2022 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part VI
Welcome back to installment Six of the Study Architecture Student Showcase series! This week we share six student projects that take a look at the role of architecture in conflict. From Korea to Russia to Afghanistan, these projects show how conflict effects the identities of communities and how architecture fits into that balance.
For a recap on the 2022 Student Showcase series so far, check out Part I, Part II, Part III, Part IV, and Part V.
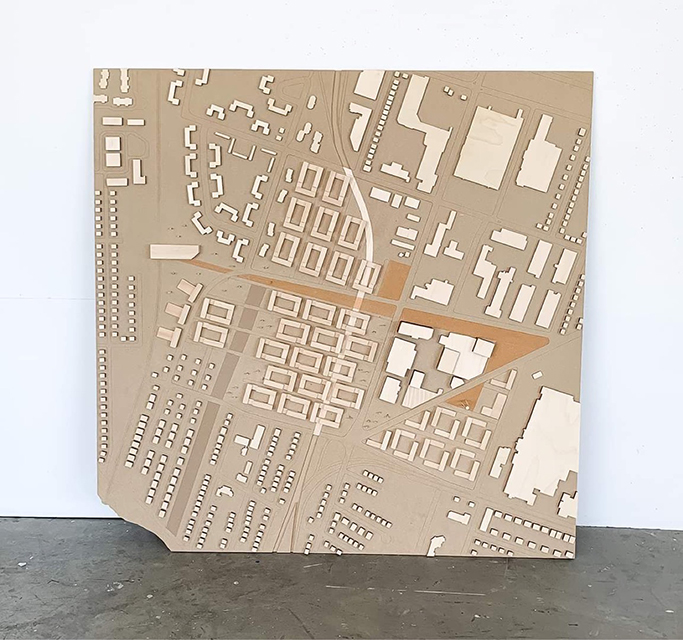
Angle Masses: Korean War Memorial Museum in Seoul, Korea by Joo Young Lim, B.Arch ’22
Auburn University | Advisor: Il Kim
History of Korean War
At the end of World War II, Joseon (archaic name of Korea) was freed from Japanese occupation. Soon, the victorious countries drew the border line on the Korean Peninsula based on 38th degrees north latitude. The north side of this border, the 38th Parallel, was occupied by the Soviet Union’s socialist force, and the United States’ capitalist force took the south. As Kim Il-Sung (North Korea) invaded the south across the 38th Parallel, the peninsula became a field of proxy war of ideological forces.
Design
A history timeline is set as X-axis, and a territorial shift between the north and the south as Y-axis. The representation of the 38th Parallel is parallel to the X-axis. Various historical events, including conflicts, were expressed as slits on the passage of the 38th Parallel.
The triangular masses are designed to pierce across the representation of the 38th Parallel. These triangular masses symbolize the military forces in the Korean War, and they vary in size depending on the strength of the forces. Interlocking with the axis of time, each of four triangular masses represents Kim Il-Sung’s invasion of the South Korea, U.S. and U.N.’s military supporting the South, the Chinese People’s Army supporting the North, and lastly, months of long siege.
Each of reversed-pyramid triangular masses elucidates war’s grave consequences. They are seemingly unstably connected to each other, and their dark metal exterior panels represent the gloomy war. Inside, the viewer, walking on the ramp between RC concrete columns, thinks she/he is passing through the ruins of war. The floating tips of the reversed pyramids are visible in the underground gallery. This sense of floatation was achieved by extending the RC concrete columns in the middle of the structures. The shards of glass-like tips represent the agony of the victims and refugees. These tips visually connect the upper gallery and the lower, underground gallery. The upper gallery illustrates the power game of the war written by the political forces who started the war, while the underground gallery displays the relics of the victims who were anonymous citizens.
Instagram: @limarch94
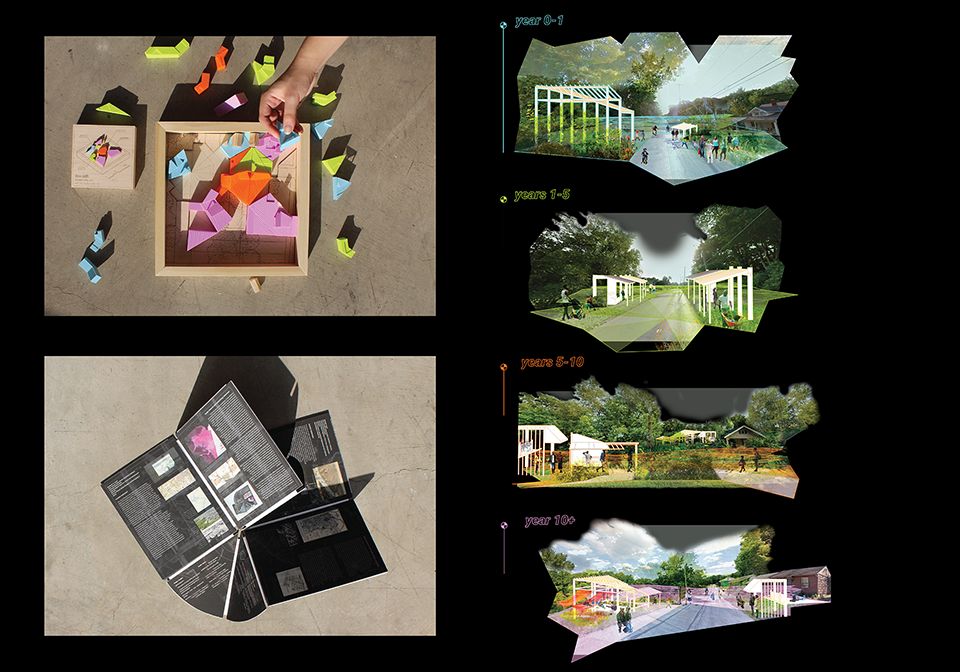
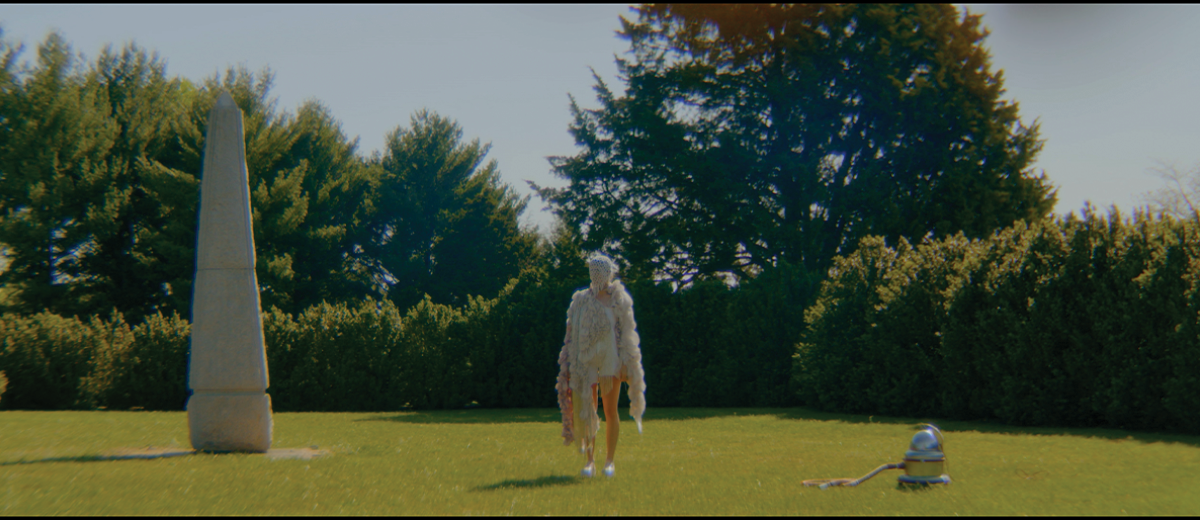
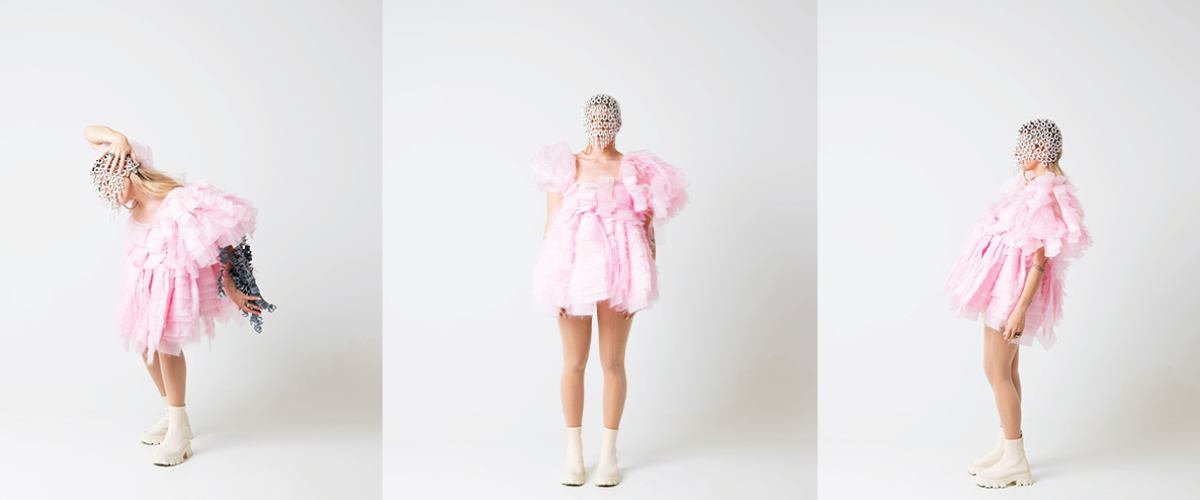
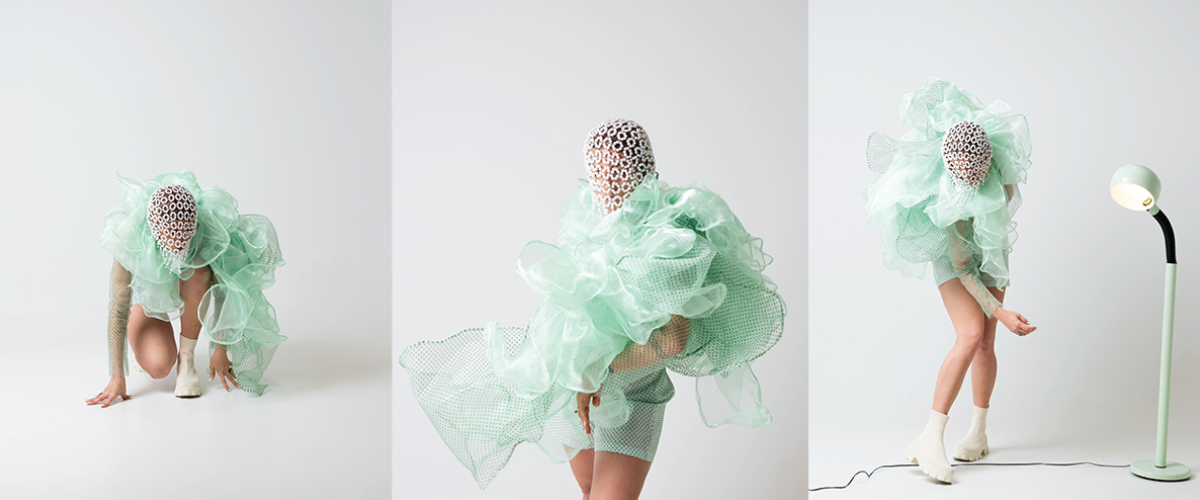
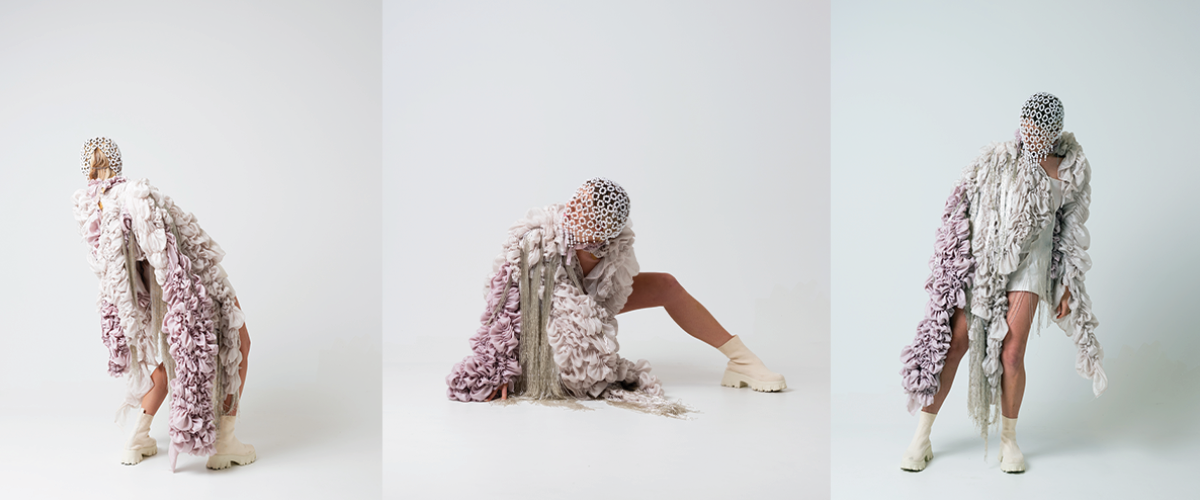
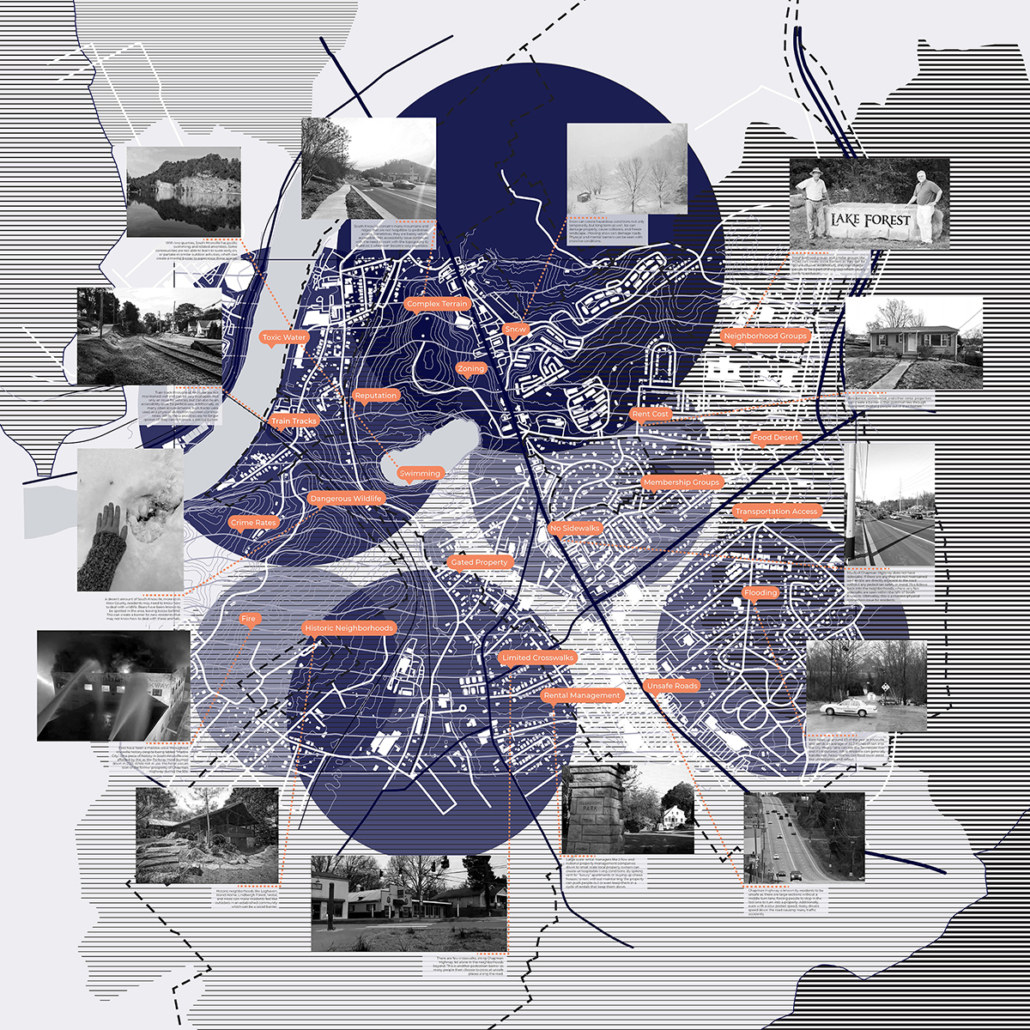
The Two Sides of Otherness: A Cross-Cultural Regeneration of Reality by Daniel Porwoll, M.Arch ’22
North Dakota State University | Advisor: Stephen Wischer
In our current context, “identity” often stands as an edge where one being ends and the next begins; simultaneously separating and unifying. Yet, this inherent overlapping between self and other continues to be threatened by ideological and homogenizing narratives; either as a force of assimilation or division.
Among the many affected areas around the world is the Korean Demilitarized Zone, the Russo-Ukrainian Border, and the Carlisle Pennsylvania Indian Cemetery, in which hostile situations pose a unique yet difficult edge condition that might be mediated by empathetic imagination instigated by architecture. Responding to each situation, we examine how architecture might act as an archive for deeper understanding and exchange in an attempt to mediate new realities.
Philosopher Maurice Merleau-Ponty confirms this method through his concept of “flesh”, which examines the relationship between oneself and the Other as “reversible,” wherein edges become folds in order to gain a deeper interpersonal, intercultural and intersubjective understanding of the Other ourselves.
Instagram: @dkp.arch
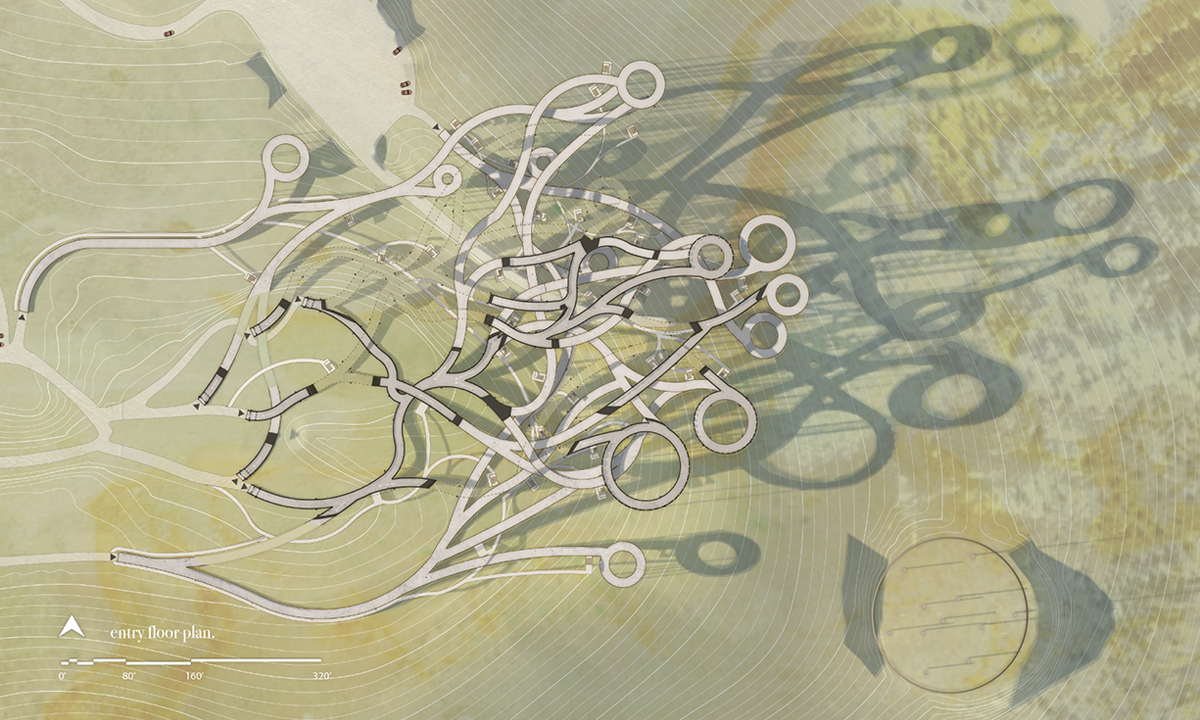
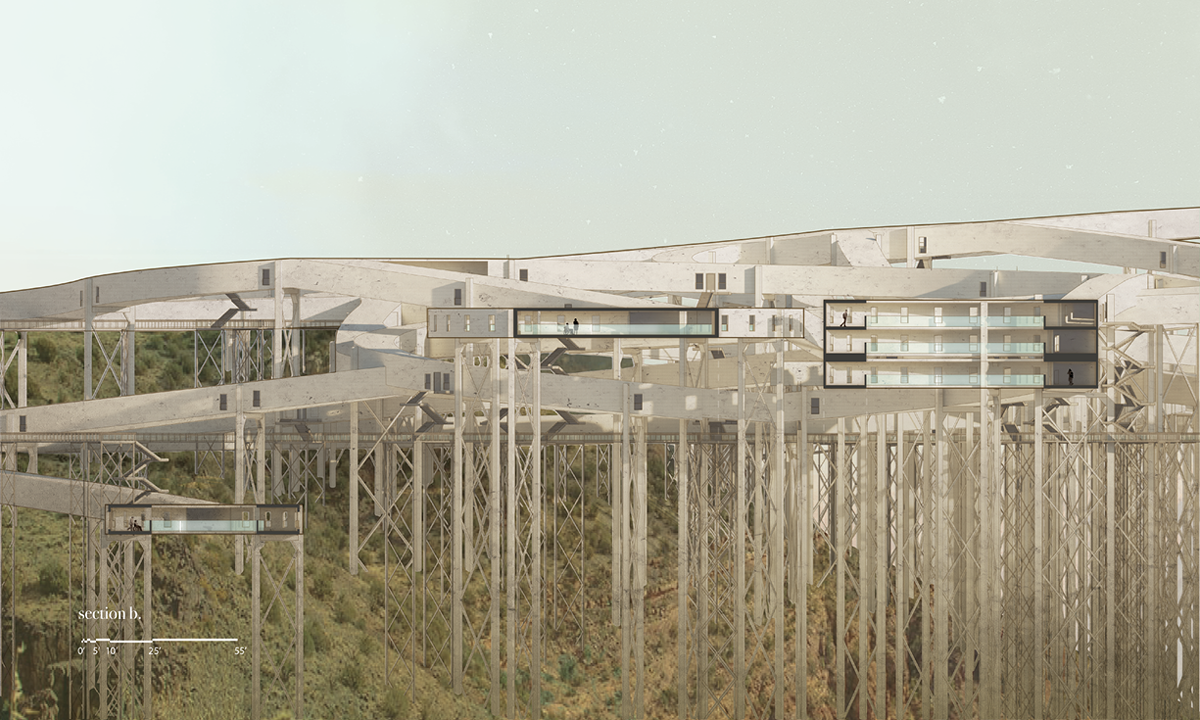
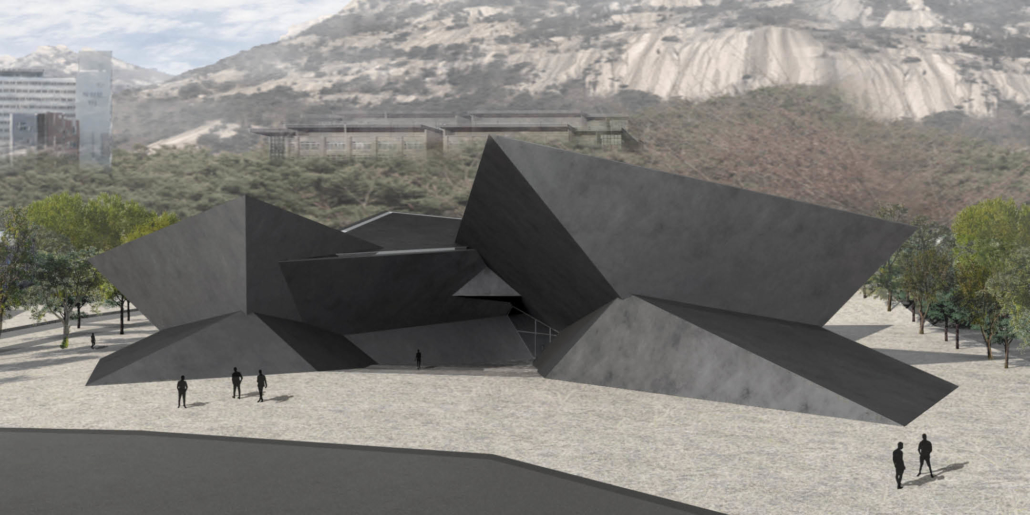
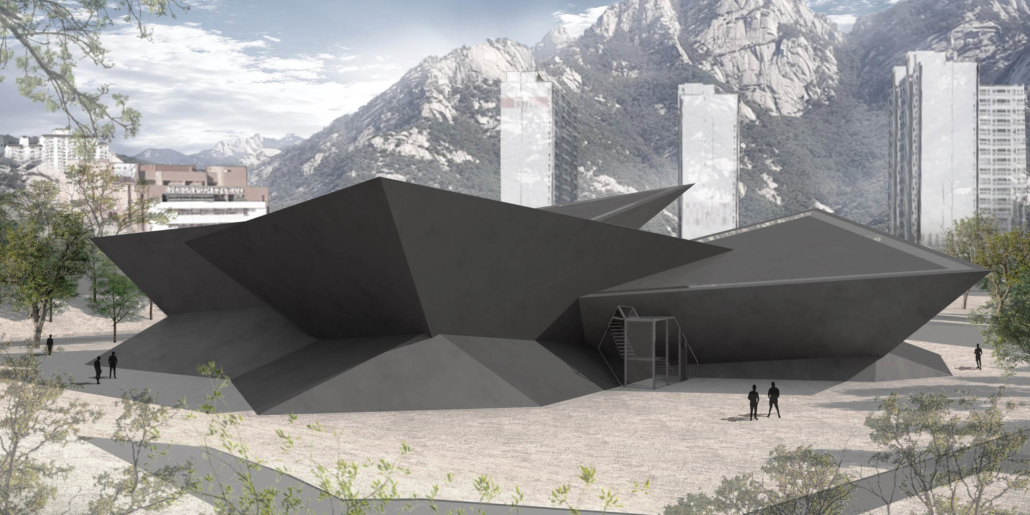
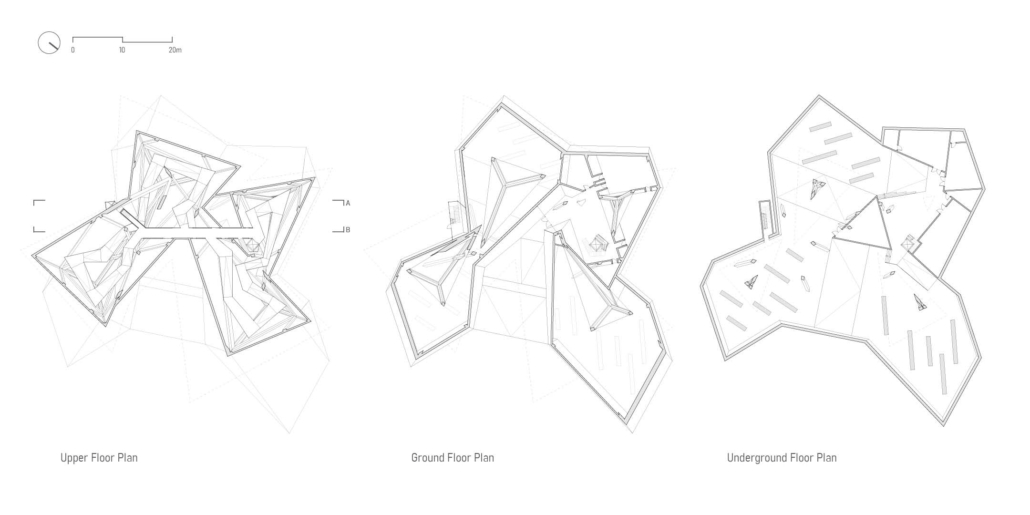
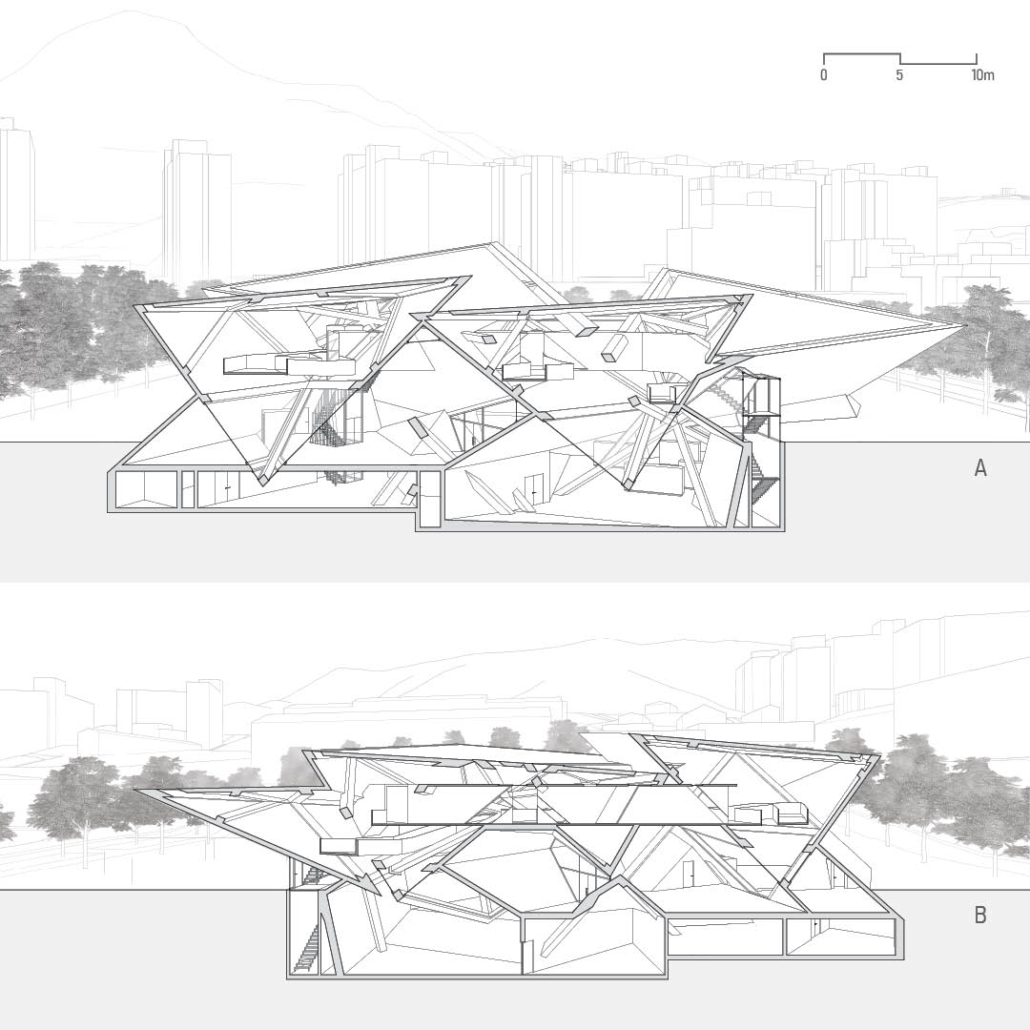
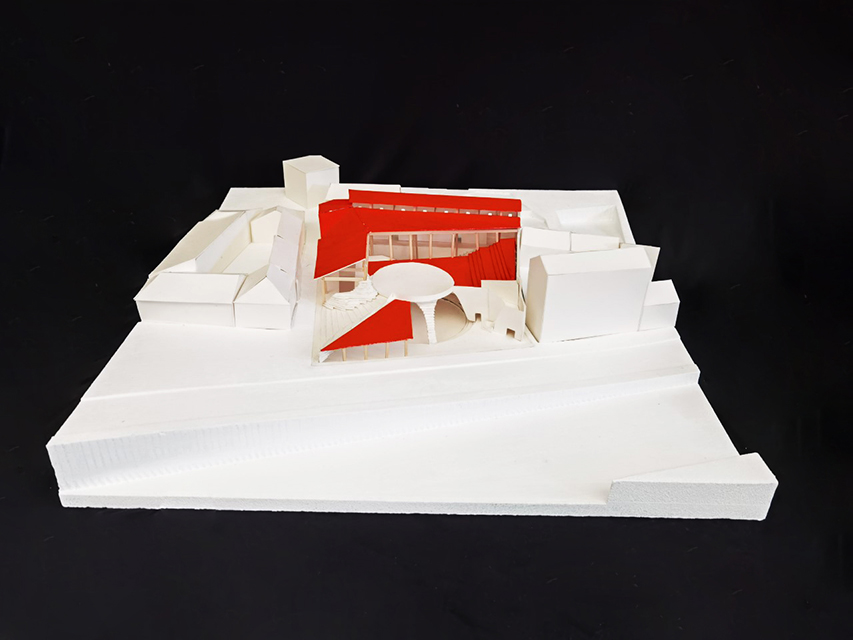
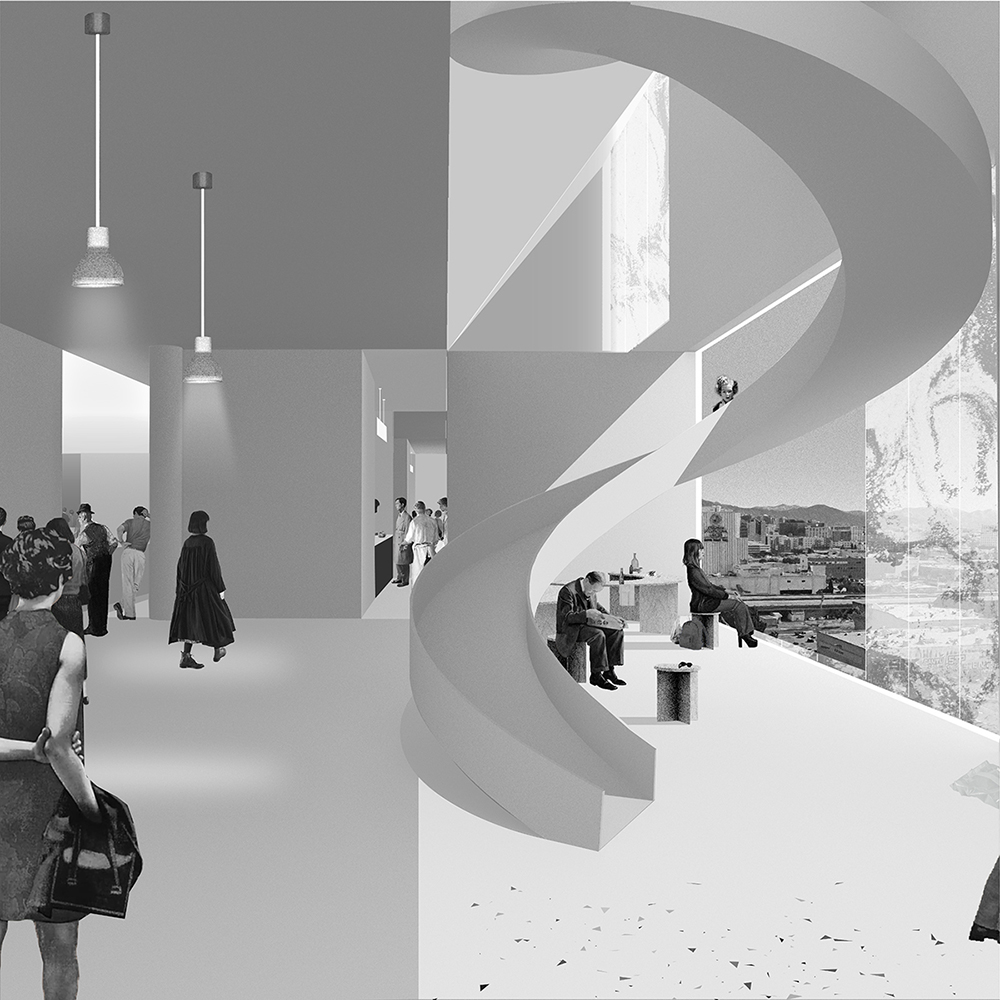
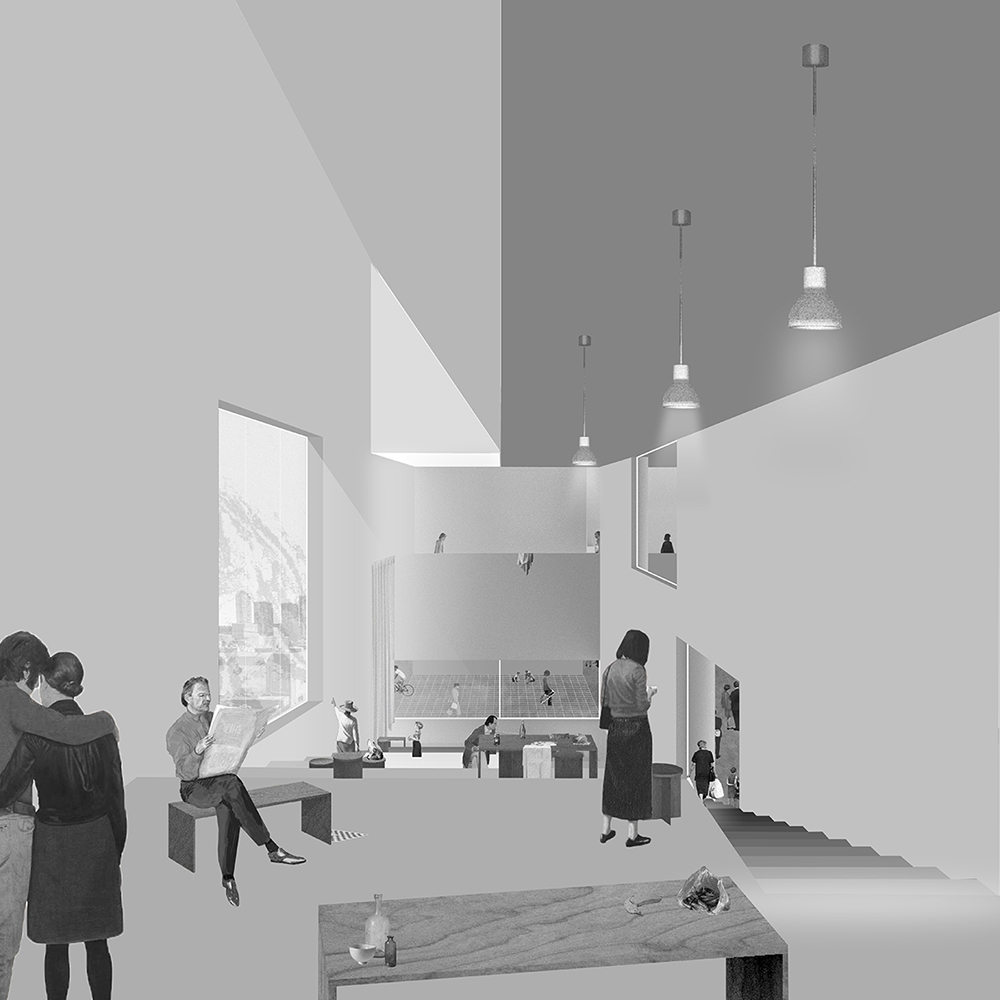
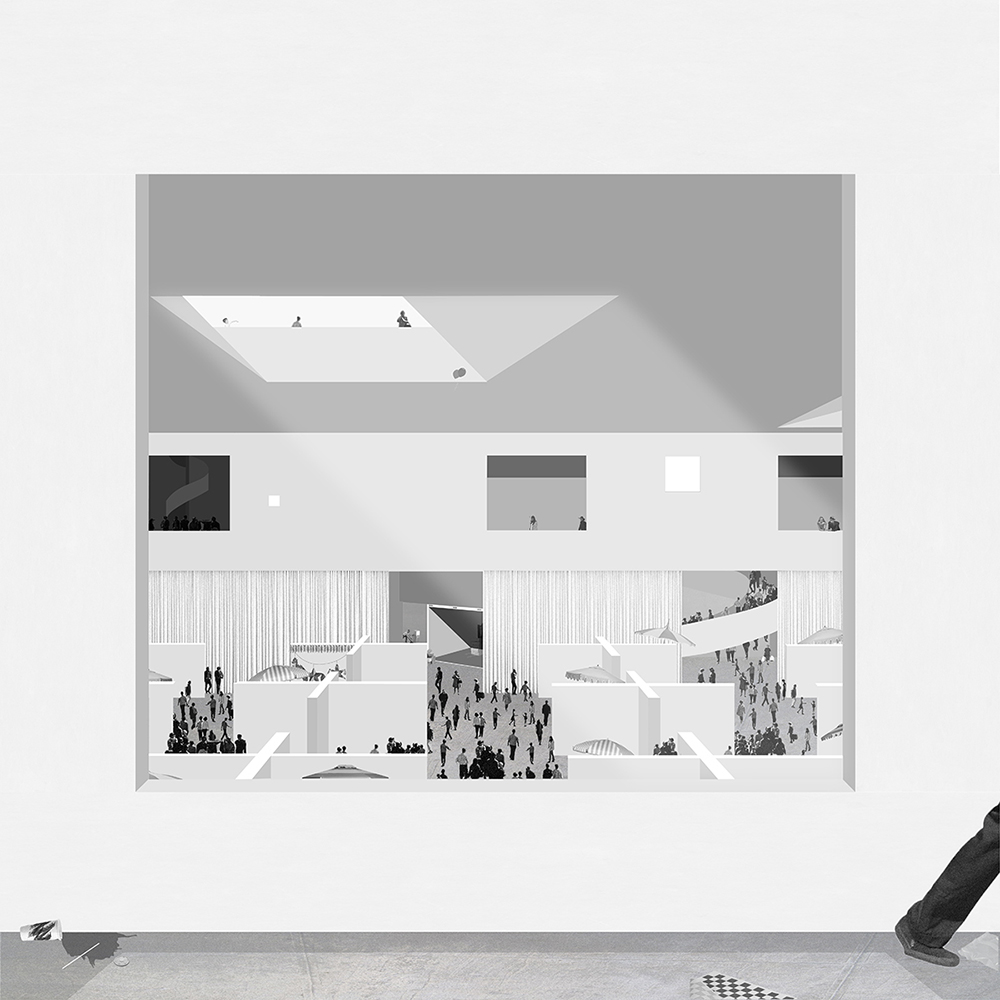
[IN]visible by Ying Xuan Tan and Xi Xiang, B.Arch ’22
Syracuse University | Advisor: Lawrence Chua
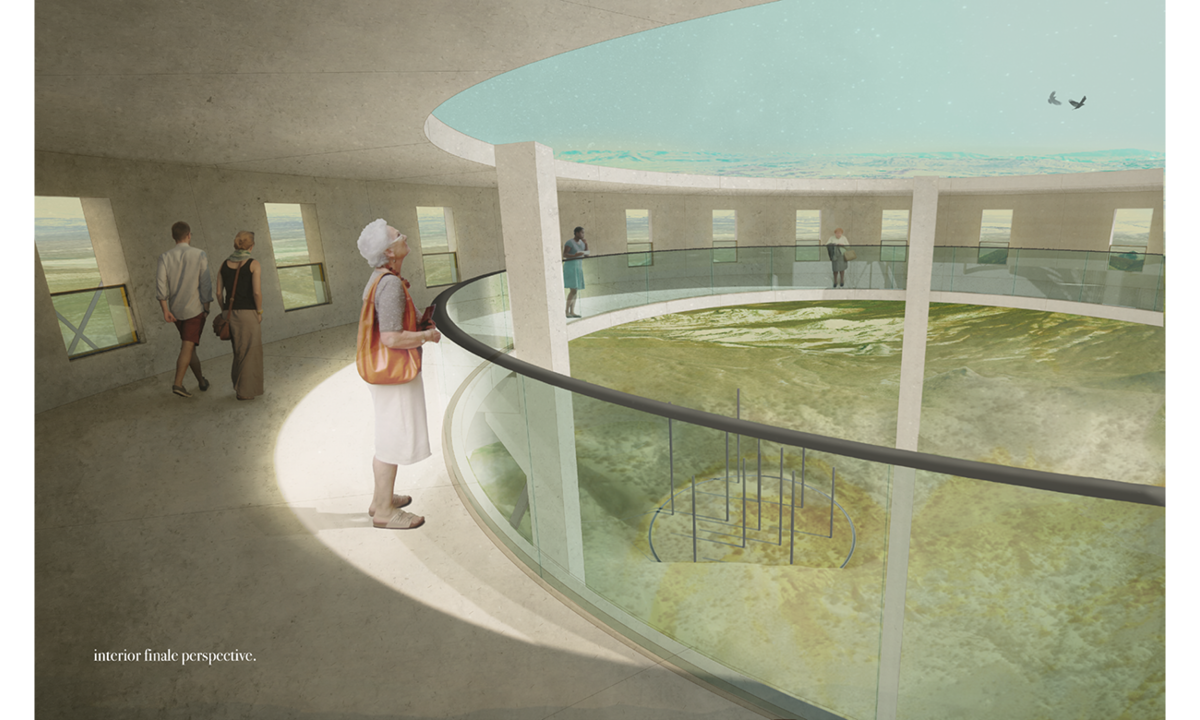
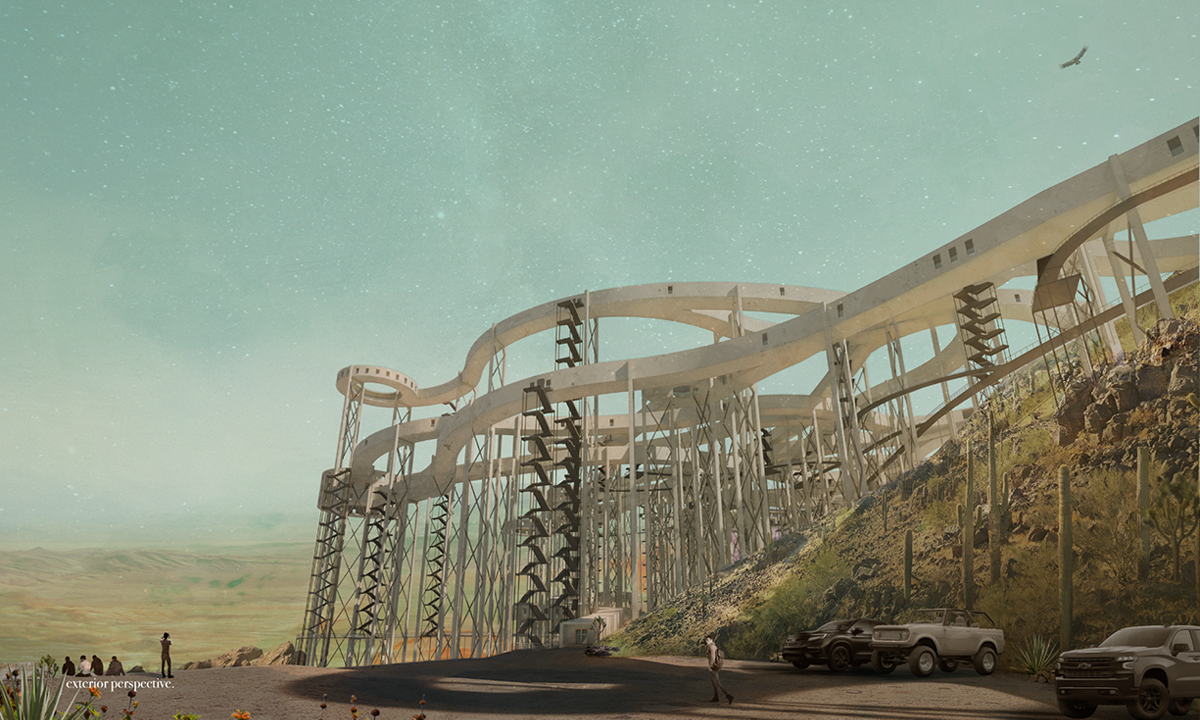
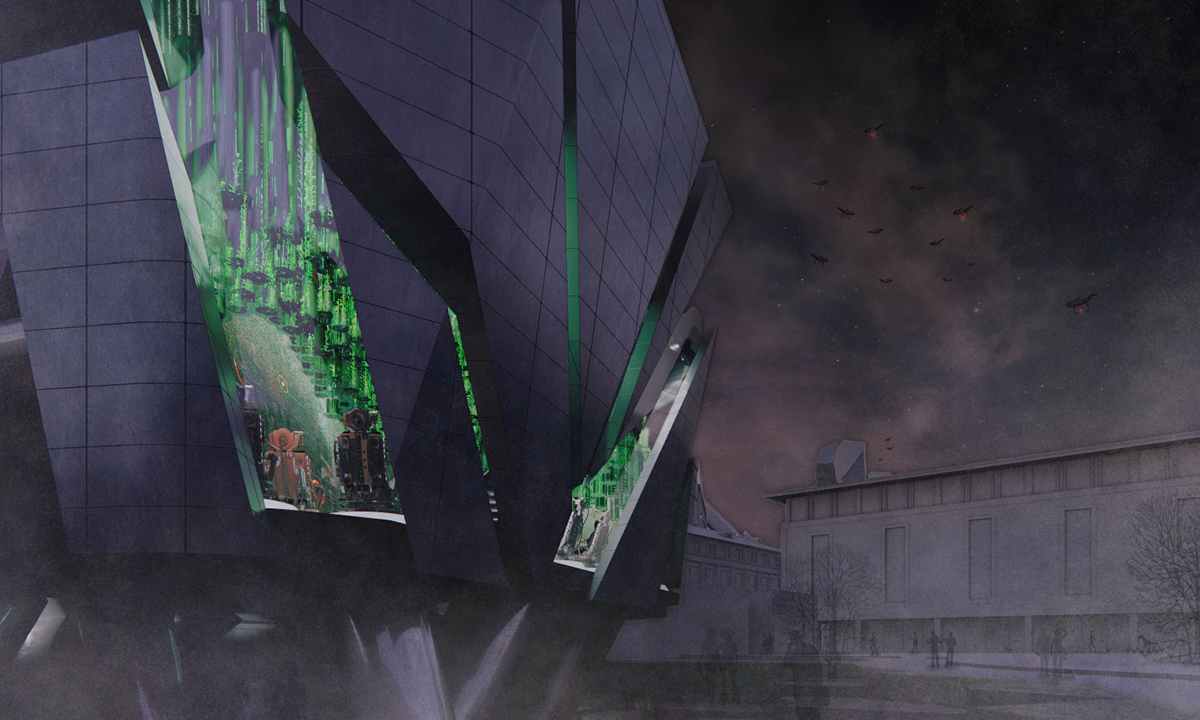
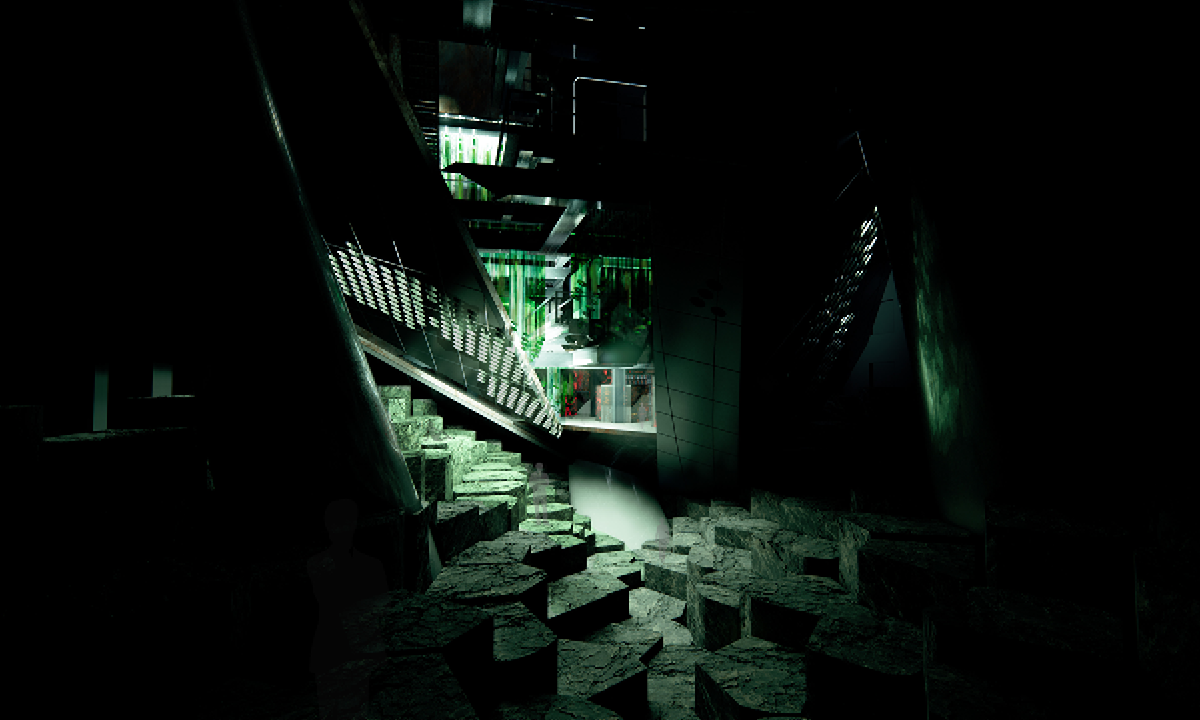
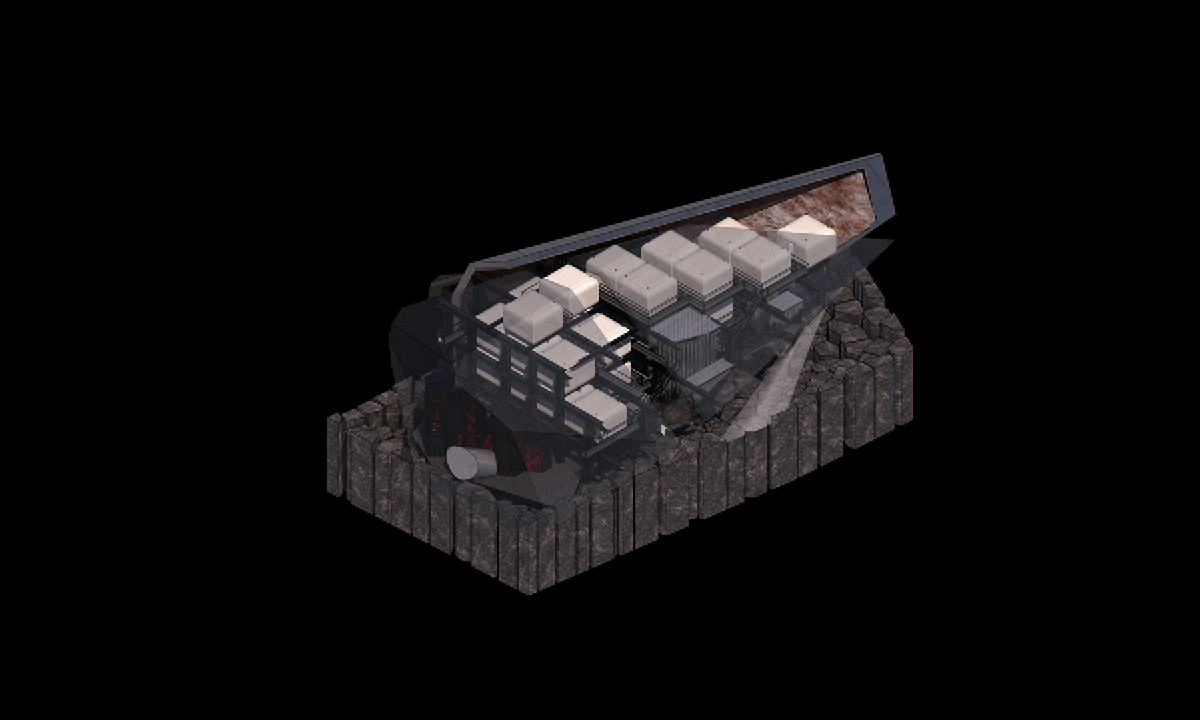
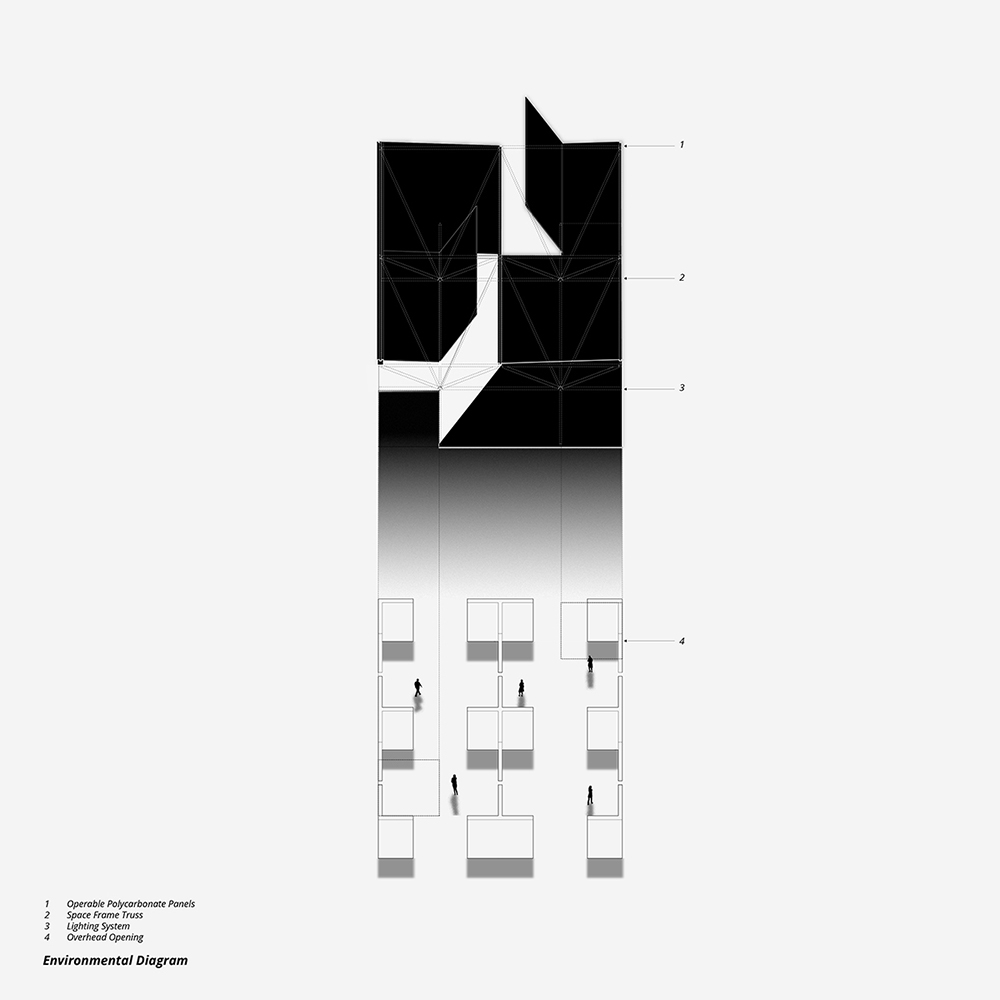
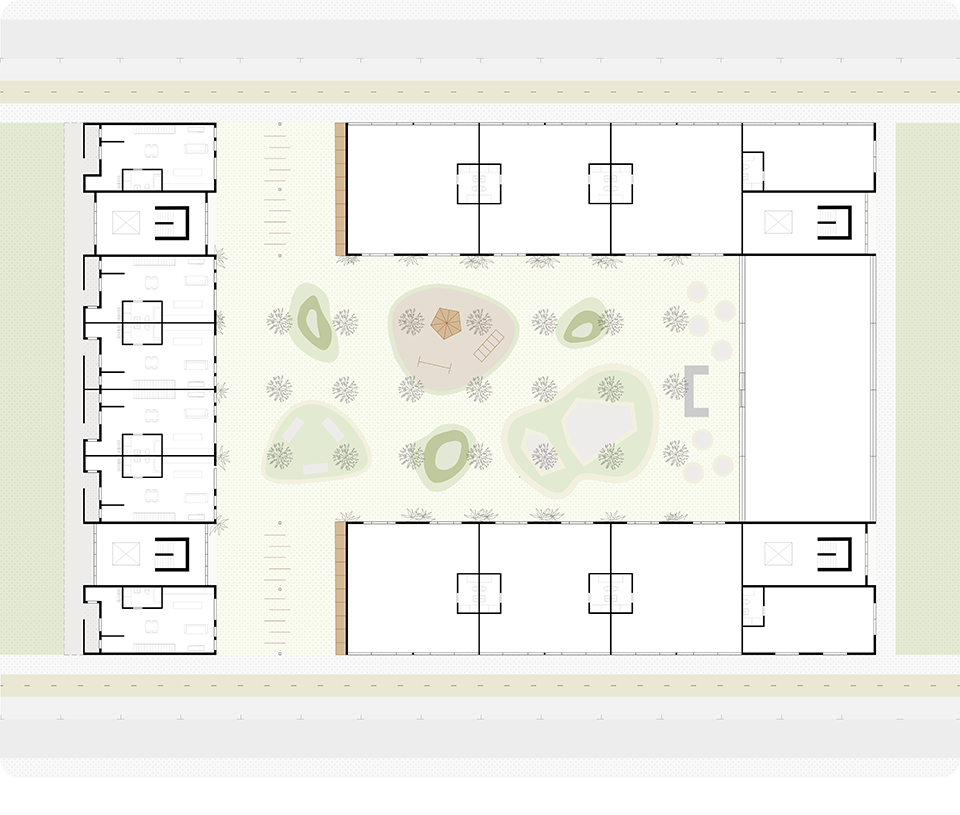
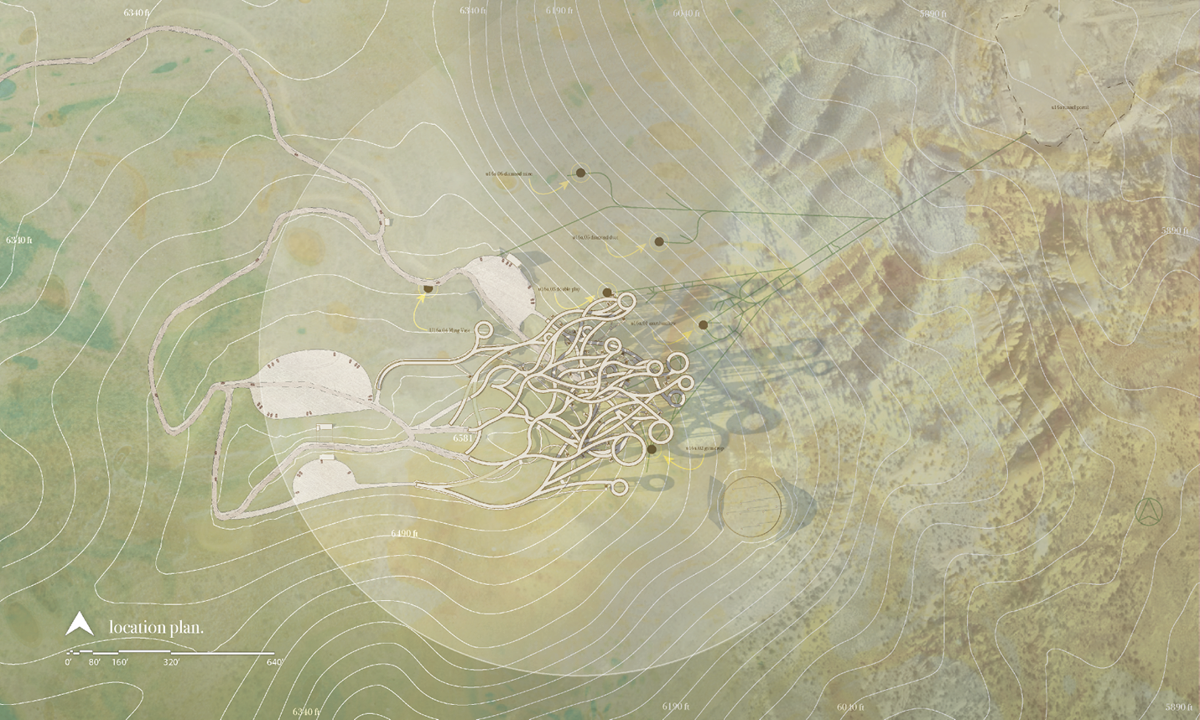
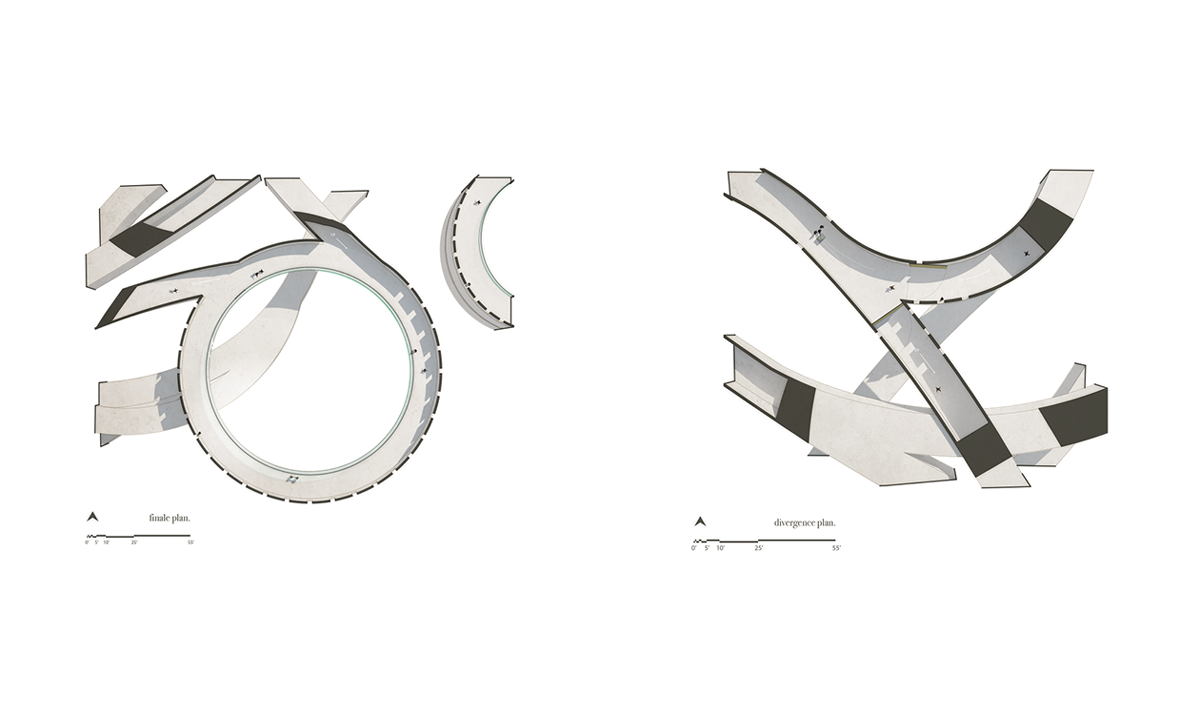
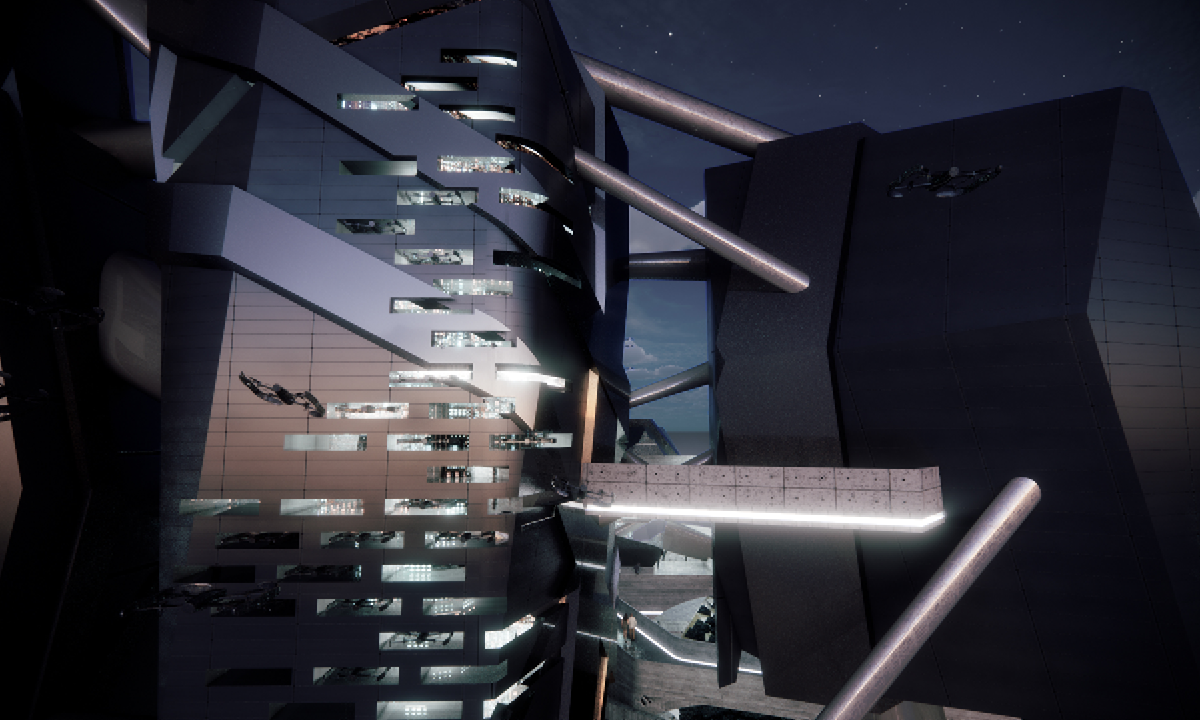
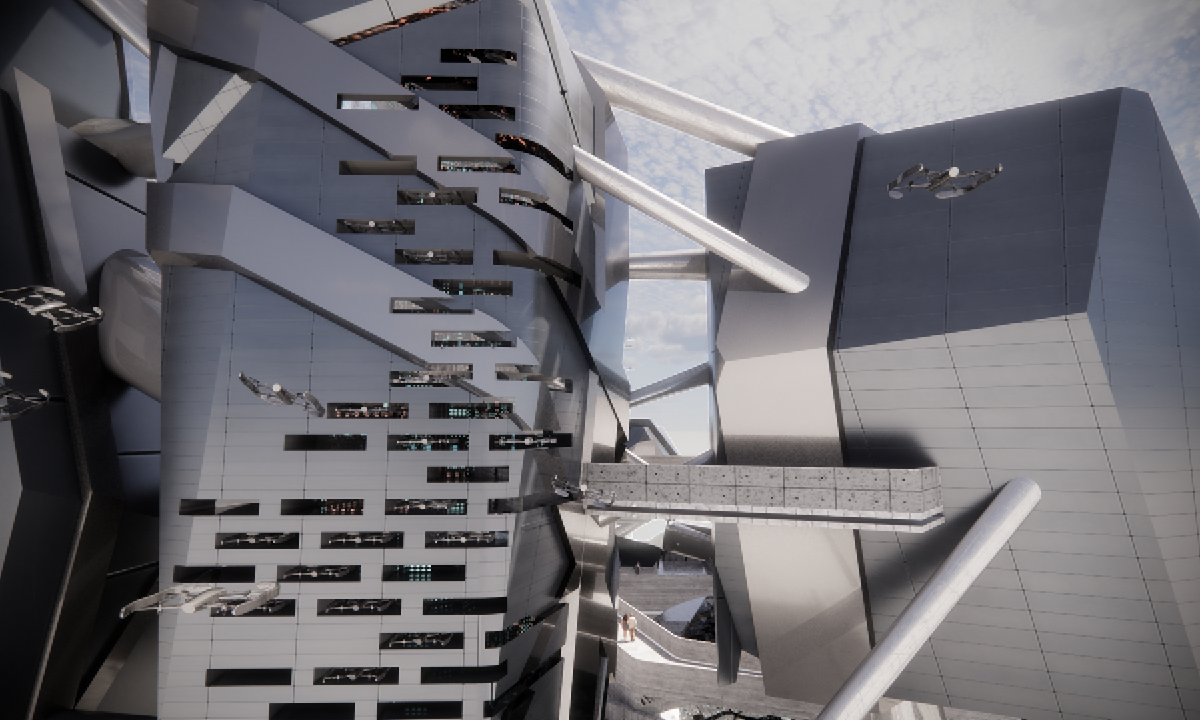
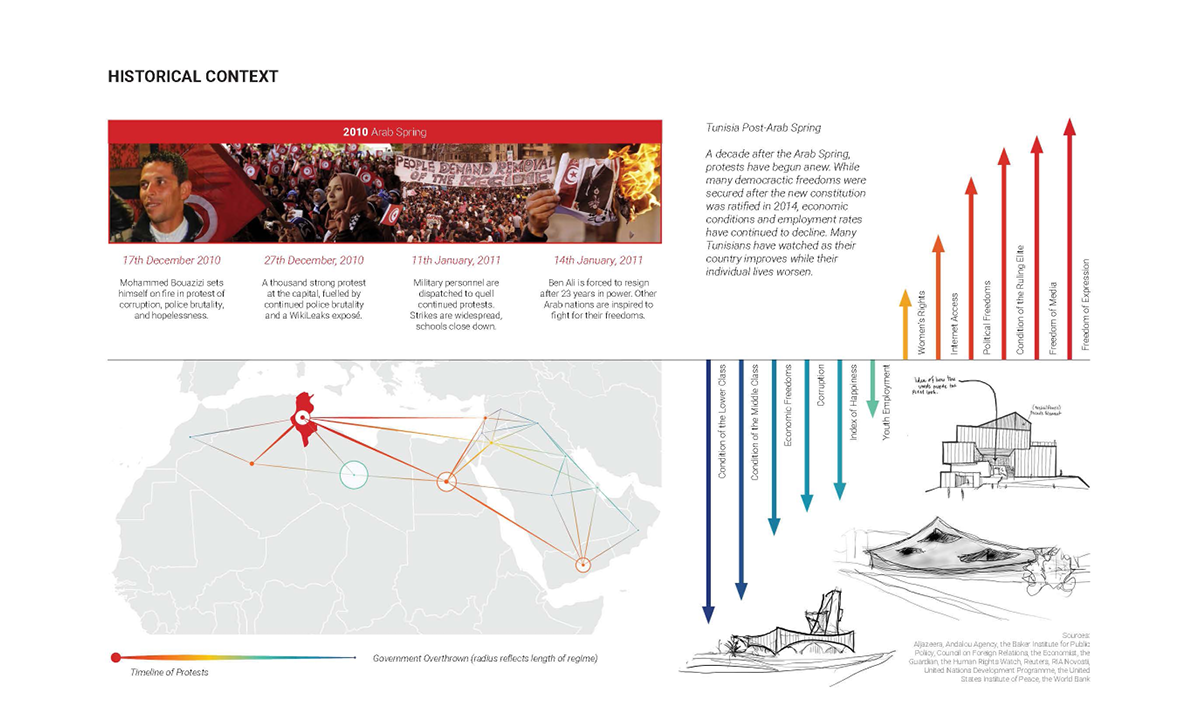
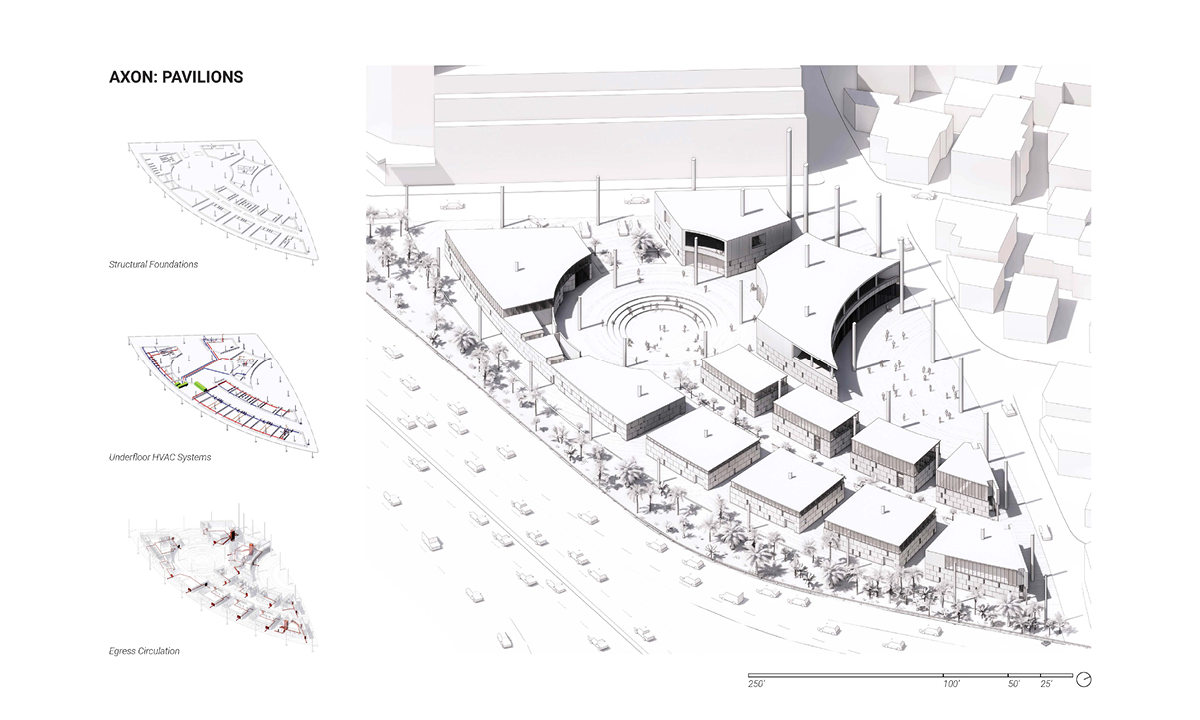
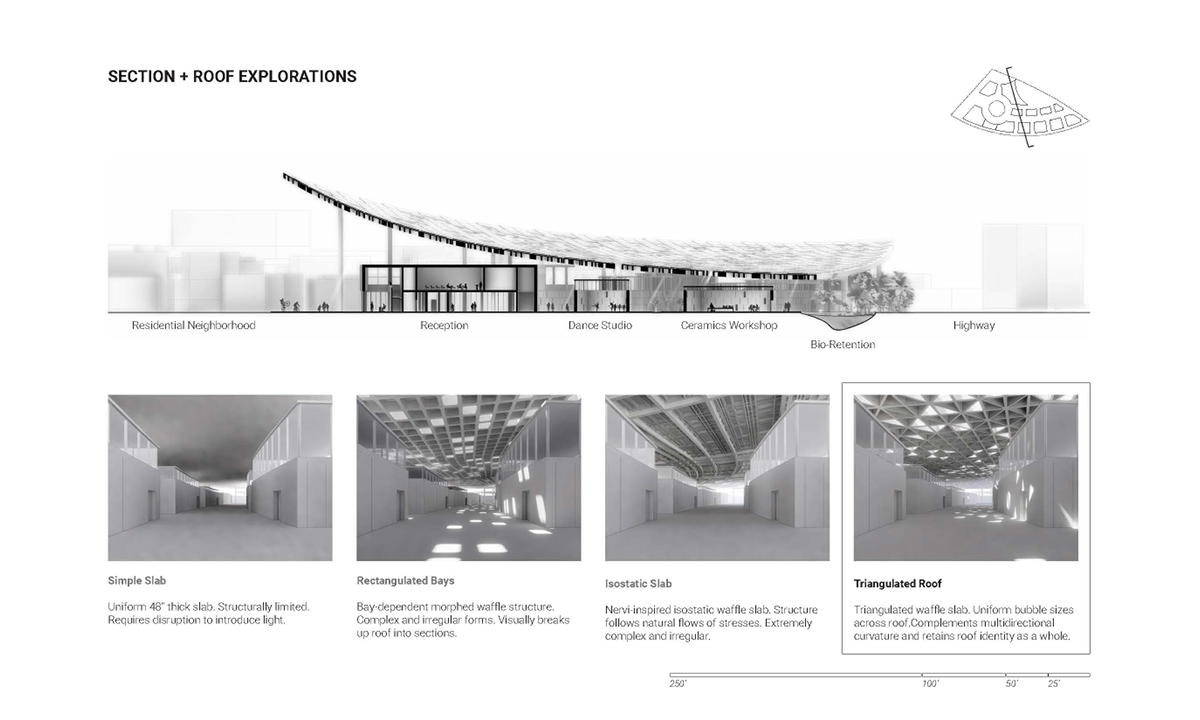
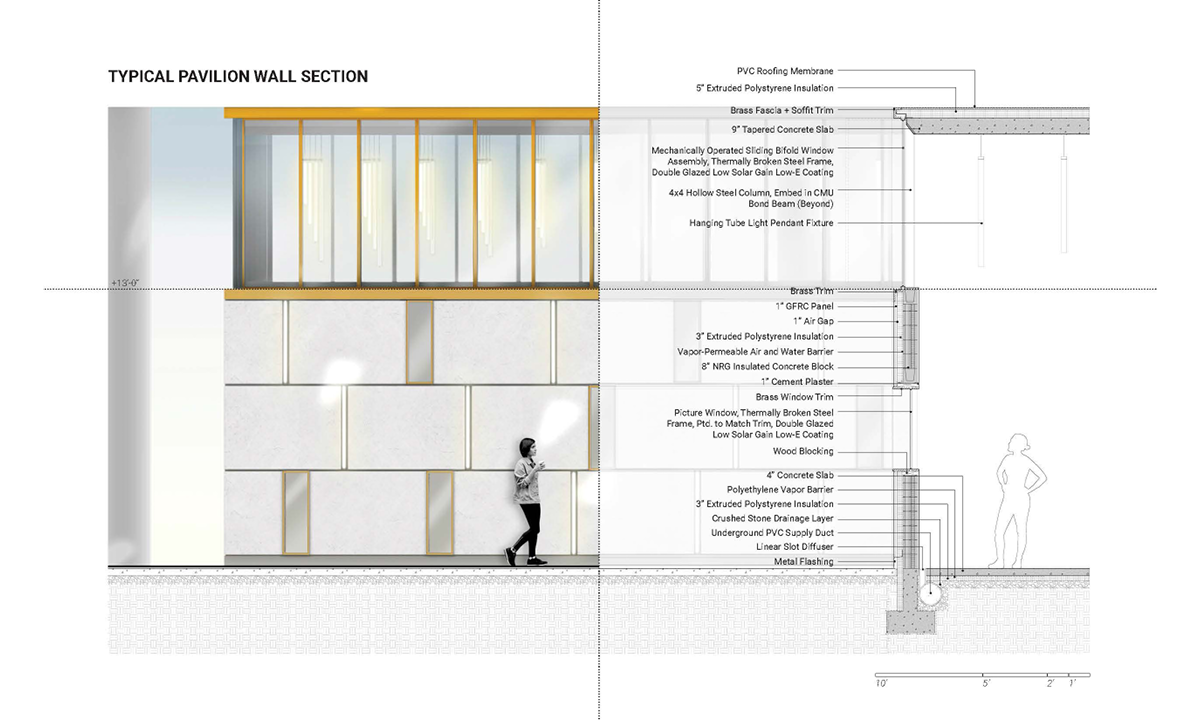
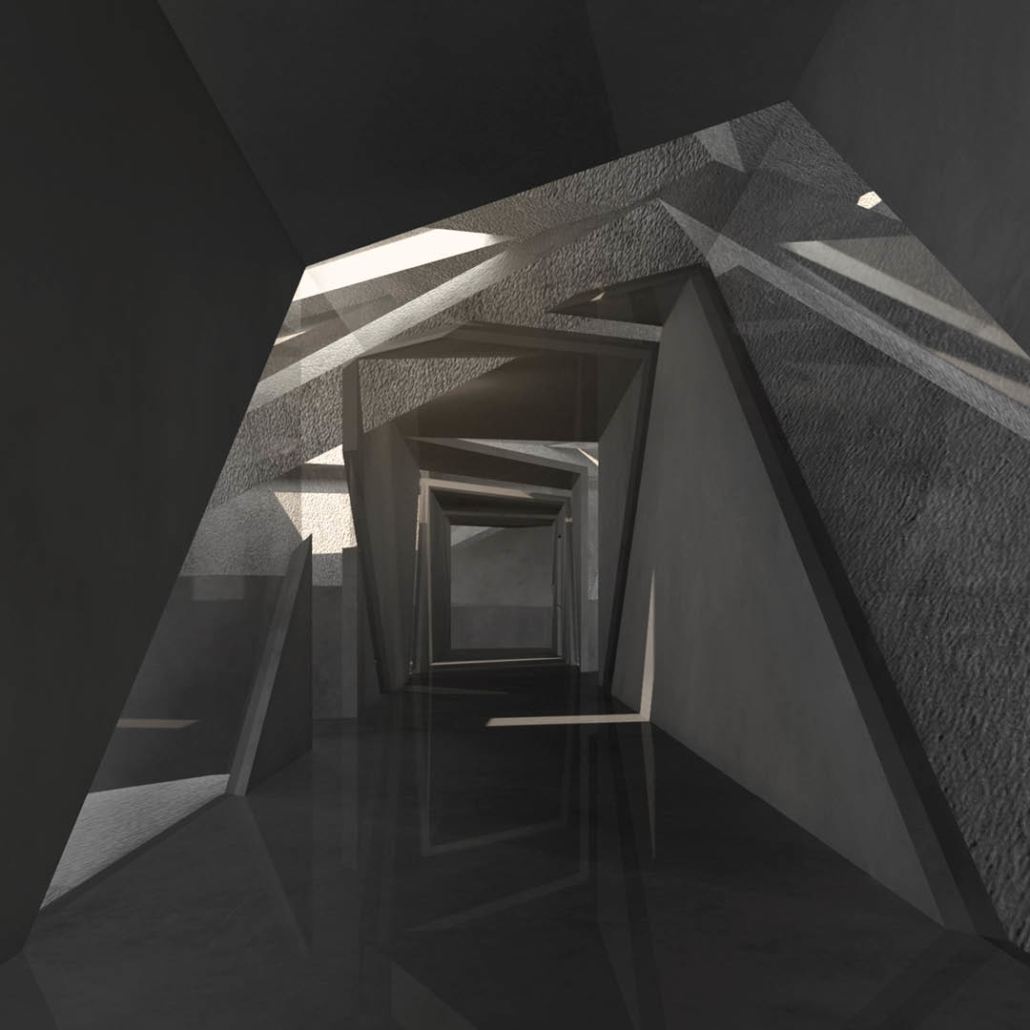
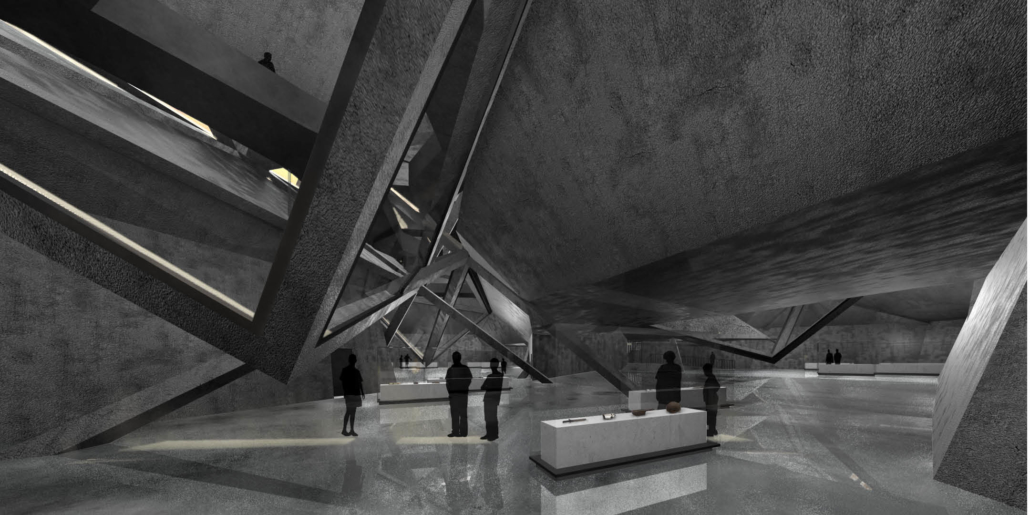
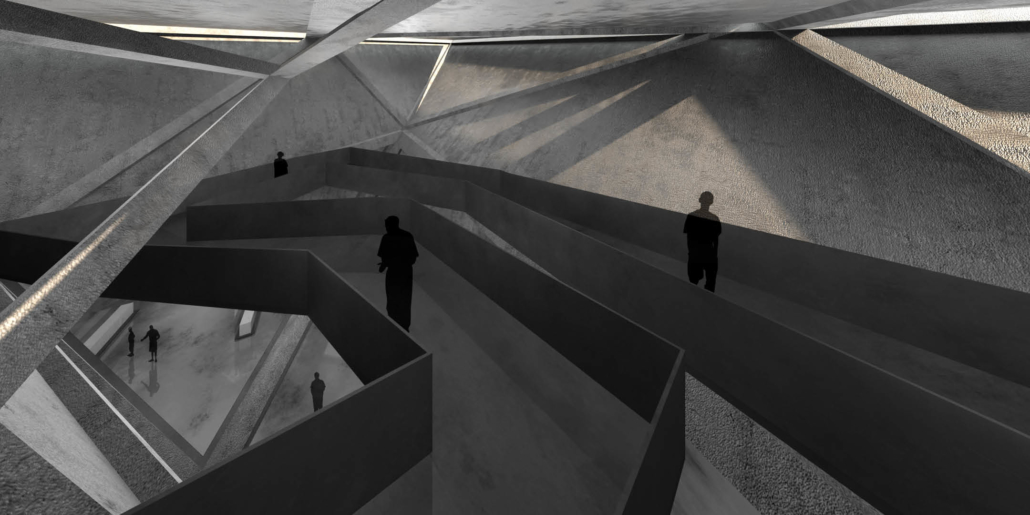
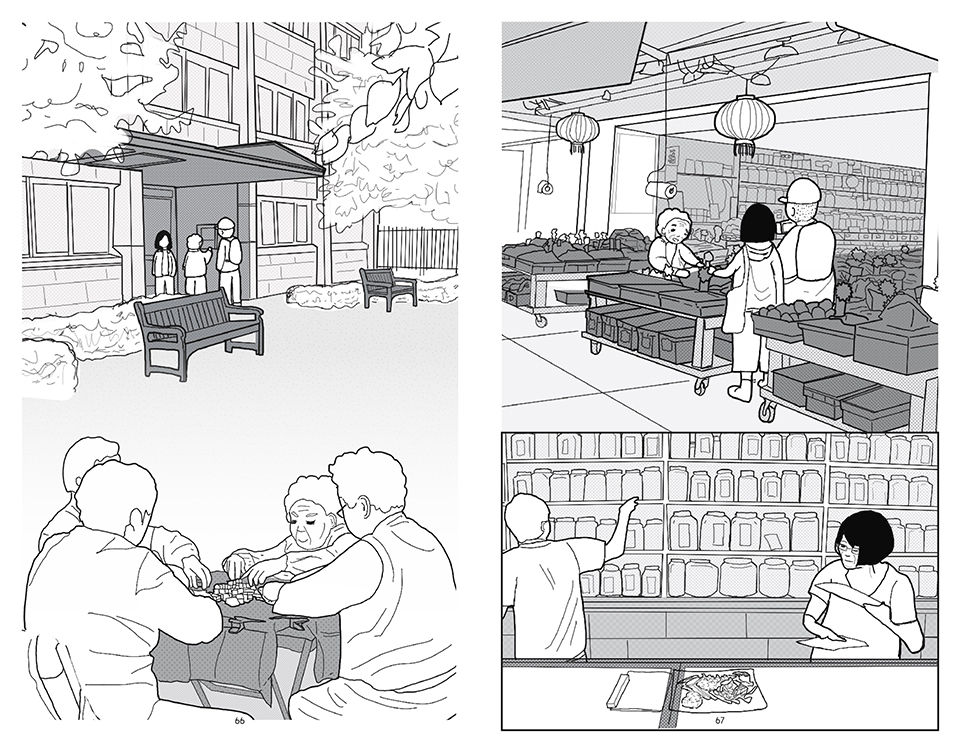
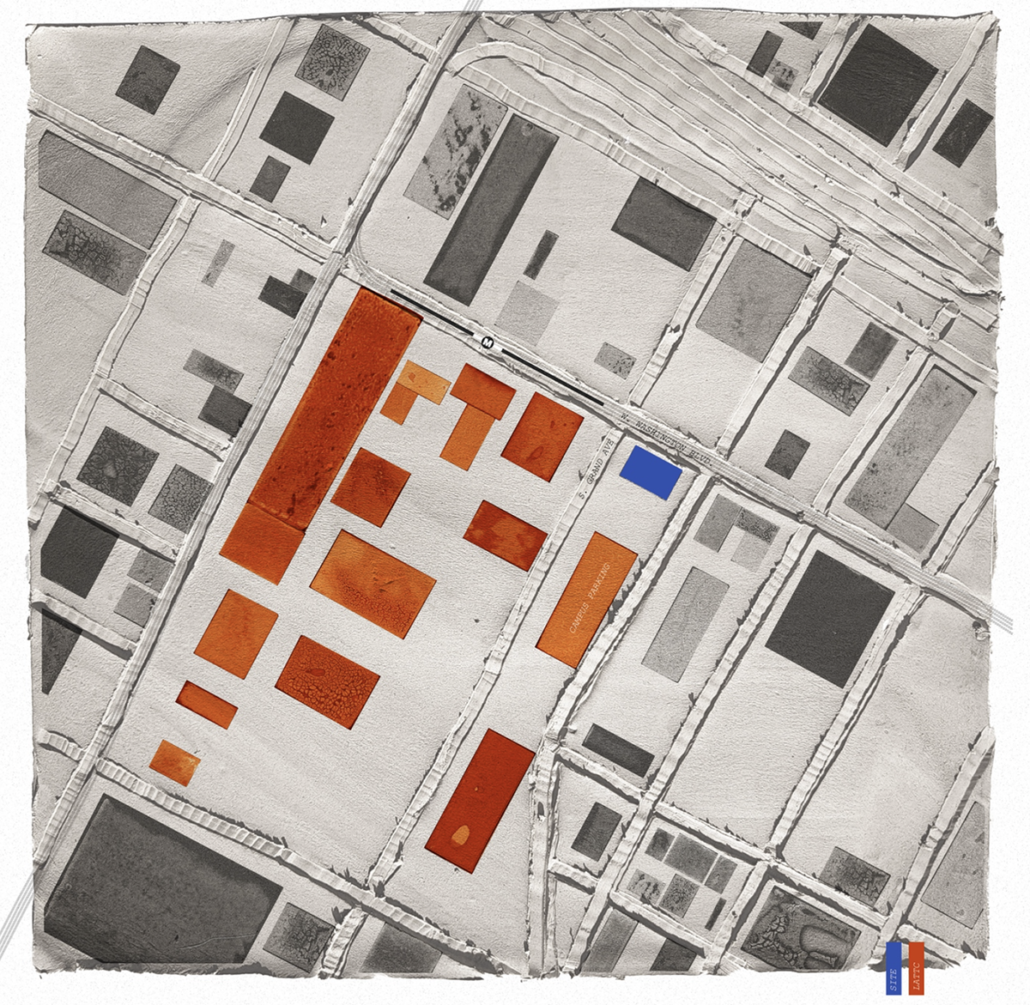
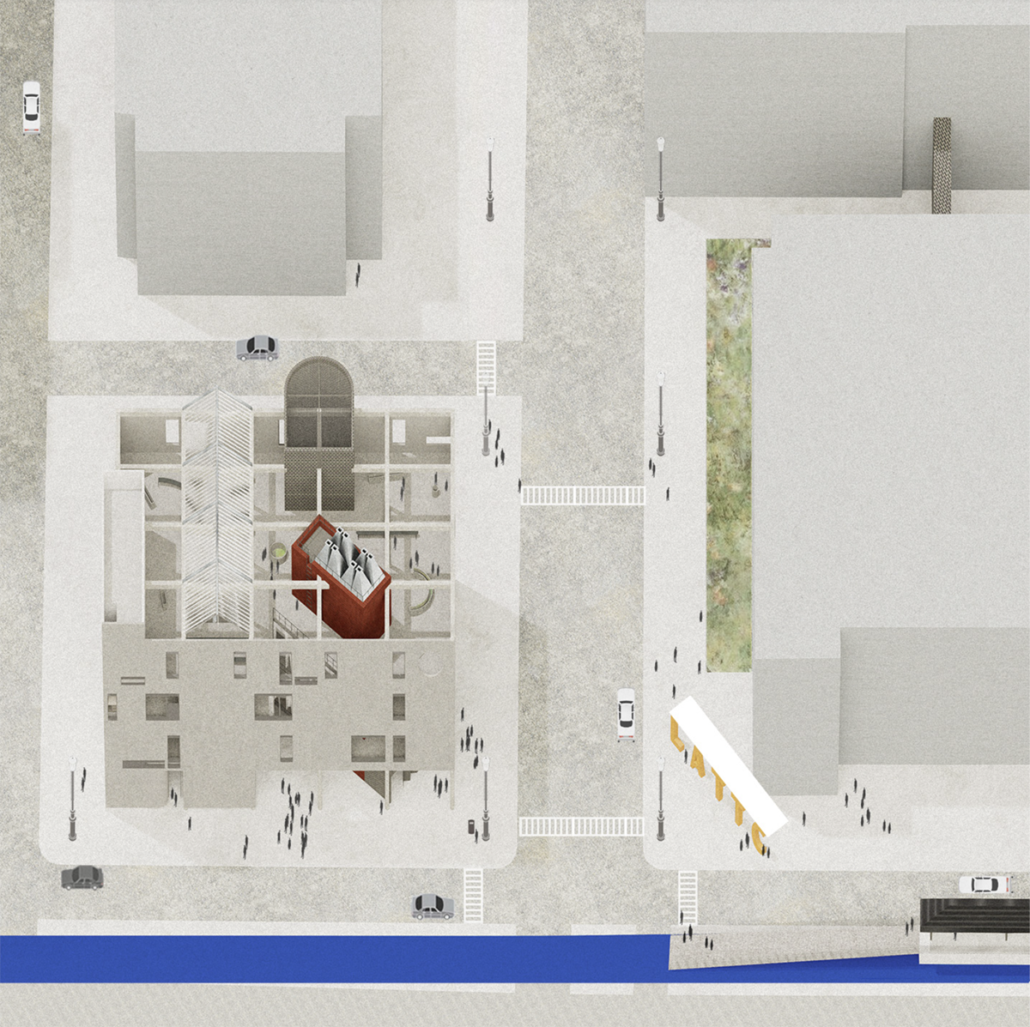
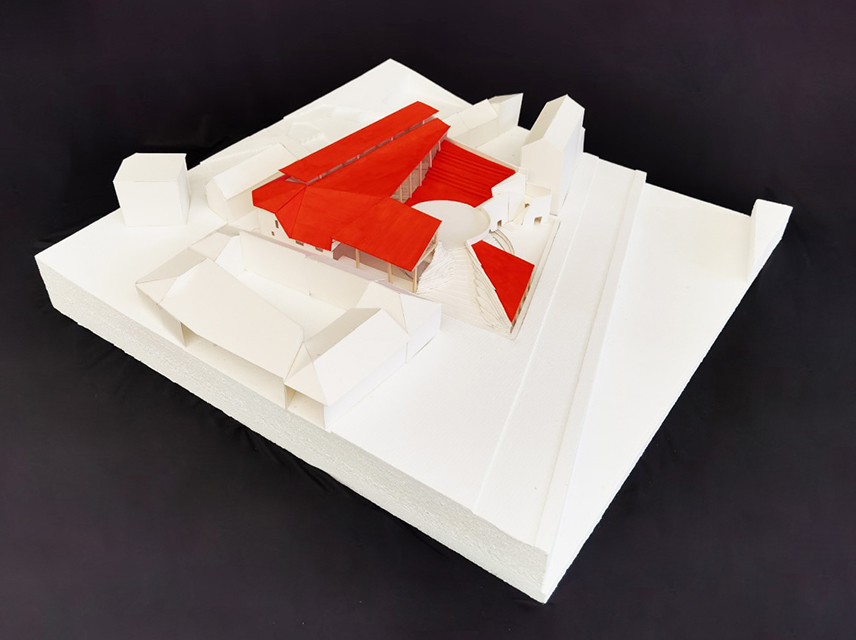
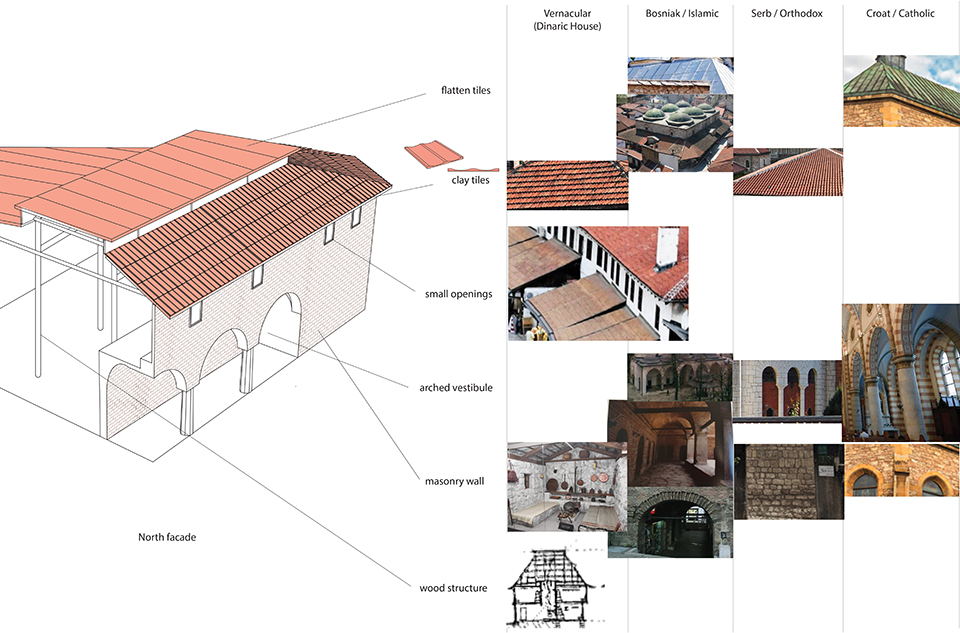
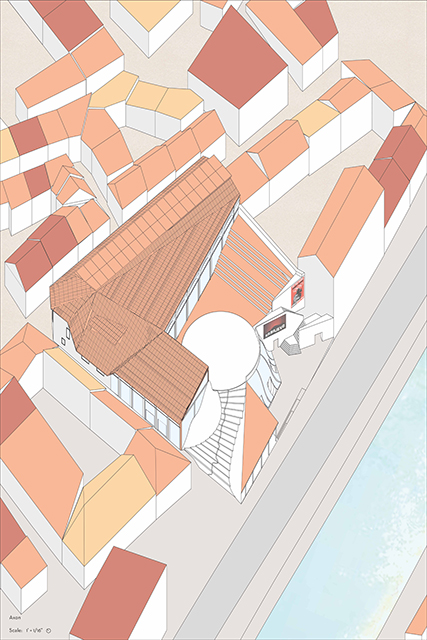
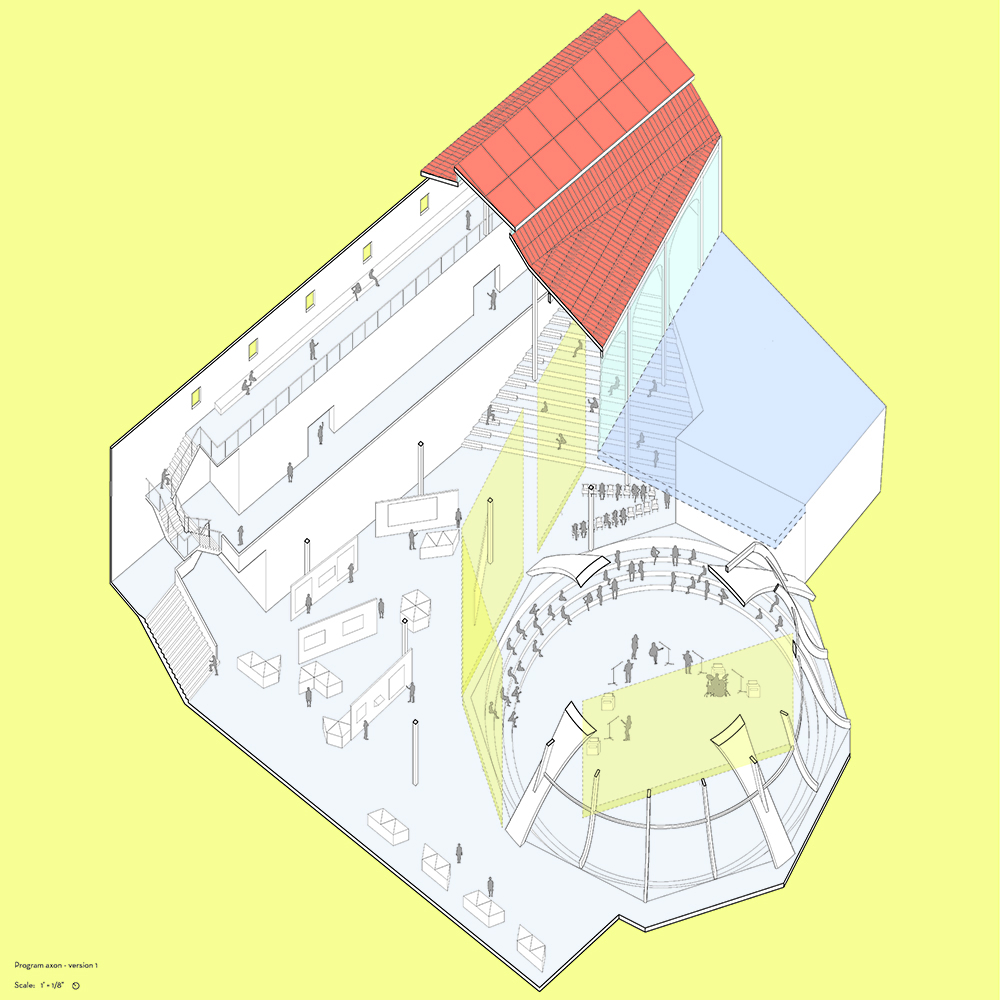
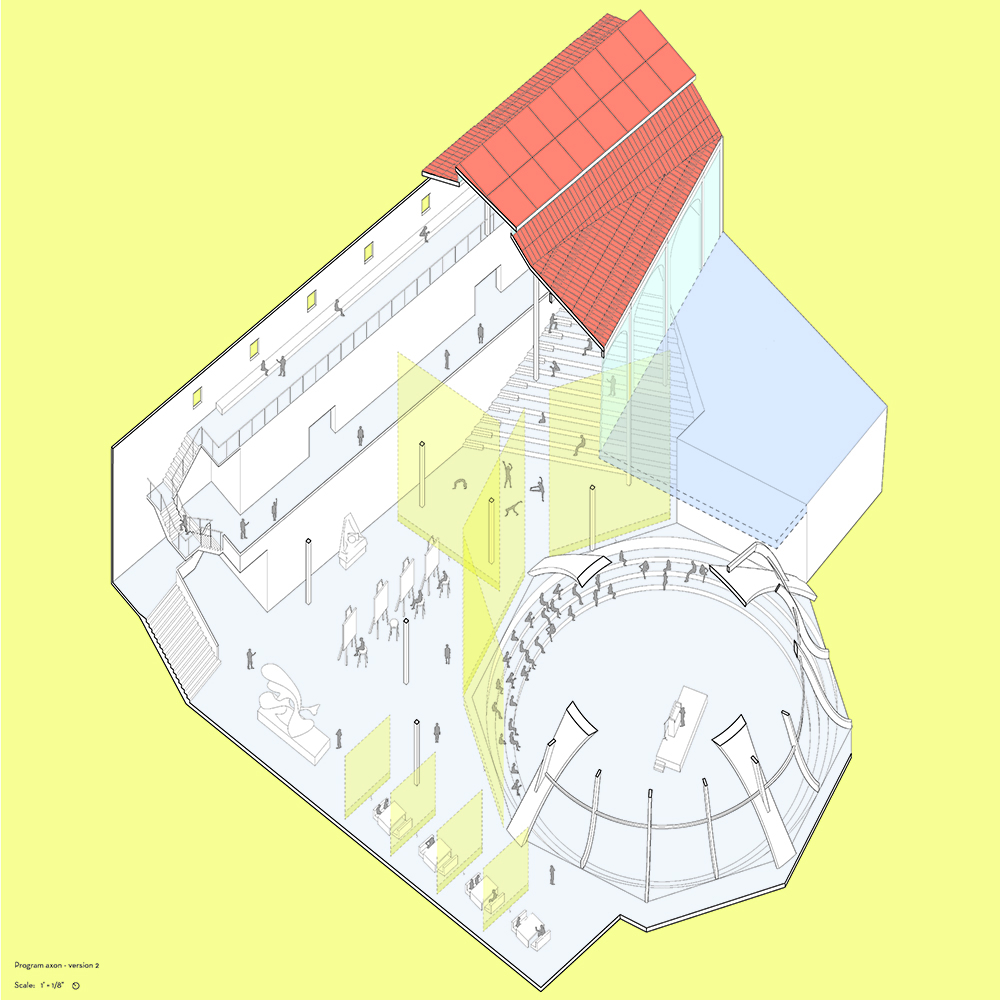
This thesis is a conservative proposal seeking an eclectic solution to provide a stable environment for Afghanistan’s people and the preservation of human history. The project [IN]visible seeks to create a point of balance between the turbulent environment and its rich historic heritage meanwhile following a preliminary, iconoclasm.
Bamiyan valley was marked as an important trans-cultural portal for Afghanistan and Central Asia. Statues, stupas, viharas, shrines, and grottos here have all witnessed the cultural creolization of this land. The government today had promised to engage in international diplomacy and make compromises. Preserving artifacts at Bamiyan is a humanitarian act and brings the government financial income.
The project seeks to find ways to preserve precious artifacts in the age of the Taliban’s regime, respecting the Taliban’s ideology on the surface while showing the real deal on the inside. Using various materials, water, and light as a tool to hide the artifacts from the surface. The design process discovers methods of visual illusion. Water, an essential element in Middle East architecture, would orient throughout the project. The stream would lead the locals and visitors to enter the project to see the actual side of these cultural artifacts.
This thesis is a pioneer experimental practice toward religious conflict that does not follow mainstream standards. It is also a conservation proposal seeking an eclectic solution to ensure a stable environment for Afghanistan’s people. In the end, no matter how the government change, it is the people’s life happiness that matters the most.
Instagram: @tototan_yx, @xxixixiwest
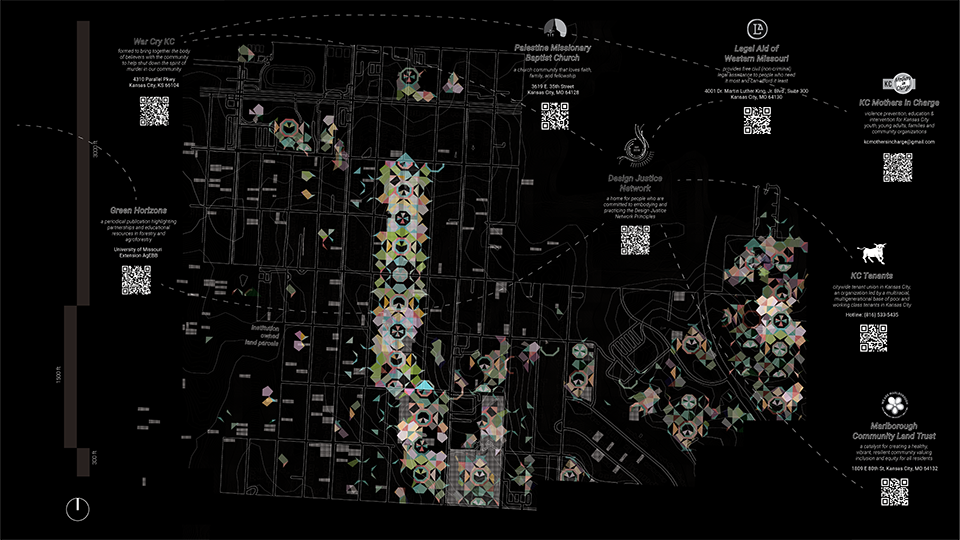
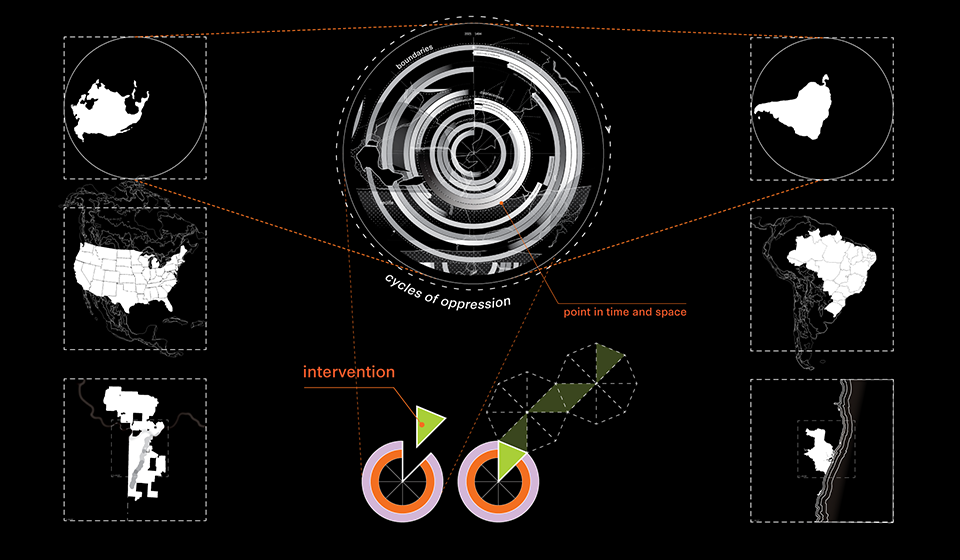
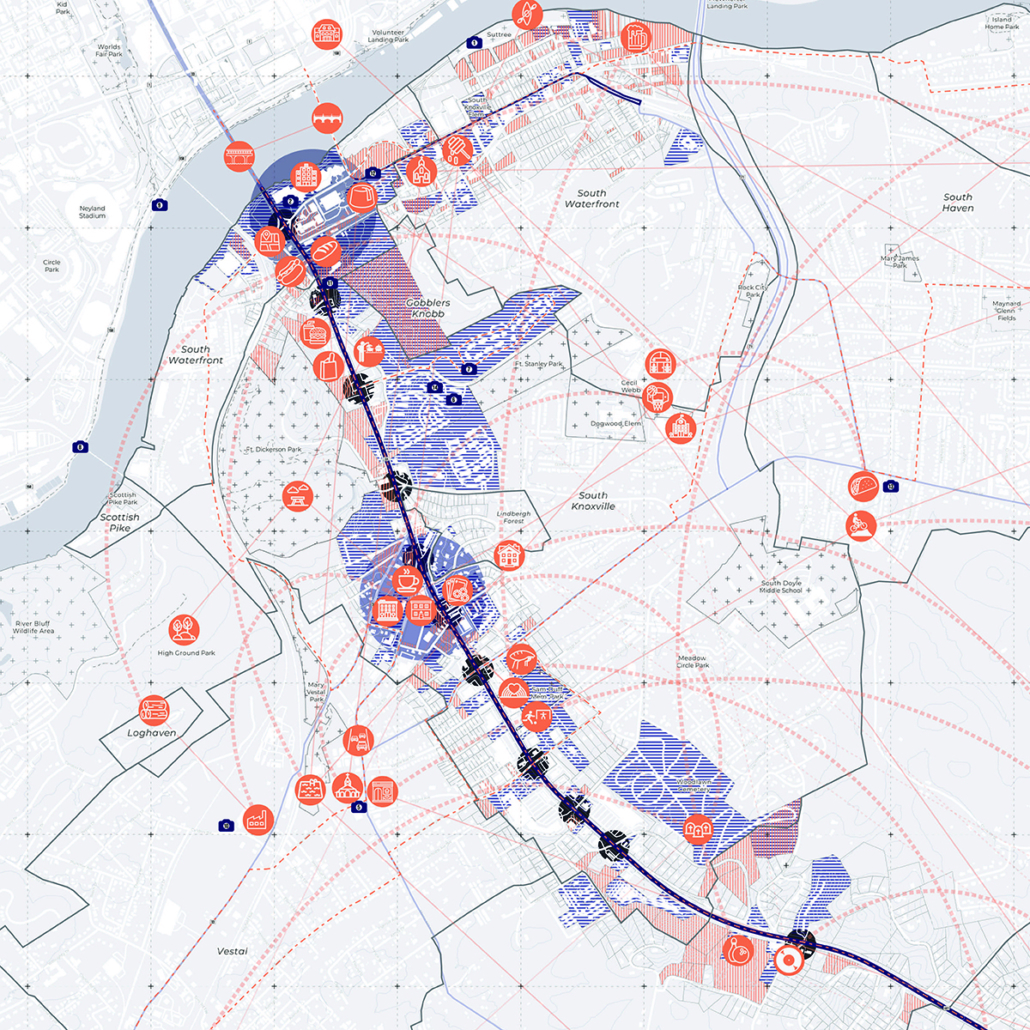
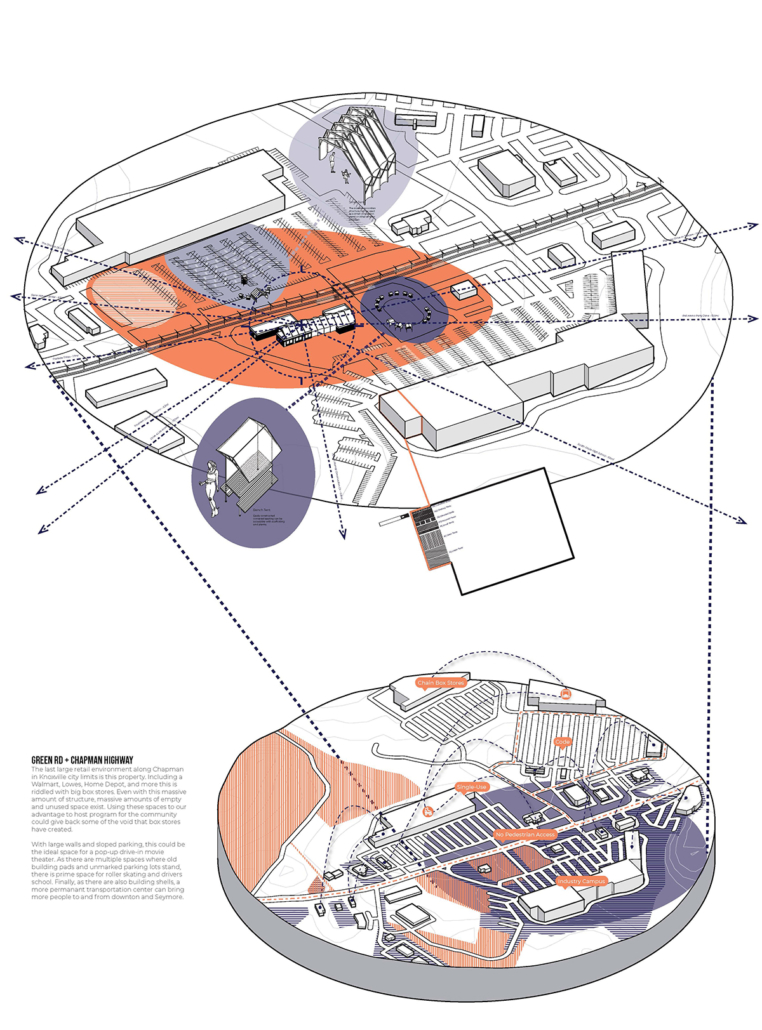
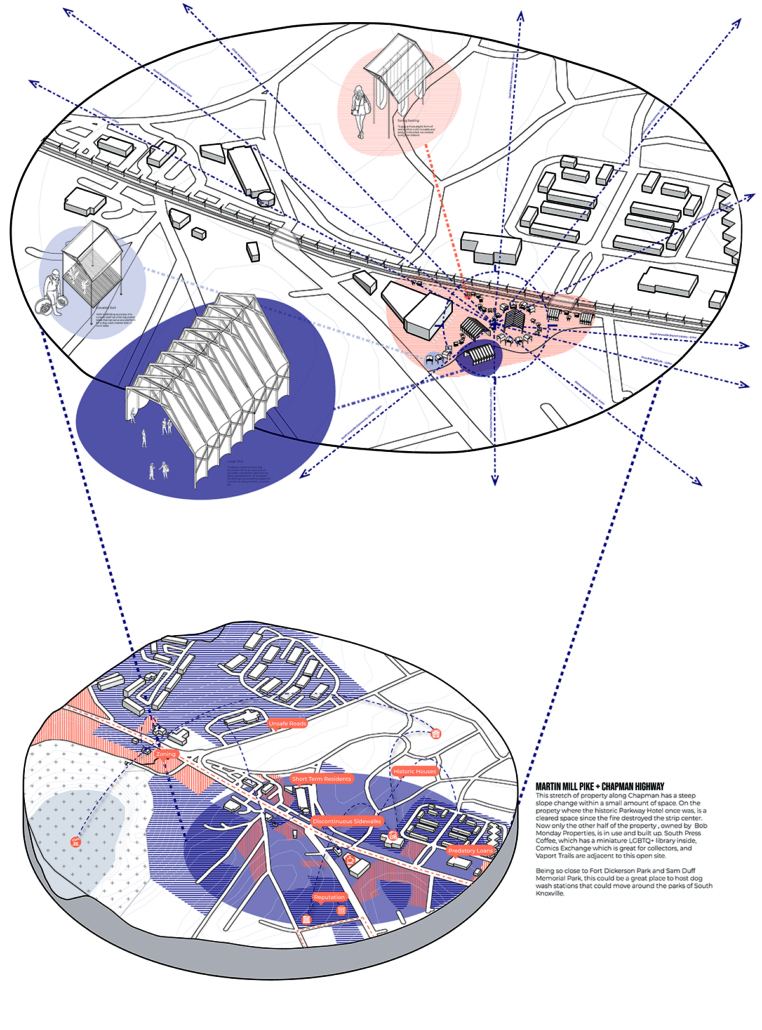
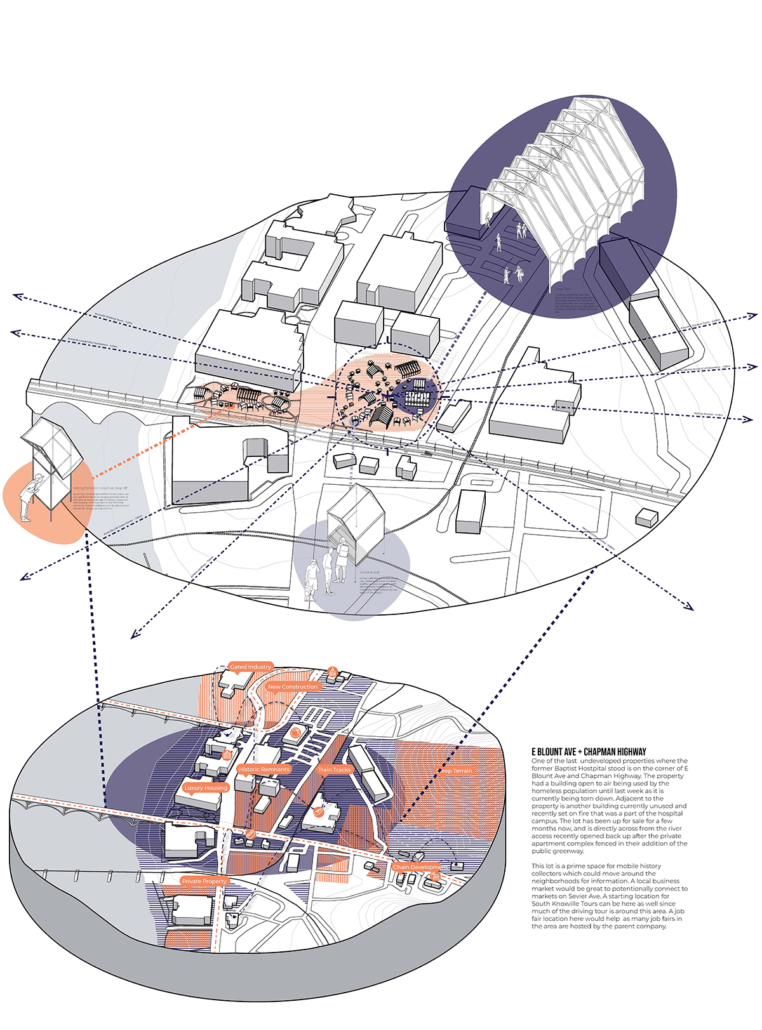
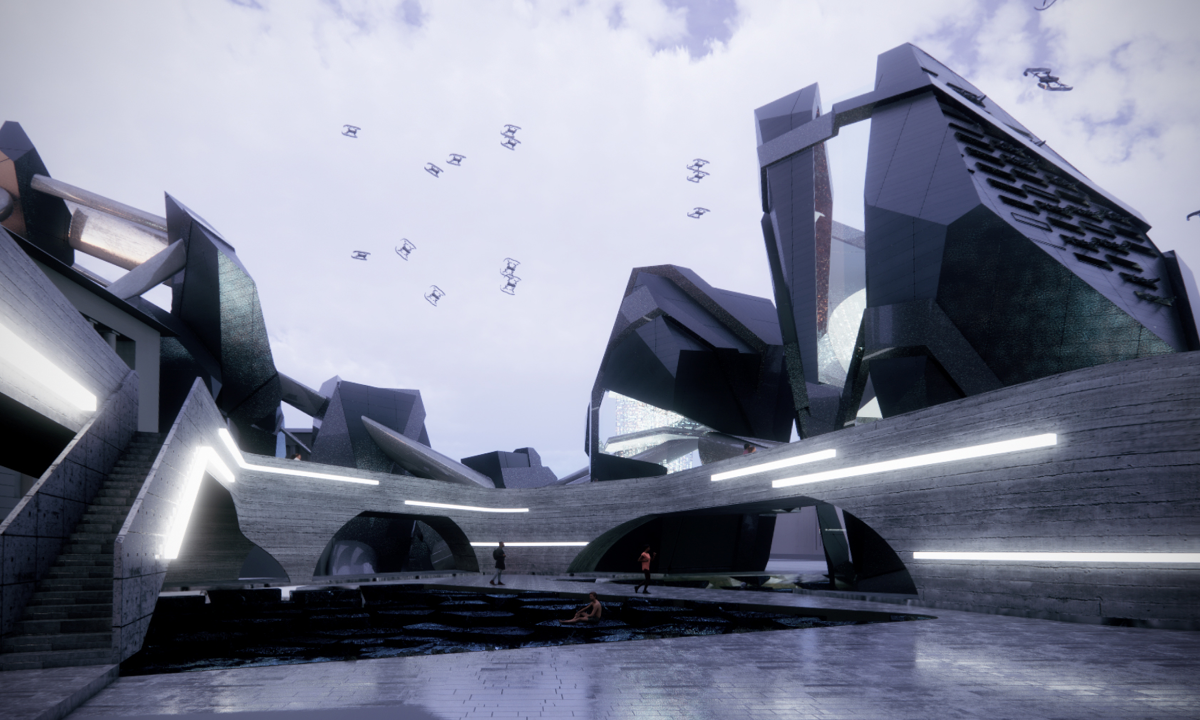
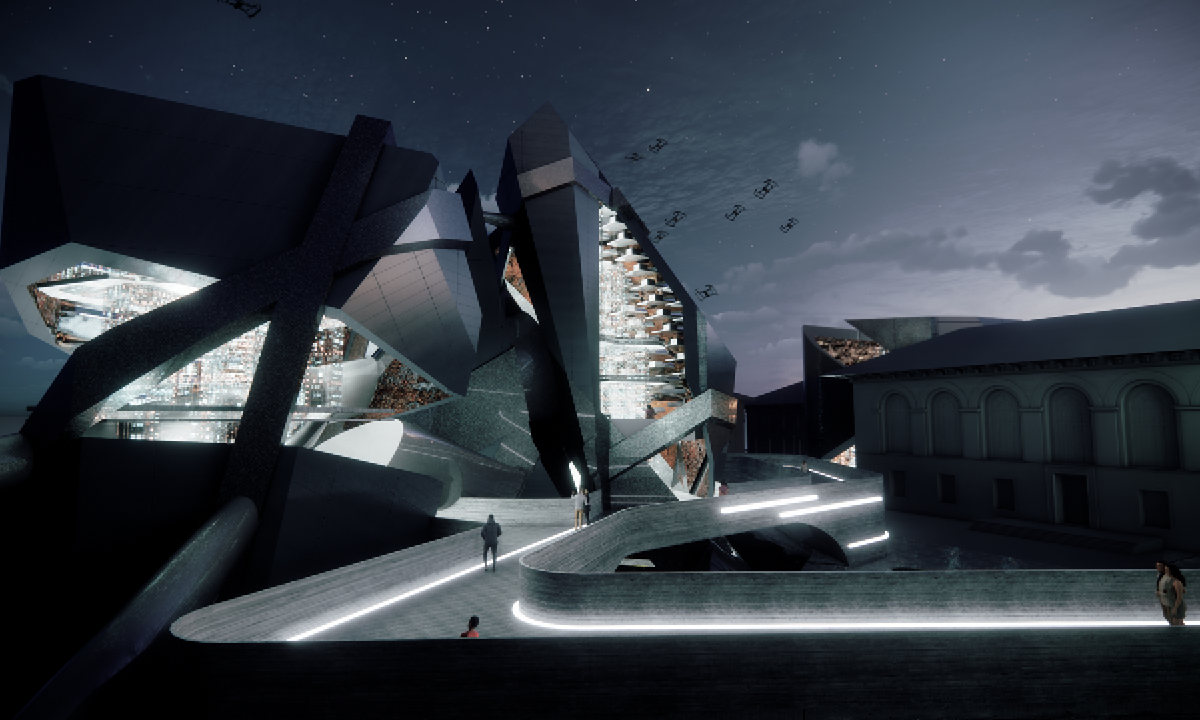
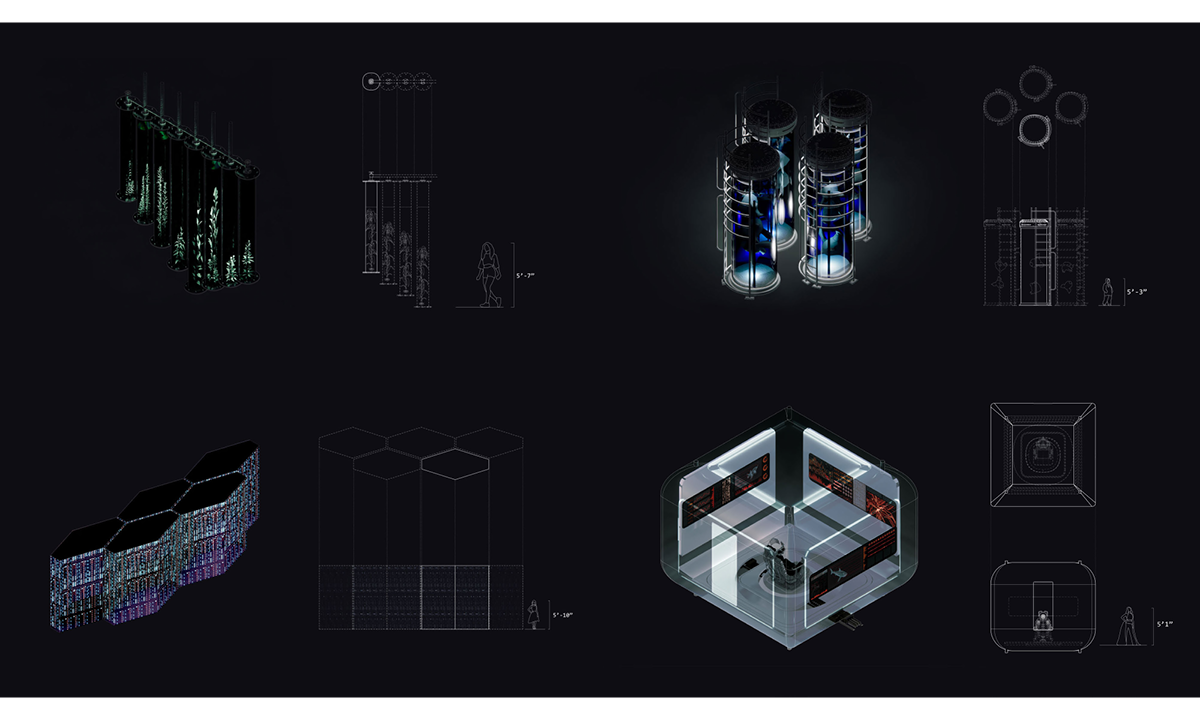
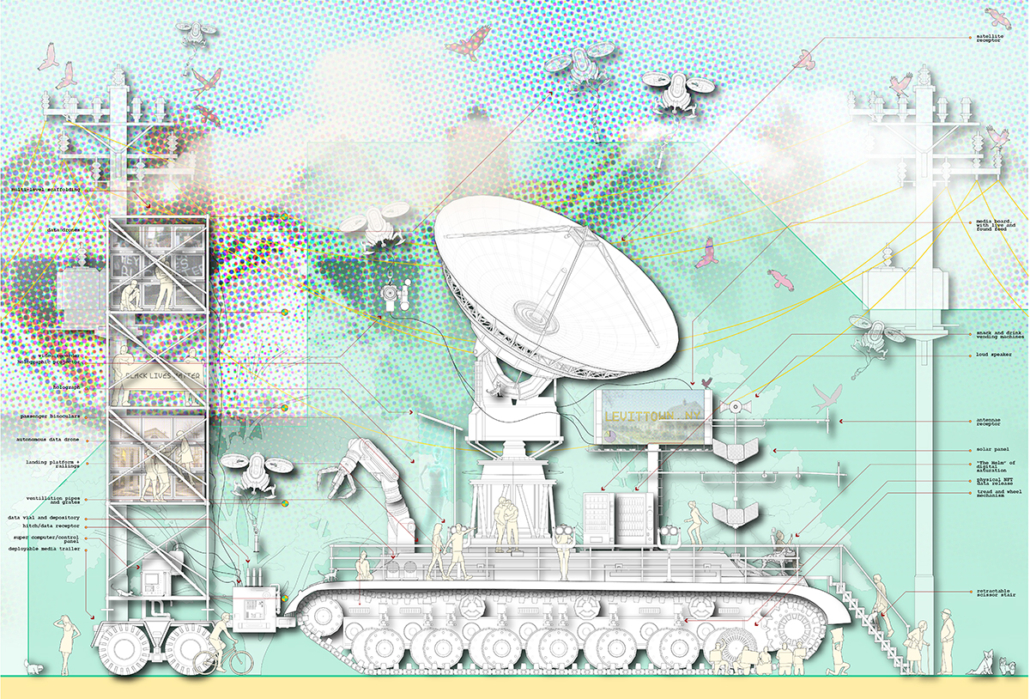
Guerilla Museology: By All Means Necessary by Brendan Wallace, B.Arch ’22
University of Tennessee | Advisor: Jennifer Akerman
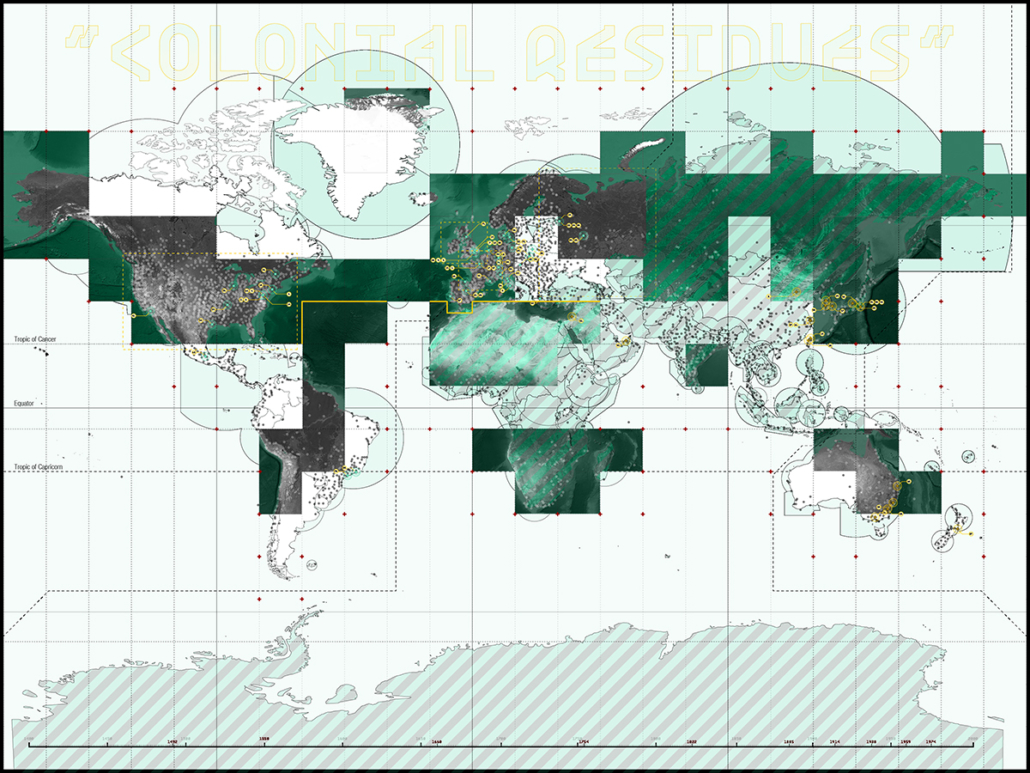
For many, it is believable that colonialism has met its end. The latter half of the 20th century witnessed a global spirit of liberation, specifically within African and Asian continents. New annexations of land allowed nations to declare sovereignty in watershed spirit. Yet, the residual effects of the colonialist era has effectively perverted contemporary spaces, especially those typologies which have a legacy deeply rooted in the violence of looting, stealing, raping, and pillaging- namely, the museum.
While direct subjugation under colonialism may have met its end, the 21st century has challenged this premise, understanding that colonized structures remain to inhibit this “autonomy”. The likes of the Louvre, The Met, The British Museum, and the Saint Hermitage Museum, are all national treasures which lie of the heart of an imperial memoryscape. Their educational commentaries have transitioned from the national to the global scale as they are catapulted into the role of a universalist museum with artifacts from all parts of the globe. Their objects represent a past which has been bastardized, deceptively rewritten, and Westernized. Their place in the arena of global memory has prevailed on top and contribute to modern day racism, xenophobia, necropolitics, and various forms of othering.
The museum is unyielding, working as a contemporary agent for cultural genocide.
This thesis works to acknowledge these power structures and subvert them as a way of envisioning a new, equitable museumscape. I am interested in all scales of museum work to invite democratized curatorial practice. The steps are as follows:
1. creating a new museum infrastructural system to ensure curation is achieved as a global practice
2. engaging the city as a system of participatory intelligence
3. decolonizing the museum aesthetic whose expression implies subordination
4. proposing curatorial machines as curatorial agents
5. ensuring the appropriate and holistic contextualization of all objects
These steps are meant to ensure the redevelopment of public trust and redefine the everyday museumgoer as a worthy contributor to curation and exhibition practice. Guerilla Museology inspires an aggressive reclamation of curation by acknowledging the possibility of a post-museum world where the globe itself is a museum site.
Instagram: @brendan.com_, @j_akerman
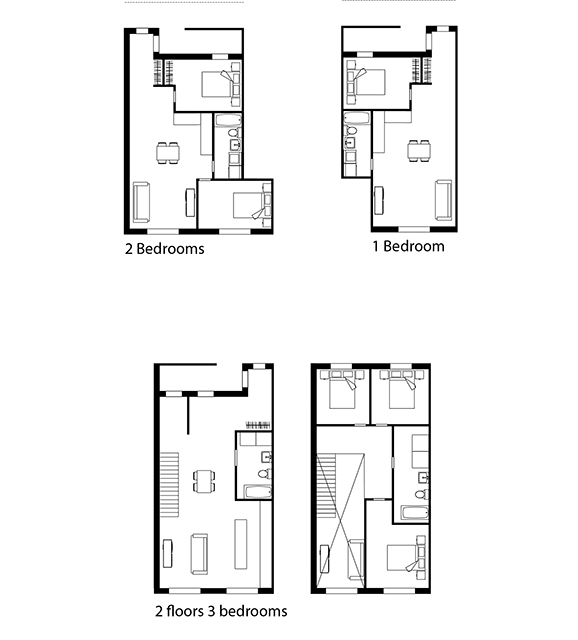
Stored Labor by Kristabel Chung, B.Arch ’22
Syracuse University | Advisor: Lawrence Chua
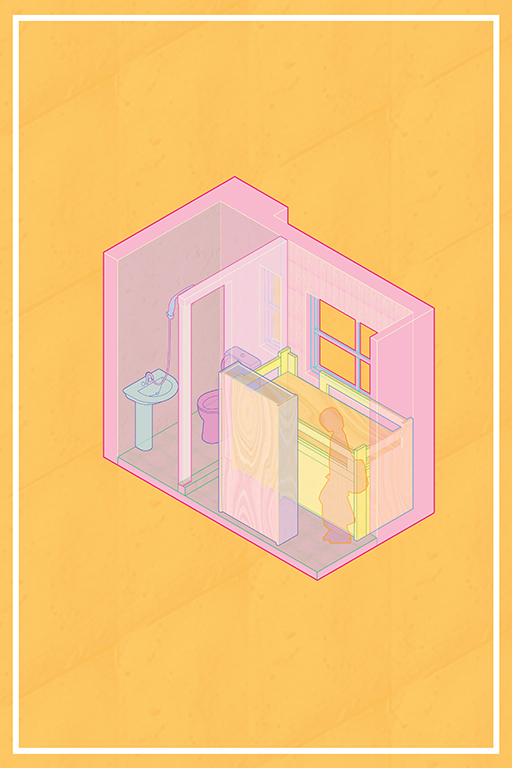
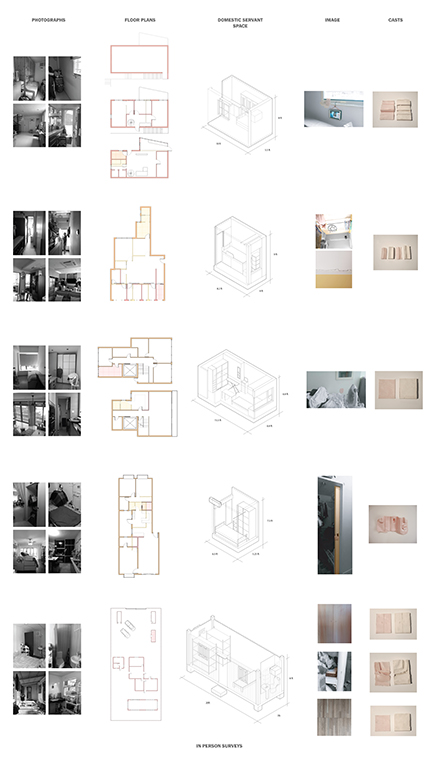
This project examines the relationship between domestic labor laws and the “spatial practices” of migrant domestic worker (MDW) spaces in Hong Kong. The project asks, how do the designed and spatial practices of domestic worker accommodation inform us about the hierarchy and future of domestic space in Hong Kong?
In 2003, Hong Kong issued a law requiring domestic workers to live with their employers. For apartments without a designed servant space, makeshift accommodations have been created within those apartments to comply with the law. The research studies these modifications within the home and creates spatial abstractions through differently scaled models.
The spatial practice of employers and the designs of residential developers of migrant domestic worker accommodations in Hong Kong creates a hierarchy between the servant and the served through varying means, ranging from porousness to confinement. We see this in examples such as sharing spaces with other household members, living in the living room or kitchen, and in objects such as fabric partitions, unlockable doors, or security cameras.
The research is based on a survey that was carried out in collaboration with the Mission for Migrant Workers, an NGO in Hong Kong. Additionally, in-person interviews revealed that employers renovated servant spaces antithetically to the developer’s designs. The survey asked questions about privacy and had the workers draw a floor plan of their accommodations, while the interviews allowed for an intimate understanding of spaces and casts that preserve the material damage due to their labor. This project proposes shifting furniture and structural changes to the participants’ apartments to expose the absurdity of the condition.
Since many employees struggle to voice their opinions about space, the passive-aggressive act of rethinking the functions of these household objects as weapons to ensure privacy also critiques power dynamics in the household. Furniture alterations allow for the employee to play more games of resistance during the hours when the employer is at home. It utilizes what is of importance to the employer as leverage for the employee to get privacy, respect, and dignity.
Instagram: @kristabelchung
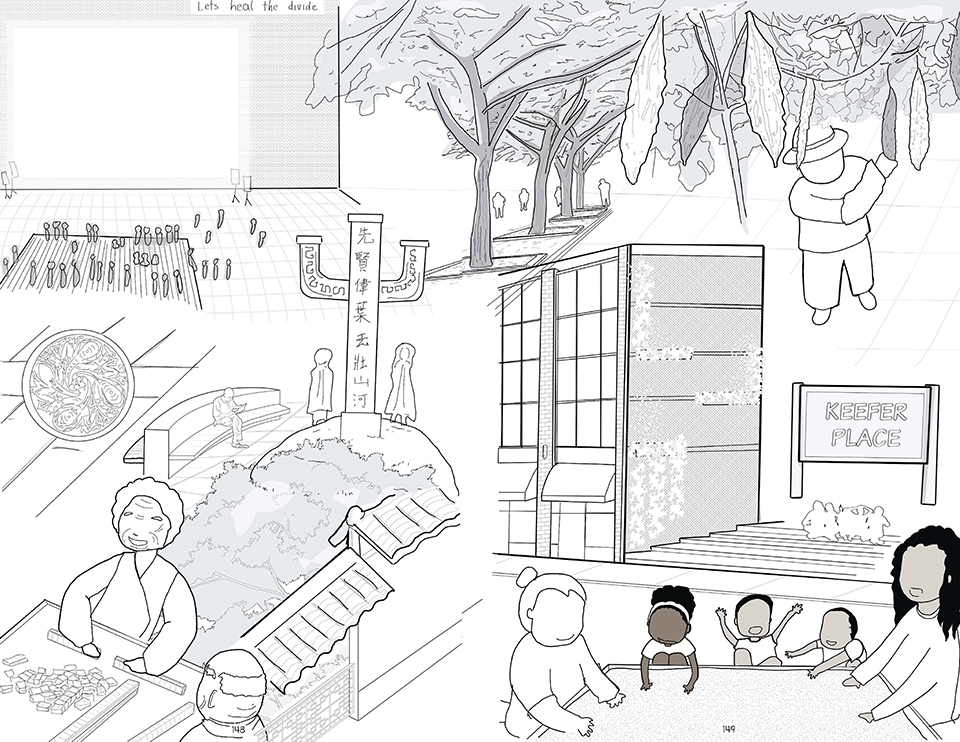
Living with Ghosts by Ximeng Luo and Shihui Zhu, B.Arch ’22
Syracuse University | Advisor: Lawrence Chua
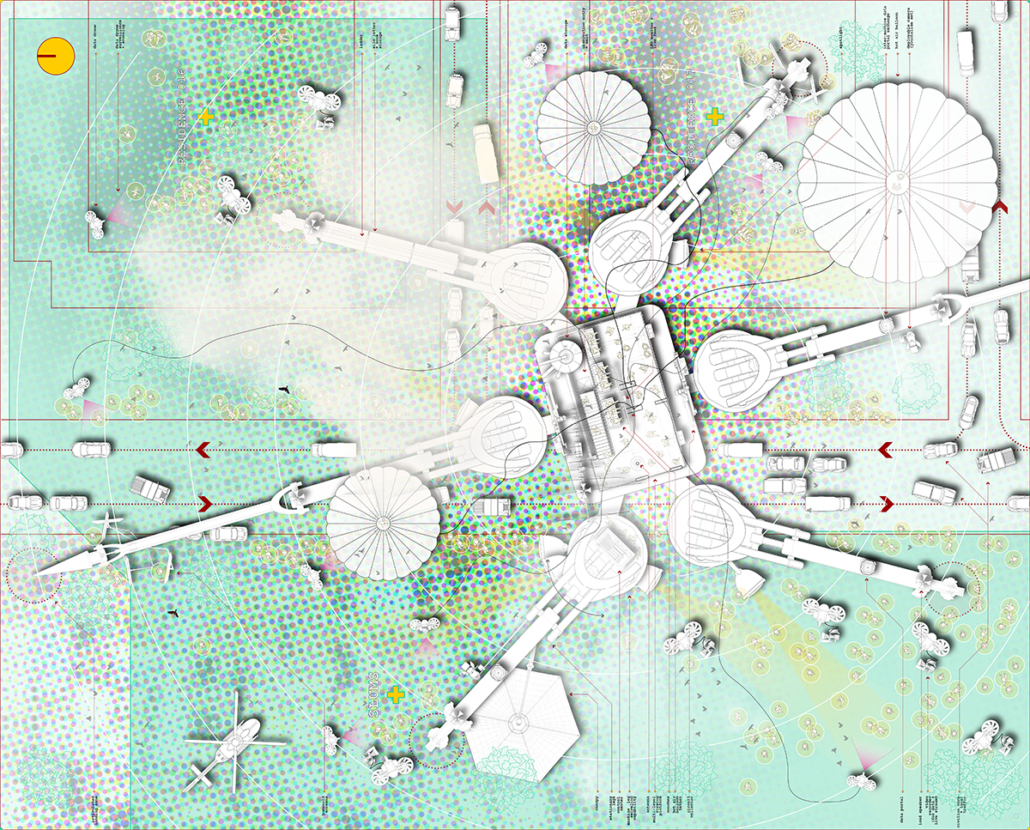
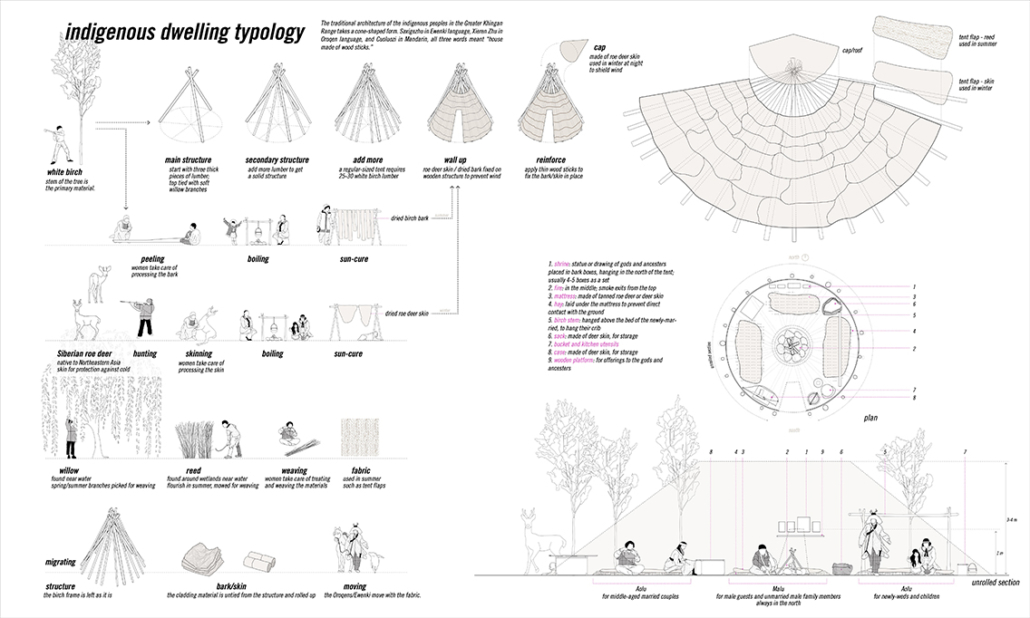
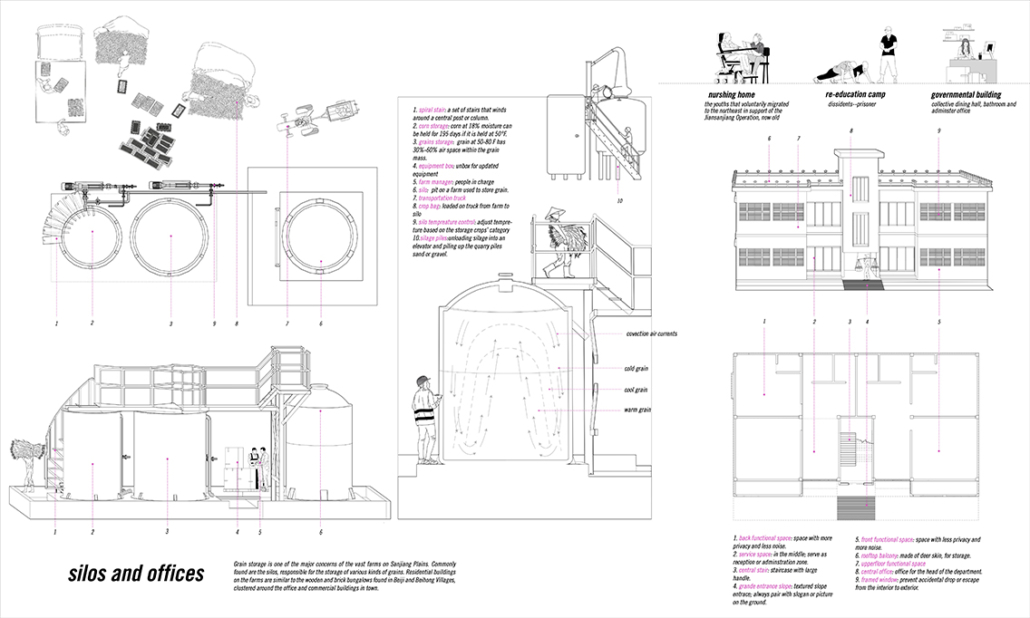
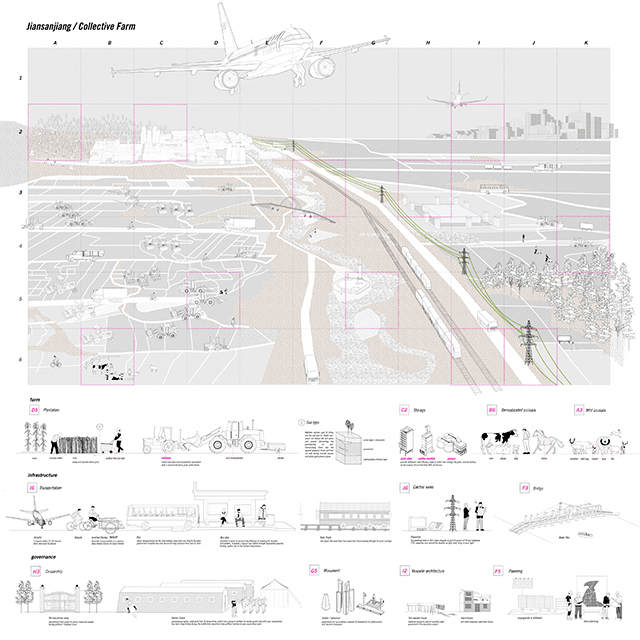
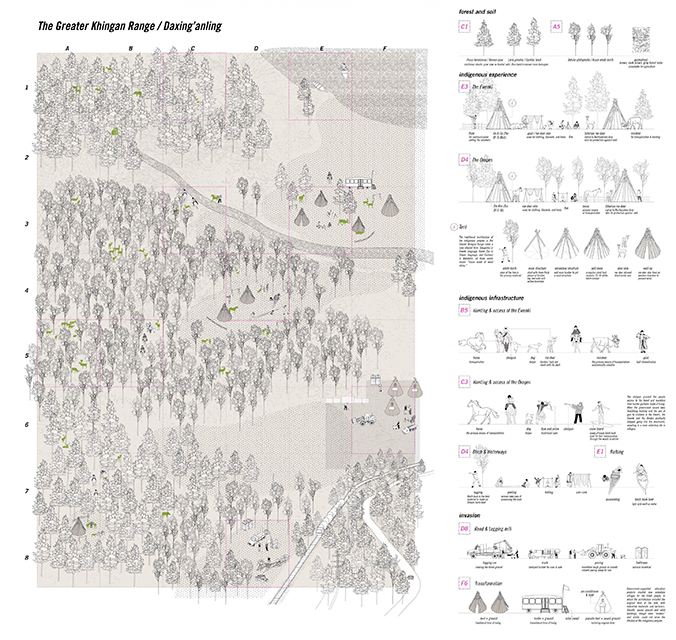
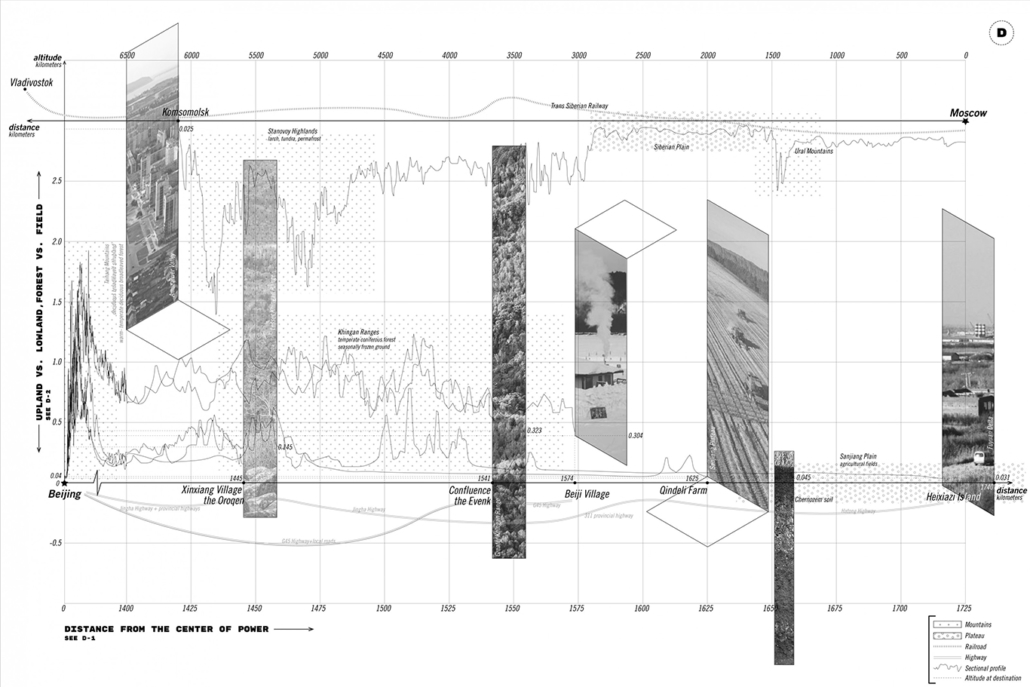
“Maps! Living with Ghosts” is a thesis project on representation based off from our research of the border region between China and Russia, in which we translate the data collected from official statistics, policies, documents, and more private travel logs, interviews, diaries, memoirs, and literature, into a composite drawing, to explore the possibilities of images and representation techniques.
In the contemporary context, the same piece of natural land often displays a superimposition of various truths. The collapse of overlapping spacetime can be found in marks created by human construction activities, compressed into the concept of contemporaneity.
Indigenous knowledge and local understandings get lost in the supersession of the old understanding of space by the new that is observably dictated by modern maps. Hence, memory itself becomes a representation of the space being understood and remembered, and it continues to influence people’s perception of reality, like a ghost that haunts the living. While the nation state can easily encroach upon ungoverned spaces and wipe out their past, the people who lived on the land carried their ghosts with them as they proceeded in life.
In the project, individual memories are collected and translated into certain forms of representation and overlaid on top of the scientific map, showing transparency as well as complexity, a new composite representation of spatial relationships and identities.
The scene is set along the Heilongjiang. A fluid water body that feeds populations in the Russian Far East and Northeastern China, simultaneously delineates the long and winding national border between contemporary Russia and China.
The project traces the river downstream, investigating five specific sites. From man-made landscapes in the forms of nomad camp, temporary settlement, village and town, and cities in this borderland far from the state’s central power, we are looking into both the natural landscape and environment, presence of the authority, and the resulting forms of living.
Instagram: @sximengl, @sunnyynnuss
Part VII of the Student Showcase coming soon!













![[IN]visible_site - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_site-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x644.png)
![[IN]visible_1-render - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_1-render-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x579.png)
![[IN]visible_2-render - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_2-render-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x579.png)
![[IN]visible_longsection - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_longsection-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x297.png)
![[IN]visible_plan1 - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_plan1-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x1030.png)
![[IN]visible_plan2 - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_plan2-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x1030.png)
![[IN]visible_short section - Ying Xuan Tan](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/INvisible_short-section-Ying-Xuan-Tan-1030x386.png)



























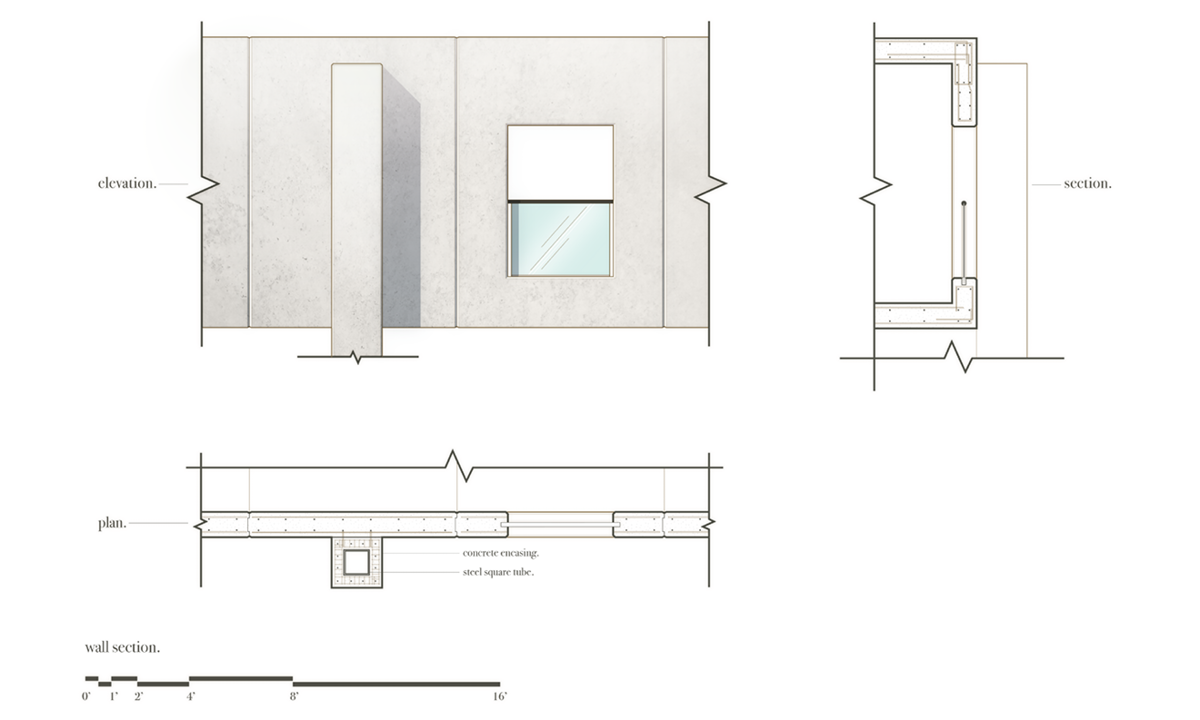
![wall section revised [Converted]](https://studyarchitecture.com/wp-content/uploads/Josue_05-Robert-Alexander.jpg)