2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part V
In Part V of the 2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase, we take a look at projects centered on equity. From natural highways to aid centers, the featured student work includes design solutions catered toward migrants, widows, and other historically marginalized groups. By providing culturally sensitive architectural interventions, each project fosters resilience, equity, and empowerment.
Scroll down to learn more!
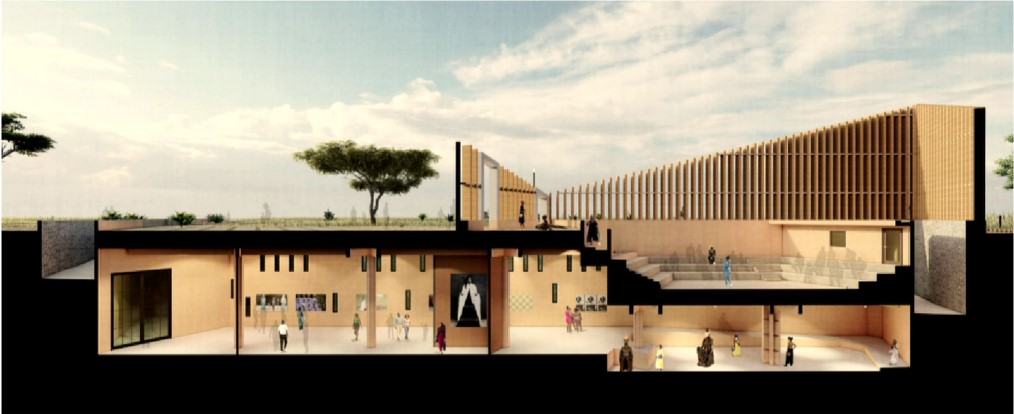
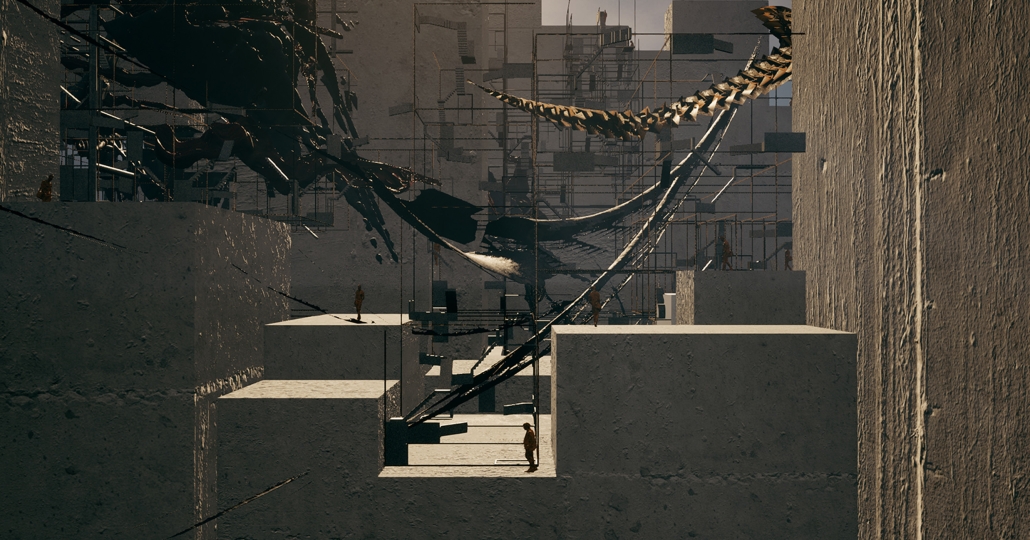
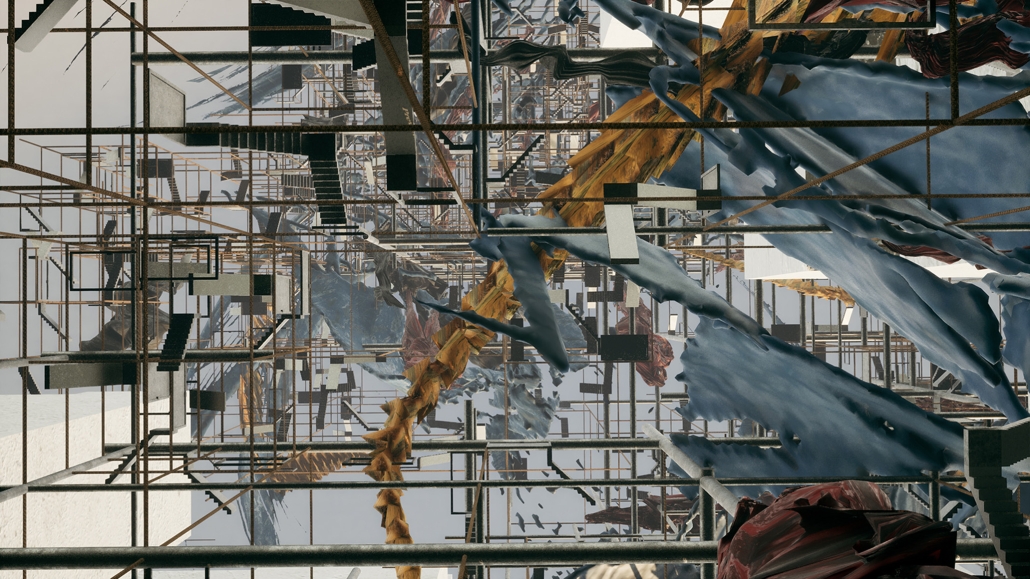
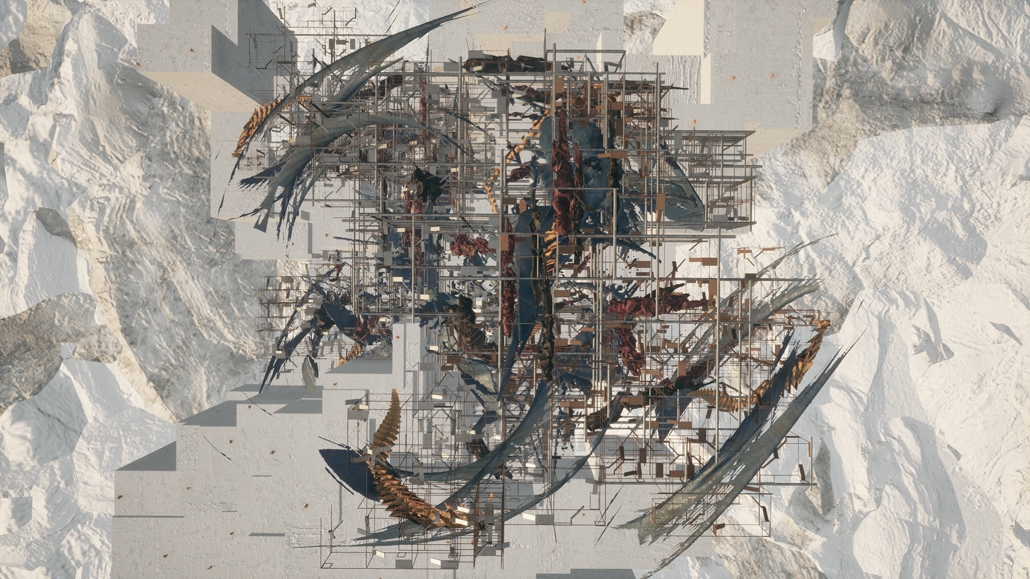
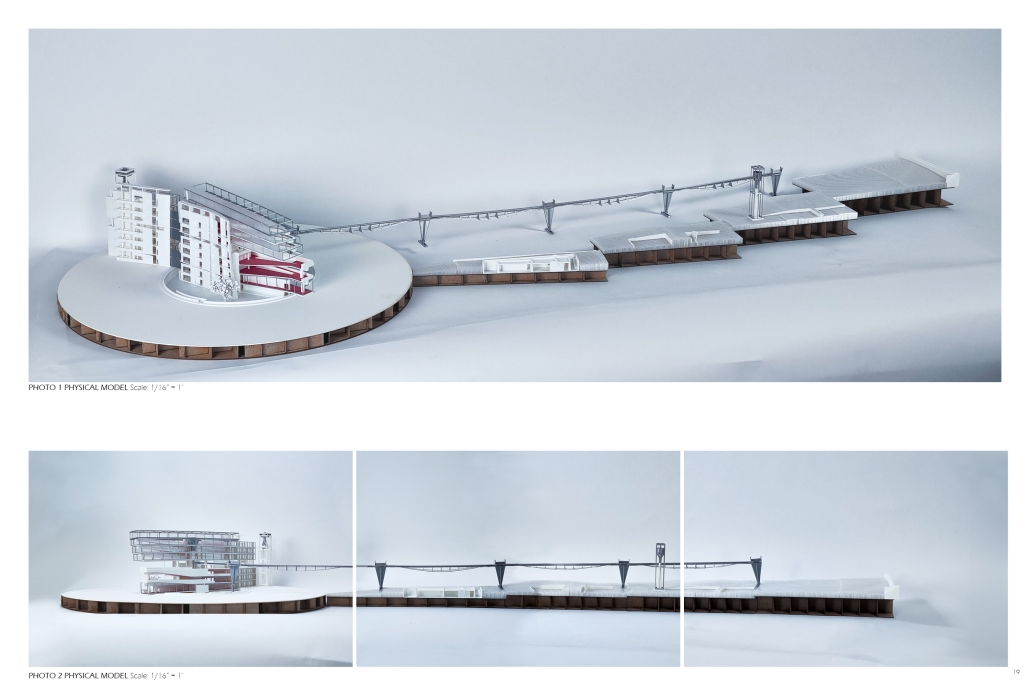
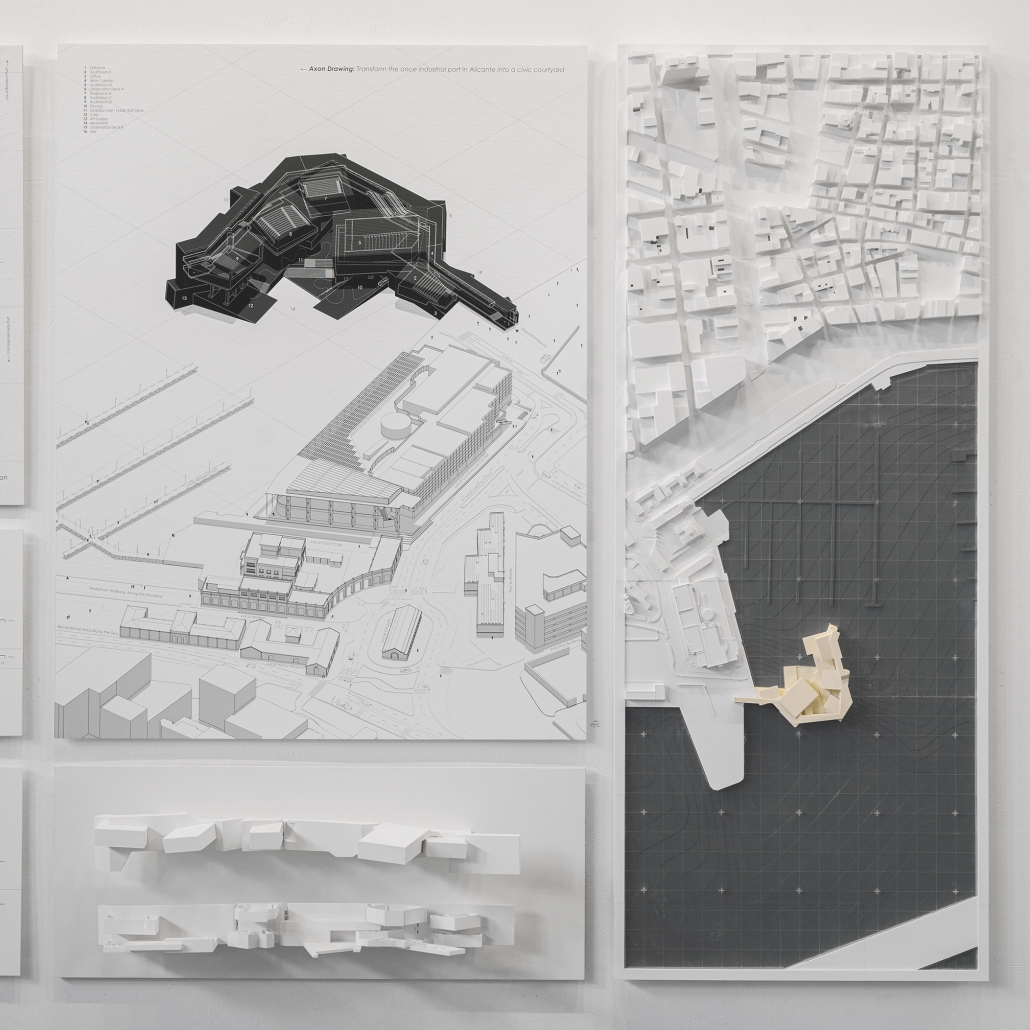
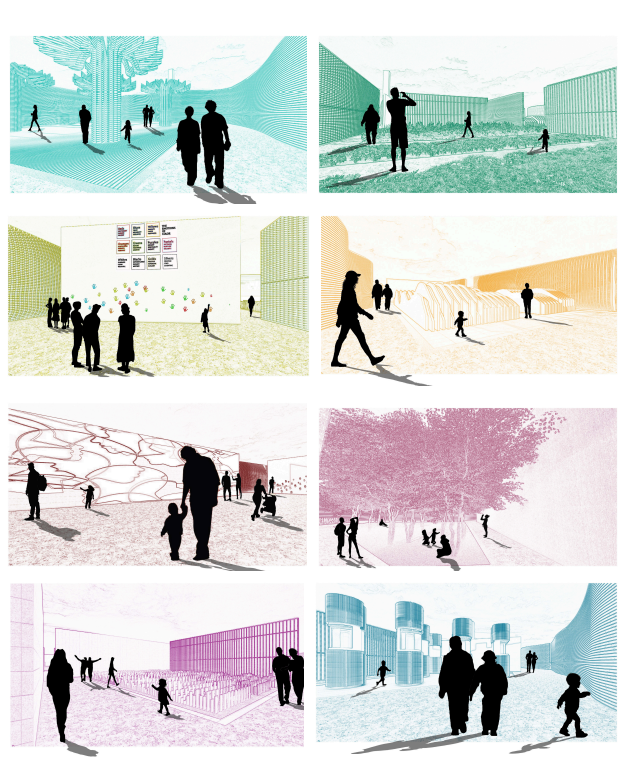
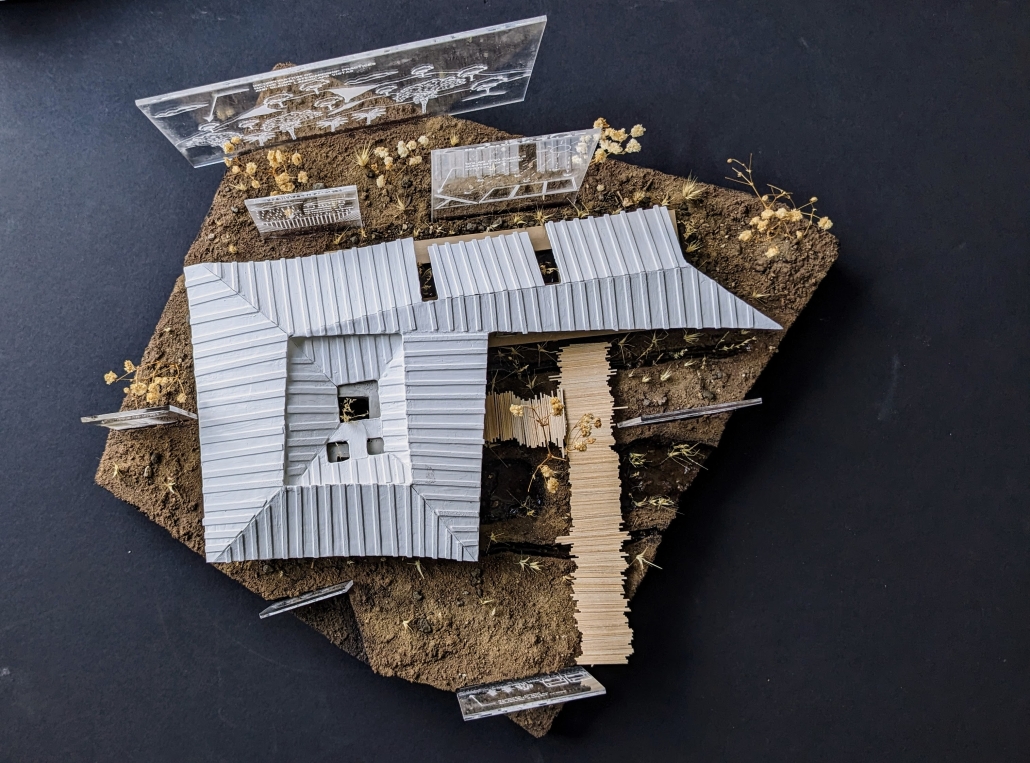
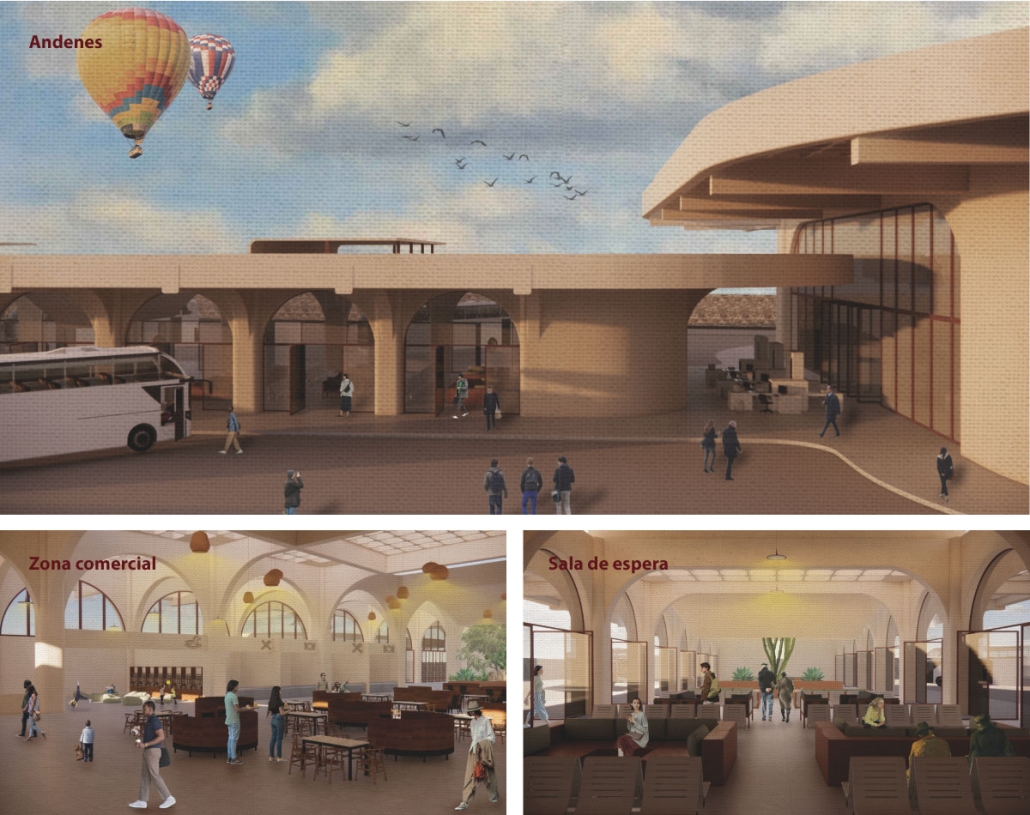
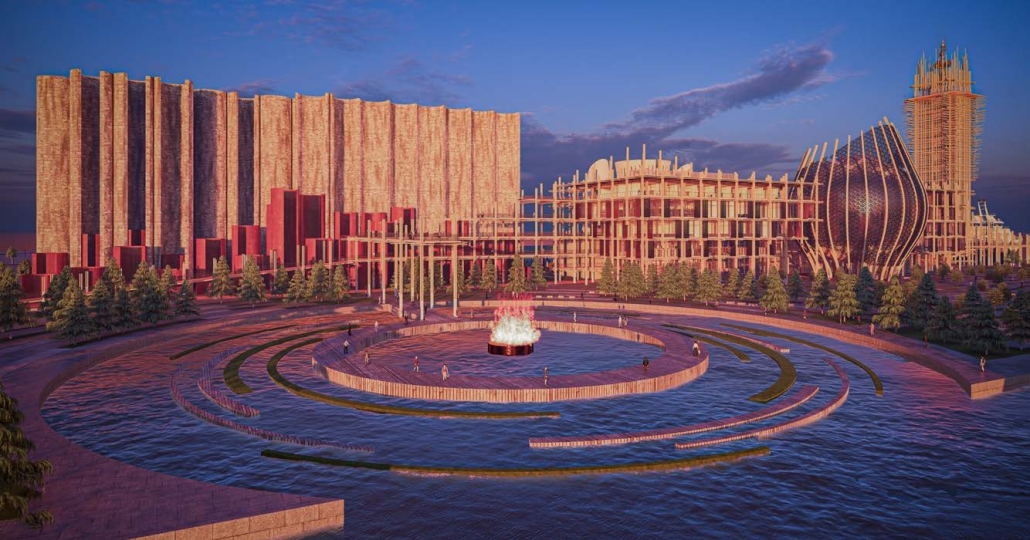
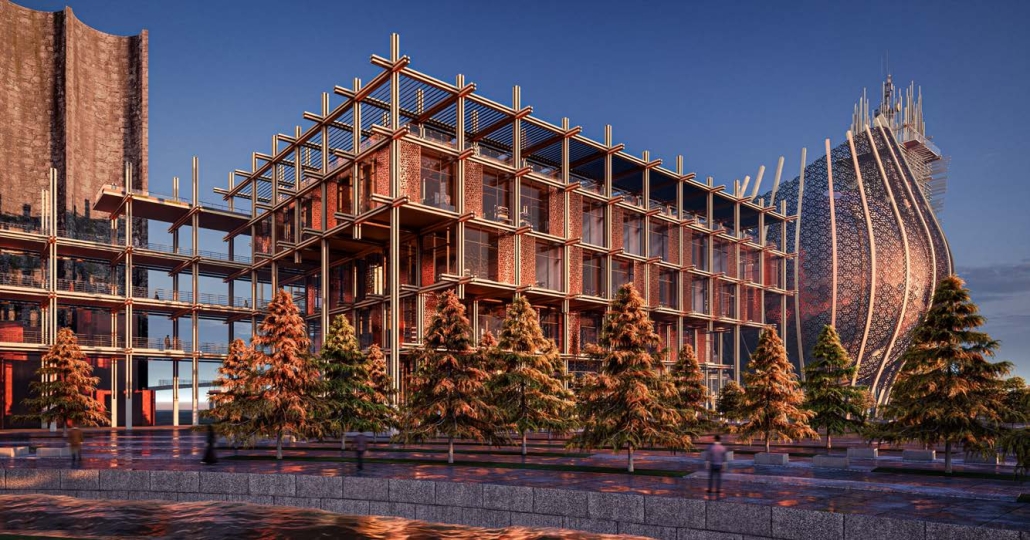
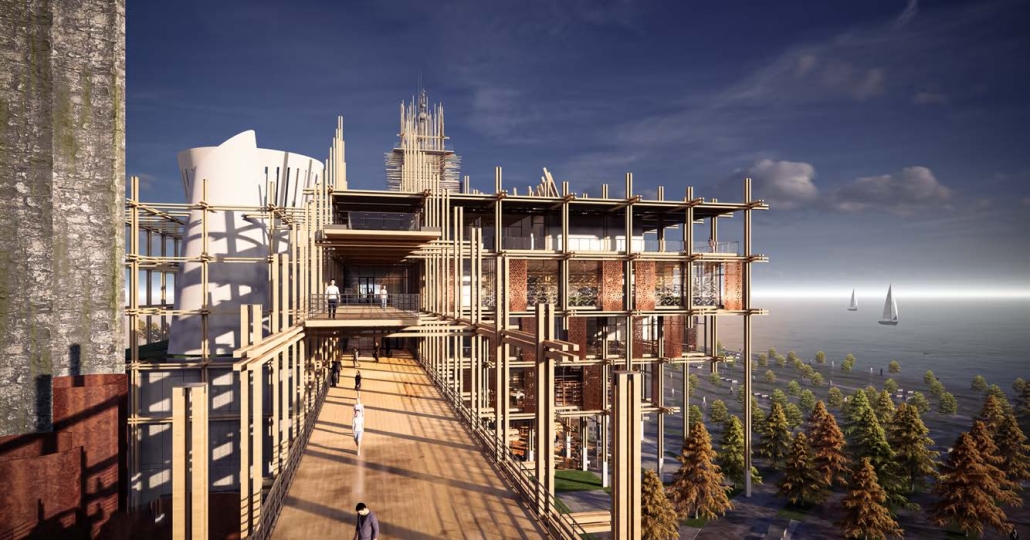
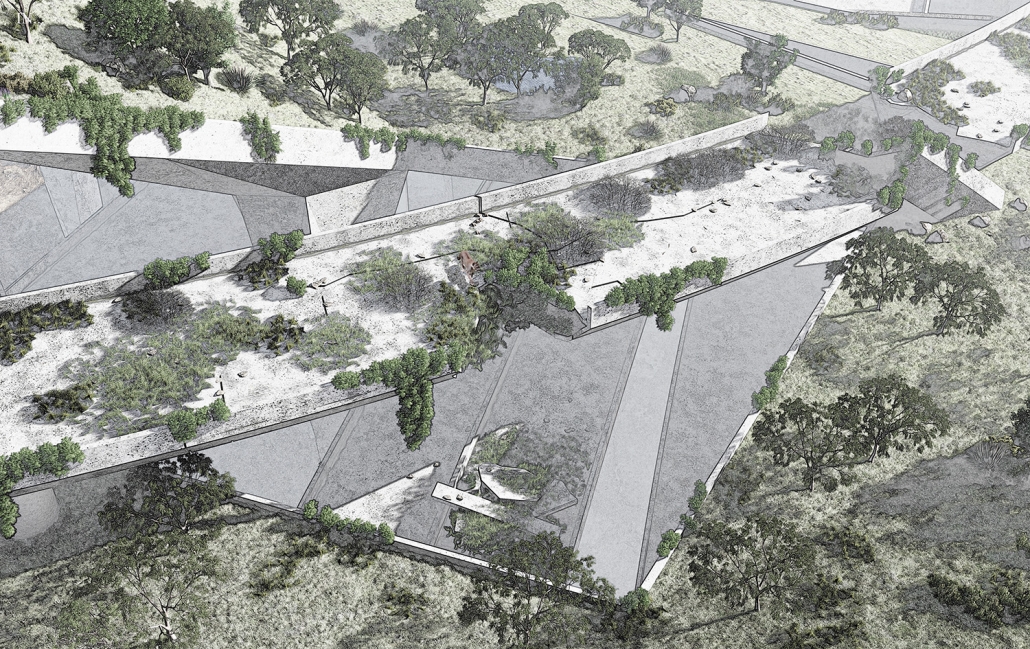
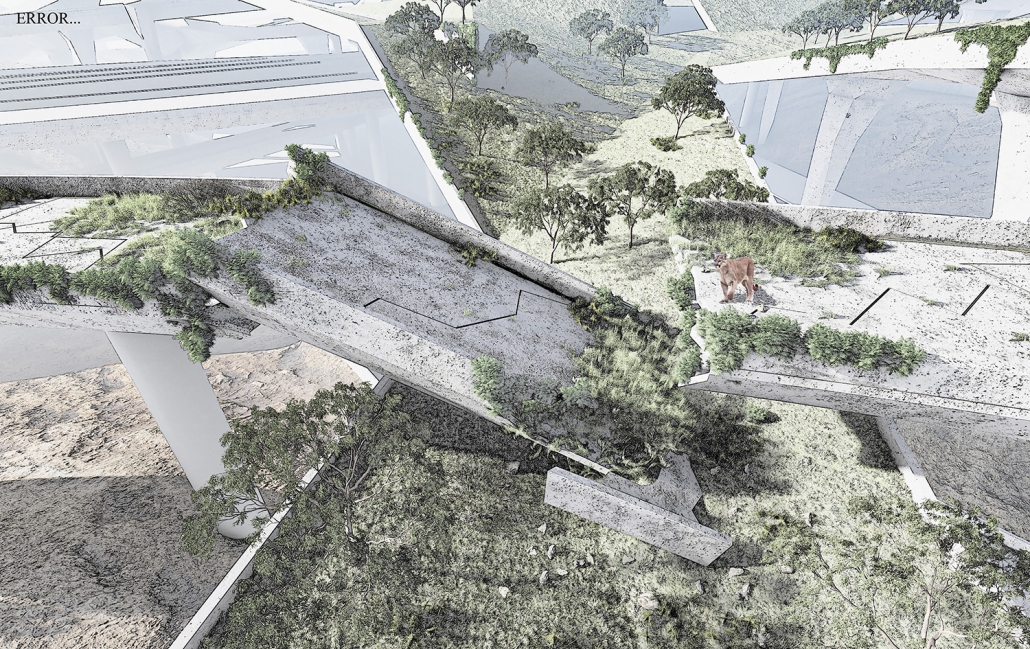
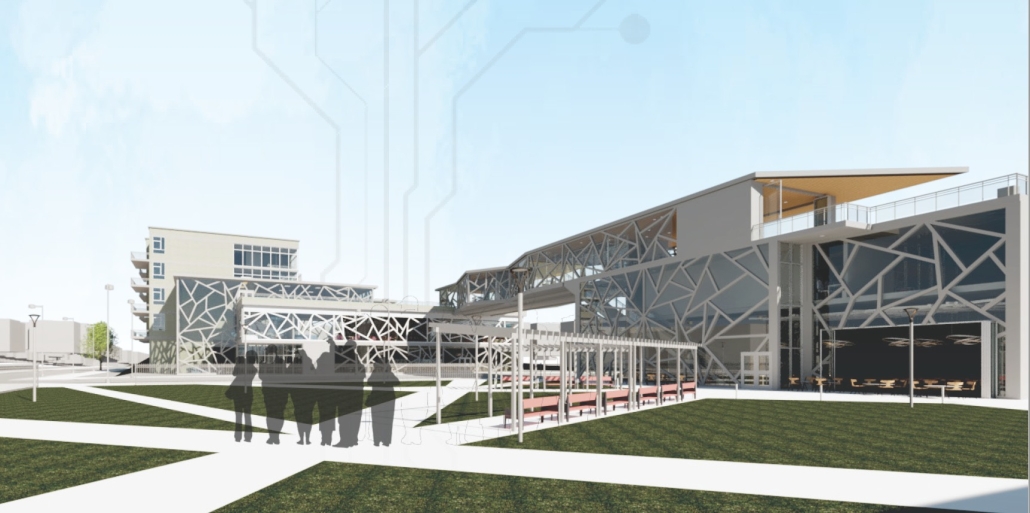
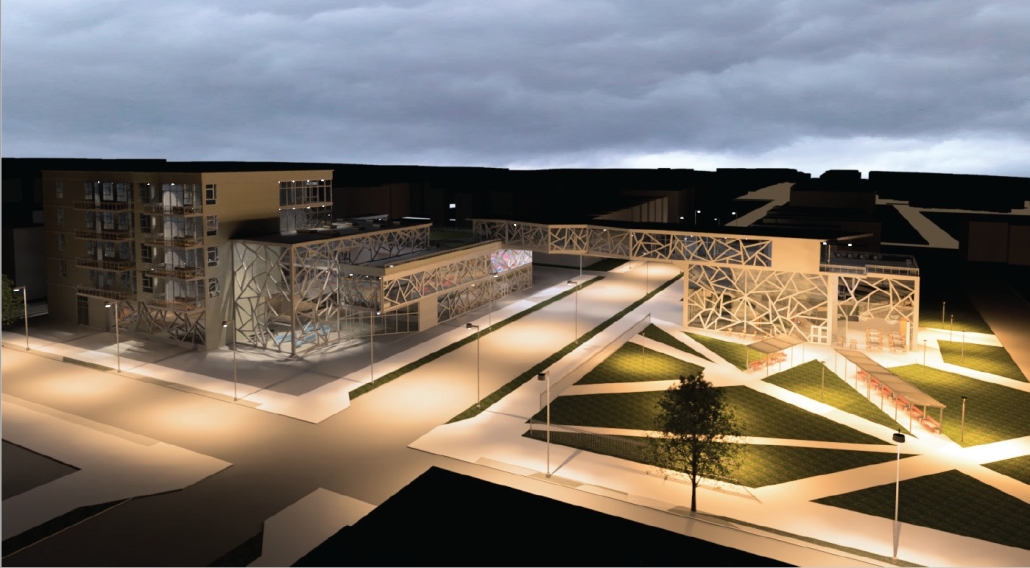
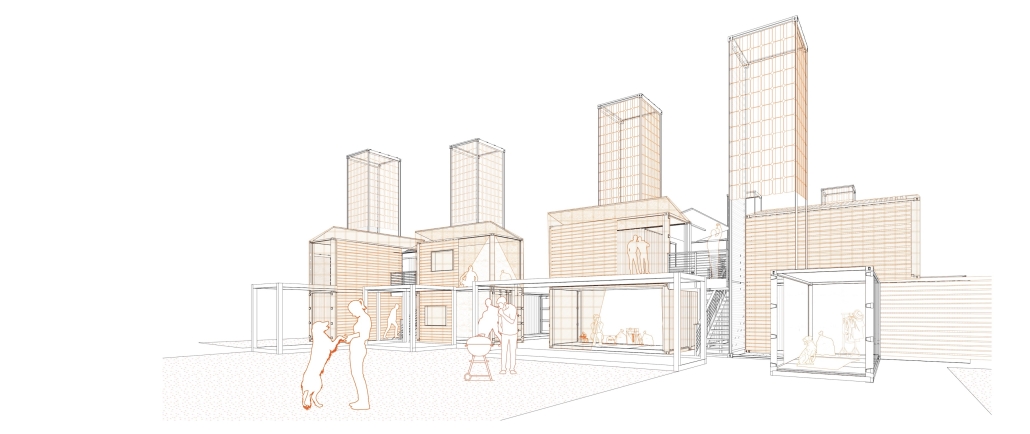
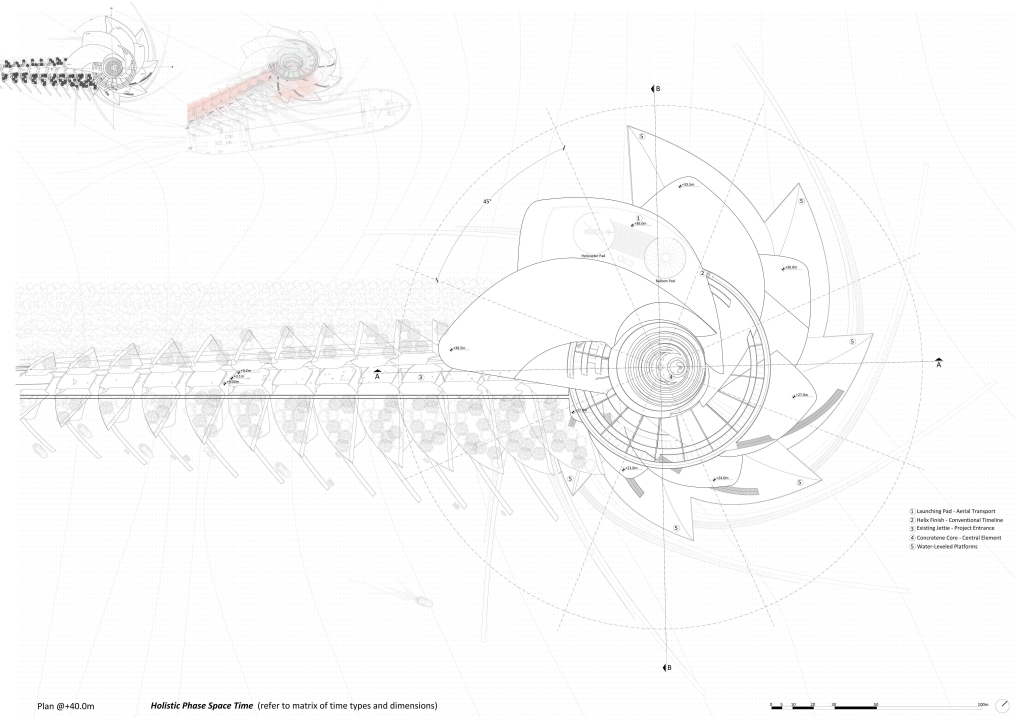
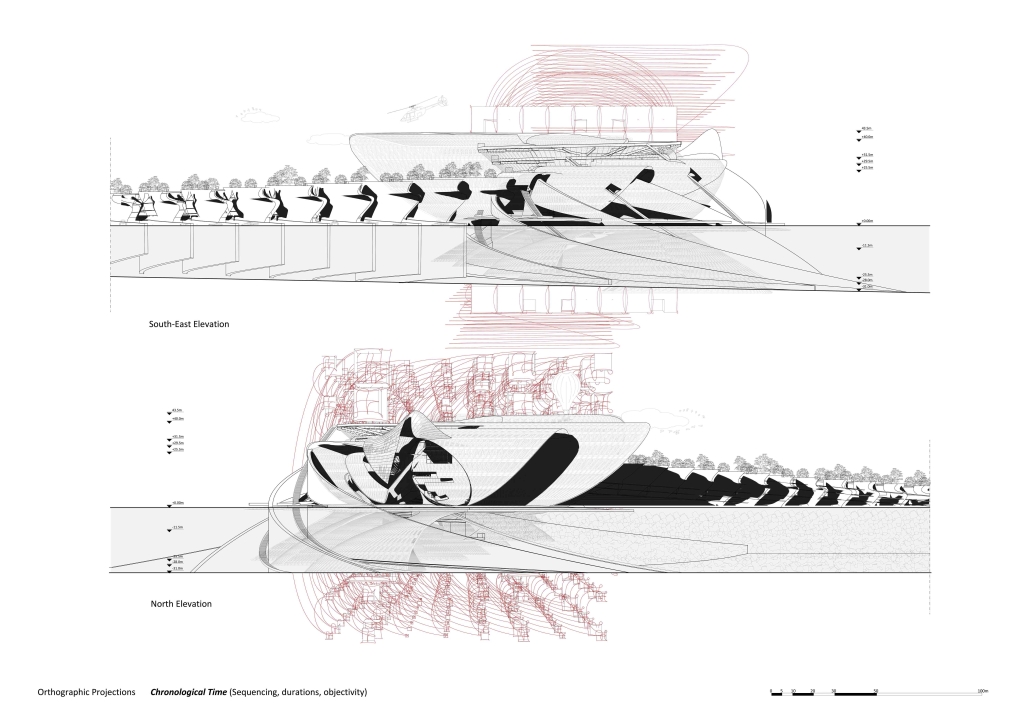
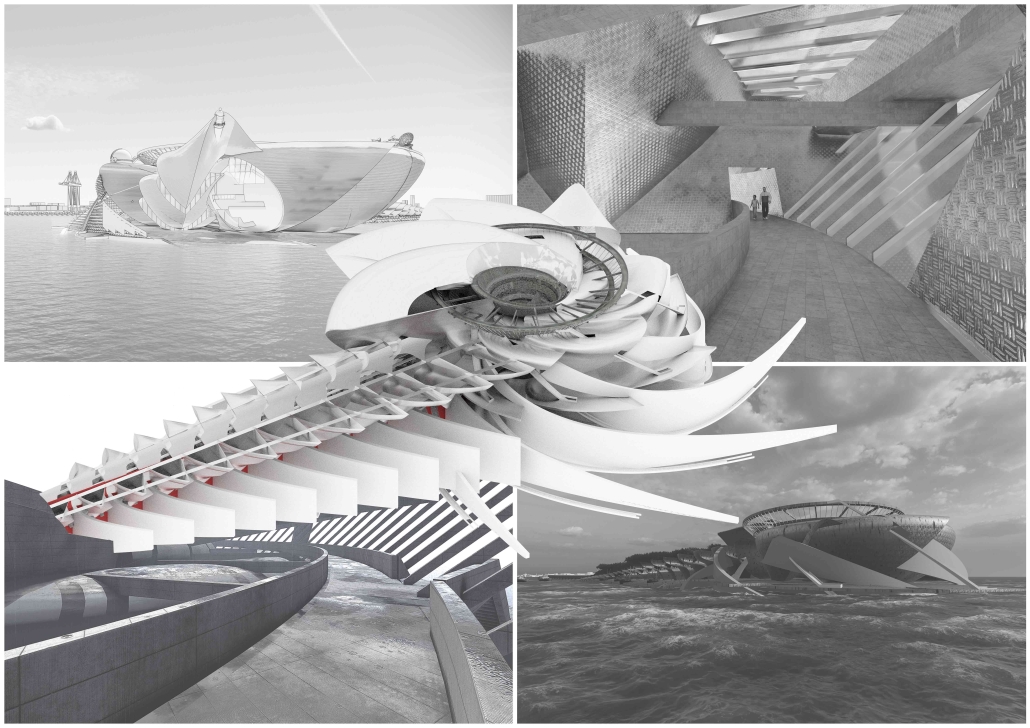
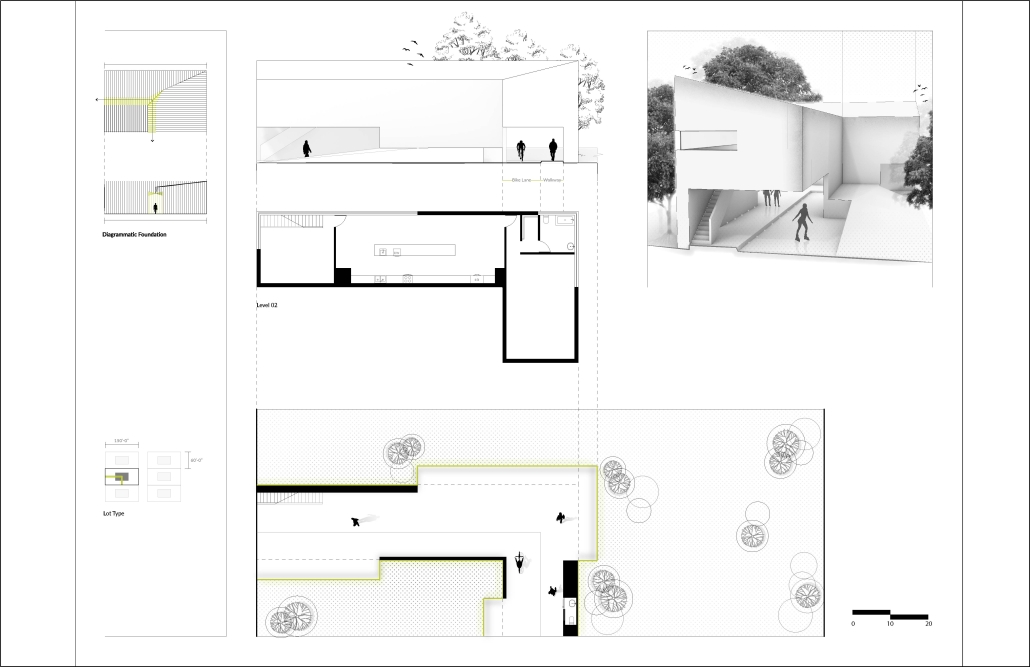
BARRA DA TIJUCA MARITIME TERMINAL by Justyn D. Grant, M.Arch ‘25
Florida A&M University | Advisors: George Epolito, Andrew Chin & Ronald B. Lumpkin
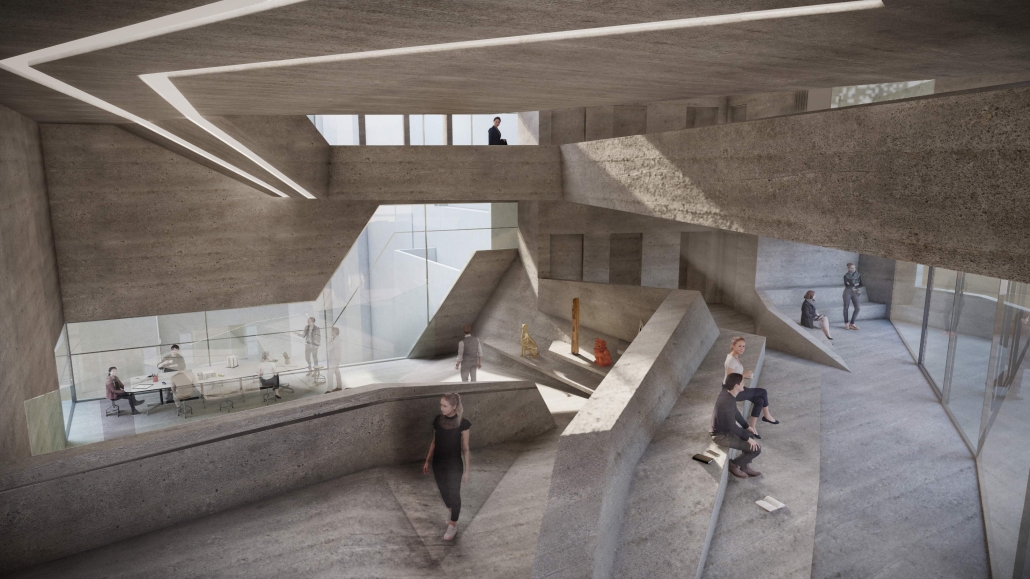
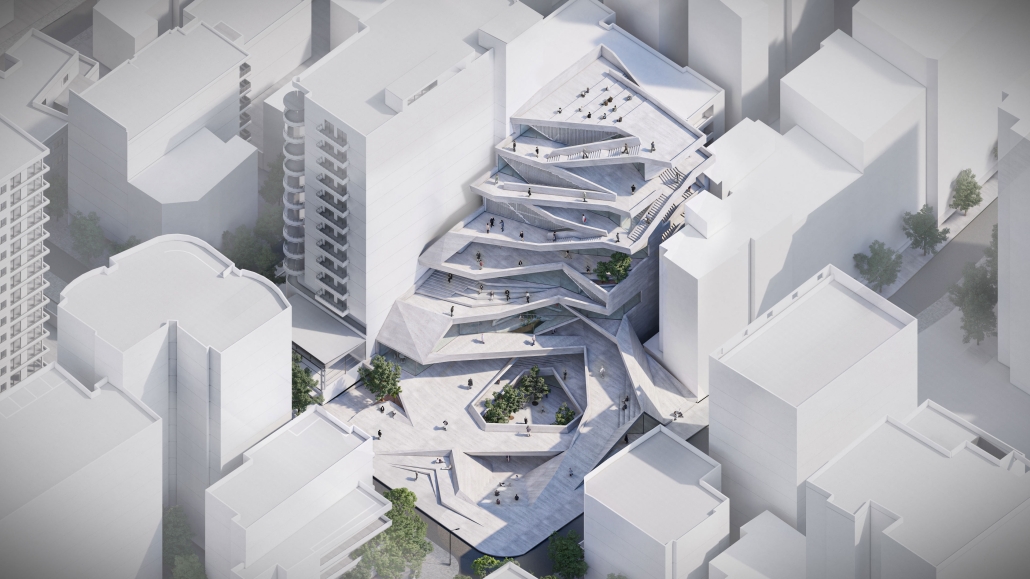
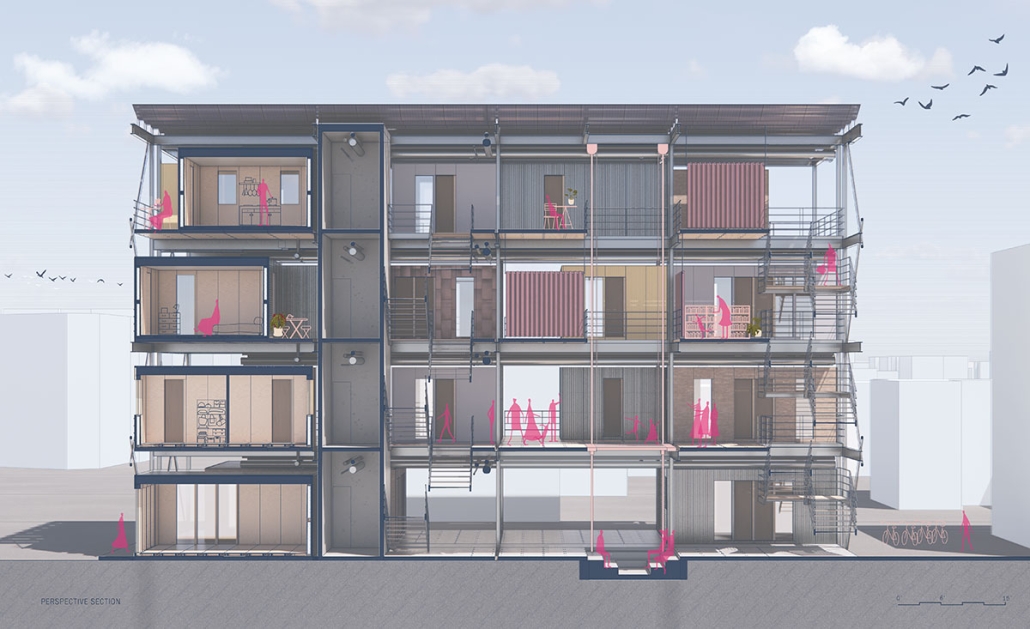
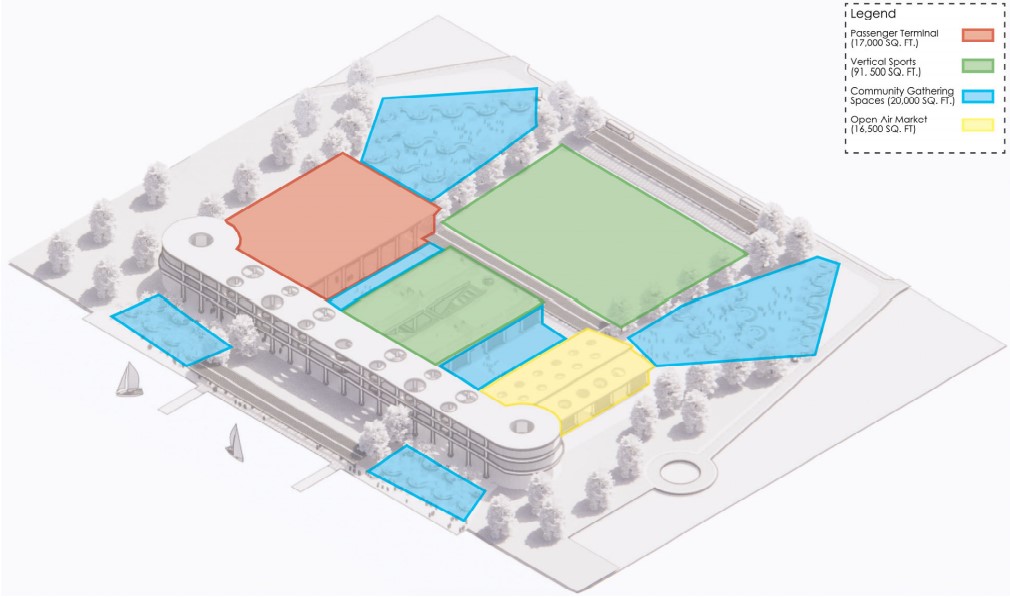
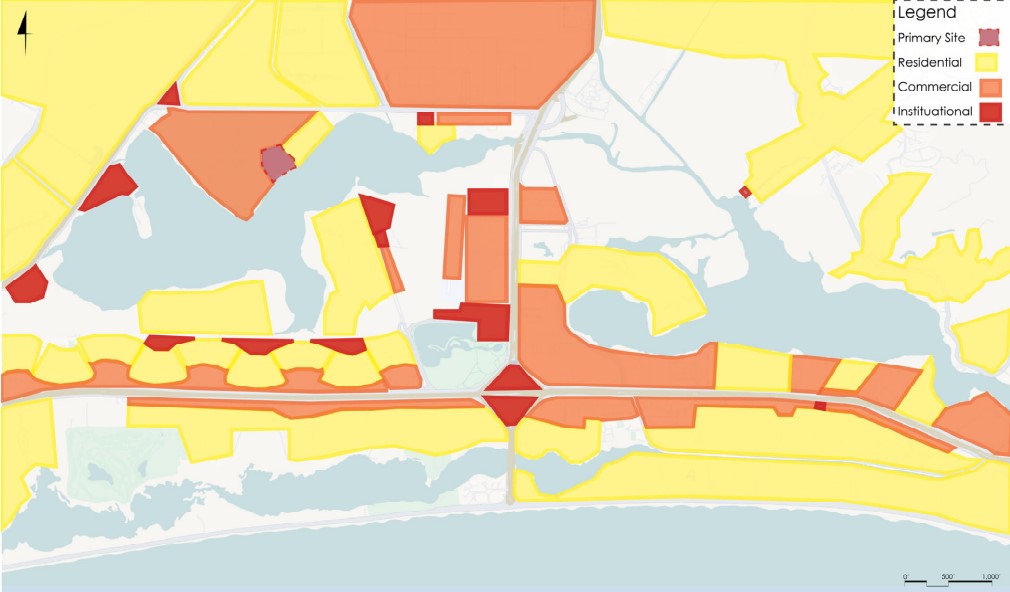
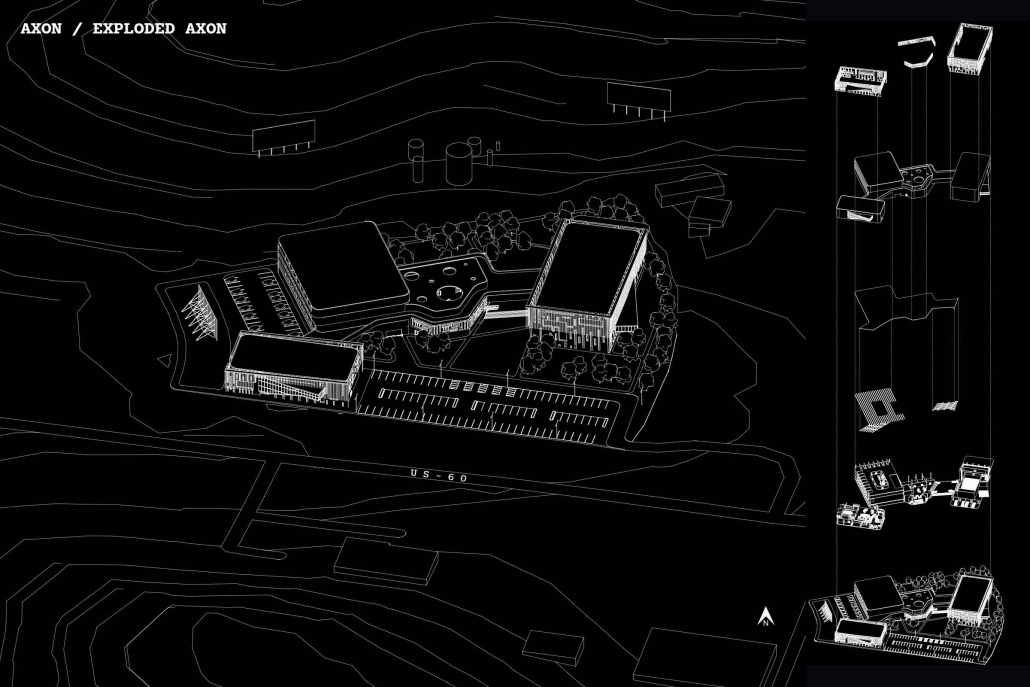
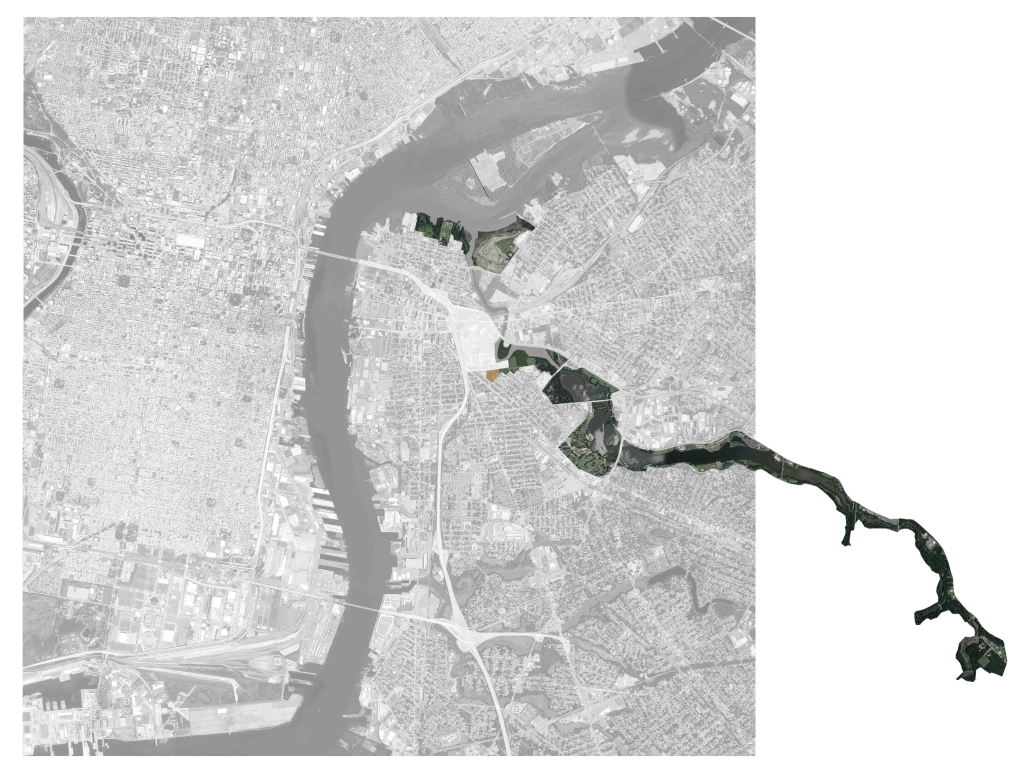
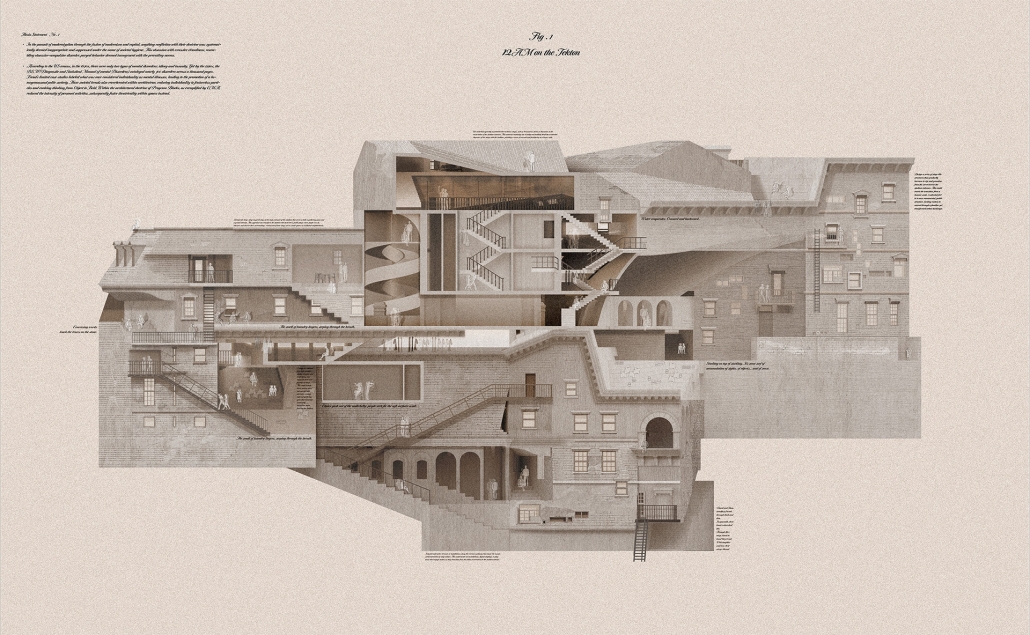
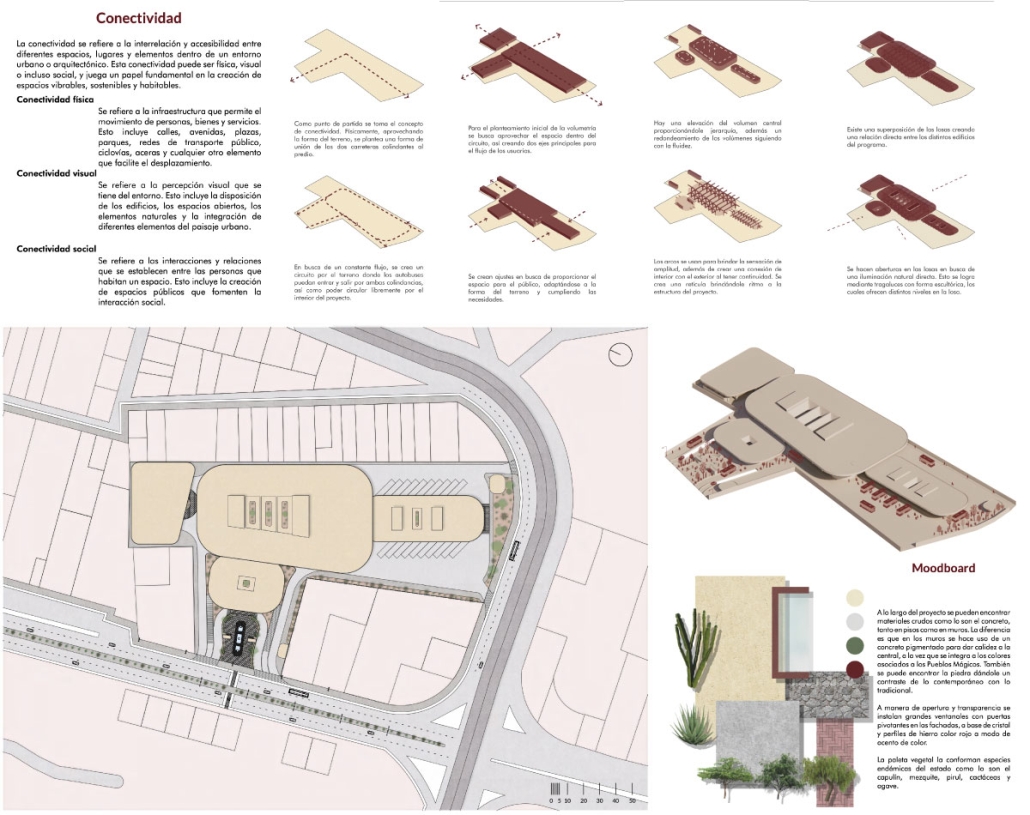
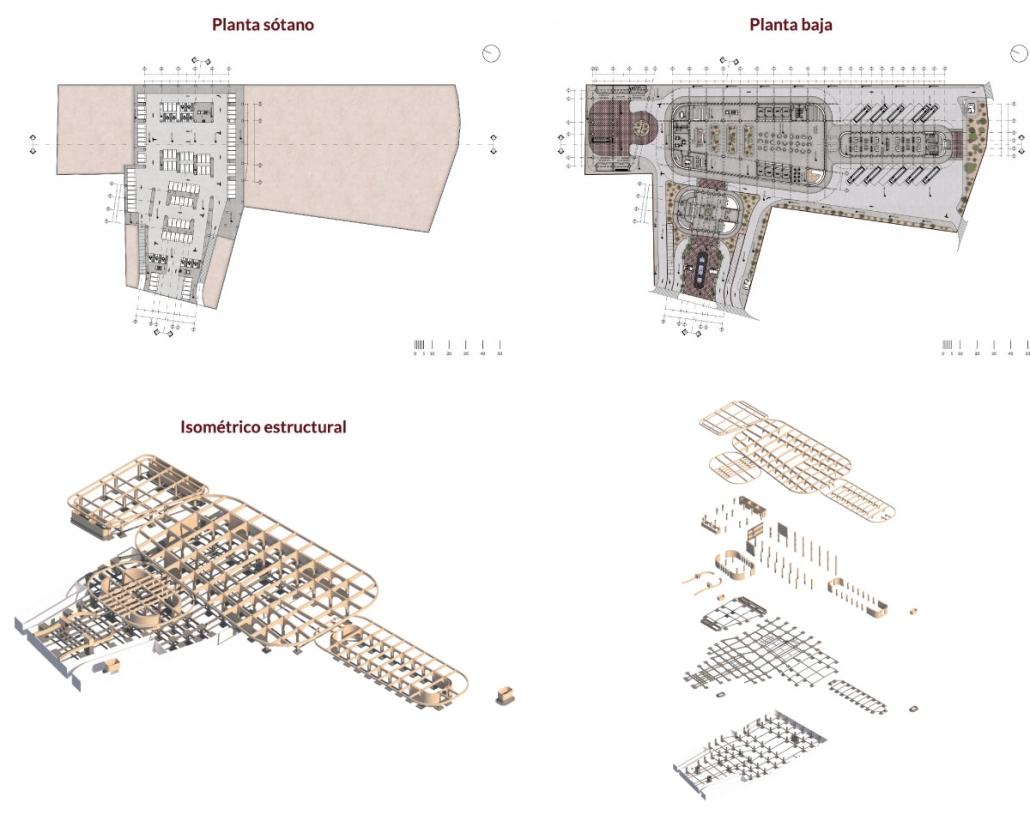
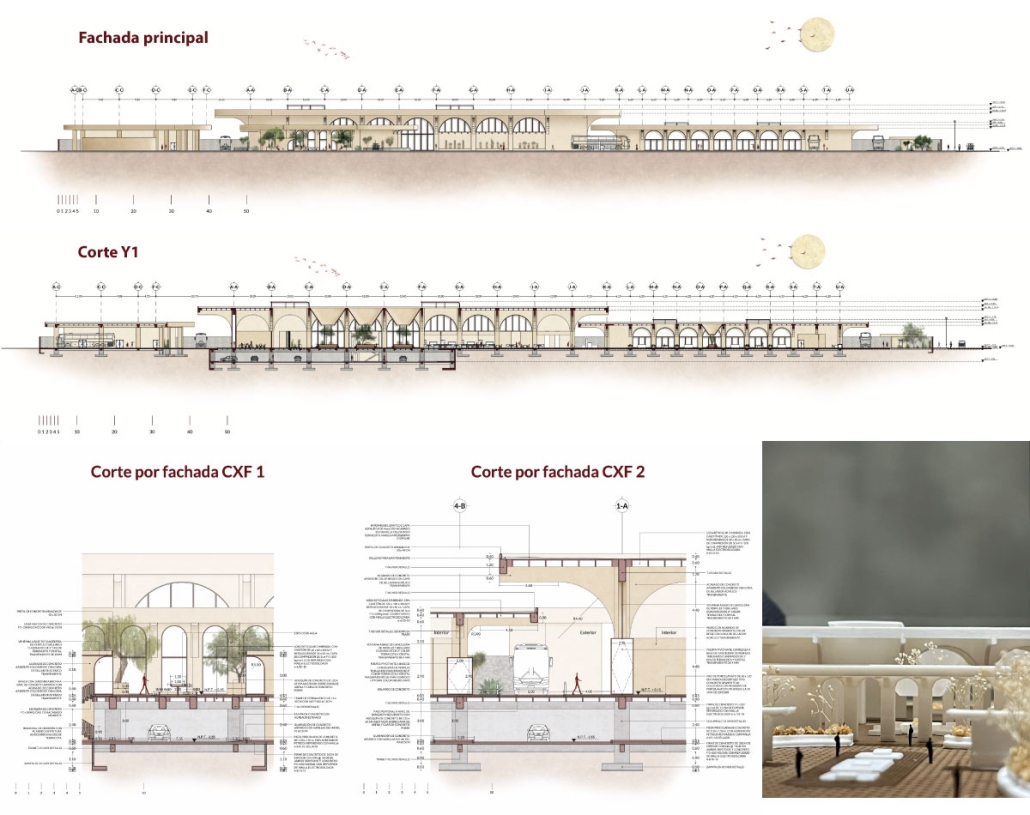
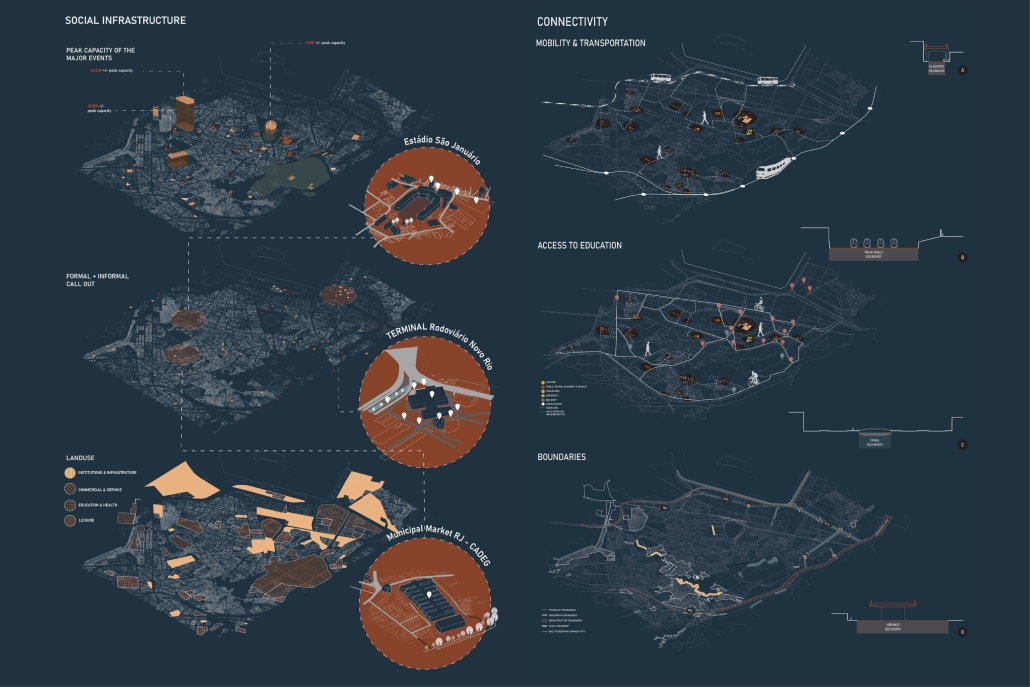
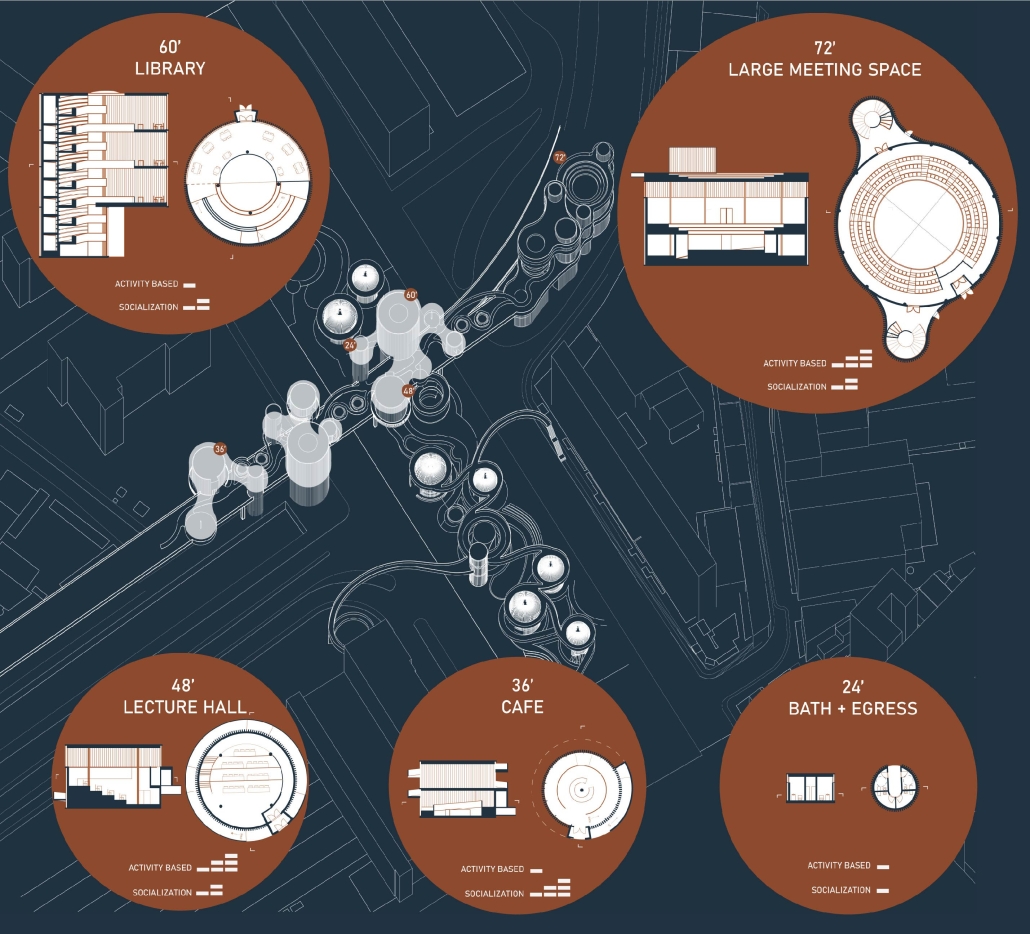
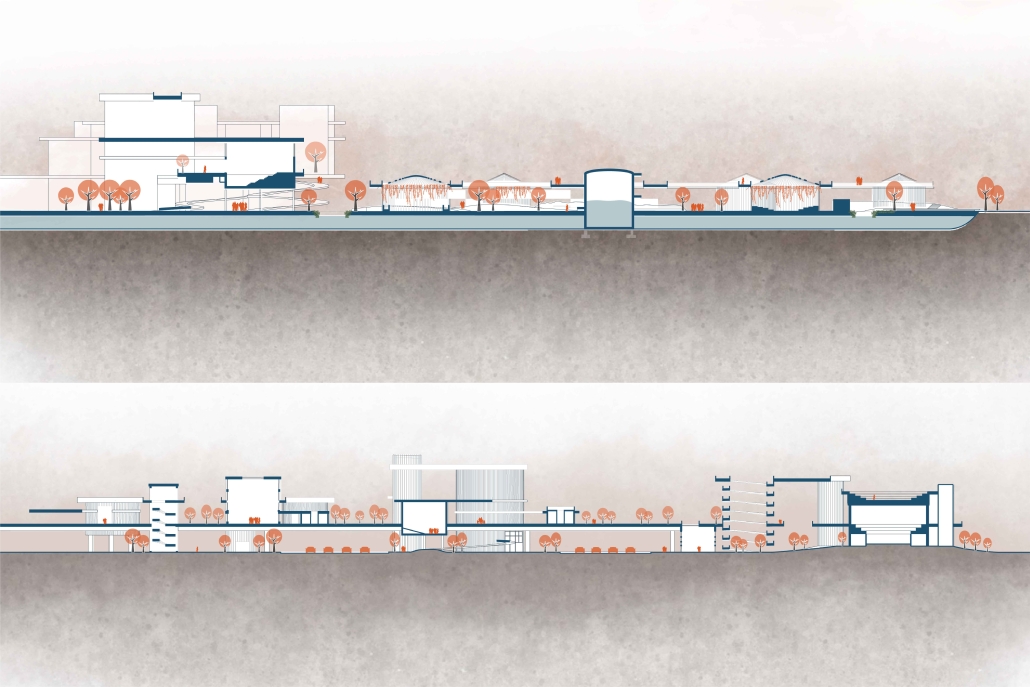
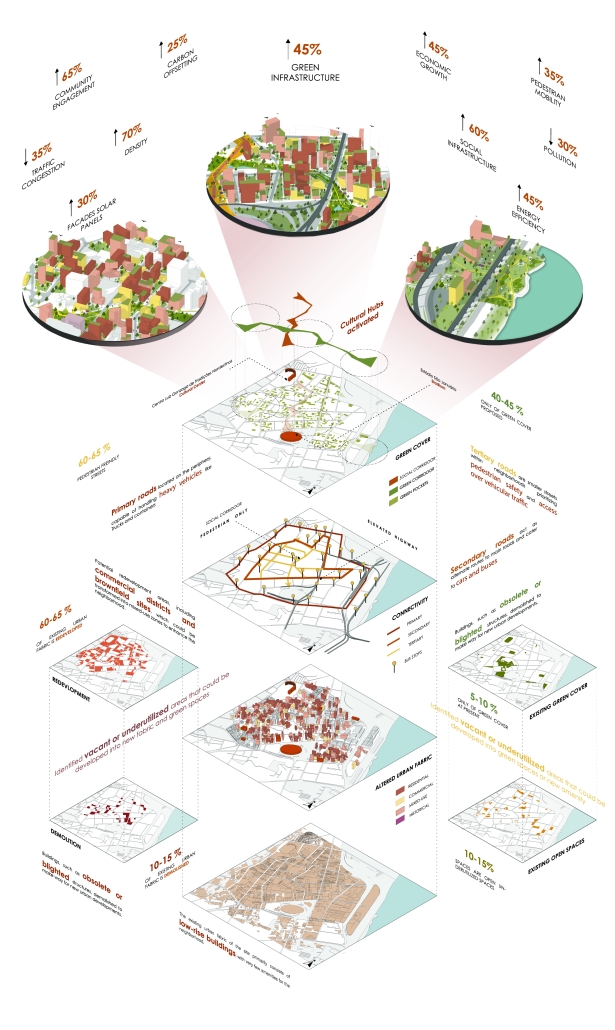
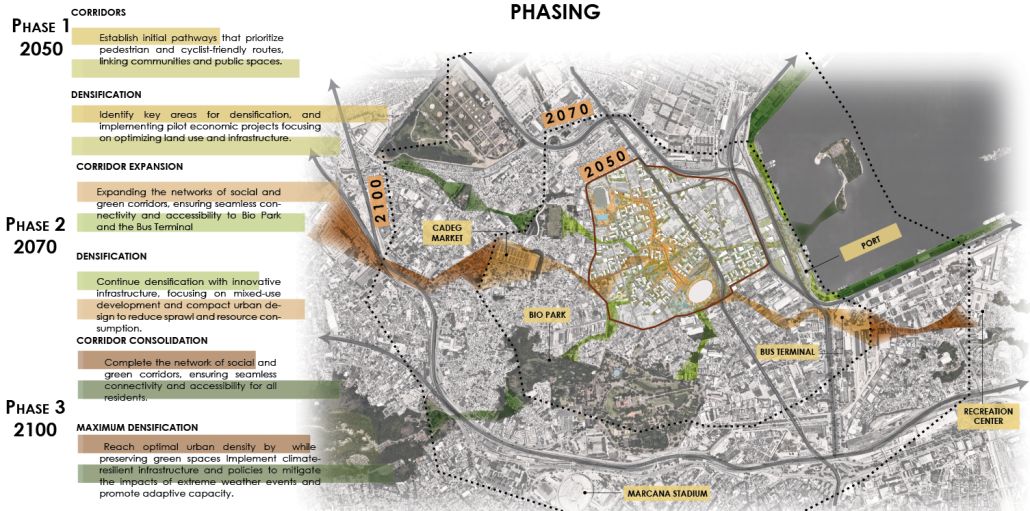
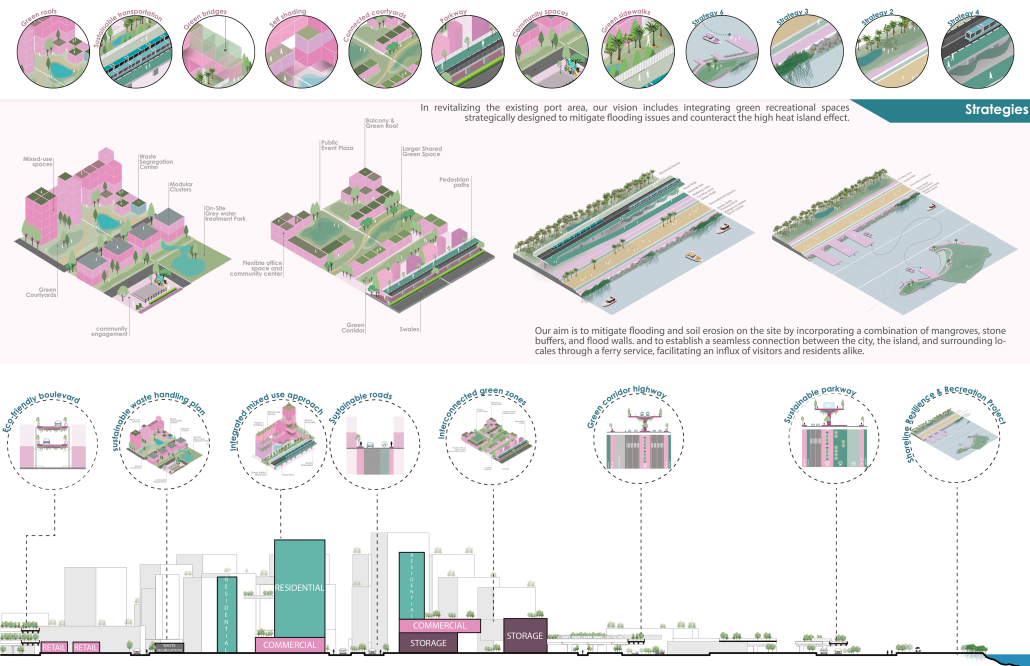
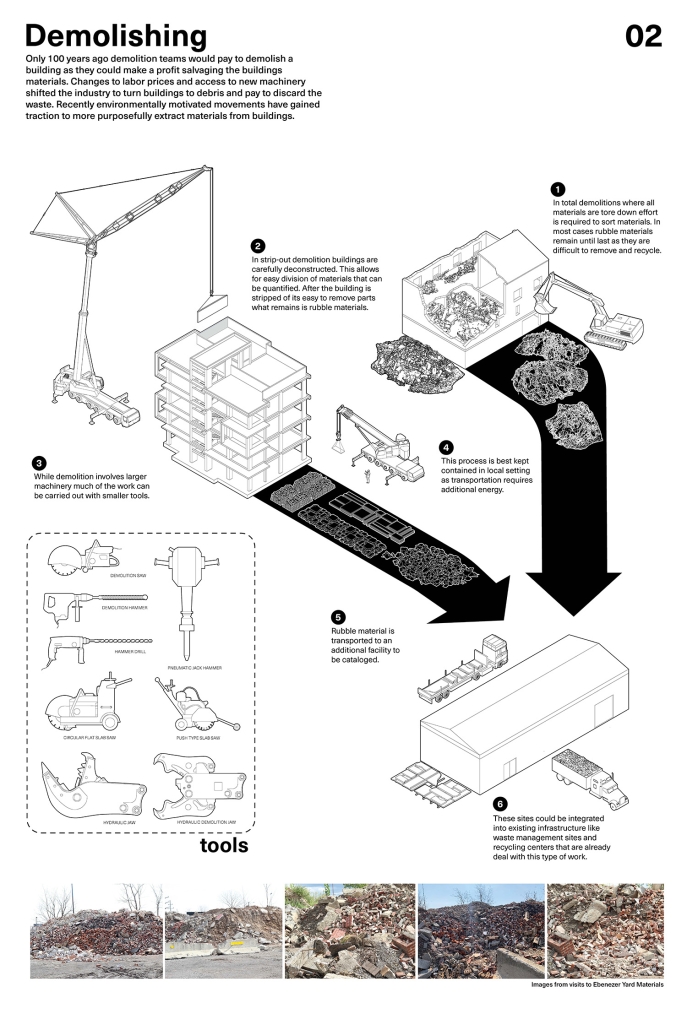
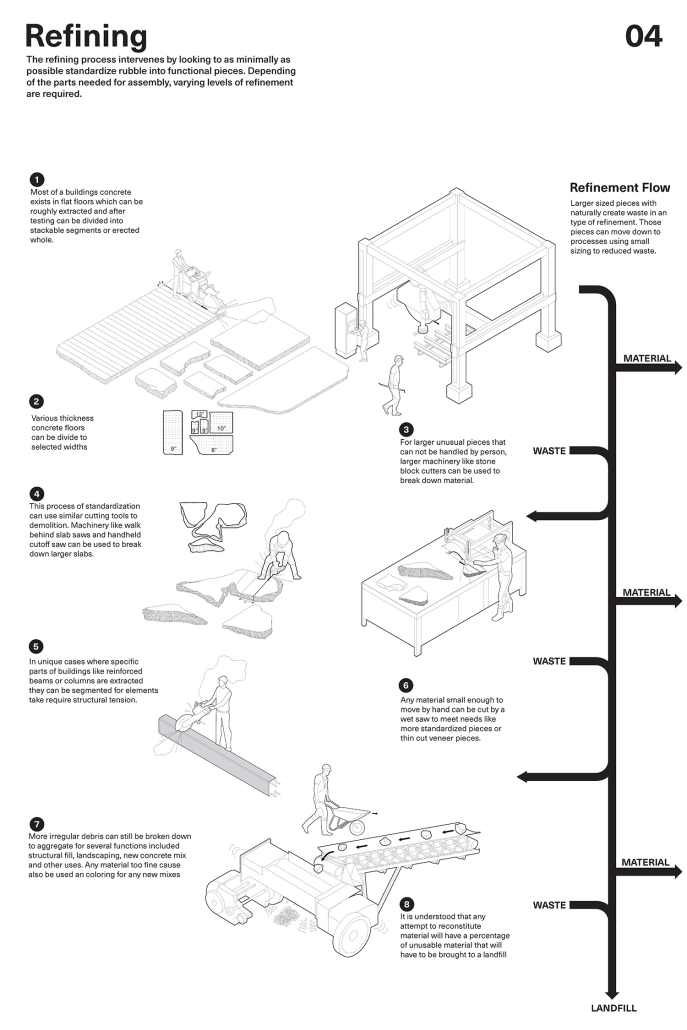
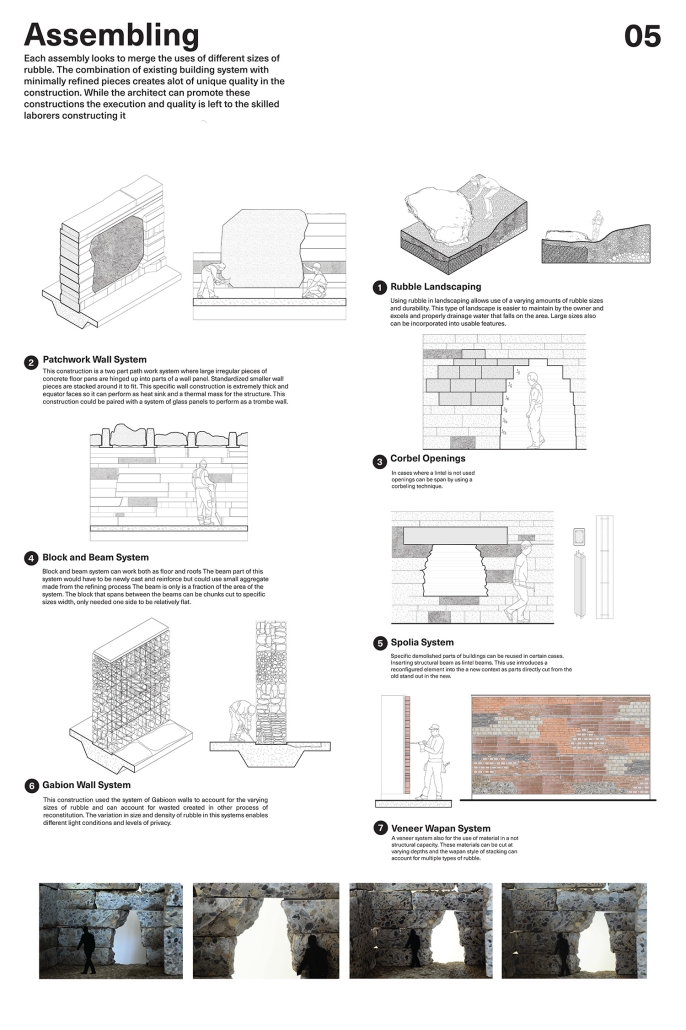
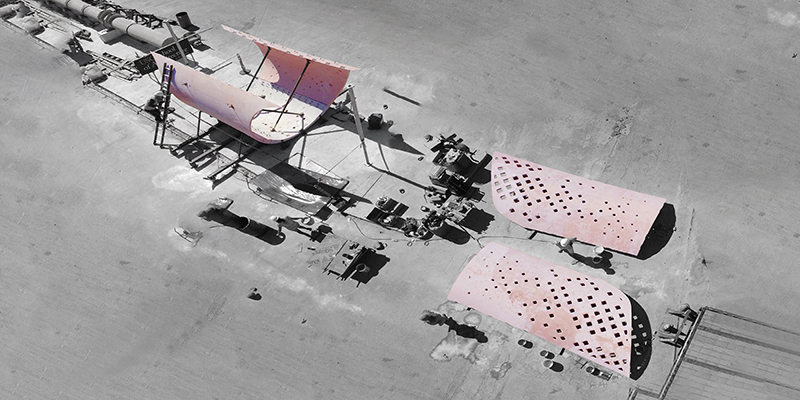
Barra da Tijuca Maritime Highway Terminal responds to a long-standing pattern of neglect toward disenfranchised communities impacted by large-scale global events like the Olympics. This thesis focuses on Rio das Pedras, a self-built favela in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, that, despite being in proximity to the 2016 Olympic sites, remains disconnected from the infrastructural and economic benefits promised during the event’s planning and execution.
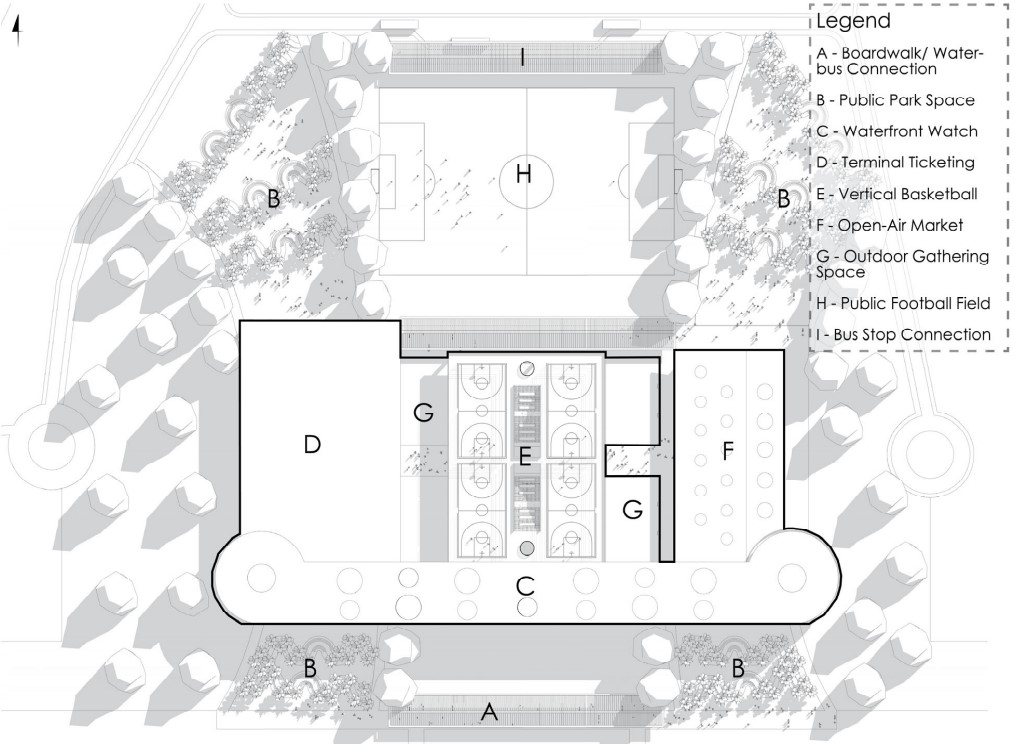
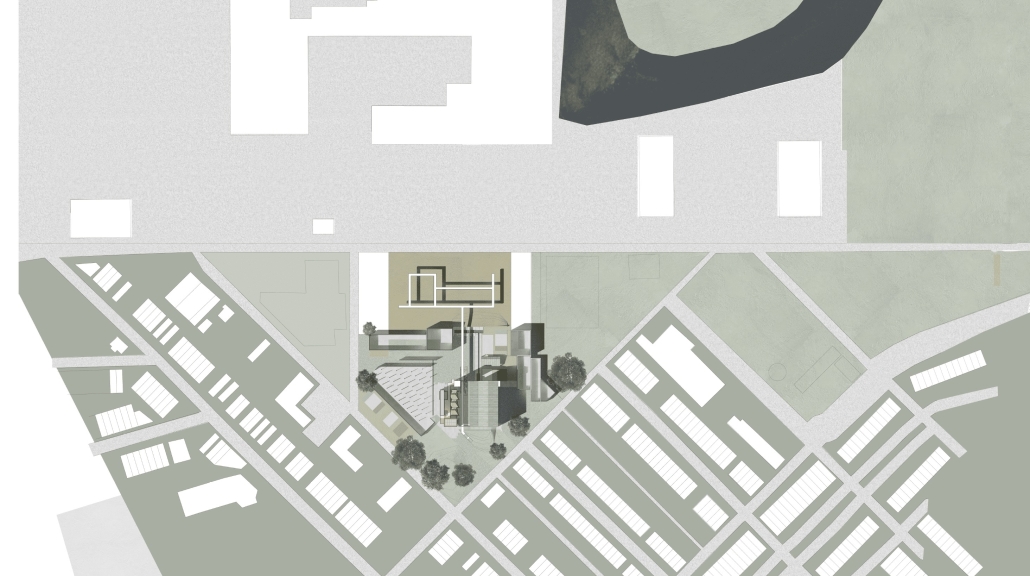
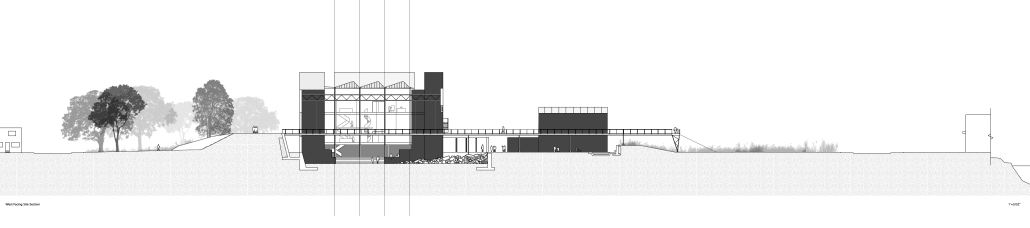
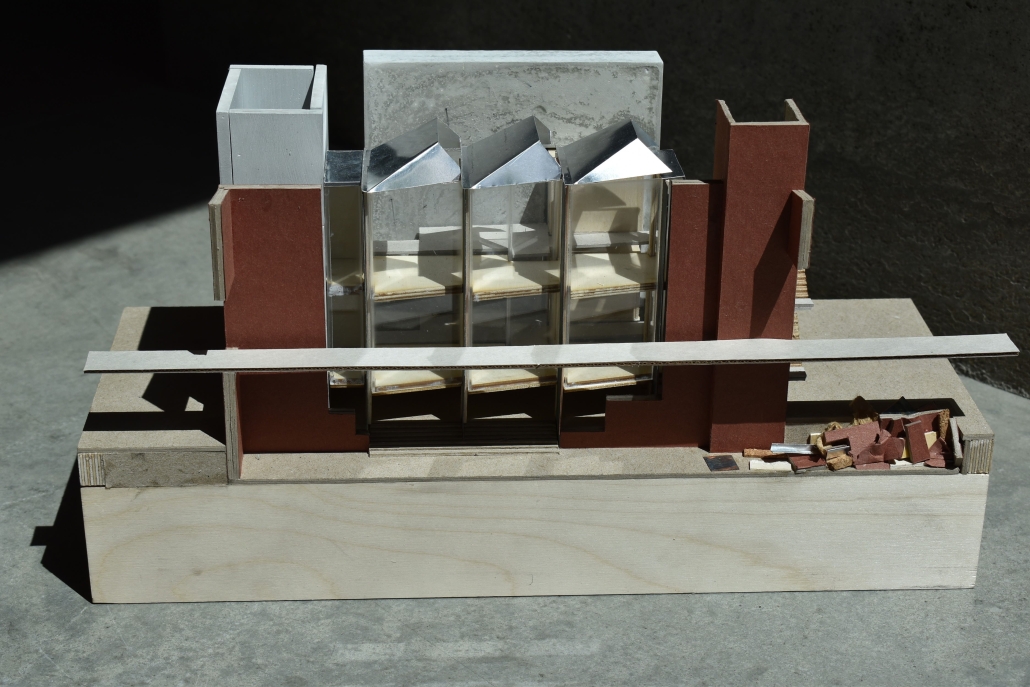
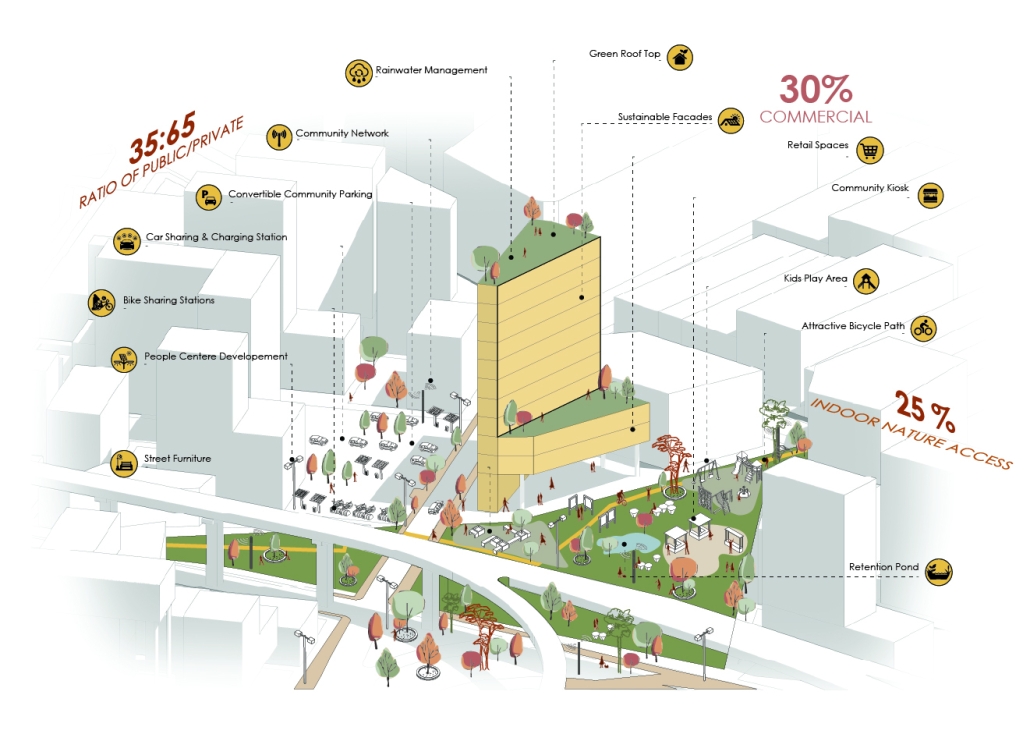
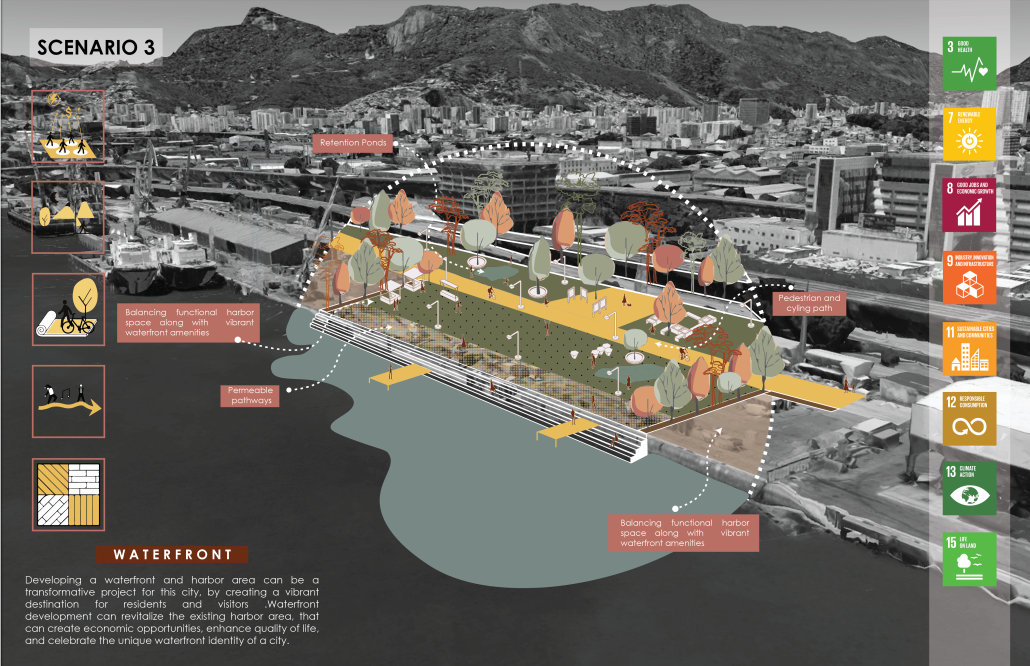
The project proposes a bold intervention: a maritime terminal located at Athlete’s Park that connects Rio das Pedras with the broader Barra da Tijuca area via the lagoon system. This “natural highway” avoids disruption within the favela while offering a culturally sensitive, environmentally harmonious transit solution. The terminal is envisioned as more than a transportation node—it will be a space for economic empowerment, community gathering, and cultural exchange, serving both residents and tourists.
Architecturally, the design draws from the spatial and material logic of Rio das Pedras to promote familiarity, dignity, and inclusivity. By integrating construction practices and vernacular forms found in the favela, the terminal becomes a home away from home—bridging class divides and reshaping perceptions of informal urbanism.
This thesis critiques the post-Olympic urban landscape and interrogates the broken promises of legacy investments. It reframes infrastructure as a tool for equity, proposing design strategies that center the needs and aspirations of historically marginalized communities. In doing so, it advocates for a model of development that honors cultural identity, fosters connection, and plants the seeds for long-term resilience and economic vitality.
Instagram: @famusaet, @famu_masterofarch
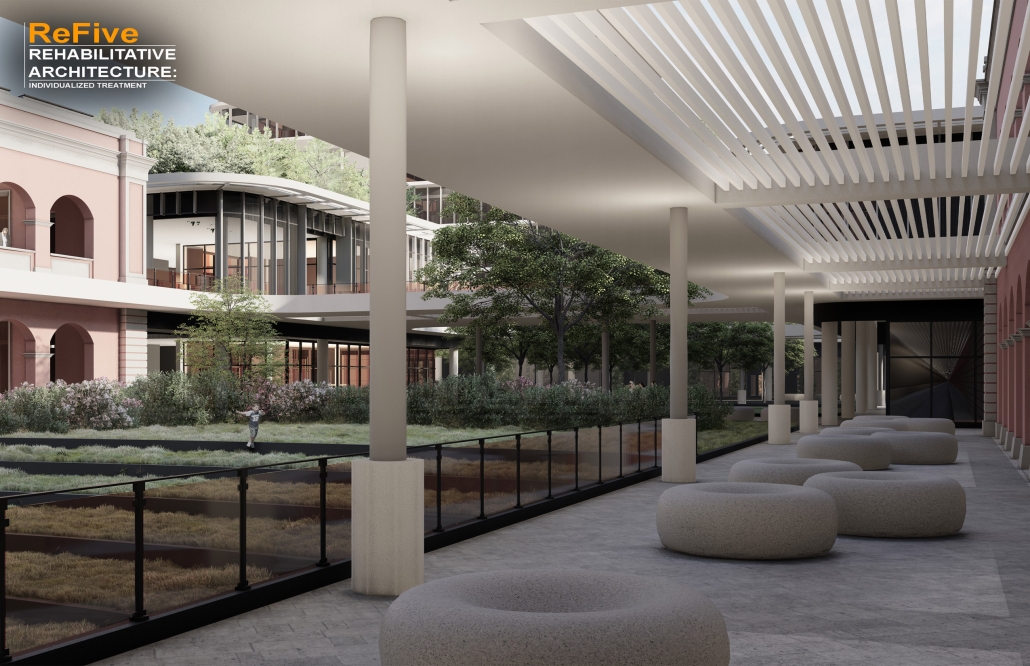
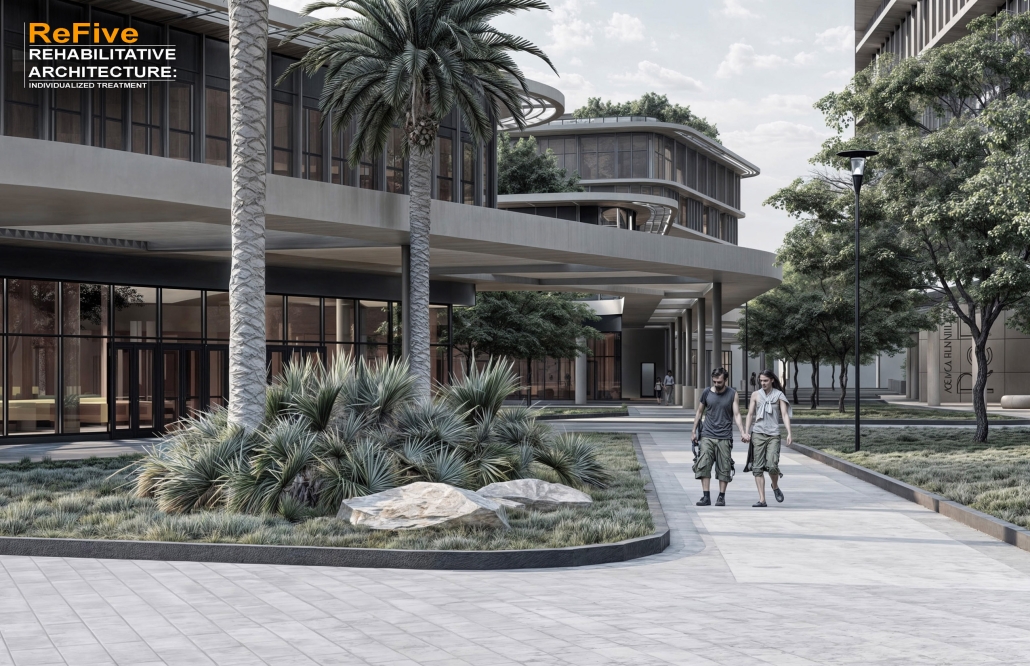
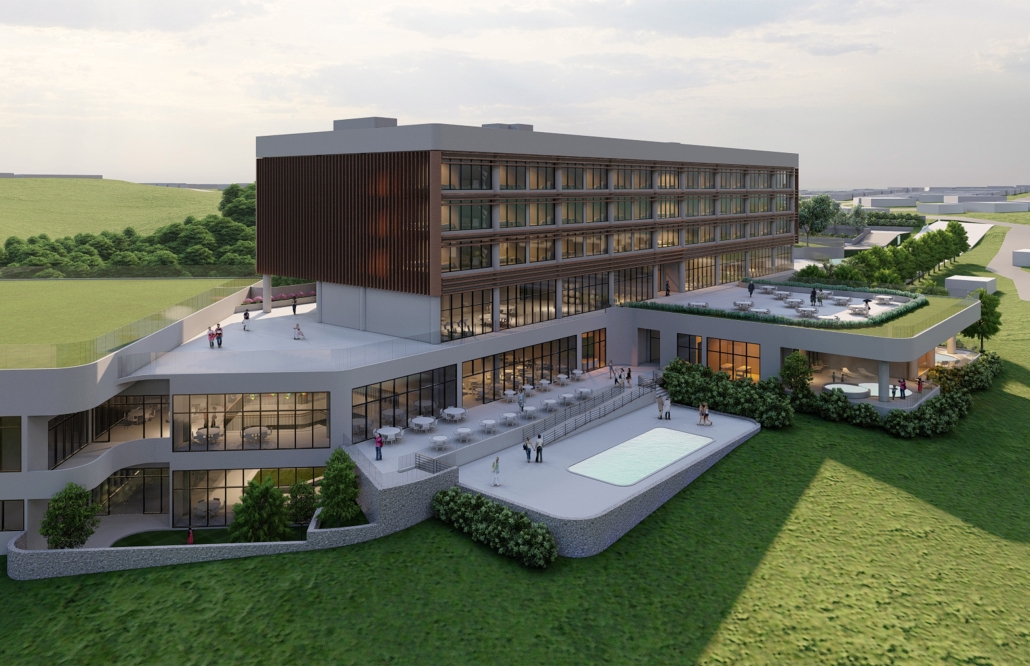
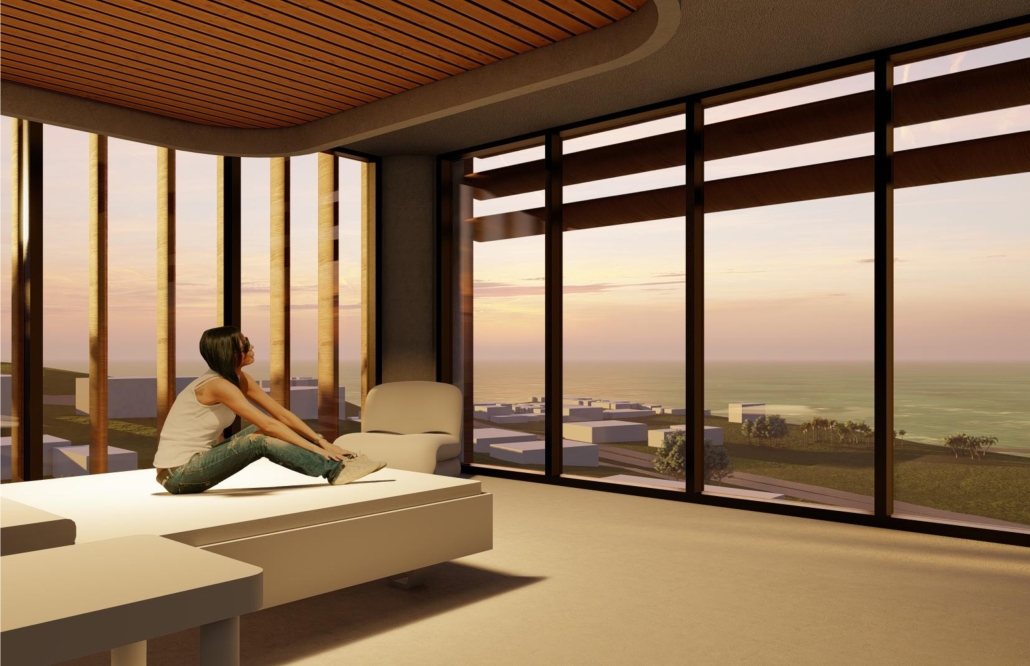
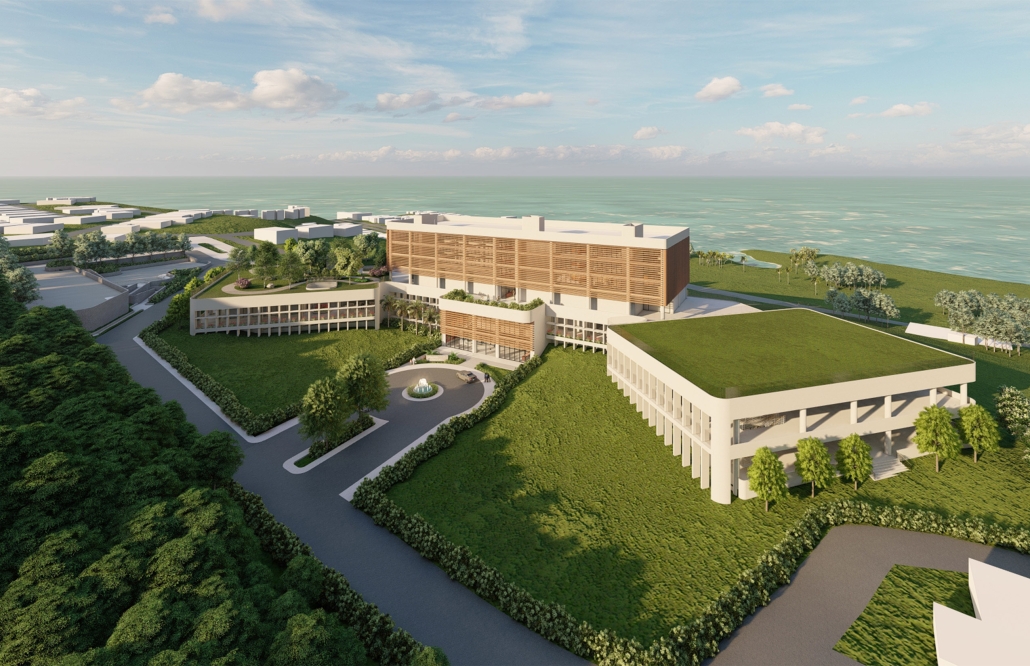
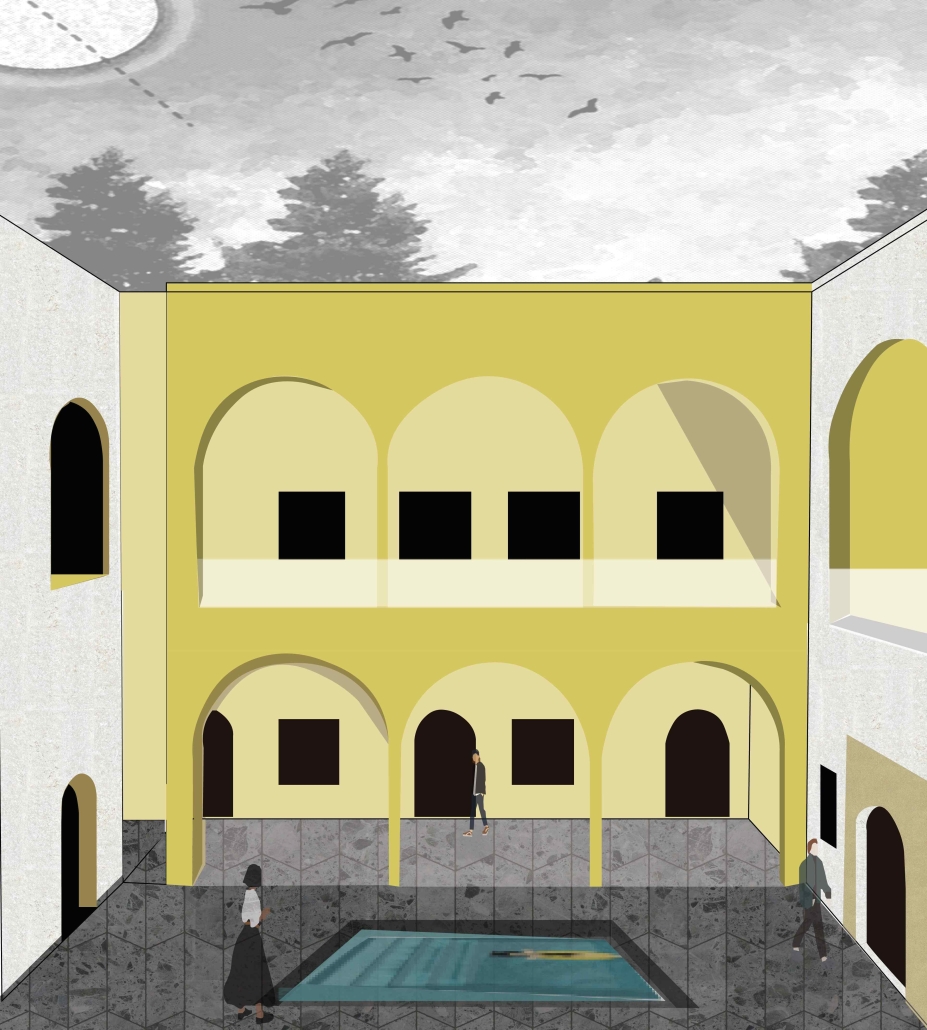
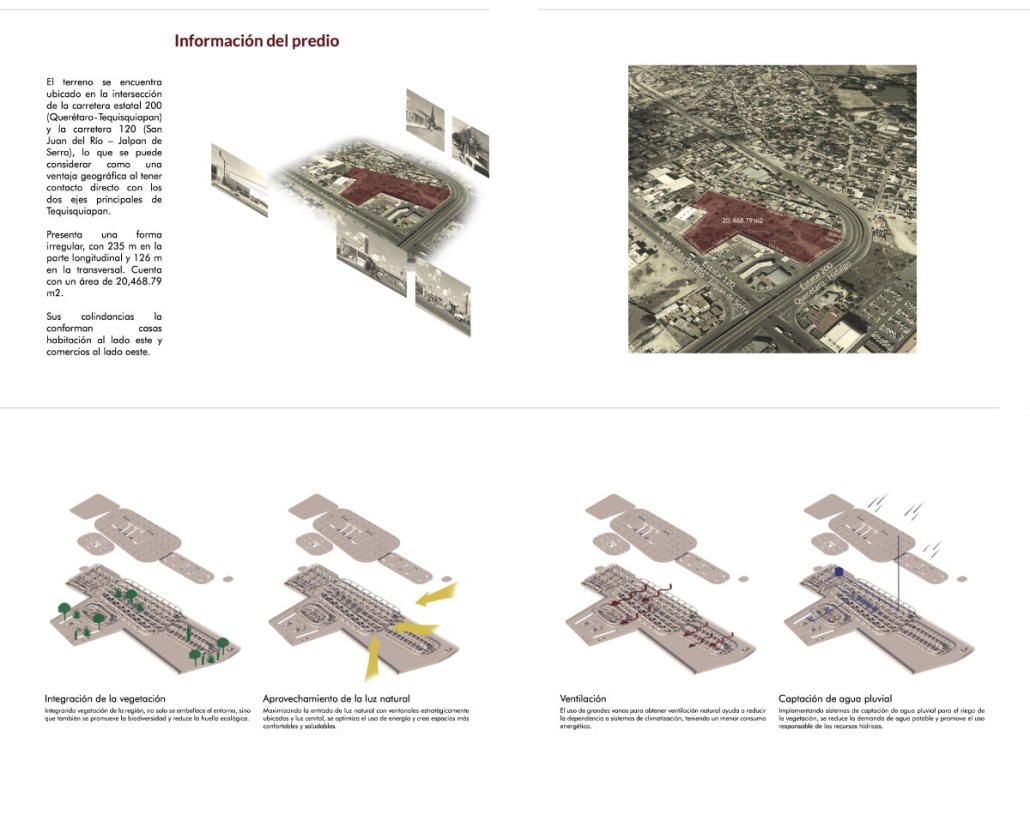
Centro Mariposa: The Refuge of Wings, Women’s Shelter, Querétaro by Leslie Bocanegra Valdivia, B.Arch ’25
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Guillermo Márquez, Patricia Cutiño & Jorge Javier
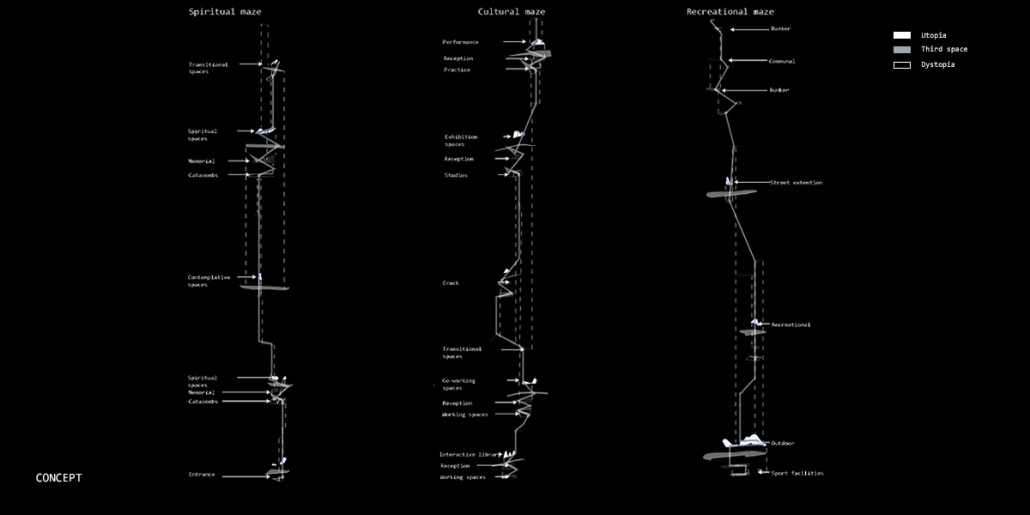
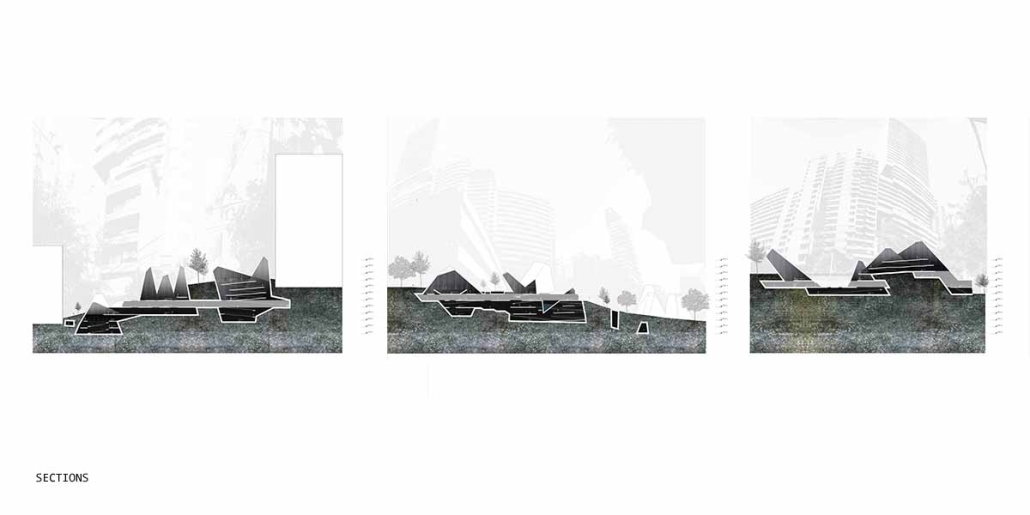
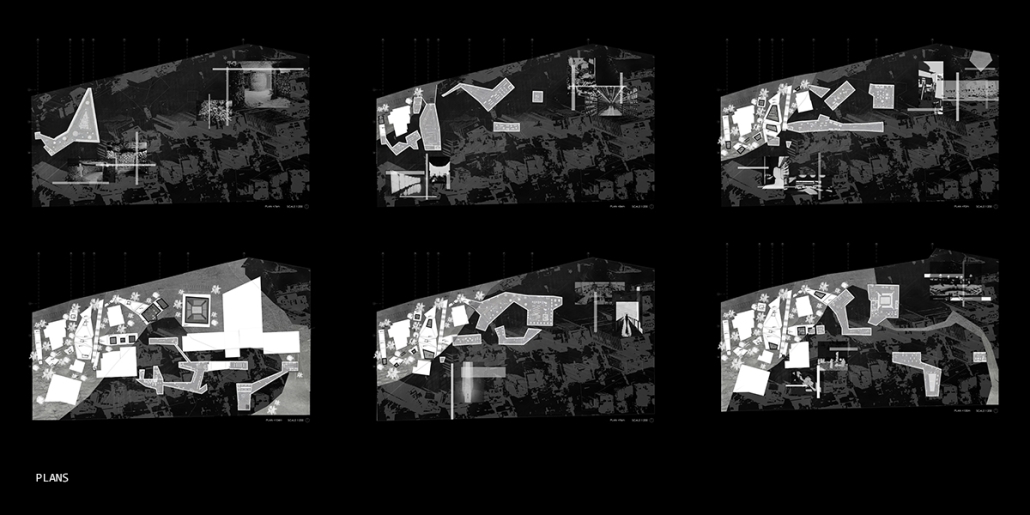
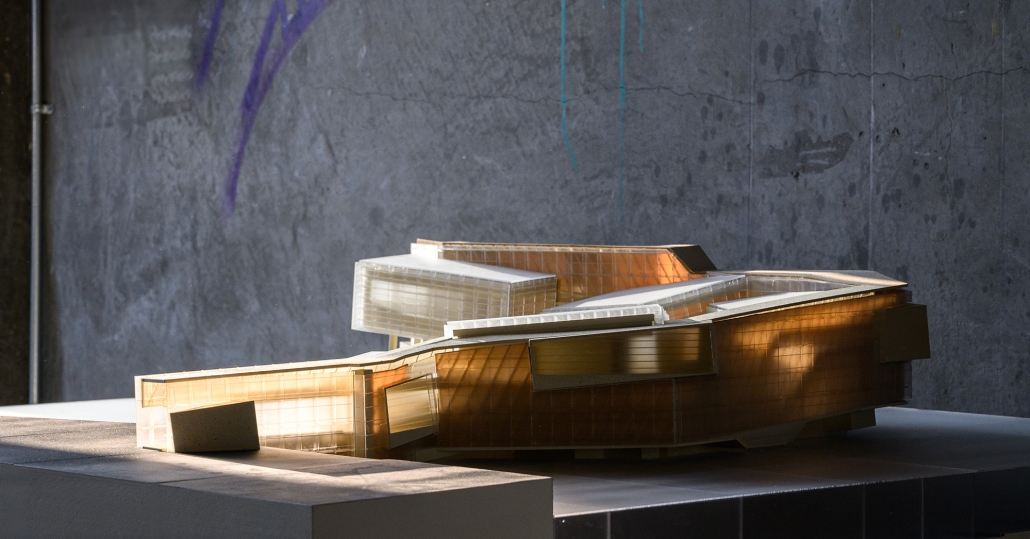
At the heart of the indigenous neighborhood of San Francisquito, Querétaro — a city affected by gender violence and inequality — [is] CENTRO MARIPOSA, inspired by the butterfly’s journey of rebirth, emerges as an architectural space for transformation. In response to the lack of safe spaces for women, the project offers more than refuge; it provides a place to heal, rebuild identity, and begin anew, surrounded by physical, symbolic, and collective protection.
A pavilion marks the entrance — a civic gesture that transforms a neglected corner into a new community anchor. More than a threshold, this space invites gathering and recreation, intervened with messages of resistance. It is here — where the intimate and the public intertwine — that the transition from pain to rebirth begins.
The proposal integrates a network of spaces that respond to women’s needs: medical, legal, psychological, and physical support combine with workshops on crafts, art, recreation, connection, entrepreneurship, and empowerment — all within an atmosphere of mutual care and healing. A temporary shelter area offers safety, professional support, and dignity to those in urgent need, the architecture draws inspiration from metamorphosis: Organic paths, contemplative patios, and warm materials create a nurturing environment. Every architectural gesture is an act of care. The design respects the neighborhood’s heritage and connects with the land and its people.
The impact of CENTRO MARIPOSA extends beyond its walls. It seeks to heal a community, rekindle hope in forgotten spaces, and offer Querétaro a model of architecture grounded in social justice and gender equality.
Like a butterfly, each woman who finds strength here takes flight — lighting the way for others to rise, transform, and soar.
Instagram: @leslie_bocanegra, @bocle.architecture, @arquitectura_anahuac, @arqwave
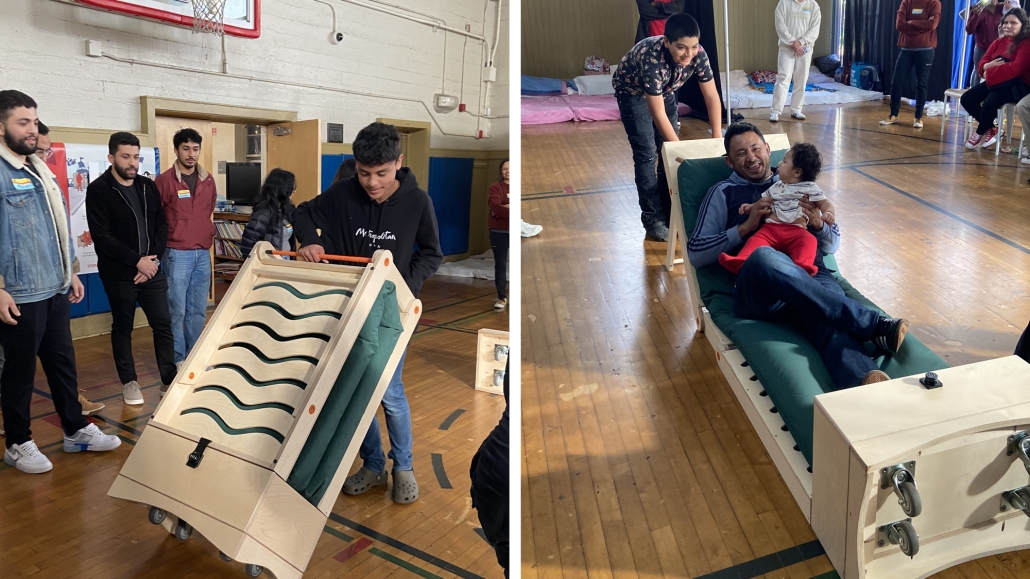
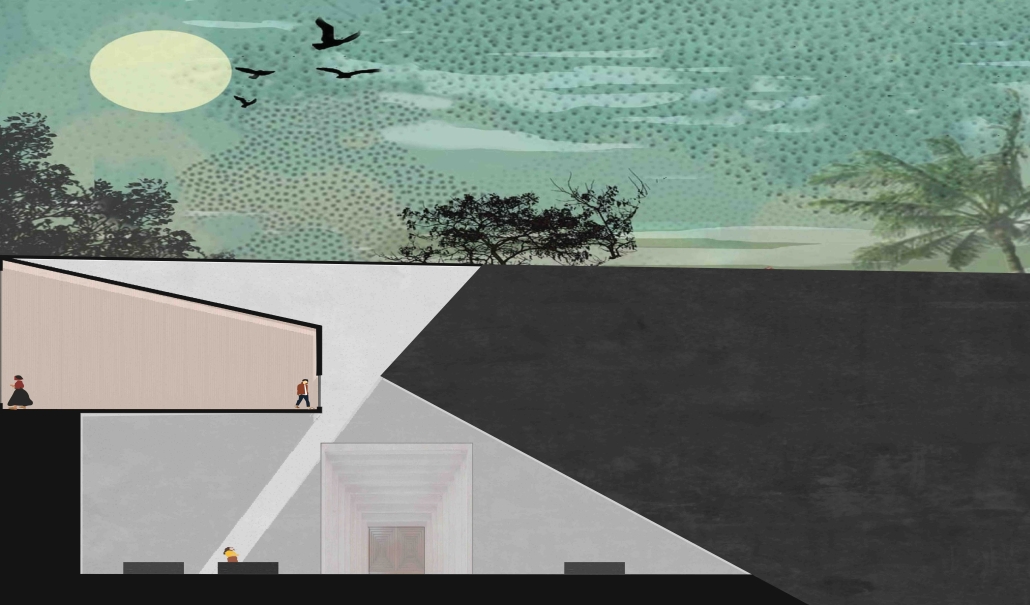
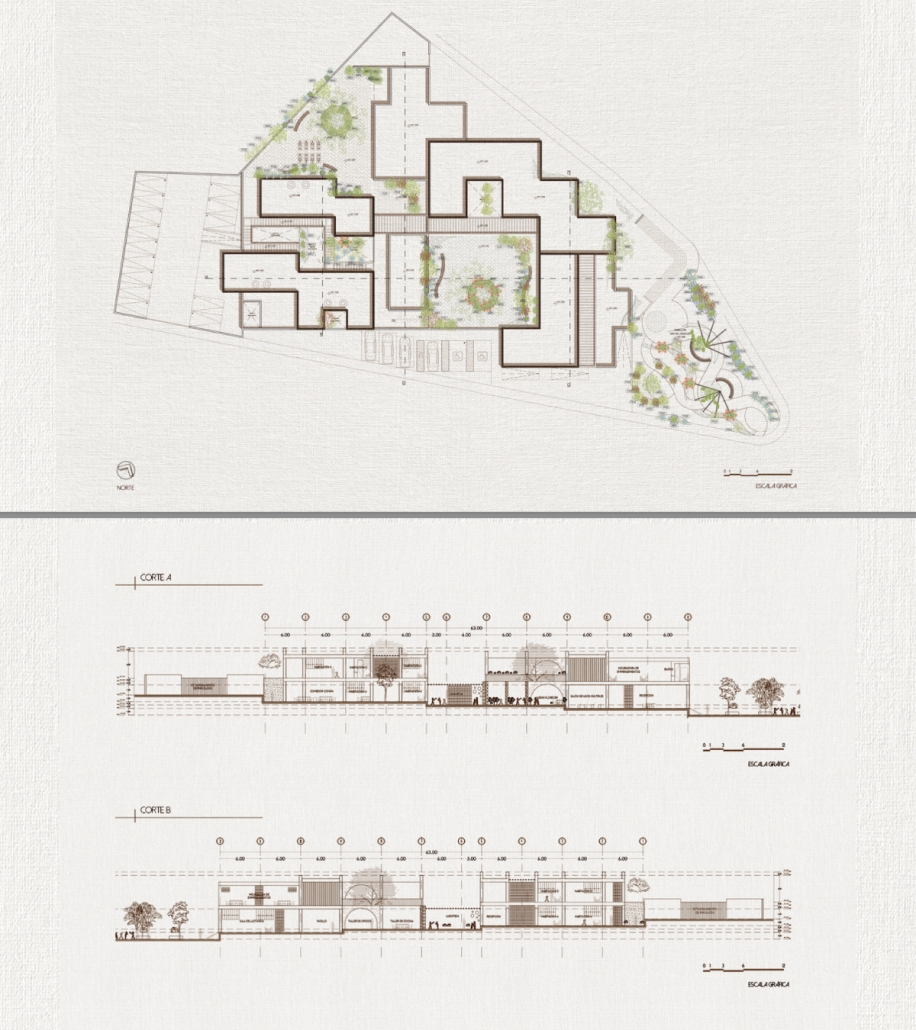
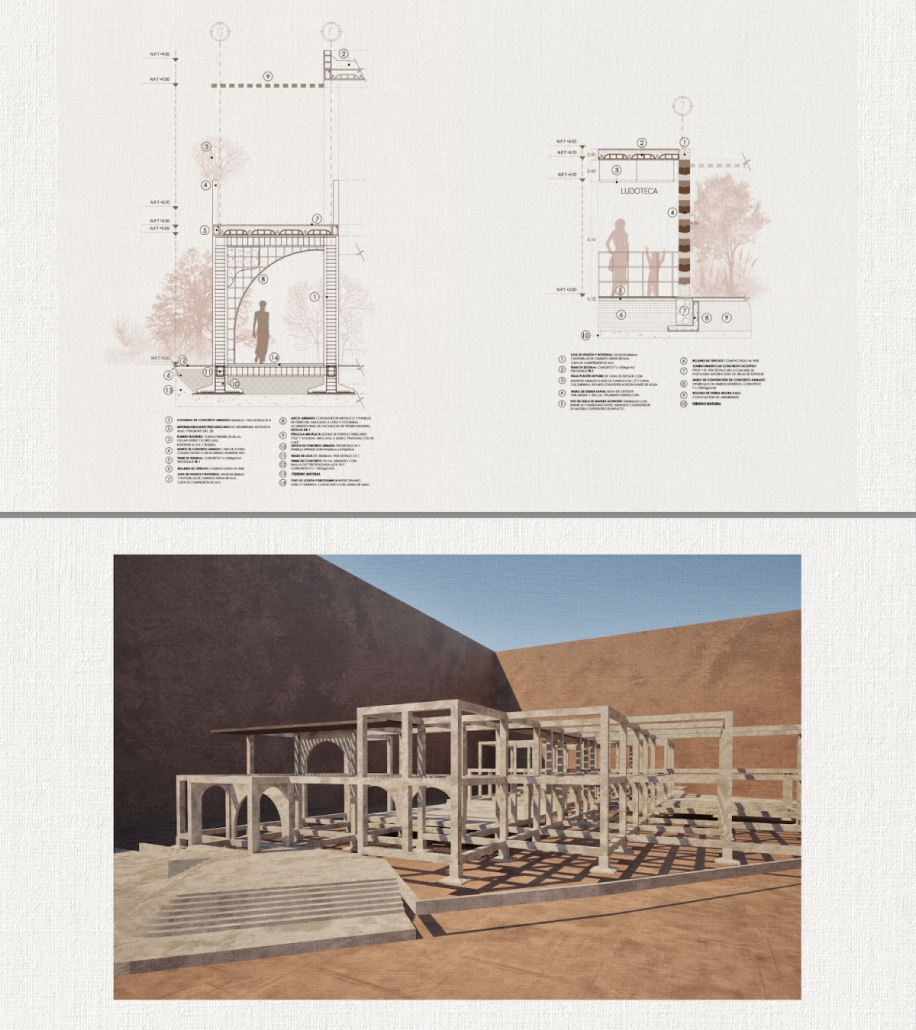
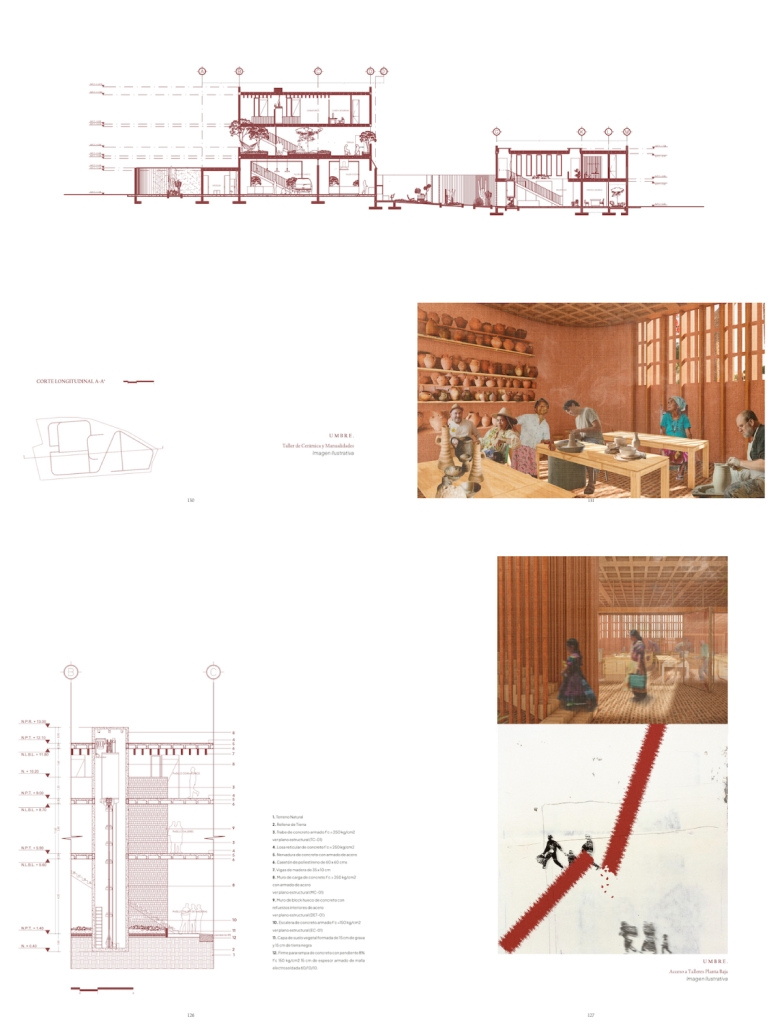
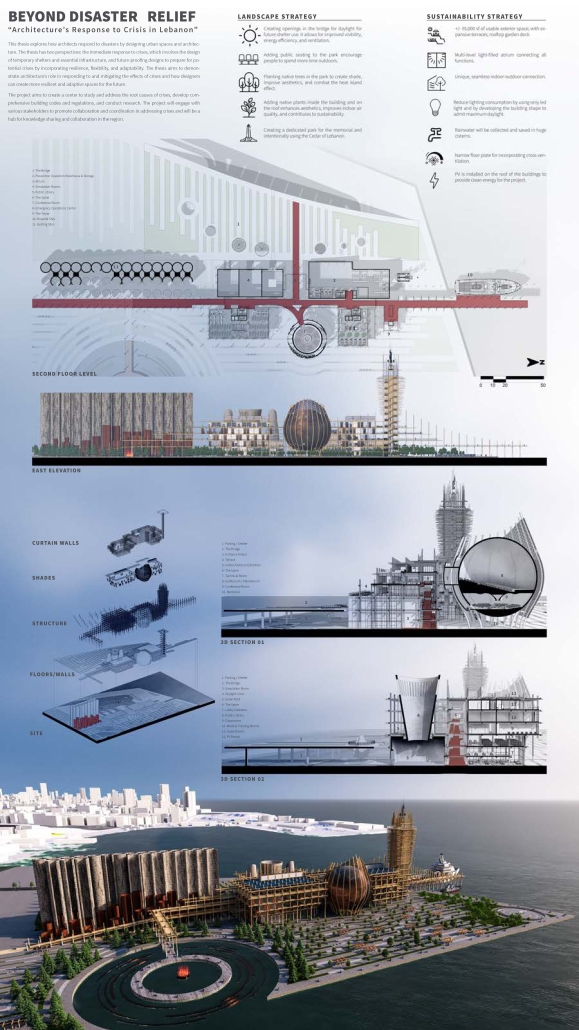
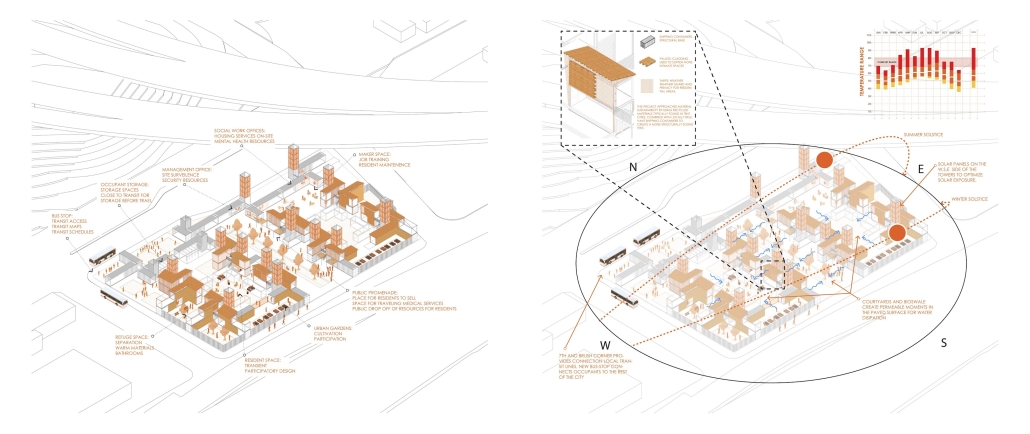
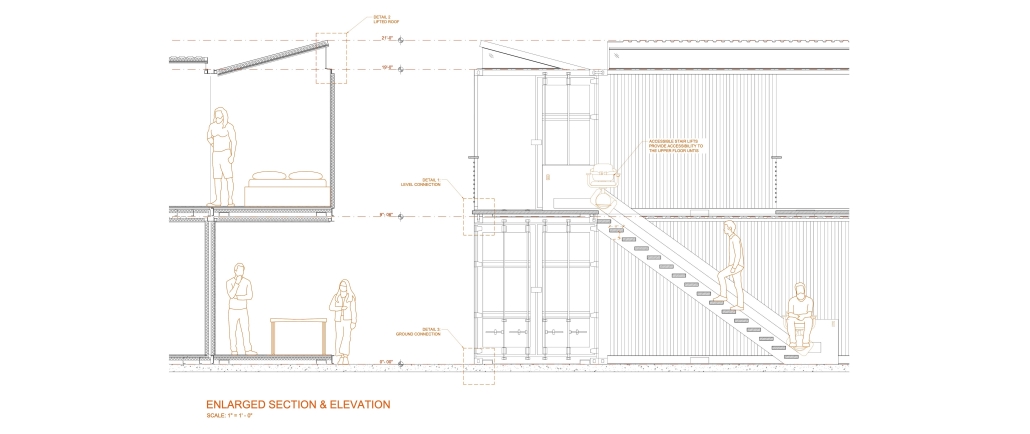
UMBRE Comprehensive Aid Center for Migrants by Natalia Pérez Pereyra, B.Arch ’25
Universidad Anáhuac Querétaro | Advisors: Guillermo Márquez, Patricia Cutiño & Jorge Javier
The project offers a temporary stay of up to six months, intended as a preparation and support period so that people on the move can decide their next step: settling in Querétaro or continuing their journey. During this time, workshops, talks, and training sessions are held focused on their labor and social integration. In addition, the center provides outpatient services for those not temporarily housed there. This includes food, sanitation, medical and psychological care, legal assistance and support, training workshops in various sectors, and support in finding employment.
These services do not have a strict time limit, allowing them to be adapted to the migrants’ different trajectories and needs. In coordination with volunteers and specialists, support is also offered in finding housing and managing legal documentation, such as a humanitarian visa, which can be completed in approximately 20 days. The goal is to offer a safe, dignified, and connected environment to the city, strengthening users’ autonomy and integrating them into the social fabric of Querétaro.
Instagram: @nataliaprzp, @perezparch, @arquitectura_anahuac, @arqwave
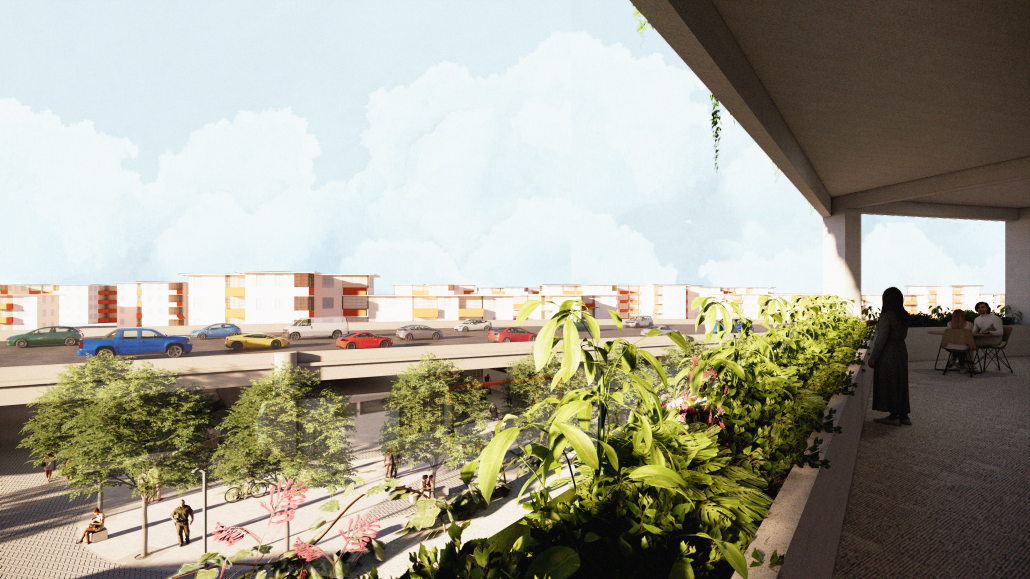
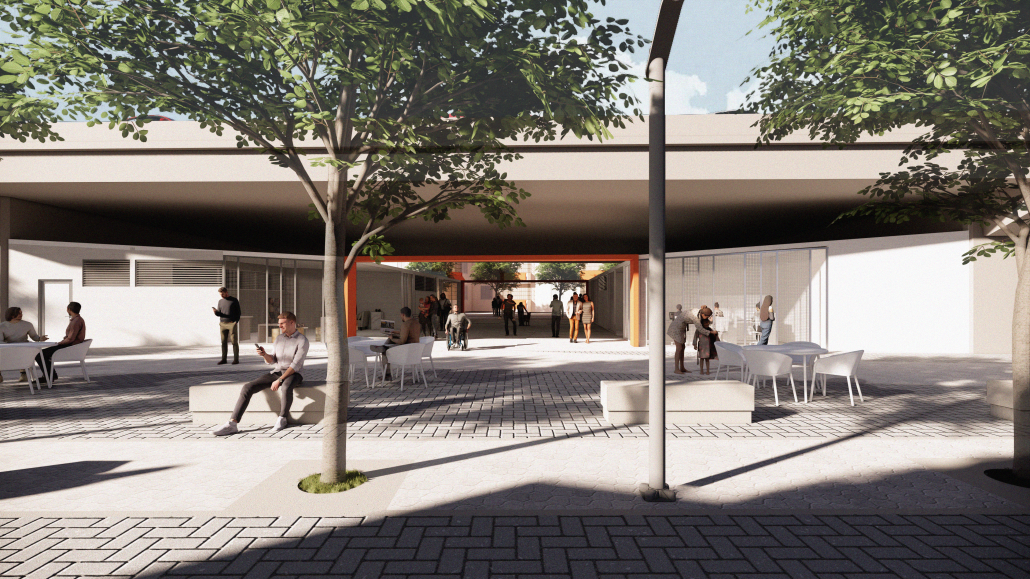
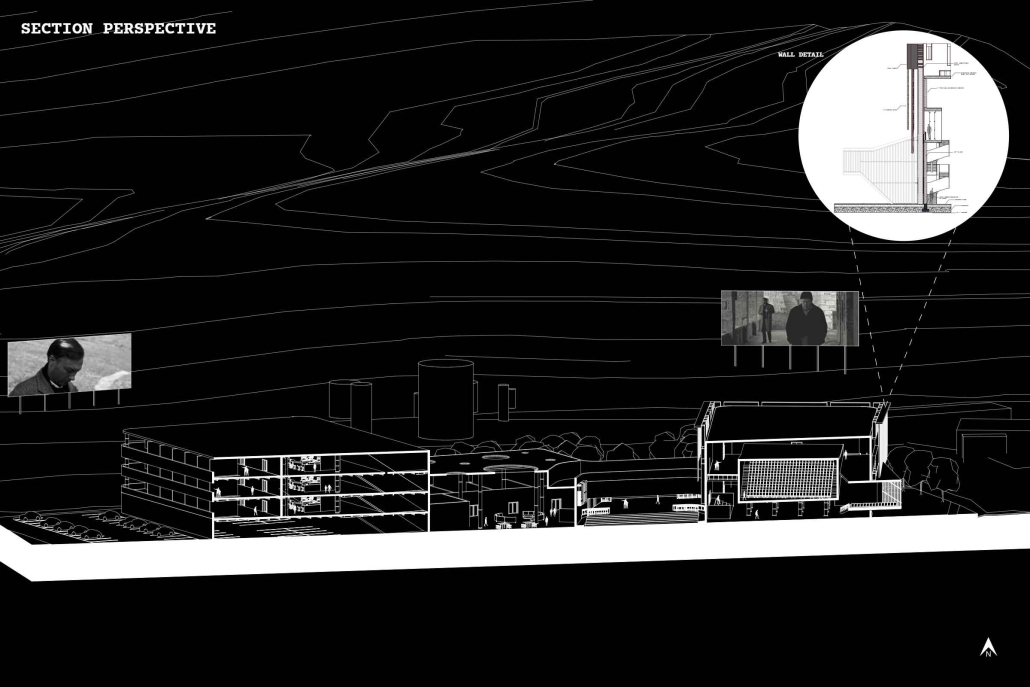
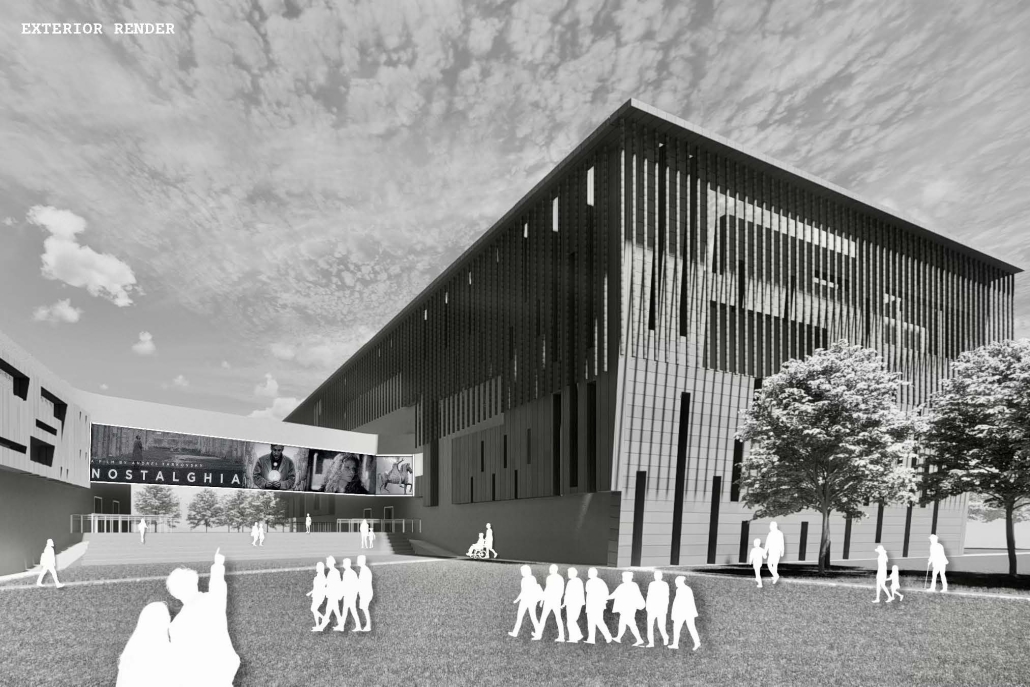
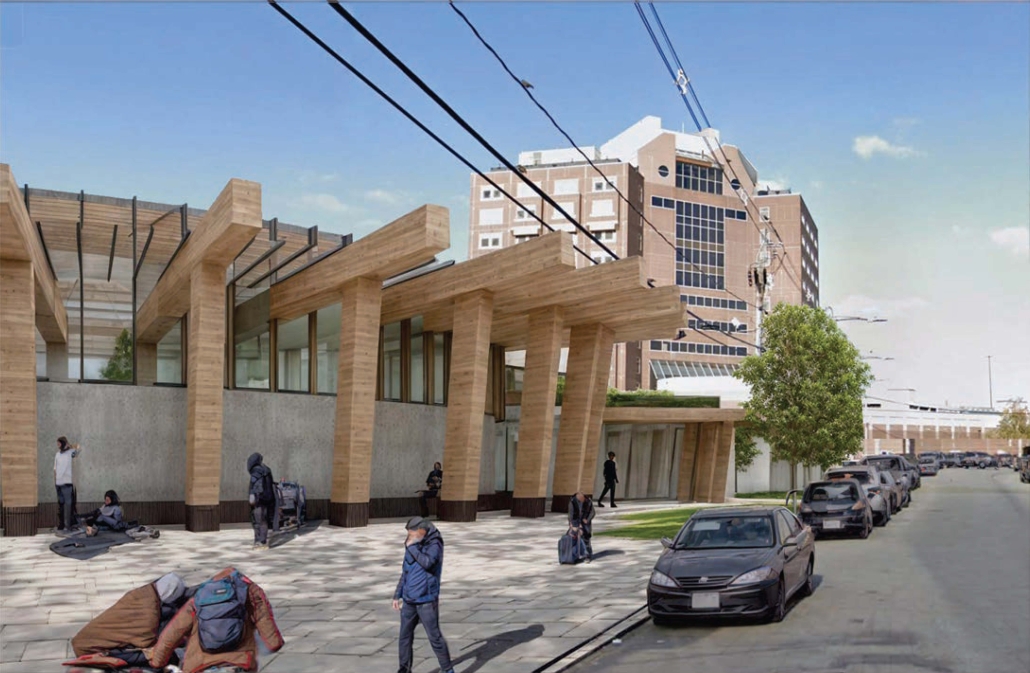
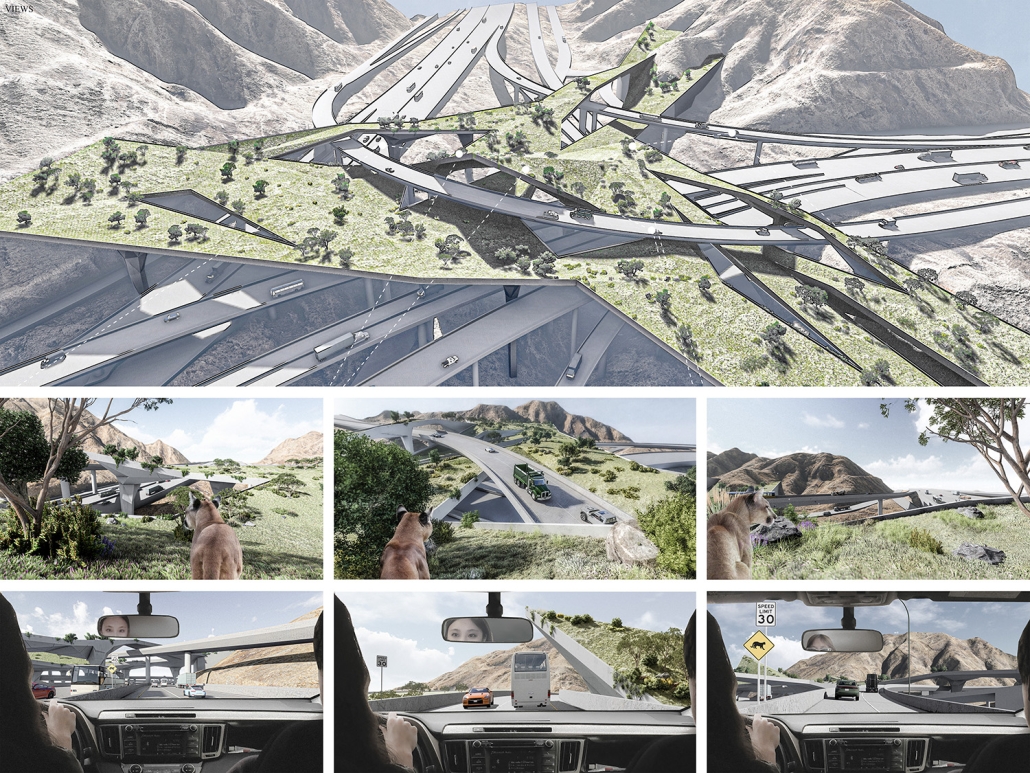
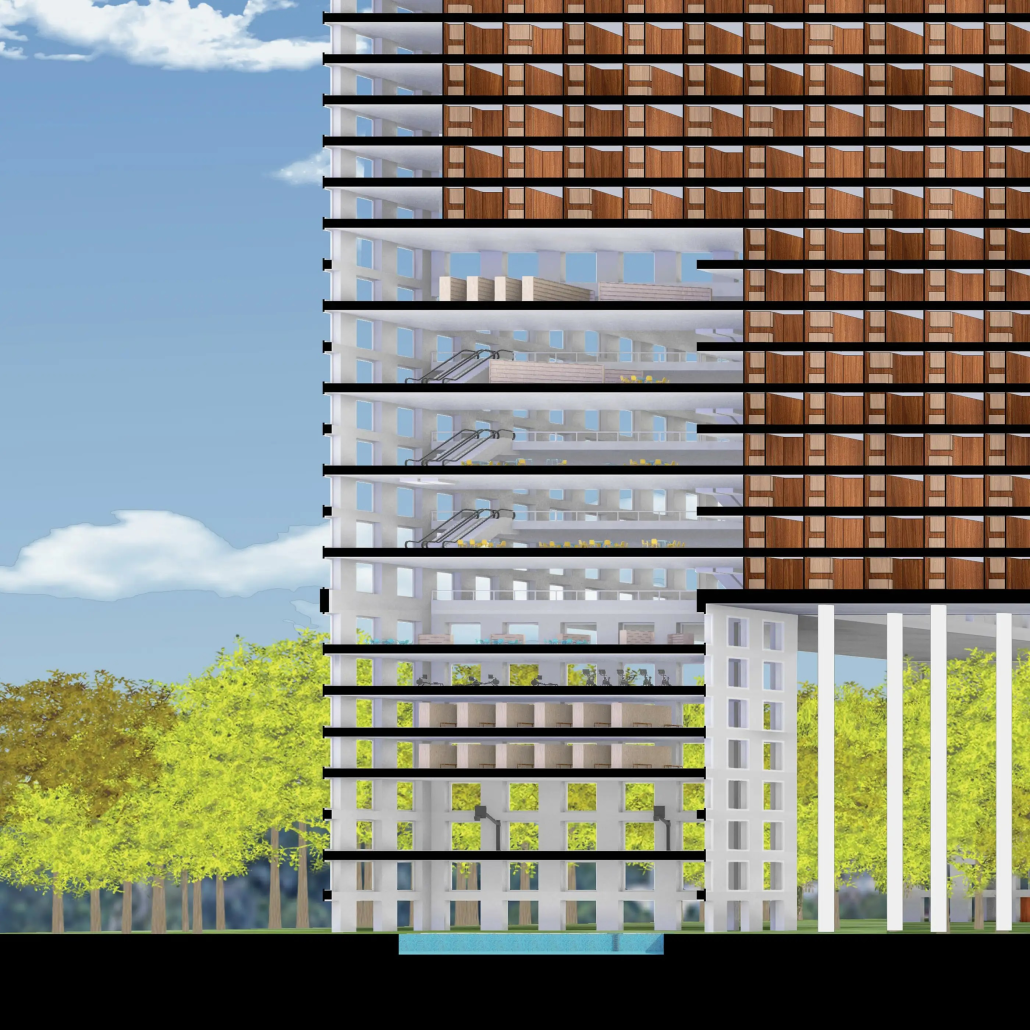
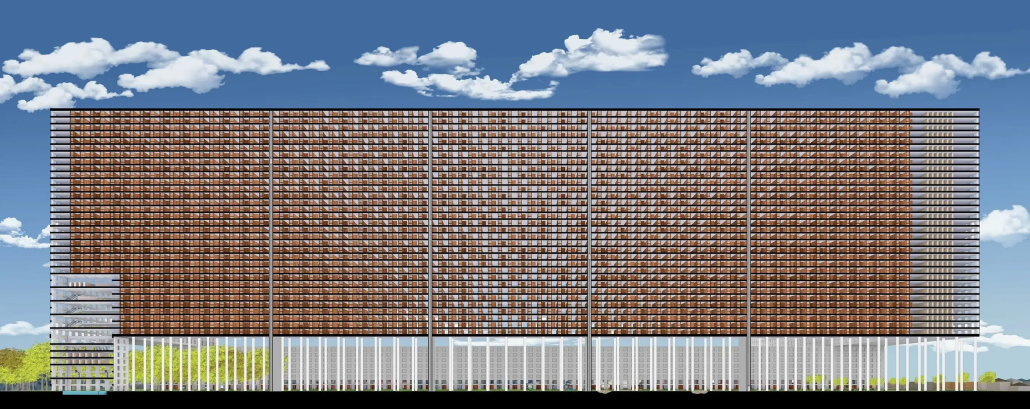
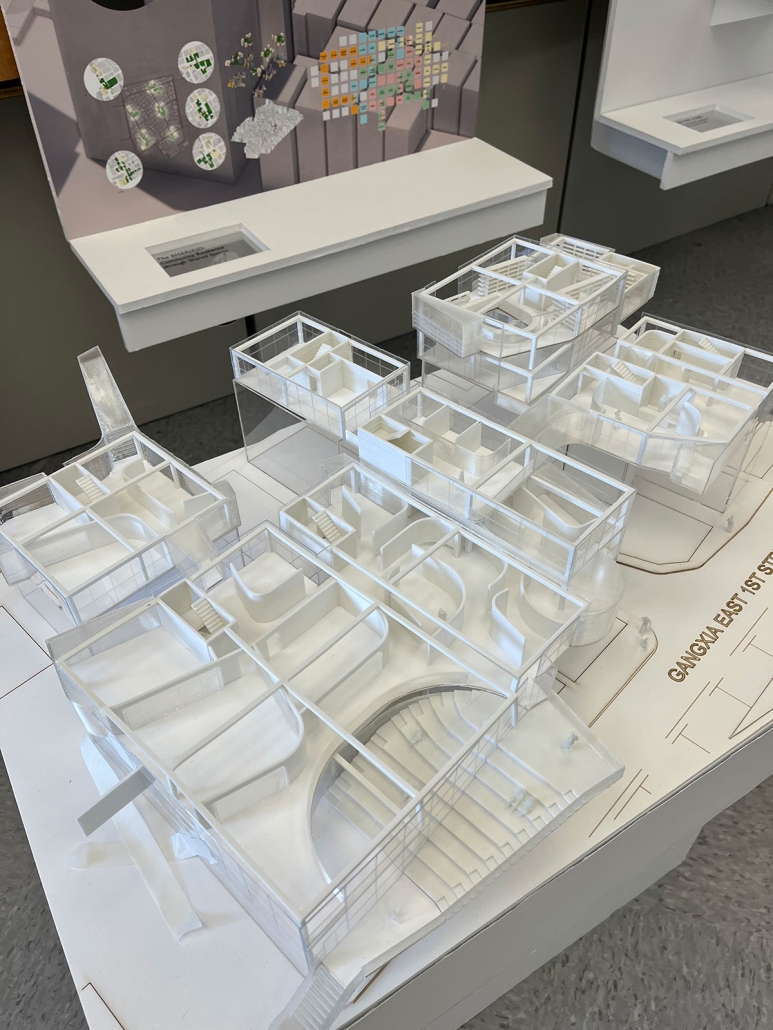
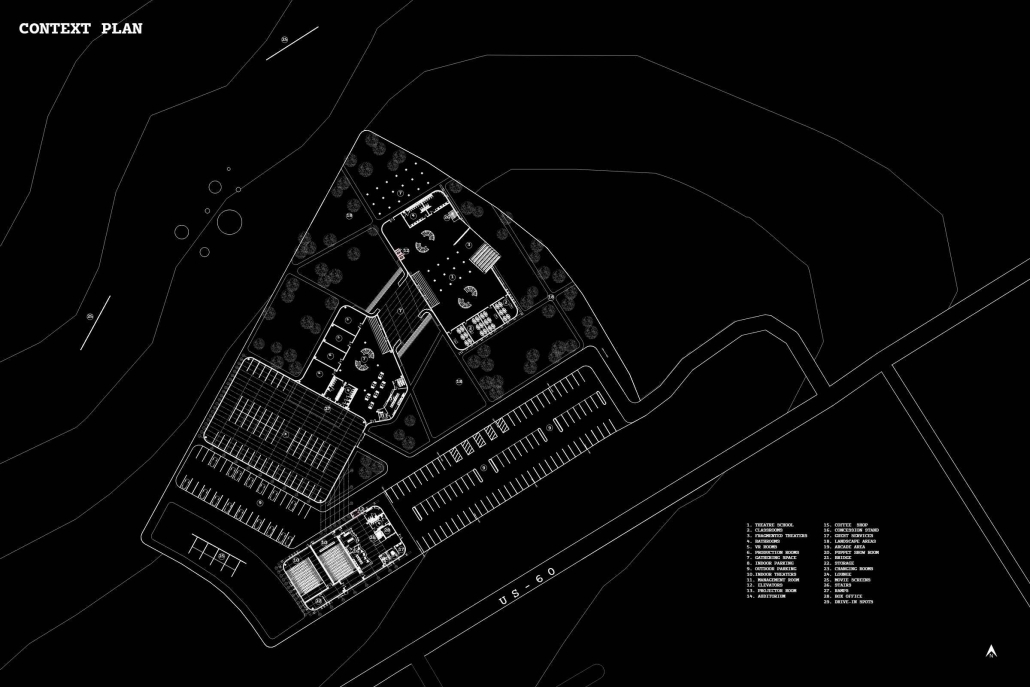
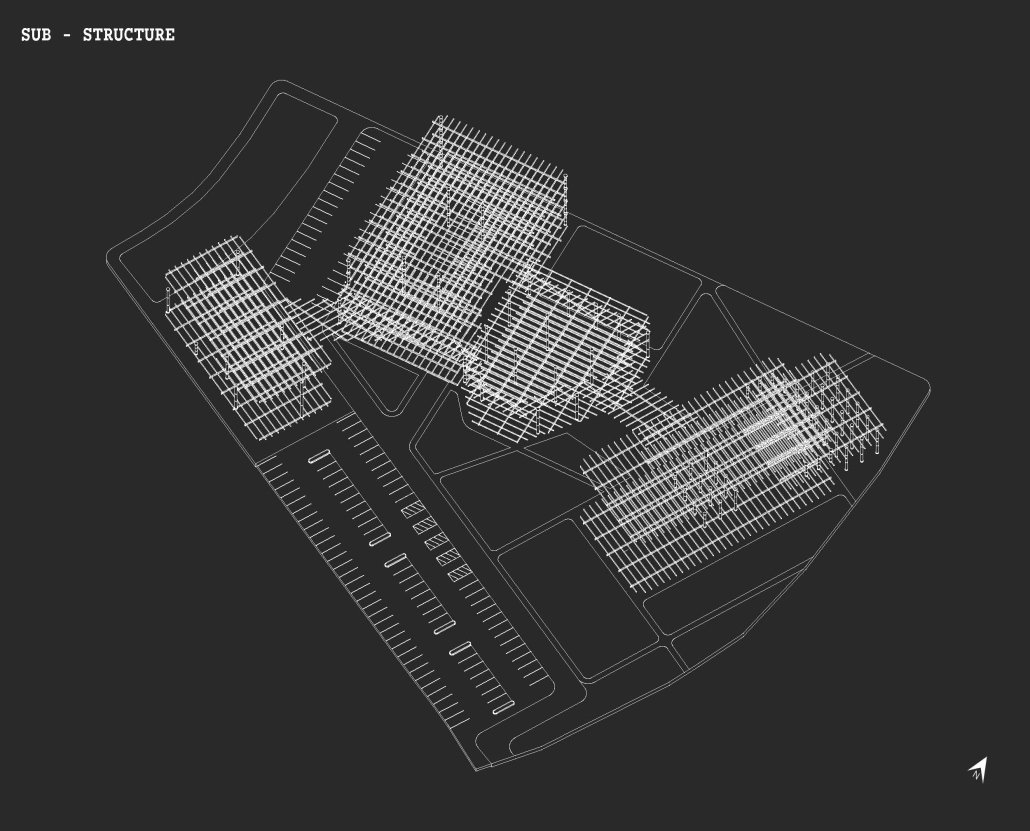
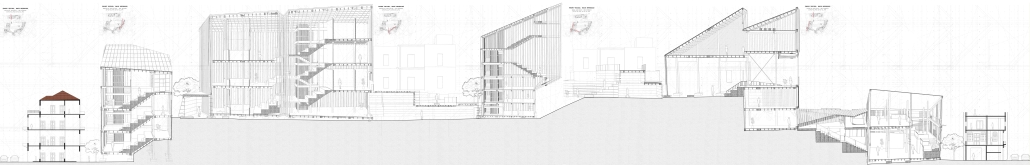
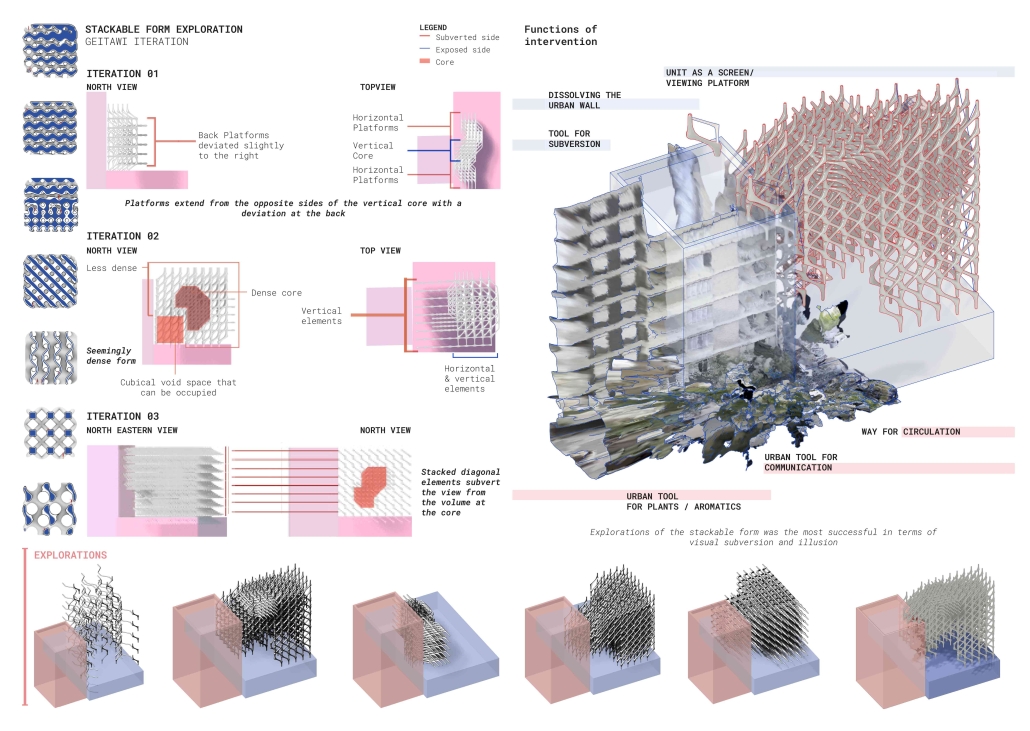
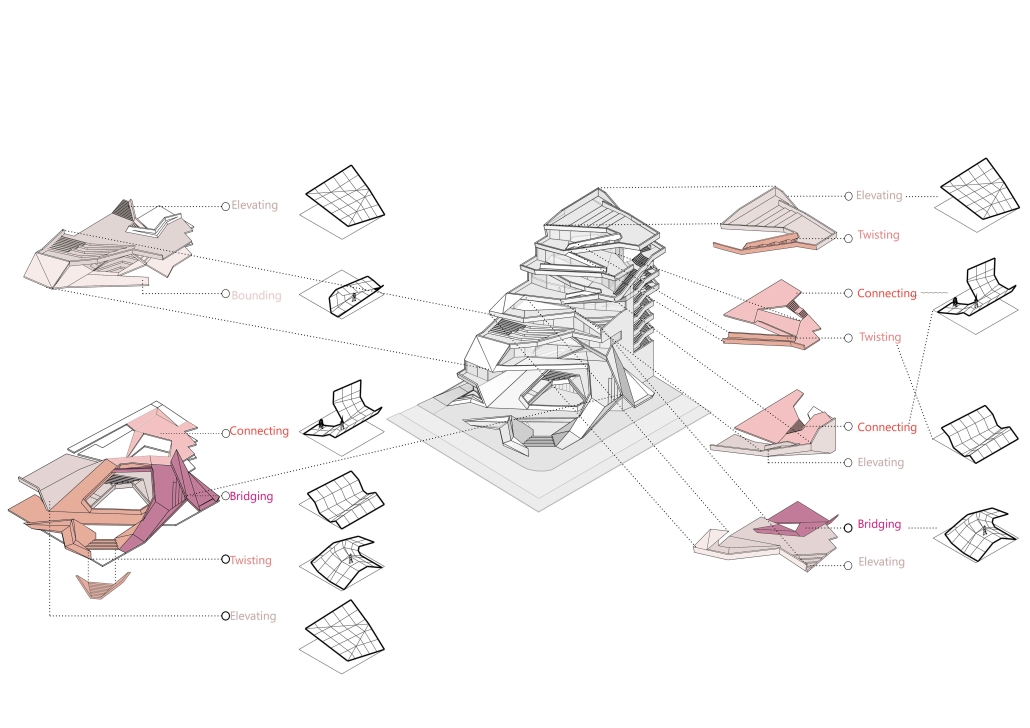
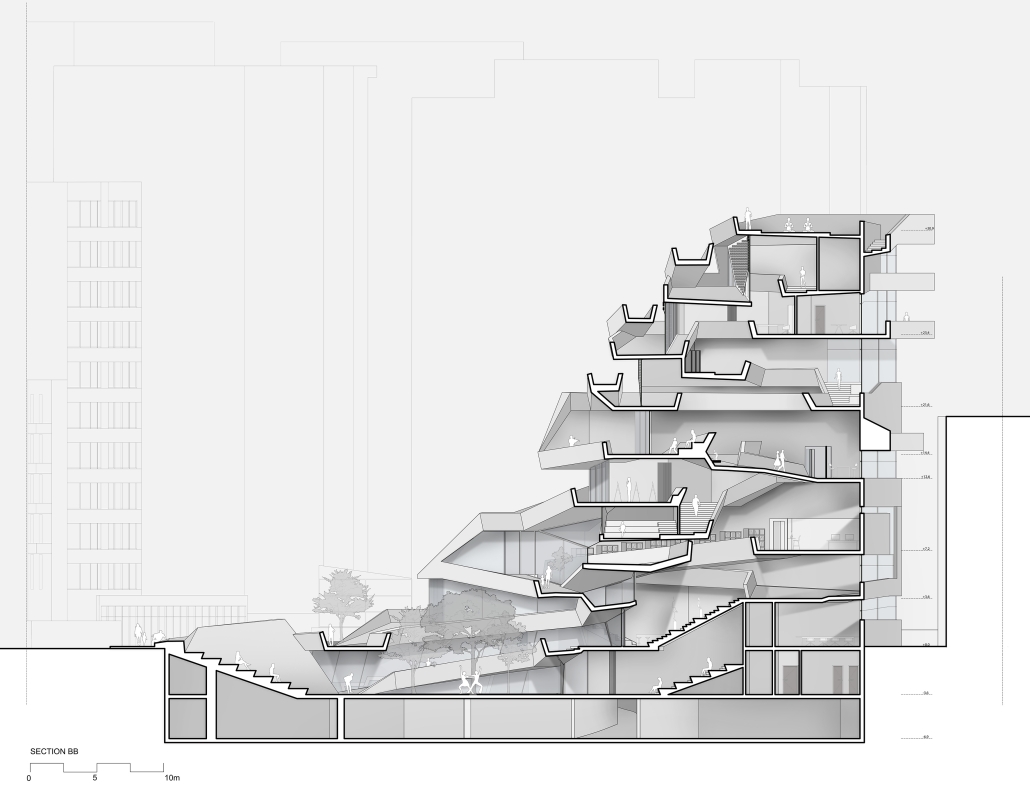
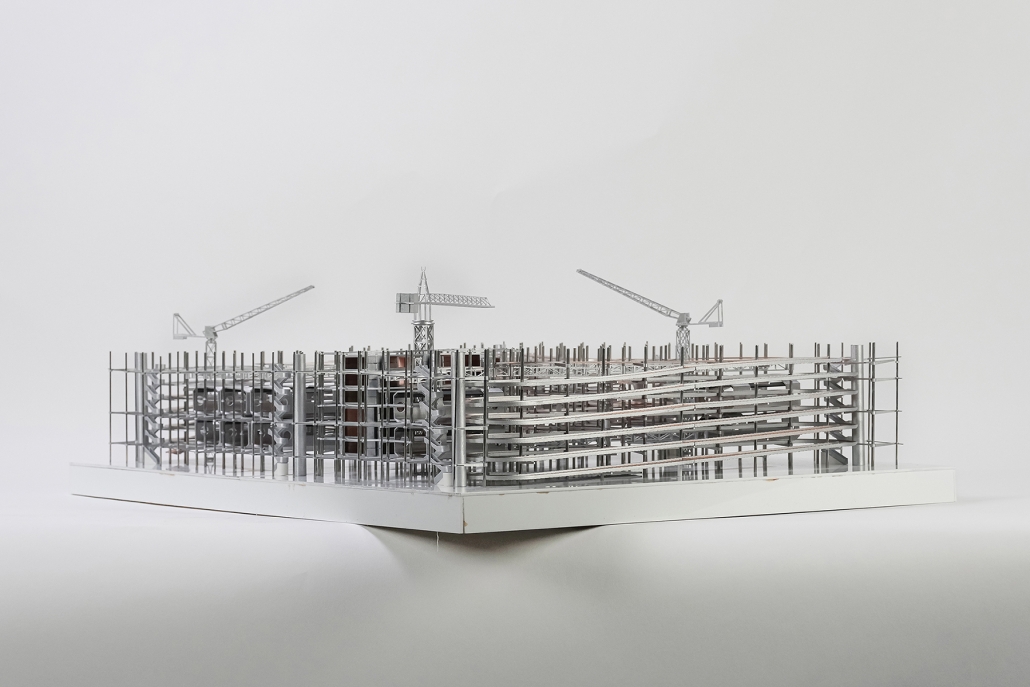
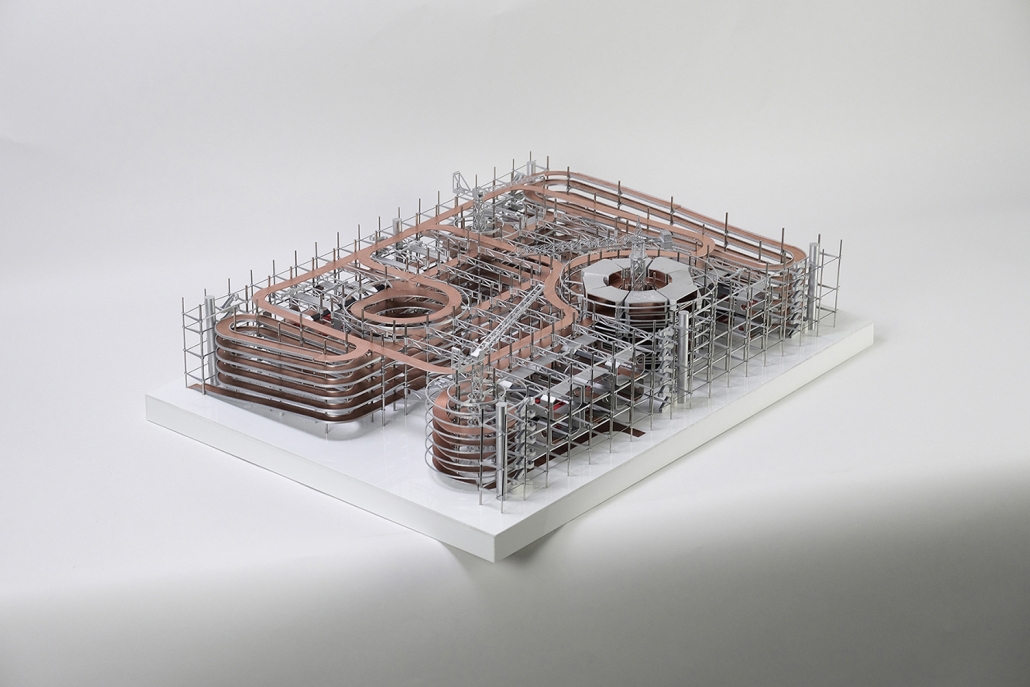
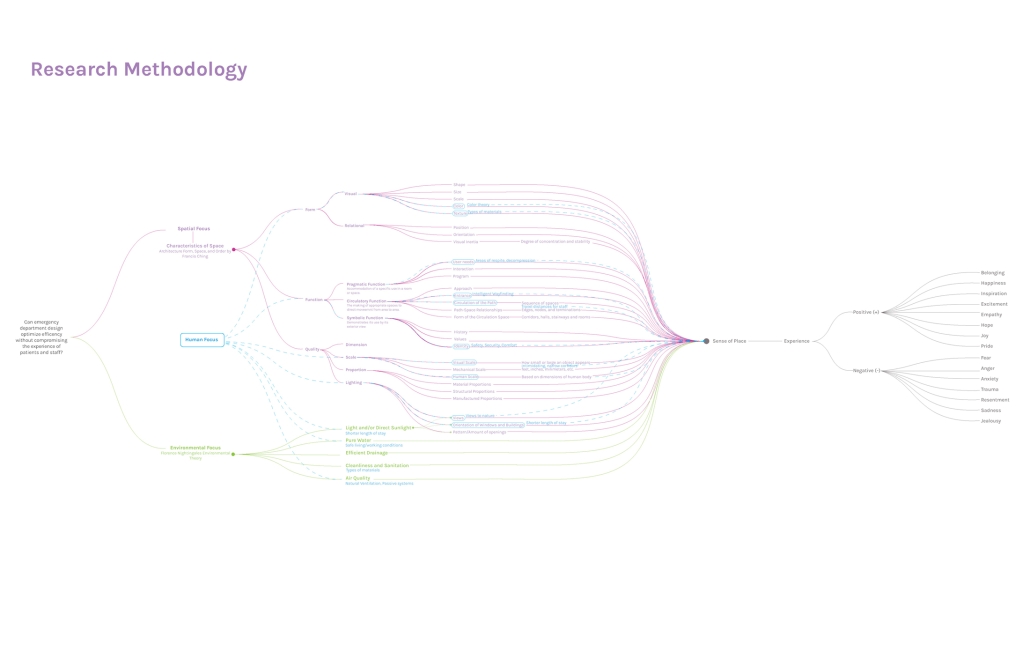
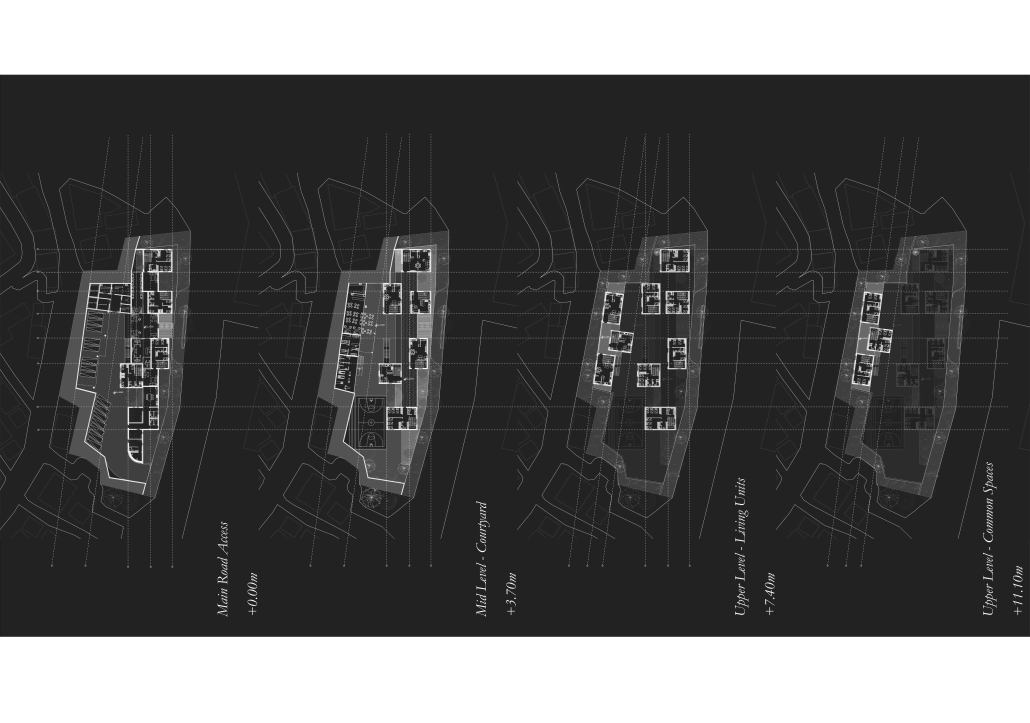
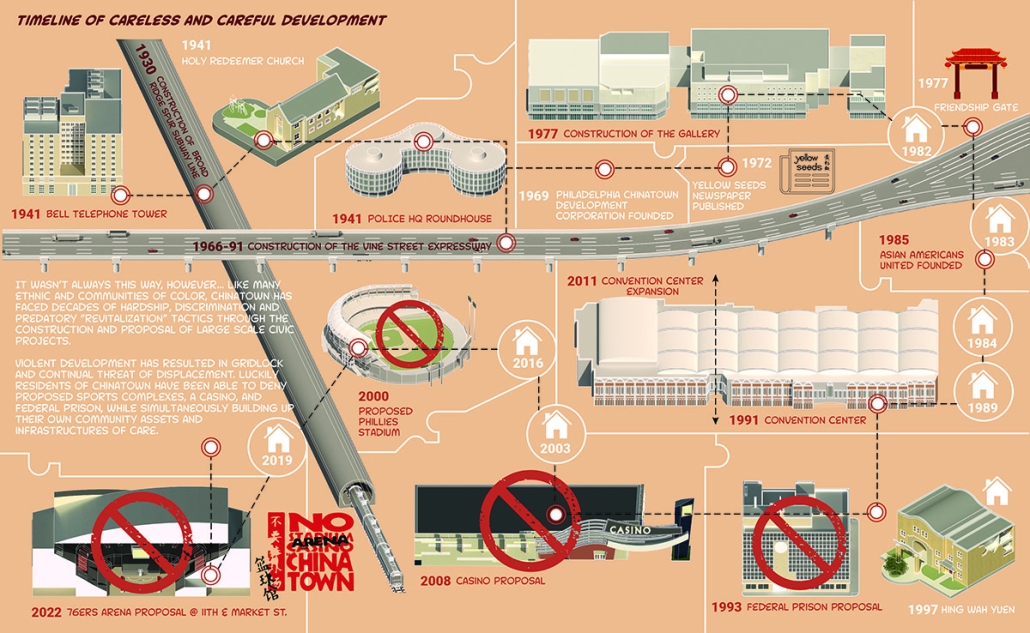
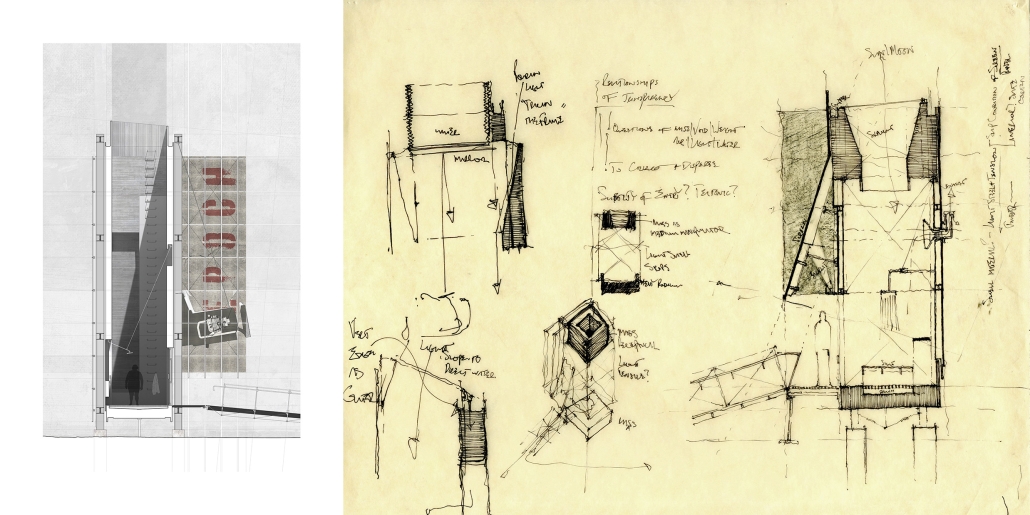
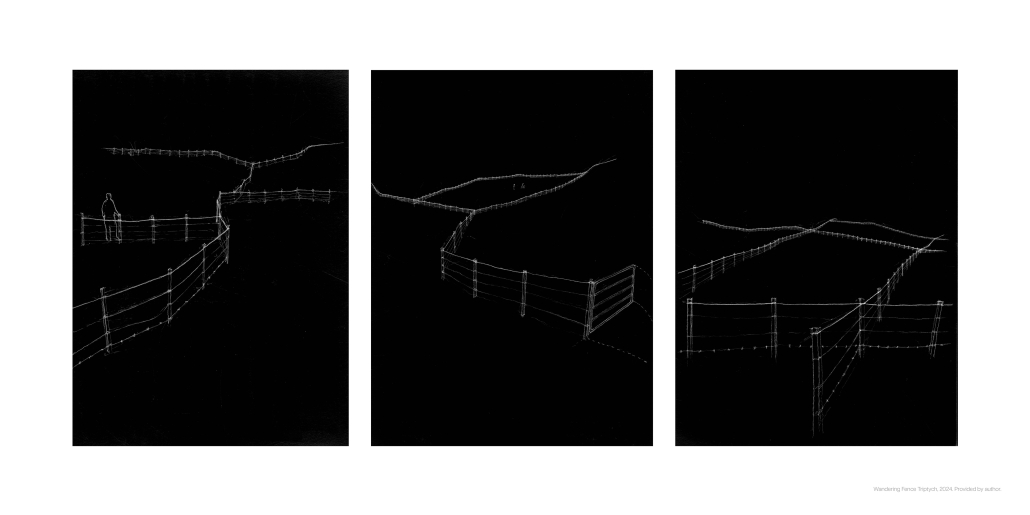
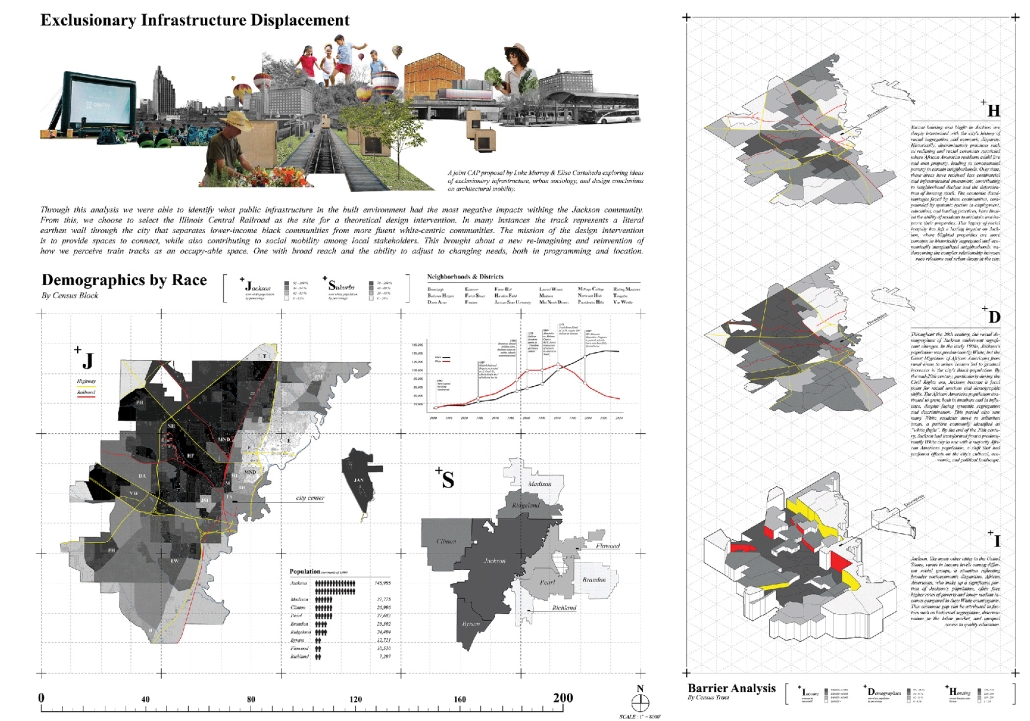
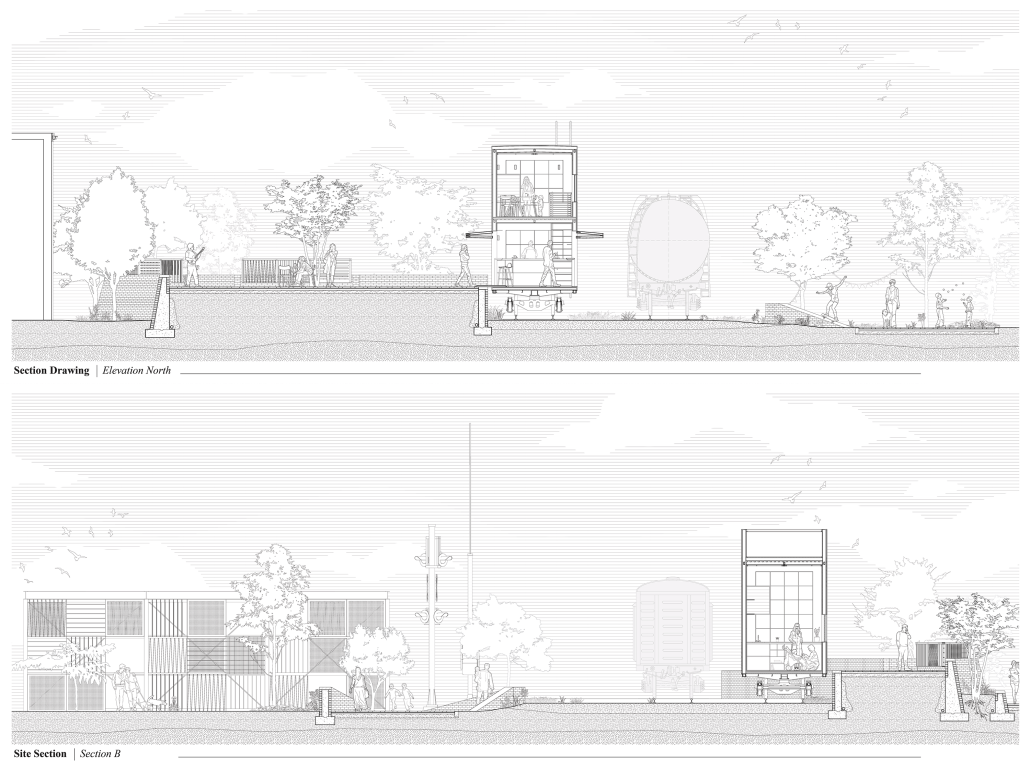
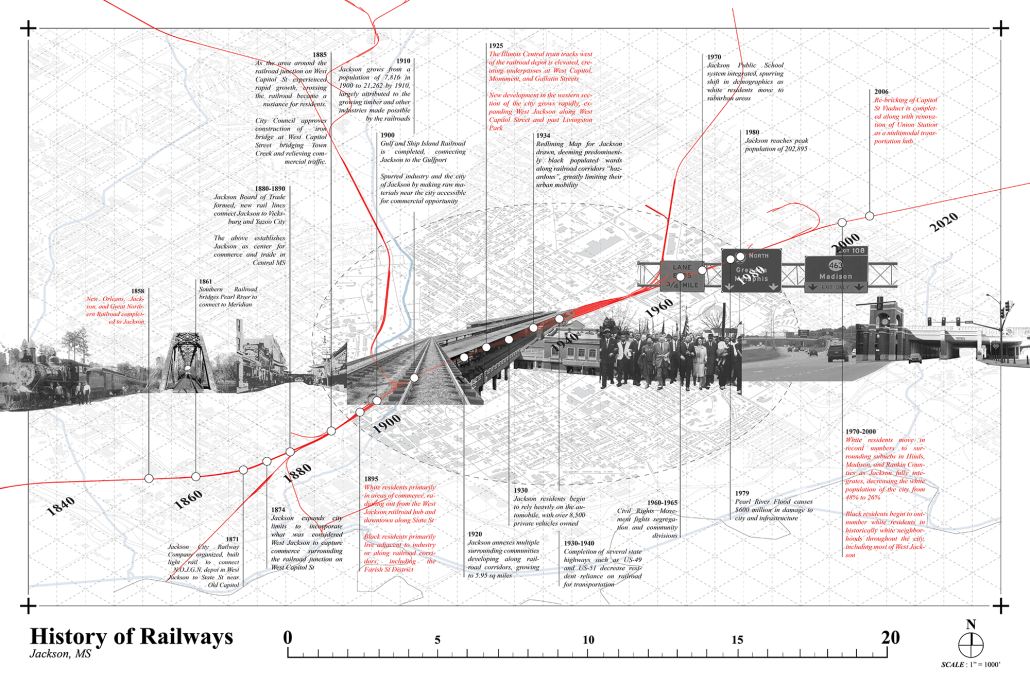
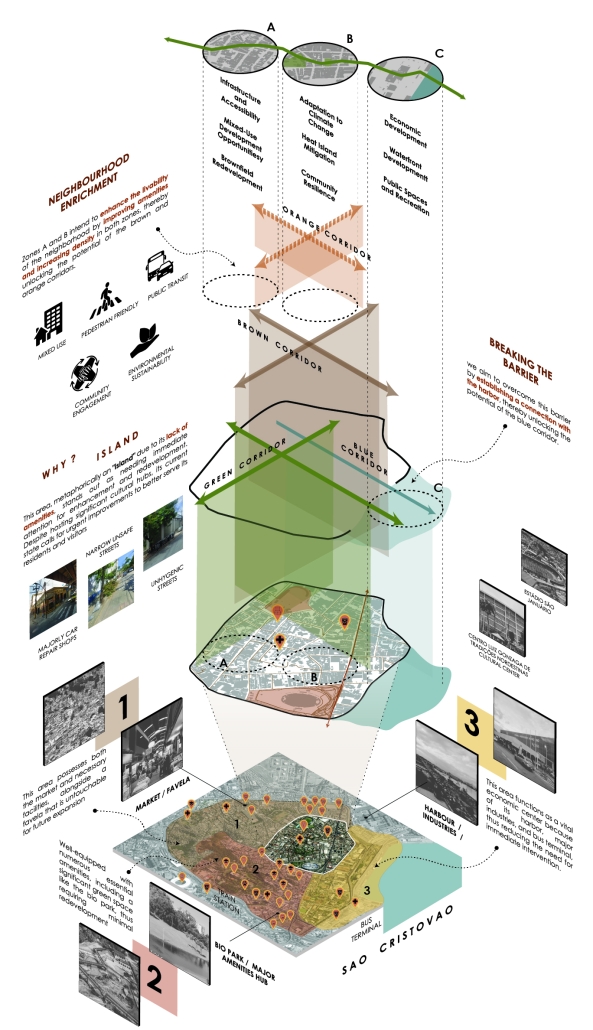
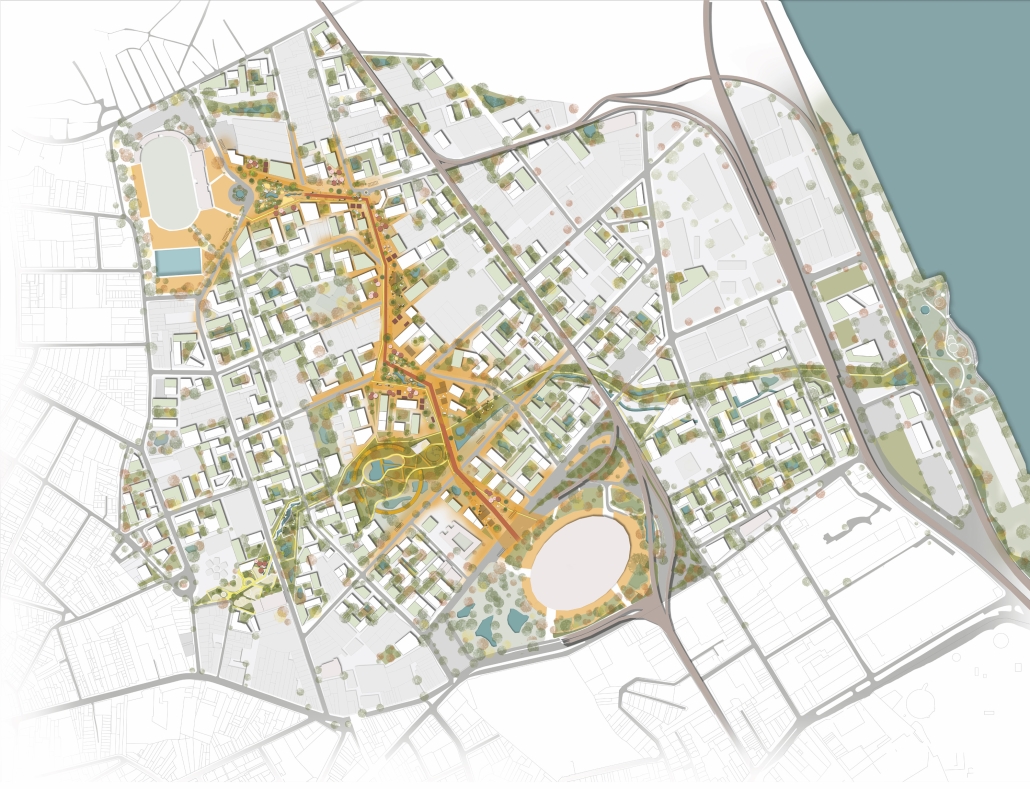
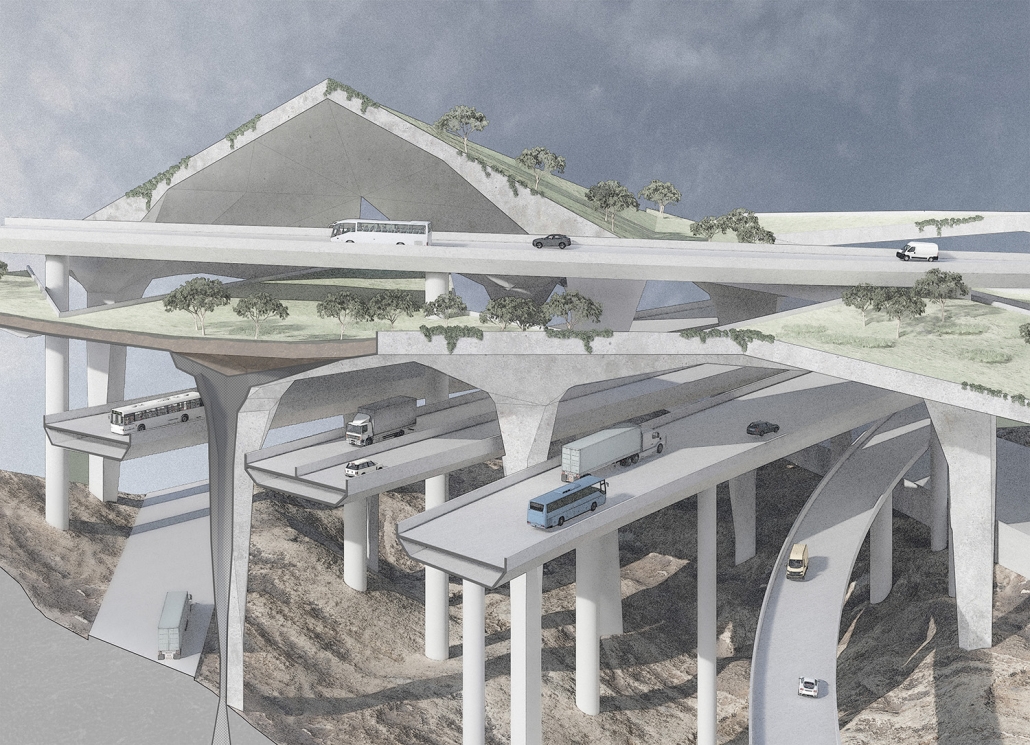
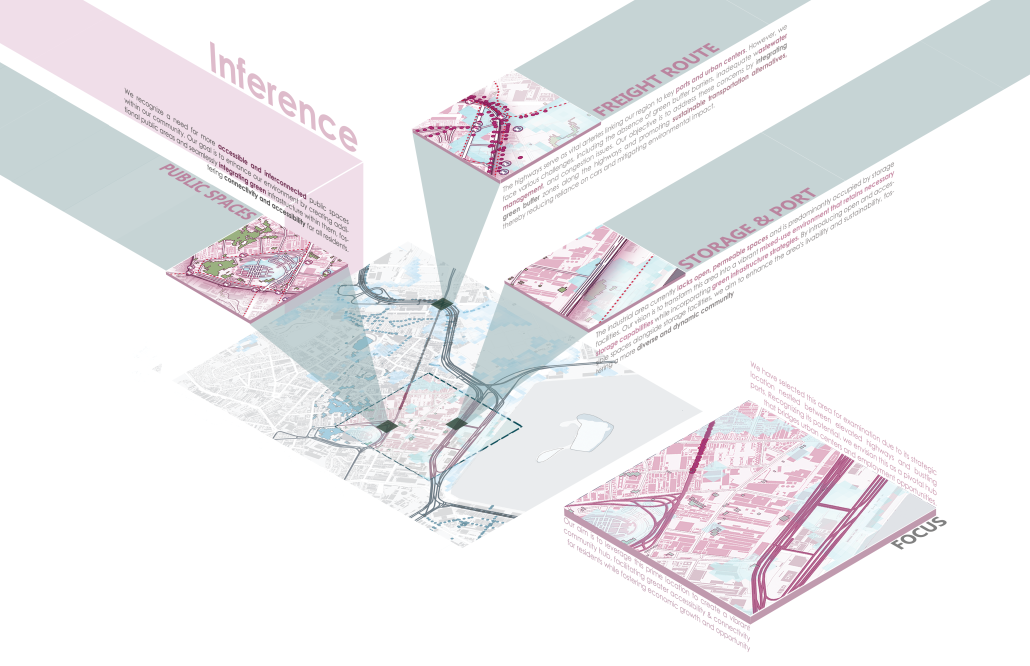
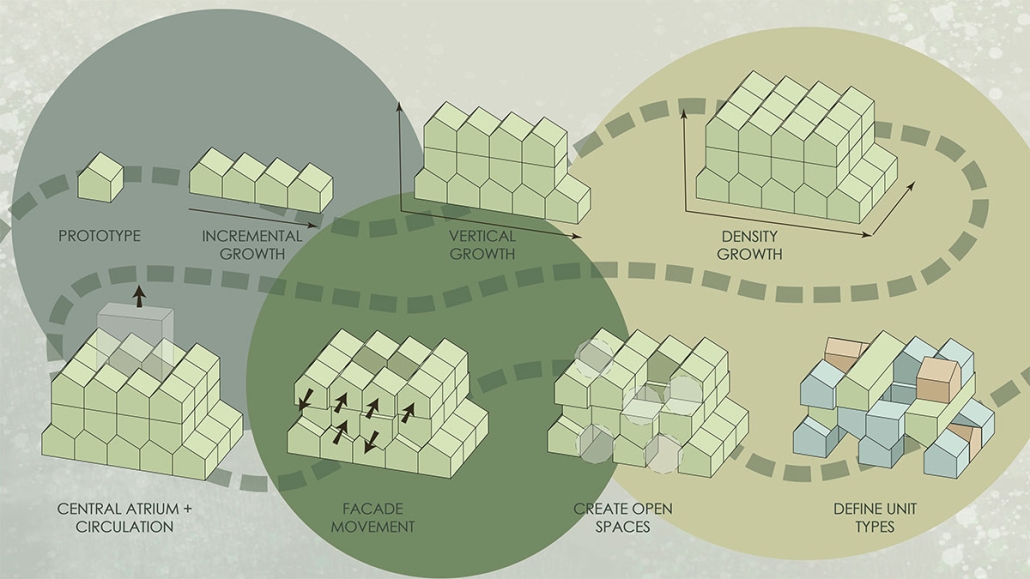
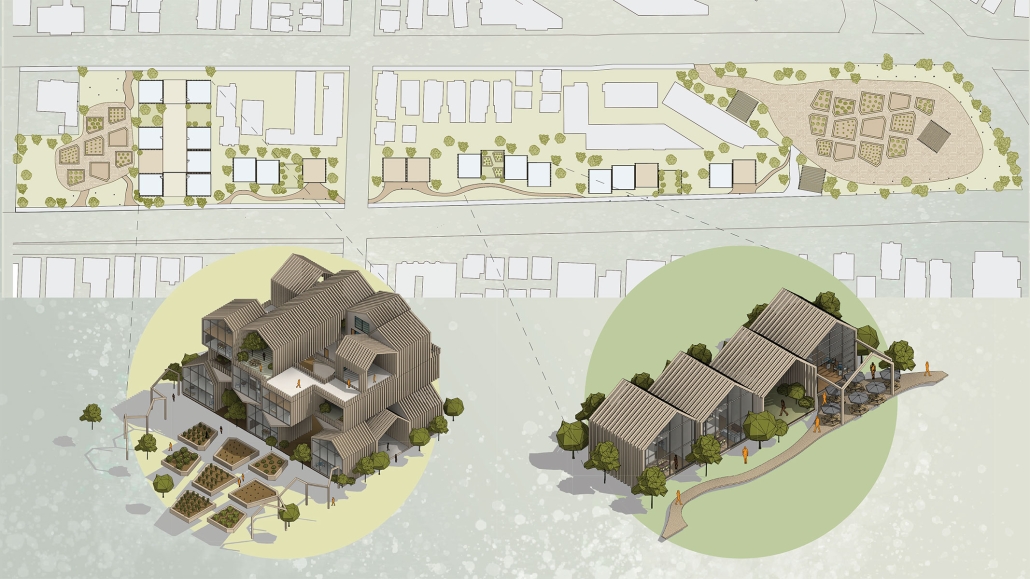
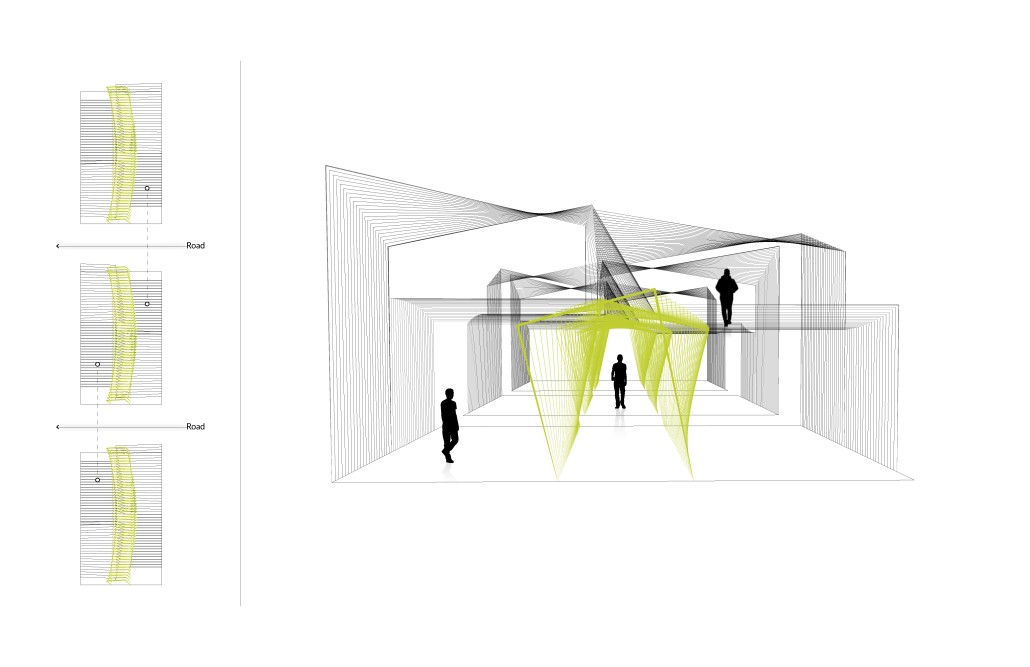
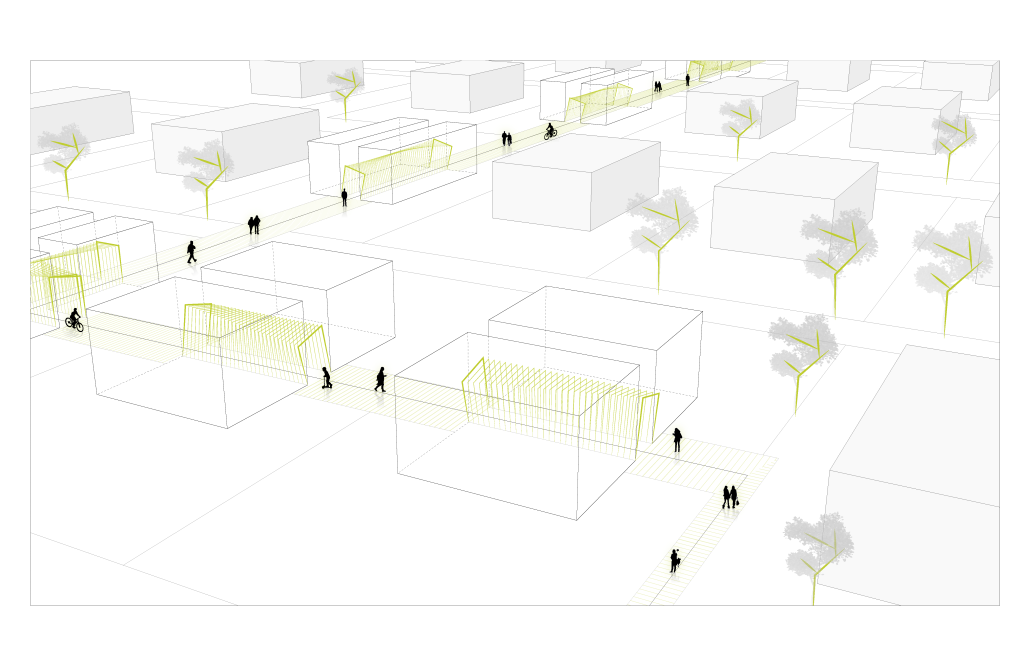
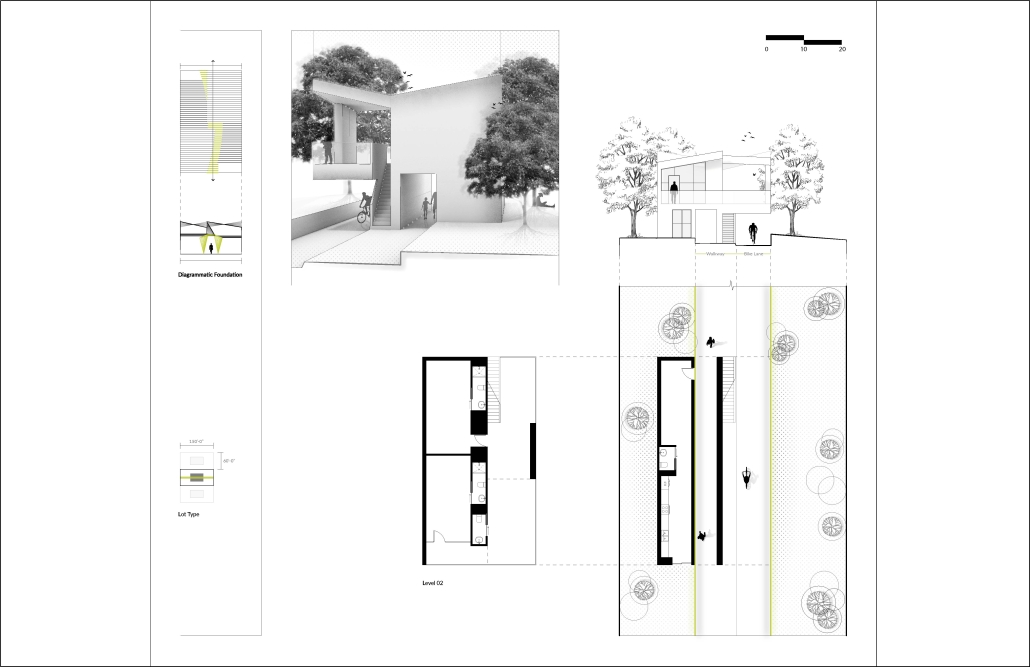
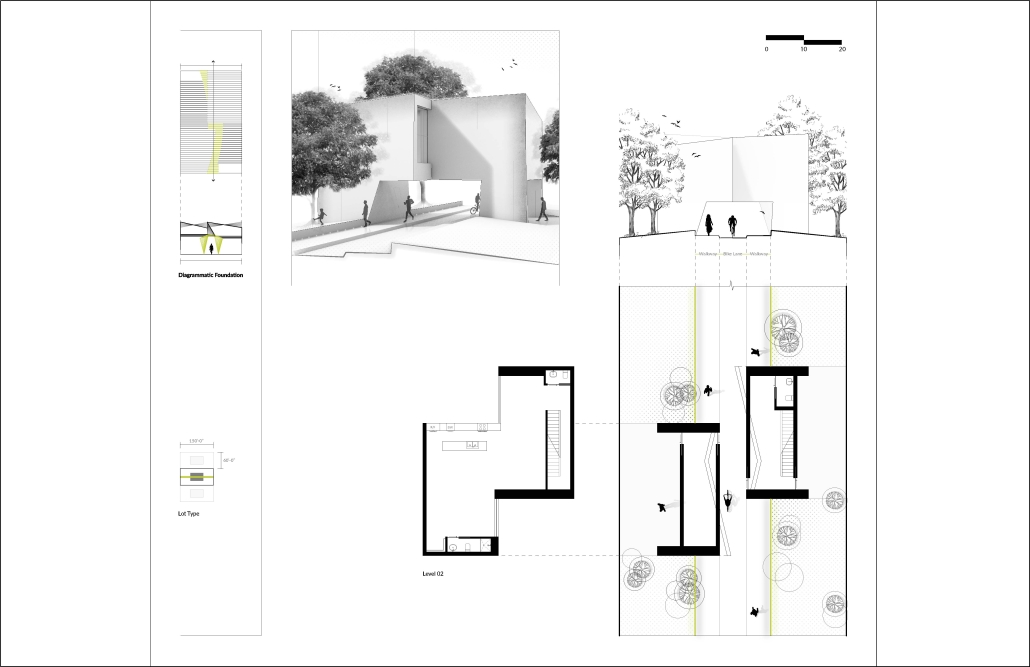
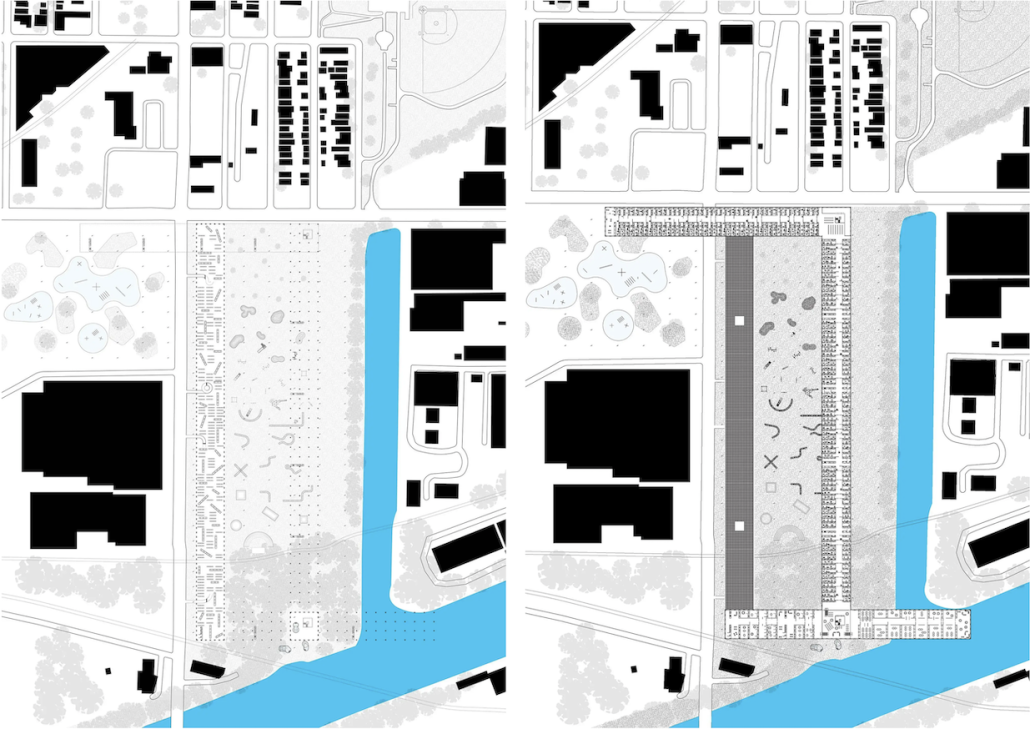
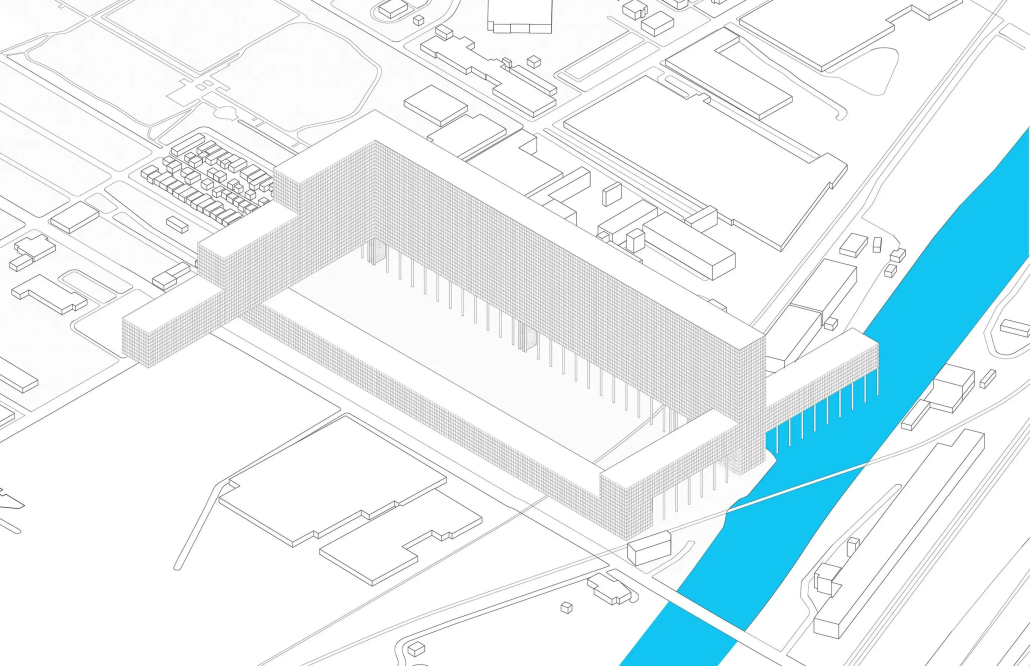
URBAN FRAGMENTATION AND SOCIAL ISOLATION: The Impact of High-Speed Expressways and the Reconnection of the Luis Lloréns Torres Public Housing Complex with Its Surrounding Communities by Lara S. Pérez-Fuentes, M.Arch ’25
University of Puerto Rico | Advisors: Omayra Rivera Crespo, José R. Coleman-Davis & María Helena Luengo
In the Luis Lloréns Torres Public Housing Development and its neighboring communities, such as Shanghai and Villa Palmeras, physical and symbolic barriers, resulting from its architectural design and the Baldorioty de Castro Expressway, have generated urban fragmentation and social isolation. This isolation has limited mobility, access to essential services, and economic opportunities, while perpetuating the social stigma associated with public housing. Based on this context, the study proposes designing an integrative public space as a strategy to mitigate barriers, foster social cohesion, and improve residents’ quality of life.
The research combines qualitative and quantitative approaches, including interviews and surveys, which highlight the challenges of mobility, community disconnection, and lack of adequate infrastructure. Key elements of identity and belonging are also identified, guiding the proposed interventions. The design program includes a pedestrian corridor, a Community Connection Center, and a Cultural Center, along with strategies to revitalize informal commercial spaces and promote social interaction.
This integrative approach not only responds to the functional needs of accessibility and connectivity, but also seeks to transform the perception of residents and neighboring communities, fostering a sense of unity and active participation. The research underscores the importance of inclusive and collaborative urban planning as a means to overcome exclusion and build resilient, cohesive, and equitable communities.
Instagram: @larita0013, @uprarchitecture
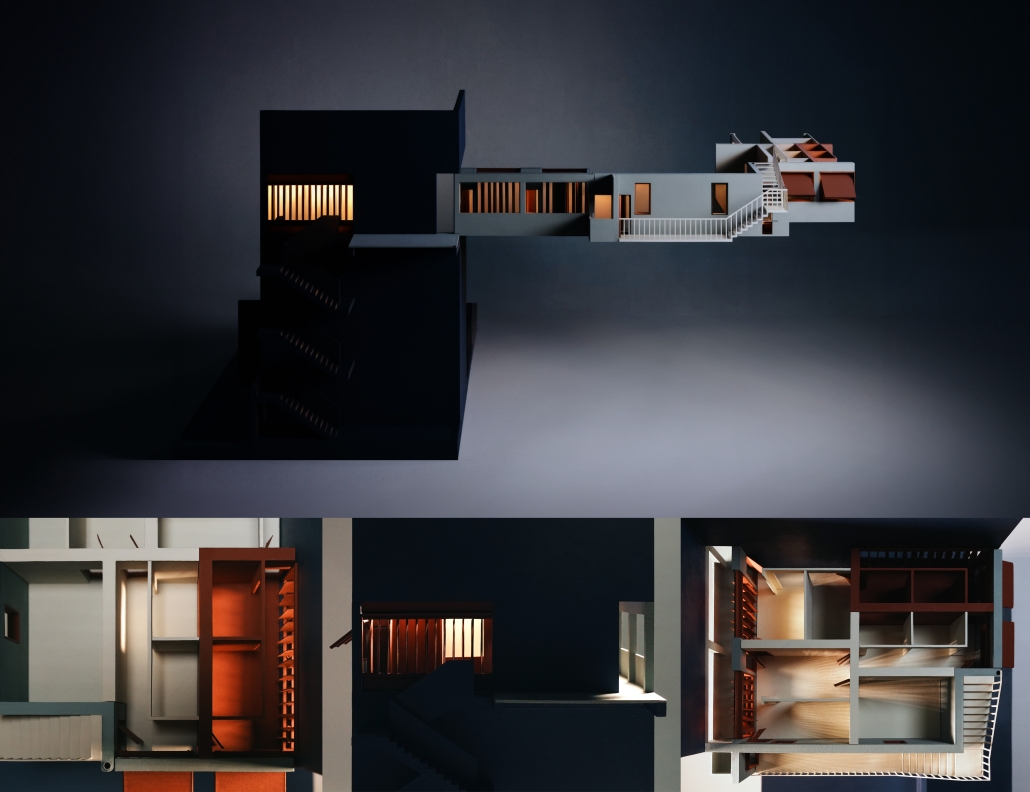
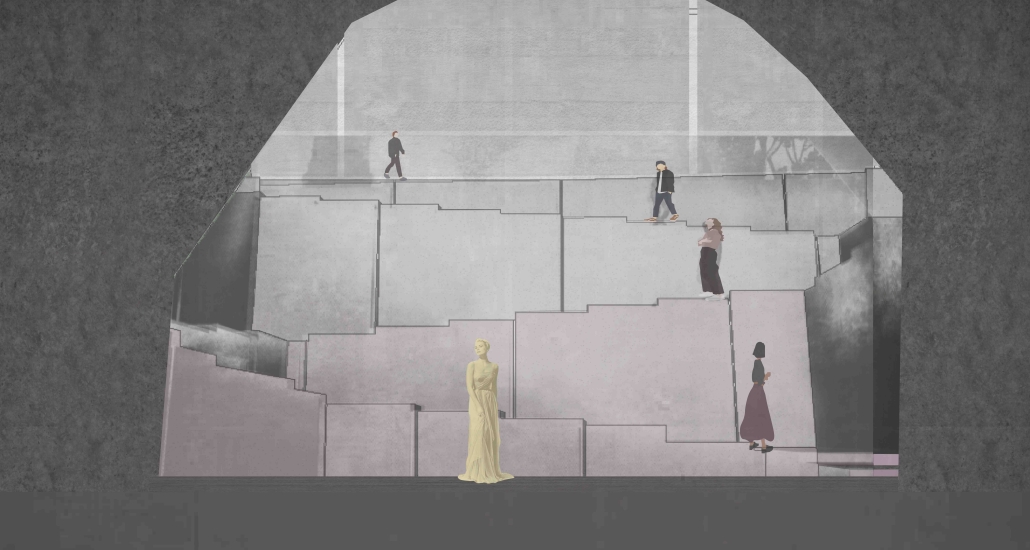
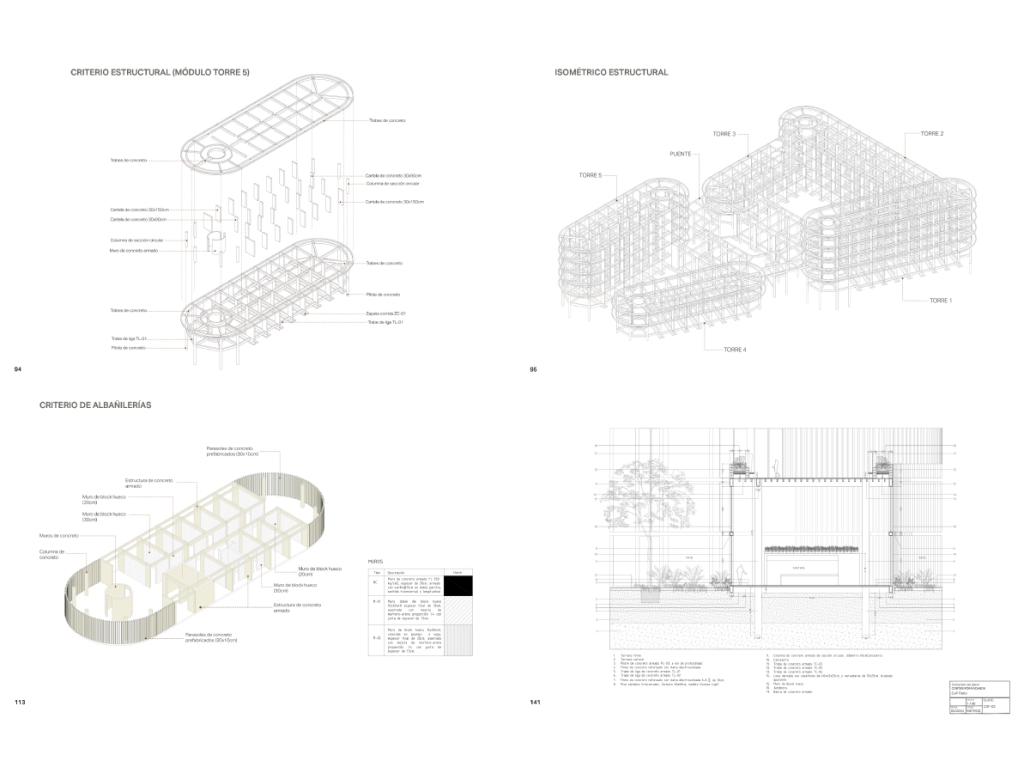
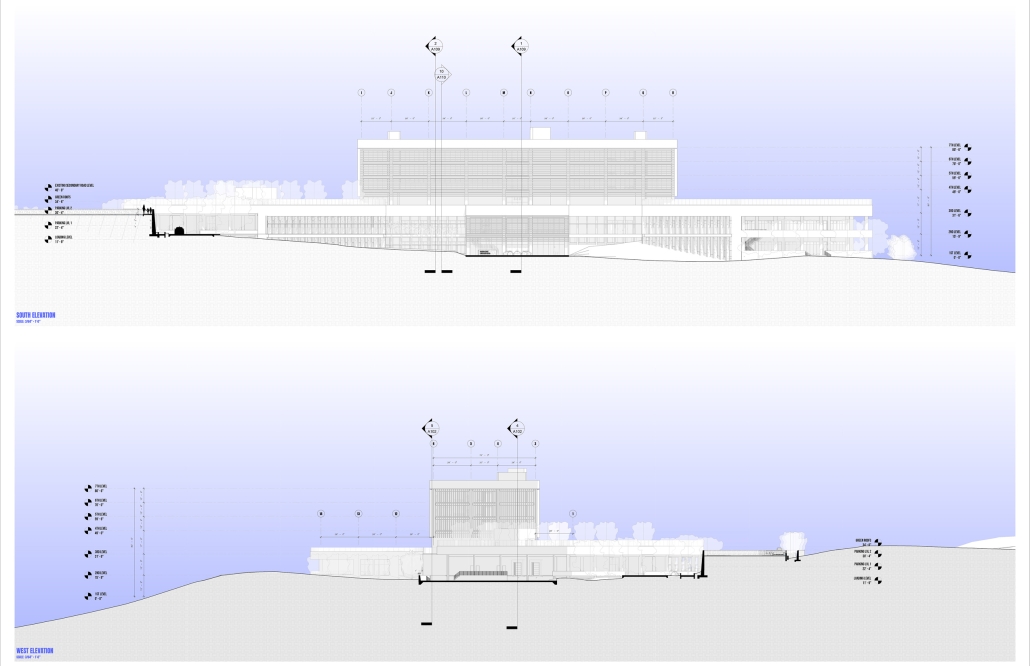
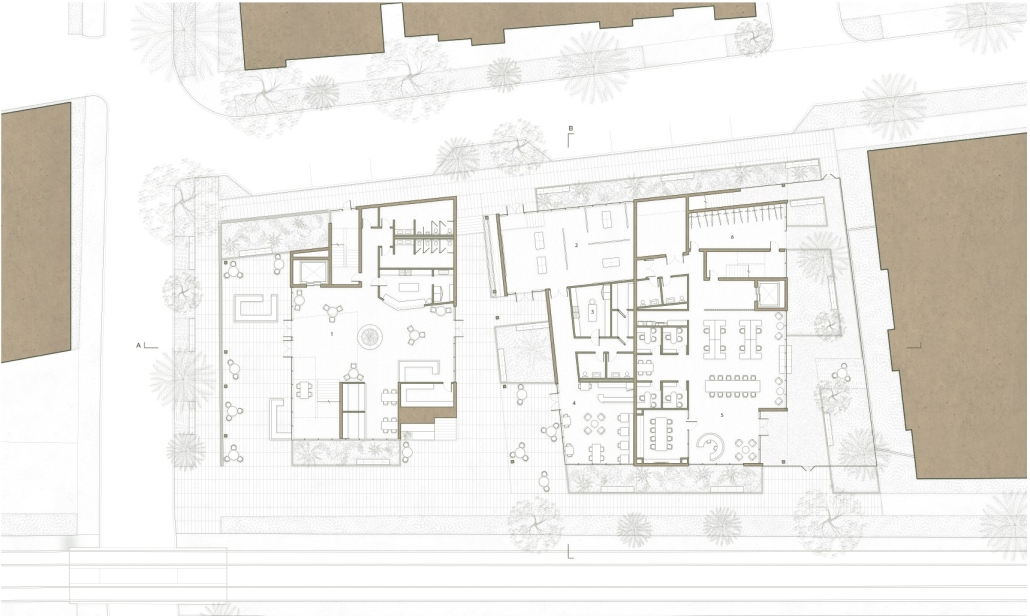
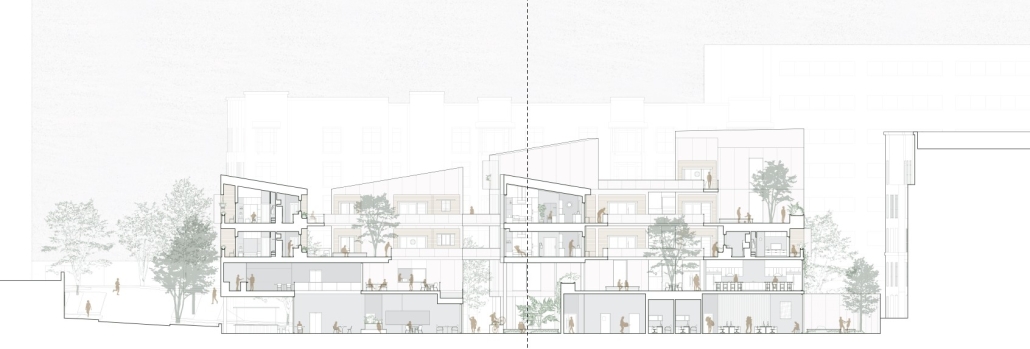
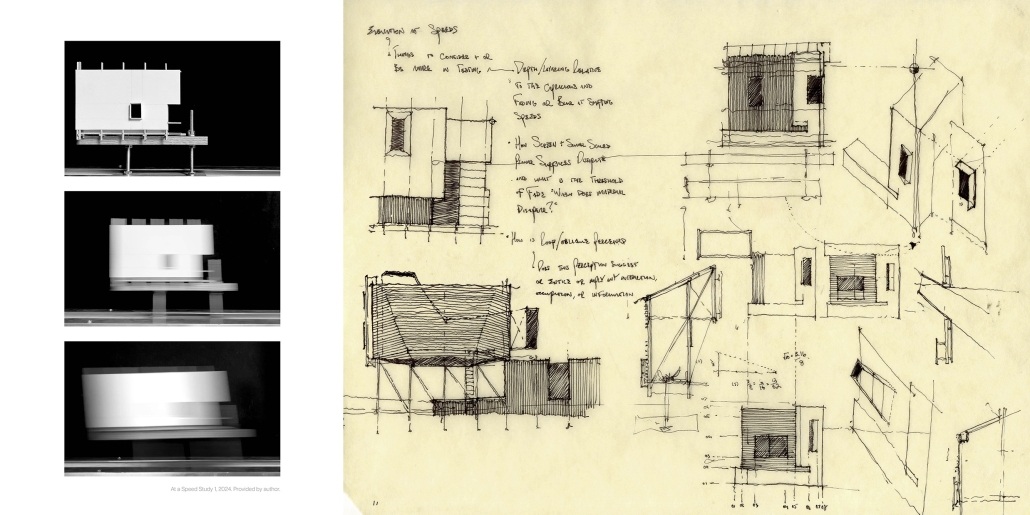
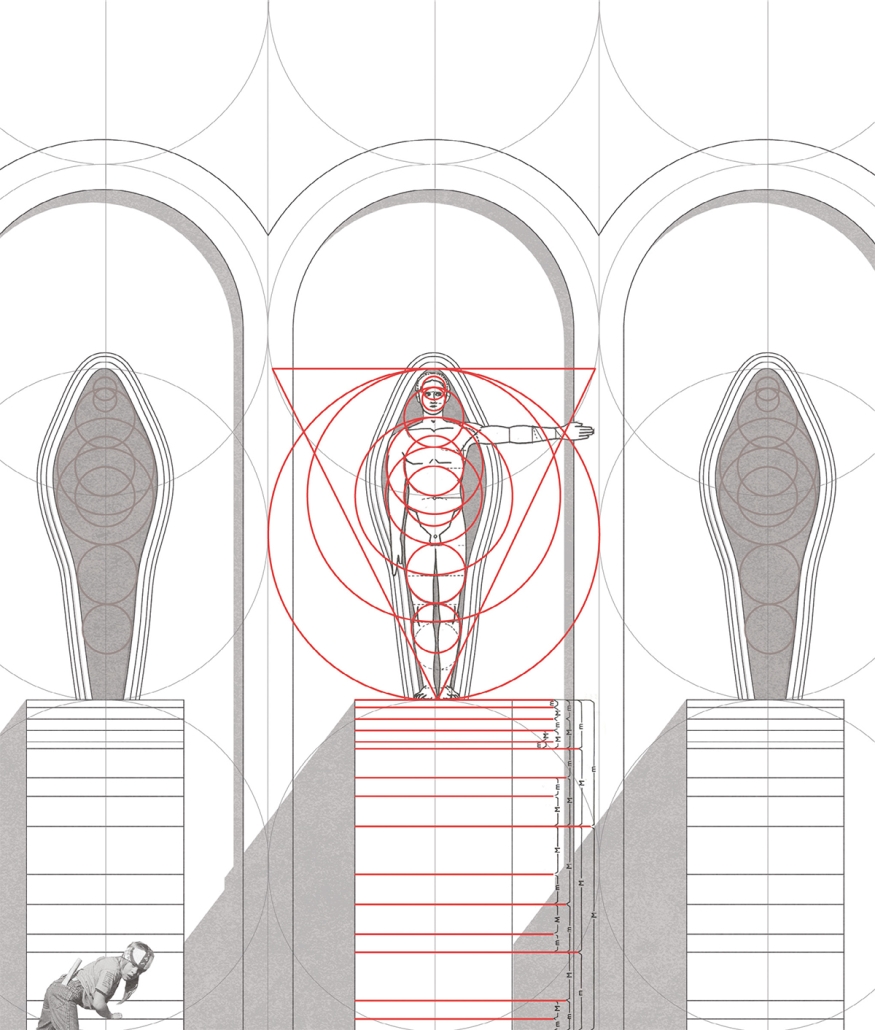
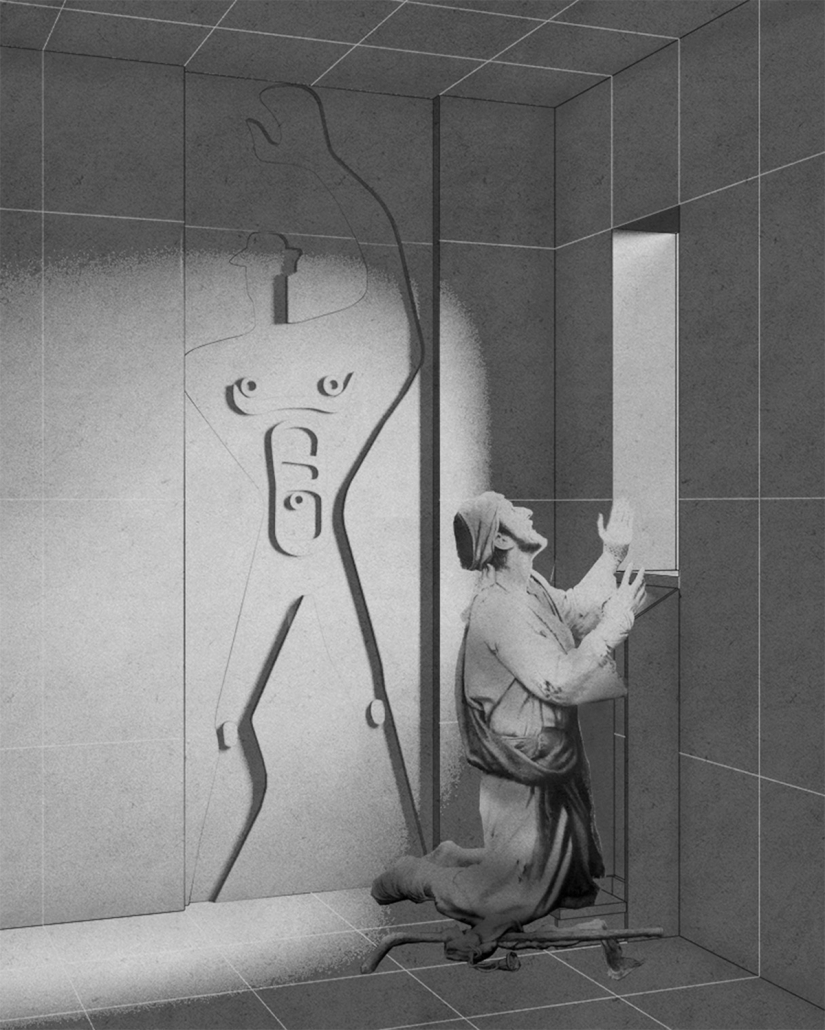
Jackson Center for the Blind and Visually Impaired by Anna Kate Horn, B.Arch ’25
Mississippi State University | Advisors: Jassen Callender, Mark Vaughan, Aaron White, David Perkes & David Buege
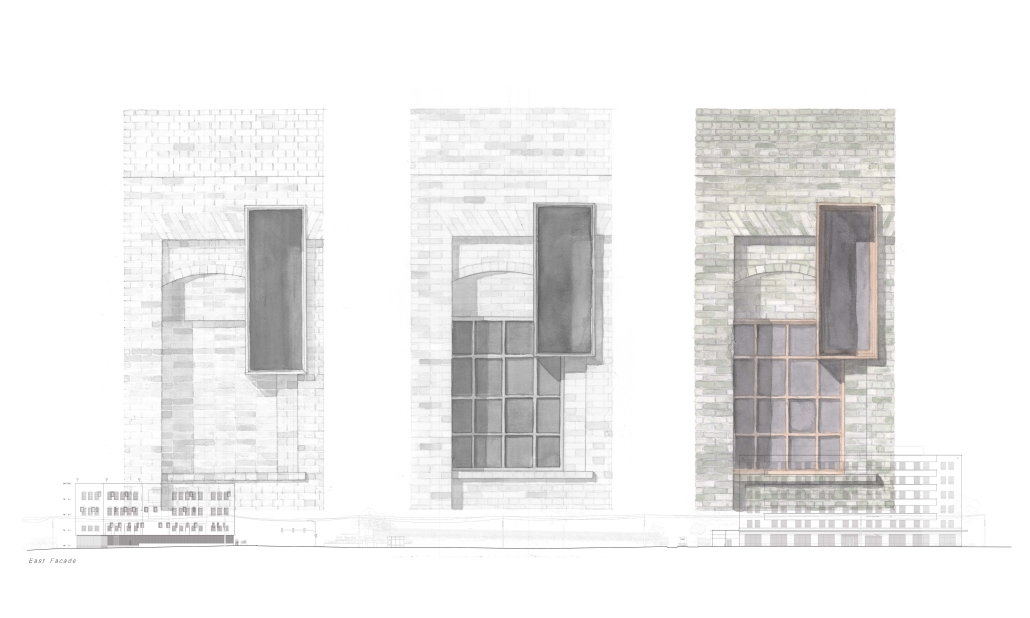
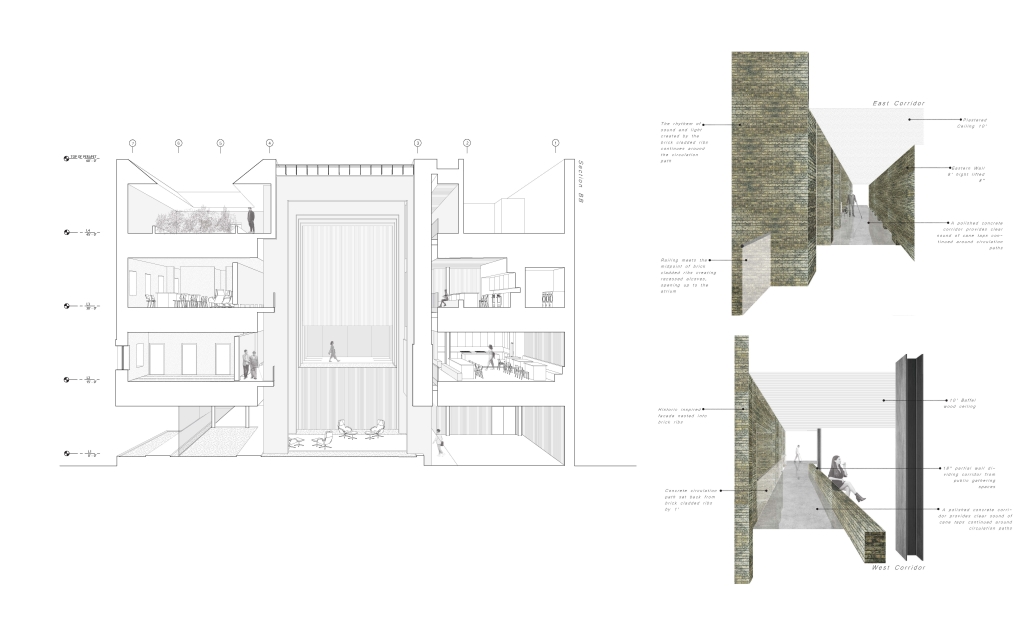
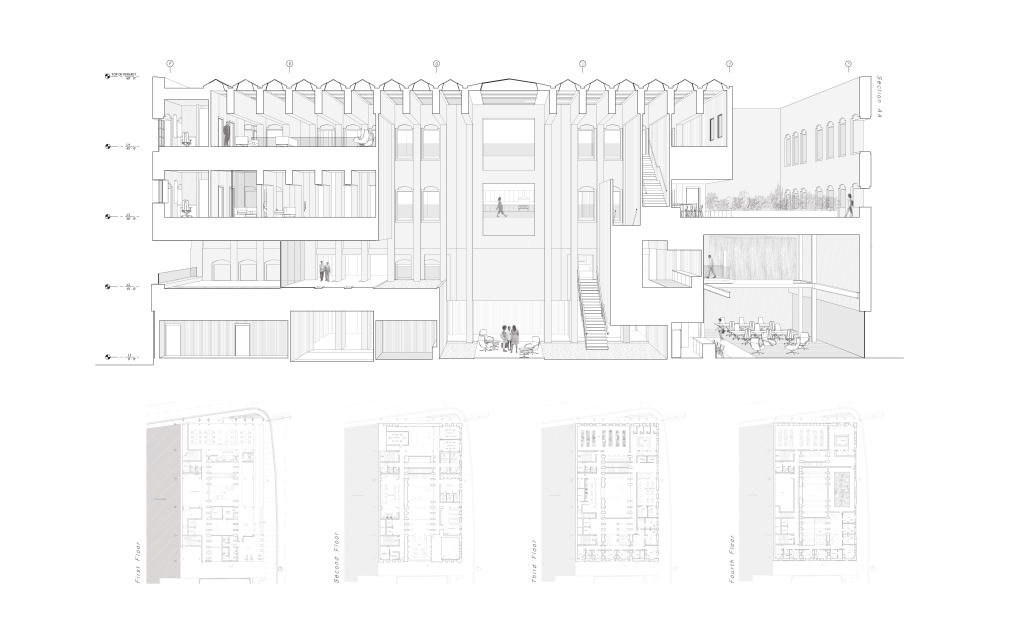
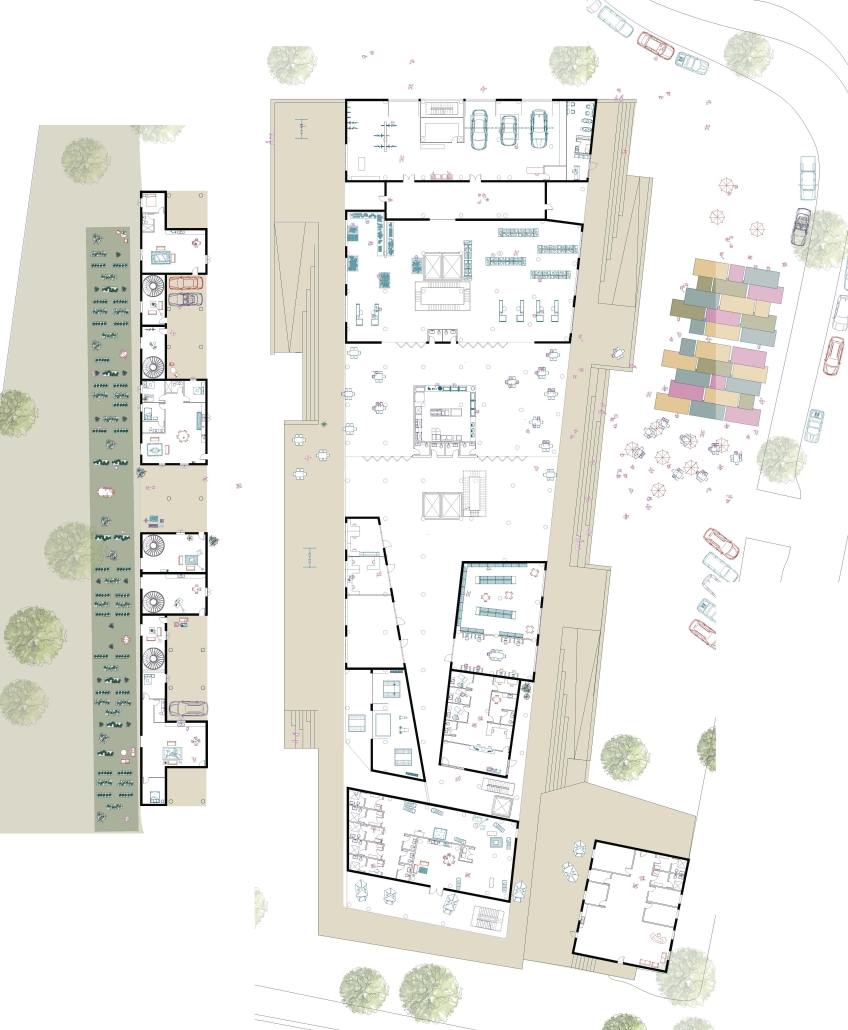
“Jackson’s Center for the Blind and Visually Impaired” is a training facility that empowers individuals with vision loss to gain greater independence. This project explores the understanding that design solutions addressing the needs of the blind and low-vision communities are universally beneficial—enhancing the spatial experience for all users by deepening the sensory richness of the environment. Located at one of the most prominent and sensory-rich intersections in Jackson, Mississippi, the training center creates a space for its user group within the city that celebrates the acceptance of diverse perspectives in urban environments.
Across the street once stood the first location of the Institute for the Blind in Jackson. The geometry of this original building has become the base of the façade, which is intentionally disrupted with boxed bronze window openings that pierce through the underlying rhythm, contradicting the established grid to create moments of tension. Sculpted from green glazed brick with medium gray mortar, the materiality speaks to the context and historic structure without attempting to replicate the past, while celebrating the primary user group’s history within the community. The green glazed mass levitating above the ground reveals a district condition of light and sound from the street at the entry to indicate arrival.
Transforming a visual gesture of the façade becomes a spatial and sensory one by folding the façade into the atrium. This fold generates a dynamic threshold, one that informs circulation and invites engagement. Brick-cladded ribs, consistent in their cadence, wrap the atrium like a metronome marking time in built form. Each cardinal direction of the atrium is delineated by the program that borders the path in a distinct manner – designed to communicate wayfinding and the presence of others.
This project received the CDFL Capstone Studio Travel Award.
Instagram: @designs_by_akhorn, @jassencallender
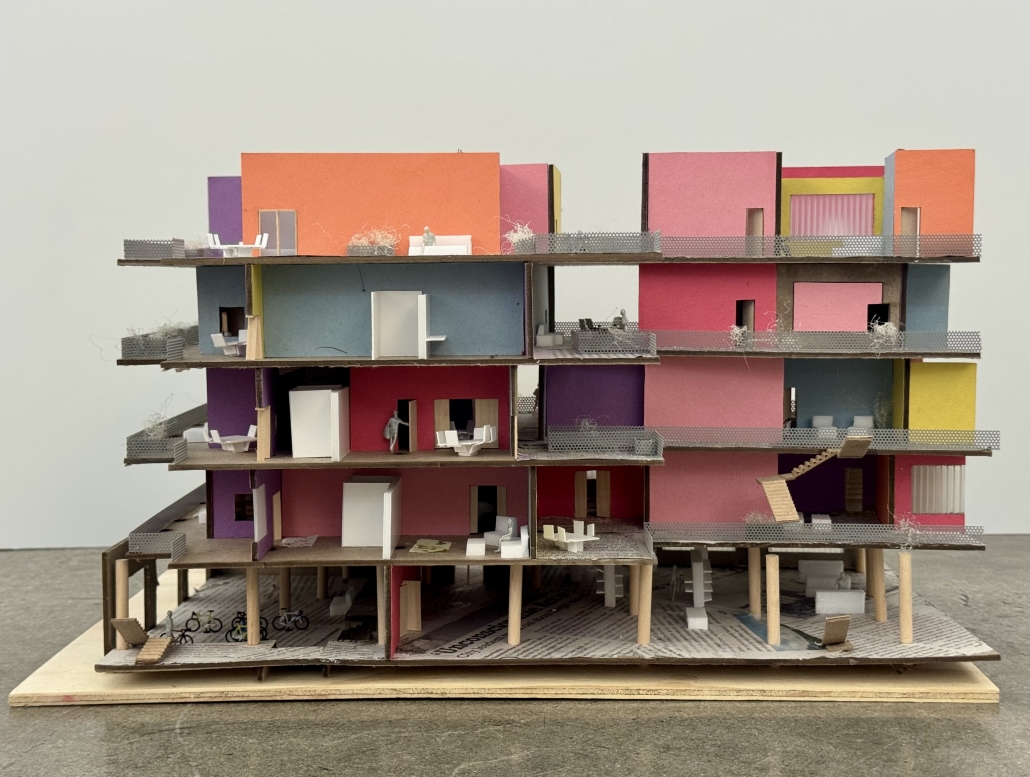
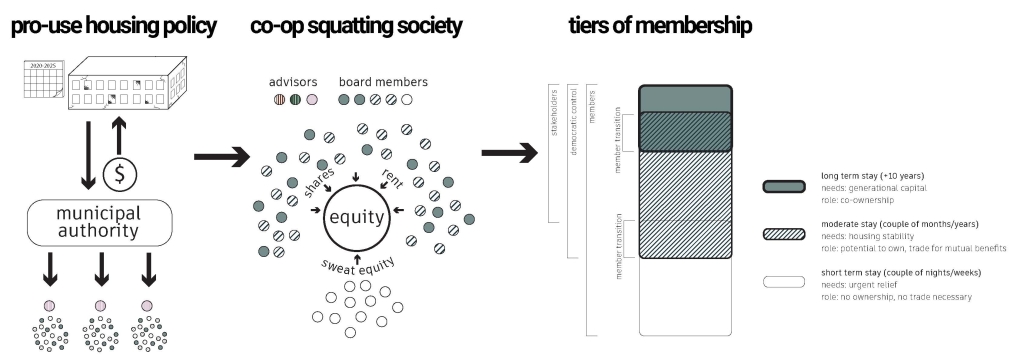
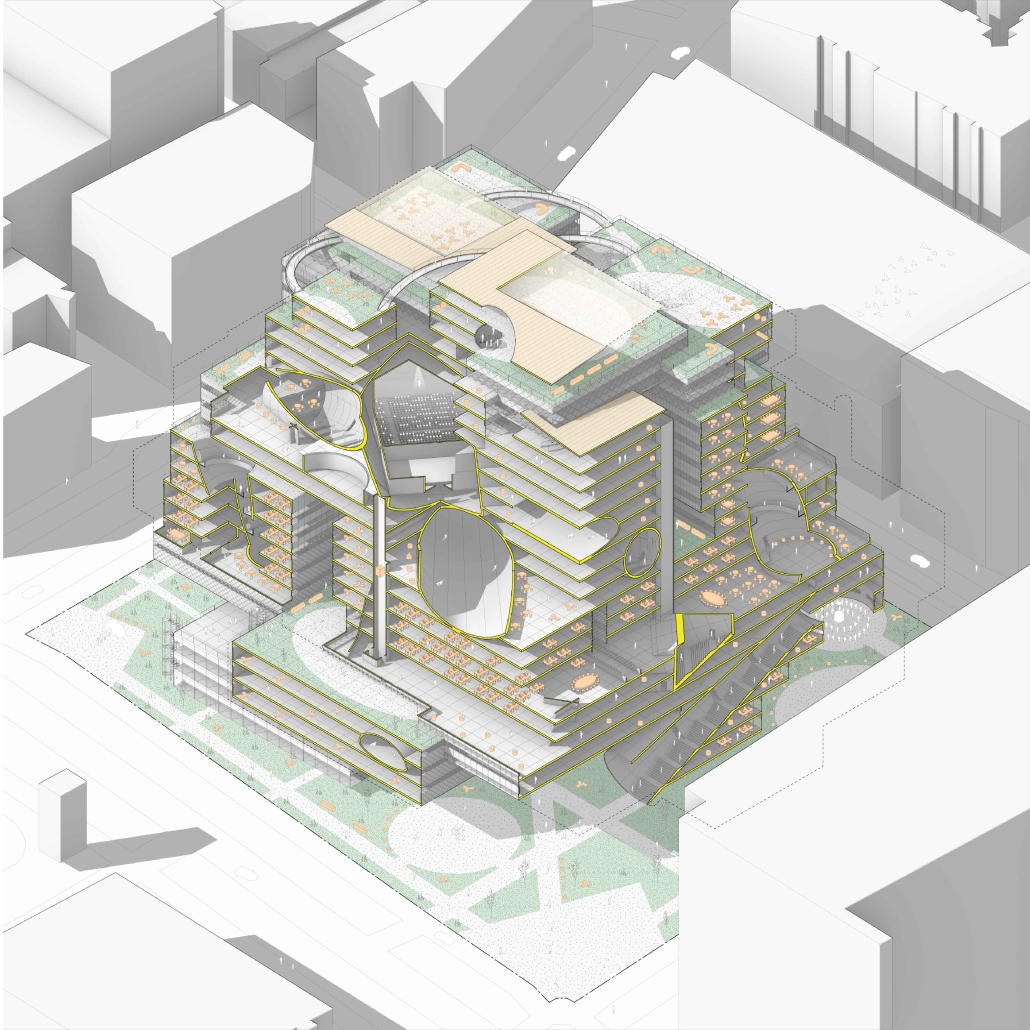
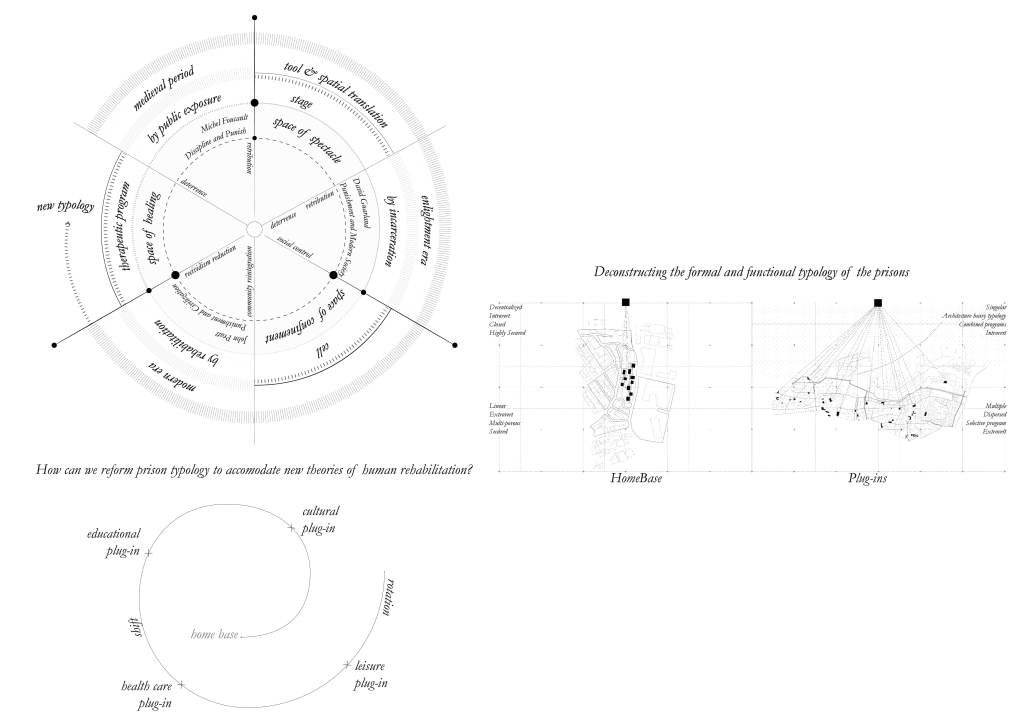
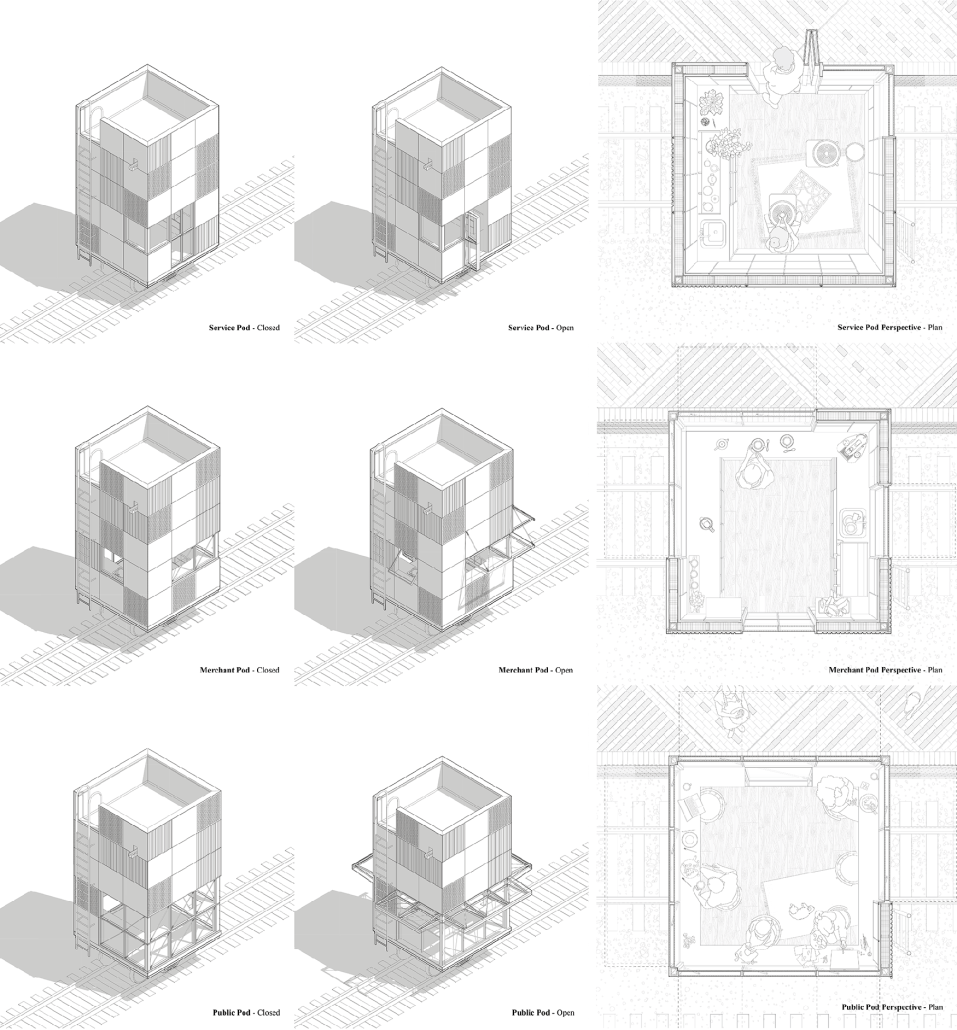
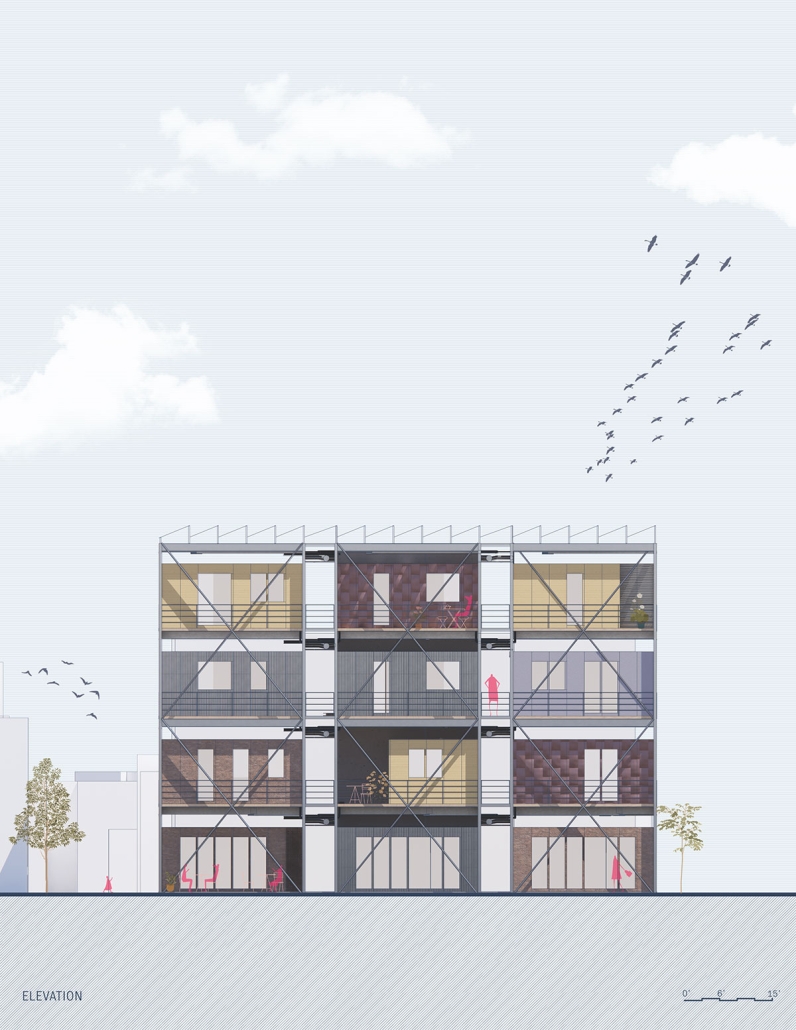
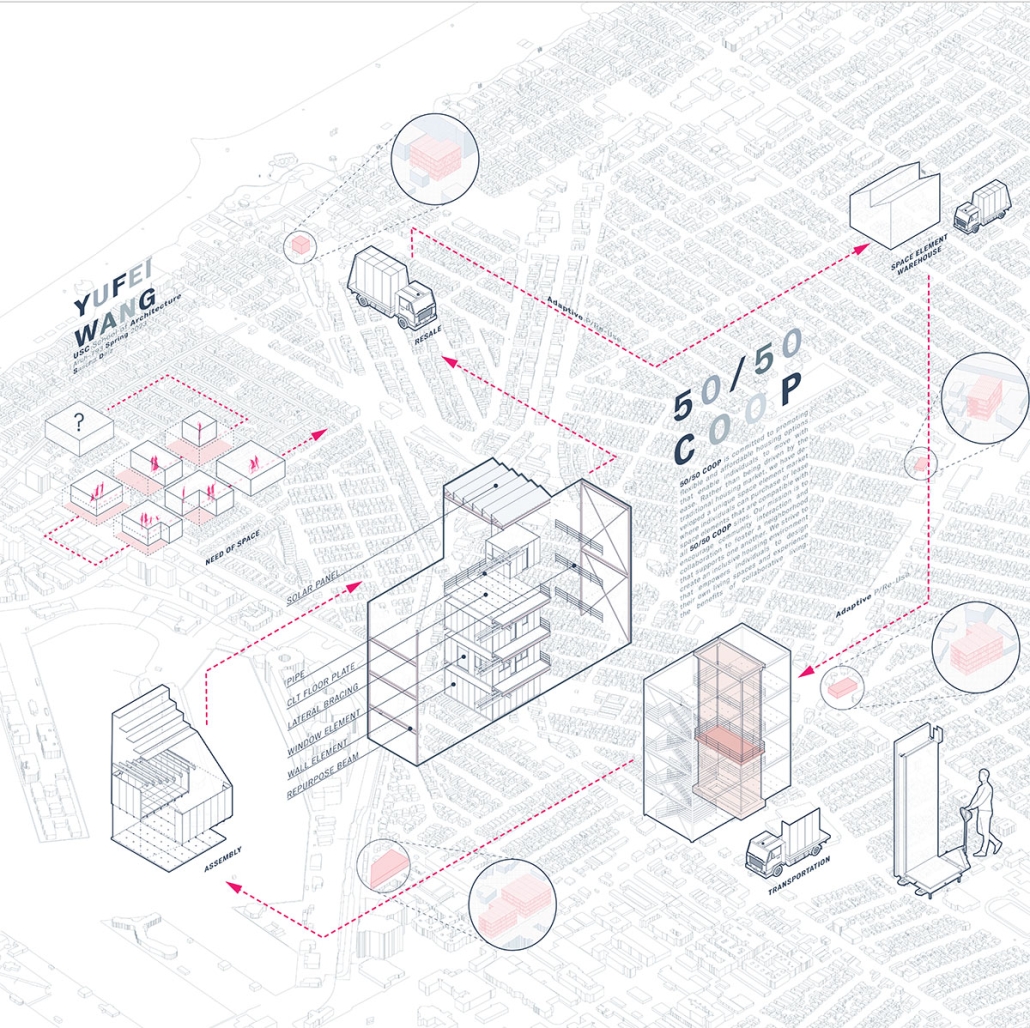
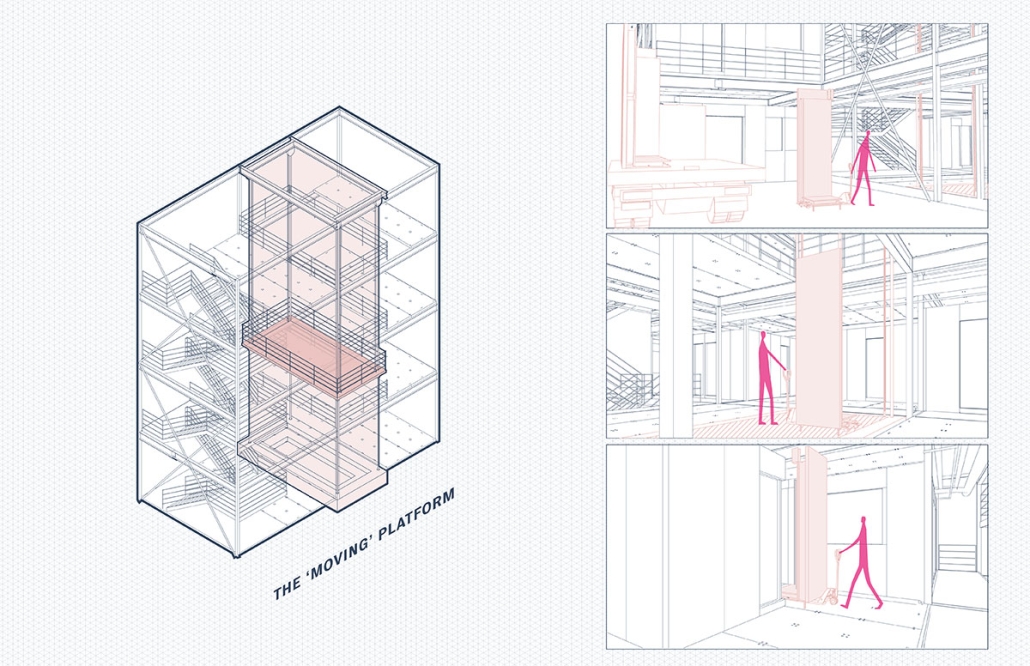
ReOCCUPY Your City – The Co-operative Squatting Society by Nour Kaddoura, M.AARS City Design + Housing (CDH) ’25
University of Southern California | Advisor: Sascha Delz
For many marginalized individuals and communities, informal practices are an essential means of gaining access to services and spaces that are otherwise unavailable or unaffordable. This is especially true for shelter and housing, where squatting often serves as a last resort. While property owners have broad legal means to evict squatters, squatters also hold limited rights, leading to often adversarial and protracted legal battles.”ReOCCUPY Your City” offers an alternative approach to squatting. By combining a supportive legal framework, a Pro-use Housing Policy, and formalized Co-operative Squatting Societies, it empowers squatters to take control of vacant industrial properties, transforming them into collaborative spaces that provide affordable housing for Los Angeles.
Under the Pro-use Housing Policy, a group of dwellers can form a Co-operative Squatting Society, claim collective ownership of an abandoned building, and gradually inhabit and manage it democratically over time. As residents join, their involvement in the co-operative can evolve from emergency occupancy to transitional and ultimately permanent residency. ReOCCUPY Your City thus enables a community-driven, democratic reuse of vacant buildings, empowering squatters to not only claim and improve these structures but also to contribute to the city’s housing stock. The project also allows the city’s housing administration to make underutilized spaces progressively productive, offering affordable, self-governed housing solutions.
Instagram: @coop_urbanism
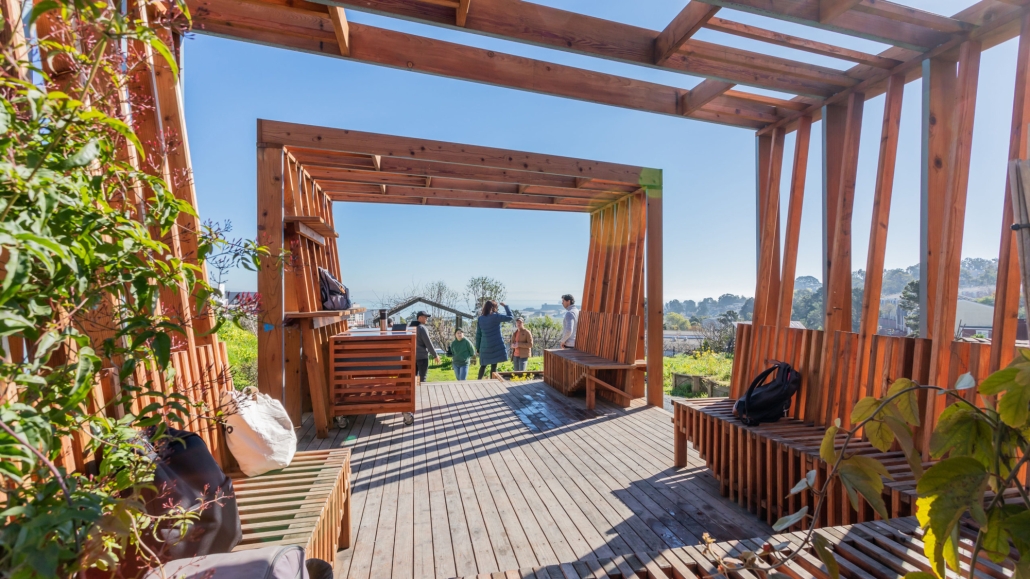
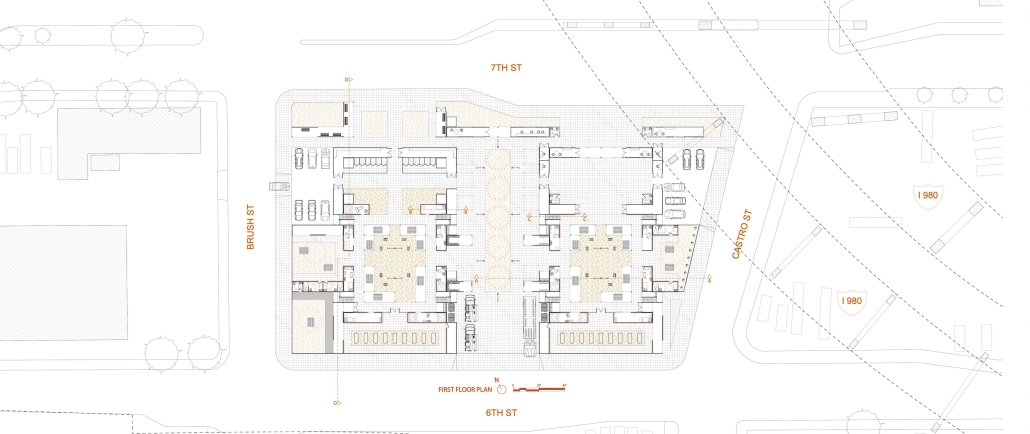
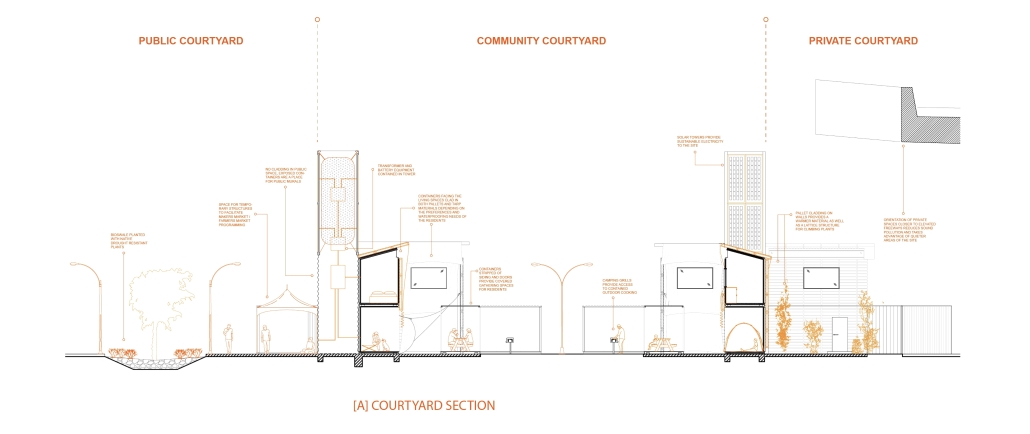
B.lab Community-Based Design by Lowai Ghaly, Mazen Ghaly, Mohamed Meawad, Andrew Hart, Kim Ebueng, Kenny Soriano, Edgar Castillo, Peter Peritos, Shadi Vakilian, Amanda Estrada, Giewel David, B.Arch ’25
Academy of Art University | Advisor: Sameena Sitabkhan
The B.lab program at the Academy of Art University was founded in 2018. Through robust partnerships with our neighbors and local nonprofit organizations, the program has implemented several projects in the Bay Area. At its core, the B.lab program is a community-based design program promoting spatial justice and advocacy for future designers. Through radical listening and co-creation, we empower communities and bring positive change to the built environment.
This project received the B.Arch Community Building Award.
Instagram: @studio.sideproject
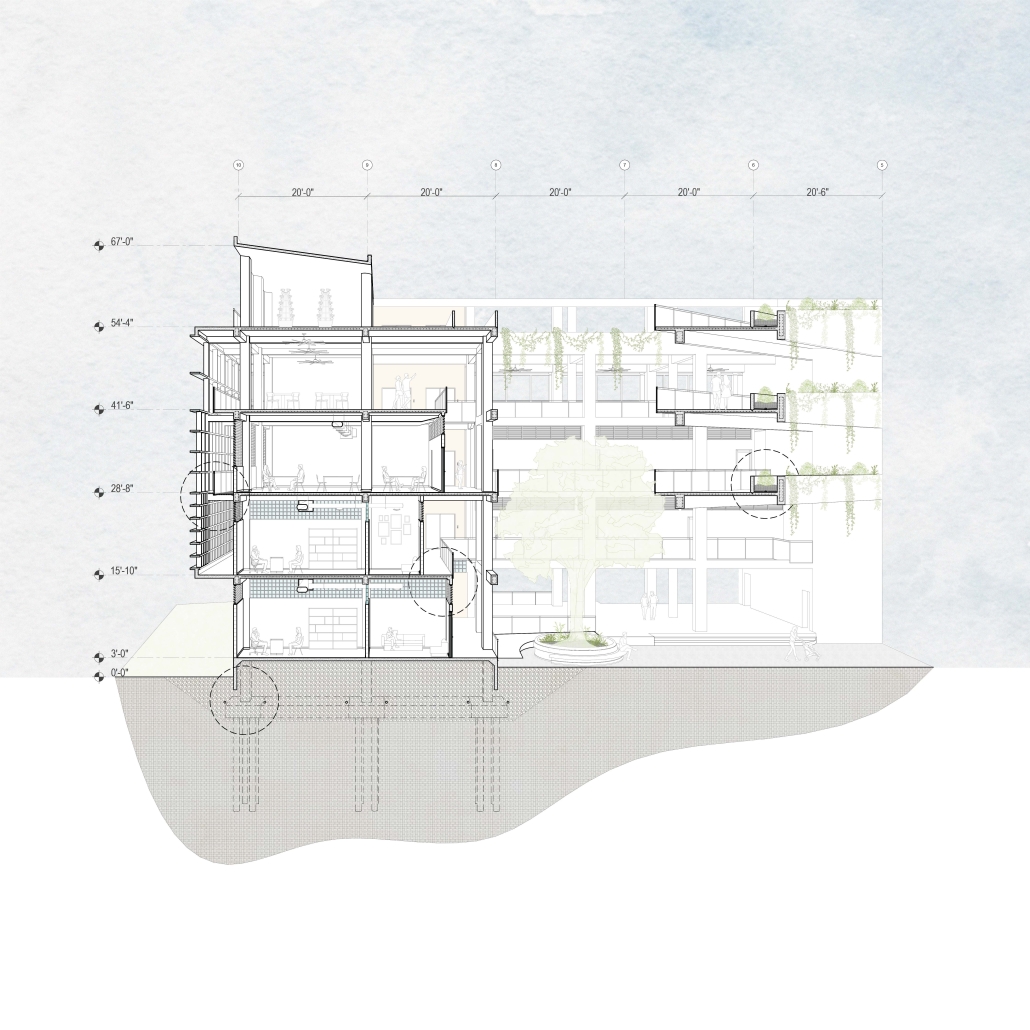
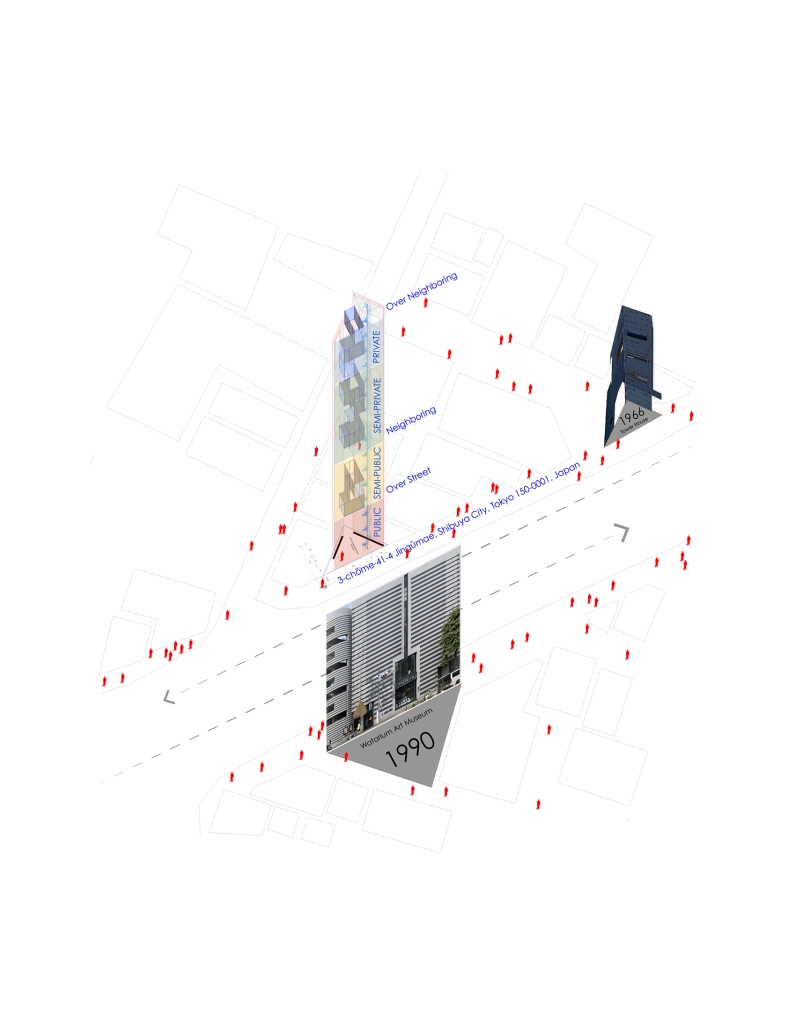
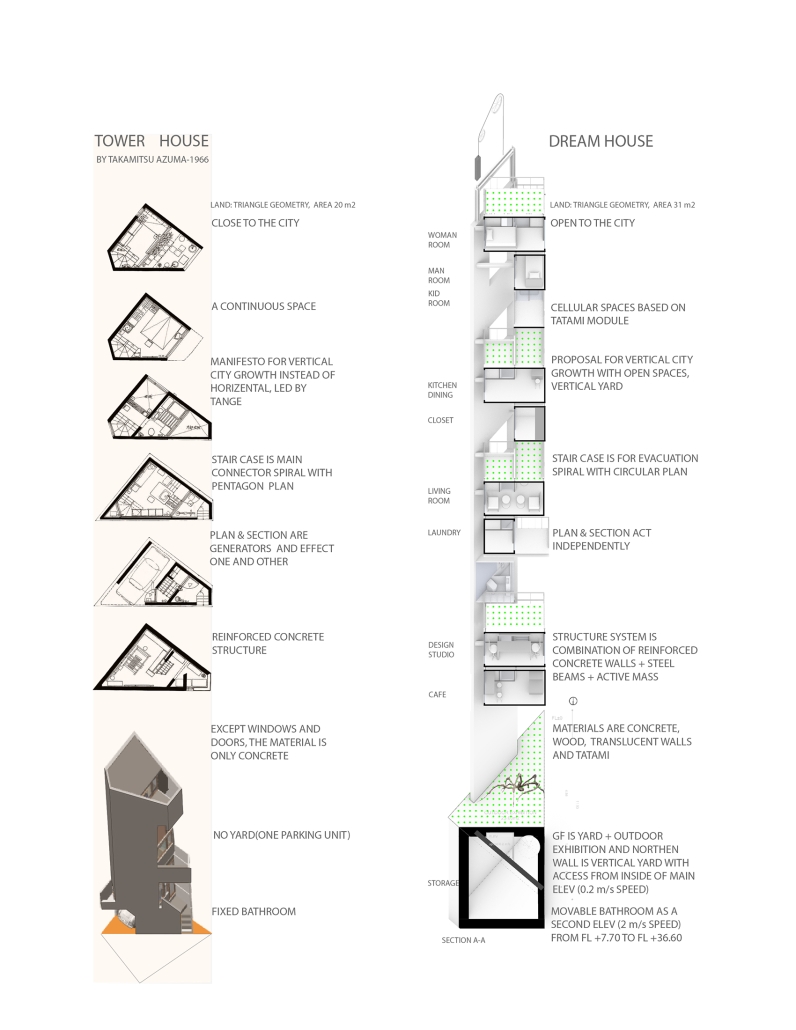
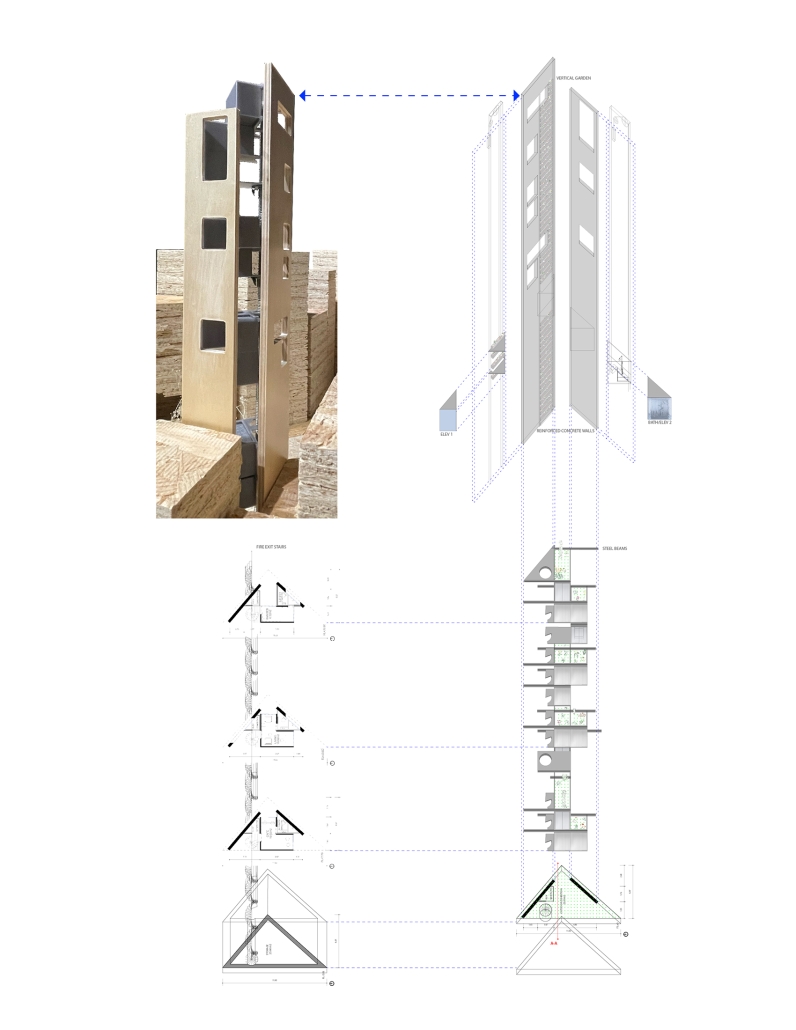
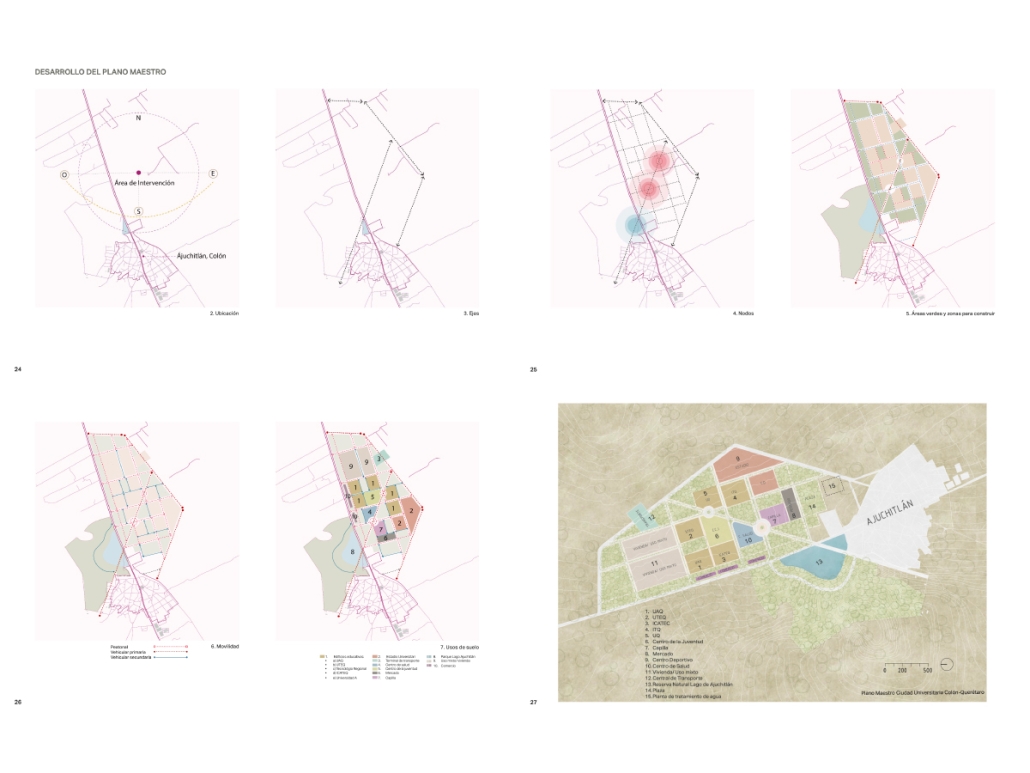
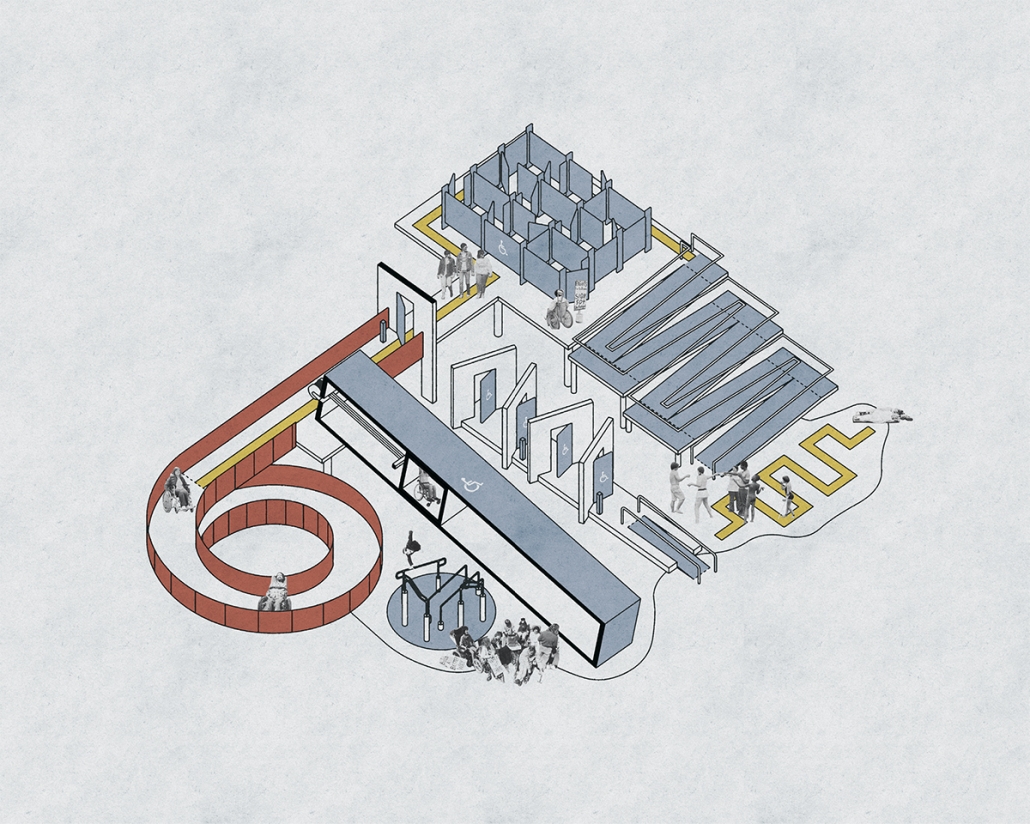
Empowerment Center by Devangi Patel, M.Arch ’25
Boston Architectural College | Advisors: Emeline Gaujac, AIA. & Ian F. Taberner, AIA.
This thesis proposes the design of an Empowerment Center for Women in Vrindavan, Uttar Pradesh, India, as a response to the social, cultural, and economic marginalization of widows and single mothers in the region. Vrindavan, often referred to as the “City of Widows,” is a place of profound spiritual importance. It is home to thousands of women who are abandoned and forced to live in poverty, social isolation, and emotional distress.
The Empowerment Center aims to restore dignity, independence, and resilience to these women by offering a comprehensive, community-based center that integrates education, skill development, emotional healing, and economic empowerment. The architectural vision emphasizes a balance between safety and openness, combining secure, private zones with transparent and inclusive spaces that encourage connection, confidence, and personal growth.
Key features of the design include sustainable green areas such as gardens and courtyards, and also form is Inspired by inspired by local vernacular architecture and supported by research. These spaces foster mindfulness, promote physical and emotional well-being, and create opportunities for community interaction and collective healing. The project incorporates flexible, adaptive spaces for workshops, training, and communal living to support the evolving needs of its users.
Using techniques including demographic analysis, community participation, and contextual site study, this thesis, which is based on collaborative research and cultural sensitivity, informs an inclusive, accessible, and responsive design. The Empowerment Center seeks to establish a standard for gender-sensitive, socially conscious architecture that not only meets immediate needs but also sparks long-term structural change.
In conclusion, this thesis demonstrates how architecture can serve as a cause for social transformation by addressing the needs of marginalized women in Vrindavan. The Empowerment Center offers a dignified, inclusive, and healing environment that fosters education, independence, and community. By integrating cultural sensitivity with sustainable design, the project aims to empower women and inspire broader change toward gender equality and social resilience.
This project received “Commends for Thesis.”
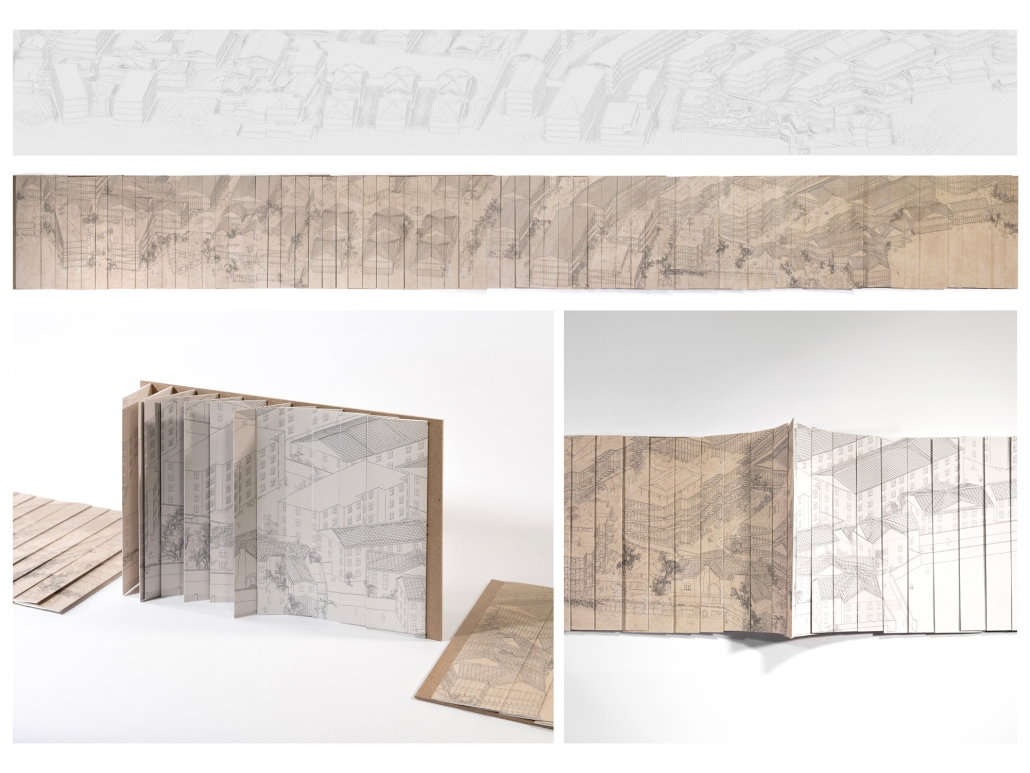
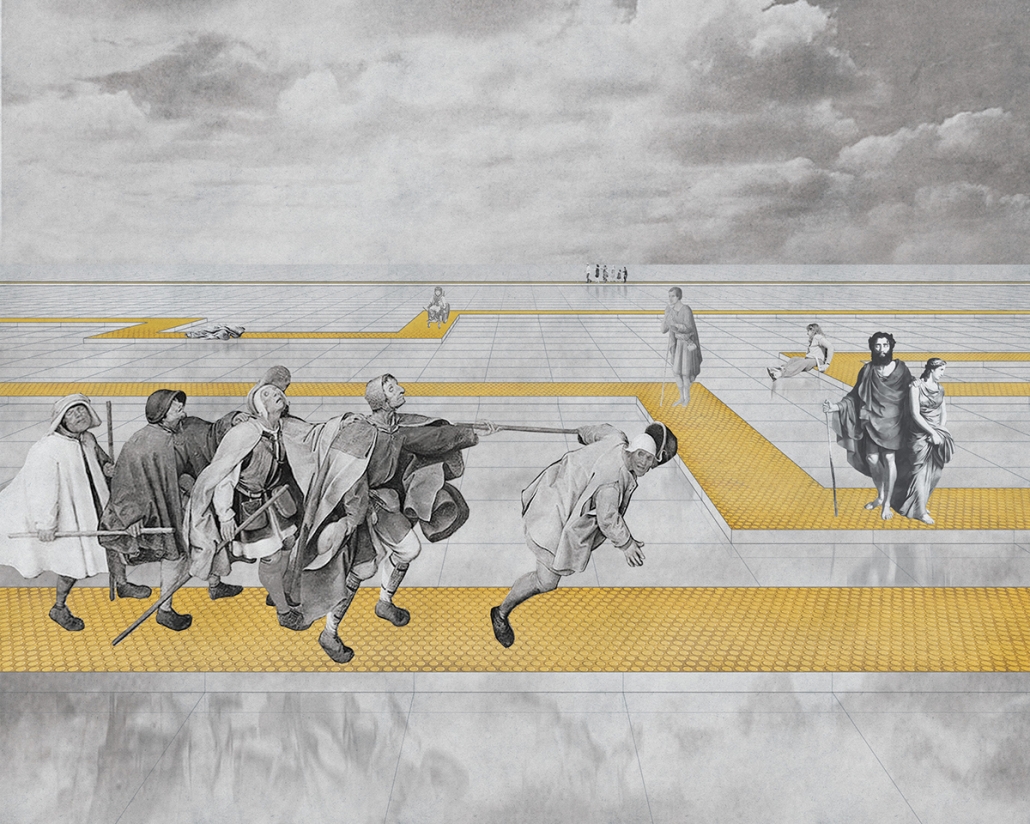
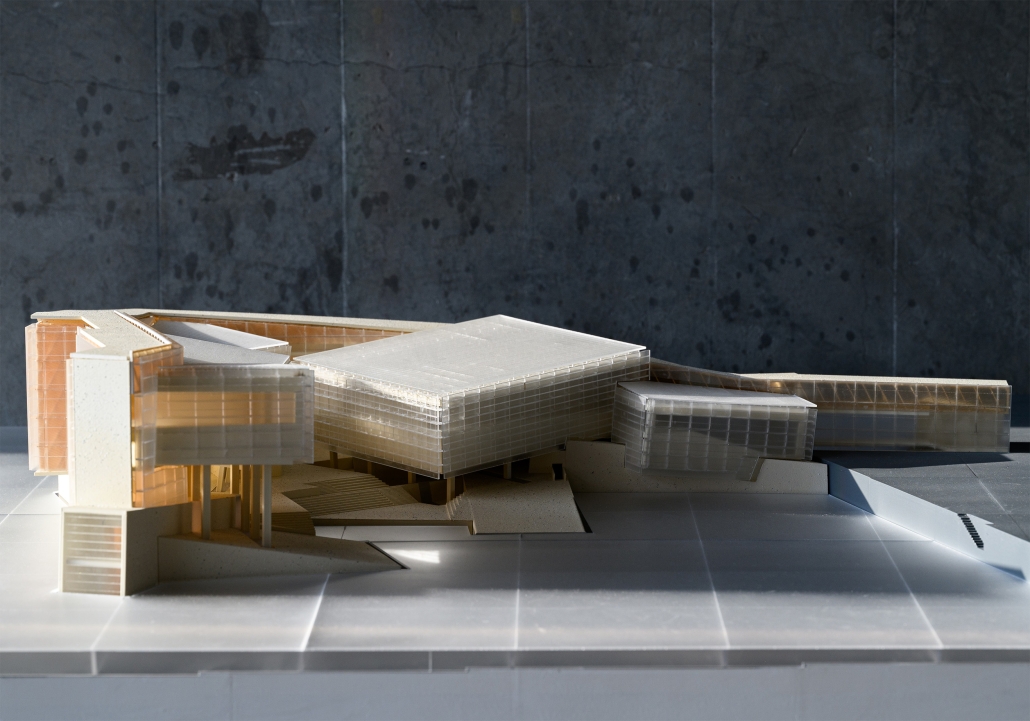
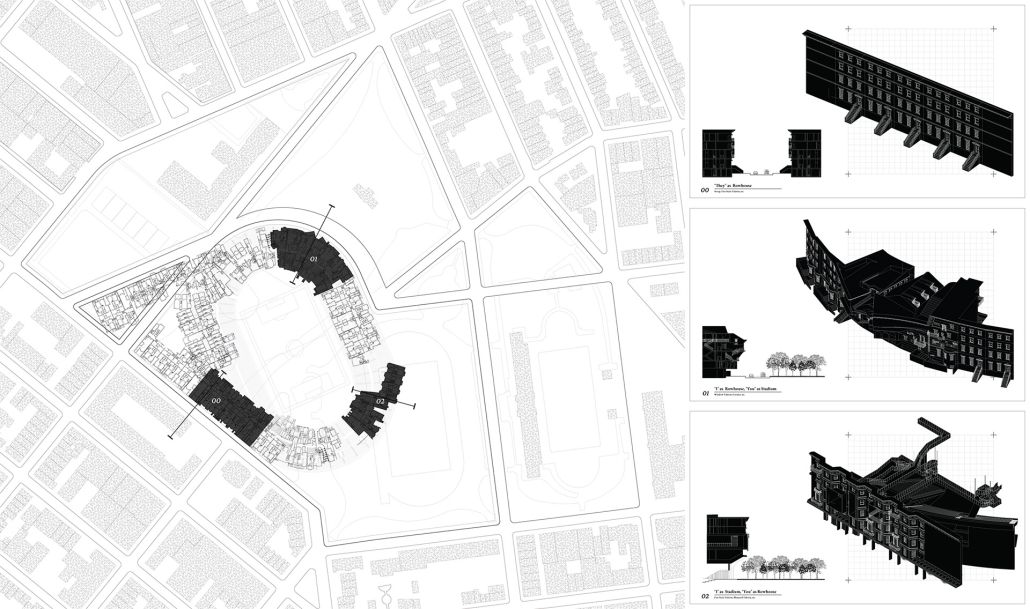
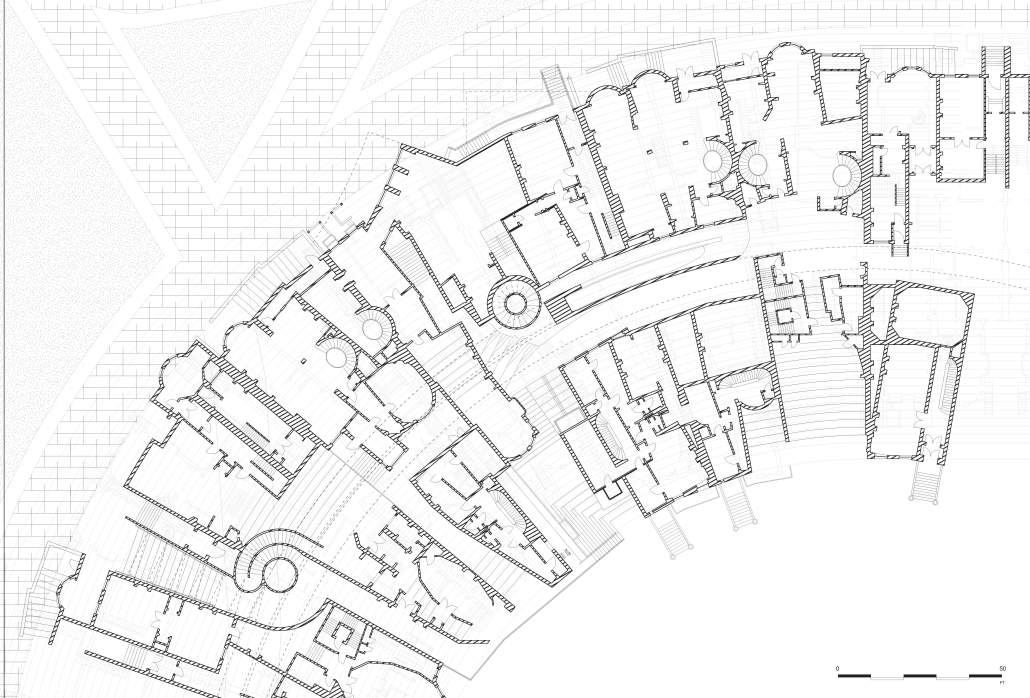
The right to the city by Cindy Caitong Duan, M.Arch II ’25
Yale University | Advisors: Andrei Harwell & Alan Plattus
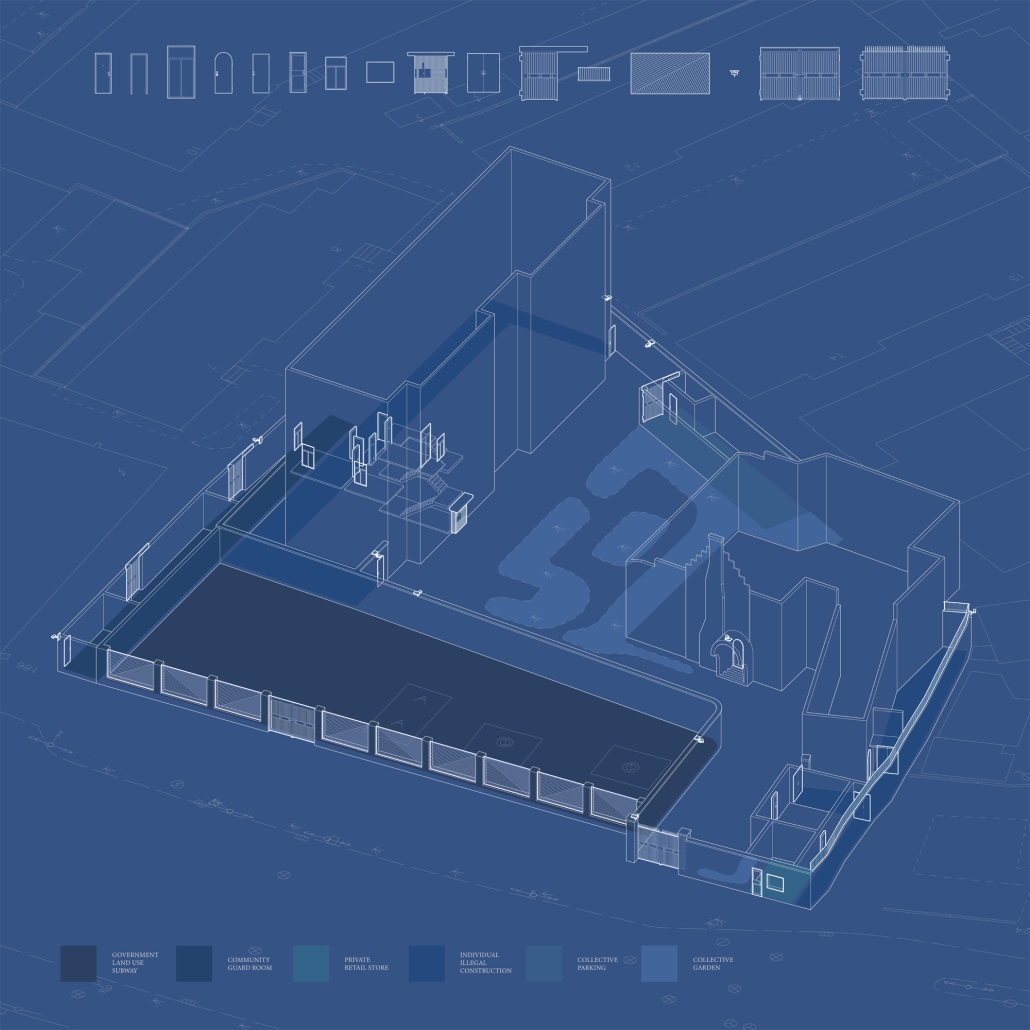
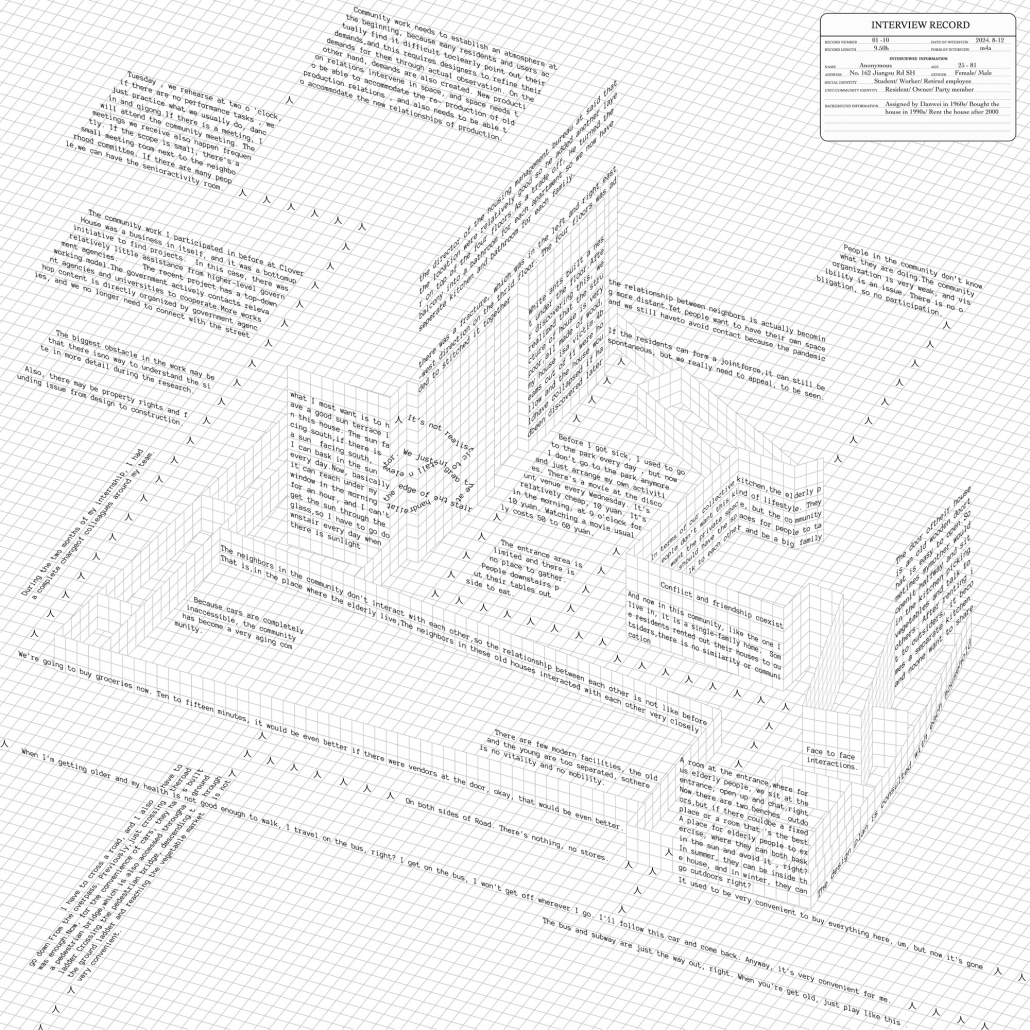
The cities in China have a long tradition of planning based on the gated unit – a collective residential form strictly controlled by entrances, walls, and different levels of thresholds. People live within walls, which define the space of a gated unit; and in the wall that is the building itself. Walls gather us but also limit us, until their imprints are etched into our minds and build obedience and indifference to life. These spaces are both the metaphor and the embodiment of power in Chinese society.
In this way, I feel it is necessary to ask: What is a city? What should the balance be between governance and defending people’s rights to the city?
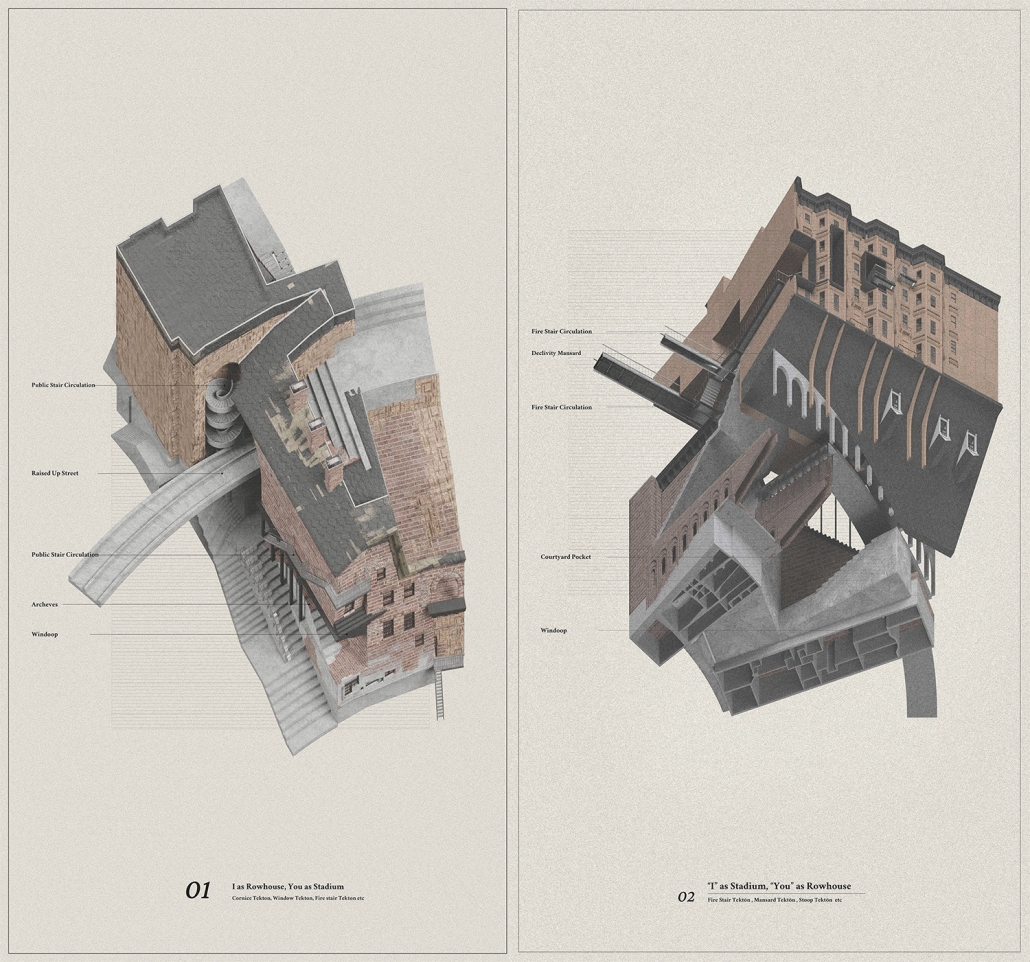
This thesis addresses these questions through a close study of the gated unit where my grandaunt lives in Shanghai, China. The project comprises two parts: first, research analyzing the formation of collectivism and the gated unit; second, a design proposal exploring how gated communities can actively foster local identity and autonomy while mitigating surveillance and urban segmentation.
The concept of “collectivism” fosters a stronger sense of solidarity but also poses the risk of deindividuation by homogenizing people. As a result, the notion of collective space shifts from being a symbolic space of belonging to a geographically defined common space, diminishing the notion of individual residents’ rights.
However, I believe a city and its built form should be the second self of the individual, responding to and encouraging open narratives. Gated units and their communities can be transformative, connecting individuals while forming a new entity based on shared agency. More importantly, whenever the collective emerges, it arises from countless “I”s—each independent, each different—reaching a timely commonality through mutual agreement. There is no single form.
Thus, this project is not the solution but a demonstration of how to regain an individual’s right to the city. It can strike a balance between you and “I”, between us and “I”, and between them and “I”, and the city is its metaphor and site.
This project received the Yale Drawing Prize.
Instagram: @Cindycaitongd, @andrei__simon
Stay tuned for Part VI!