2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XIII
Public spaces take the spotlight in Part XIII of the 2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase. The featured projects include recreation centers, parks, memorials, performance spaces, multi-faith facilities, city centers, and more!
Each student’s design was crafted with community needs at the top of mind. They utilize strategies ranging from reducing height in response to residential locations and combatting hostile architecture. They are also intentional about the use of materials with mediums such as wood, steel, and glass playing a role in curating the visitor experience. Each project aims to promote equity, education, belonging, socialization, and connectedness within their communities.
Scroll down to view these inclusive, accessible, and vibrant public spaces!
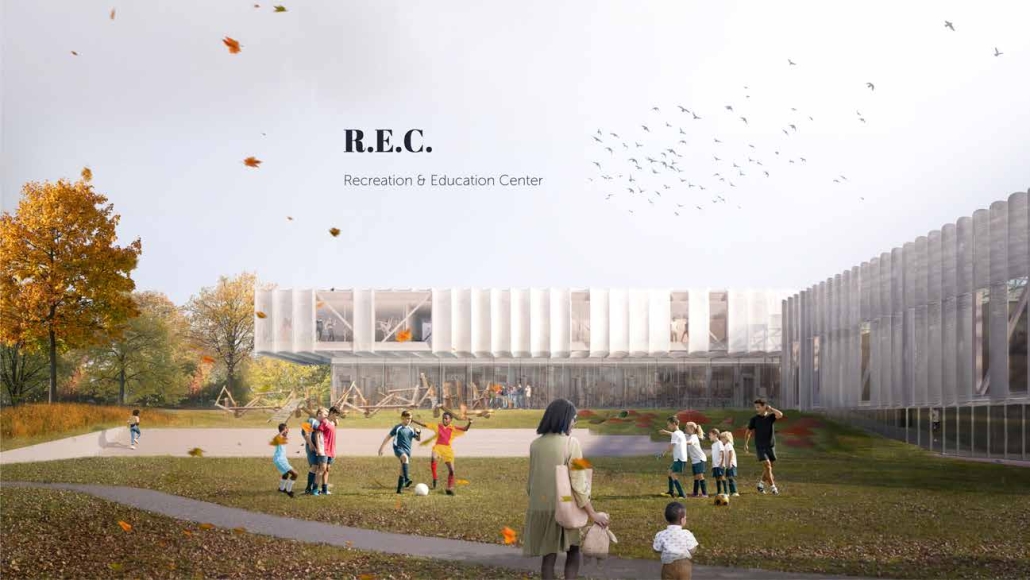
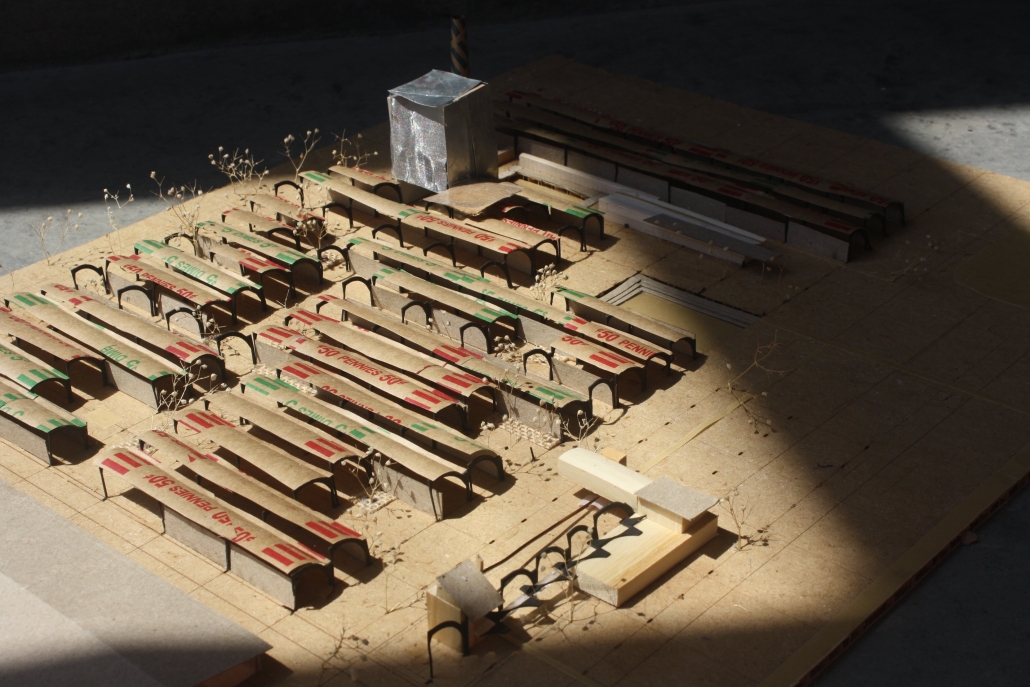
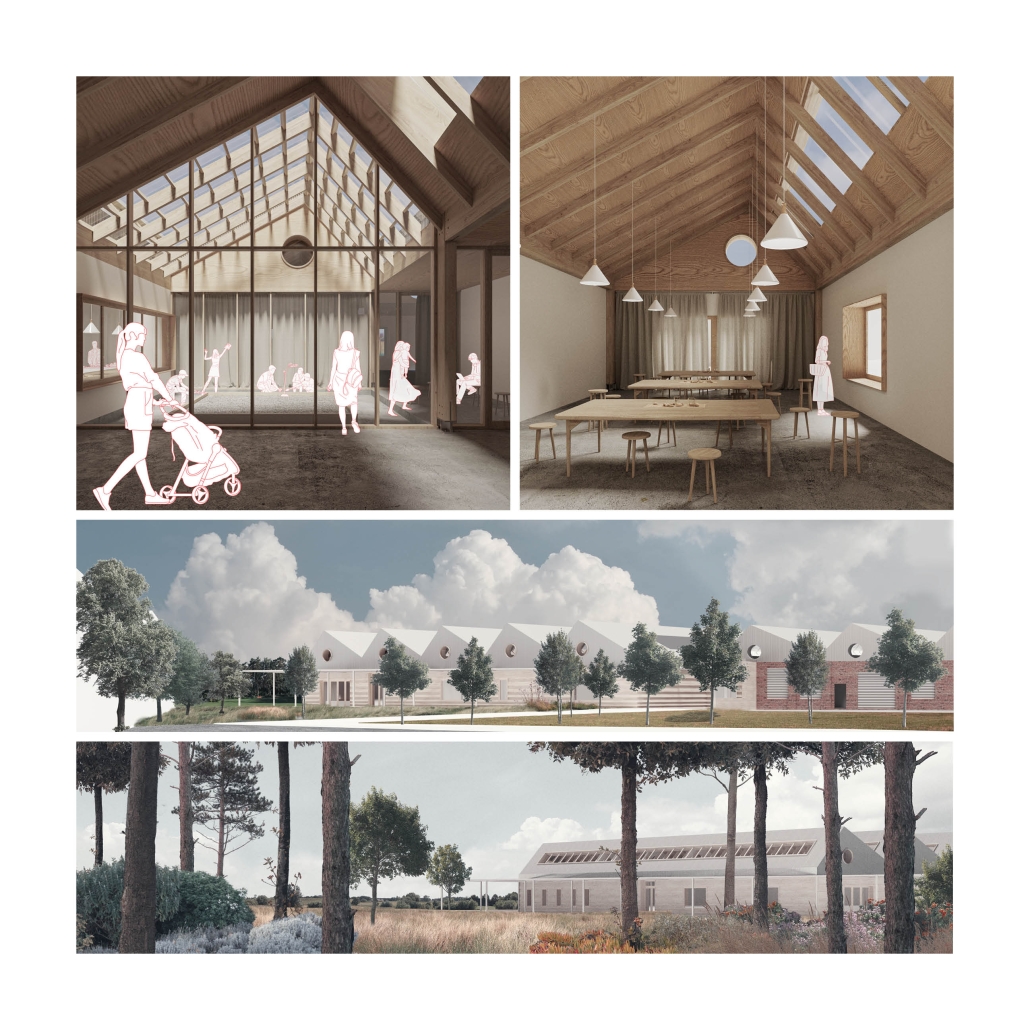
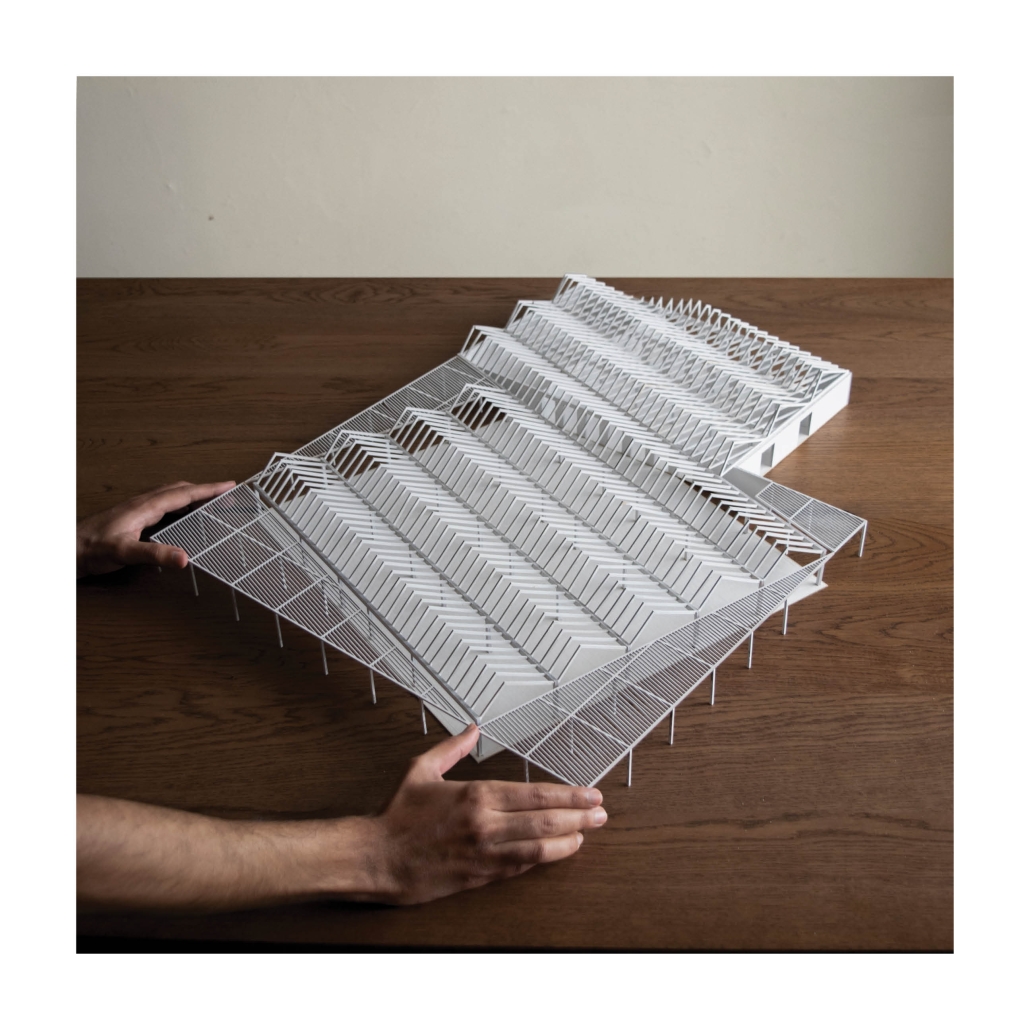
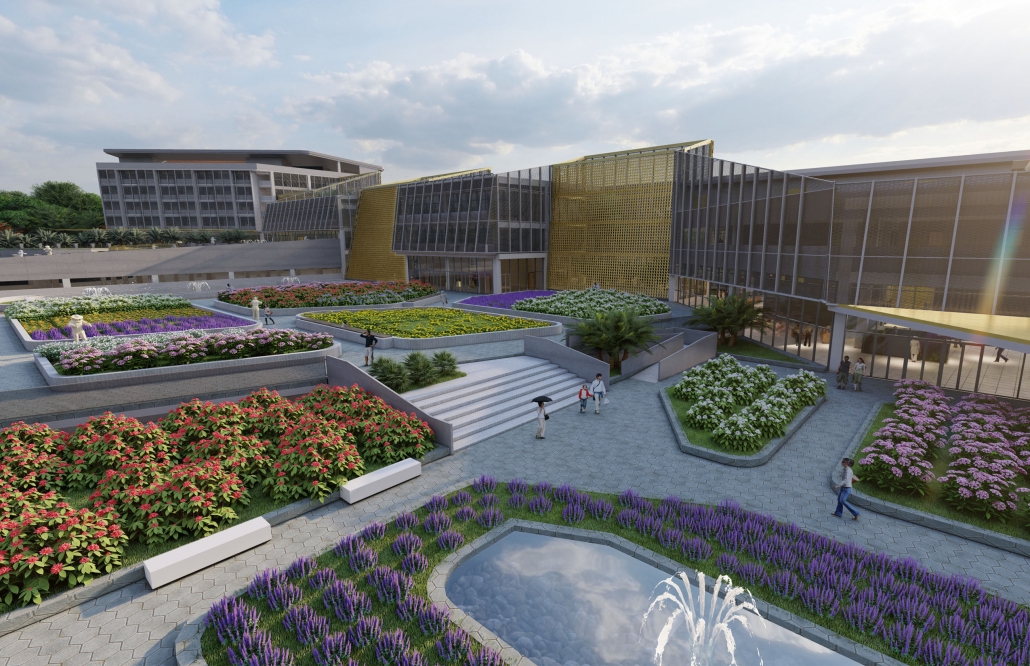
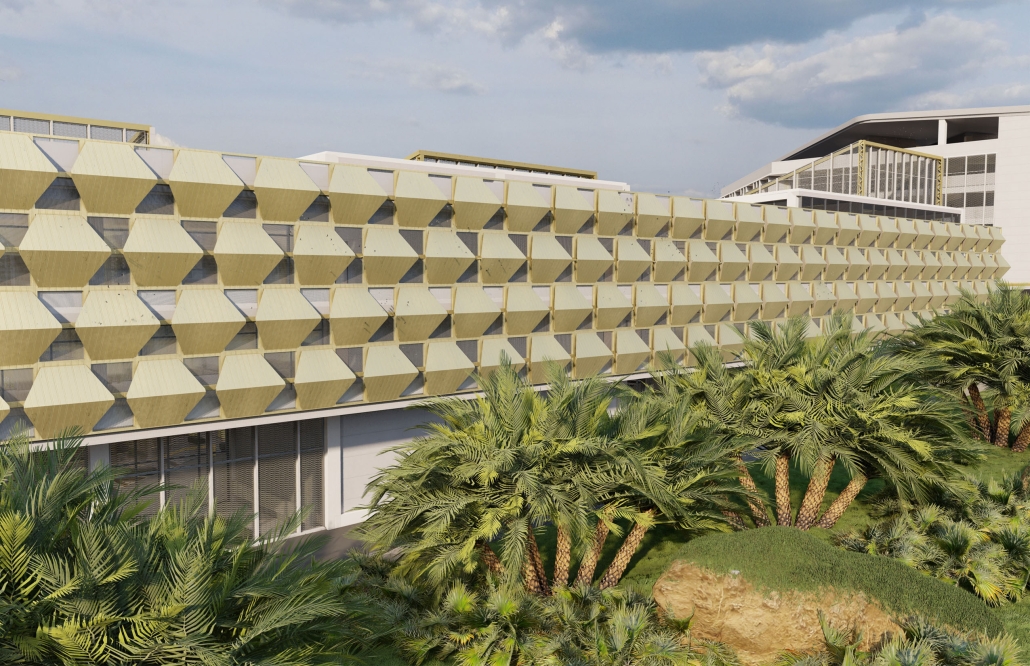
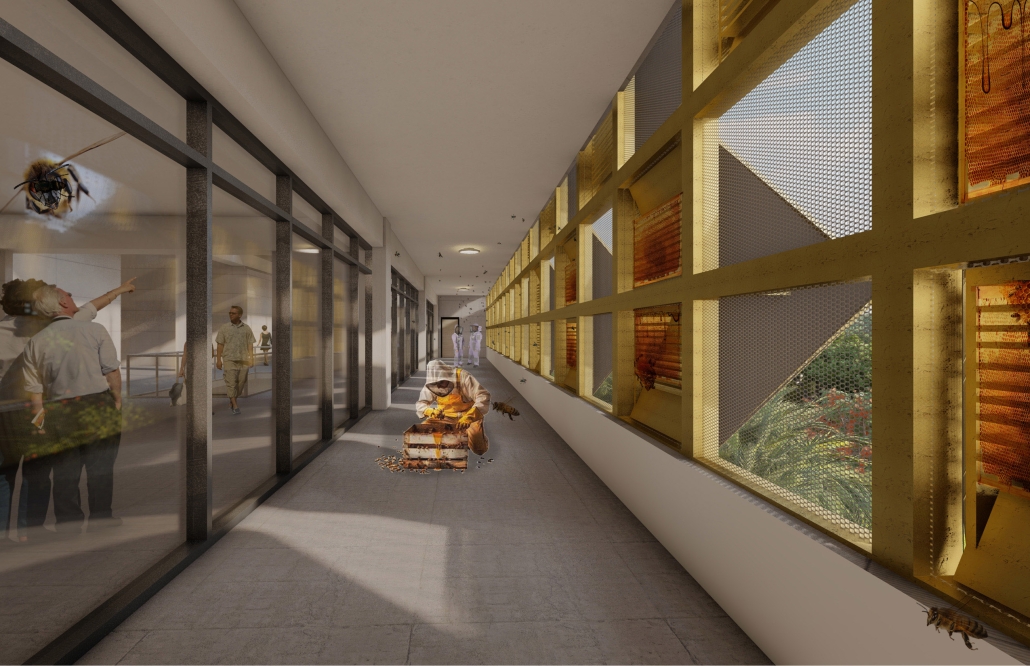
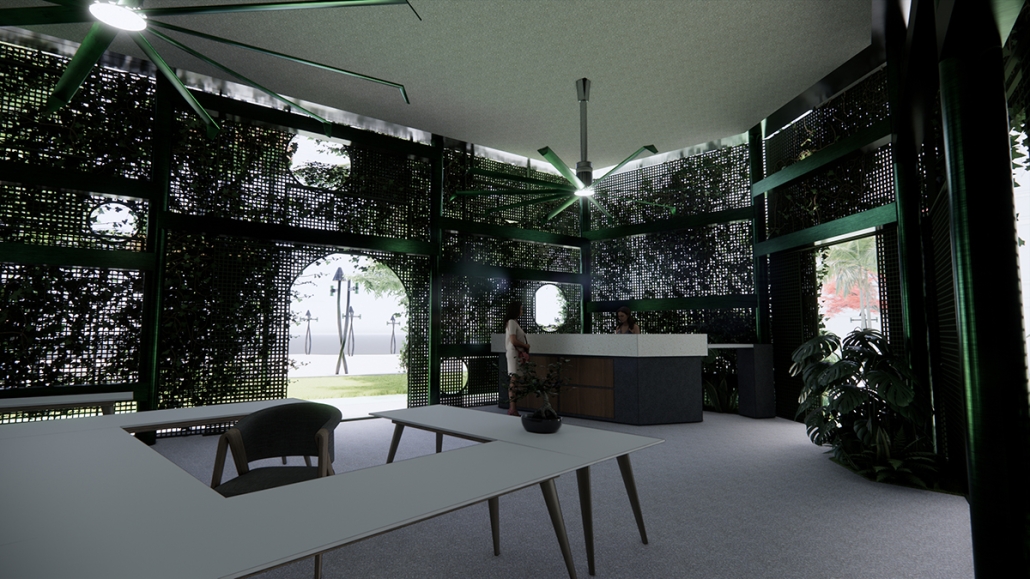
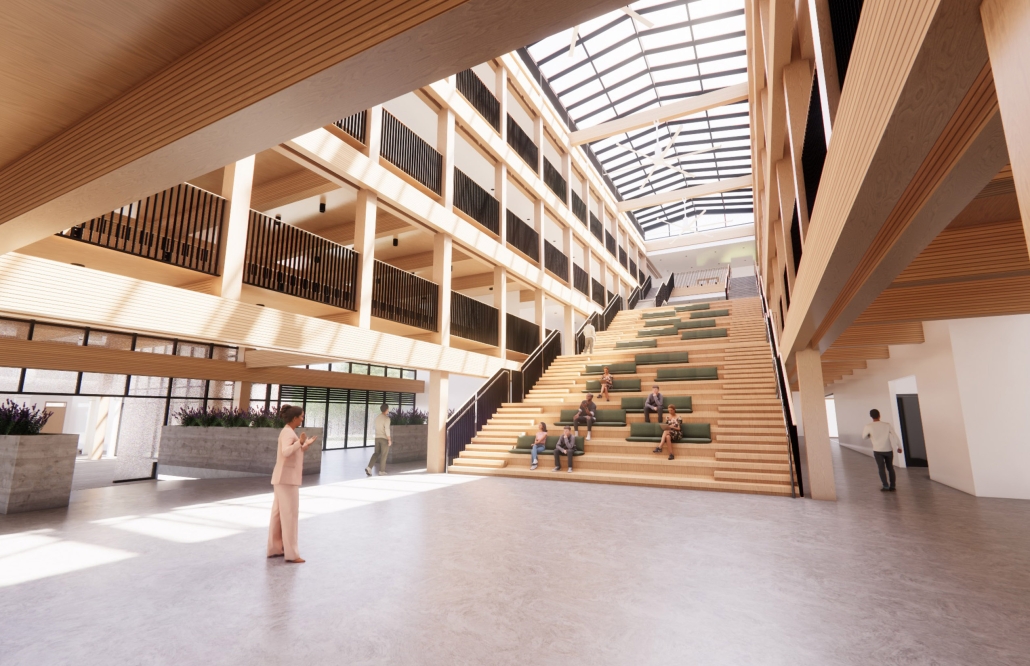
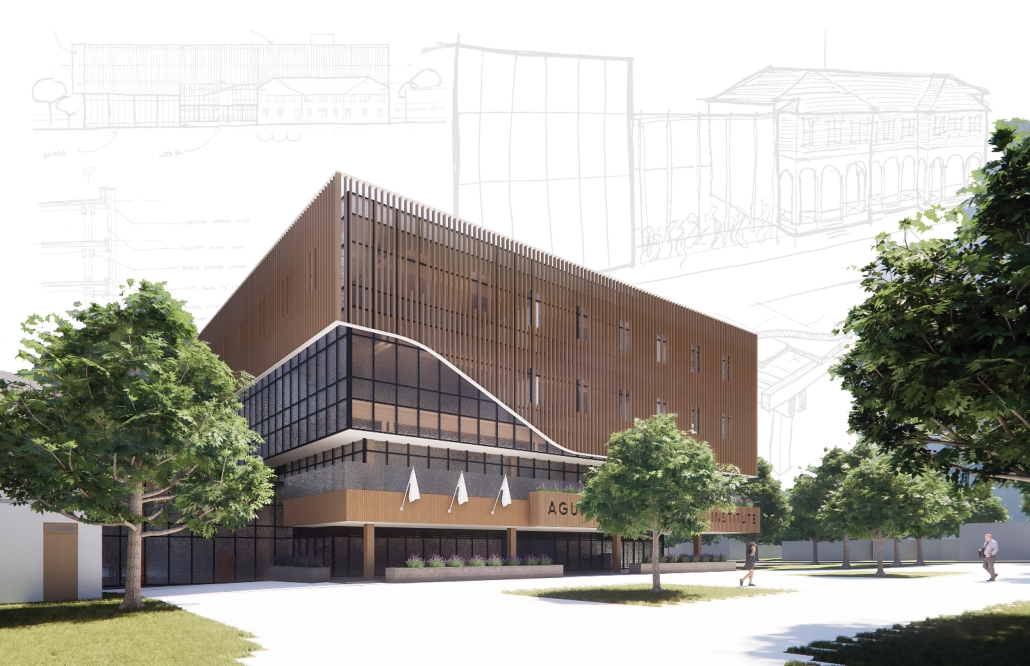
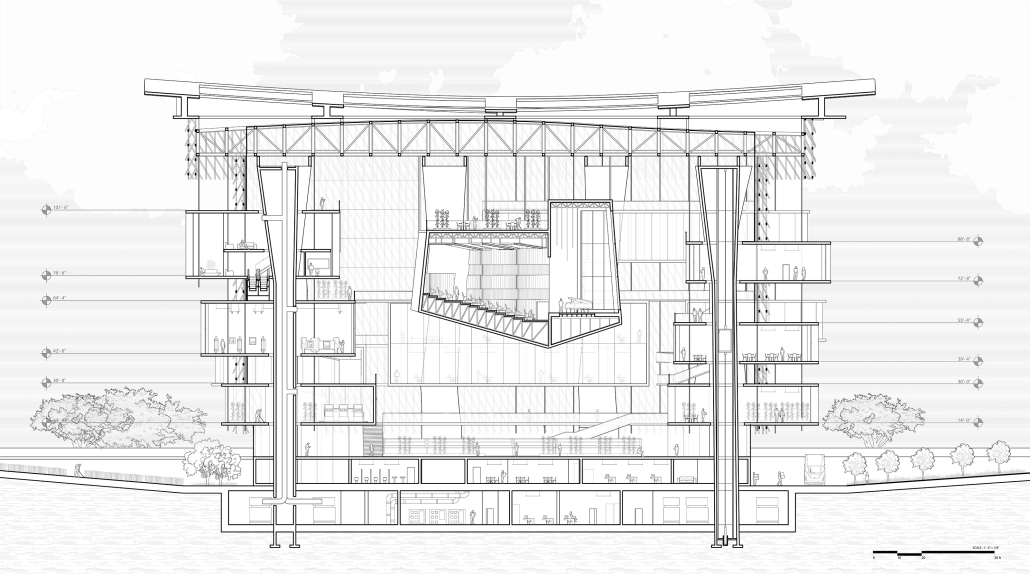
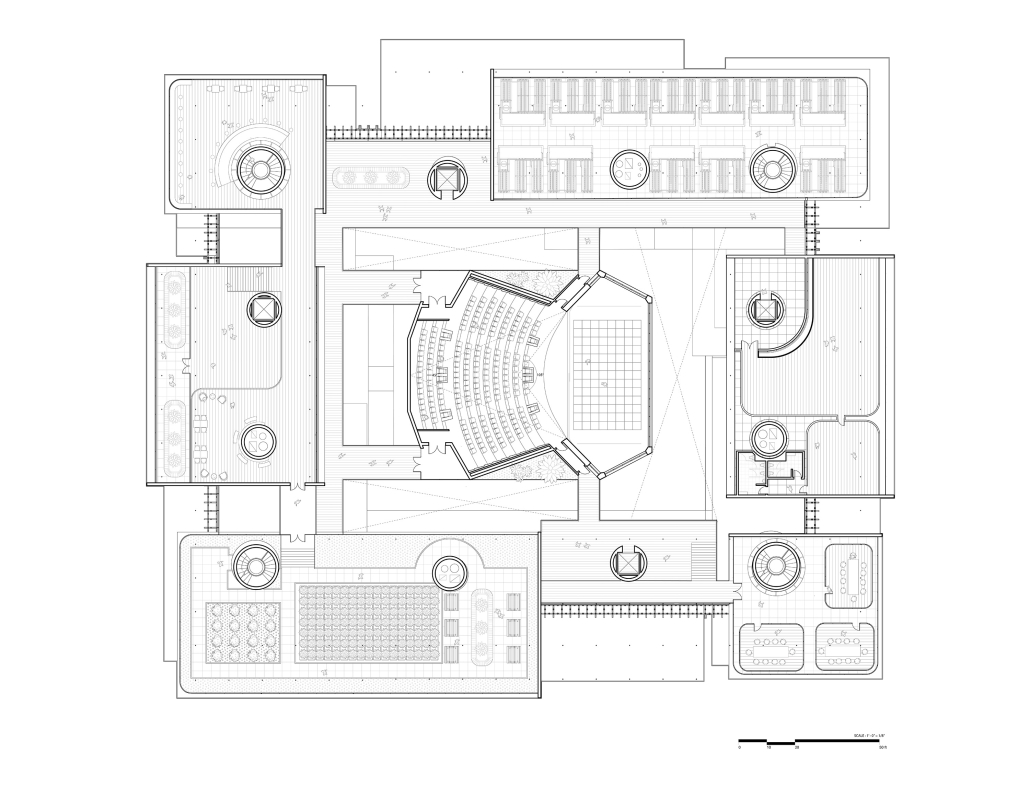
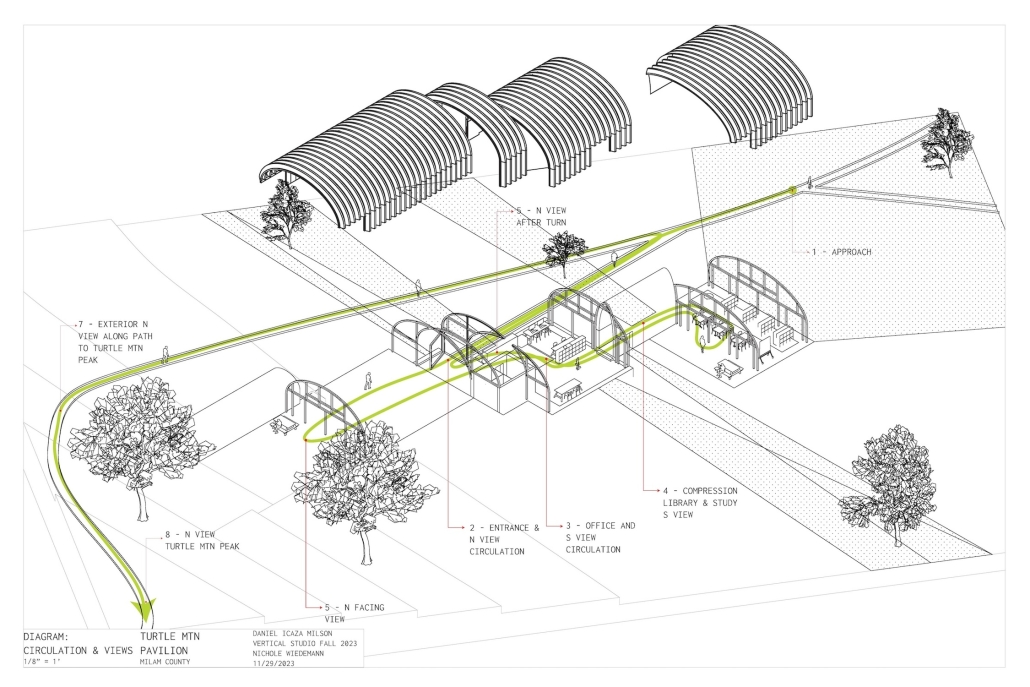
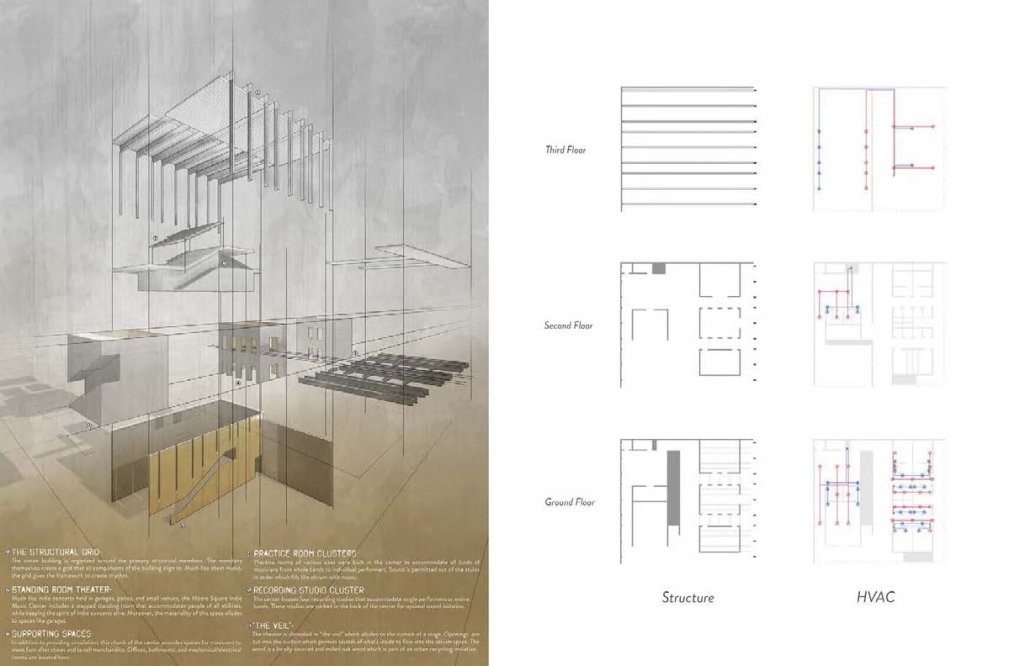
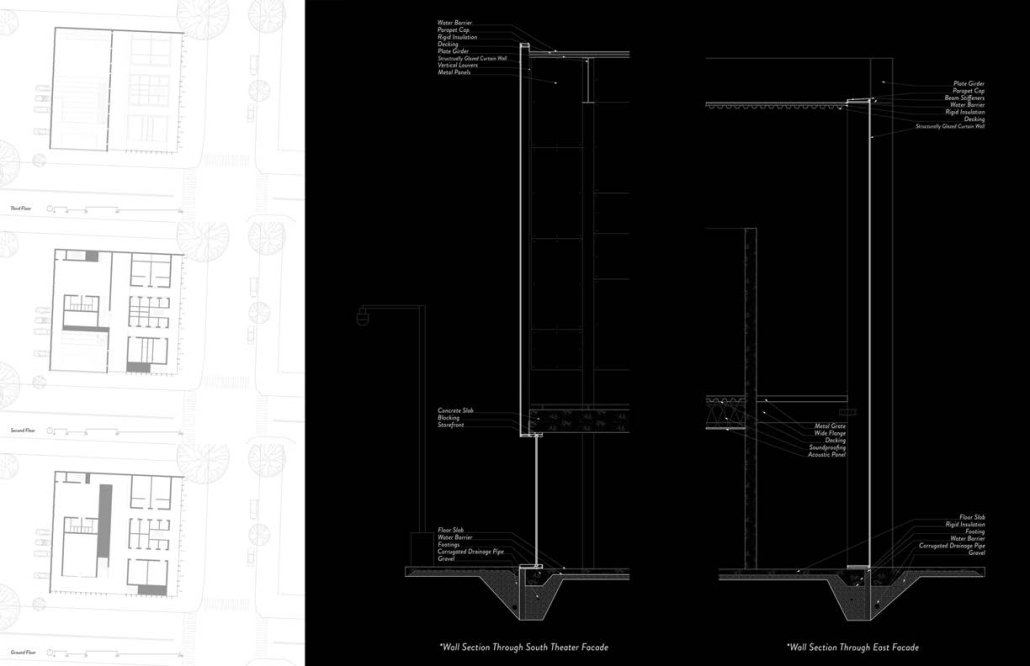
Tarboro Road Recreation Education Center by Lucas Stott, B. Arch ‘24
North Carolina State University | Advisor: Marshall Purnell
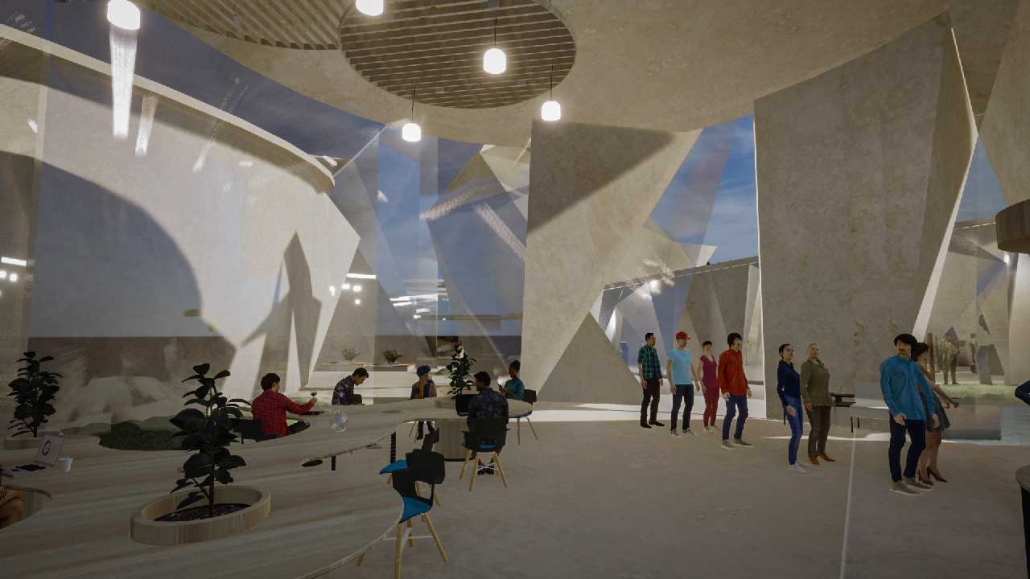
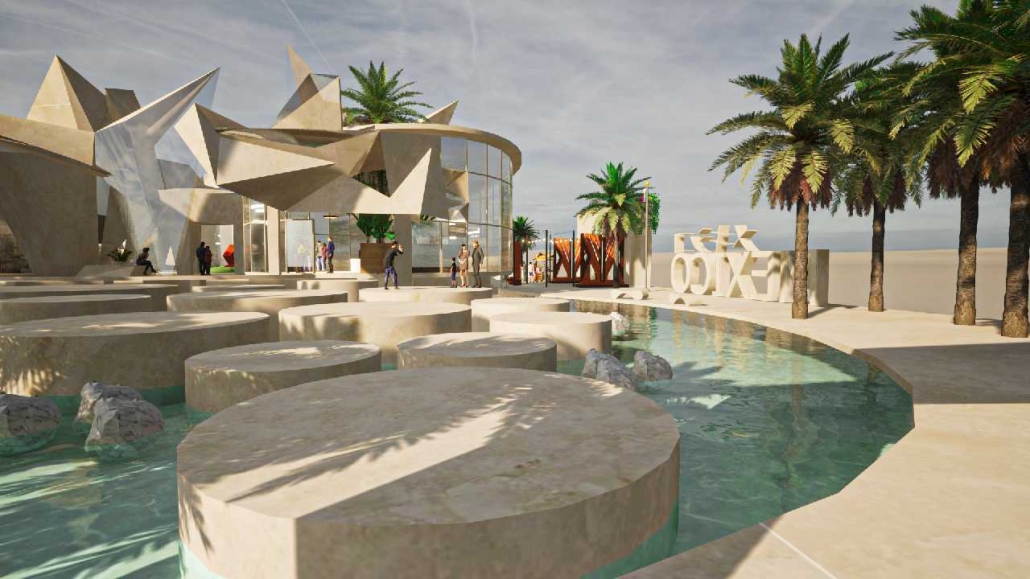
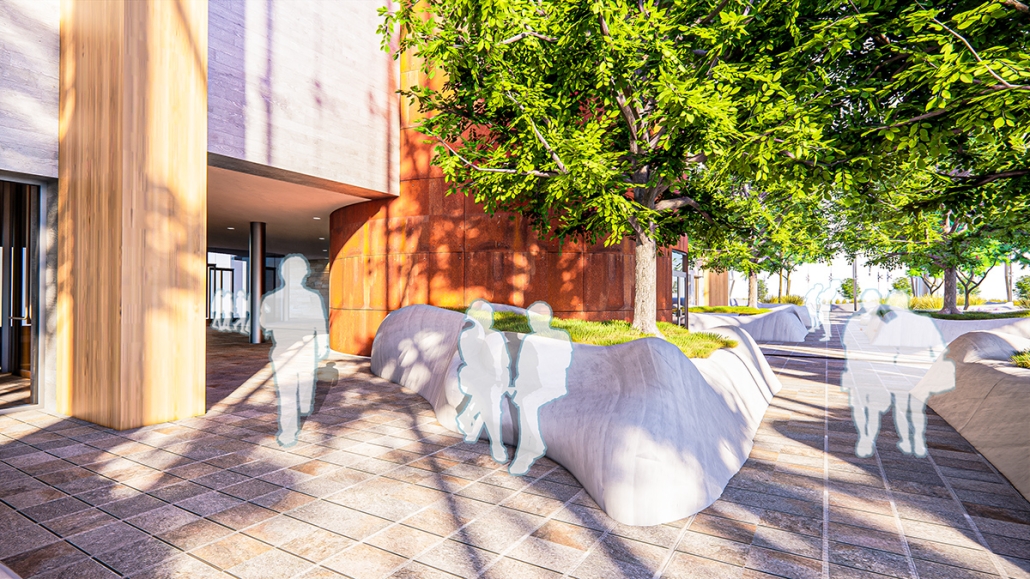
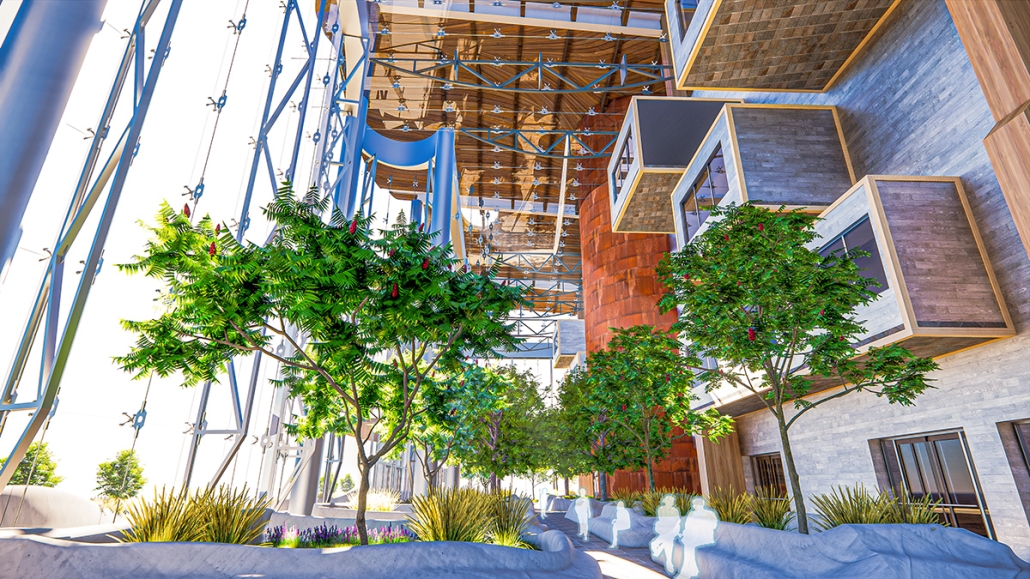
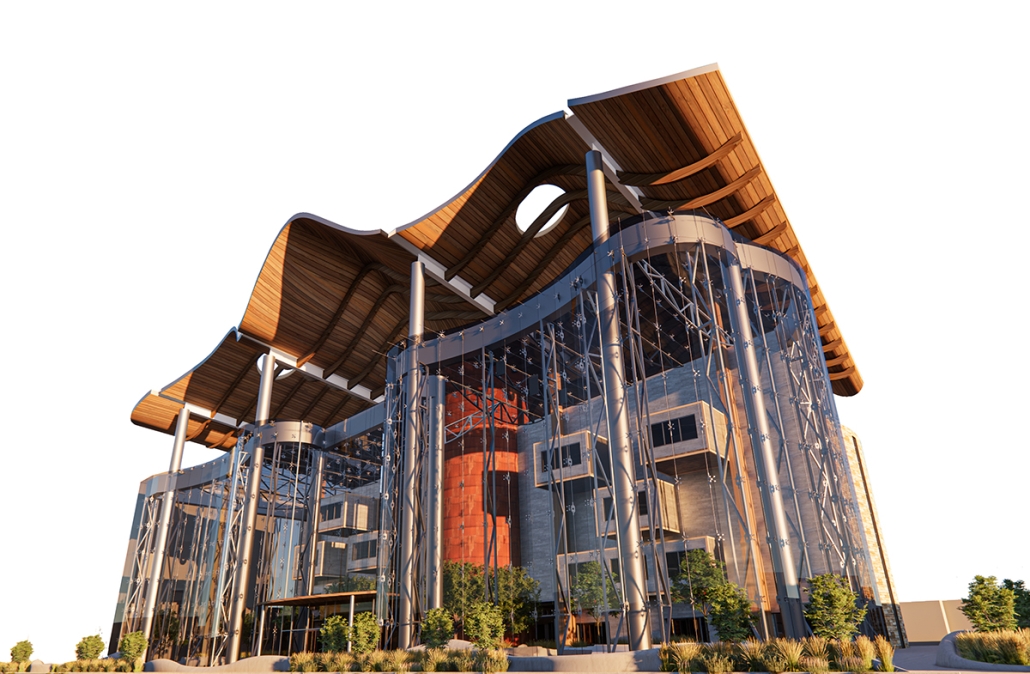
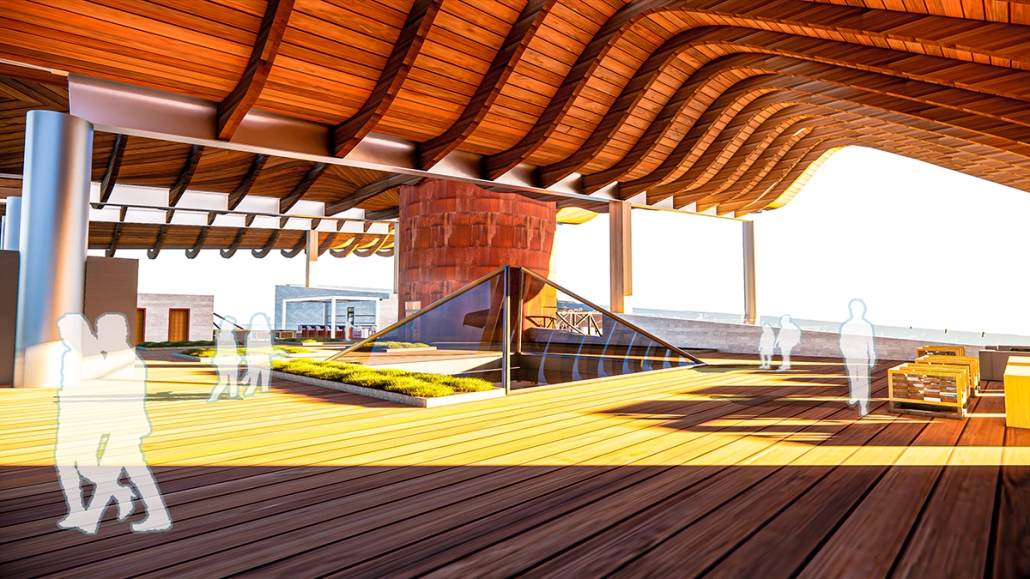
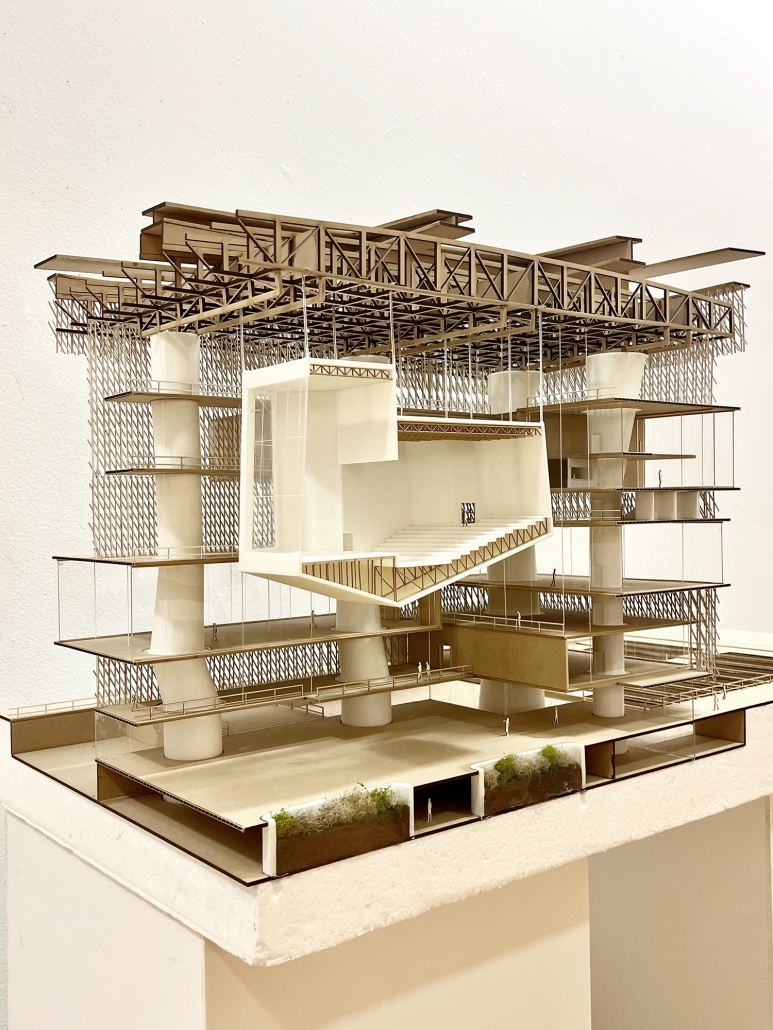
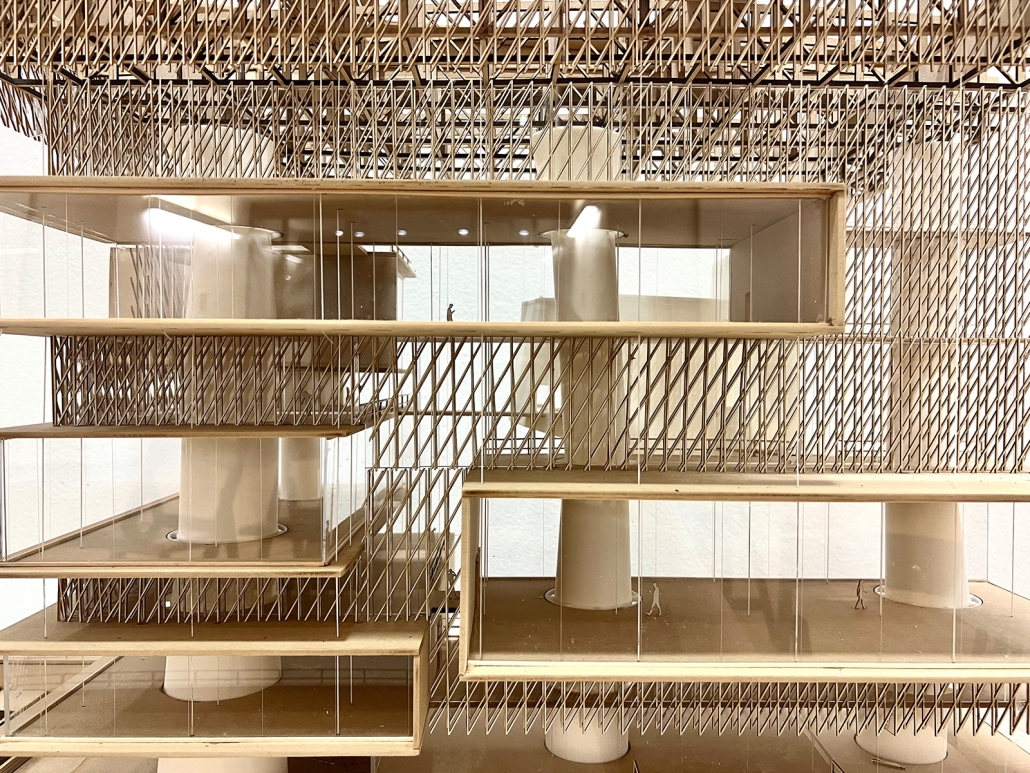
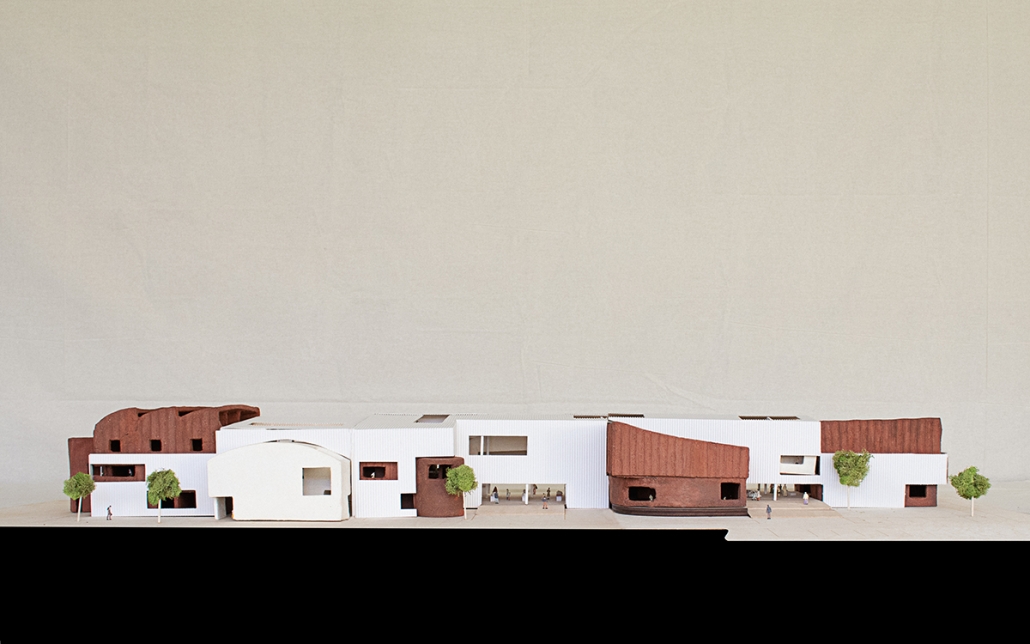
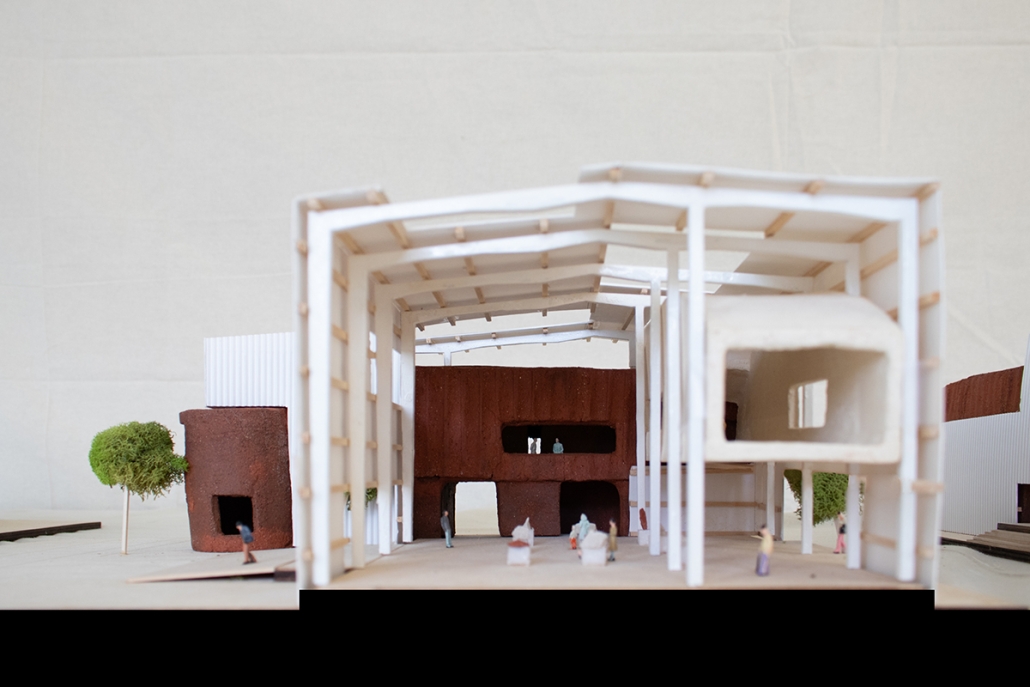
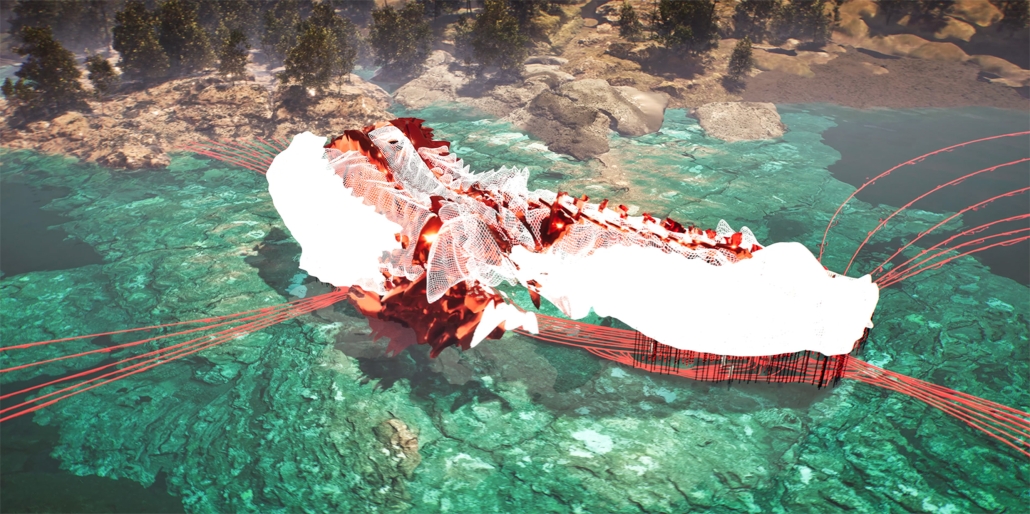
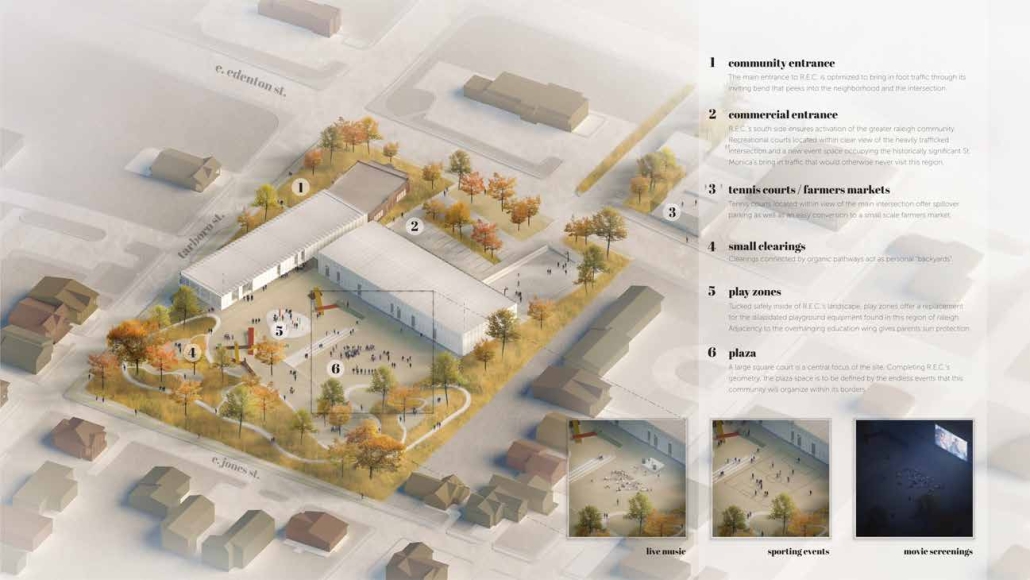
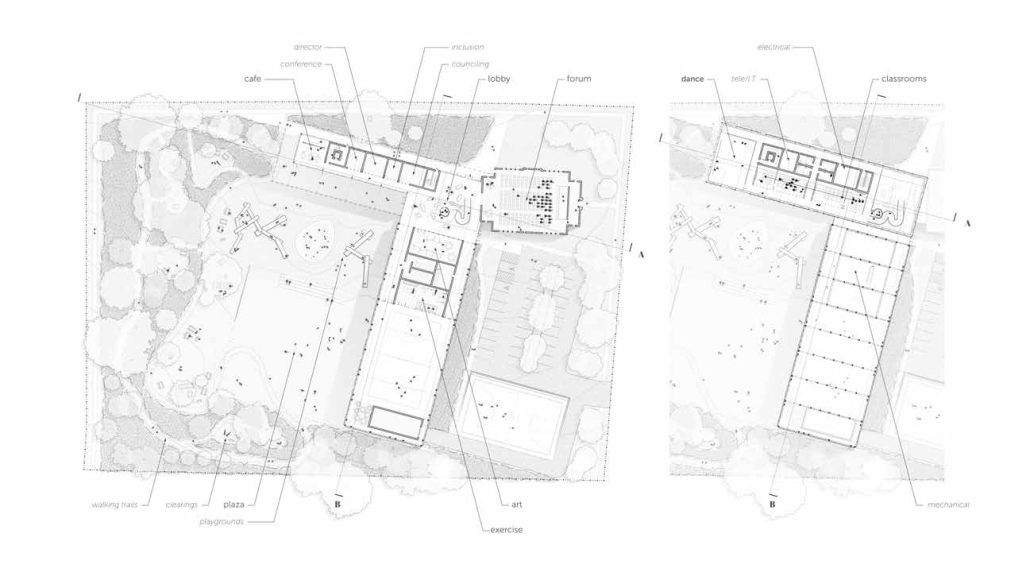
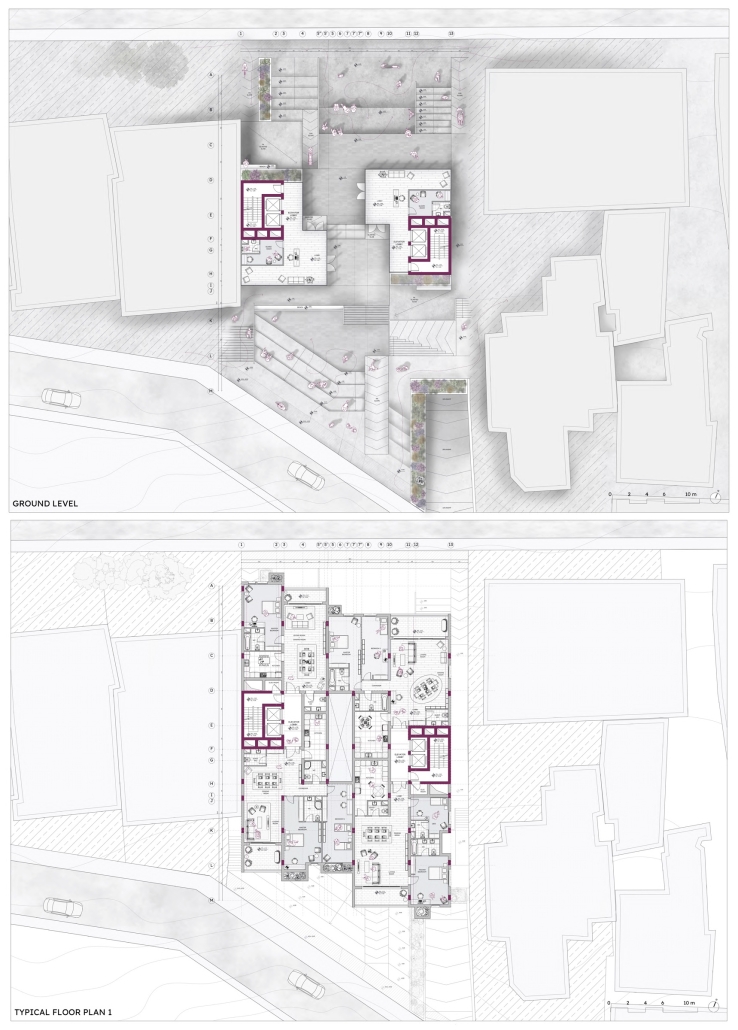
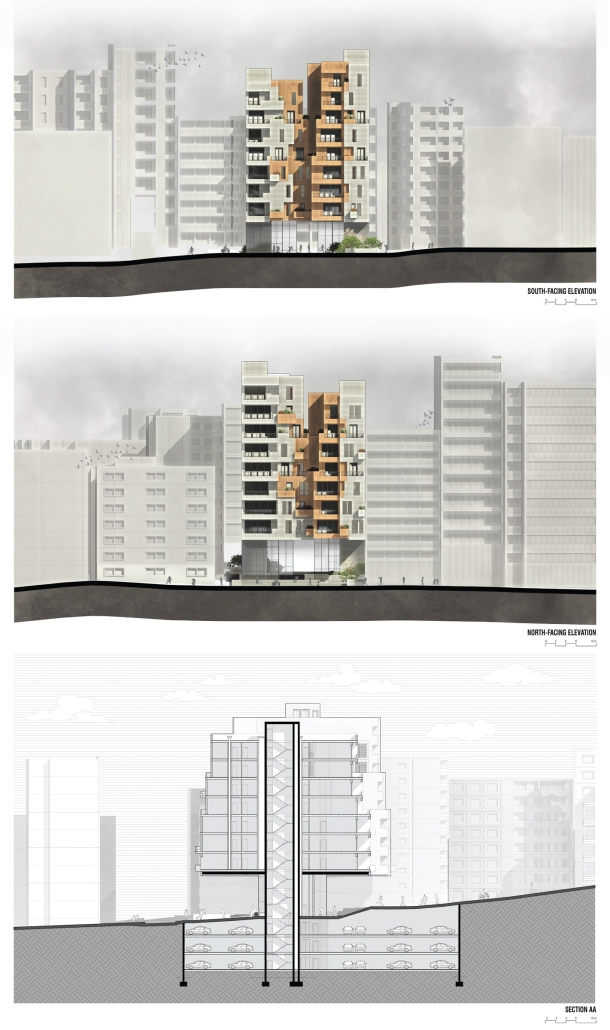
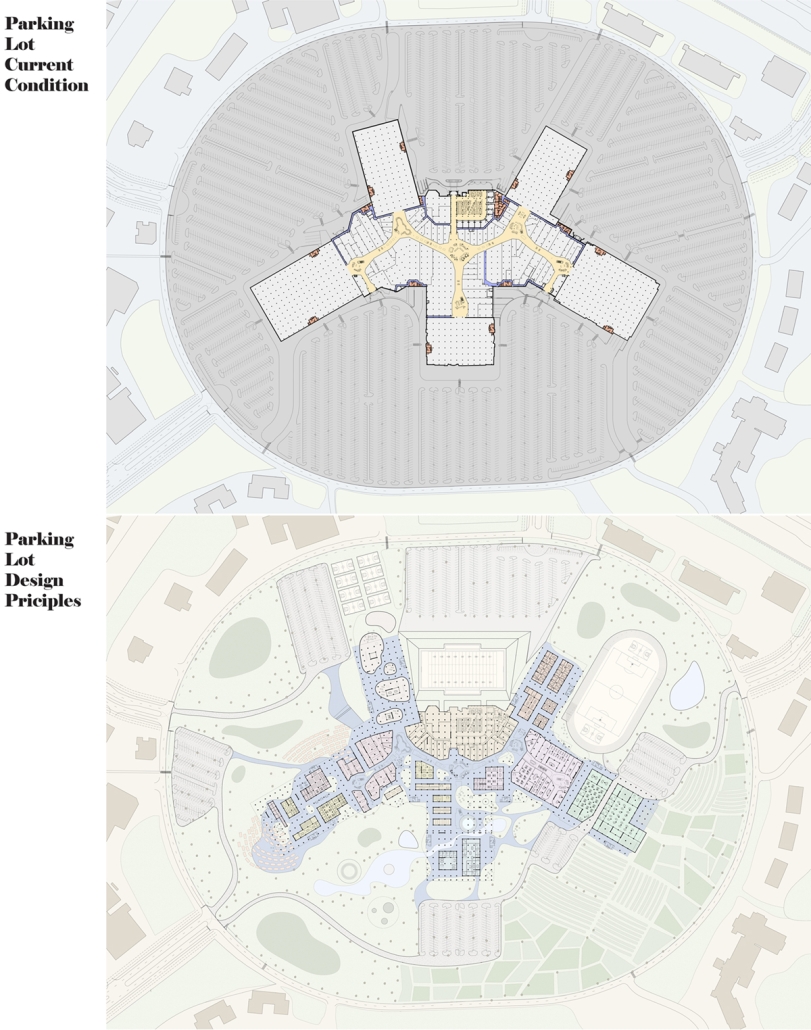
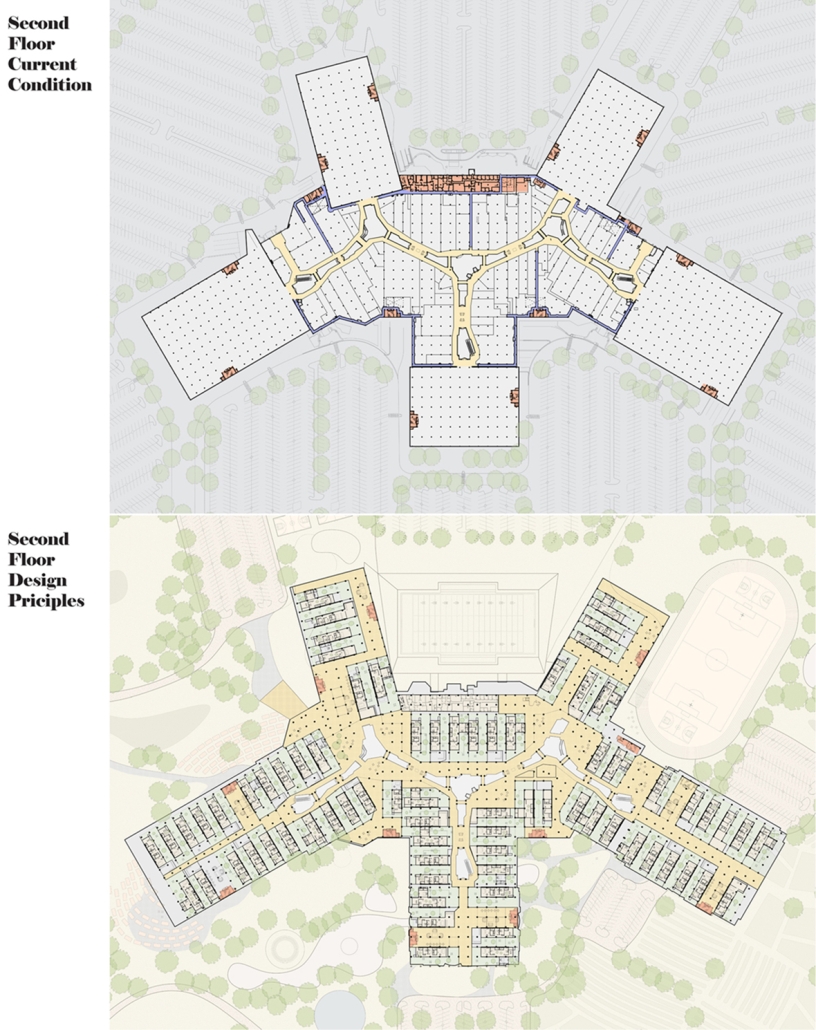
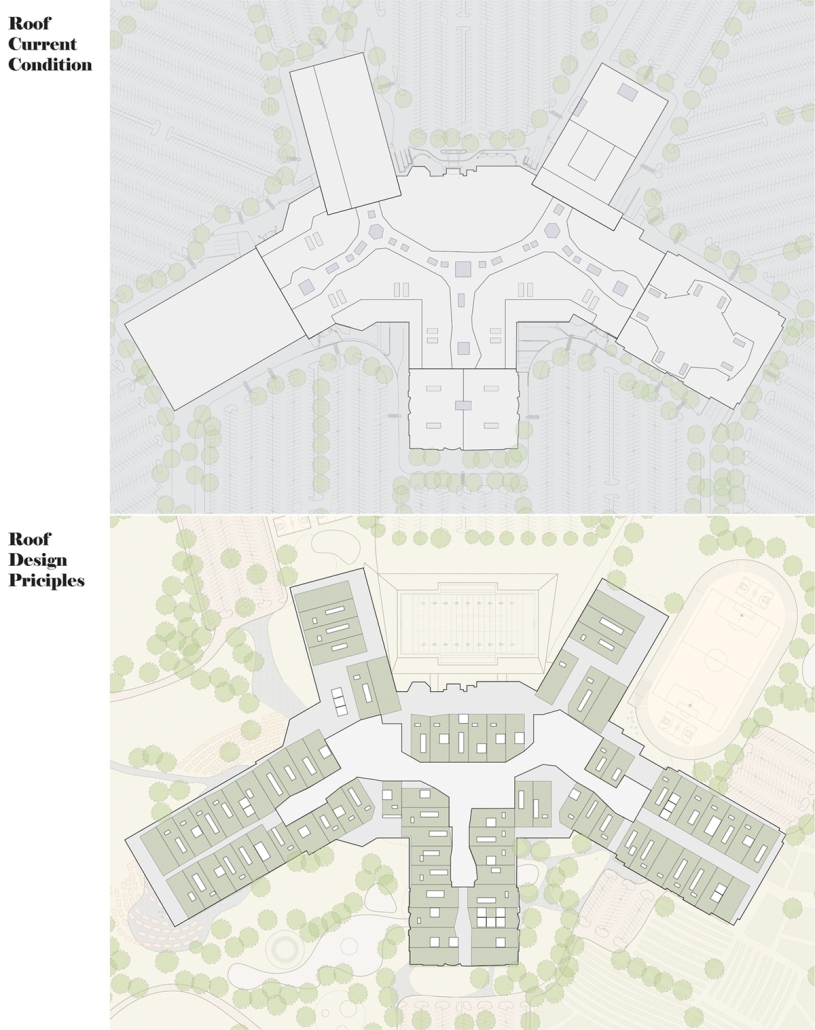
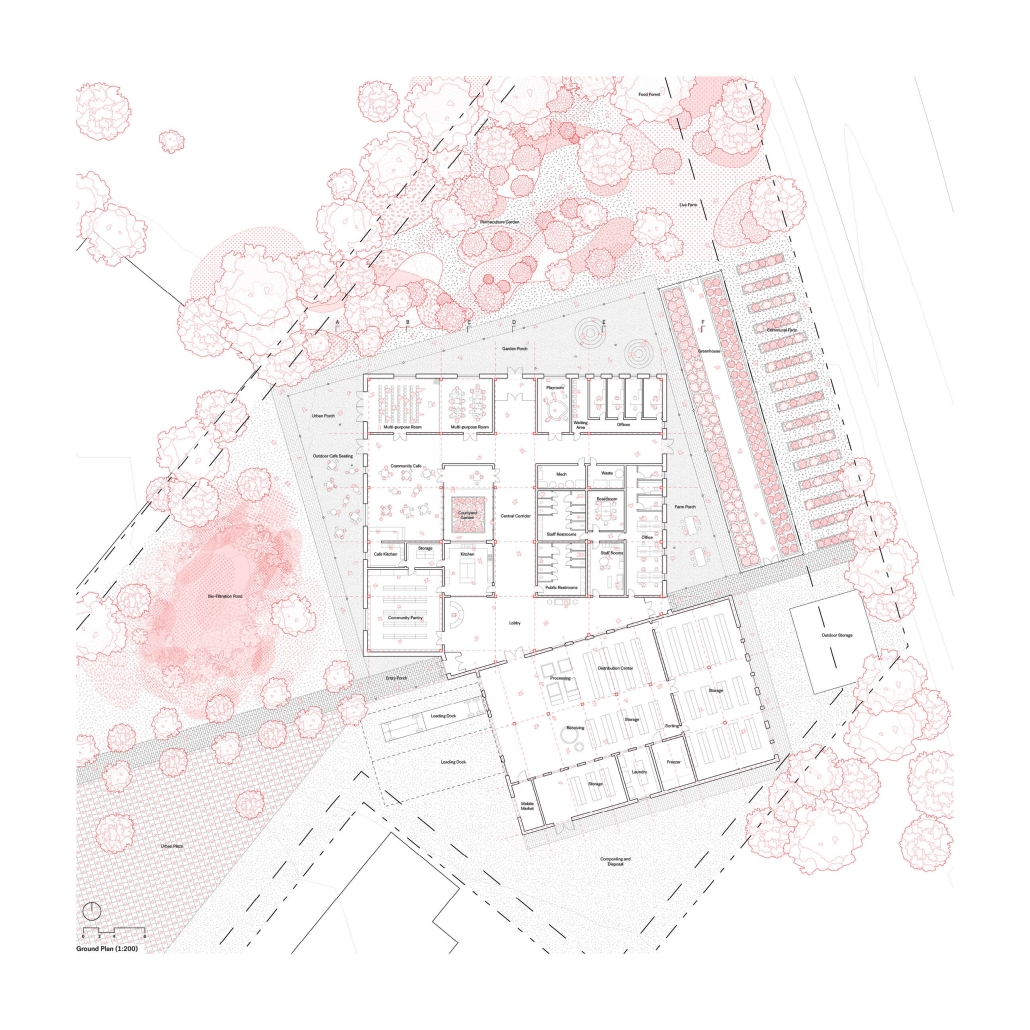
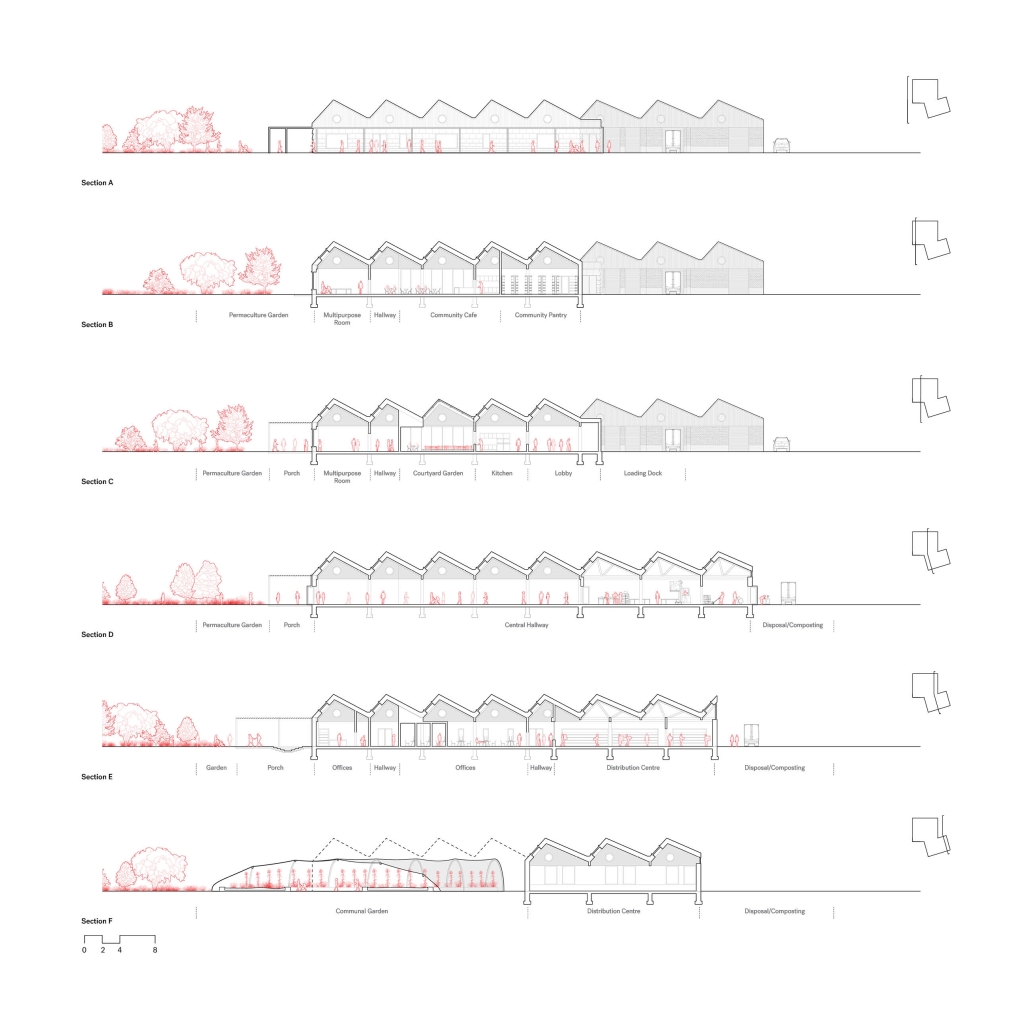
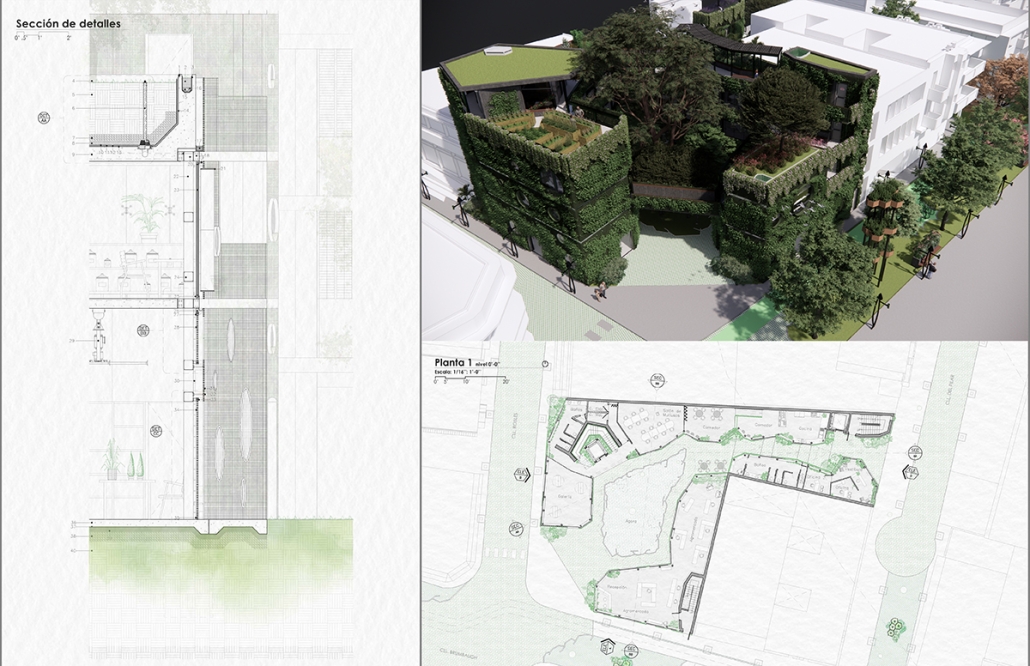
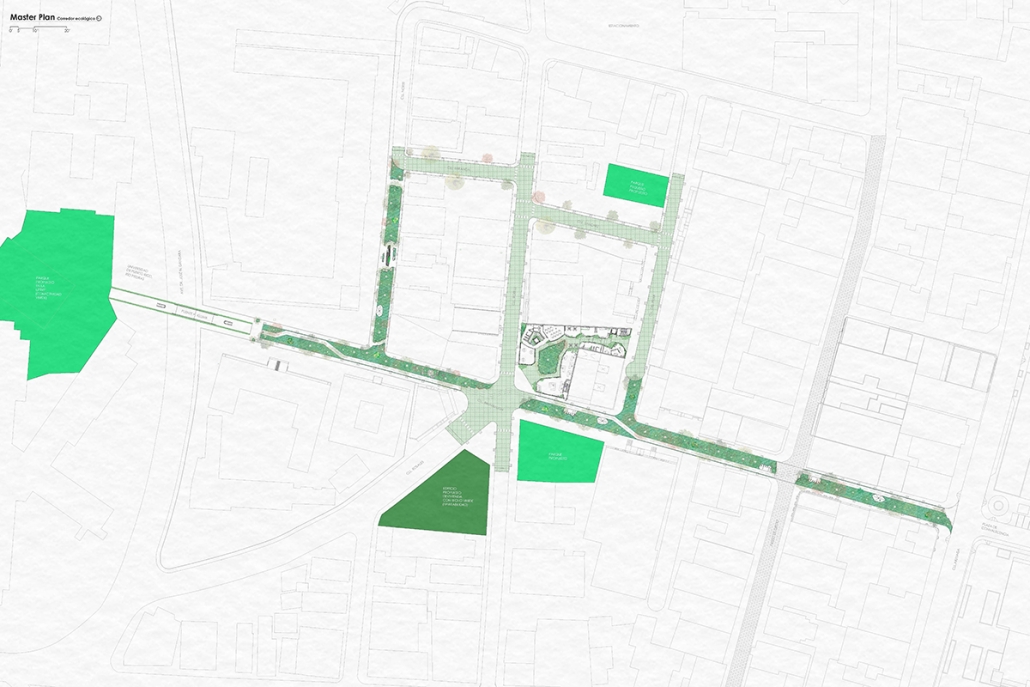
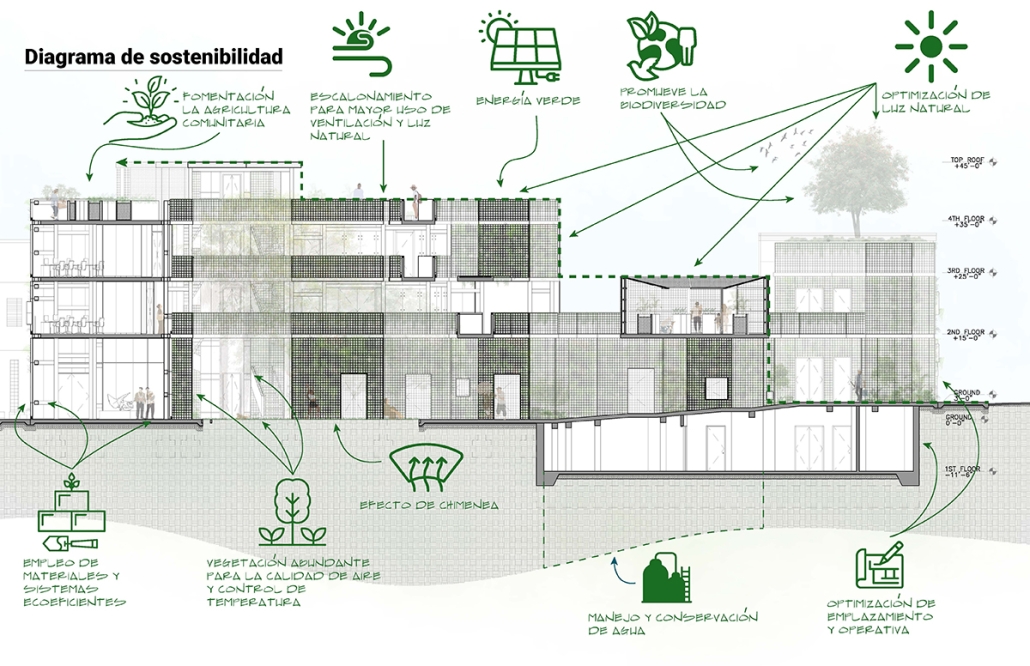
Compelled to provide vital community forums, recreation, and green spaces to East Raleigh, the 30,000-square-foot Recreation Education Center (R.E.C.) has created a gathering location for residents while linking local neighborhoods to Raleigh on a broader scale.
E. Edenton St. and New Bern Avenue have become defining features of East Raleigh, bringing in a surge of traffic from Downtown Raleigh. This results in a corridor of commercial properties and roadways that divide low-income neighborhoods. R.E.C. uses its visibility of these high-traffic roads to revitalize the region.
R.E.C.’s L-shape shields the neighborhood, opening towards the local community and protecting it from the intruding larger-scale city. Two diaphanous frames visible from the intersection attract new visitors intriguing fresh faces that would otherwise never visit the region. The existing historical educational building, converted into a 200-seat event hall, encourages public forums and community-building, breaking down barriers that traditionally separated East Raleigh from the rest of the city.
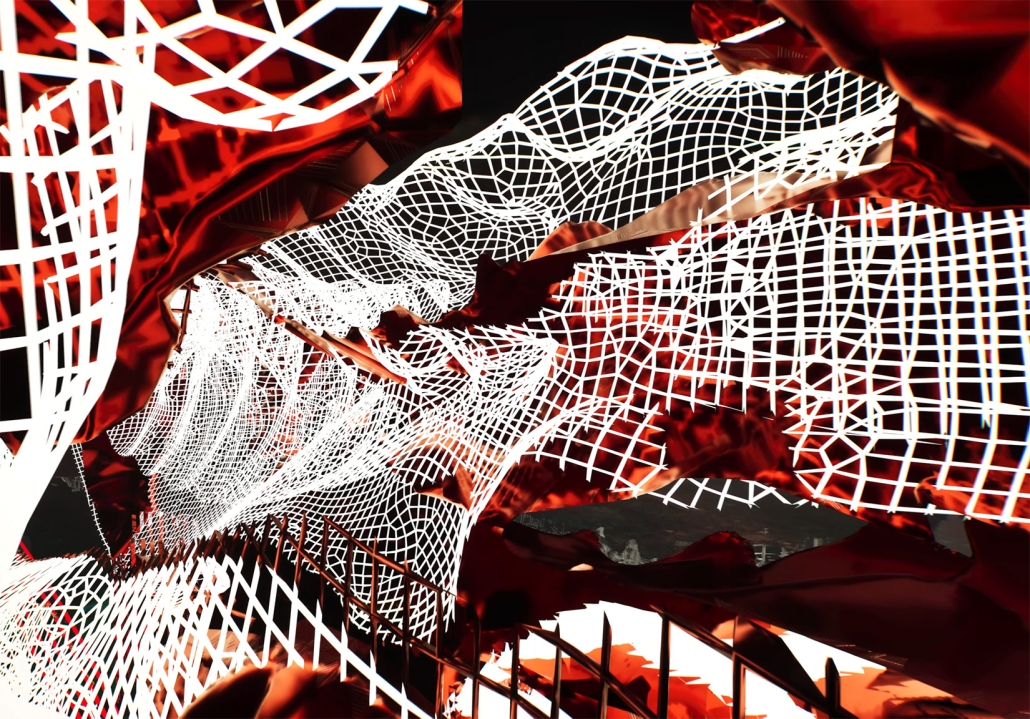
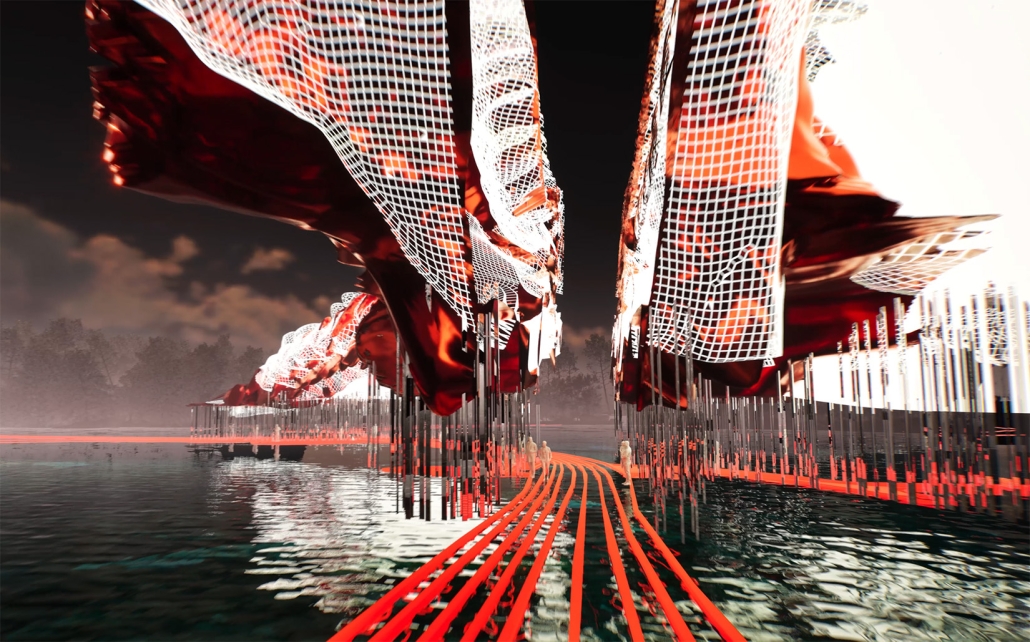
Commercial spaces and community resources are organized separately into two elevated frames, with an atrium acting as the convergence point and entry. The first frame, a 24-foot deep truss, suspends across the landscape, revealing the commercial gymnasium and activity spaces it protects. Ramps down to the gym address difficult topography to reduce the R.E.C.’s height in response to its residential context. The second frame floating over the atrium provides vital educational resources to the underprivileged community, fostering skill development to improve employment chances in a rapidly transforming economic landscape. Curved aluminum panels coating the floating frames are perforated with a pattern that interacts with light and shadow, creating a unique experience.
The north end of the site is grafted into the neighborhood’s skin. The form tilts open to reveal an outdoor space optimized to bring in local pedestrian traffic, encouraging residents to treat it as their backyard. Enclosed between the building and forested paths on the north side, a large open court becomes an important anchor on the site, freely defined by community-organized events and activities.
This project won a 2024 AIA Triangle Student Design Award.
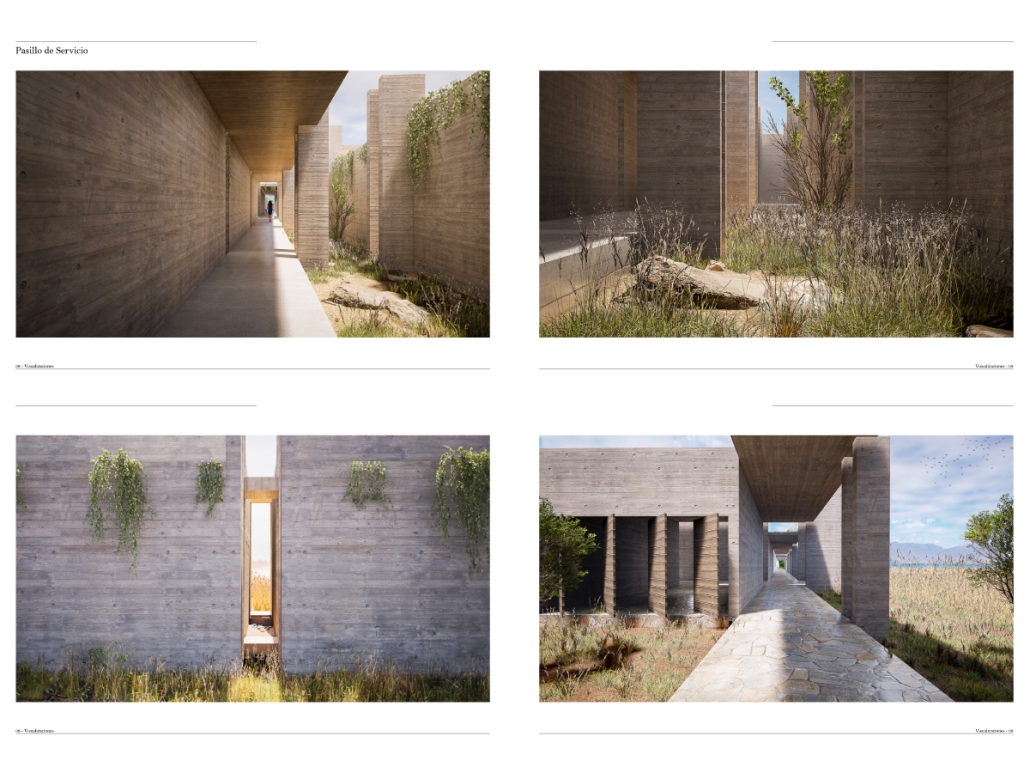
A Hostile City, Inequitable Privatization of Public Spaces by Bailey Berdan, M. Arch ’24
Lawrence Technological University | Advisor: Scott Shall
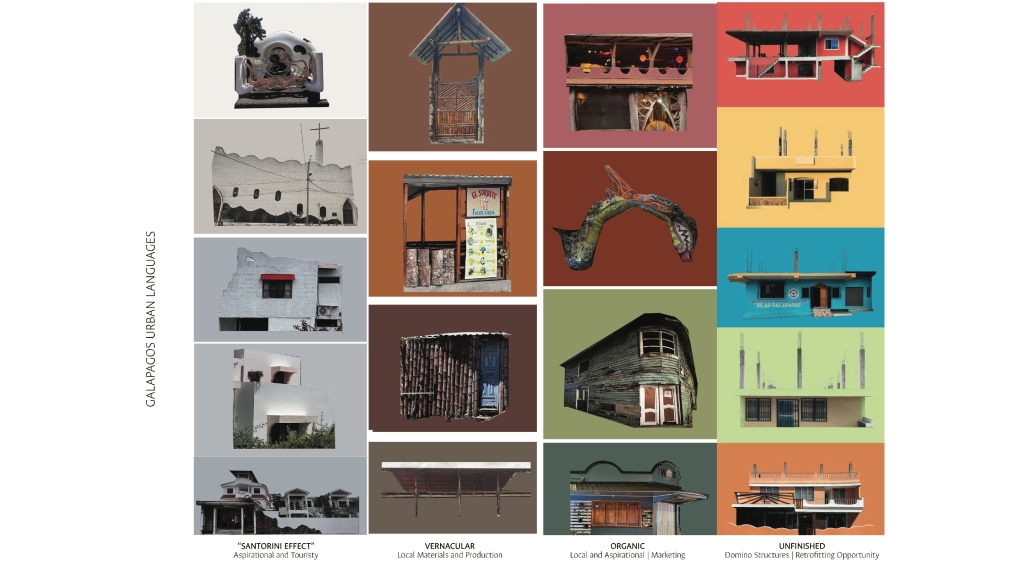
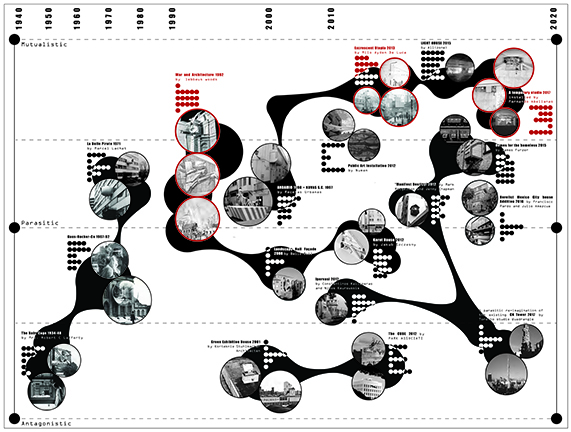
Hostile architecture is a term used to describe design strategies that are intended to deter certain groups of people or behaviors in public spaces. While bench dividers and ground spikes are widely recognized examples of hostile architecture, their impact goes beyond these small-scale designs. Hostile architecture is pervasive in areas such as policy, law, and privatization, and it can have serious negative consequences on a community’s economy, walkability, and overall environment.
To address this issue, one potential solution is parasitic architecture, which is a practice that is not commonly used but is often employed as a response to dysfunctional conditions. Parasitic architecture involves the creation of structures that are attached to or embedded within existing buildings or infrastructure, utilizing underutilized or overlooked spaces. This approach has the potential to combat hostile architecture and empower communities to reclaim their right to public spaces.
By repurposing underused spaces, parasitic architecture has the potential to increase the availability of public spaces, reduce the costs of new construction, and foster a sense of community ownership and engagement. Additionally, these structures can be designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing them to evolve and respond to changing community needs over time. Overall, parasitic architecture represents a promising approach to combat hostile architecture and create more inclusive, accessible, and vibrant public spaces. By empowering communities to collaborate and take ownership of their public spaces, parasitic architecture has the potential to create more livable, sustainable, and equitable cities.
This project was a finalist for the ARCC King Student Medal Award.
Instagram: @__b.berdan__, @scott_shall
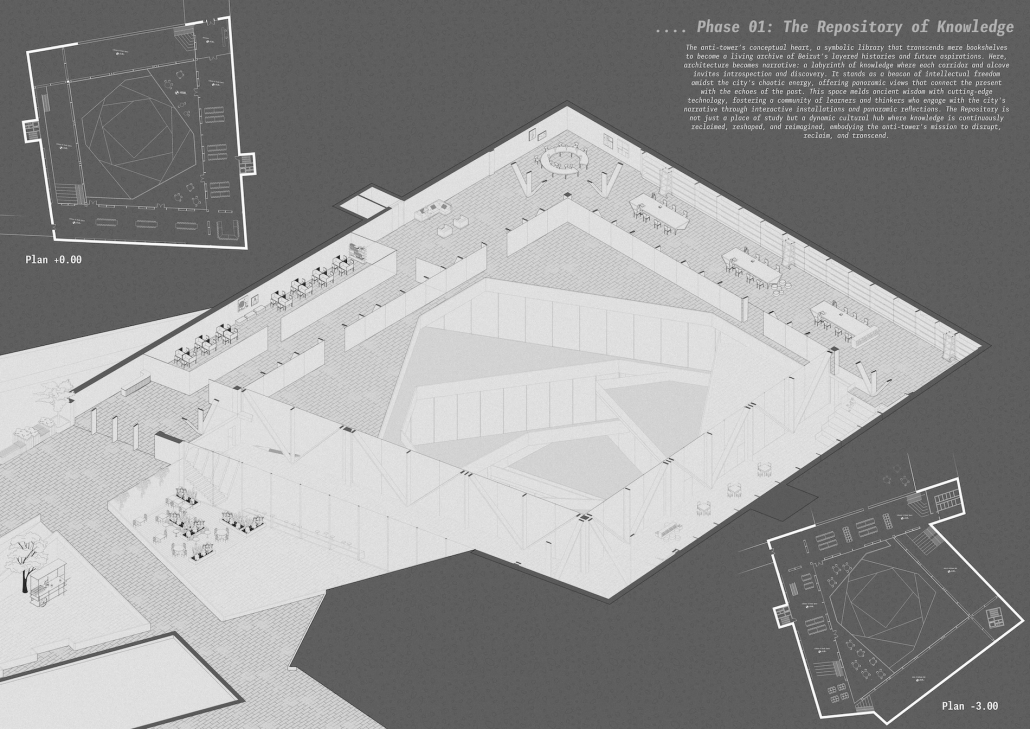
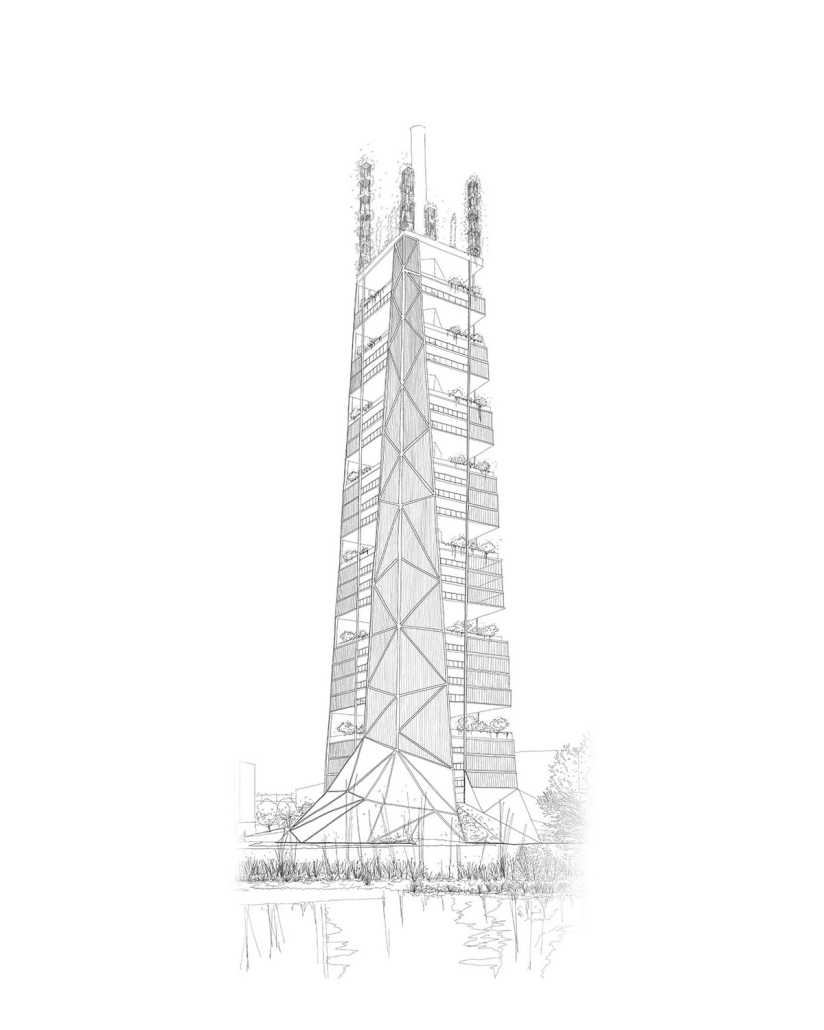
Counter [con]text by Zeina Medlej, B. Arch ‘24
American University of Beirut | Advisors: Rana Haddad & Dr. Howayda Al-Harithy
This thesis investigates how tactical public space interventions within Beirut’s neoliberal landscape can create heterotopic spaces that counteract dominant urban narratives. The study is grounded in the theoretical frameworks of Michel de Certeau, David Harvey, Henri Lefebvre, and Michel Foucault, focusing on how architectural constructs can reflect and engage with diverse social narratives beyond the homogenized, capitalist-driven designs.
The central question guiding this research is: How can tactical public space interventions within Beirut’s neoliberal landscape create heterotopic spaces that counteract dominant urban narratives?
The research is structured into two phases:
Phase 1: Initial disruption through punctual tactics. This phase involves programmatic interventions at 18 strategically chosen sites around Beirut. Each site is selected to reflect and challenge various neoliberal rationalities, aiming to create a series of small-scale disruptions that collectively unsettle the status quo and open up possibilities for transformation.
Phase 2: Tactical integration for large-scale disruption. This phase focuses on a single, impactful site—Martyrs’ Square—to implement a significant tactical intervention. The intervention transforms Martyrs’ Square into a multifunctional, dynamic urban space that serves as a cultural hub and community center. By integrating historical, cultural, and social elements, this transformation challenges and redefines the socio-spatial narratives of Beirut. The thesis proposes a heterotopic constellation of spaces that operate outside conventional time-space frameworks, fostering inclusivity, resilience, and public engagement. By opposing the dominant urban narrative, these tactical interventions aim to contribute to the creation of a more diverse and inclusive urban environment in Beirut.
Through this research, the thesis aims to demonstrate how tactical interventions can serve as powerful tools for social critique and urban transformation, ultimately fostering spaces that are not only physically distinctive but also socially transformative.
Instagram: @ard_aub
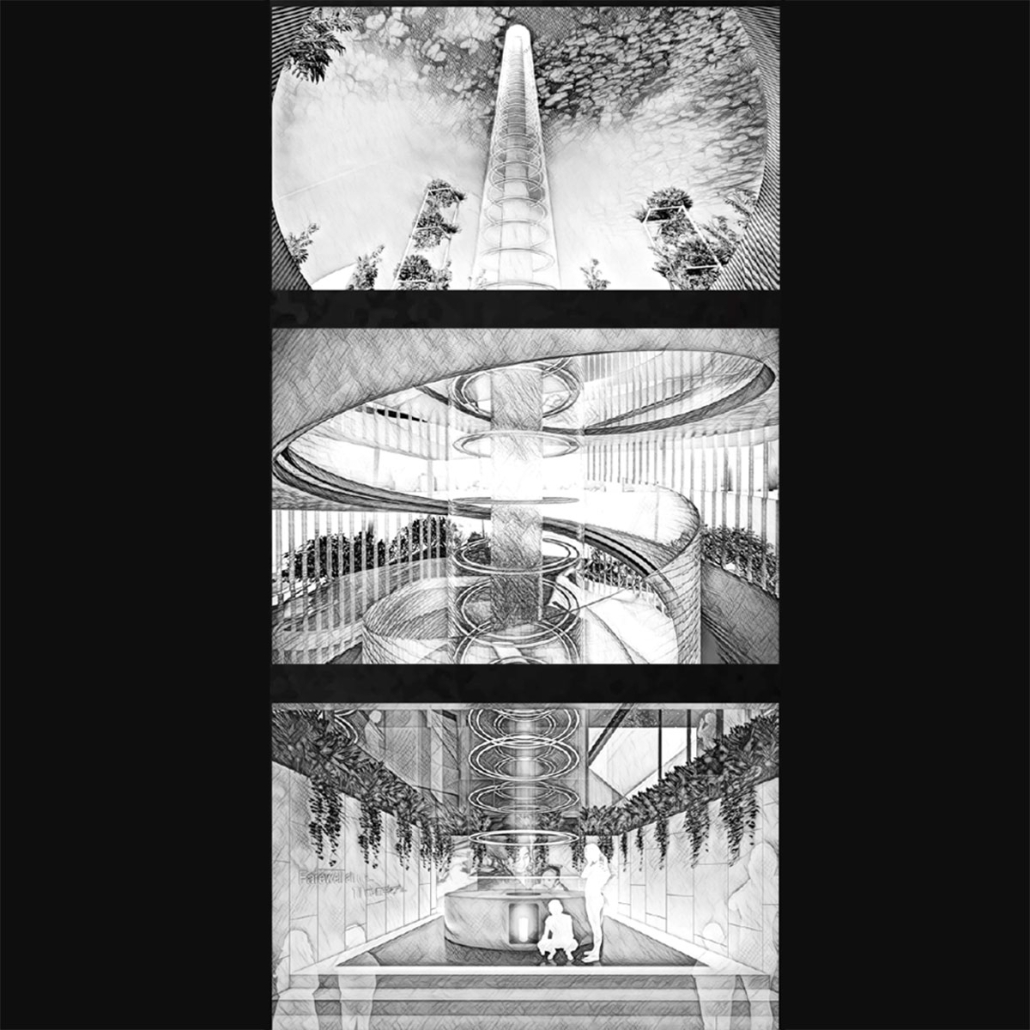
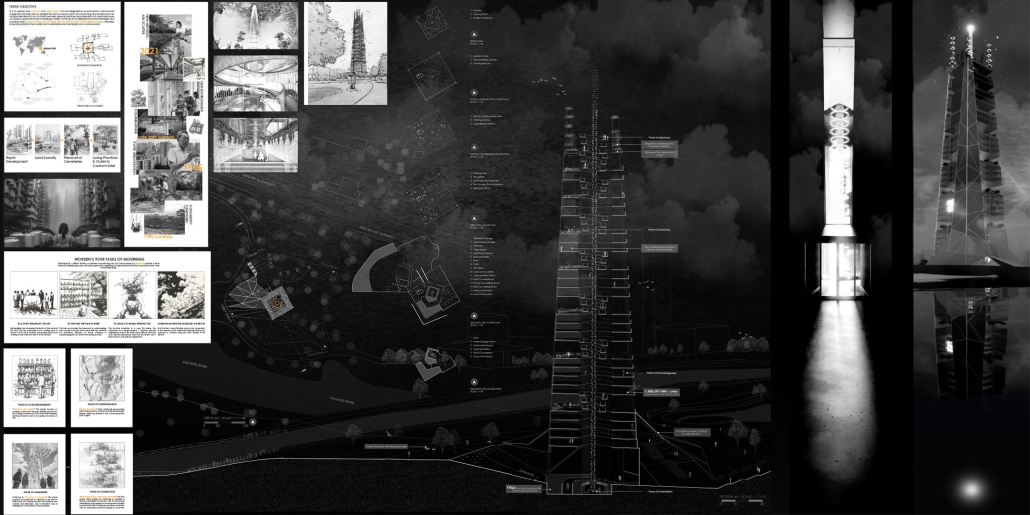
Urban Legacy – Preserving Cultural Continuity in Land Scarce Singapore by Denzyl Zhang, M. Arch ’24
Savannah College of Art and Design (SCAD) | Advisors: Andrea Bertassi, Aaron Wilner & David Gobel
This thesis looks at how memorial spaces might be integrated into urban parks, with an emphasis on the Sanctuary of Passage, a prototype for ecological and culturally sensitive memorial architecture in Singapore’s Ang Mo Kio-Bishan Park. The design tackles the issues of urban congestion and the displacement of customary burial grounds caused by the urgent requirement for living space in increasingly urbanizing regions. The thesis suggests a paradigm in which memorial spaces coexist alongside recreational places while also improving the ecological and social fabric of urban surroundings. The Sanctuary of Passage is based on the idea of a journey through sorrow, expressed by a series of ascending spaces that represent the phases of bereavement.
Each level of the construction provides a unique experience with nature and architecture, allowing for a gradual shift from grieving to recollection and healing. The proposal draws on the natural dichotomies of visibility and obscurity, enclosure and exposure, and nature and architecture to create a dynamic place that respects and reacts to Singapore’s unique cultural traditions around death.
The thesis concludes with a design that reimagines the function of memorial spaces in urban environments, arguing that they may be effortlessly incorporated into the city’s landscape, acting as crucial public places that provide consolation and connectedness. By doing so, it establishes a precedent for future developments across the globe, implying that combining urban growth with memorialization techniques may produce places that commemorate the past while also benefitting the present and future.
This project won the AIA Savannah Thesis Honor Award.
Instagram: @denzyl.zhang, @andre_bertassi
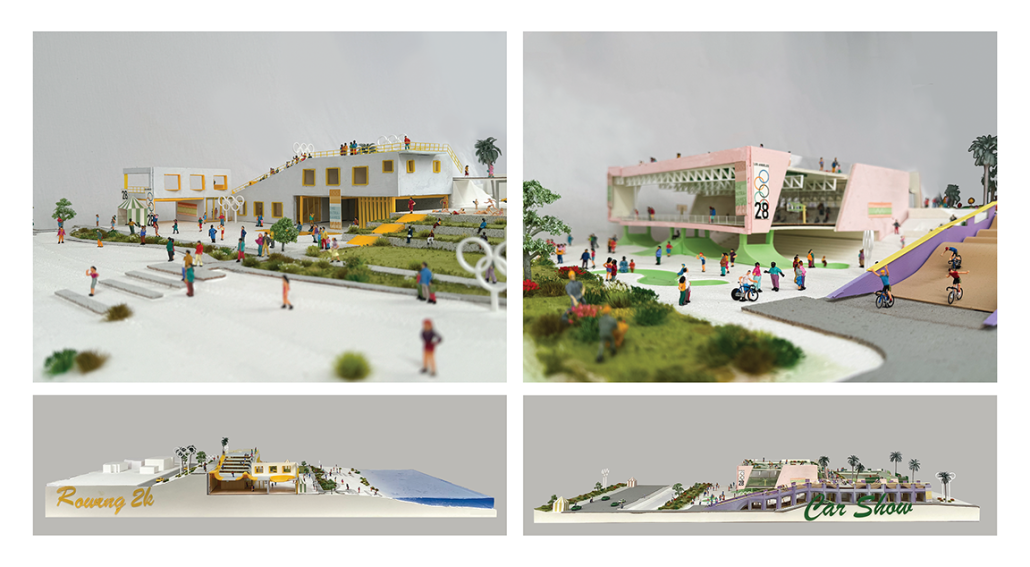
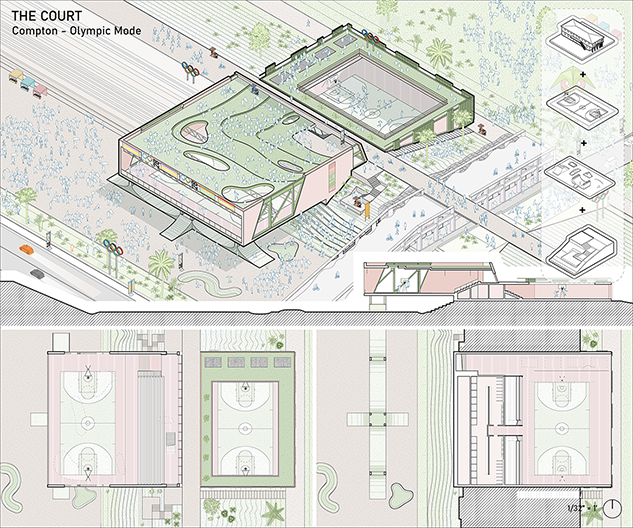
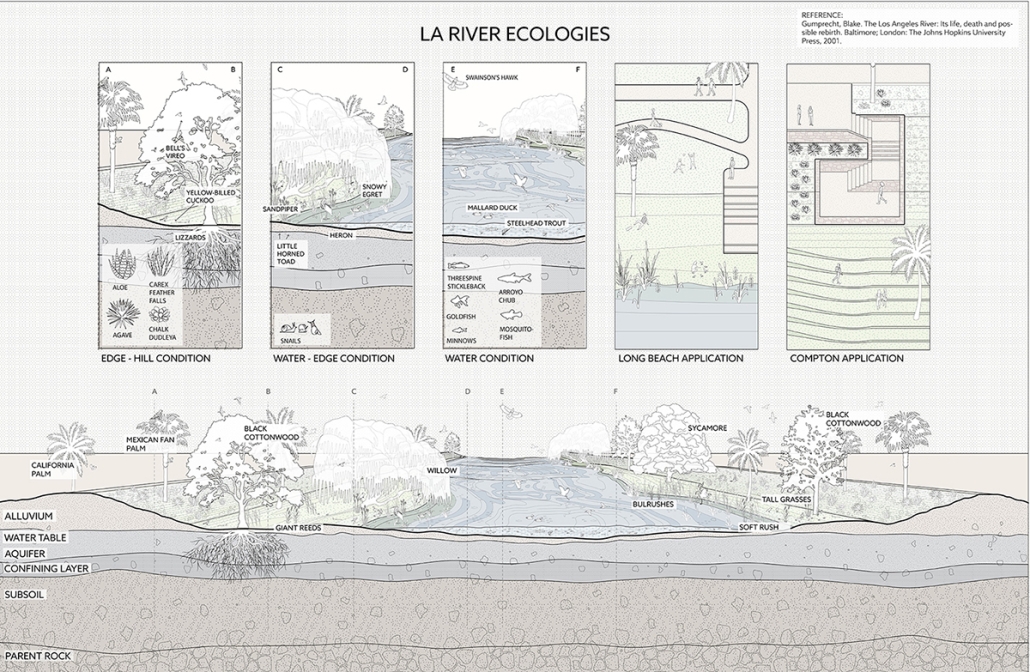
The Intragames: Shaping the Olympics for Local Publics by Weilin Berkey & Valentine Batteur, B. Arch ’24
Pratt Institute | Advisors: Evan Tribus, Cathryn Dwyre & Alex-Pierre de Looz
The nonprofit known as the International Olympic Committee can influence real-world social conditions through its corporate and financial power, thus making the [Olympic] Games a potential catalyst for new participatory publics. However, historically, the Olympic Games have struggled to benefit the host city beyond economics. Based on our research of previous Olympic Villages in recent years, they fail to acknowledge and engage with local programs and architecture, which we identify as the vernacular of the host city.
Ironically, the goal of the Olympic Games is to embrace different cultures and to promote collectivity. Our research shows that, in fact, it produces negative effects on the host city by standardizing the way it deploys new venues and temporary housing. World-scale events like the Olympics often ignore local communities for profit. How might distributed hybrid vernacular venues amend the relationship between corporate goals and local needs to create new participatory publics within resident neighborhoods?
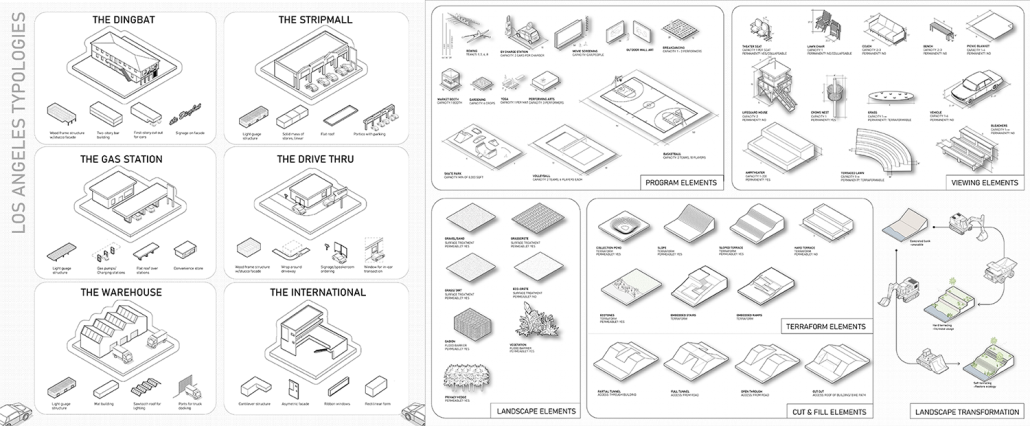
The Intragames hypothesizes that the use of vernacular typologies in combination with public spaces, will encourage locals to participate in collectivity sponsored by the Olympics. Currently, the upcoming Los Angeles 2028 Olympic plan focuses on improving existing infrastructure but neglects the potential connectivity among/between distributed venues. Layered with the existing competitive events, we want to incorporate new recreational and leisure Olympic events that the local fans can participate in along the LA River. Experimenting with combinations of vernacular typologies and Olympic programs is critical to our distributed venues’ longevity and future use. Additionally, having a deep understanding of the vernacular landscape will allow us to revitalize the forgotten concrete banks of the LA River and its connection to the city.
This formula for designing new public venues will allow local spaces to be integral to urban-scale events. These additional programs will surpass the short timeframe of the Olympics, leaving new integrated publics along the river and changing the lasting impact of the games.
This project won The Best Degree Project of 2024, Undergraduate Architecture at Pratt Institute.
Instagram: @wberkarch, @v.b._design, @pressg5, @pneumacat, @delicatemunch
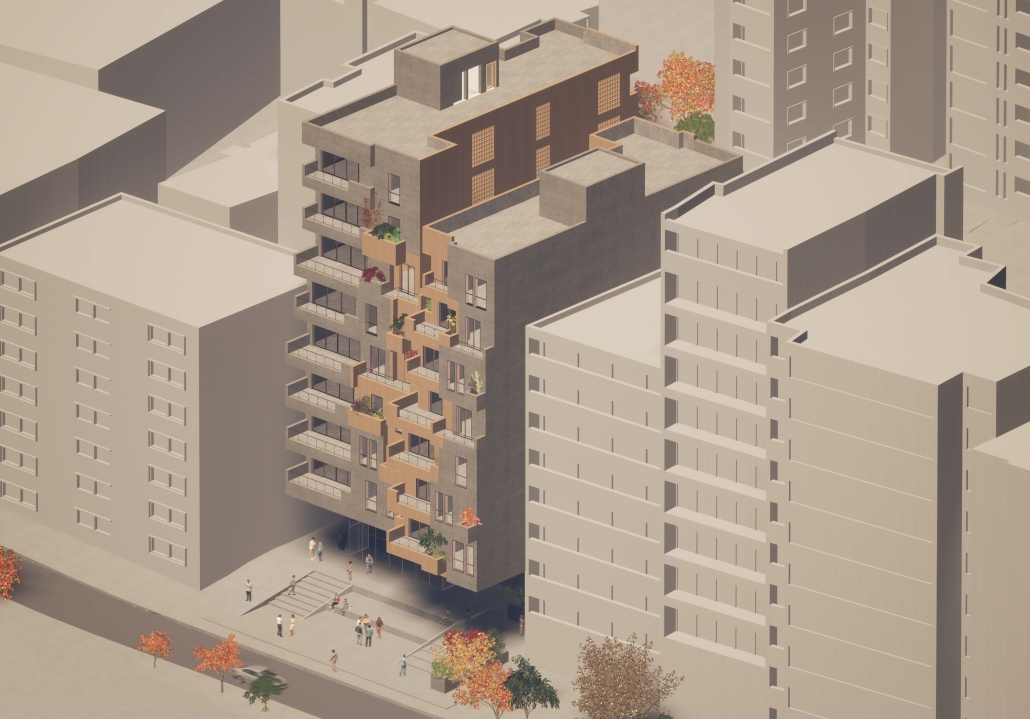
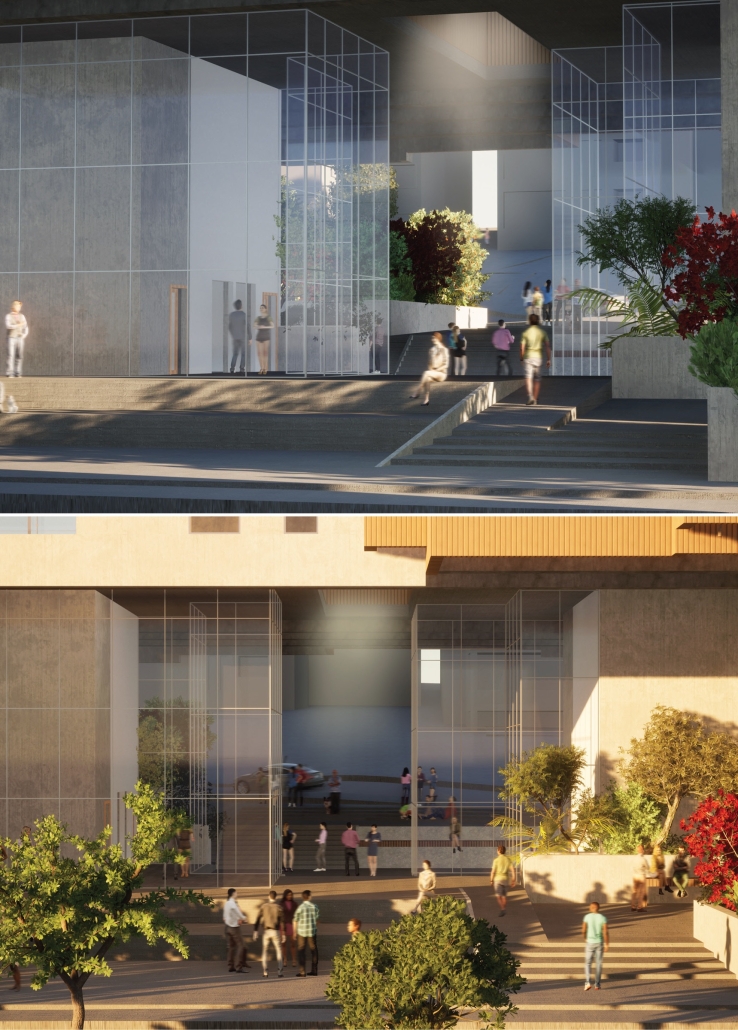
The Spaces In-Between: The Making of an Urban Network by Dana Kanaan, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Dr. Howayda Al Harithy
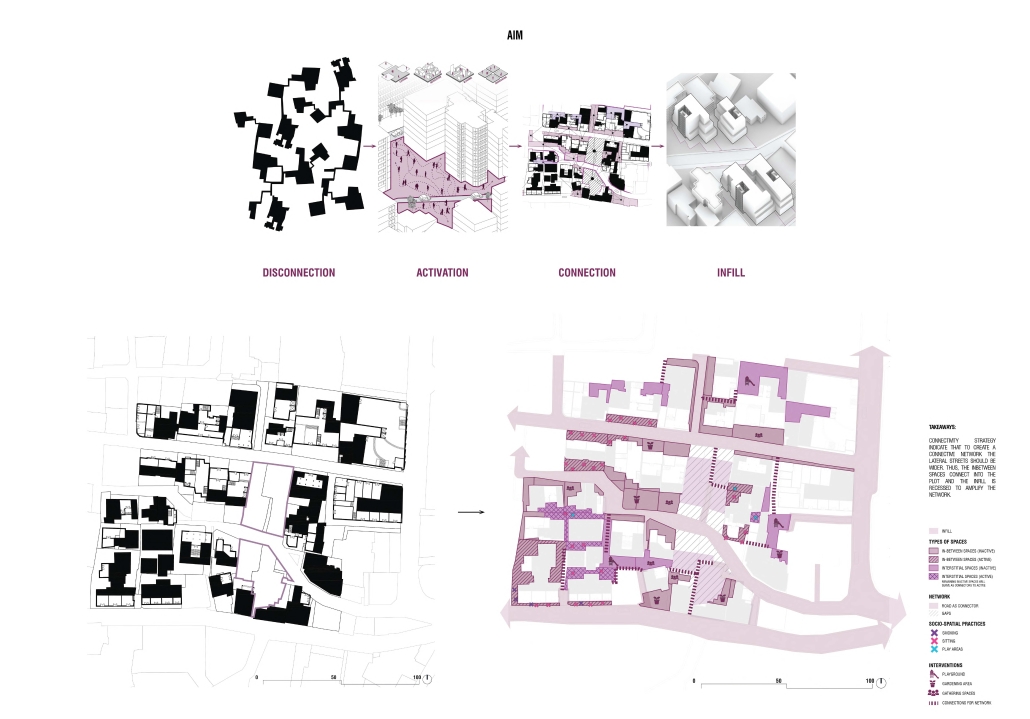
In Beirut’s urban environment, the absence of and the treatment of public spaces has led to the weakening of community ties, fragmentation of communities, and urban isolation. This is exacerbated by rigid boundaries that separate districts and hinder social interaction, as public spaces are crucial for community cohesion. Moreover, there is an abundance of interstitial and in-between spaces that are underutilized and leftover. The rigid boundaries that separate districts and neighborhoods, whether physical or mental, combined with the neglect of these leftover spaces contribute to the fragmentation of urban communities and hinder social interaction. This is because social interaction occurs in the public realm. Thus, this fragmentation in the public sphere exacerbates the weakening of community ties and urban isolation.
Interstitial spaces in between buildings, especially those that act as ruptures in the urban fabric, can be activated and used as an opportunity for a network of connectivity. These interstitial areas can be activated through methods such as layering, dissolution, dissociation, and blurring. The objective of creating a blurred space is to foster social interaction, which emerges during periods of liminality and ambiguity. Therefore, a network of private spaces is created in the absence of public spaces utilizing interstitial and in-between spaces.
This project was nominated for the Areen Projects Award for Excellence in Architecture
Instagram: @ard_aub
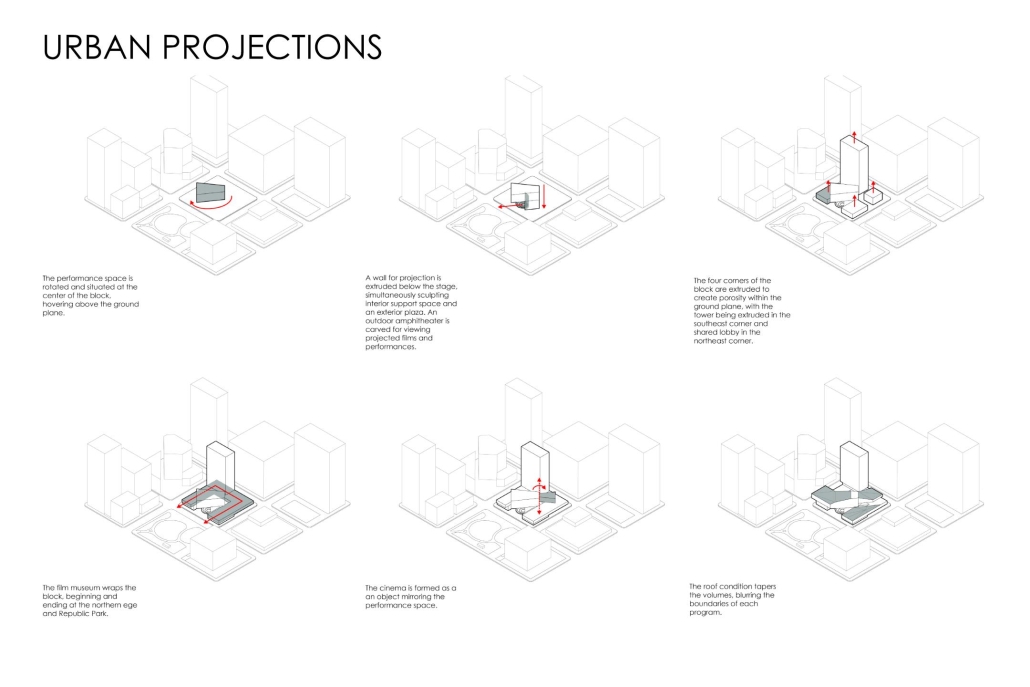
Urban Projections by Tessa Laplante & Julia Nahley, M. Arch ’24
The University of Texas at Austin | Advisor: Matt Fajkus
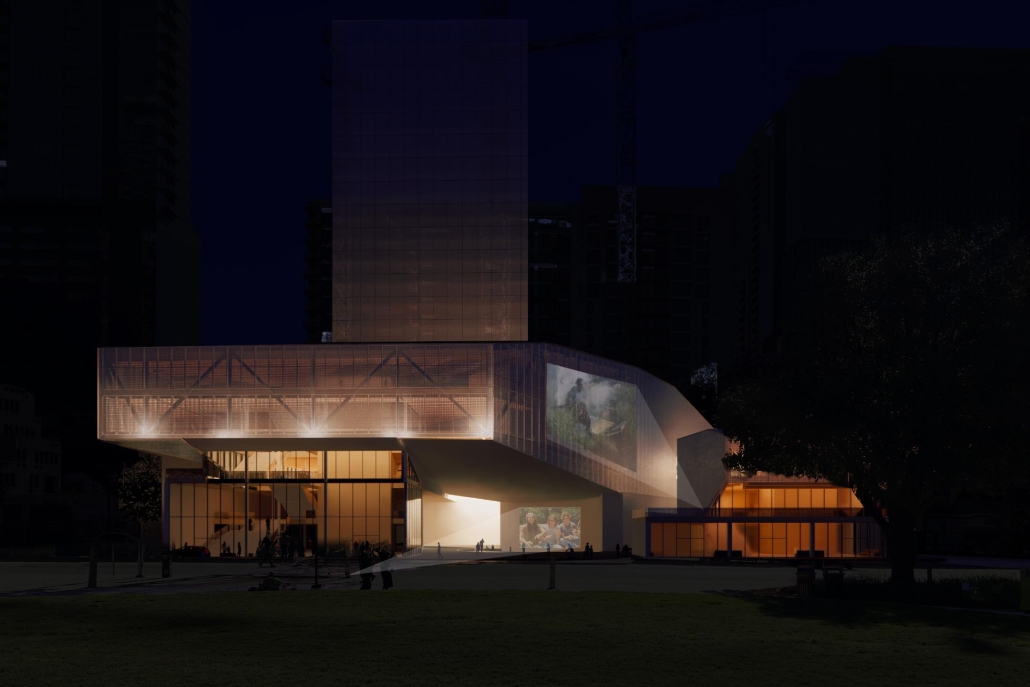
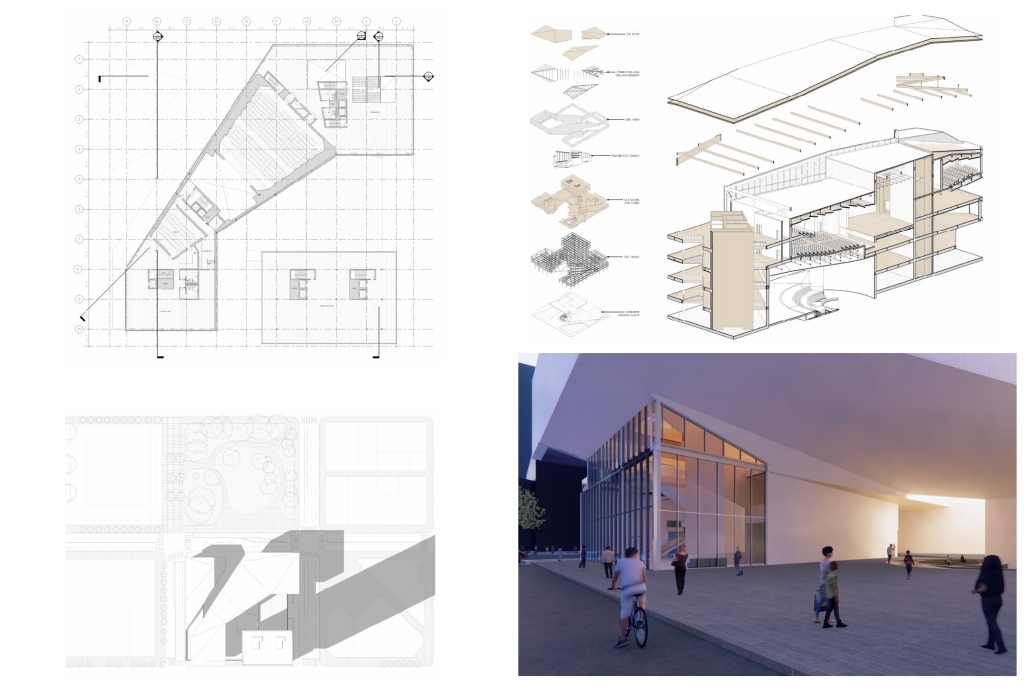
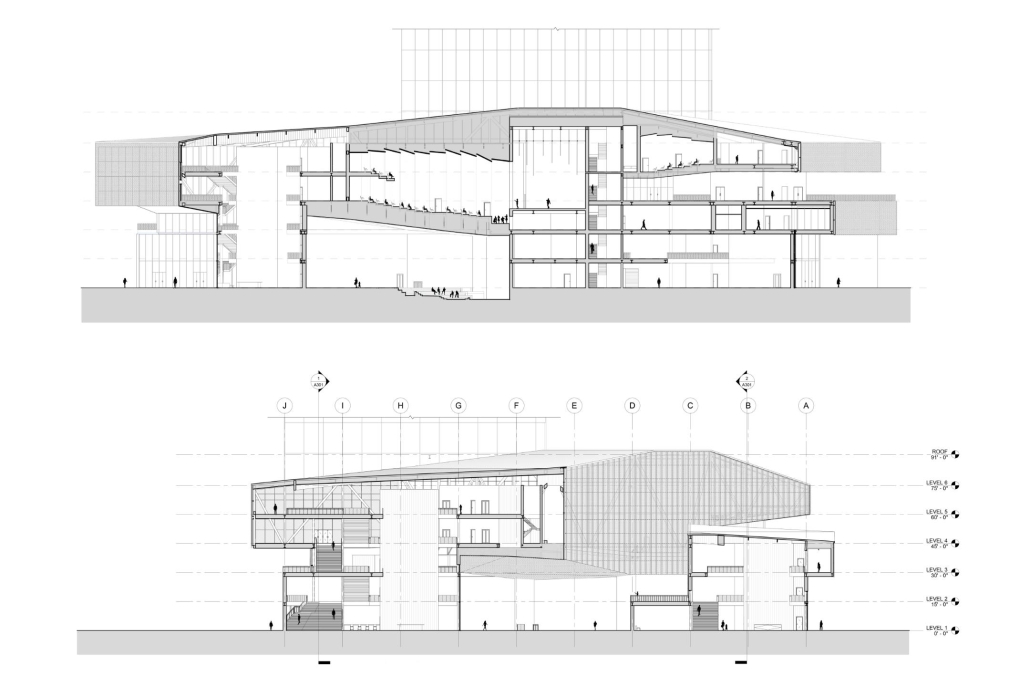
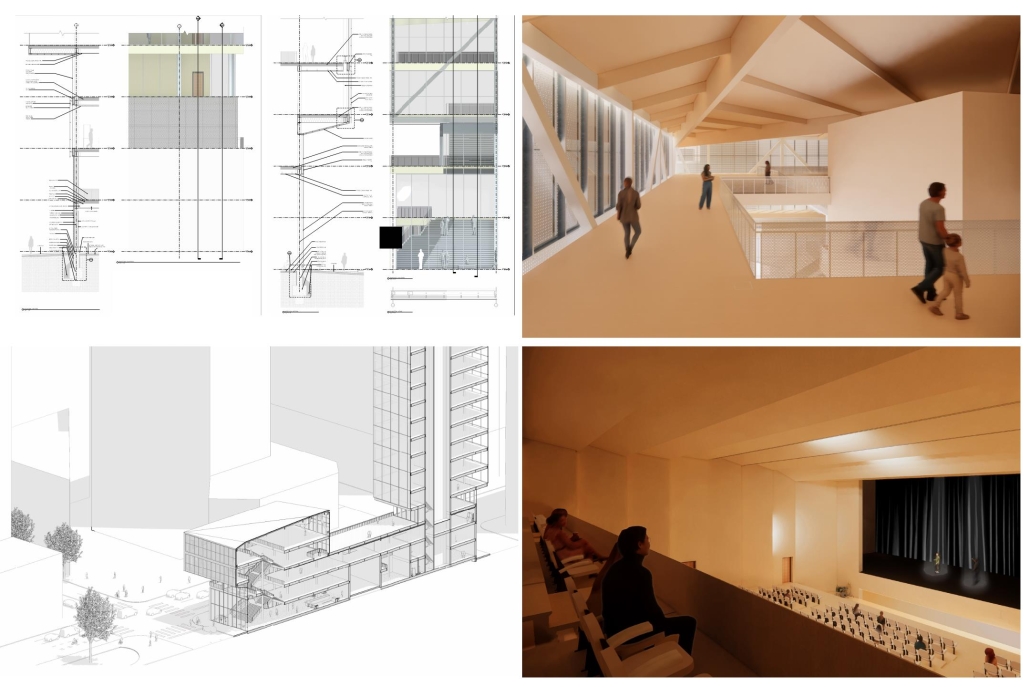
“Urban Projections” addresses the notion of a cultural landmark in the context of an evolving city. With the massive amount of development happening at such a rapid pace in Austin, it raises the question of how the city will maintain and continue to define its own cultural identity. In order to maintain it, [this] design includes a film museum, while live performance spaces continue to define the city’s culture. A key intention for the site is to encourage circulation through the urban block towards nearby greenspaces including Republic Park and Shoal Creek. The heart of the block is defined by an elevated and rotated performance space, which sculpts the public plaza beneath. A film museum wraps around the block at the third level, serving as a plinth that begins and ends at Republic Park. Liminal spaces are emphasized in the project, with vertical circulation and intermission spaces celebrated and shared between programs.
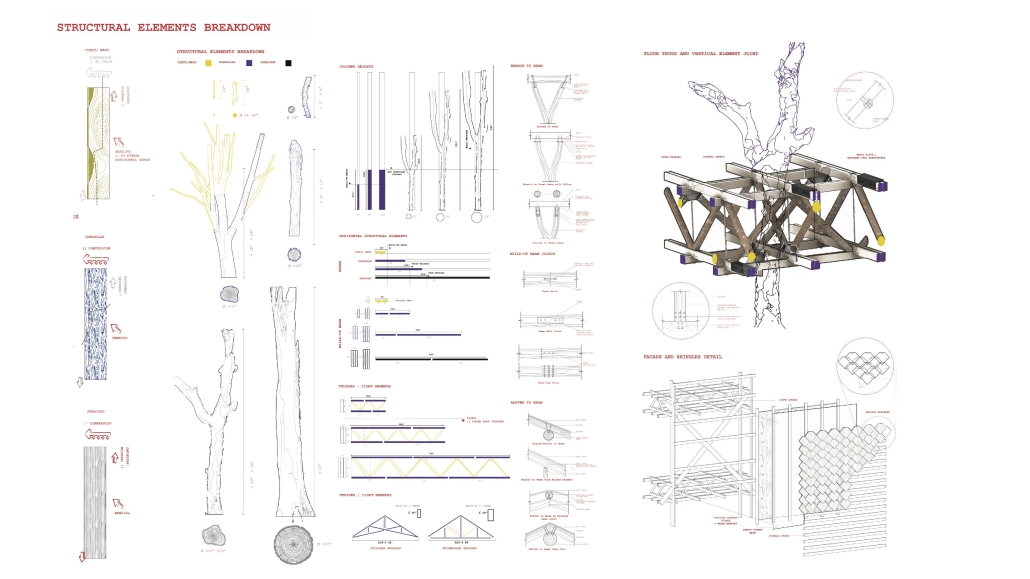
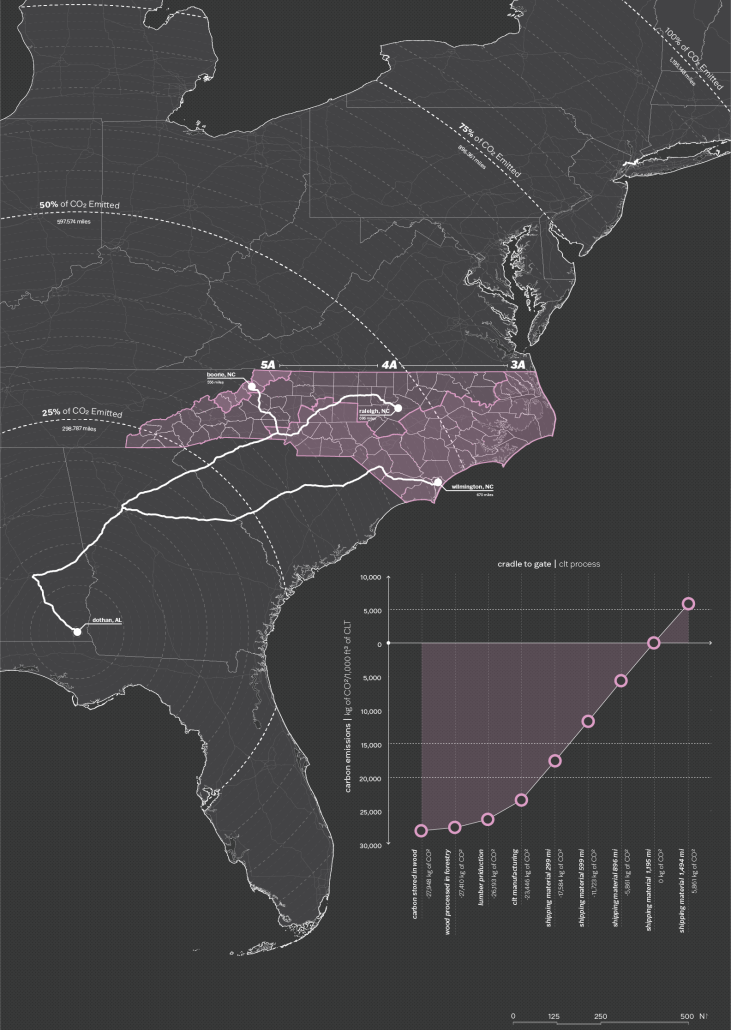
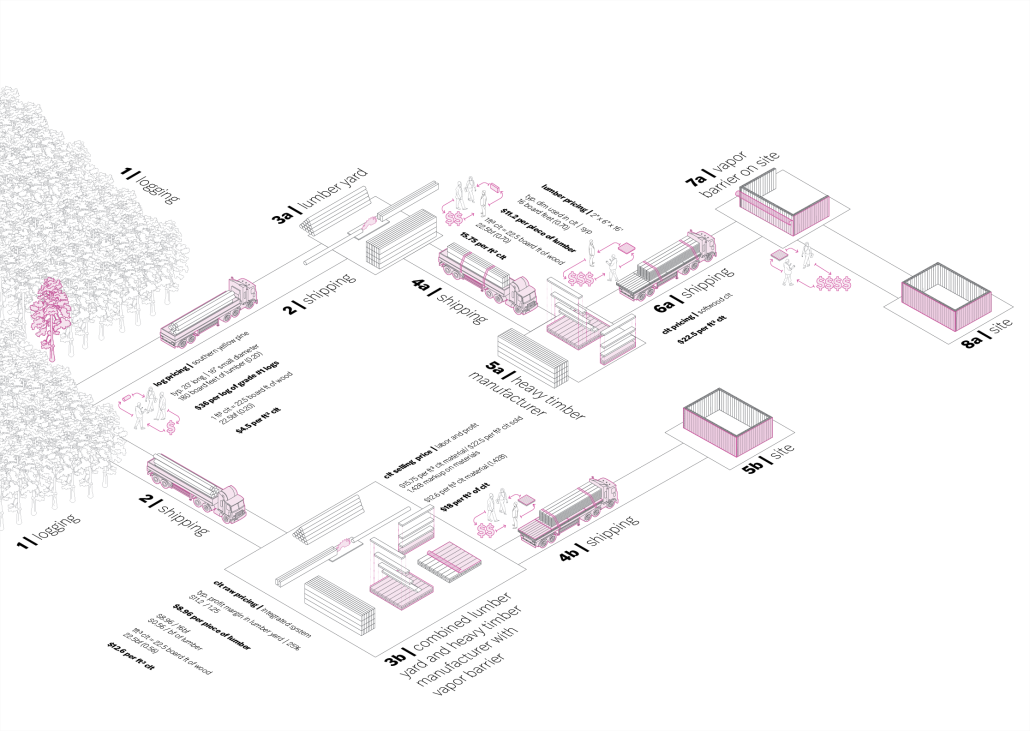
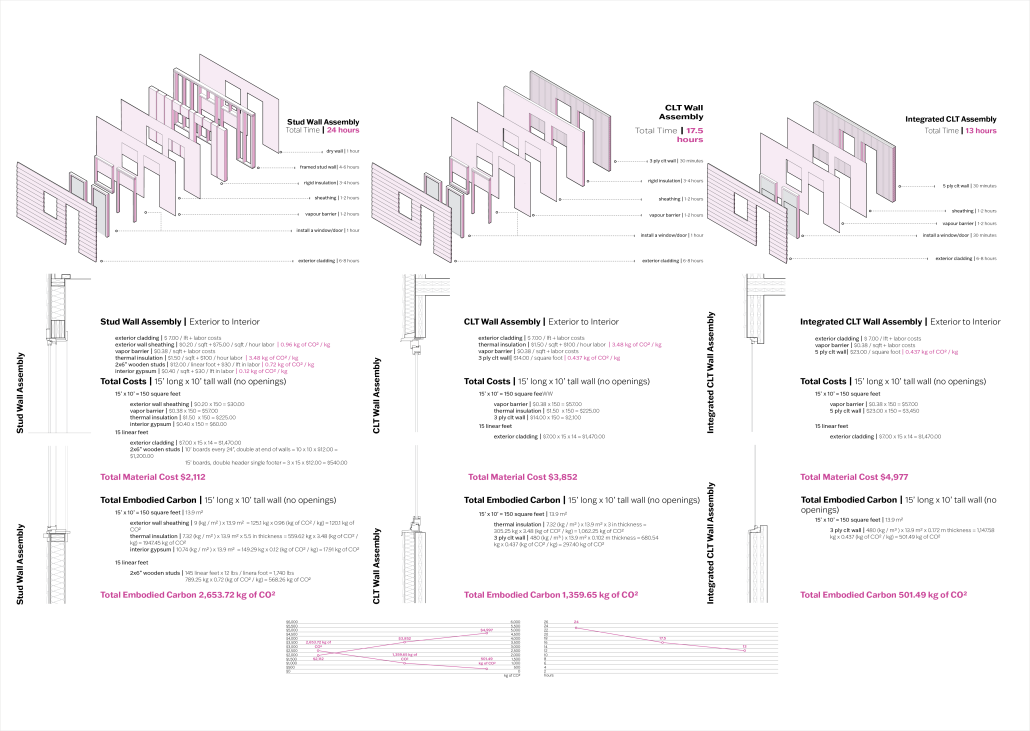
The notion of projection is repeated at all scales of the project, reflected in the projection of the building’s structure onto the exterior facades. A steel mesh acts as a surface for the projection, as well as a thermal barrier to filter light and movement between interior and exterior spaces. A steel frame with CLT cores and floors is utilized as a replacement for concrete in conjunction with steel trusses that support the cantilevered theater spaces and wrap the upper levels. As visitors process from the main lobby into the more private spaces, they experience a sequence of atmospheres generated by different relationships between wood and steel. Specifically, in spaces where the program is flexible, the relationship between materials is clear, with transparent glass exposing the building’s primary steel members and CLT floors. In contrast, the interiors of the theaters are entirely wood to encourage concentration for the experience.
This gradient of privacy through materiality reflects the project’s overarching intention to blur the boundaries between programs without compromising the essence and needs of the programs themselves. In an effort to establish a cultural landmark, liminal spaces are celebrated to encourage new relationships within the site, rendering them just as important as the more defined programs. These shared moments exist as a stage for the city to maintain and continue to define its cultural identity.
Instagram: @tessamarie108, @julia_nahley, @mf.architecture
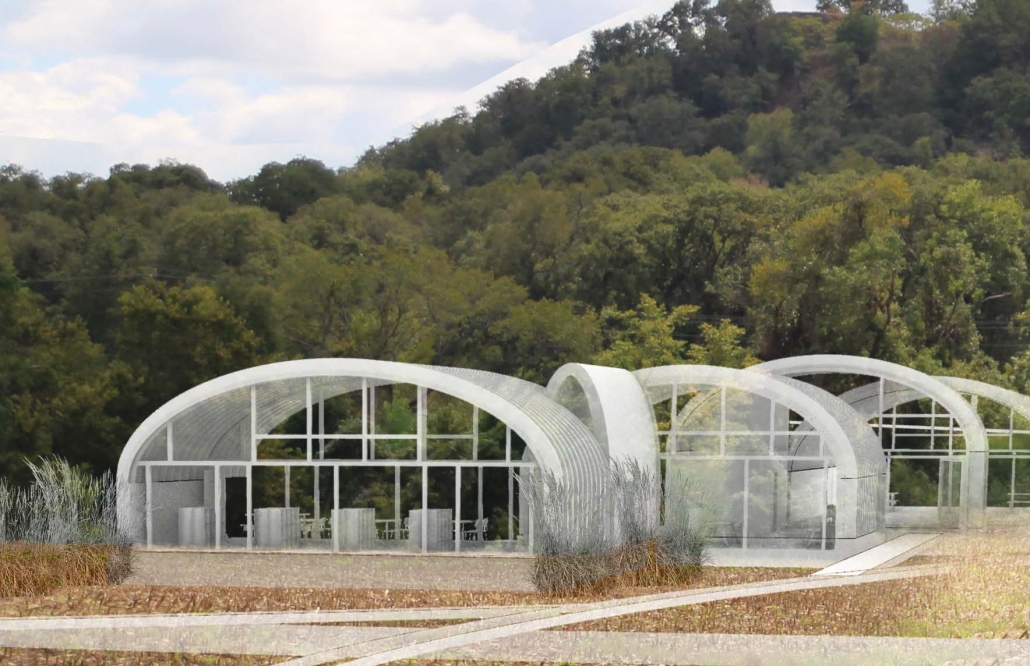
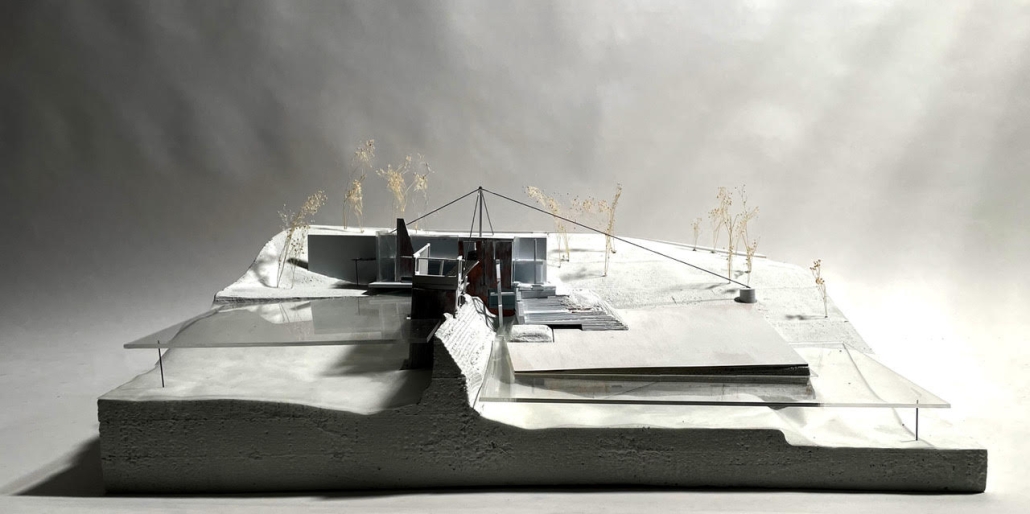
Expo 2025 by Trever Bellew, B.Sc in Architecture ’24
University of District of Columbia | Advisor: Golnar Ahmadi
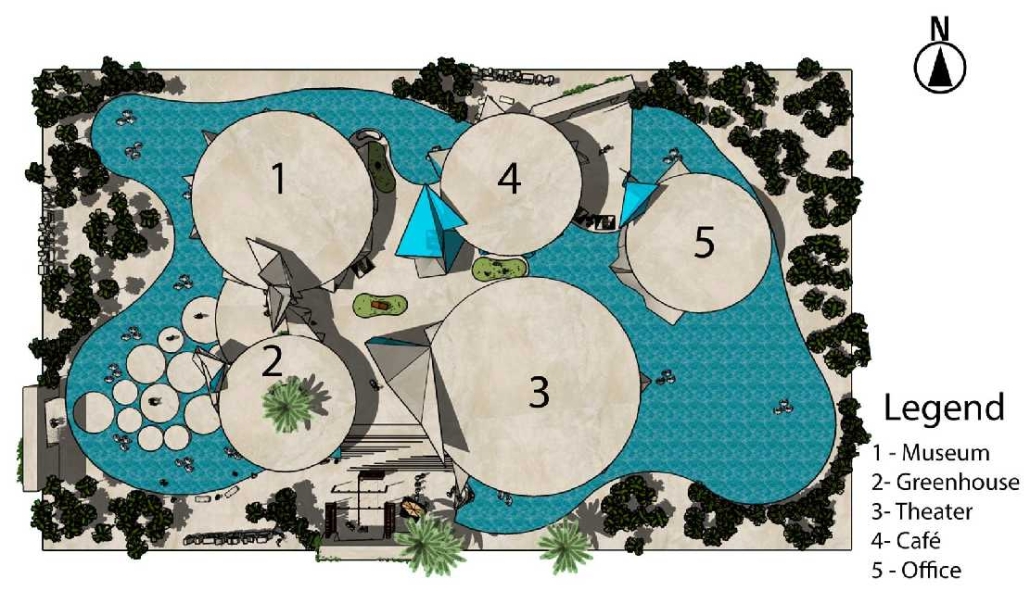
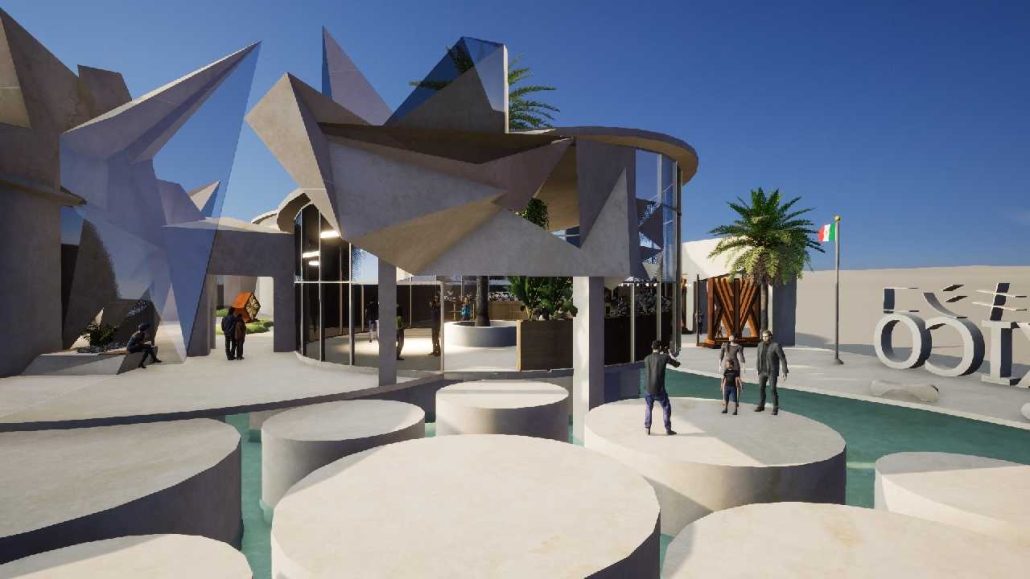
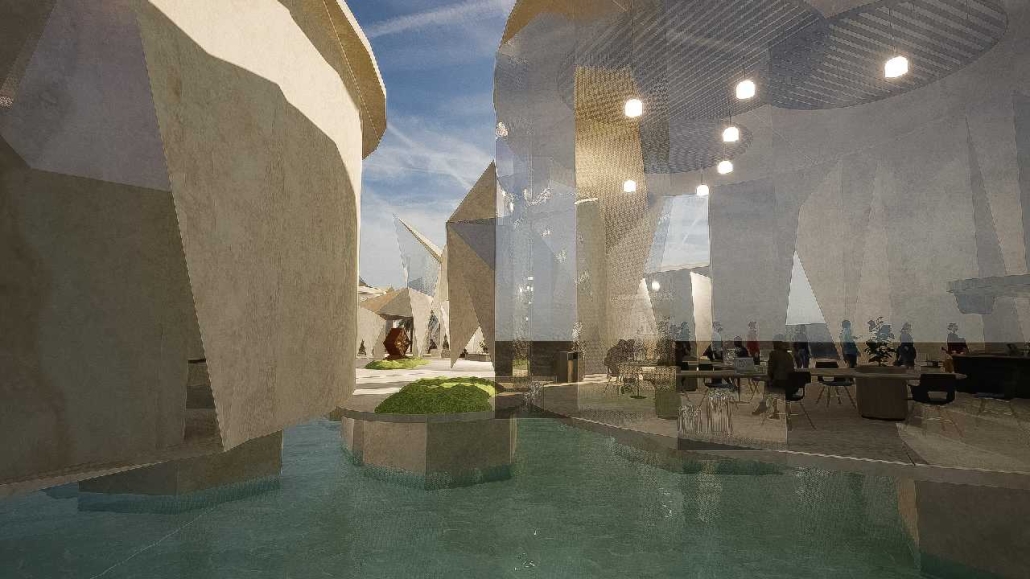
For the spring semester of 2023, students were required to design a pavilion for the 2025 World Expo that will take place in Osaka, Japan. The World Expo is a global event that showcases the best in technology, sustainability, and architectural design. With the theme “Designing Future Society for Our Lives,” the Expo aims to present innovative solutions and ideas that positively impact human lives. It focuses on sub-themes such as saving lives, connecting lives, and empowering lives, highlighting the Expo’s commitment to addressing global challenges and creating a better future.
Being originally from Brazil, I challenged myself to create the Brazilian pavilion. [This design drew] inspiration from Burle Marx, a plastic artist, and architect who designed the most iconic boardwalk located in Copacabana, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. I crafted an organic shell that encompasses the entire pavilion program. The project’s aim was to create an immersive experience that transports visitors to a jungle-like setting while educating them on various topics related to mental and physical health through the exhibit rooms.
Instagram: @Golnarahmadi
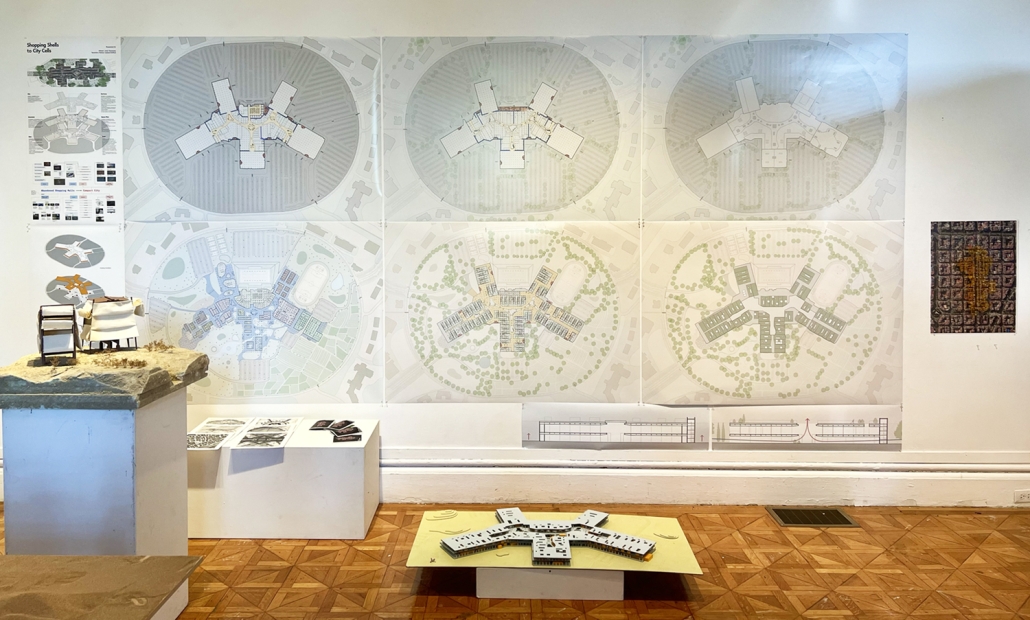
Shopping Shells to City Cells by Ruyue Qi, B. Arch ’24
Rhode Island School of Design | Advisors: Junko Yamamoto & Leeland McPhail
Shopping malls, spanning an area equivalent to 33+ Manhattans, are key symbols of consumerism. Built for short-term savings, these malls often become abandoned due to high maintenance costs and the rise of e-commerce. In the United States, out of an estimated 1,150 malls, it is forecasted that only about 150 may remain operational by 2032. Despite numerous closures, new mall construction continues as developers aim to attract shoppers with the Next Big Thing. Abandoned shopping malls (large size, connected layout, huge parking, enclosed structure, and strategic positioning) have the potential to be transformed into compact cities to nurture a future that is both eco-efficient and interconnected.
Large abandoned shopping malls are large enough to become diverse and mixed-used neighborhoods. They can provide housing units with fixed infrastructure cores and flexible layouts, depending on the climate and needs. Additionally, abandoned malls could evolve into walkable neighborhoods connected by escalators and platforms. Existing escalators can create a unique urban environment where residents can easily navigate between different areas. Transforming vast parking lots into parks, gardens, and farms could enhance connectivity to nature and mitigate the urban heat island effect. Enclosed shopping malls depend solely on mechanical systems to provide a controlled climate inside, introducing natural ventilation could significantly lower their carbon footprint. By strategically repurposing abandoned shopping malls, we can revitalize neighboring areas by enhancing community involvement, boosting the local economy, and creating new communal spaces and facilities.
This project was a Thesis Award Nominee.
Instagram: @julyqi_, @junkoyamamoto_
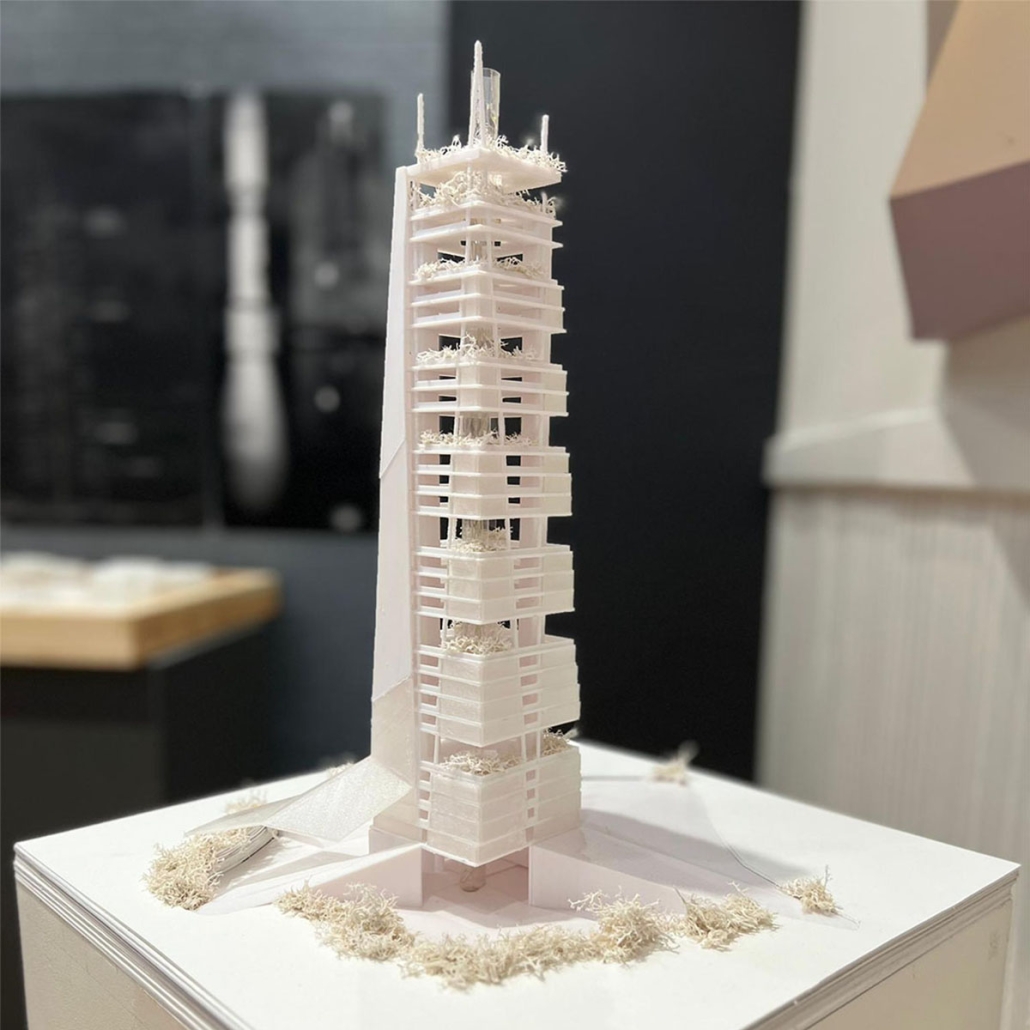
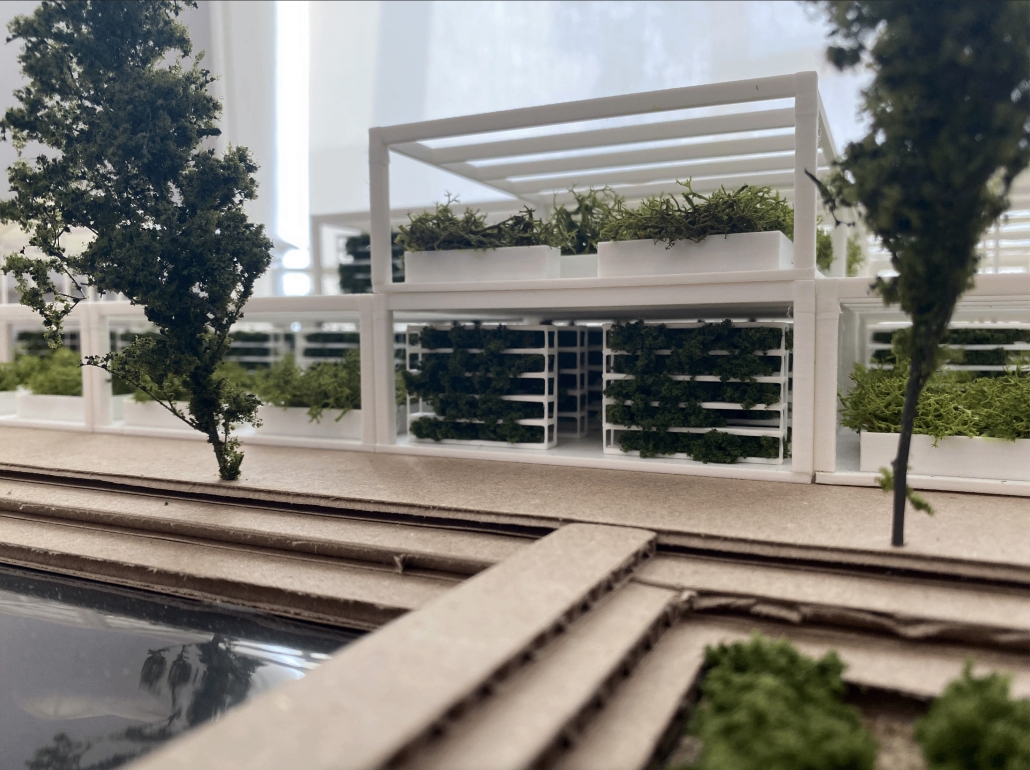
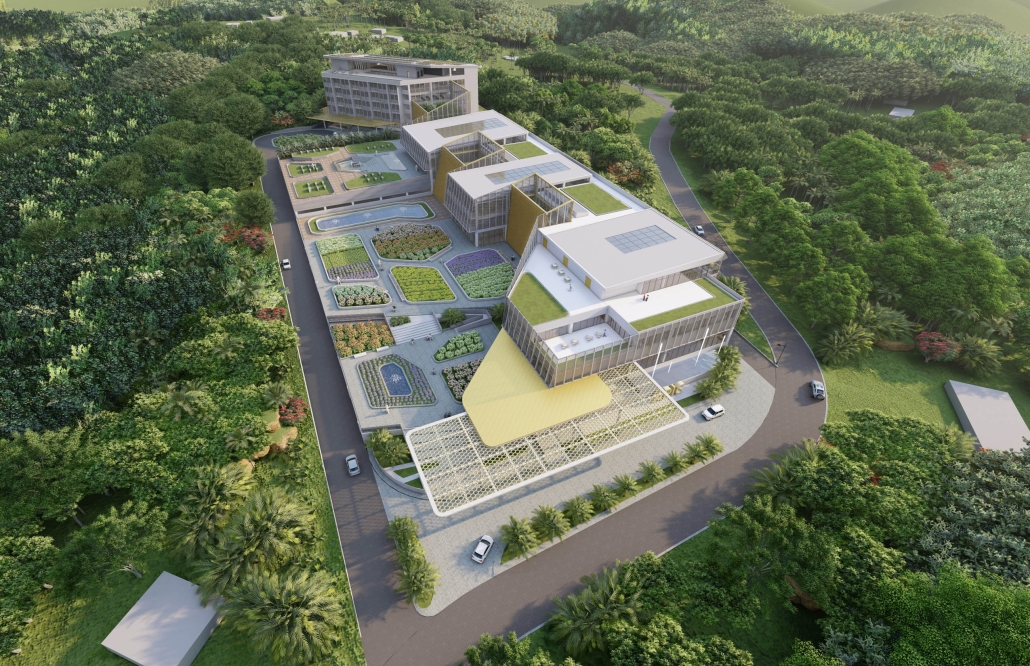
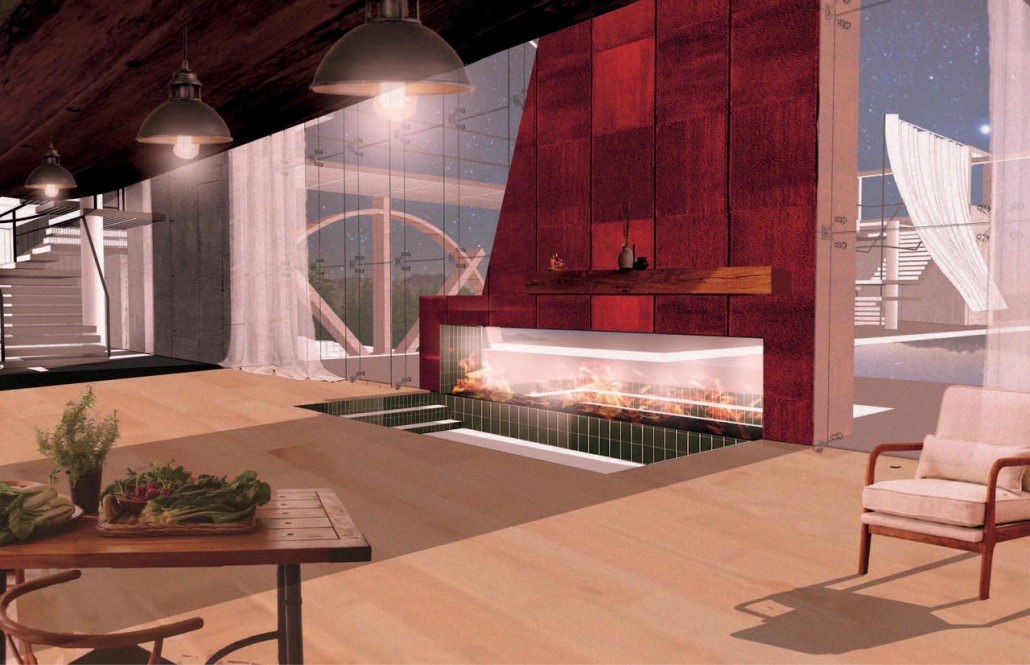
Beating Heart: A Joe Biden Presidential Center by Nick Biser, Aidan Knupsky & Kaiden Estep, B. Arch ’24
Marywood University | Advisors: Jodi La Coe & James Eckler
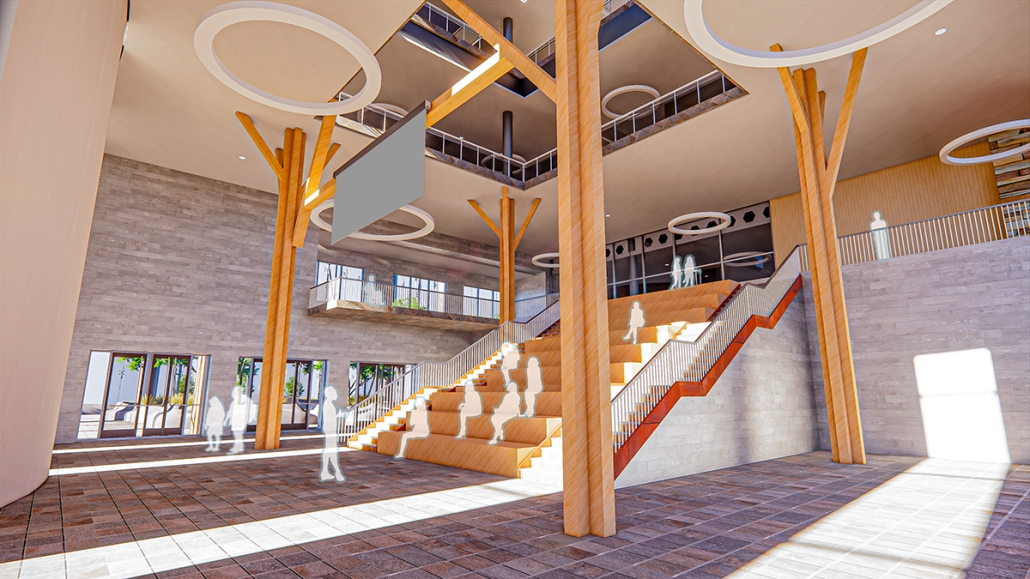
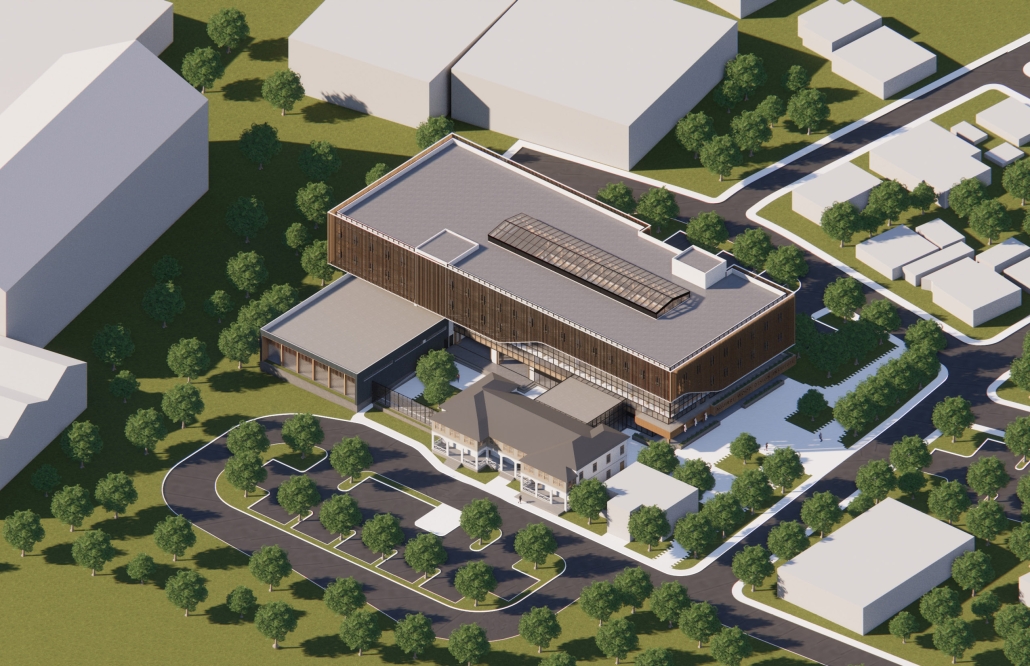
Located in the heart of Scranton, Pennsylvania, Beating Heart is a Presidential Center for Joe Biden housing his presidential archives, a museum, and a new gathering space for the community. Taking a symbolic approach to the design, the building is split between a massive tension cable glass facade and a tall stone building. These two different approaches are brought together by an all-encompassing canopy. This symbolic design follows President Biden’s aim to unite individuals, no matter how different they may seem on the outside. The organic shape of both the canopy and facade represents the changing nature of the American spirit and people. Instead of a traditional Presidential Library, Beating Heart conveys more of Biden’s wishes and beliefs.
At the center of the building is a massive cylindrical Heart of America – a brilliant spiral stair clad in Cor-ten steel that stands in contrast to the rest of the building. The Heart extends over 120’ high, going past the roof for all of Scranton to see. The entirety of the first floor diverts from the typical museum program of a Presidential Library. The front half is surrounded by seemingly endlessly tall glass that surrounds the occupant in an indoor/outdoor space. This winter garden preserves native vegetation and reclaims what was once a desolate parking lot into a reborn green space. The glass facade supported by thin tension cables creates a visually seamless transition between the reworked streetscape and the interior.
In coordination with the winter garden is a Living Learning Lab serving as a space for the Scranton Community to learn more about the vegetation in the winter garden as well as ecological conservation techniques. Lastly, the first floor hosts a large, double-height Community Room, which features a large learning stair for the community to gather and discuss current events and issues. The museum section occupies the upper stories having the occupant flow in and out of the central Heart. The exhibits rotate around two symmetrical interior atriums allowing clear visibility and transparency throughout the museum. The active rooftop provides a space to fully view the Electric City of Scranton.
This project won a 2024 MUSOA Studio Award.
Instagram: @nick_biser, @biser_architecture_and_designs, @aidanknup07, @kaiden_estep, @jodilacoe
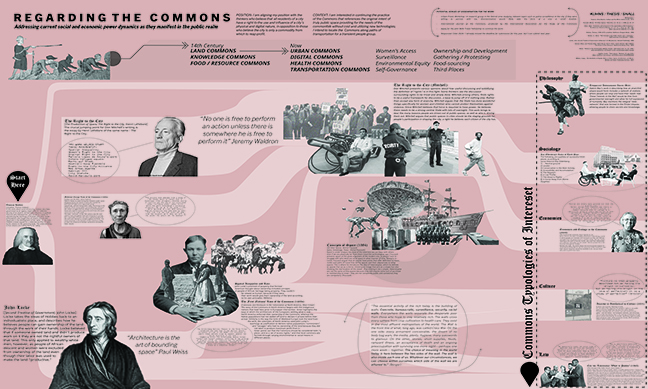
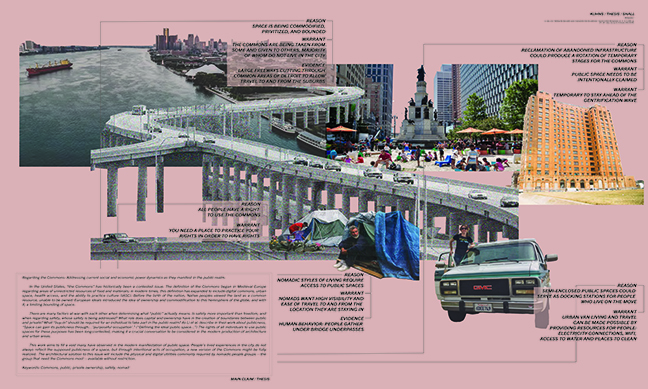
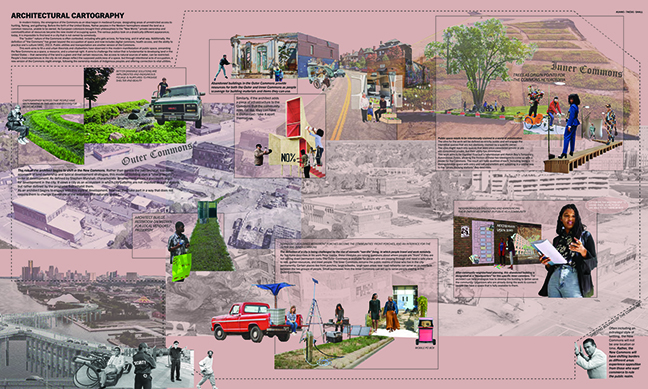
Regarding the Commons: Addressing the current social and economic power dynamics as they manifest in the public realm by Magdaline Kuhns, M. Arch ’24
Lawrence Technological University | Advisor: Scott Shall
In the United States, “the Commons” has historically been a contested issue. The definition of the Commons began in Medieval Europe regarding areas of unrestricted resources of food and materials; in modern times, this definition has expanded to include digital commons, urban space, health access, and the ability to practice culture (IASC, 2023). Before the birth of the Nation, Native peoples viewed the land as a common resource, unable to be owned. European ideals introduced the idea of ownership and commodification to this hemisphere of the globe, and with it, a limiting bounding of space.
There are many factors at war with each other when determining what “public” actually means. Is safety more important than freedom, and when regarding safety, whose safety is being addressed? What role do capital and ownership have in the creation of boundaries between public and private? What “buy-in” should be required for an individual to take part in the public realm? As Li et al. describe in their work about publicness, “Space can gain its publicness through…’ purposeful occupation’.” (“Defining the ideal public space…”) The rights of all individuals to use public spaces for these purposes have been long-contested, making it a crucial conversation to be considered in the modern production of architecture and urban areas.
This work aims to fill a void many have observed in the modern manifestation of public space. People’s lived experiences in the city do not always reflect the supposed publicness of the space, but through intentional acts of occupation, a new version of the Commons might be fully realized. The architectural solution to this issue will include the physical and digital utilities commonly required by nomadic people groups – the group that needs the Commons most – available without restriction.
Instagram: @ace_kuhns, @scott_shall
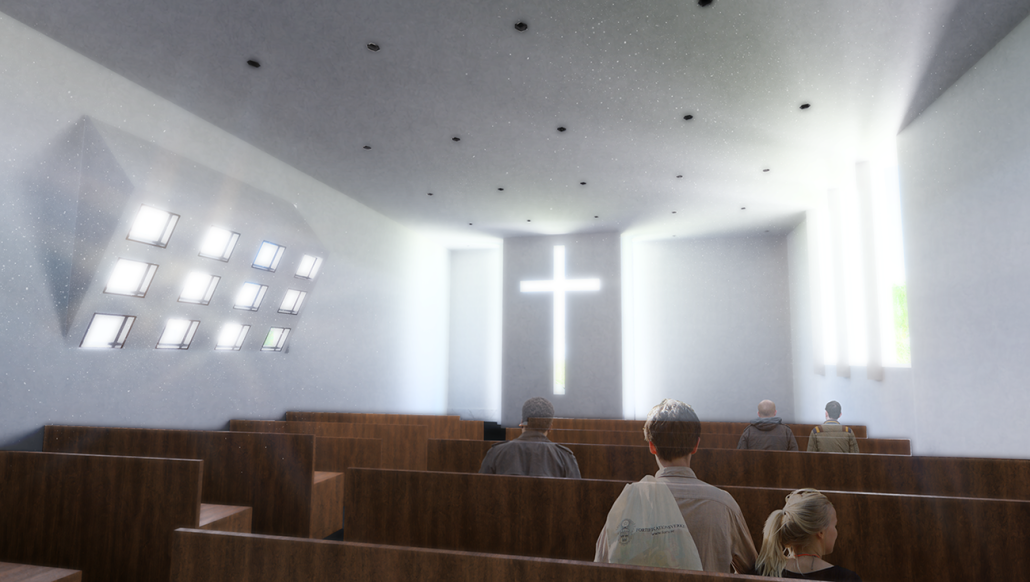
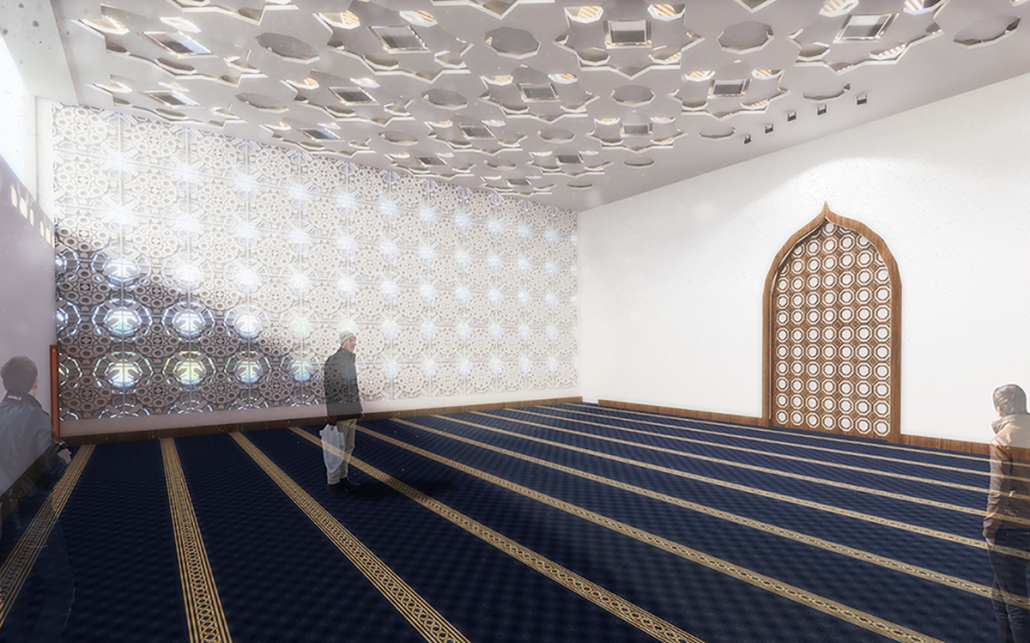
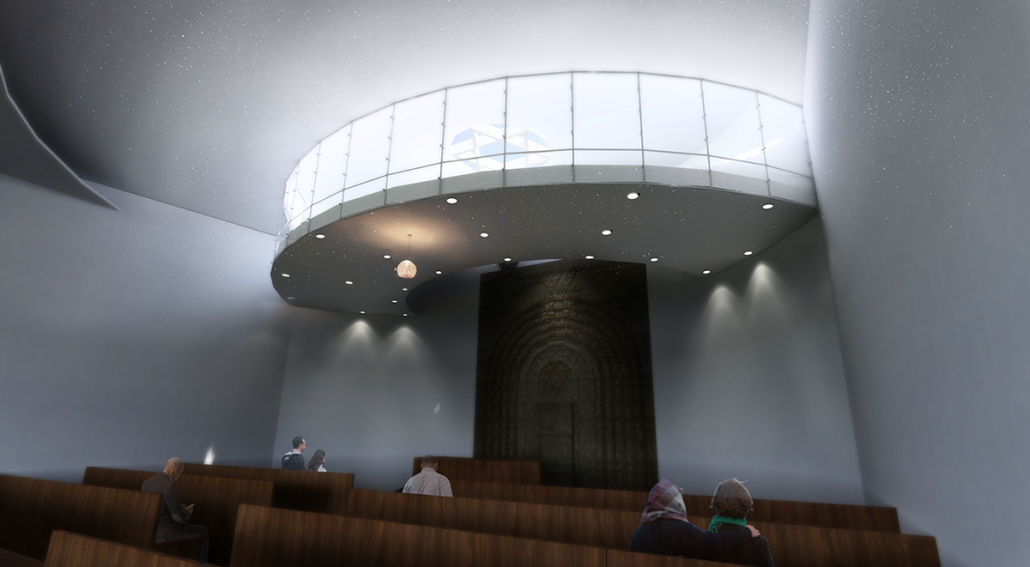
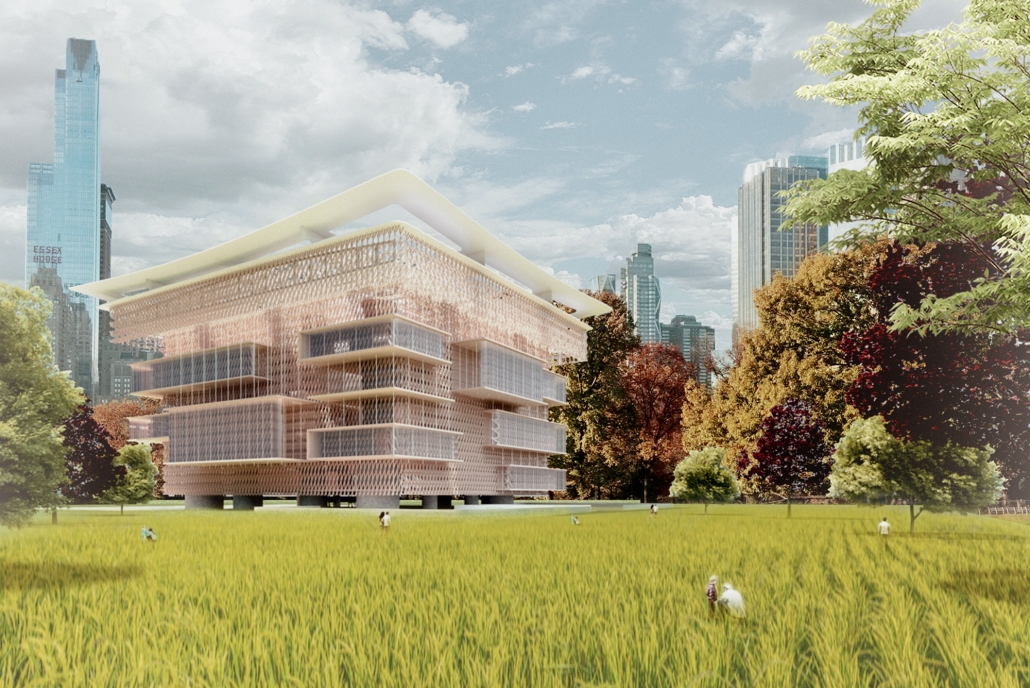
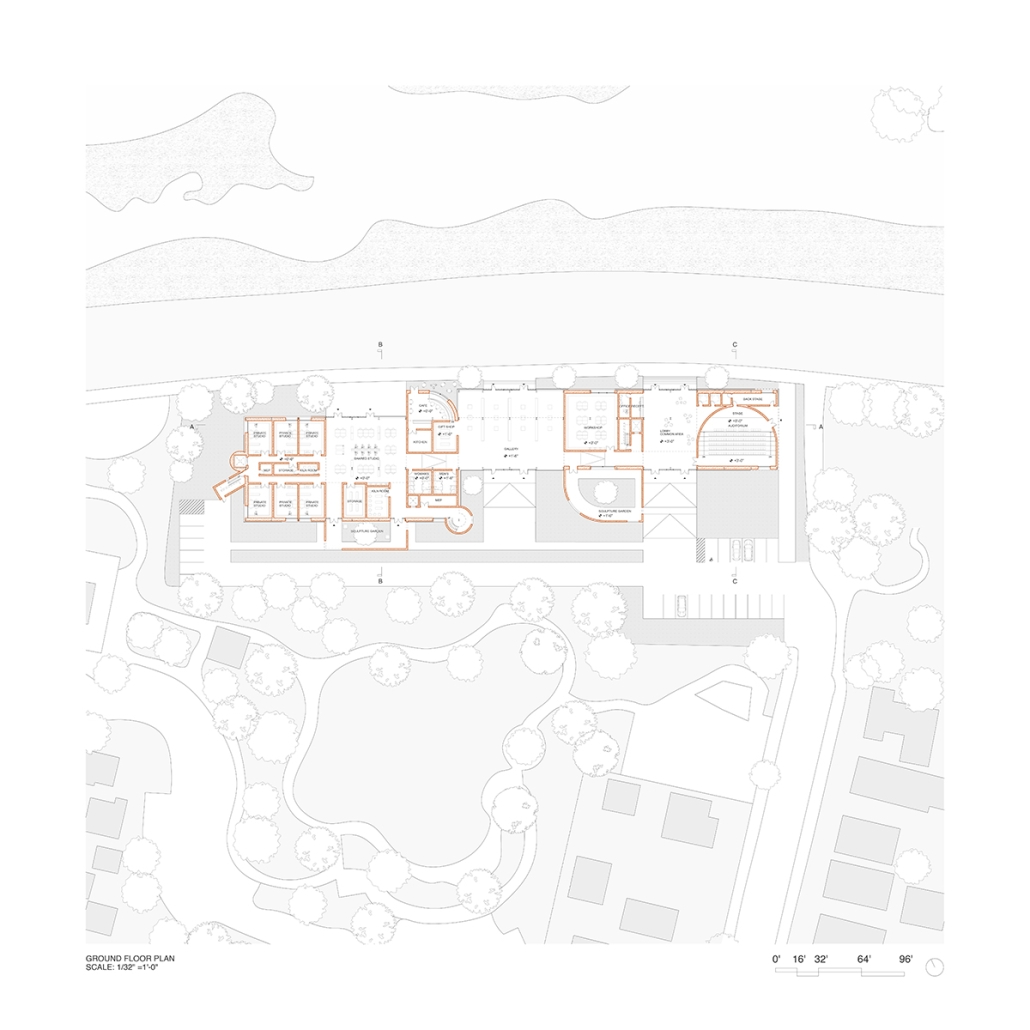
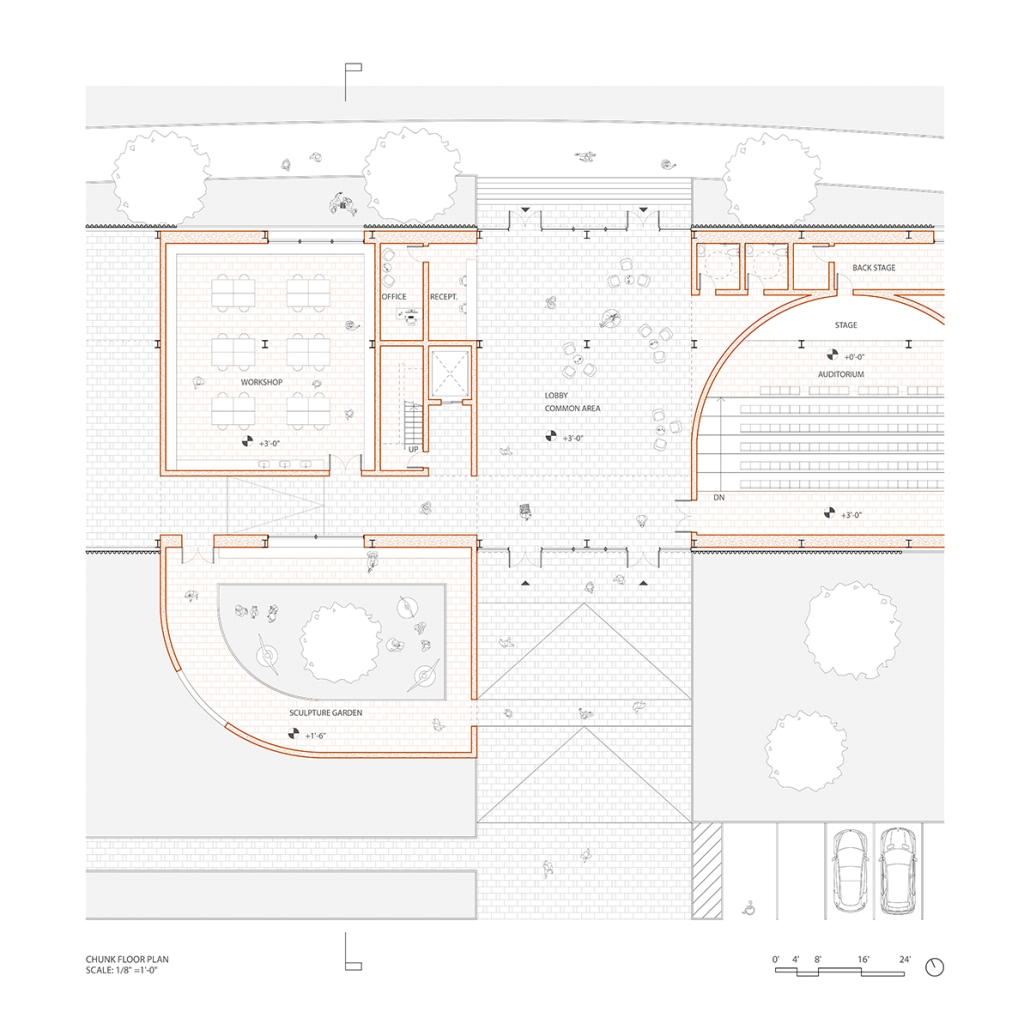
Manus Mouvere by Dillon Alexander Brown, M. Arch ’24
Pennsylvania State University | Advisor: DK Osseo-Asare
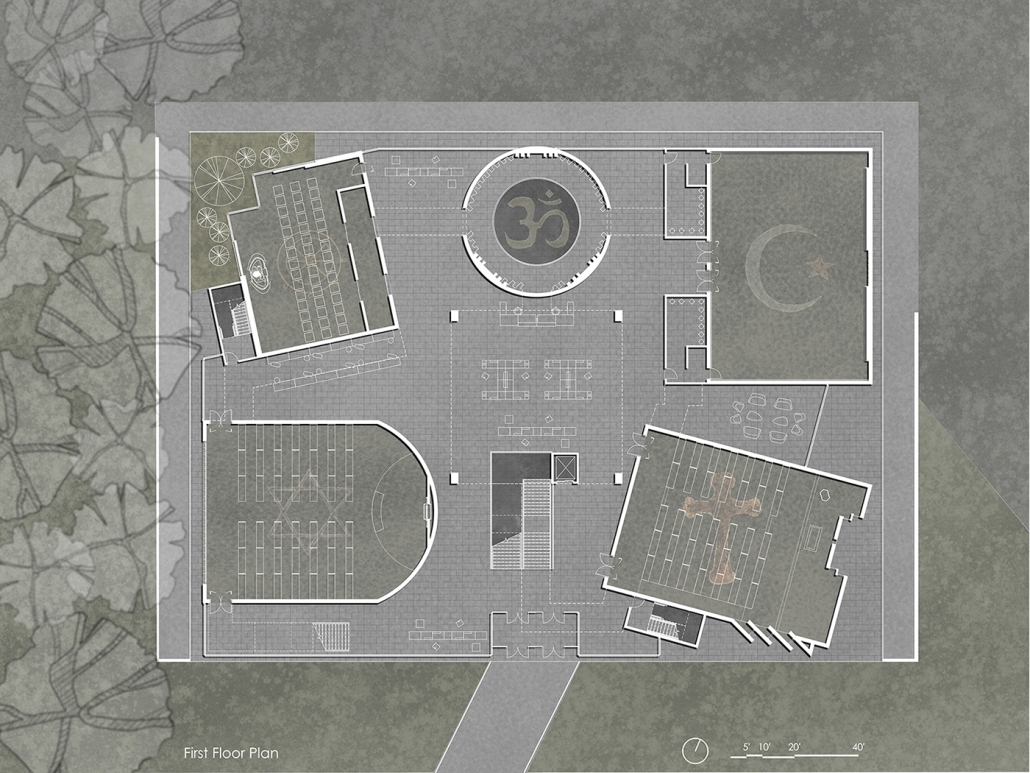
This project seeks to explore ineffable ideas in a physical space: designing a multi-faith facility in a multi-faith society. Based in Central Park, New York City, this building facilitates five distinct religions: Christianity, Judaism, Islam, Buddhism, and Hinduism. These five were selected from the census data of New York City.
In preparation for the design, interviews were conducted at a temple with a religious leader for each religion, coinciding with a tour. Additional interviews with fellow students occurred to gain a more rounded understanding of each faith, their temple needs, and what could possibly lie for the future of the religion. With this information, five temples were designed within a single building and connected by a neutral secular space.
Additionally, to explore the form of space the use of watercolor and pigment theory was used to see how different colors blended, or didn’t blend. This was done to explore how the culture of one faith may physically reside with another faith. The intuition gained from this exercise granted knowledge of how an idea may become overwhelmed and how much contrast is physically needed to keep a faith true to its own idea.
The exterior of the temples are angled to face their respective religious customary directions, but also act as geometry that encourages visitors to sit and face each other, a gesture to encourage dialogue. The building is designed to cross-pollinate understanding and promote tolerance between its visitors. It is representative of the existing religious landscape of New York City, and America as a whole.
This project won the 2024 Jawaid Haider Award.
Stay tuned for Part XIV!