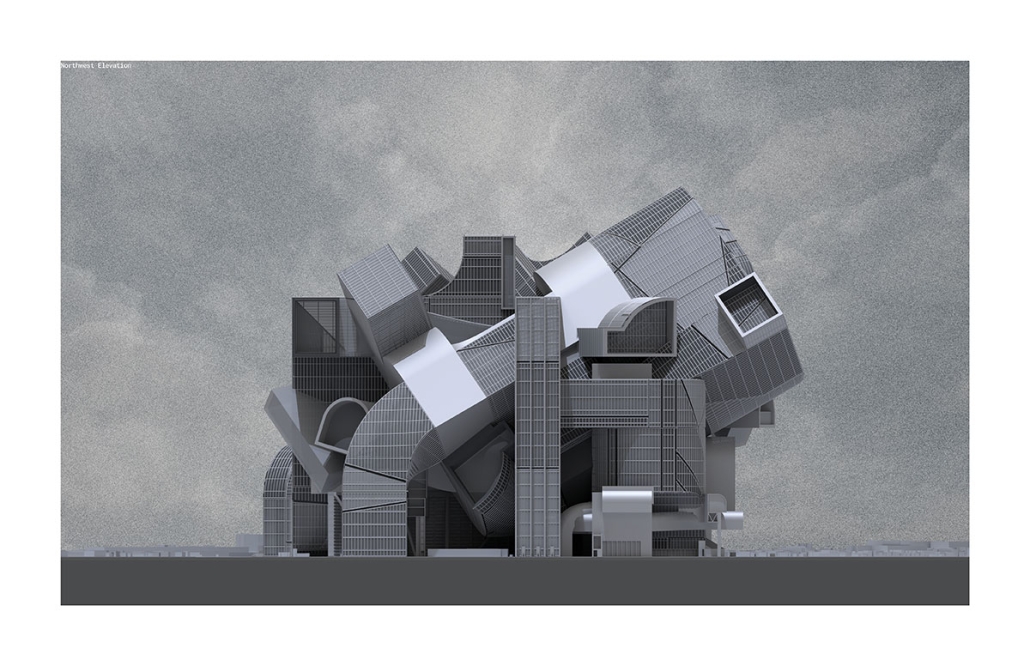
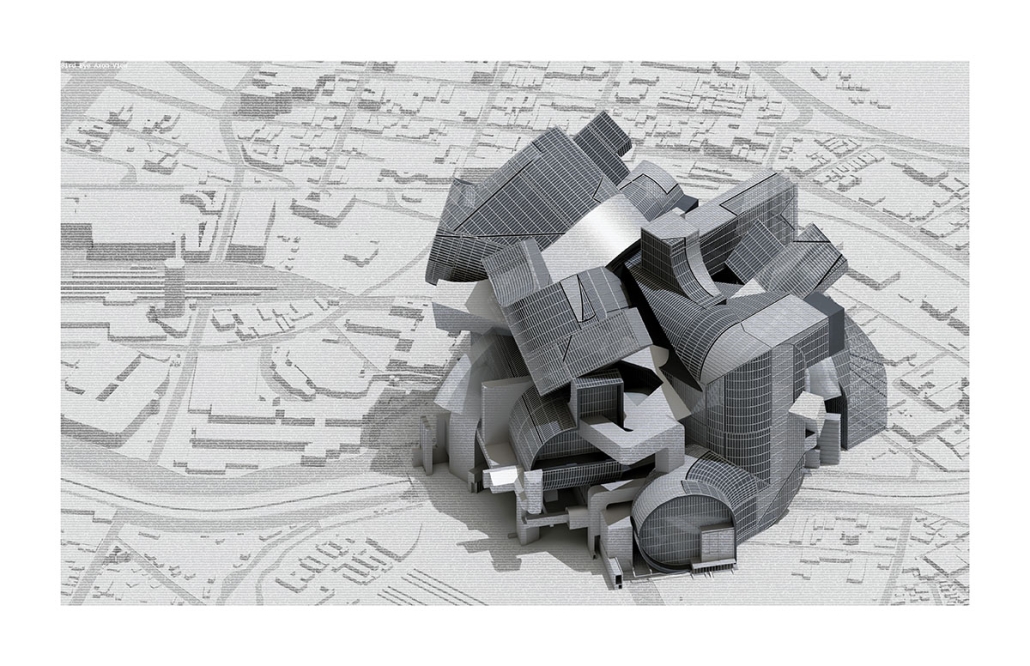
Gamu-Gamo by YJonathan Marcos, B.Arch ‘23
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute School of Architecture | Advisor: Hseng Tai Lintner
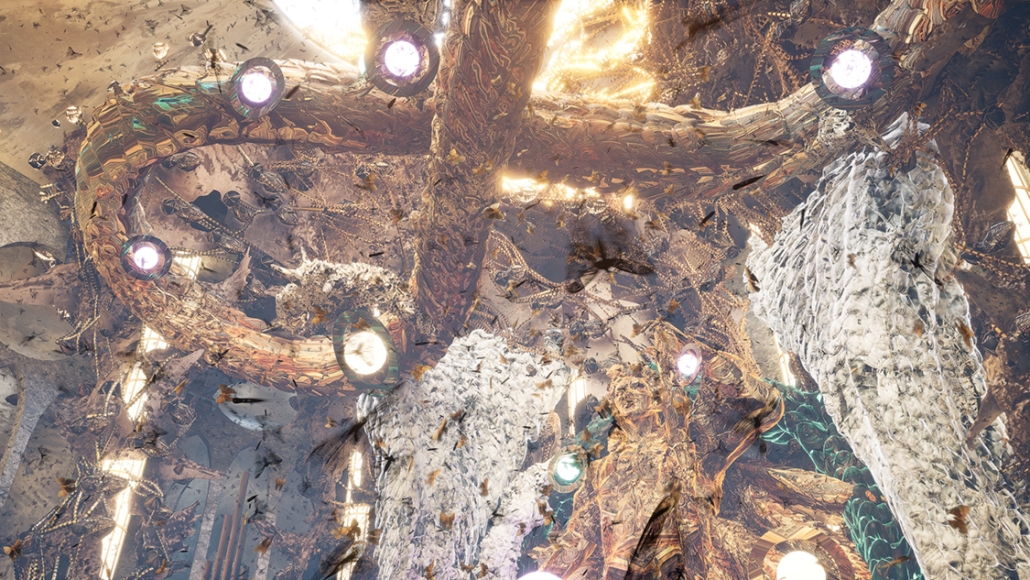
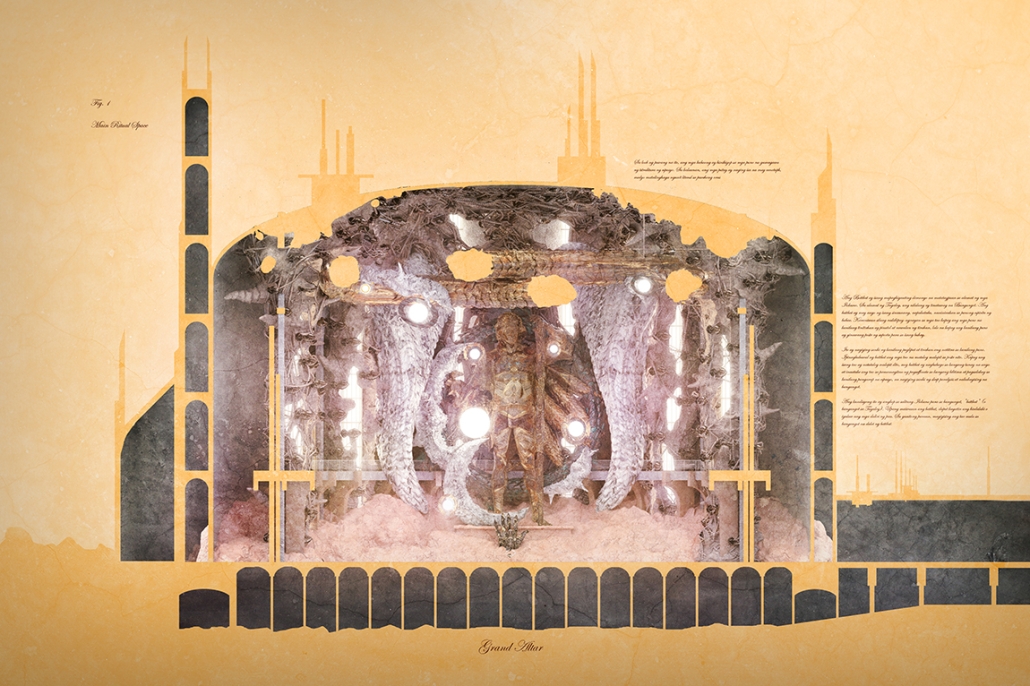
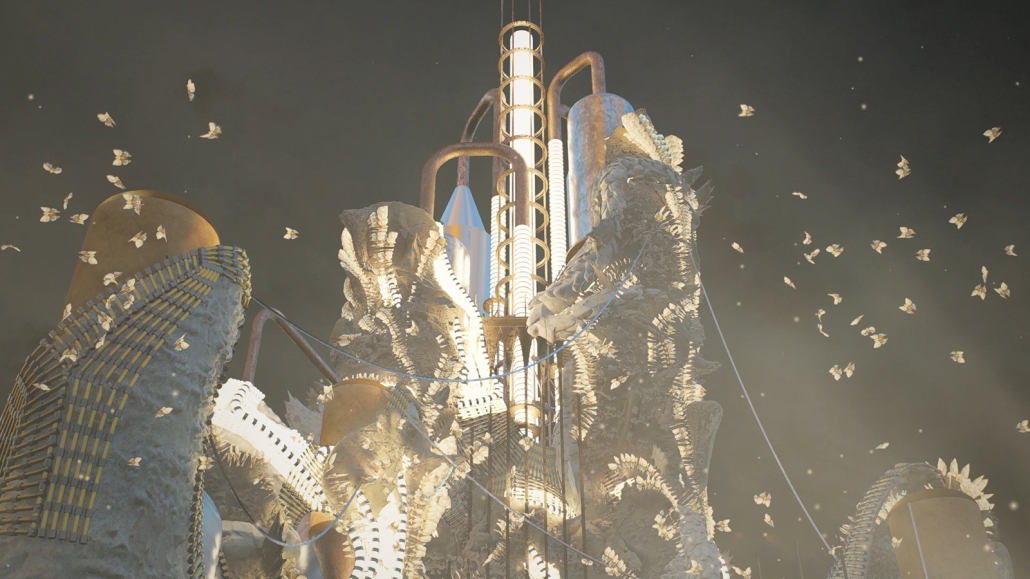
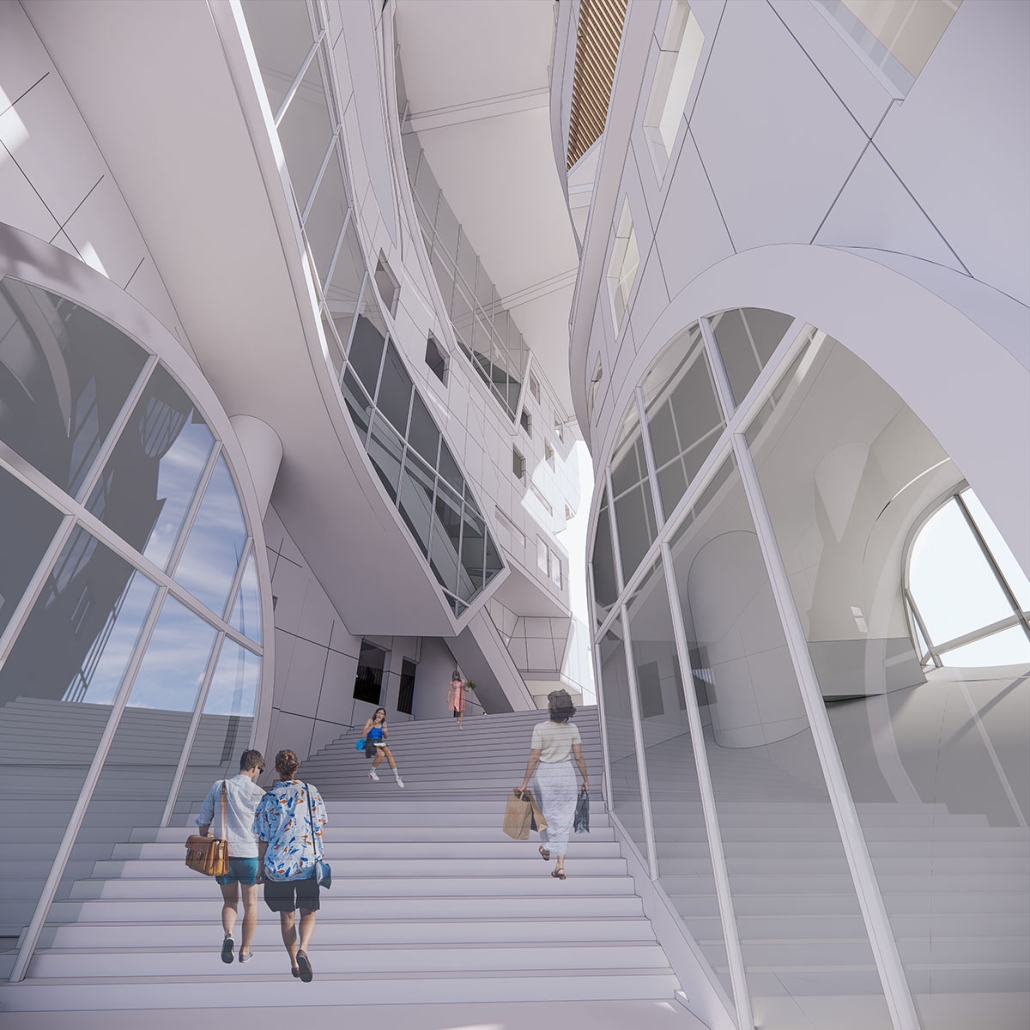
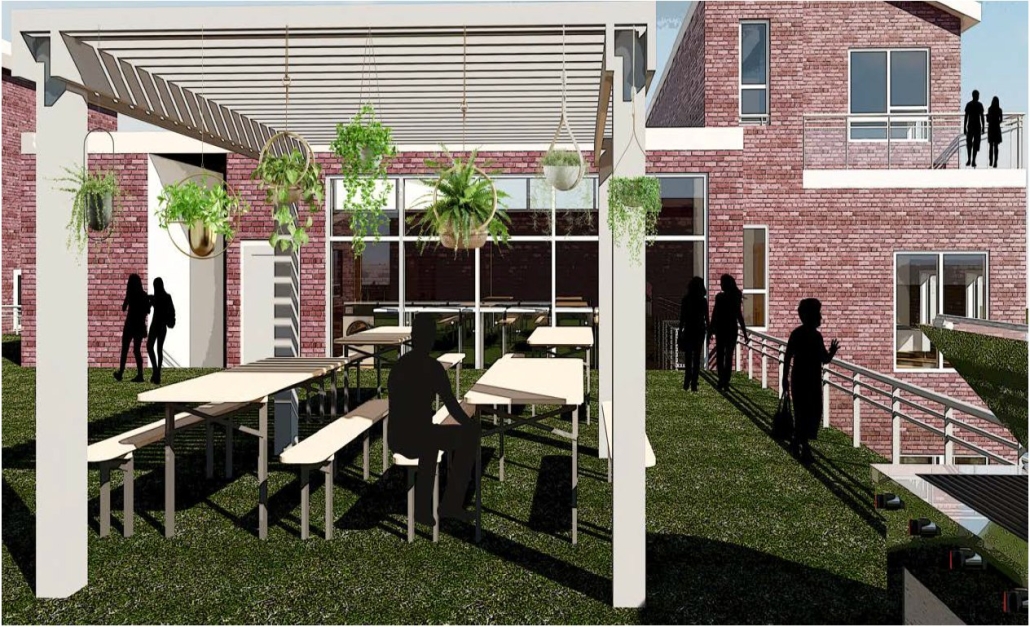
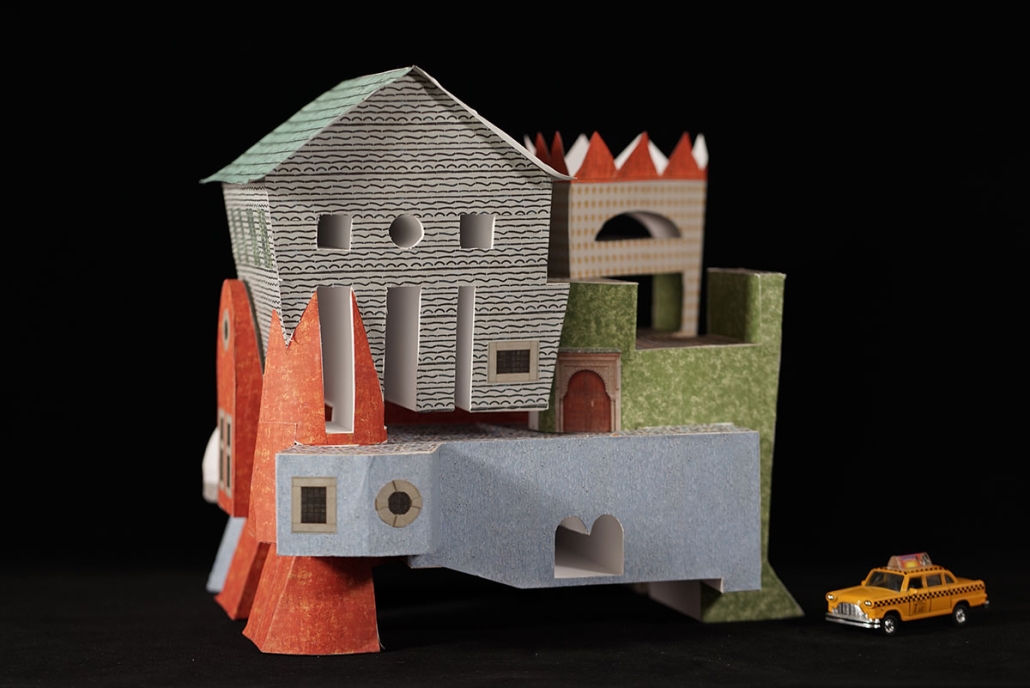
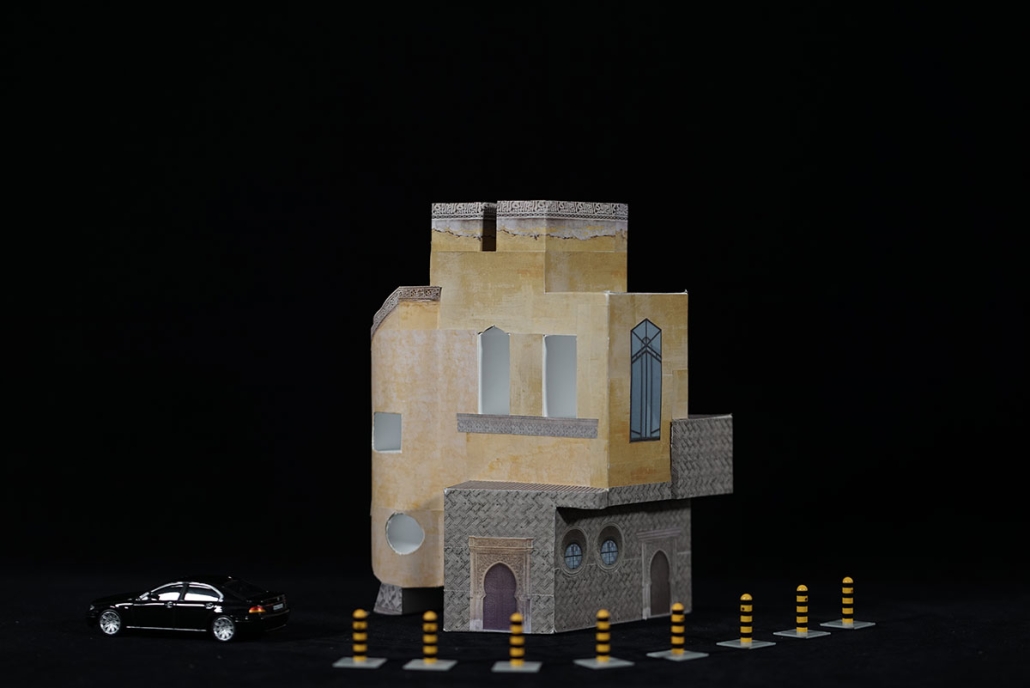
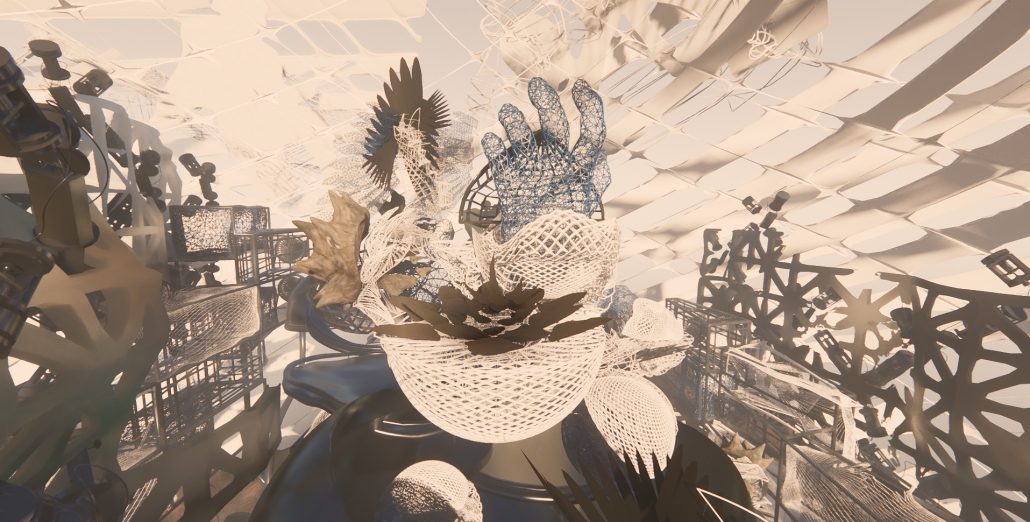
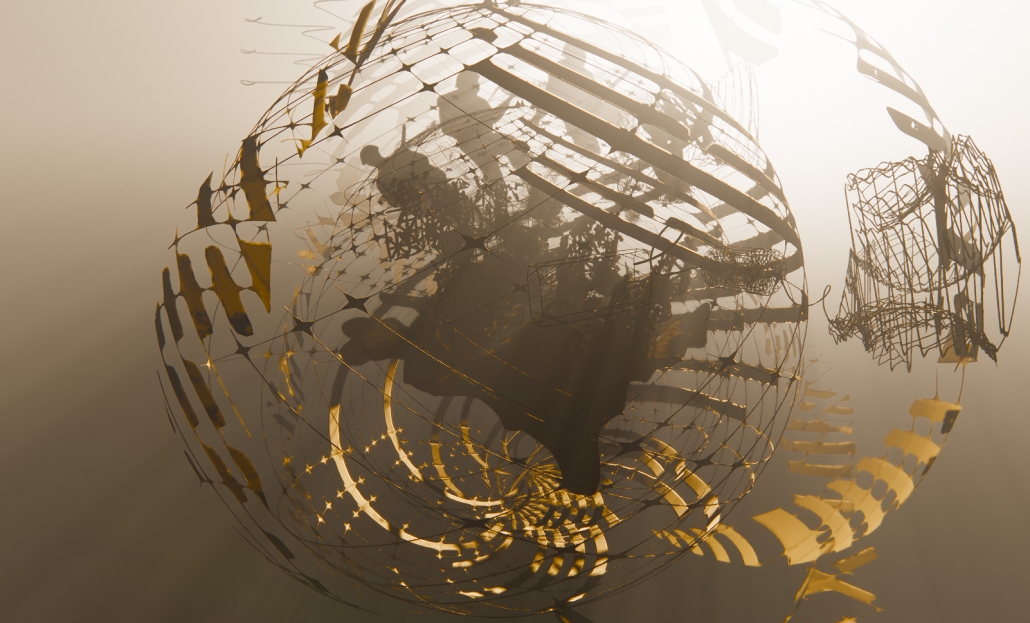
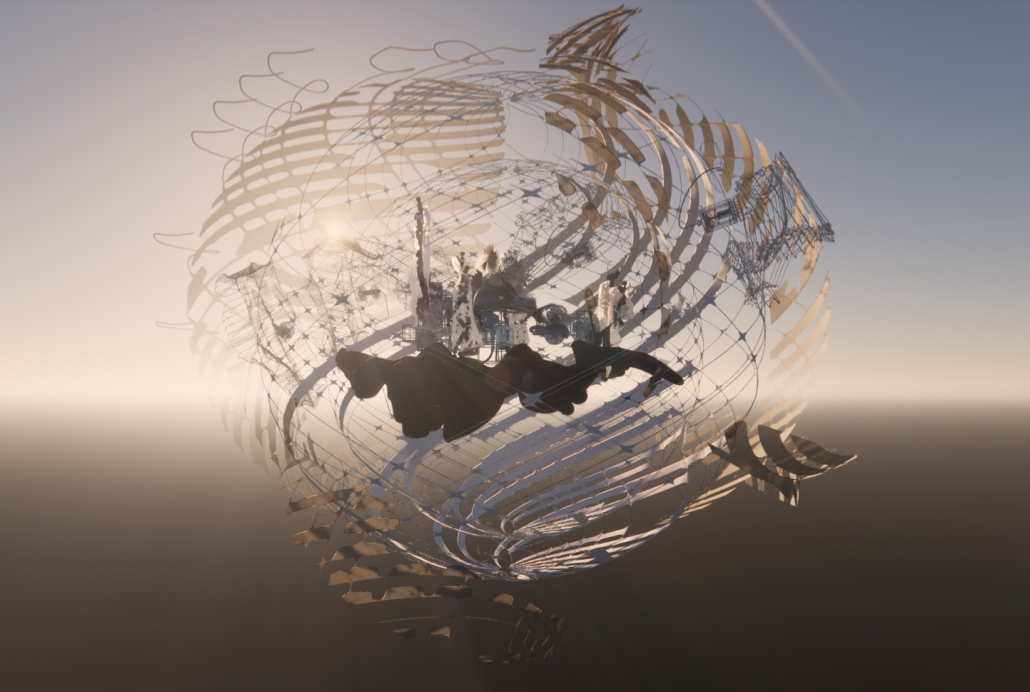
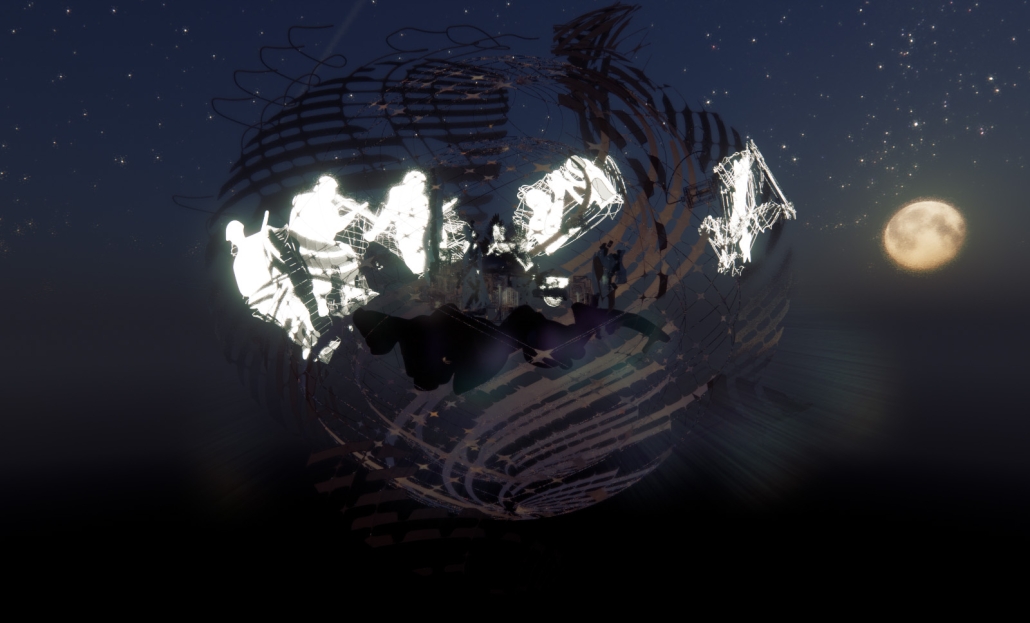
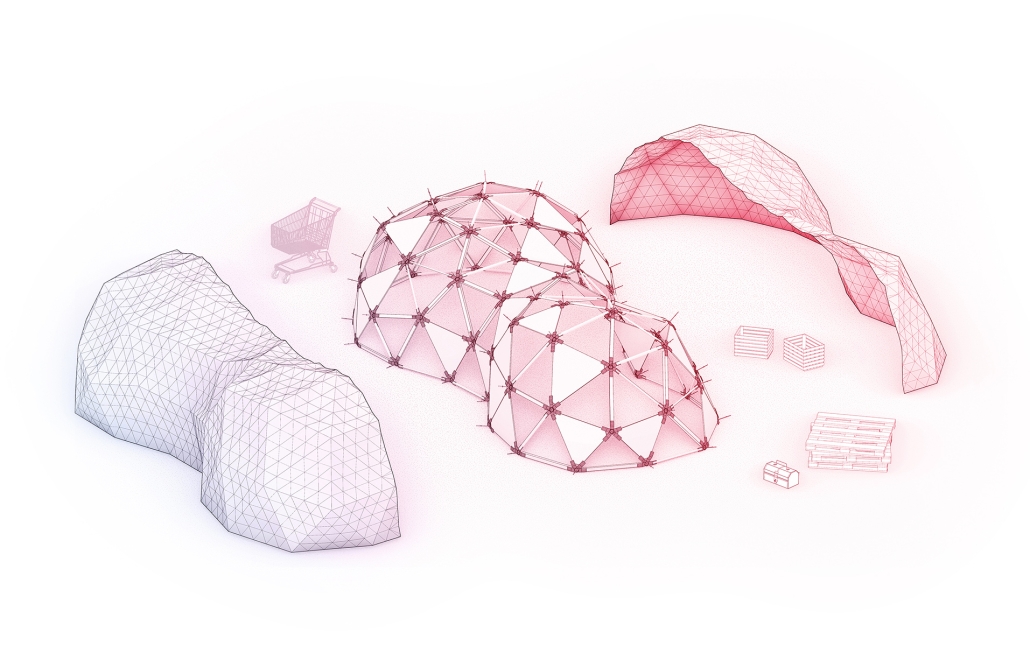
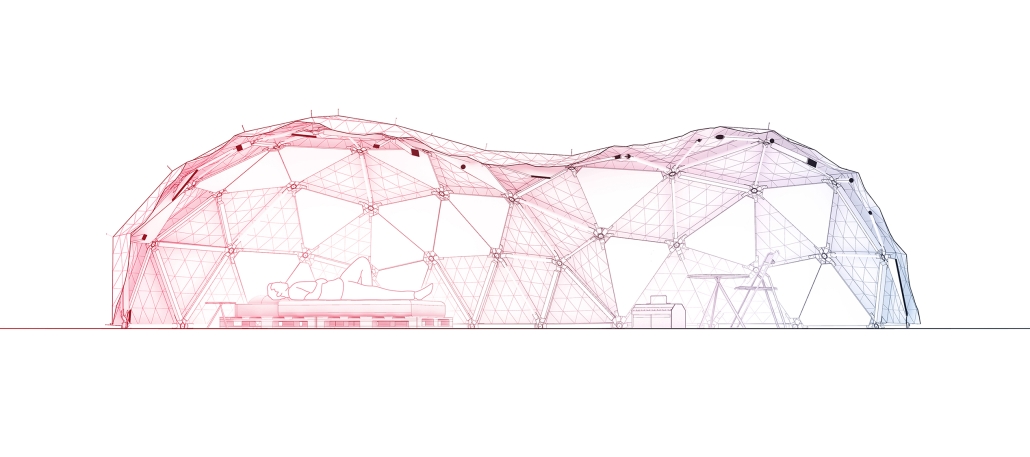
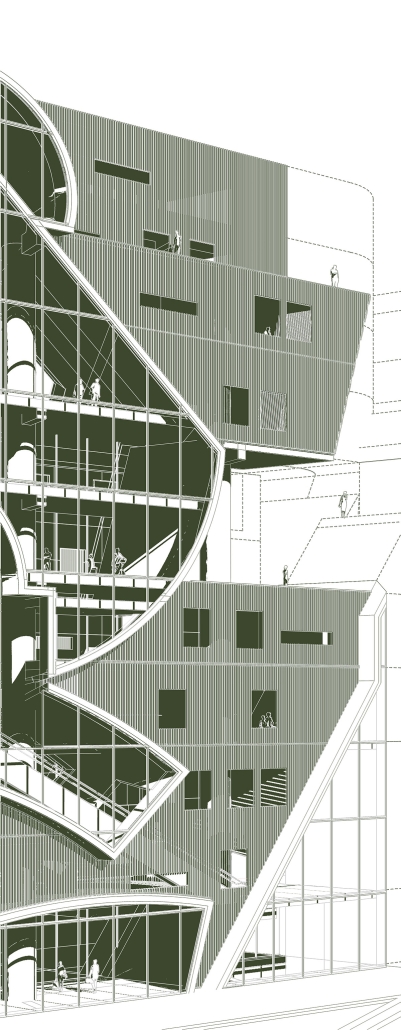
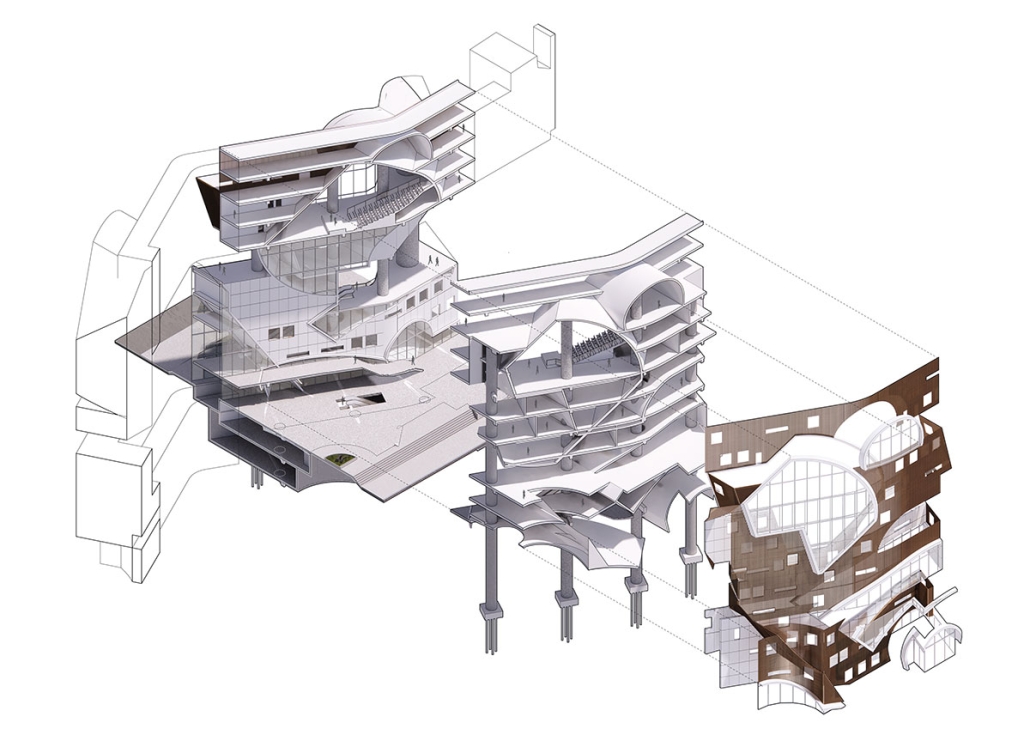
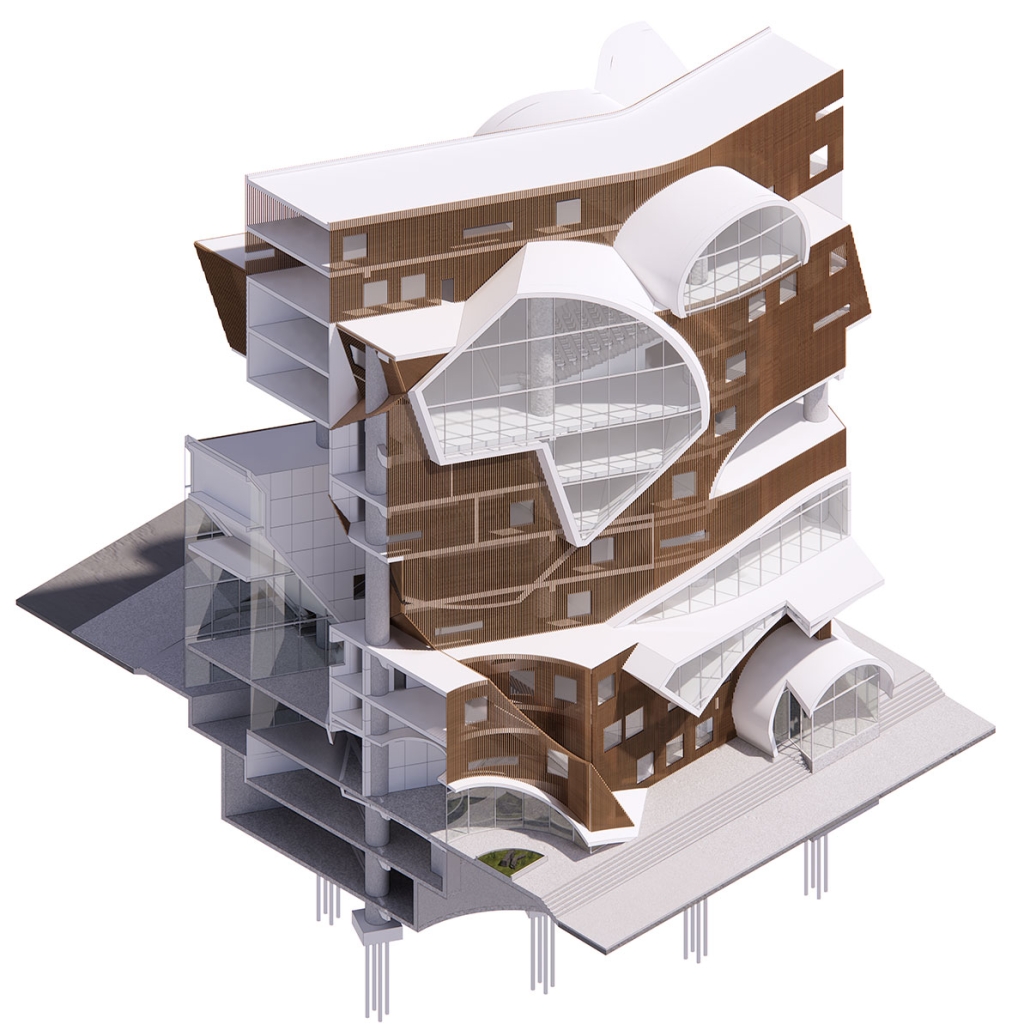
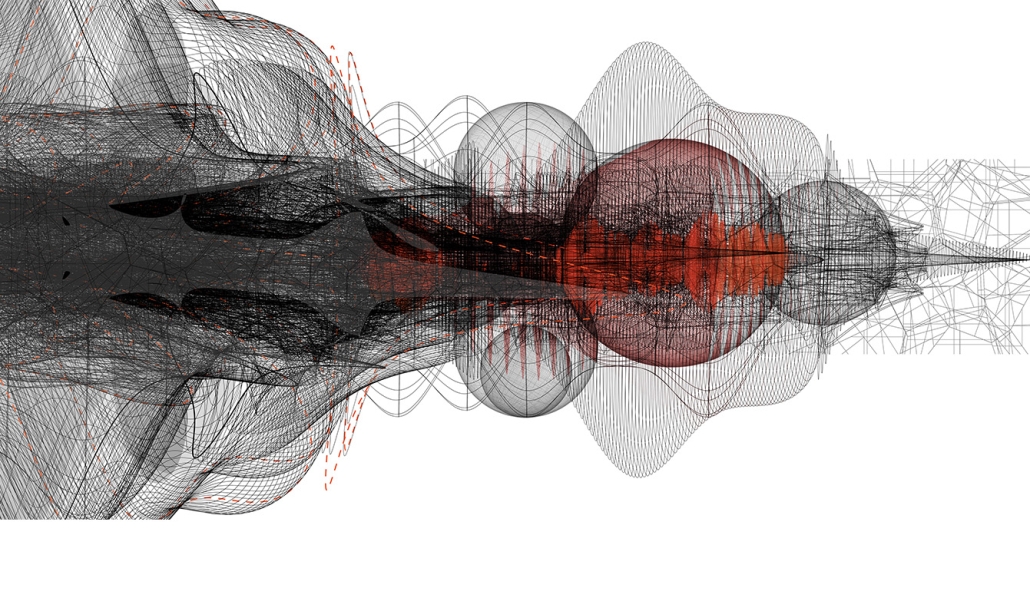
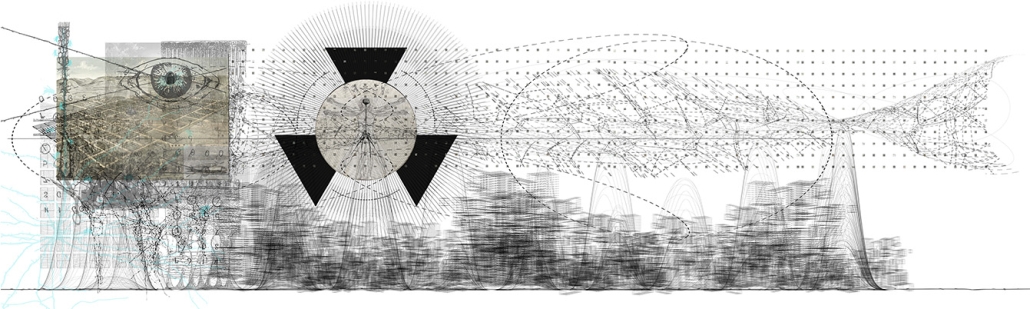
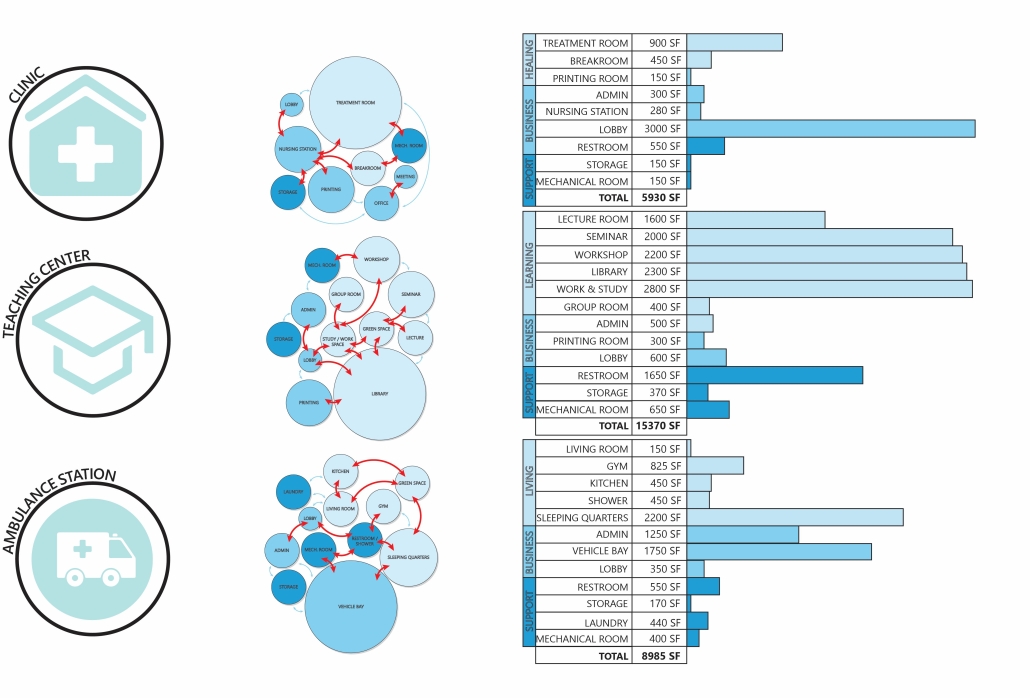
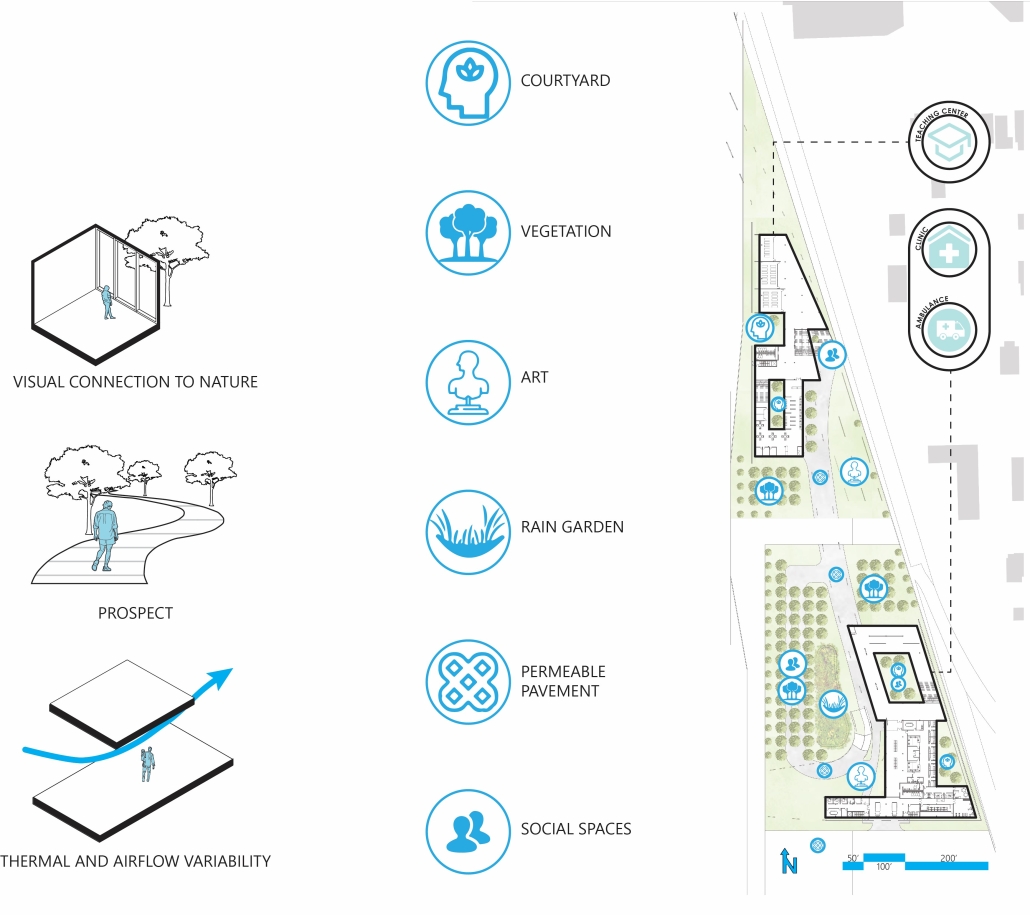
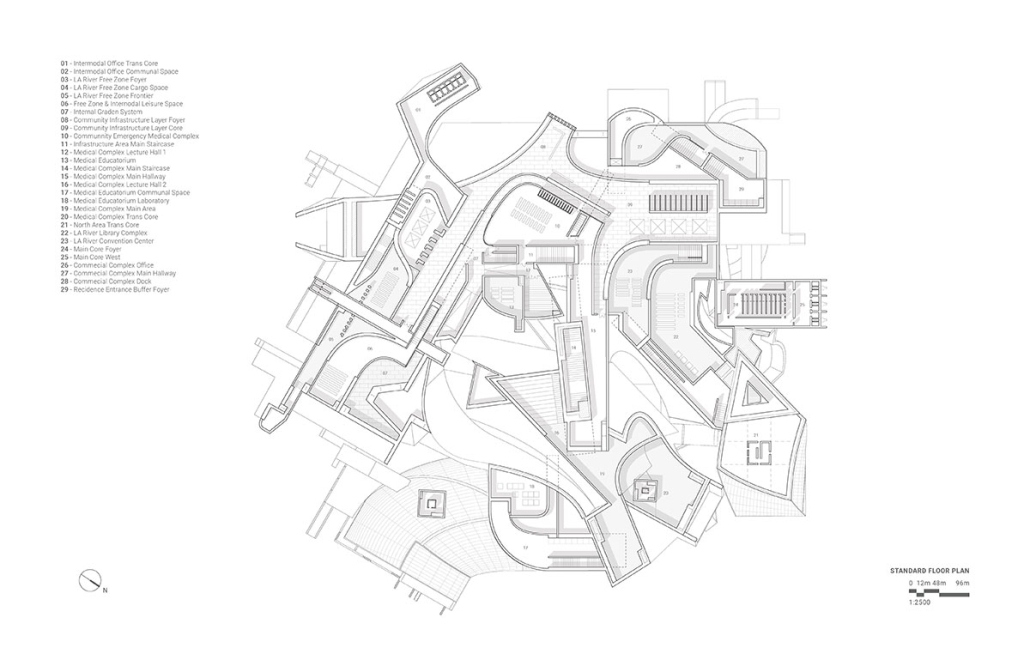
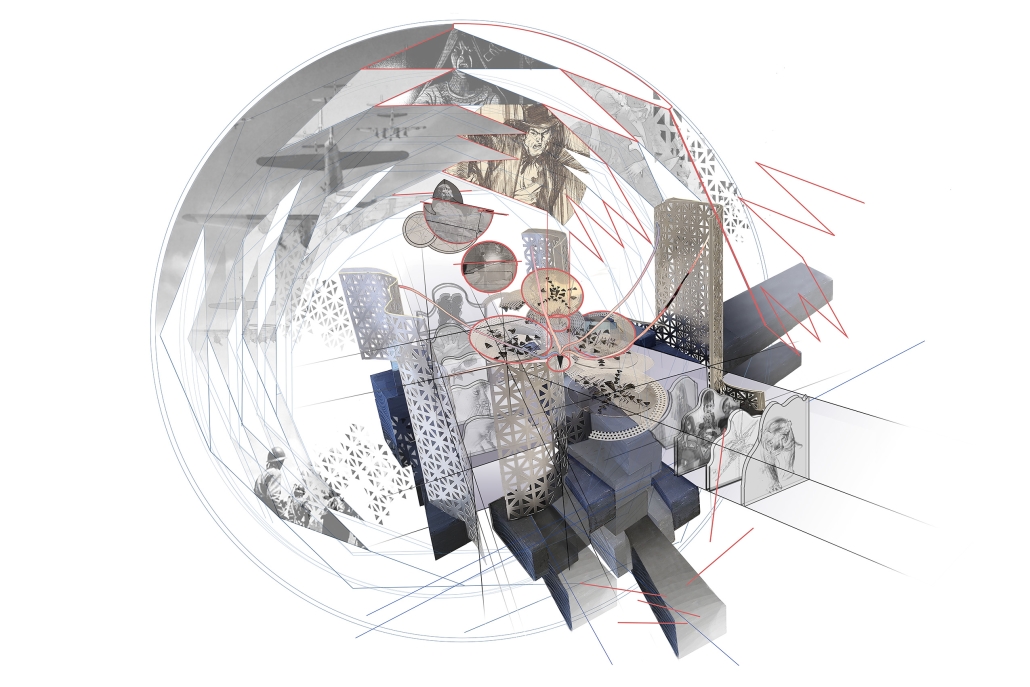
Gamu-Gamo explores the agency of architecture to construct new cultural symbols and monuments of power in the information age. Set in metro Manila, the project proposes a new typology of funerary architecture that recontextualizes Filipino death rituals, belief systems and folklore within emerging technological conditions. Part cemetery, part religious space and part data center, the project is an urban network of cenotaphs that store and circulate the memories and consciousnesses of the deceased throughout the fabric of Metro-Manila. A direct response to the overflowing of local slum cemeteries and illegal burial practices, Gamu-Gamo takes the idea of funerary compression to an extreme– compressing the body into hyper-dense units of digital assets and biological material. The digital assets take the form of digital spirits and various incumbent Filipino funerary rites, traditions and celebrations evolve into new immersive experiences that not only celebrate Filipino folklore and mythology, but also project simulations of the afterlife onto the population of Metro Manila.
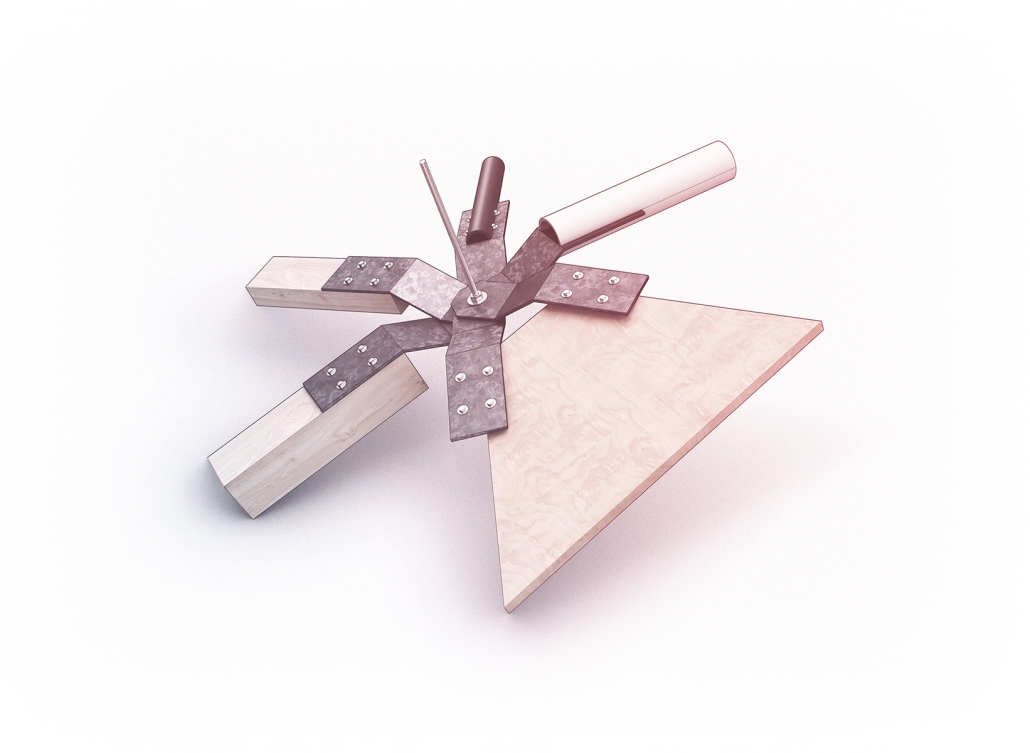
The biological material is processed into new building material, forming an ossuary envelope for the cenotaph, where embedded figures and scenes depict narrative representations of local folklore. Typically, data centers exist as an afterthought; hidden away from the technology they facilitate, however, Gamu-Gamo inverts this position, celebrating the data center as a standing monument and cultural object in the heart of the city. It articulates possible emerging relationships and intersections between technology, culture and tradition and the role that technology can play in the construction of new cultural narratives.
Instagram: @jon.marcos_ , @m.arch.os, @hsengtailintner
See you in the next installment of the Student Showcase!