2023 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XXIV
Welcome to Part XXIV of the Study Architecture Student Showcase! Today’s featured work focuses on affordable housing and tackles topics ranging from integrating mixed-use housing to eliminating the process of temporary relocation within revitalization projects. Read on for more details!
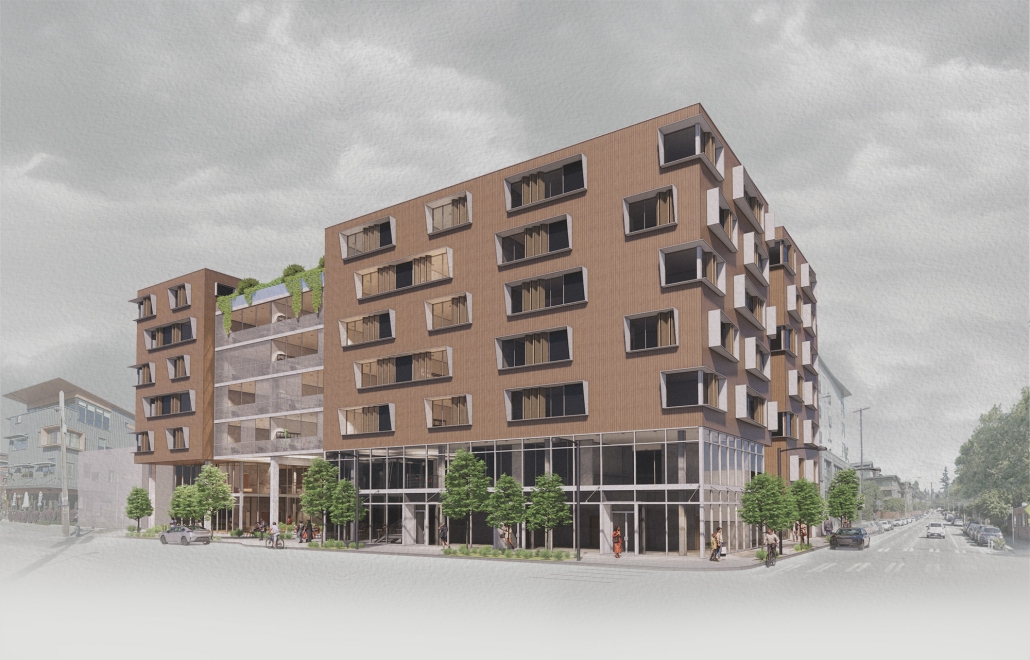
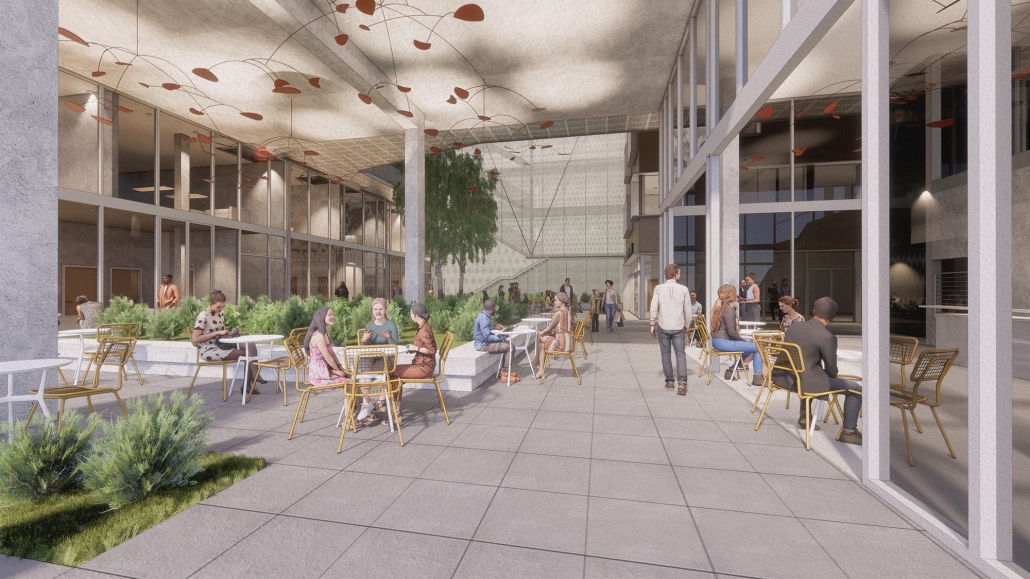
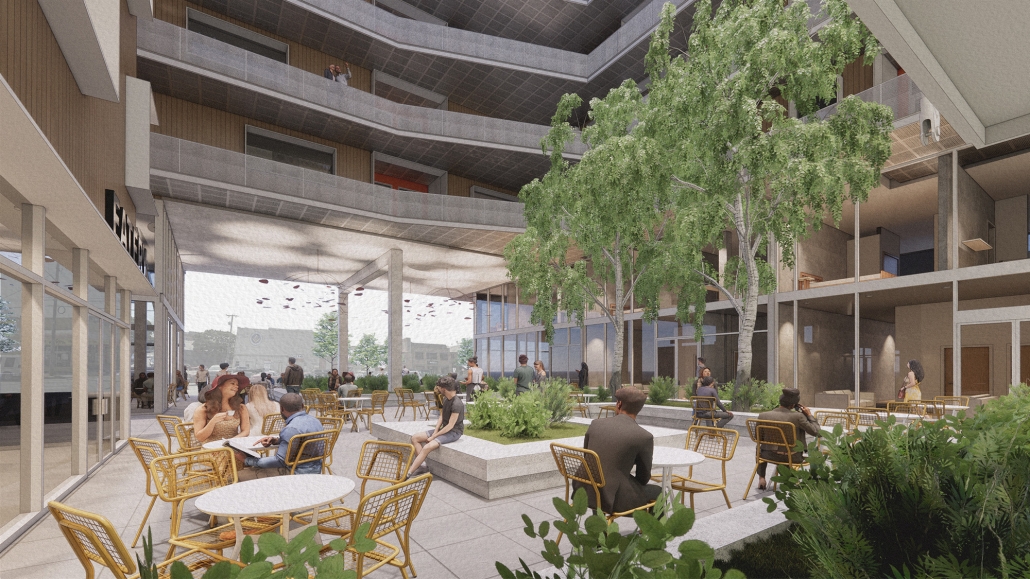
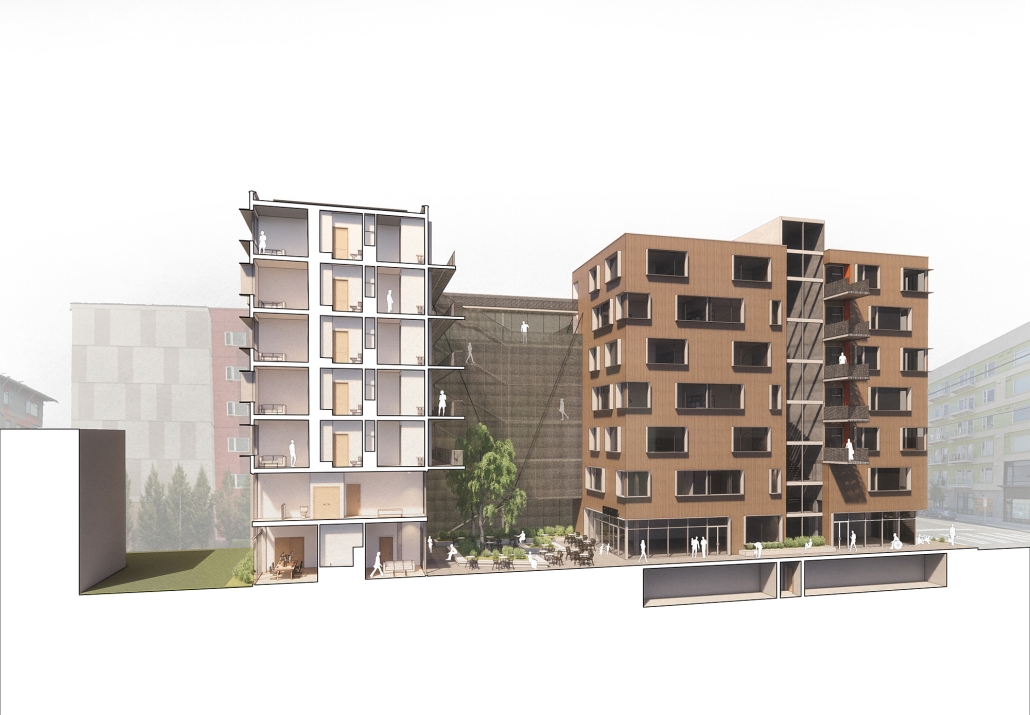
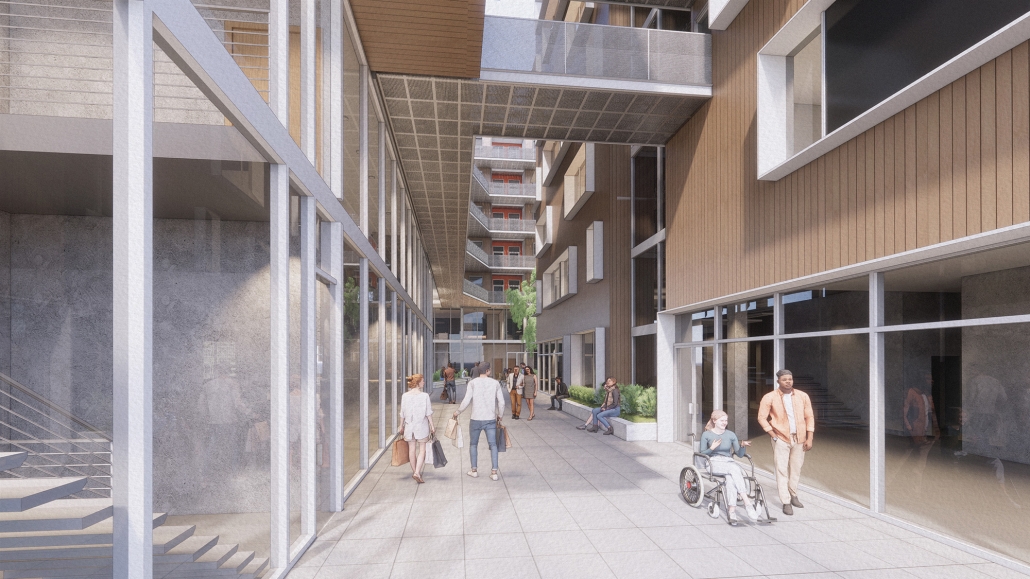
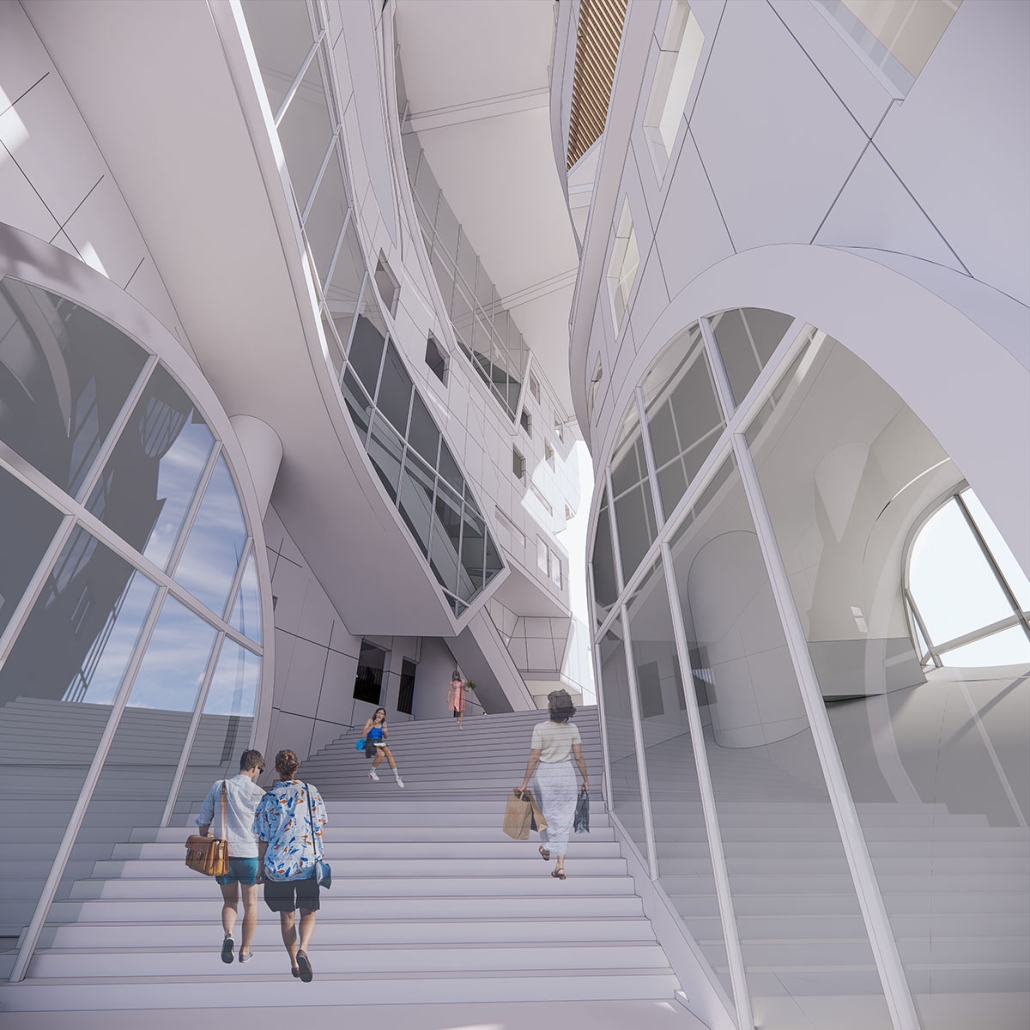
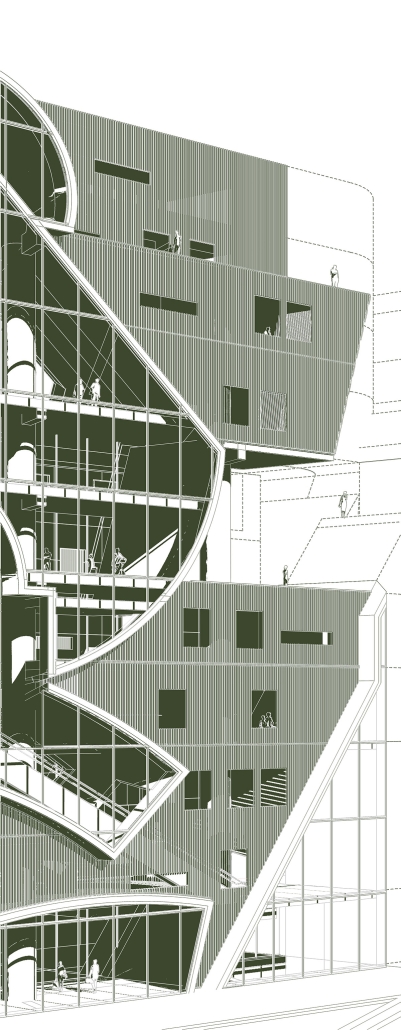
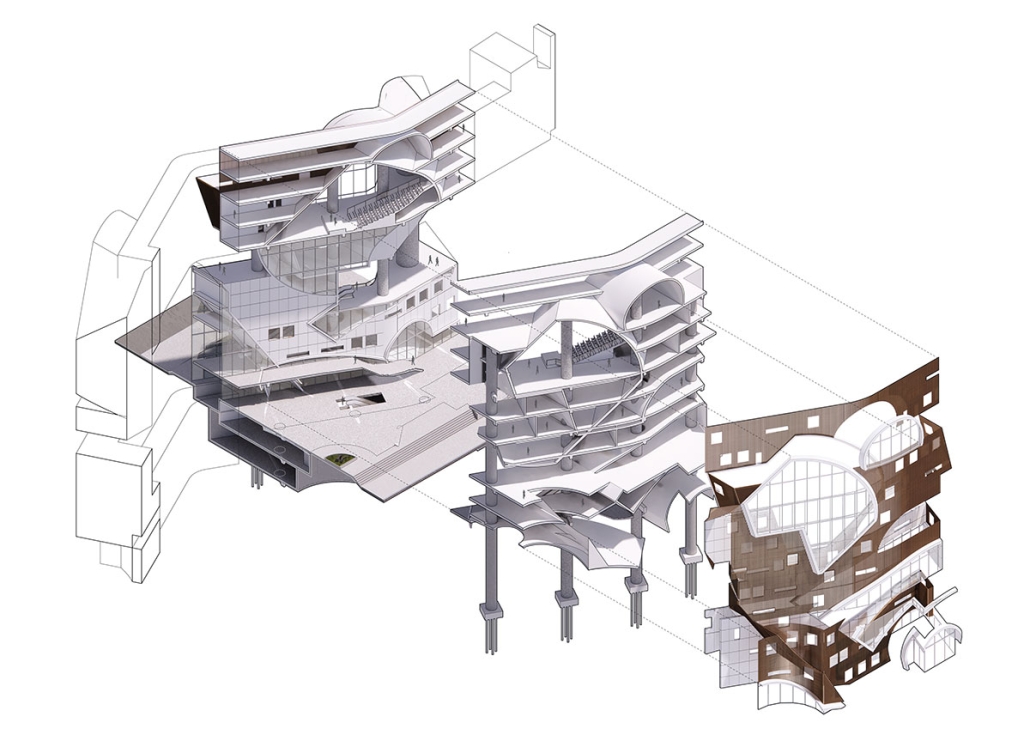
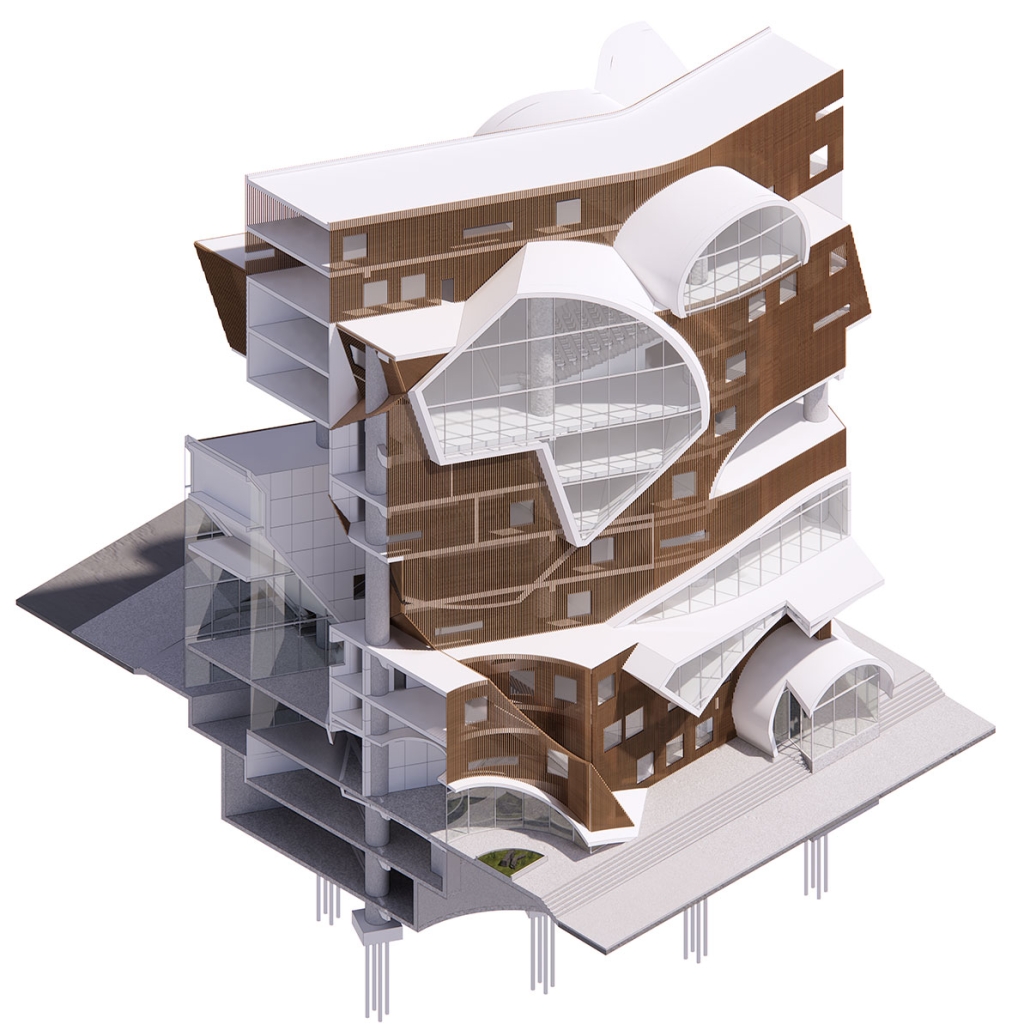
ELEVATED FABRIC DISTRICT by Briana Callender, B.Arch ‘23
The New York Institute of Technology | Advisor: Prof. Michelle Cianfaglione
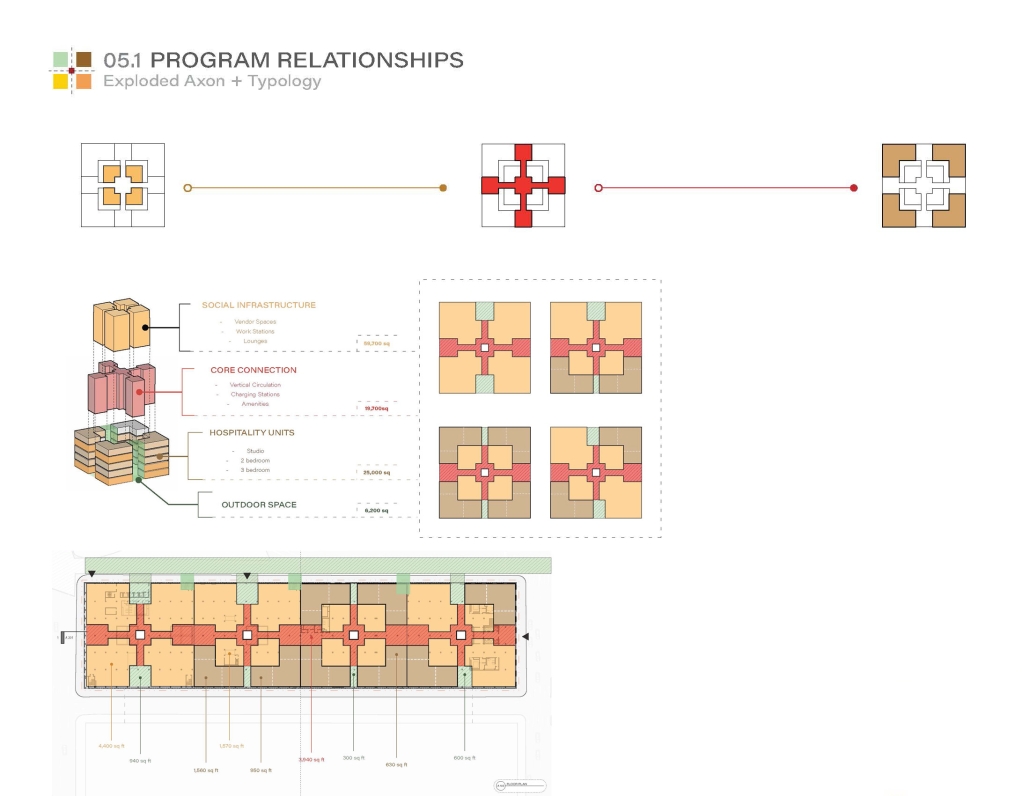
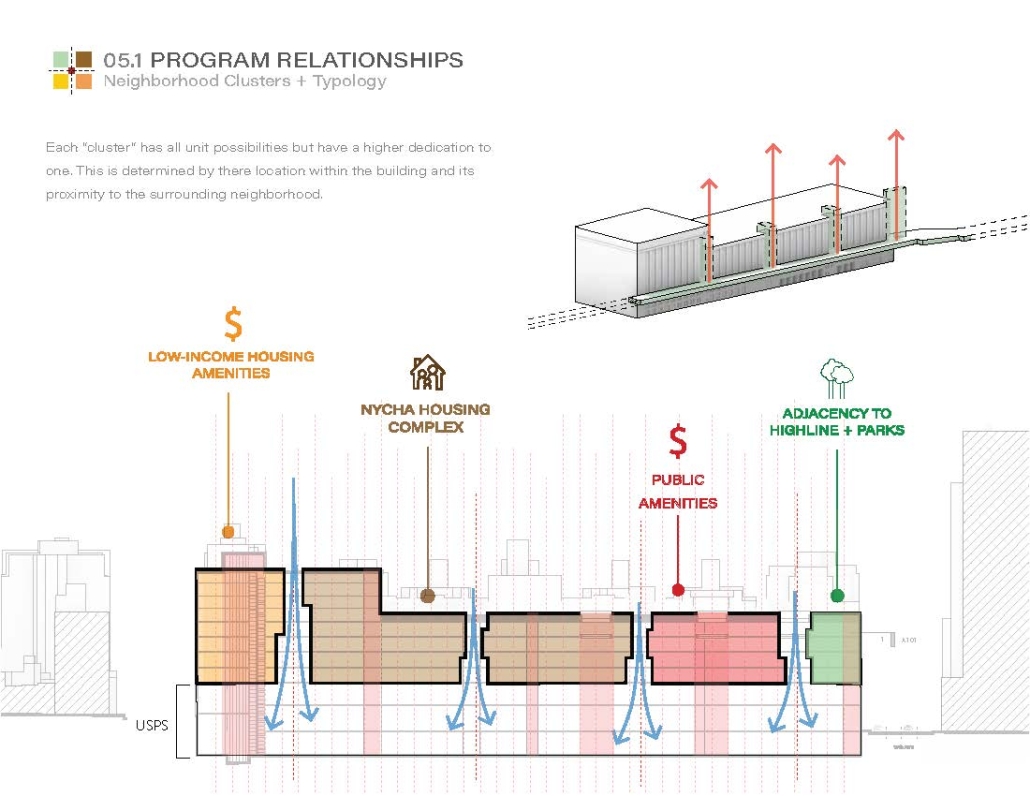
This thesis explores the past, present and future of affordable housing in New York City by understanding the typologies that define tenement housing. We can better understand what was lacking in these infrastructures and can therefore begin to assess the addition of new typologies that can better service our demographic who need housing that is affordable and functional. Such as designated spaces within the complex that allow for necessary utilities or flexible volumes that tenants can use for community-centered activities which help build social capital within the building.
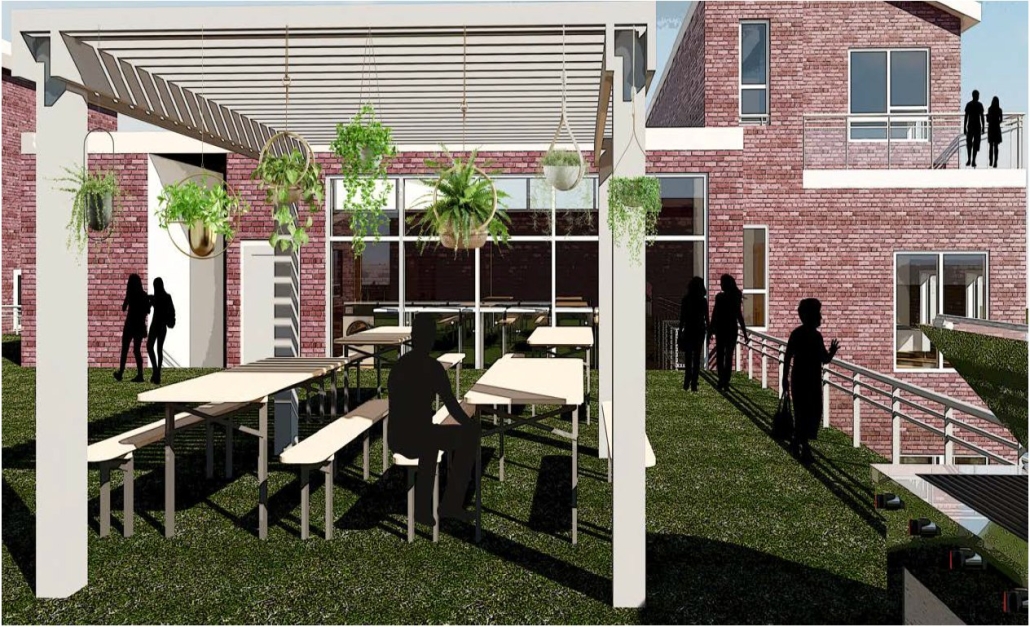
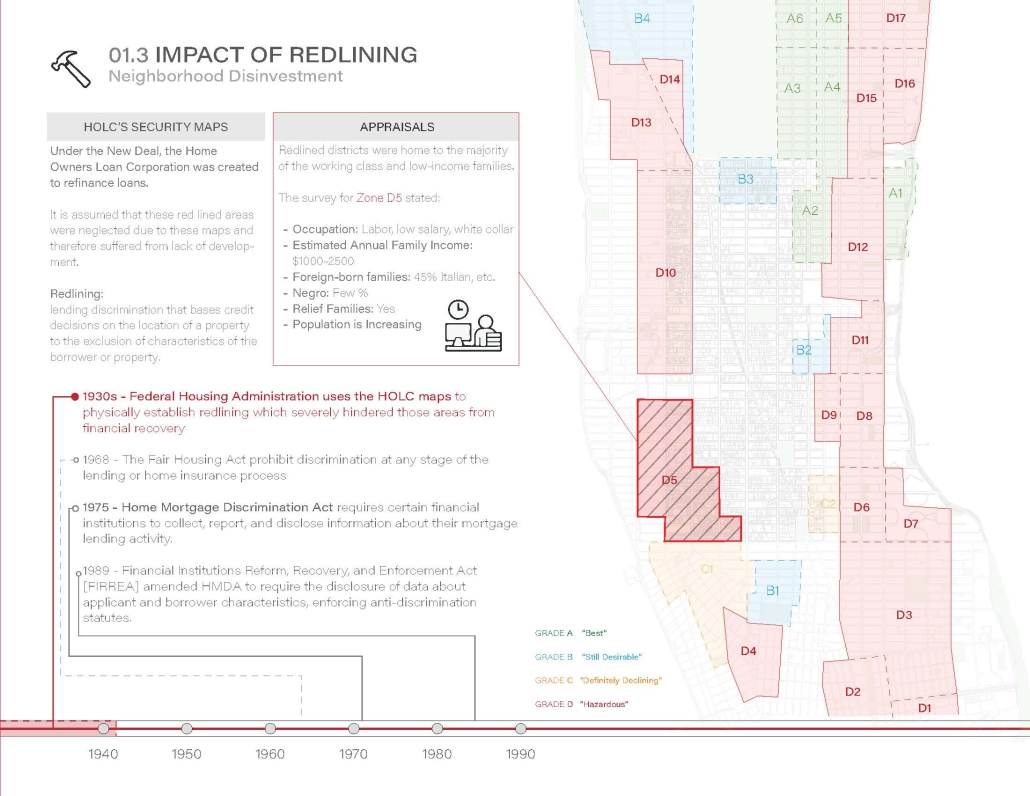
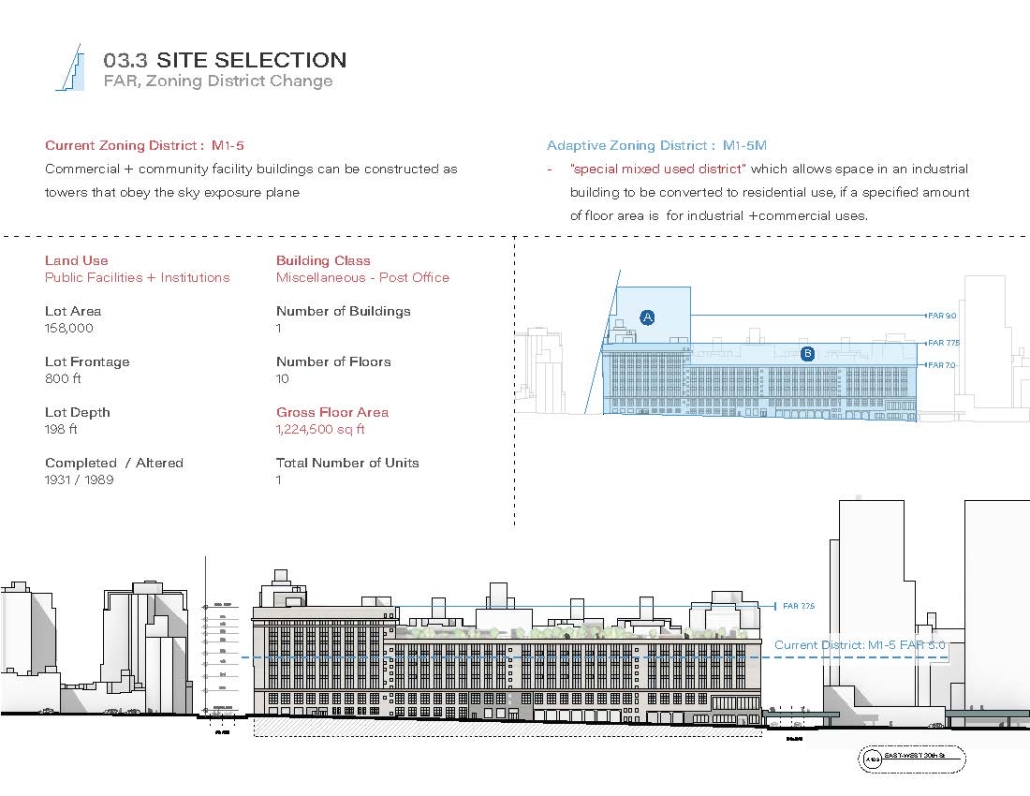
The use of office buildings with increasing vacancies is a great case study for this kind of project. For this thesis, we chose to study Morgan North Postal Facility. It occupies an entire city block, solving the issue of space but not the tenement problem of light and air. By imposing the geometry of the dumbbell plan, the creation of air wells is possible and creates open-air shared spaces —while also relating the form back to what inspired it. Some of these cavities are public, while others are only accessible by tenants.
Due to the proximity of the highline, the form was able to suggest a way to deal with excess foot traffic by extending the highline and inviting it into the cavities created by the air wells, allowing the highline to continue interweaving throughout the city and connecting similar re-adaptive projects that would soon follow suit, therefore creating an elevated network of housing which can be known as the Elevated Fabric District.
Instagram: @michellecianfaglione, @nyitarch, @exdarchitecture
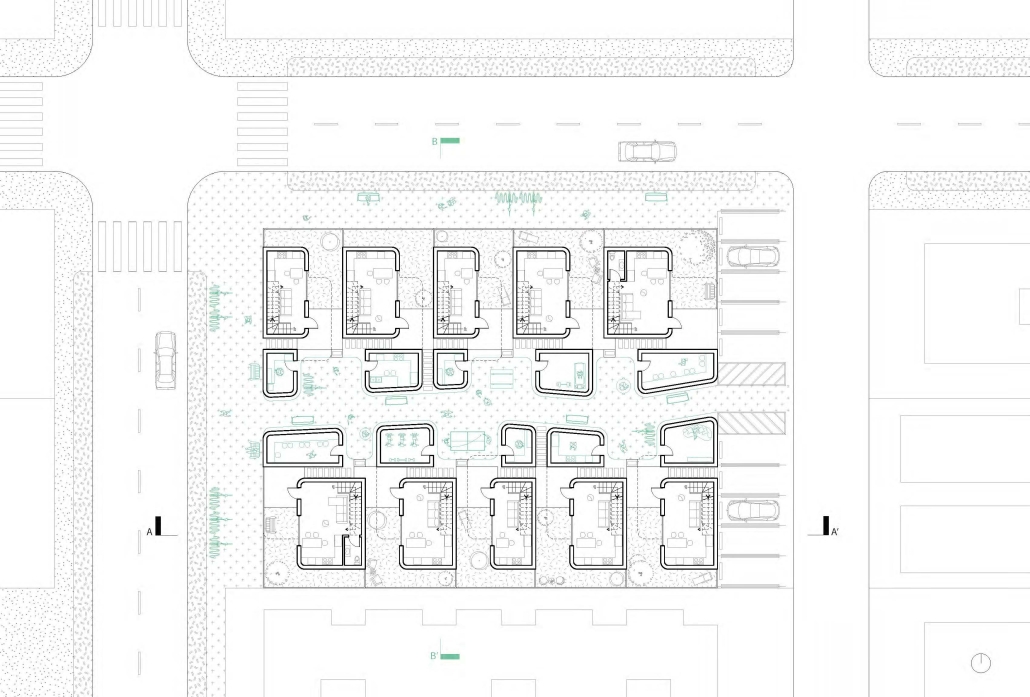
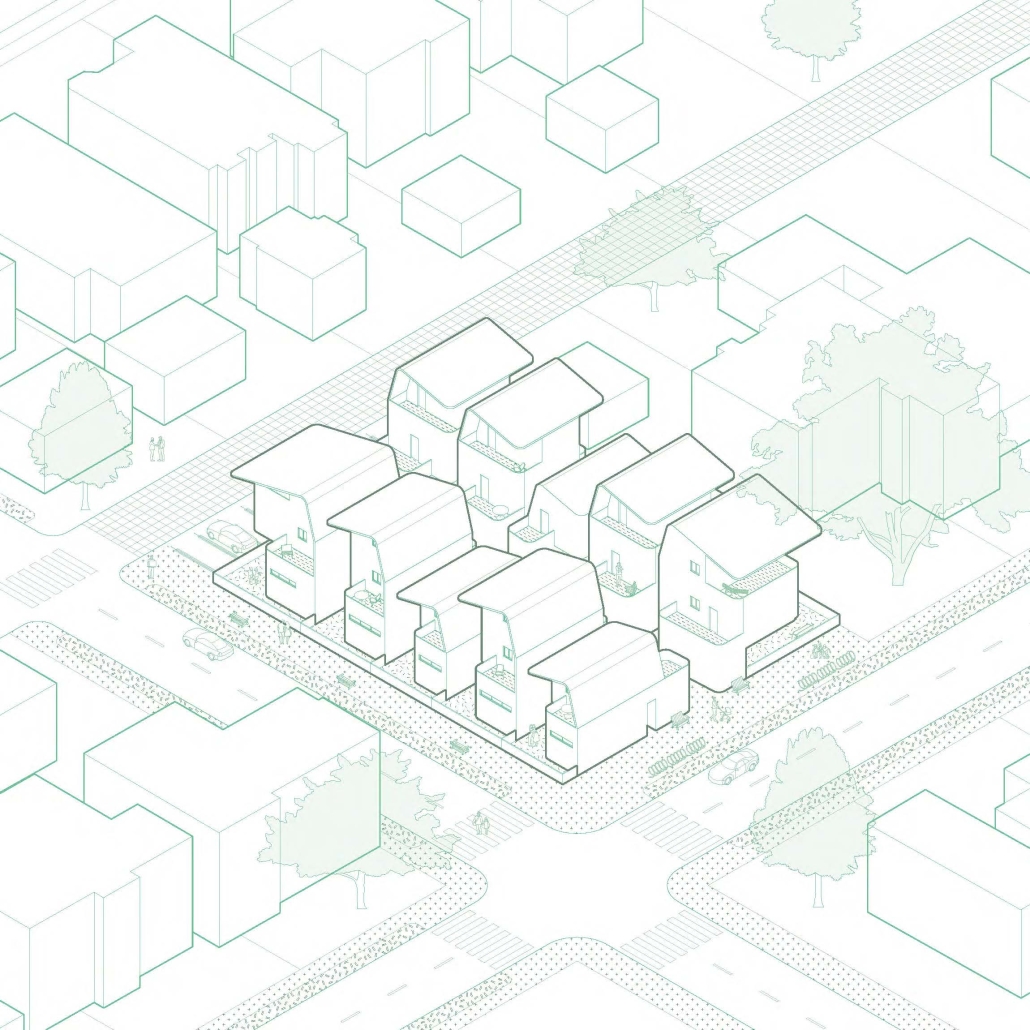
Low-Rise LNK by Luryn Hendrickson & Haley Herman, Bachelor of Science in Design: Architecture ‘23
University of Nebraska-Lincoln | Advisor: Michael Harpster
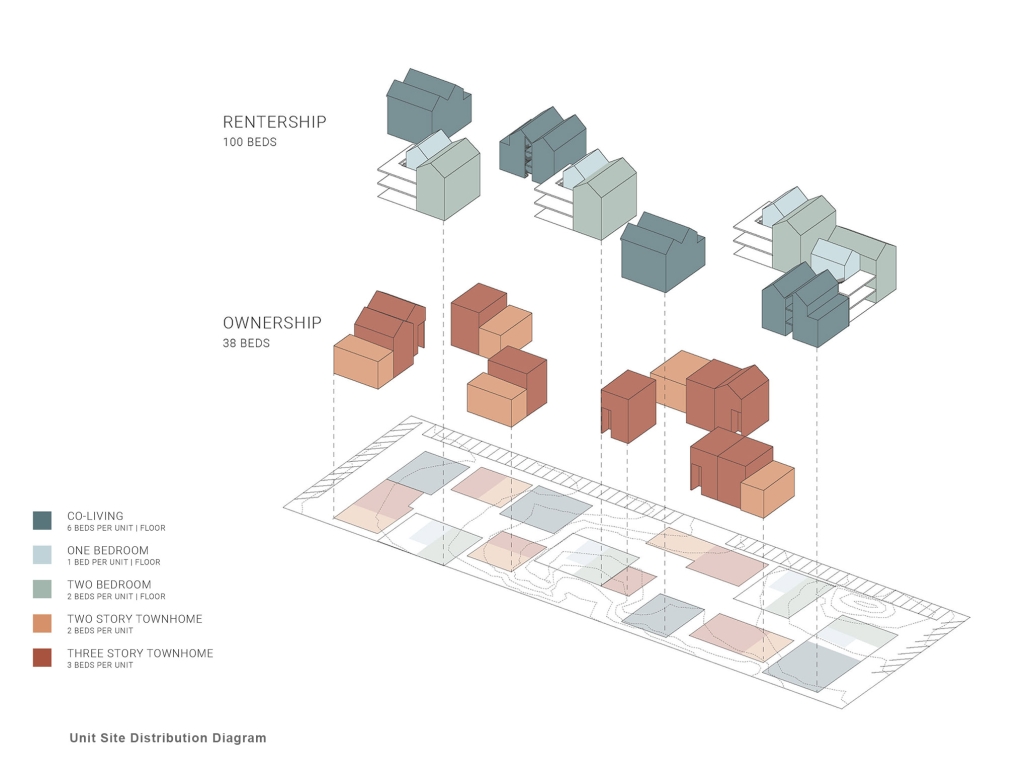
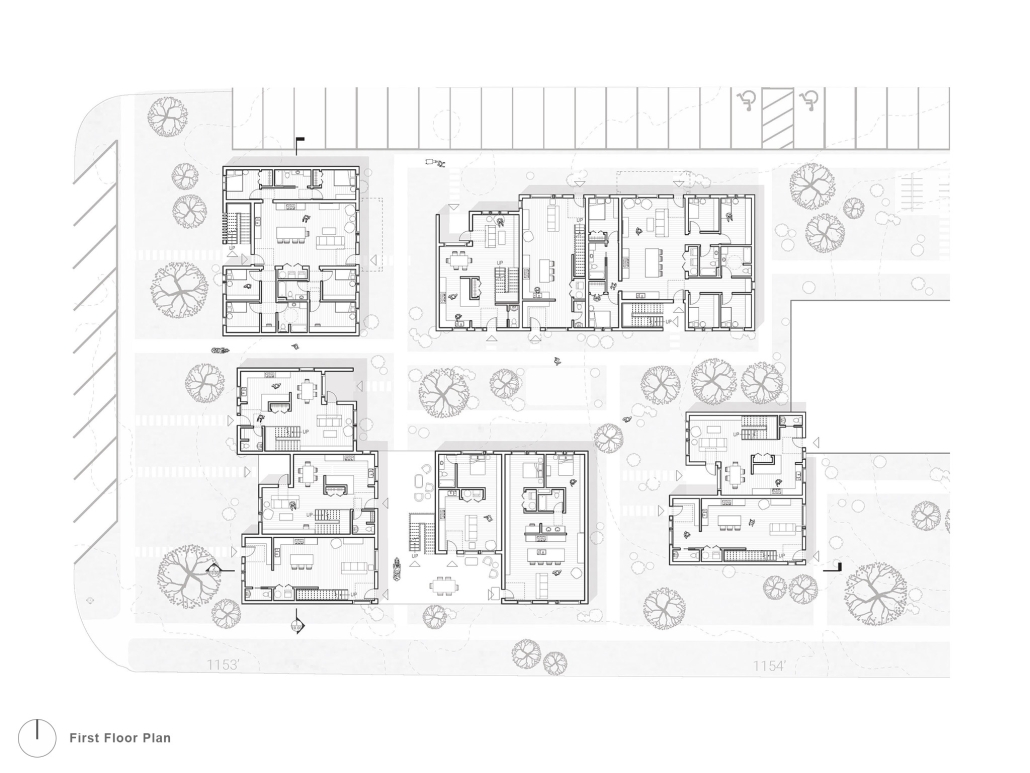
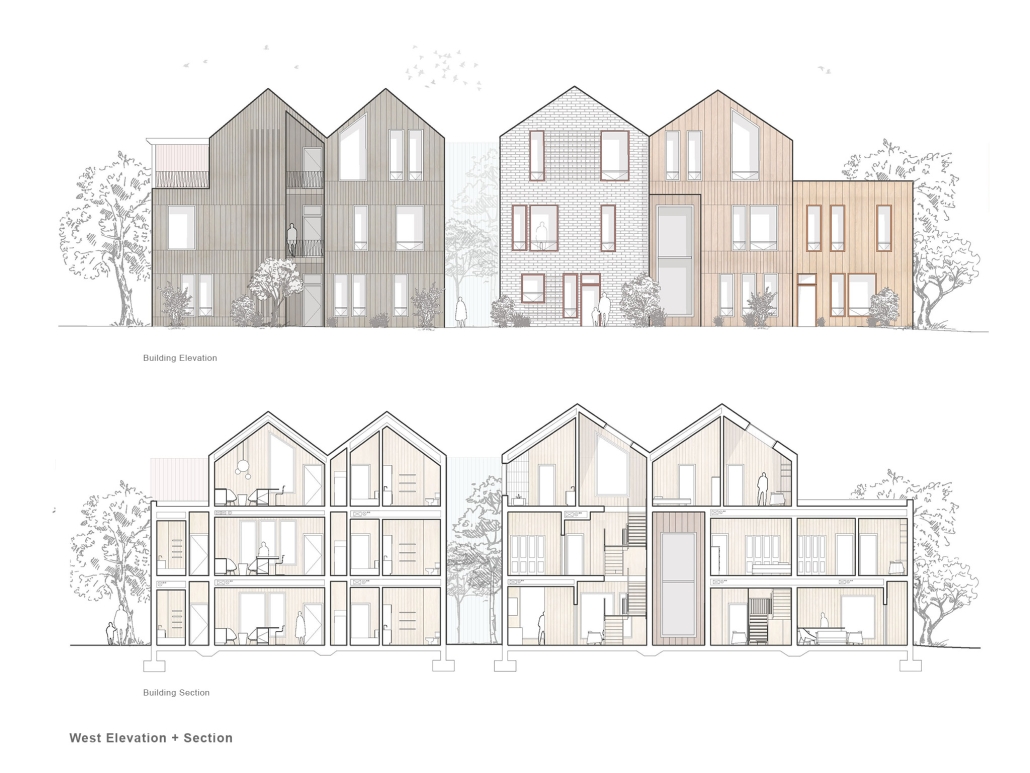
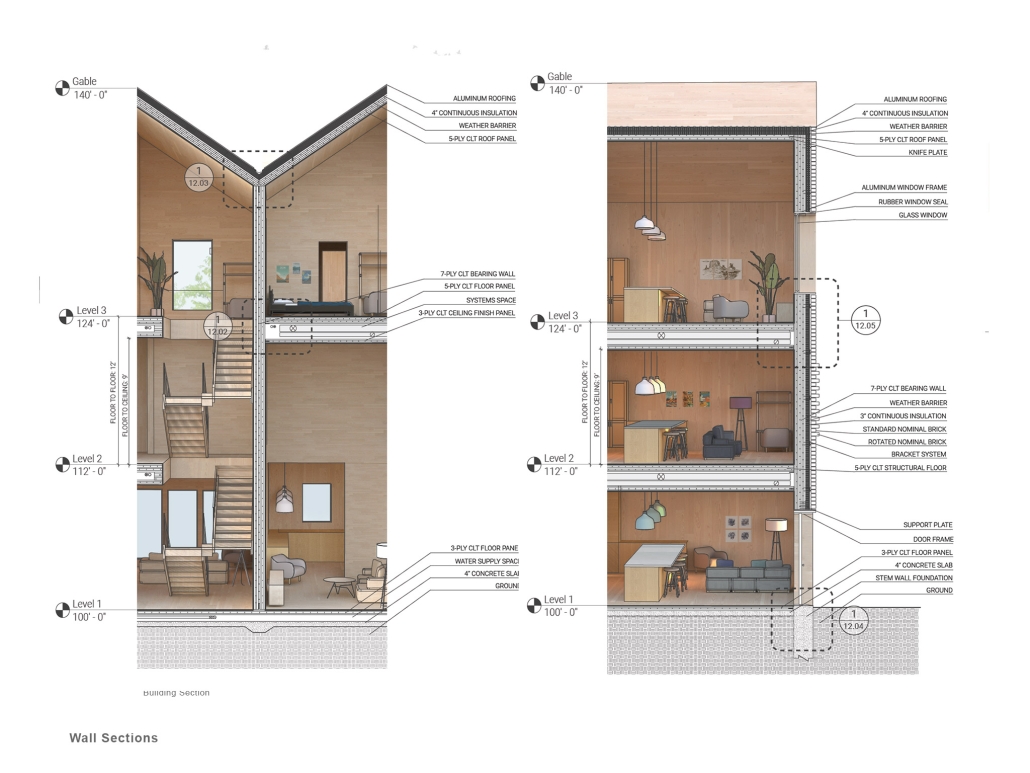
This project features a design for a dense, low-rise housing development breaks from the traditional, rectilinear apartment building. A series of user-specific apartments flats, co-op living spaces, and townhomes were designed and aggregated into separate buildings spread across the site. Each building was situated in a way that promoted a sense of ownership while also creating pockets of green space that serve as community spaces. Utilizing a Community Unit Plan zoning mechanism alongside a community land trust, the project is ultimately able to achieve greater density on the site than typically allowed while also restricting gentrification of the neighborhood and promoting a sense of community.
This project received the SGH Concepts + Dri-Design Honor Award (2nd Place): An internal UNL College of Architecture design competition for fourth-year undergraduate students.
Instagram: @unl_mharpster
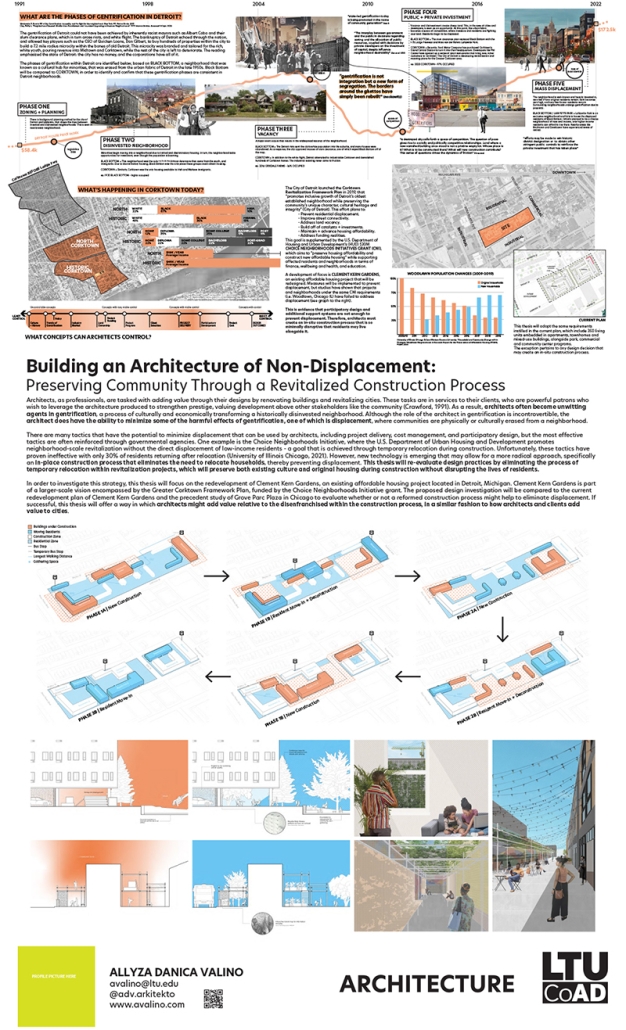
Building an Architecture of Non-Displacement: Preserving Community through a Revitalized Construction Process by Allyzza-Danica Valino, M.Arch ‘23
Lawrence Technological University | Advisors: Scott Shall (Committee Chair), Joonsub Kim (Member) & Edward Orlowski (Member)
As professionals, architects are tasked with adding value through their designs by renovating buildings and revitalizing cities. These tasks are in service to their clients, who are powerful patrons who wish to leverage the architecture produced to strengthen prestige, valuing development above other stakeholders like the community (Crawford, 1991). As a result, architects often become unwitting agents in gentrification, a process of culturally and economically transforming a historically disinvested neighborhood. Although the architect’s role in gentrification is incontrovertible, the architect does have the ability to minimize some of the harmful effects of gentrification, one of which is displacement, where communities are physically or culturally erased from a neighborhood.
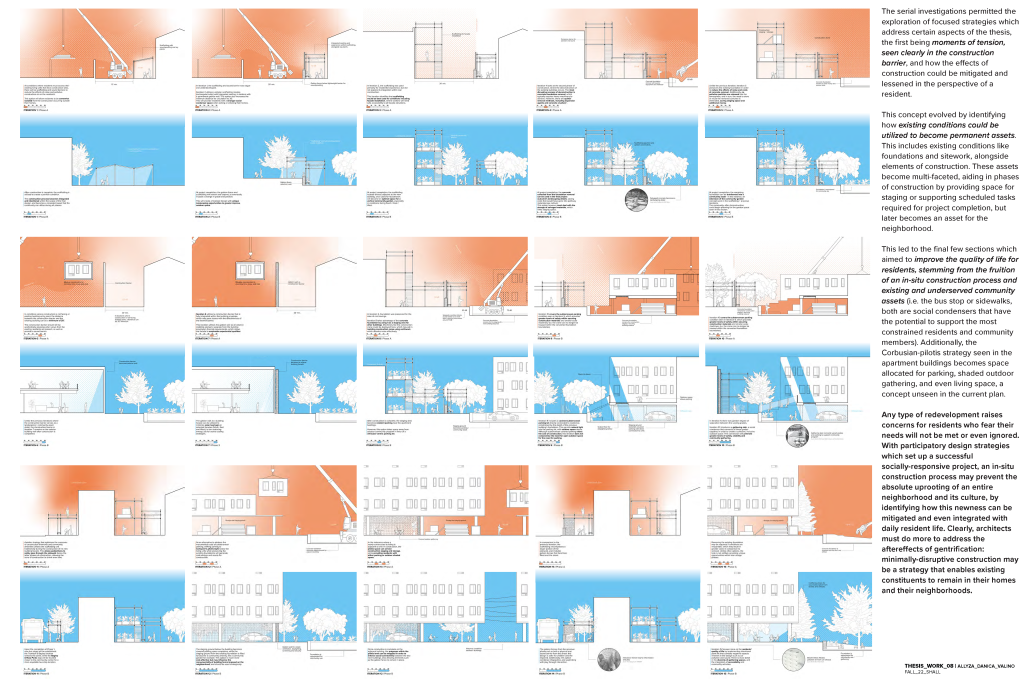
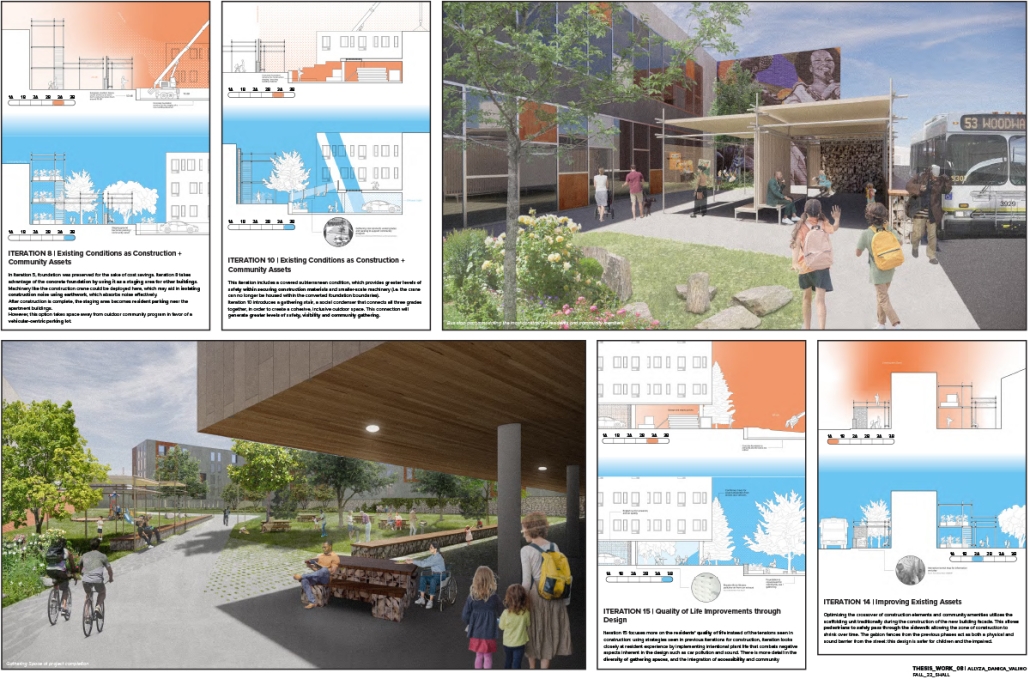
Many tactics have the potential to minimize displacement that can be used by architects, including project delivery, cost management, and participatory design, but the most effective tactics are often reinforced through governmental agencies. One example is the Choice Neighborhoods Initiative, where the U.S. Department of Urban Housing and Development promotes neighborhood-scale revitalization without the direct displacement of low-income residents – a goal that is achieved through temporary relocation during construction. Unfortunately, these tactics have proven ineffective with only 30% of residents returning after relocation (University of Illinois Chicago, 2021). However, new technology is emerging that may allow for a more radical approach, specifically an in-place construction process that eliminates the need to relocate households, thereby preventing displacement. This thesis will re-evaluate design practices by eliminating the process of temporary relocation within revitalization projects, which will preserve both existing culture and original housing during construction without disrupting the lives of residents.
To investigate this strategy, this thesis will focus on the redevelopment of Clement Kern Gardens, an existing affordable housing project located in Detroit, Michigan. Clement Kern Gardens is part of a larger-scale vision encompassed by the Greater Corktown Framework Plan, funded by the Choice Neighborhoods Initiative grant. The proposed design investigation will be compared to the current redevelopment plan of Clement Kern Gardens and the precedent study of Grove Parc Plaza in Chicago to evaluate whether or not a reformed construction process might help to eliminate displacement. If successful, this thesis will offer a way in which architects might add value relative to the disenfranchised within the construction process, in a similar fashion to how architects and clients add value to cities.
This project received the 2023 CoAD (College of Architecture and Design) Alumni Award
Instagram: @scott_shall
YARD56 by Veronica Restrepo, M.Arch ‘23
University of Washington | Advisor: Rick Mohler
Seattle is one of the Nation’s fastest-growing cities, according to the Census Bureau. Its population has grown almost 19% over the last ten years. The supply of affordable housing has not kept up with the demand created by the booming economy and high-wage jobs in the area. Yet, 40% of Seattle households remain low-income. Yard56 aims to integrate sustainability with the rising inequities of housing affordability. Located in the fast-growing neighborhood of Ballard within the city of Seattle, Yard56 provides a total of 82,000 SF with a mix of affordable housing, live/work units, retail, and community outdoor space. Anchoring Northwest 56th Street and 20th Avenue Northwest, Yard56 is in a designated hub urban village, which provides a comprehensive growth plan. This enables and ensures a livable future and growing sustainably through accommodating a broad mix of uses and access to pedestrian and transit-oriented transportation.
Instagram: @mohler.rick, @veronicarstrepo
House to Housing by Mengru Zhao, M.Arch. ‘23
UCLA AUD | Advisor: Feghali Yara
Los Angeles has served as a storied context for the single-family home as both a site of architectural invention and cultural desire and as an instrument of wealth creation. These dual narratives persist today despite economic realities that make both stories far less suitable to their intended audiences. This studio will unpack these dual narratives in order to survey their histories and understand their widespread effects. The impact of these LA histories mirrors those of the U.S. housing market more broadly. In turn, these social, political, economic and environmental effects have severely limited housing supply, affordability and sustainability, and have shifted the site of the architectural problem from house to housing. It is this shift that the studio will engage as a set of spatial, organizational and social potentials for design to interrogate.
The value of homeownership has underpinned not only the American economy but the very image of American life for much of the past century. Homeownership provided a foothold on the economic ladder, stability in community life, and the fantasy of manifest destiny at the heart of the “American dream”. However, with the collapse of the housing market and the transformation of the economy over the past decade, the housing dream—which masked the many exclusions it had been built upon—has been revealed as such. The barrier to entry into the housing market has become impossible for most and is especially steep in Los Angeles where home prices have skyrocketed and fueled waves of gentrification and displacement, further eroding the economic prospects of Angelenos and the social and cultural fabric of the city.
Instagram: @feghali.yara
Dream Together & Miscellaneous Mutations by Brandon Smith, M.Arch. ‘23
University of Southern California | Advisor: Yaohua Wang
Dream Together is a large-scale mixed-use project that uses imaginative forms to highlight the uniqueness of each citizen who interacts with it. In addition, the project aims to heal the housing and urban sprawl issues of Los Angeles while challenging the tradition of the typology in which commercial occupies the bottom and residential occupies the top. This allows programs to sprawl throughout the building rather than simply being stacked in layers – adding to its humanistic residential qualities as is seen with the programmatic zoning of a home. Dream Together reflects this and in a sense is a mixed-mixed-use project. For an Angeleno, the most desirable residential circumstance is the home. Dream Together acknowledges this culture and molds architectural typological conventions to adequately react to its surroundings. In this project, the building formally orients, subtracts, and protrudes itself based on key urban resources such as schools, grocery stores, religious centers, or hospitals. The project acts as an urban connector in which people can access varying resources without the dependence of a vehicle; inspired by Hong Kong’s mall culture. The primitive shapes of the project introduce playfulness while breaking the orthogonal formal qualities of a typical mixed-use project.
Miscellaneous Mutations is the second part of the project and is a further study of the formal qualities of the Dream Together via the already-made physical three-dimensional pieces. Essentially, where Dream Together features these pieces assembled through defined contextual parameters from research, Miscellaneous Mutations features the pieces in a new light dictated purely by aesthetics and formal discovery. This second part creates the discussion of revisiting a design perceived as finished. Perhaps a design can become more and more contextual than meets the eye. Suffice to say, Miscellaneous Mutations celebrates the saying “Design Never Stops”.
This project received the USC Master of Architecture Design Communication in Directed Design Research Award – In recognition of the most outstanding graduate final degree project illustrating advanced presentation and graphic communication.
Instagram: @arch.brandonsmith, @yaohua_wwww
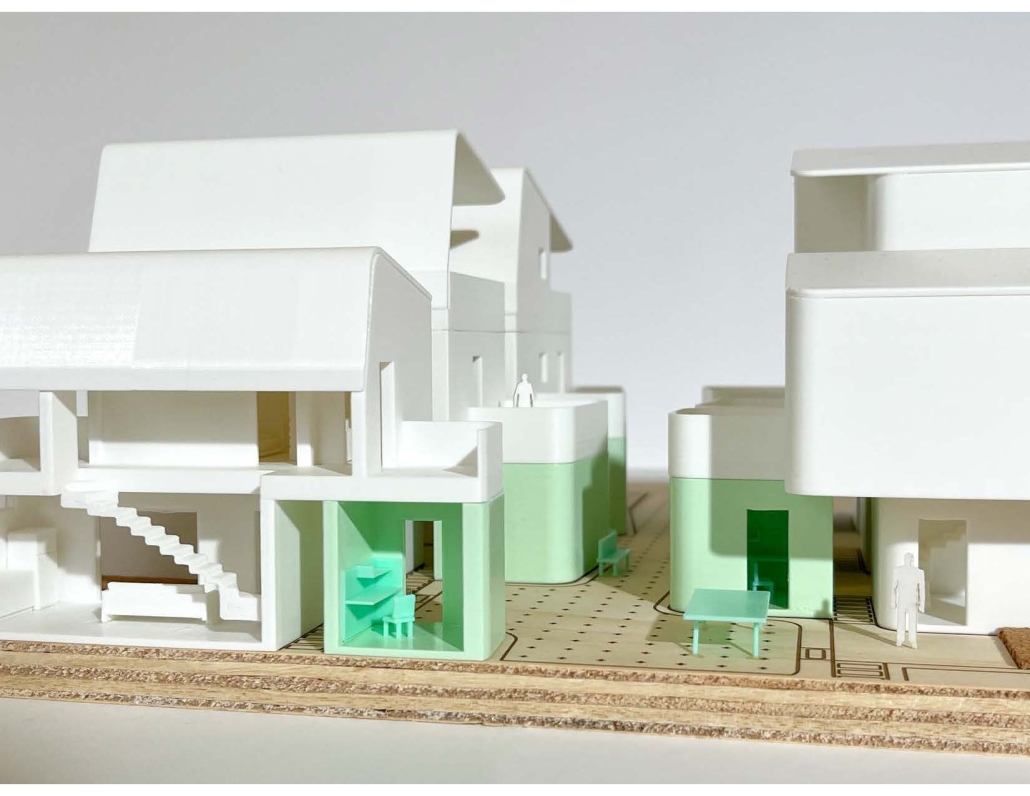
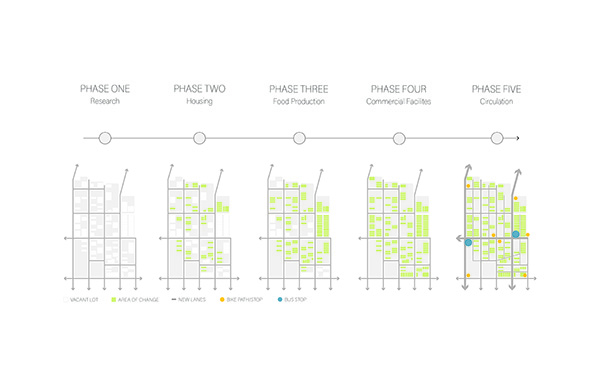
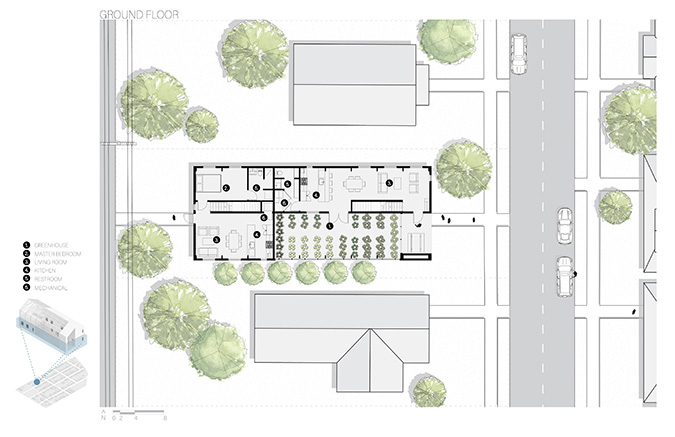
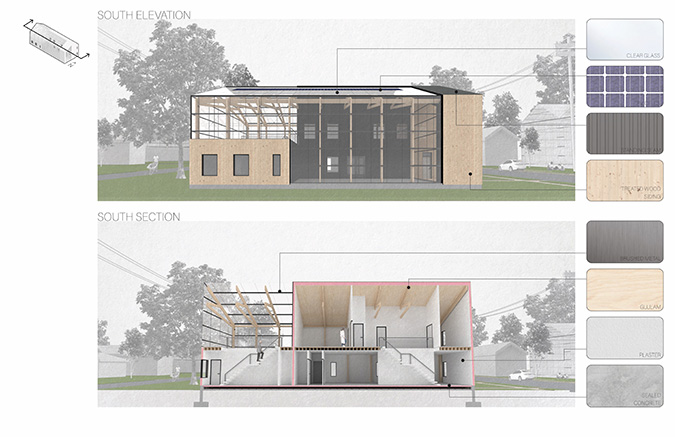
Producing Community by Tessa Hill, B.Arch ’23
Ball State University | Advisors: Robert Koester and Jonathan Spodek
Younger generations want to live in cities and yet most neighborhoods are afflicted by limited housing choices, disconnection from food sources and public transportation, and are often also dangerous environments for pedestrians. These problems have made existing neighborhoods undesirable. So, how can neighborhoods be systemically redeveloped to address current concerns so that they don’t become exacerbated in the future?
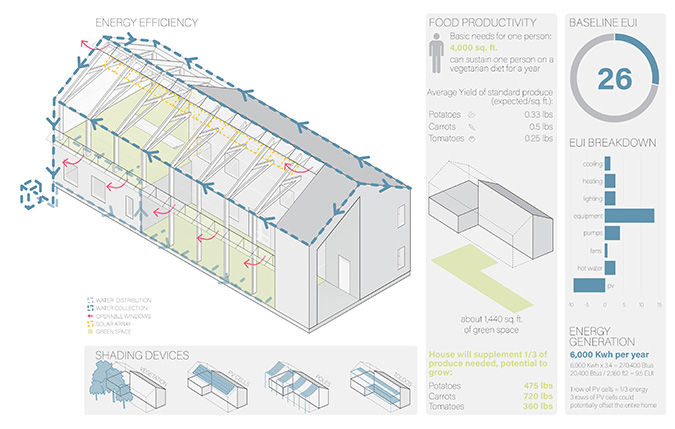
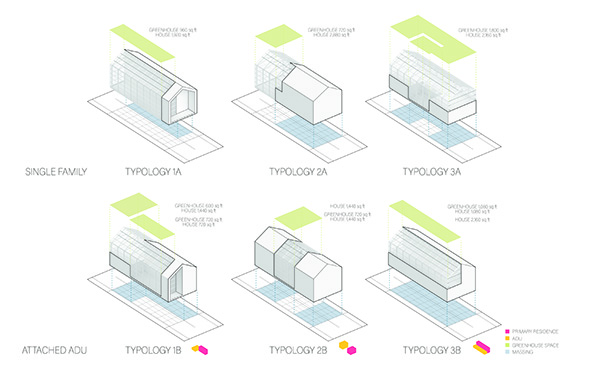
This project proposes the strategic implementation of infill housing and urban food production in the redevelopment of existing neighborhoods. The McKinley neighborhood in Muncie, Indiana was chosen as the location to test this thesis.
Initial designs create additional housing that offers different living opportunities, from single-family dwellings to accessory dwelling units. Each design enables residents to grow their own food via raised beds or vertical towers in an incorporated greenhouse. The ability to be self-sufficient and the visibility of food production will educate and inspire the community and promote continued progression toward sustainable living. Later phases could provide the neighborhood with varying scales of community spaces such as shared gardens, food markets, and education centers to attract and support community members. These latter phases will also have to address existing patterns of public transportation and correlated pedestrian paths for better connectivity.
This project received The Estopinal Group (TEG) Thesis Year Design Award.
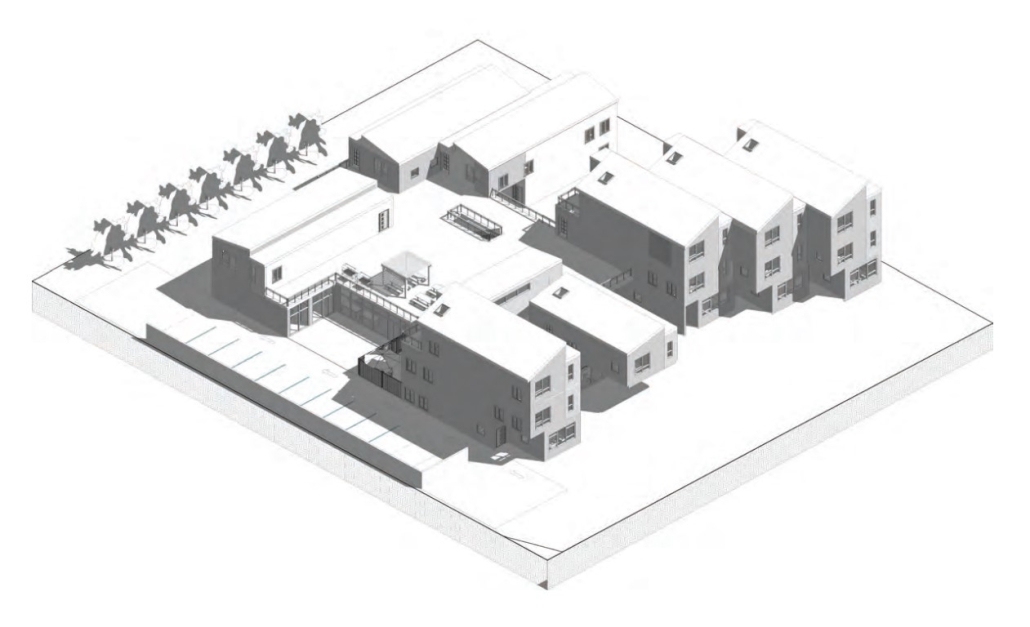
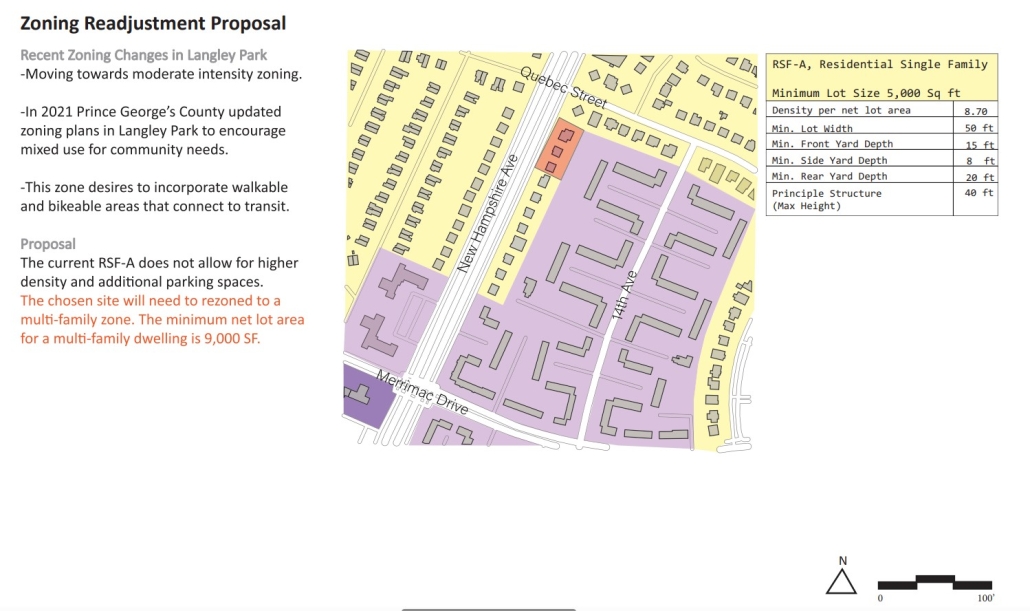
The Transition to Co-Living: Finding the Missing Middle Housing in Langley Park, Montgomery County-MD by Jenny Umana-Lemus, M.Arch ’23
Morgan State University, School of Architecture & Planning | Advisor: Carlos A. Reimers
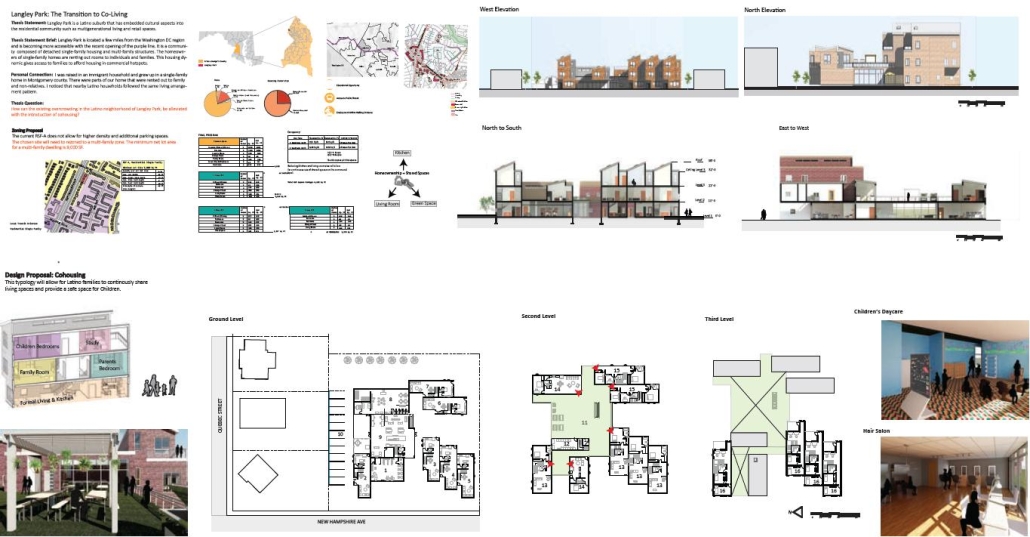
Langley Park in Montgomery County, Maryland is located a few miles from the Washington DC region and is becoming more accessible with the planned opening of the Purple Line of the DC Metro system. It is a community composed of detached single-family housing and multi-family structures.
The homeowners of single-family homes have been renting out rooms to individuals and families because of the shortage of Middle Housing (middle income) identified by the Montgomery County Planning Department in the region. This housing dynamic gives access to families who would otherwise not afford housing near transportation-accessible and commercial hotspots.
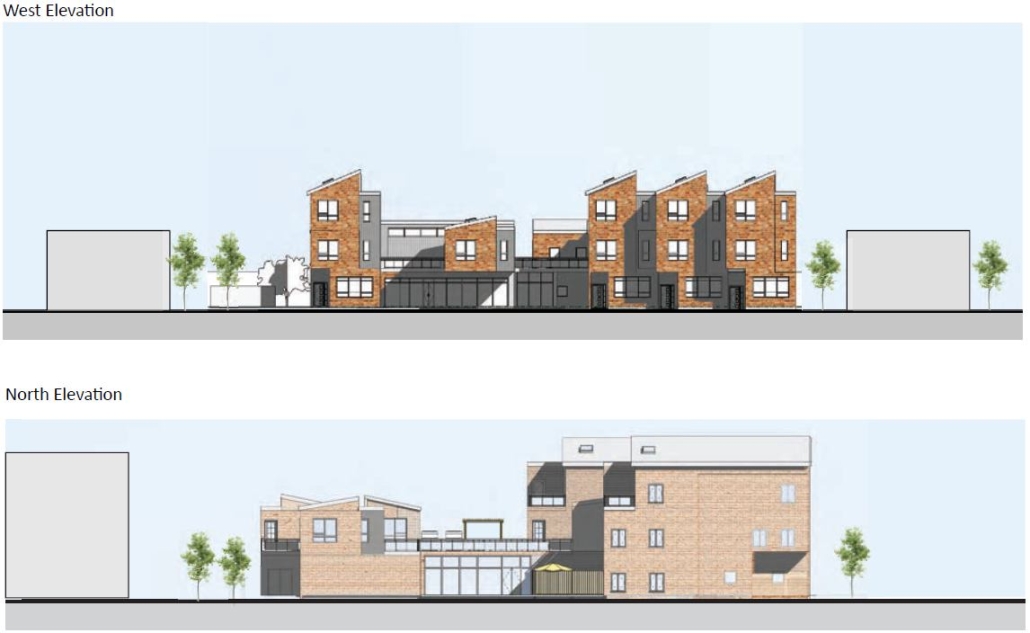
This design proposal paves a path to homeownership for the Hispanic and Latino population at Langley Park. The chosen typology is cohousing in integrated single-family land, a trend that is already ongoing for denser multifamily housing and rowhouses. Co-housing will allow densifying areas of suburban land, while allowing homeowners to own an efficient unit and have access to larger communal spaces that families do and have always shared in the Latino culture in the USA, such as the kitchen and dining areas, or living rooms.
In addition, the integration of green terraces will promote communal interaction among residents and provide safety for children to play in. Family members in Latino households often cook for their larger household and provide childcare and other services to friends and neighbors. In addition, Latinos in Langley Park are hard-working entrepreneurs supported by community members and organizations that will find space in rental retail areas added by the proposed housing typologies.
Instagram: @reimerscarlos
See you in the next installment of the Student Showcase!