2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part X
Part X of the 2024 Study Architecture Student Showcase highlights projects that address various aspects of urban morphology and city life. The featured work takes place in metropolitan settings including Los Angeles, Tokyo, Philadelphia, Camden, Ras Beirut, and Brooklyn.
The presented themes include fostering engagement in urban settings, creating spatial pauses in the city, the adaptability of urban design in response to societal changes, supporting the needs of city dwellers, and more. Scroll down to browse the award-winning student work!
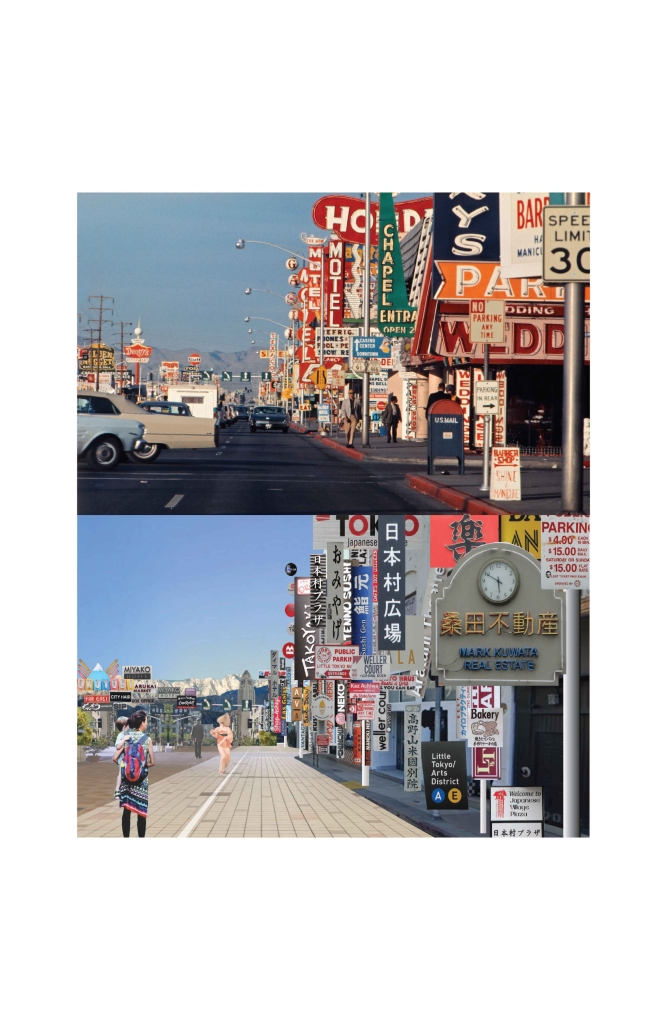
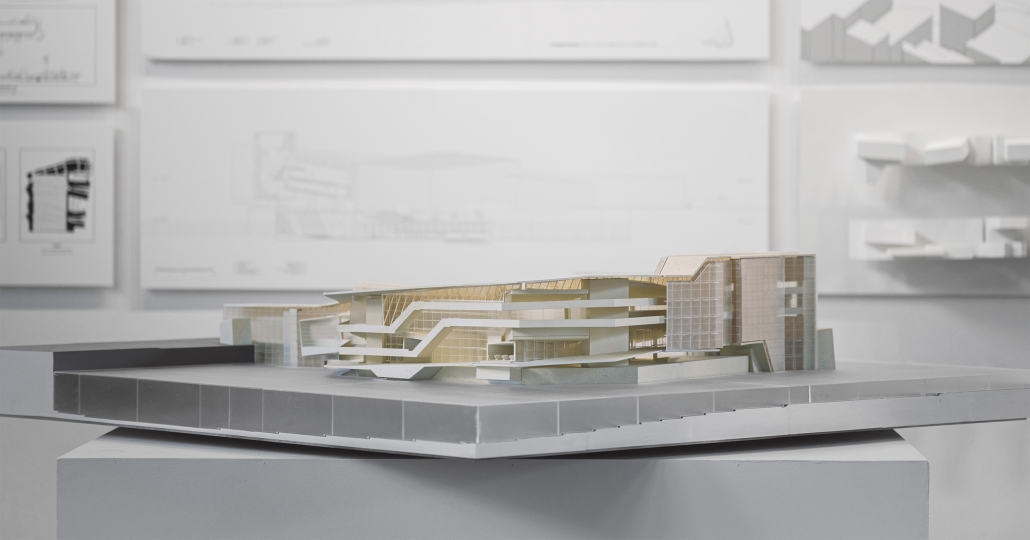
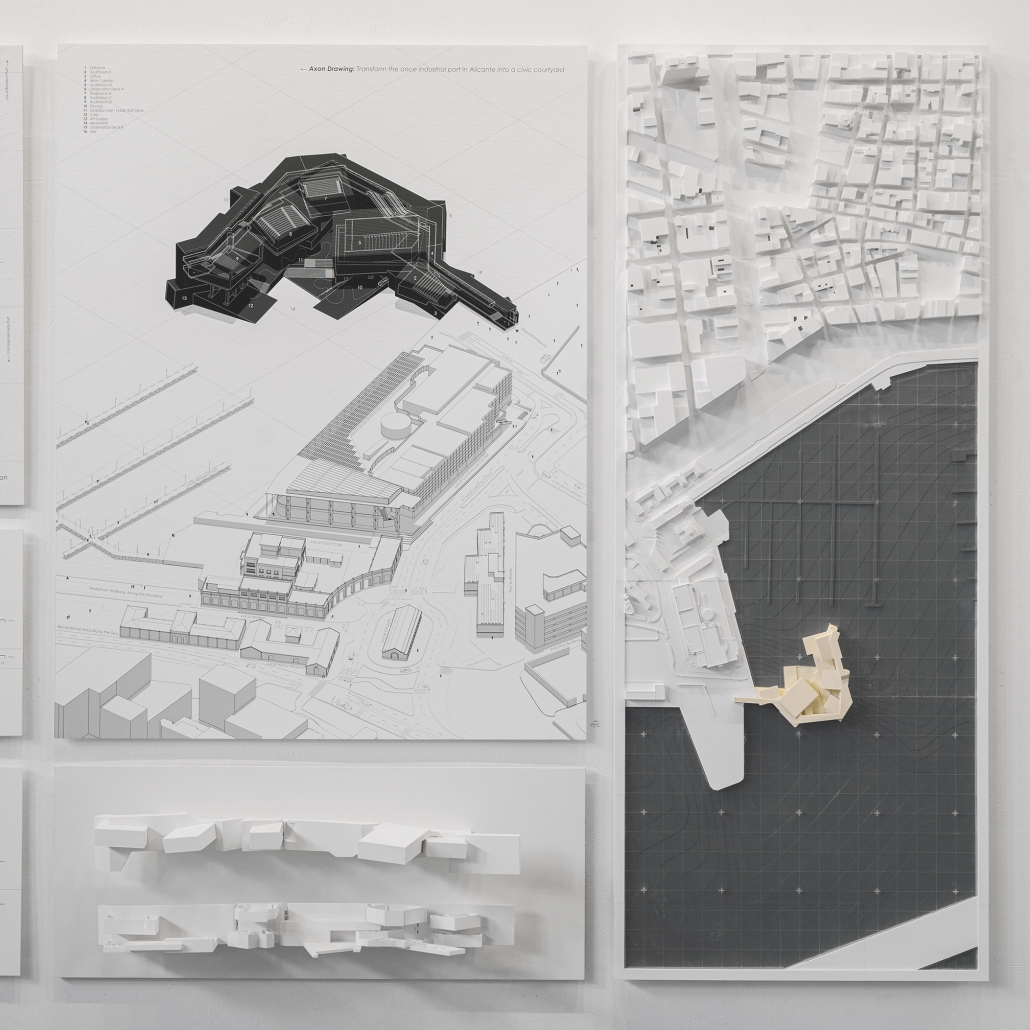
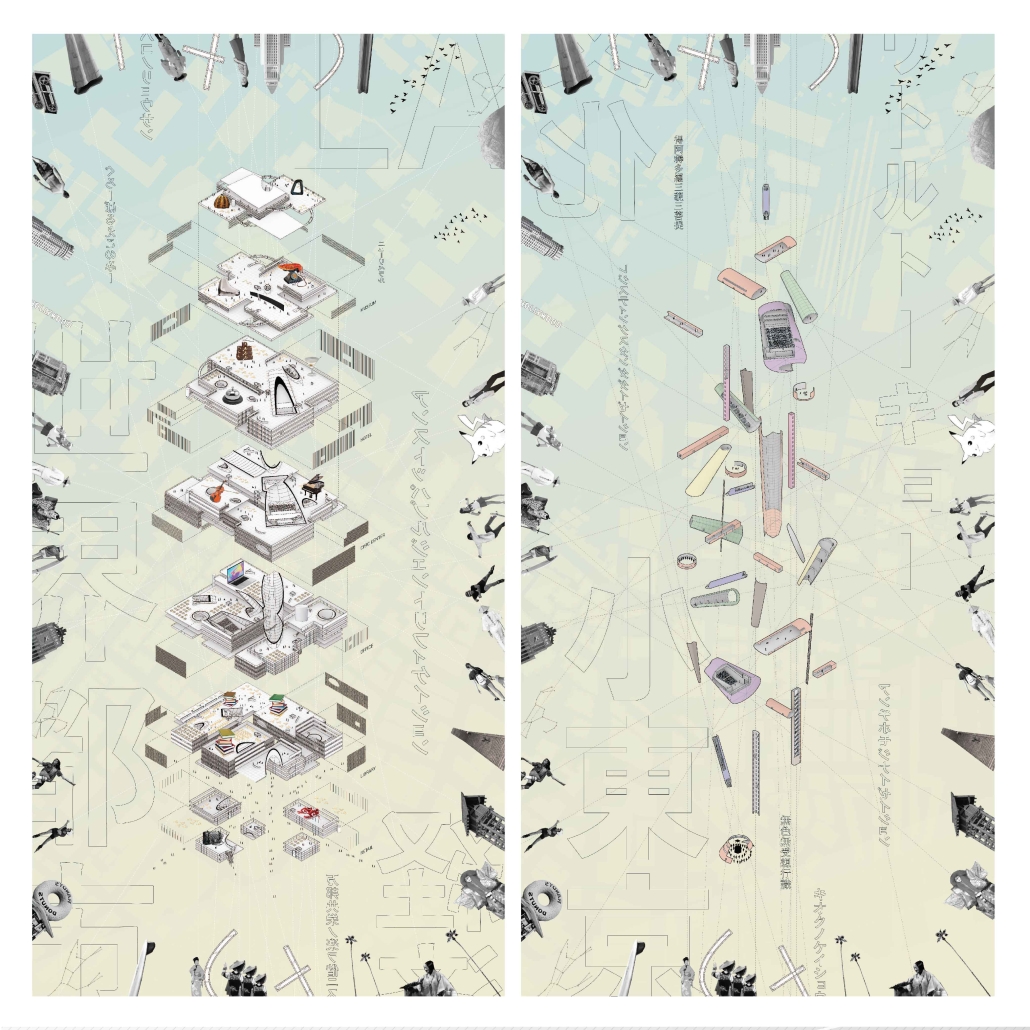
LEARNING FROM LITTLE TOKYO: MEMORIES IN GEOMETRY by Osamu Sakurai, M. Arch ‘24
University of Southern California | Advisor: Andy Ku
The loss of regional identity in urban large-scale redevelopment, accelerated by the pressures of globalization, continues worldwide, with homogeneous spaces isolated from local environments and nature taking center stage within giant monoliths. Little Tokyo in Los Angeles is no exception to this trend. The aim of this project is to contemplate regional identity within the global context, with the means being “boxes” and “free shapes.” The “boxes” symbolize both participation in and challenge to globalization simultaneously. Randomly stacked boxes serve as a gesture to incorporate the external environment and attempt to supply external spaces vertically. The “free shapes” (geometry) strive to transform the identity of Little Tokyo into tangible forms. Only these two operations shape the architecture, emerging amidst the tension between internationalism and localism. Born in the midst of internationalism and localism, this architecture seeks to preserve the regional identity within the pressure of redevelopment, further developing and passing it on to future generations.
This project won the Master of Architecture Design Communication in Directed Design Research Award.
Instagram: @osamusakurai0420
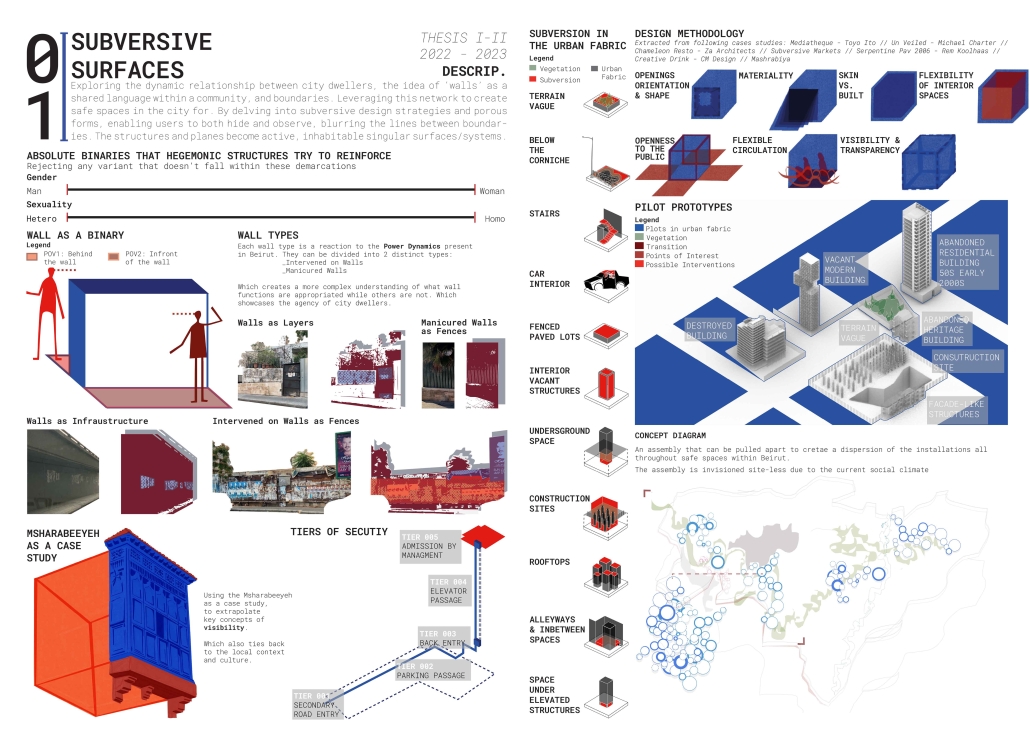
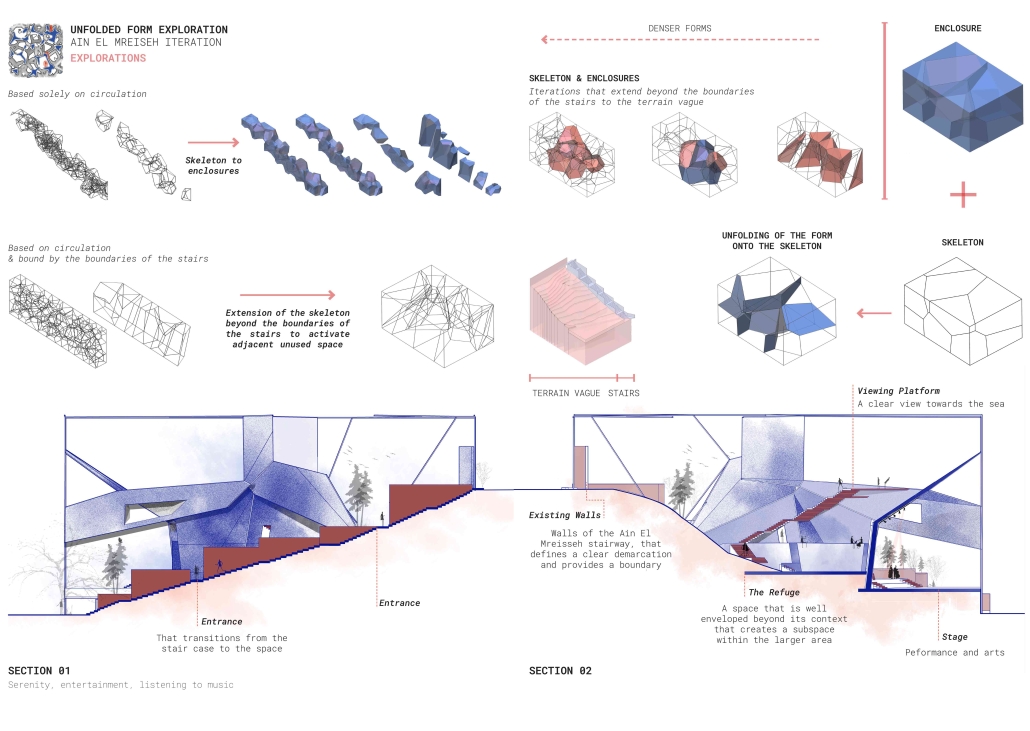
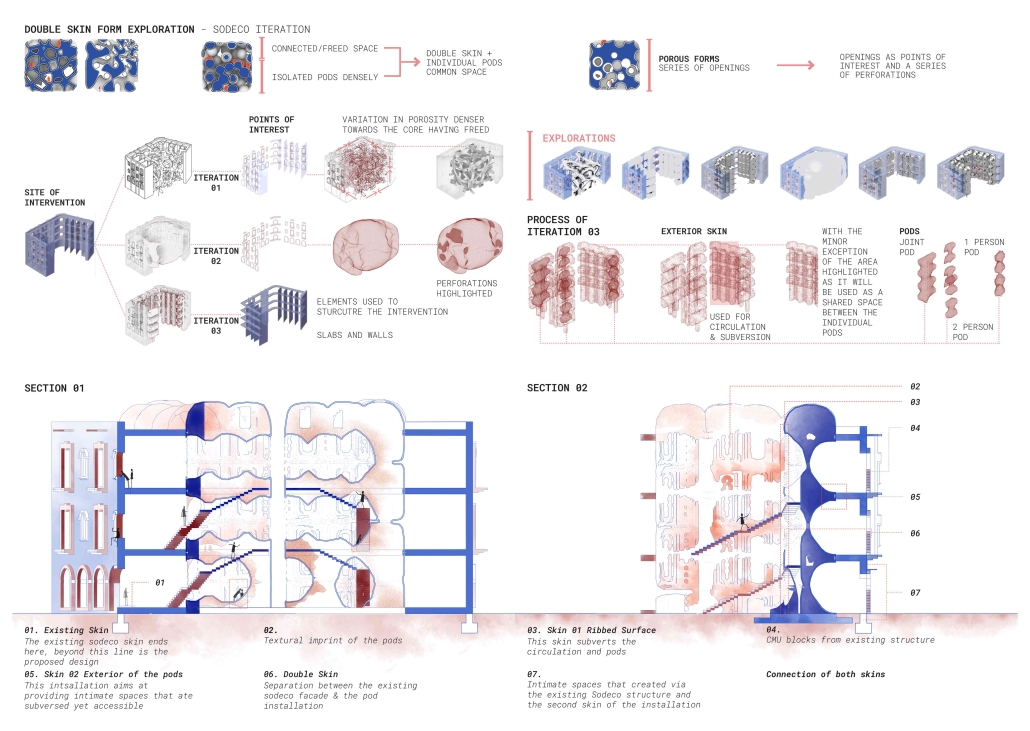
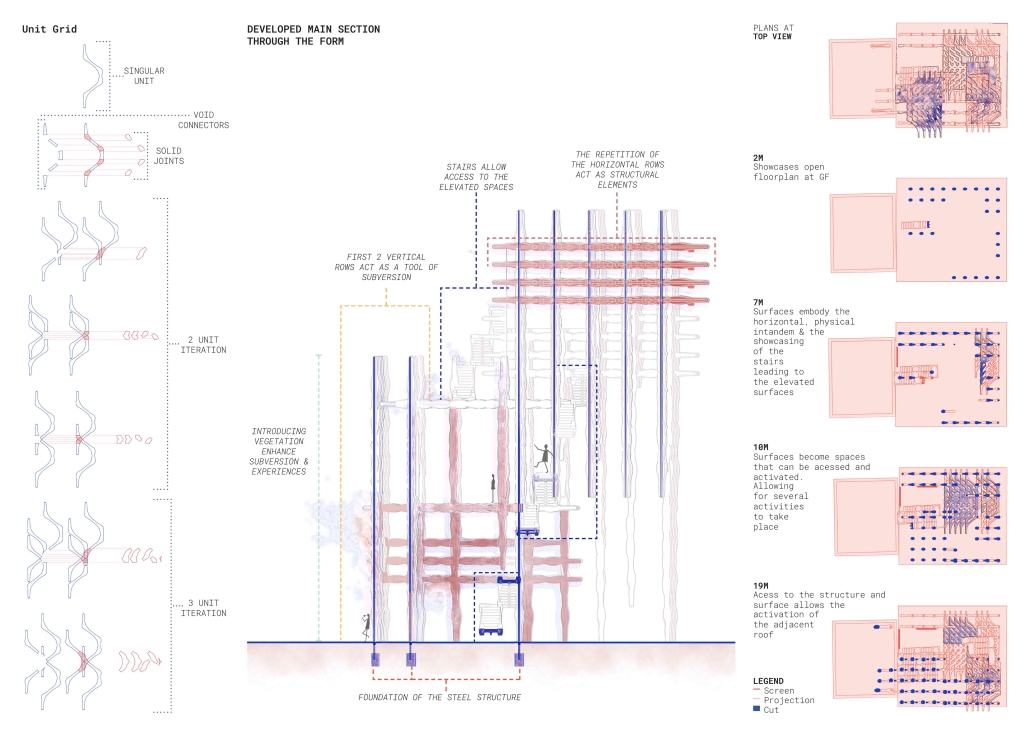
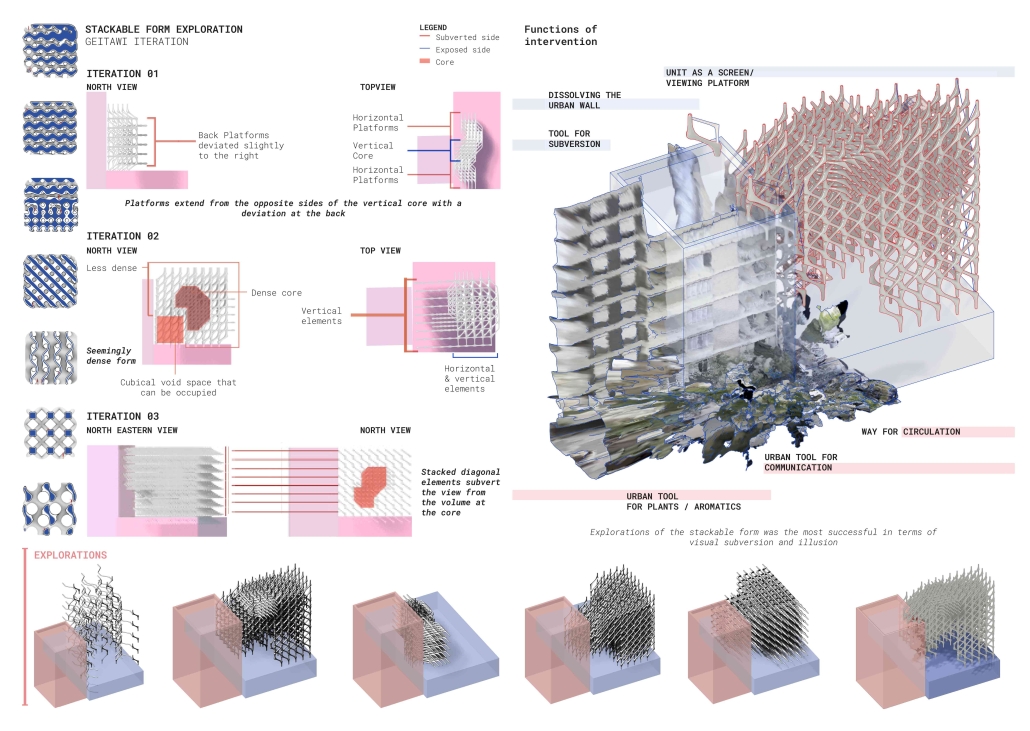
Subversive Surfaces by Aya El Zein, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Sinan Hassan
Exploring the dynamic relationship between city dwellers, walls as a shared language within a community, and boundaries that dictate the public and private understanding. The wall becomes an urban communication tool, materializing the reaction to societal power dynamics. The walls are a clear sign of the way in which the environment is dealing with the public, either by rejecting any intervention (manicured fenced walls) or by allowing for a layered intervention by the public. Following the analysis of the walls, a binary emerged, the wall itself within an architectural framework is seen as a planar separator between the indoor and outdoor/front and back. Thinking of the wall as a surface is where the forms started to emerge. Taking into account the need to subvert the users, the structures and planes become active, inhabitable singular surfaces/systems. Leveraging the surface-based network to create safe spaces in the city for minority groups. By delving into subversive design strategies and porous forms, enabling users to hide yet observe, thus granting them an added layer of agency whilst blurring the lines between boundaries. Shedding the planar notions of vertical and horizontal planes situated on top of each other. Dissolving the urban wall into a surface that inhabits the space having attributes of verticality and horizontality.
Instagram: @ard_aub
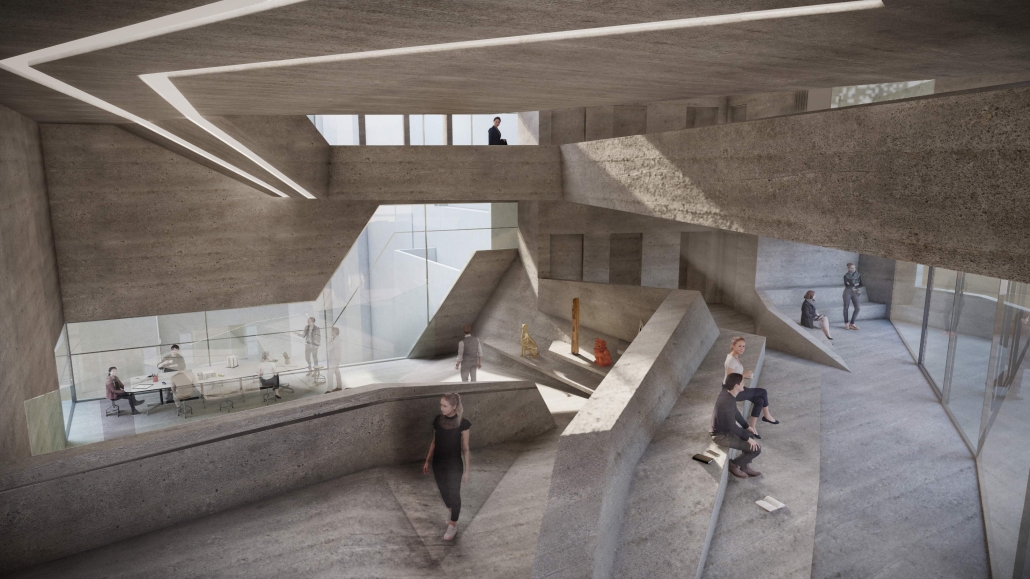
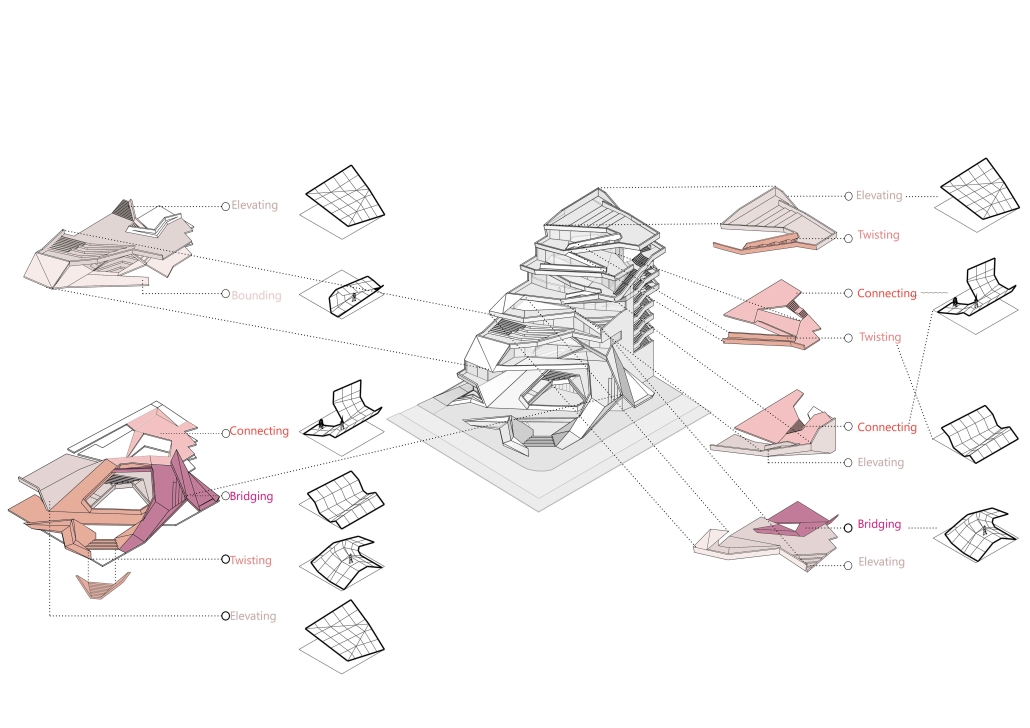
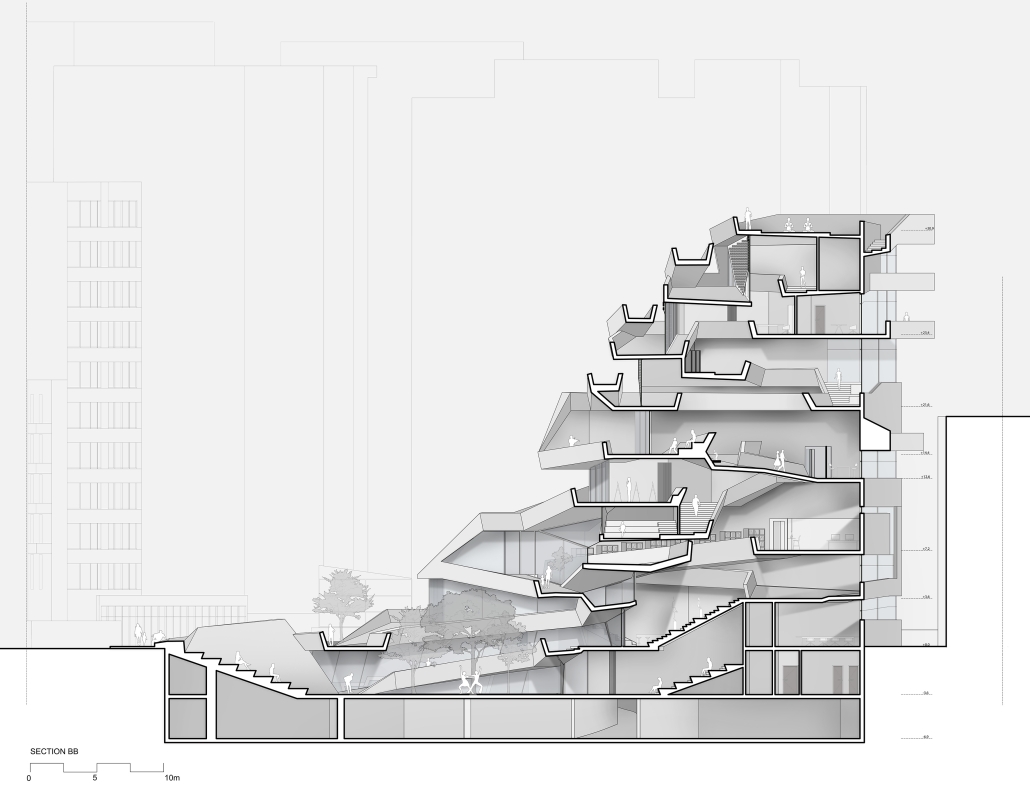
The Vertical Fold by Riwa Karanouh, B. Arch ‘24
American University of Beirut | Advisors: Dr. Howayda Al-Harithy & Hana Alamuddin
Modern-day life is fast-paced & intense which compromises the everyday experience leading to the disengagement of the urban dweller from his surroundings. The architecture is complicit in this disengagement, by not interacting at the urban level.
Therefore, how can projects in Beirut have a set of pauses to re-engage people with their surroundings, reinforcing the notion of urban citizenship and belonging?
A hypothesis of using spatial engagement strategies was explored to produce spatial pauses in the city, defining “pause” as an experiential moment of engagement with the built environment. It is not about physically stopping, but a shift in experience.
Jeanne d’Arc Street, a prominent street in Ras Beirut, has witnessed the loss of its sociocultural spatial practices compromising its experience. To reinvigorate its public realm and engage the citizens, a design system of folding was employed. Through extending, elevating, and twisting the ground plane, Jeanne d’Arc is integrated into the site, serving as a theatrical vertical extension of the street, compelling pedestrians to pause and engage with the building. The folded surfaces serve as interactive connectors, seamlessly linking the underground, ground, and vertical planes, transforming individuals into active engaged performers in the urban experience.
This project was the First Prize Winner of the Areen Projects Award for Excellence in Architecture
Instagram: @ard_aub
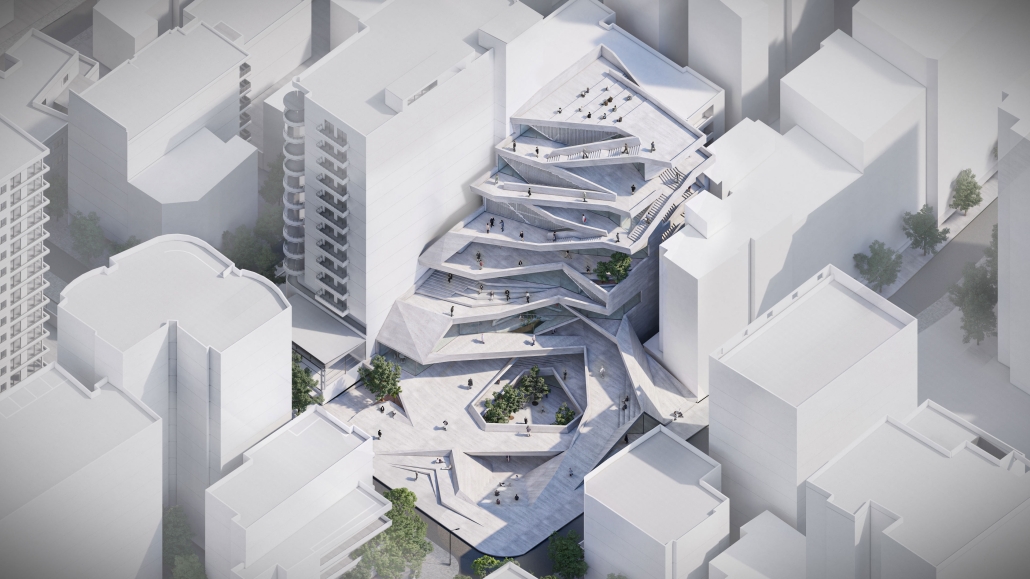
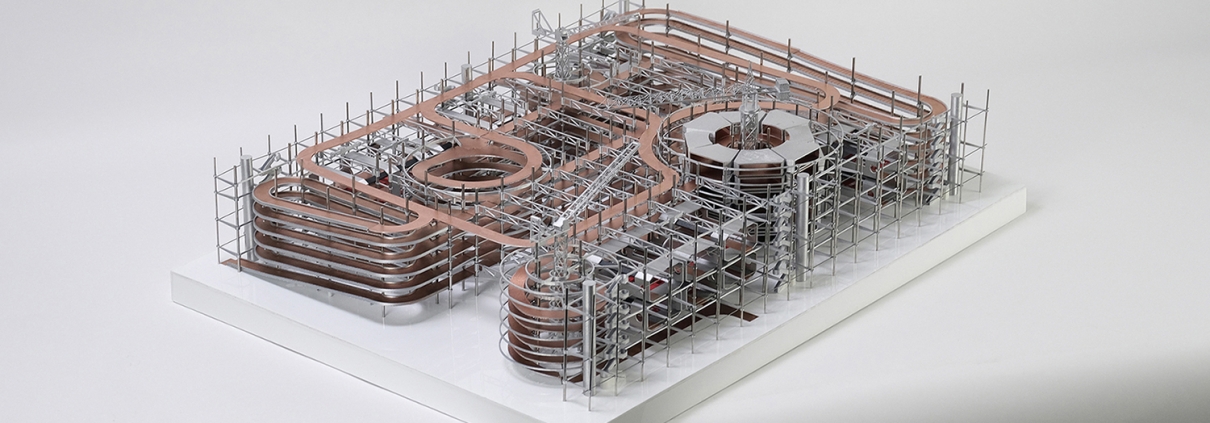
The Architectural Sublime in Artificially Intelligent Mobility Systems by Wayne Li & Jack Zhang, BS (Bachelor of Science in Architecture) ’24
Washington University in St. Louis | Advisor: Constance Vale
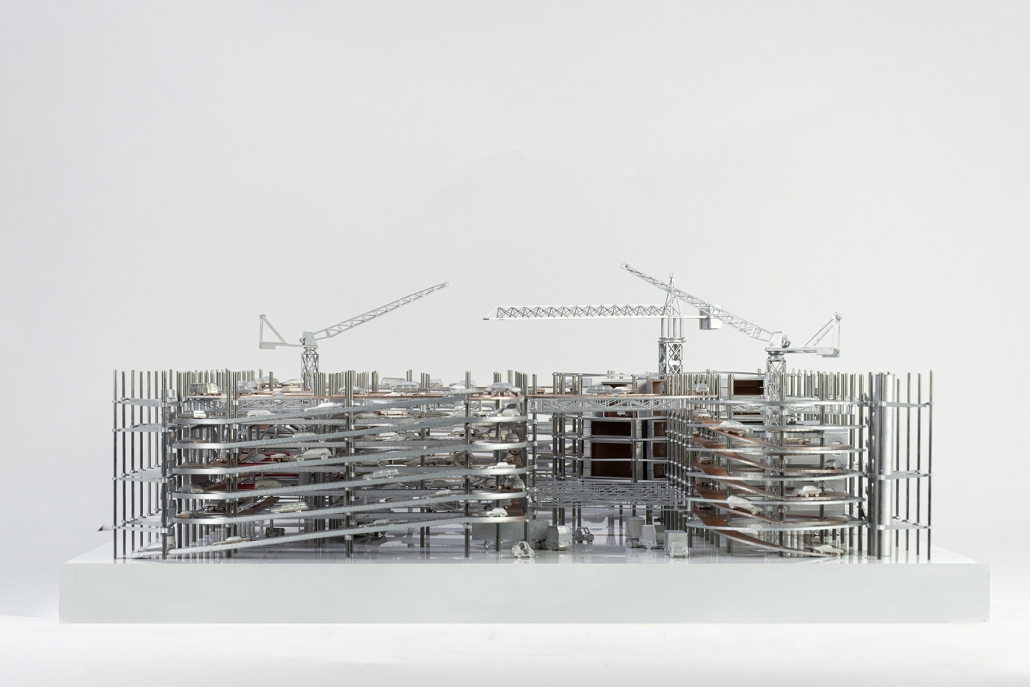
Our project aims to redefine urban mobility, shifting from private car ownership to a shared, autonomous vehicle (AV) system. This initiative tackles LA’s infamous traffic by converting parking lots near public programs into dynamic AV hubs, creating a network of connected nodes across the city. The project’s design embodies the sublime, with intricate structural frameworks that evoke a sense of awe and, at the same time, foster an enlightening experience to let people understand how AV works. AVs move around the intricate circulation, recharging as they move through the long trajectory before returning to circulate in the city, thus eliminating the need for circulating and increasing traffic in the city. Its adaptable structure allows pedestrians to witness the inner workings of AV operations, fostering engagement and education. Through transforming static spaces into active educational hubs, the project promotes a cohesive, efficient, and forward-thinking urban landscape, guiding Los Angeles into a new era of connectivity and communal urban life.
This project was collected for Washington University in St. Louis’ student work publication, Approach.
Instagram: @wayne_li_0611, @jack_arch_, @constancevale, @washu.architecture
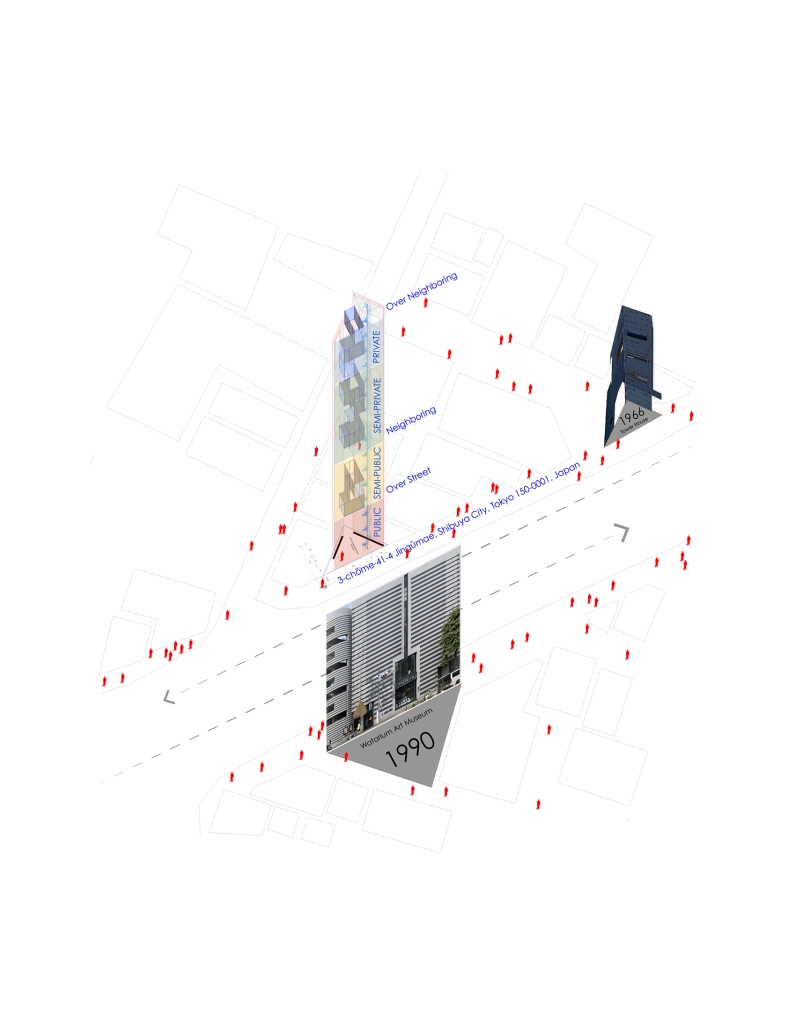
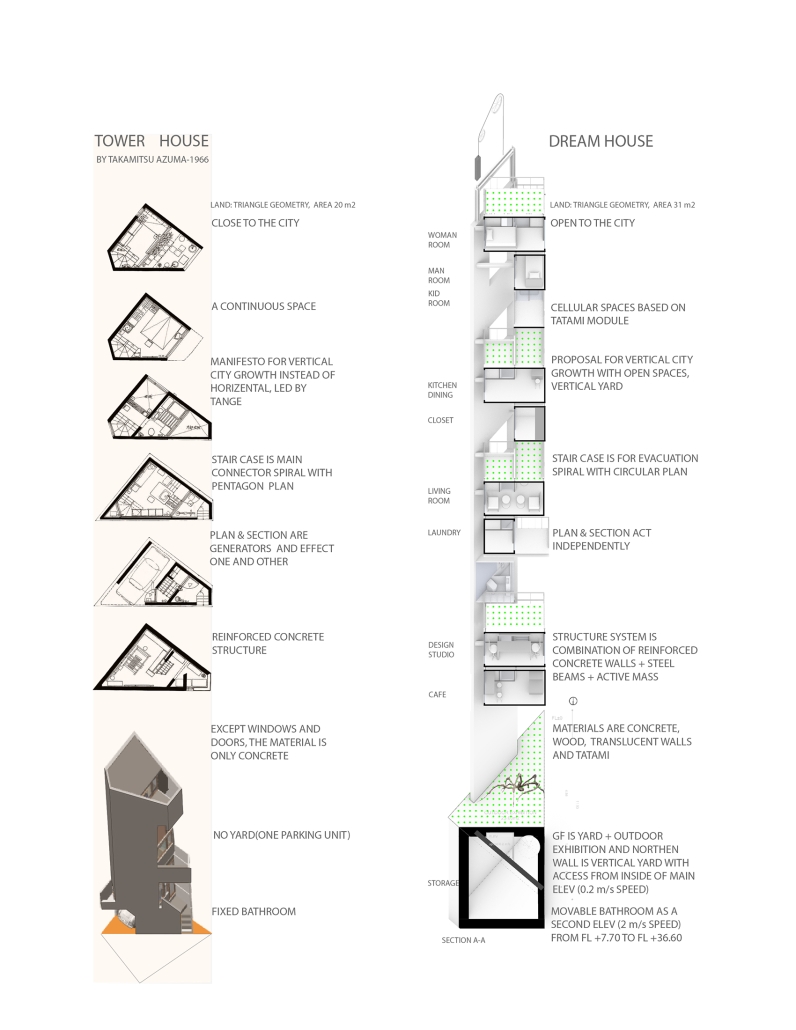
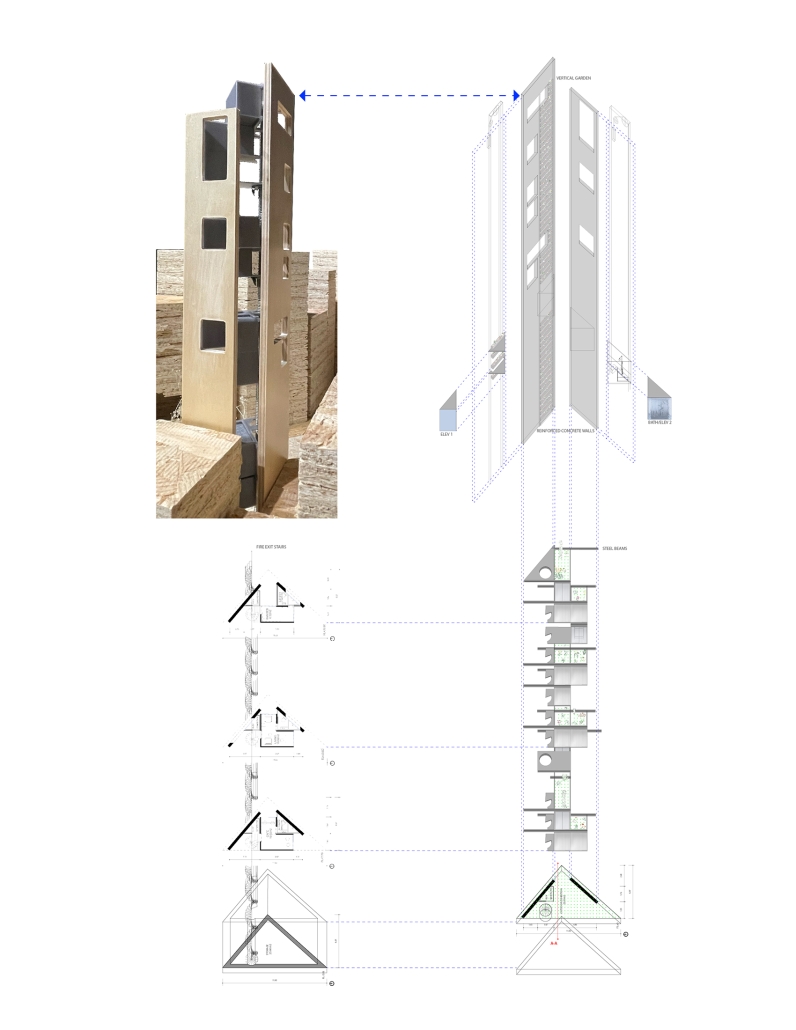
Dream House by Meisam Dadfarmay, M. Arch ’24
Pennsylvania State University | Advisor: DK Osseo-Asare
“Dream House,” is a project I designed for myself as a personal home and workplace, examining how these spaces adapt and transform to reflect the dynamic nature of dense cities and the architect’s life, and a vision for the future of architecture, where design transcends traditional functionalities and purposes. It is also a proposal for vertical city growth in Tokyo, which is a dialogue with my precedent project, ‘Tower House,’ designed by Takamitsu Azuma in 1966. Tower House, a project designed for architecture itself, is located close to my project site, and both are situated in tiny sites with almost the same geometry. Tower House stands as an impressive example of innovative architecture, illustrating how limitations in space can lead to creative and functional design solutions. It remains a testament to Azuma’s architectural vision and the adaptability of urban design in response to societal changes.
The Dream House concept, influenced by Slavoj Žižek’s theories, delves into homes composed mainly of secondary spaces, highlighting the importance of spatial arrangement in architectural design. Žižek’s critique of contemporary architecture, focusing on “Architectural Parallax” and “interstitial space,” his perspective connects Jameson’s “political unconscious” to the architectural realm. This viewpoint sees underutilized spaces as potential solutions to social issues, particularly class struggle, scrutinizing the ideological underpinnings of architectural projects and their claims of “anti-elitism.”
The connection between the “Dream House” concept and architectural critique lies in their shared interest in the ideological ramifications of architectural design. Both perspectives view space not just as physical dimensions, but as carriers of socio-political and cultural narratives. The “Dream House” concept focuses on individual architects’ choices, while the broader critique examines architectural trends and their societal impacts.
Together, these perspectives seek to uncover deeper meanings in spatial design, questioning how these designs influence or challenge the prevailing socio-political dynamics in both personal homes and public structures.
This project received the Haider Award for Design Excellence – Honorable Mention.
Instagram: @meisamdadfarmay
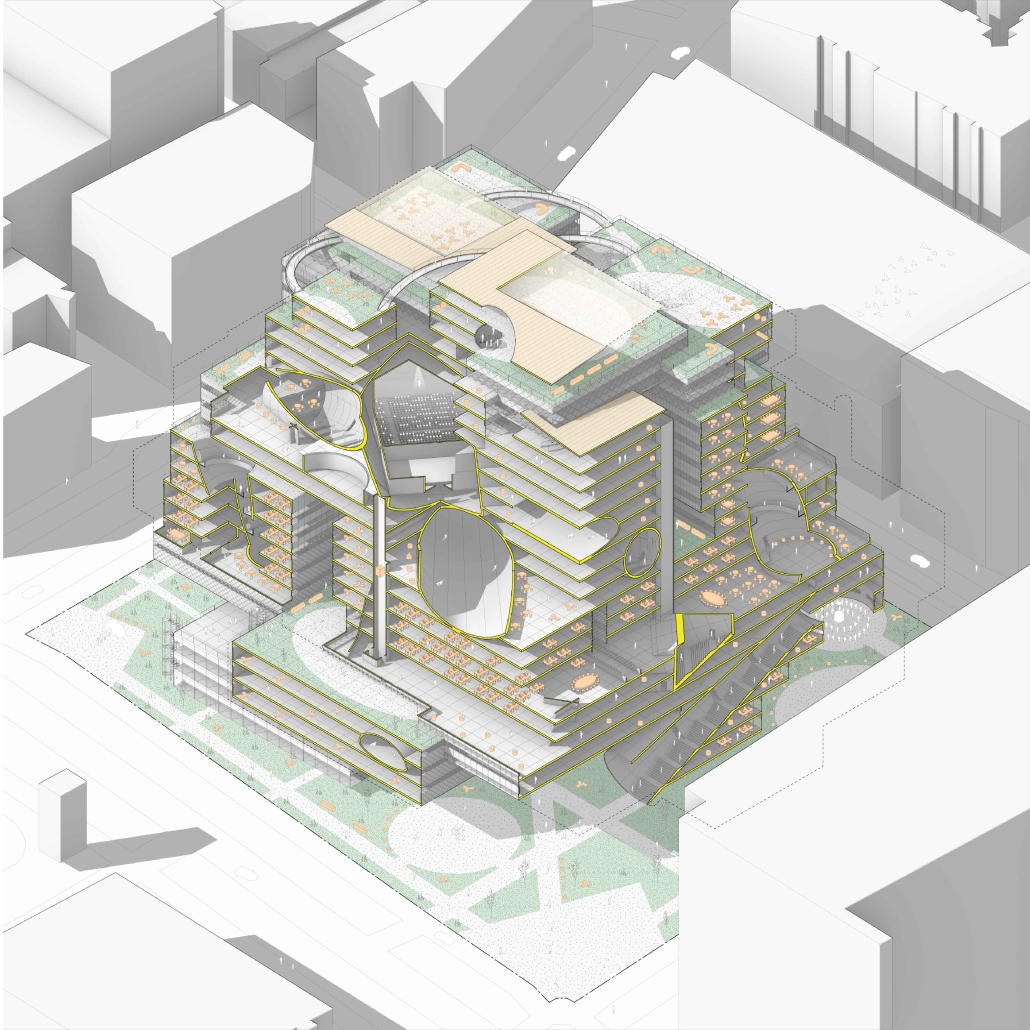
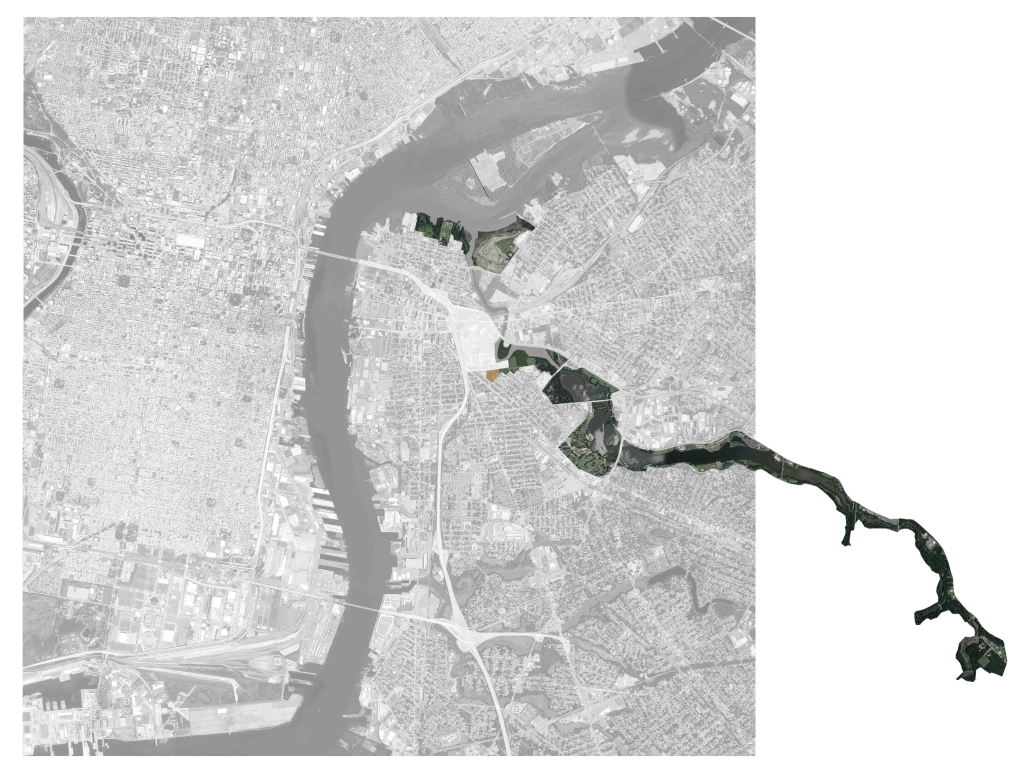
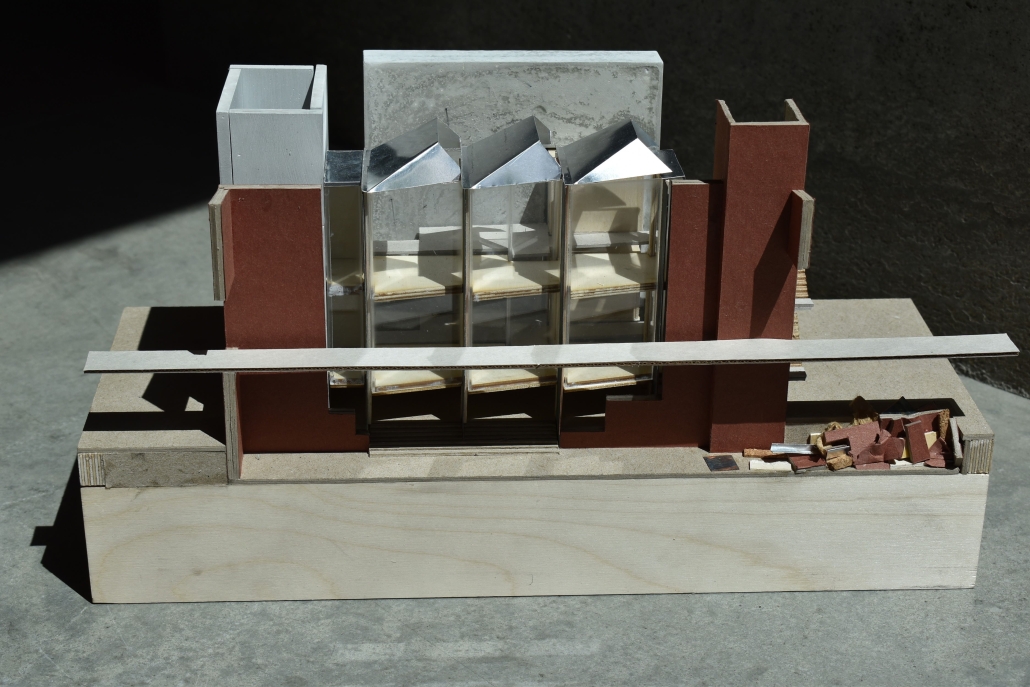
Gateway Park and Arts Center, Camden, NJ by Philip Edmonston, BS Architecture ’24
University of Virginia | Advisors: Peter Waldman & WG Clark
Situated between two industrially important rivers, Philadelphia was laid out on a grid plan in 1682 by William Penn. The city is organized around two axes and is punctuated by four public parks, each within walking distance of the others. While Penn’s ideal city was historically planned for its residents, its partner city Camden was not.
Camden, [located] on the east shore of the Delaware (A), began as an industrial zone serving Philadelphia. After the twilight of American urban industrial centers in the latter half of the twentieth century, Camden fell into deep poverty as a result of disinvestment. No longer used for manufacturing, Camden became a center for cheap office space – more affordable than Philadelphia while still benefiting from proximity to the larger city. This shift in Camden’s financial basis caused a shift in urban planning, where former industrial space was razed and new offices were built. Further, new highways bisected Camden’s neighborhoods, allowing non-residents to work in Camden’s downtown, but sectioning off some neighborhoods from others. Because of historic disinvestment and continuing urban renewal, Camden has become hostile to its residents, who are alienated from their city.
Camden has been treated as culturally secondary to Philadelphia – while there is a strong “Philly” identity, Camden’s identity has not been cultivated and protected in the same way. Because it is culturally undervalued, historic preservation is not seen as vital in Camden as it is in Philadelphia. This in turn causes a pattern of razing and building new, and it is because of this pattern that Camden is losing connection to its historic spaces. We connect with our cities through historic spaces and the weathering apparent in the material of old buildings. This project proposes not a clean-slate renewal, but rather a care for and celebration of weathering, history, and the industrial space that facilitated Camden’s development.
The Gateway neighborhood (B) in Camden is one such example. Lying between the I-676 highway to the West and the Cooper River to the east, the neighborhood is relatively isolated from Camden’s downtown and from the city’s public space. Further, the Campbell’s Soup headquarters to the North cuts Gateway off from the rest of the city. The project becomes a new Northern boundary for Gateway and connects it to the larger Cooper River Park.
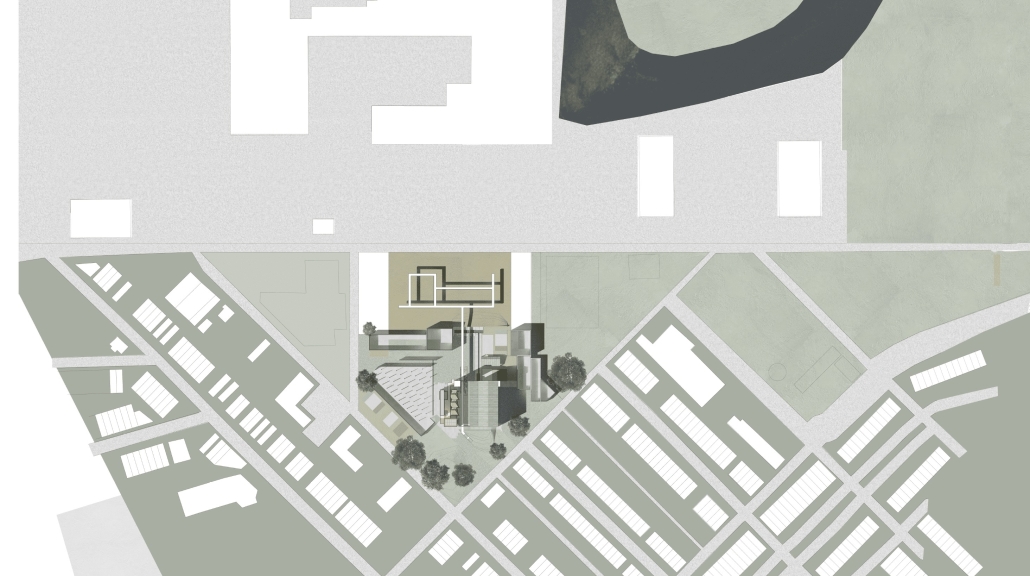
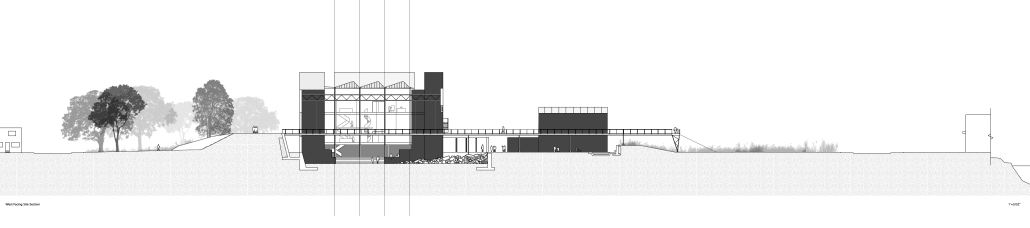
At the site scale, the project exhibits a series of methods for environmentally conscious use of formerly industrial space. These three methods: infill, excavation, and bioremediation through aeration, are shown in sequence as visitors walk across a path connecting the Gateway neighborhood to the Cooper River Park. The excavated and infilled areas are designed as park spaces, while the bioremediation space lies under a series of raised pathways.
In addition to providing residents with a new boundary and park, the project proposes an art space serving residents and visiting artists. The space, designed using principles taken from the industrial context, consists of three components: a residence and service space for visiting artists, a workspace for artists and residents, and a meeting hall for local groups.
This project was recognized as a 2024 Exceptional Thesis Project at the University of Virginia.
Instagram: @philip.edmonston, @aschool_uva
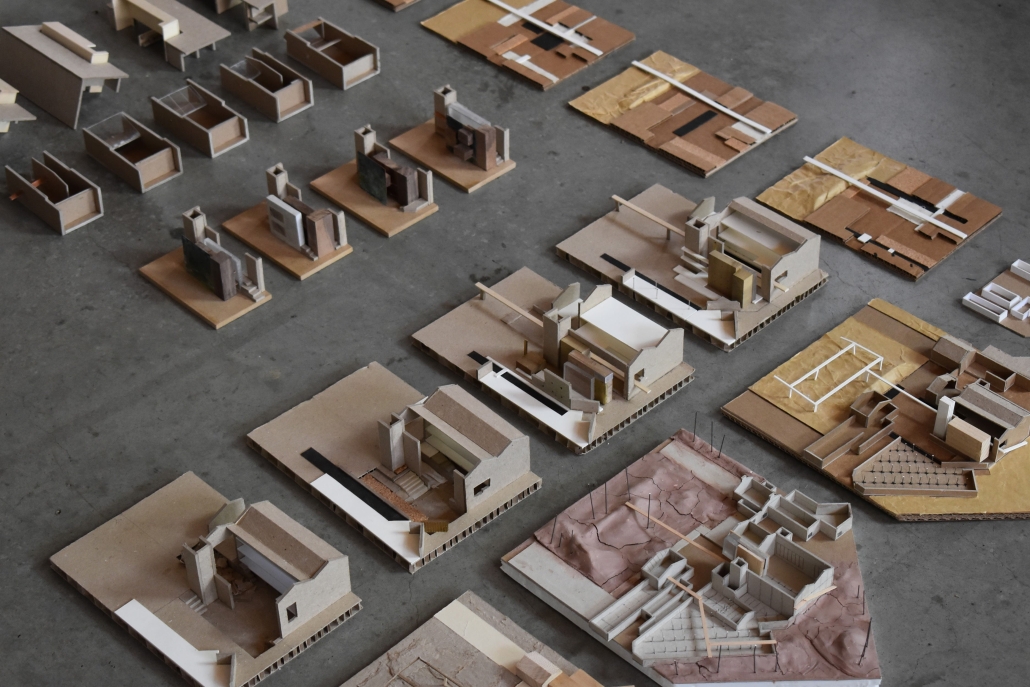
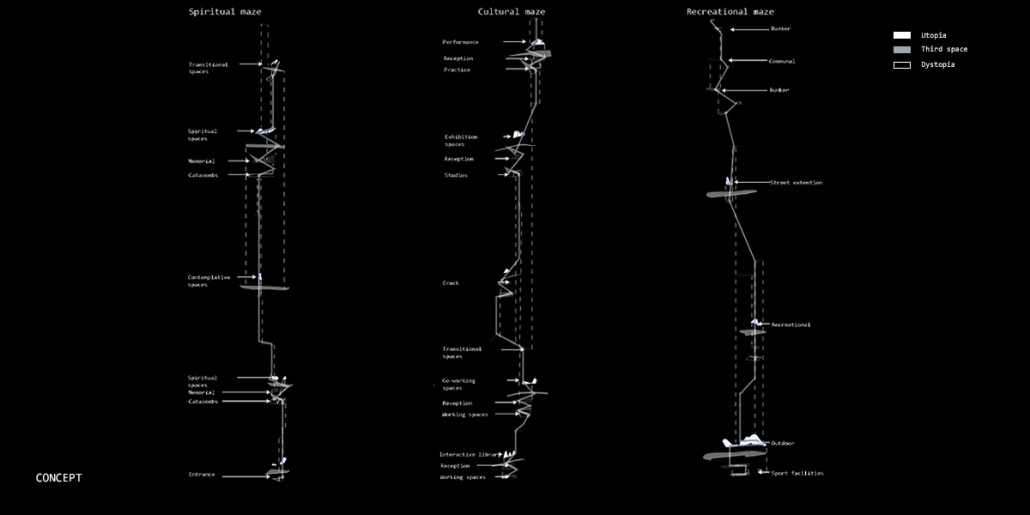
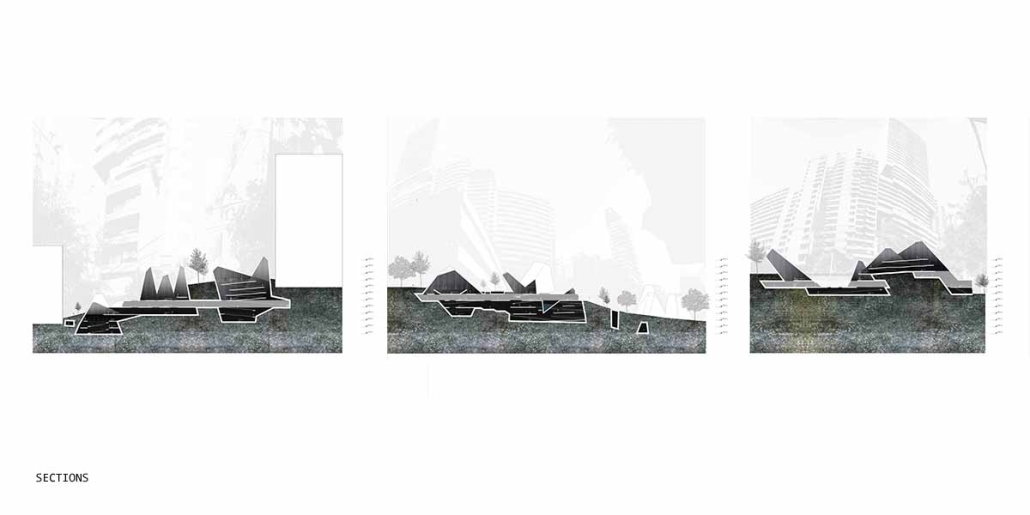
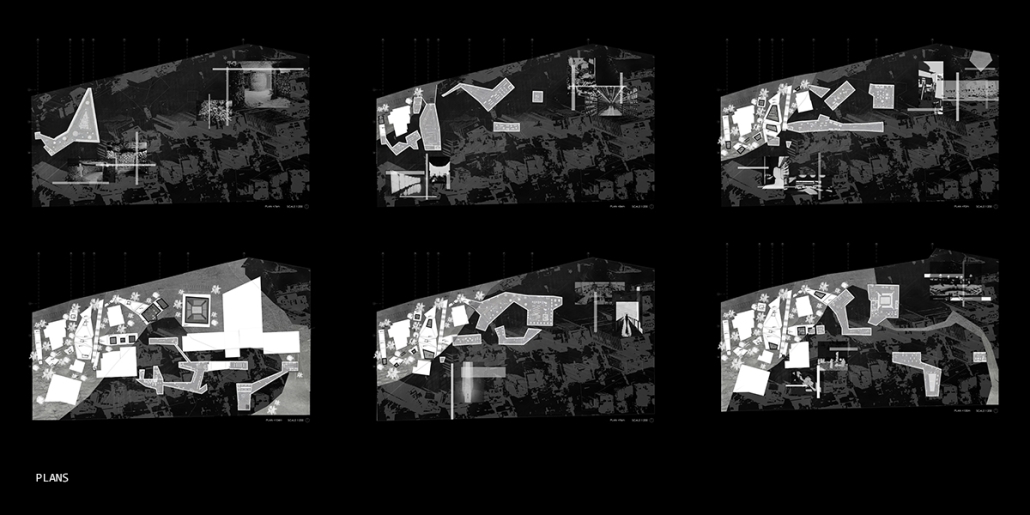
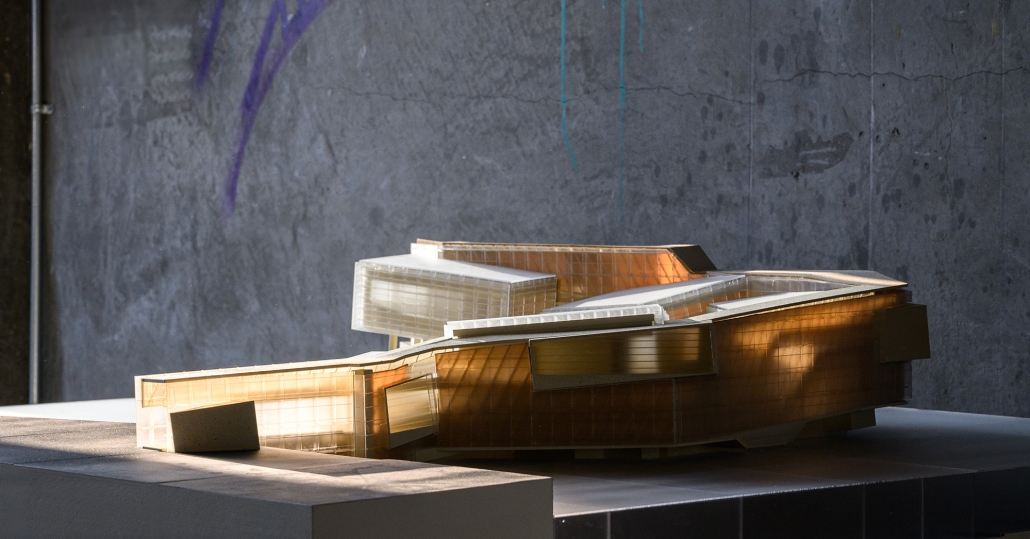
Into the [dys]utopian maze, the case for subterranean spatial re-organization and dis-orientation by Sarah Karam, B. Arch ’24
American University of Beirut | Advisor: Sinan Hassan
Inspired by Italo Calvino’s Invisible Cities and Fritz Lang’s Metropolis, this thesis envisions a novel architectural and urban morphology to uncover hidden (dys)utopian experiences within our environments. Recognizing that our mental depiction of the physical world is limited by societal conventions, this project introduces the concept of a “third space,” — a realm where conscious and unconscious aspects merge, allowing for a deeper exploration of our urban landscapes.
Drawing upon Sigmund Freud’s Oedipus complex, it is posited that humans possess an intrinsic desire to get lost, a need that can be facilitated through the architectural form of a maze. The maze acts as a connective tissue, enabling individuals to encounter new perspectives and engage with the (dys)utopian layers of their environment. The research begins with a theoretical investigation into the interplay between dystopian/utopian experiences, the third space, and the maze. This involves analyzing case studies and testing strategies to select a suitable site, ultimately choosing Sassine, Ashrafiye, Lebanon. The final intervention includes a subterranean spatial reorganization aimed at uncovering a (dys)utopian world, with the third space mediating between utopian and dystopian elements.
The project employs the maze to challenge conventional spatial orientation and organization. It rethinks circulation and spatial distribution, creating unpredictable encounters and perspectives. The maze, both above and below ground, facilitates diverse (dys)utopian experiences, blending formal and informal activities, and connecting the disjointed urban fabric of Sassine.
Concisely, this thesis proposes an architectural framework that integrates (dys)utopian thoughts into a third space through the labyrinthine design, addressing the human desire to get lost and reimagining the urban experience. Through this, the project aims to create a dynamic and multifaceted urban morphology that transcends traditional spatial conventions.
This thesis was nominated for the Areen Projects Award for Excellence in Architecture.
Instagram: @ard_aub
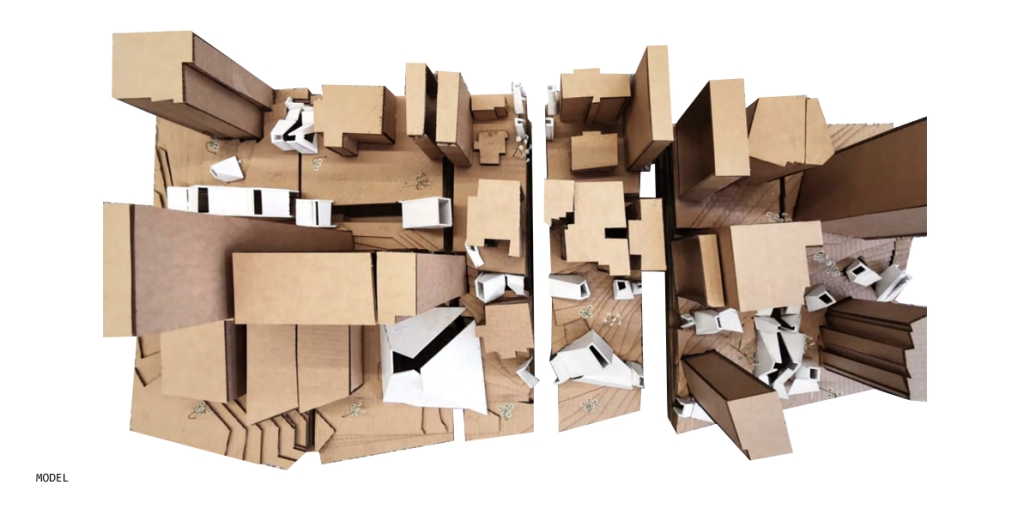
Beyond The Wall by Zili He & Wenan Hu, B. Arch ’24
Southern California Institute of Architecture | Advisor: Maxi Spina
In the past, the wall offered both contextual and functional performances by unifying the interior programs and the exterior experience along the wall. The purpose of the wall here is its security and infrastructural nature, as well as a social and organizational one. A wall is not only a figure full of turns and edges but also a linking device that connects all the spaces and experiences associated with it.
This thesis borrows from, learns from, and adopts strategies from ancient city walls and therefore transfers them into a new generator for architecture, which can be applied through articulation in multiple layers and multiple scales. Challenging the efficiency-oriented cliche of the convention center, letting the wall typology generate a sequence of experiences while responding to the large, this thesis offered a new perspective looking at large civic buildings with urban ambitions.
“The wall is what contains. defines. channels. constraints, limits. stops, articulates and divides.” —A field of walls, Dogma.
Instagram: @luke_hezili2001, @olllihu, @maxispina
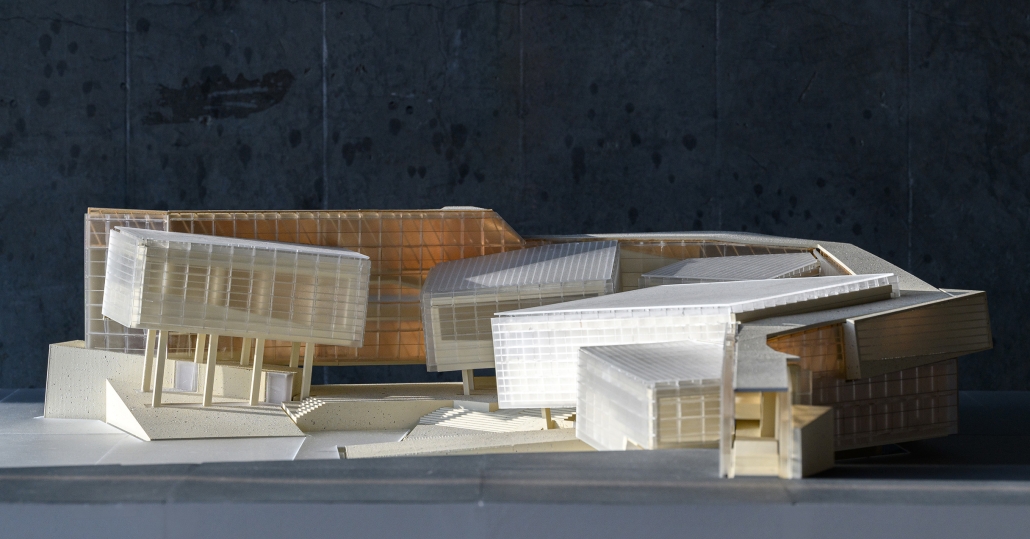
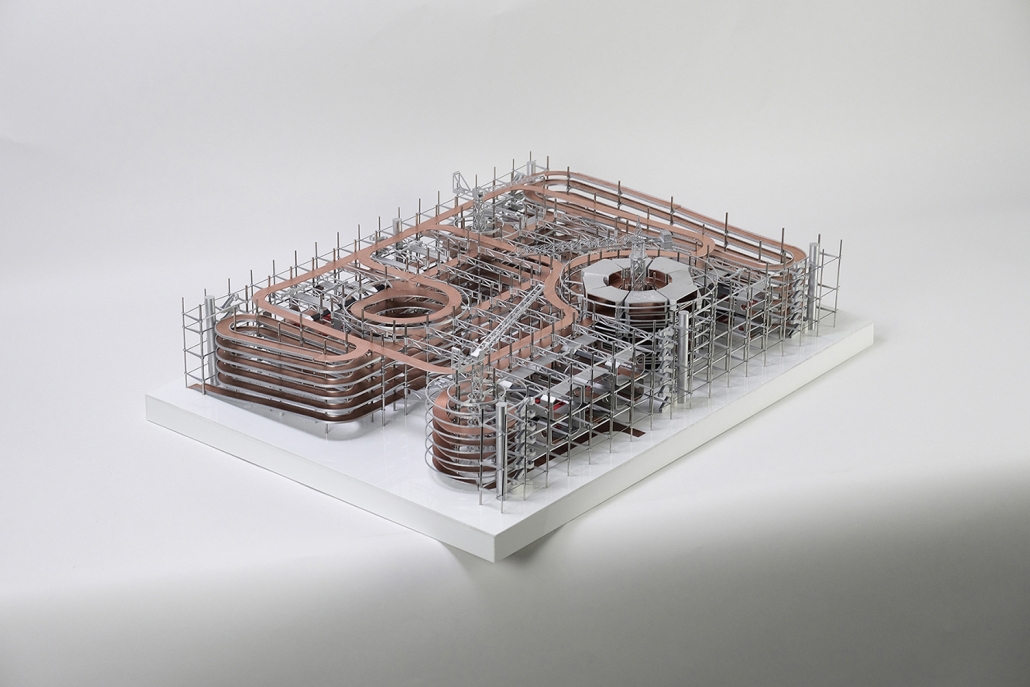
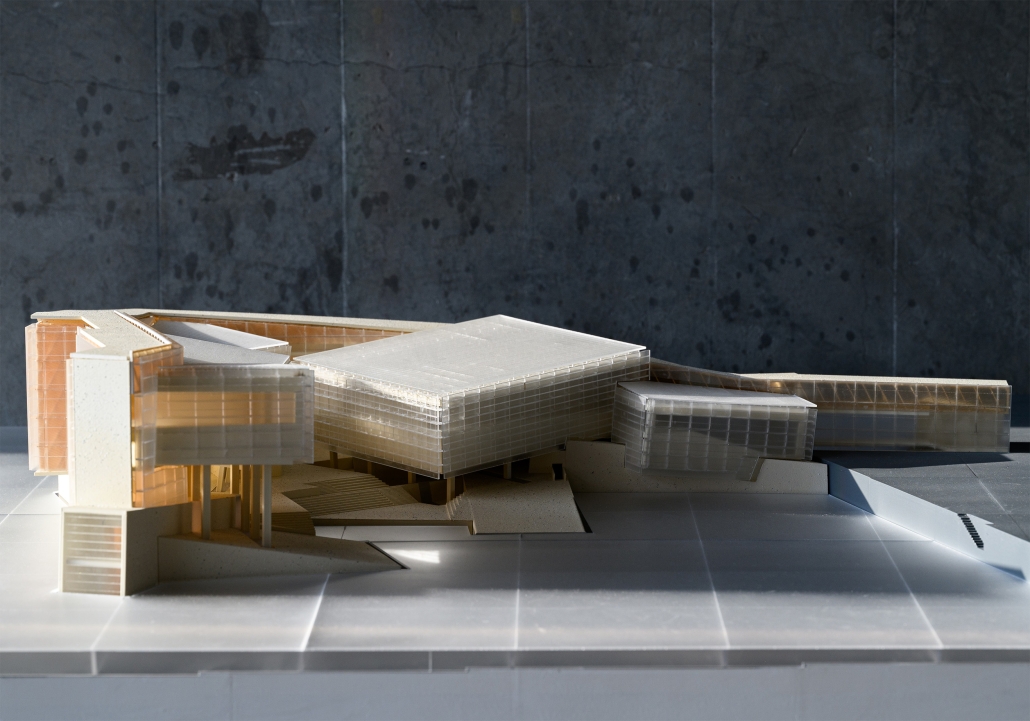
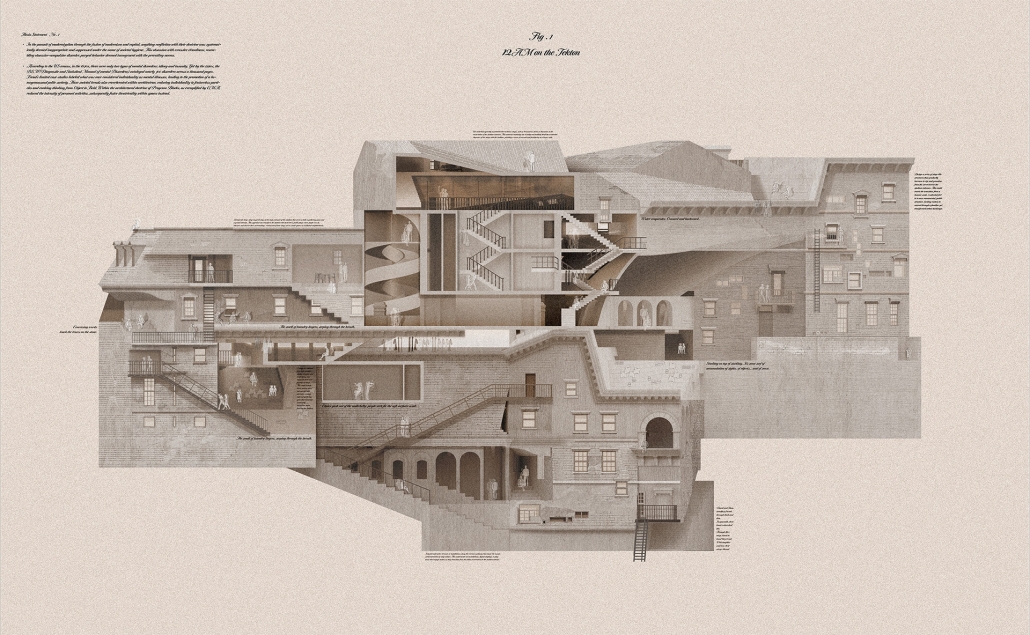
Midnight on the Stairs by Shun Sasaki, B. Arch ’24
Southern California Institute of Architecture | Advisor: Karel Klein
This project explores the reinterpretation of societal norms, architectural spaces, and individual identities homogenized by modernization by investigating the diachronic transformation of architectural elements. The fusion of modernism and capitalism suppressed behaviors conflicting with their doctrines under societal hygiene, leading to an obsession with cleanliness and, in architecture, the “theatricalization of architectural spaces.” Recently, the architectural doctrine of Program Blocks, exemplified by OMA, has disregarded individual activities that do not fit the intended program, considering activities within architecture only through the combination of programs.
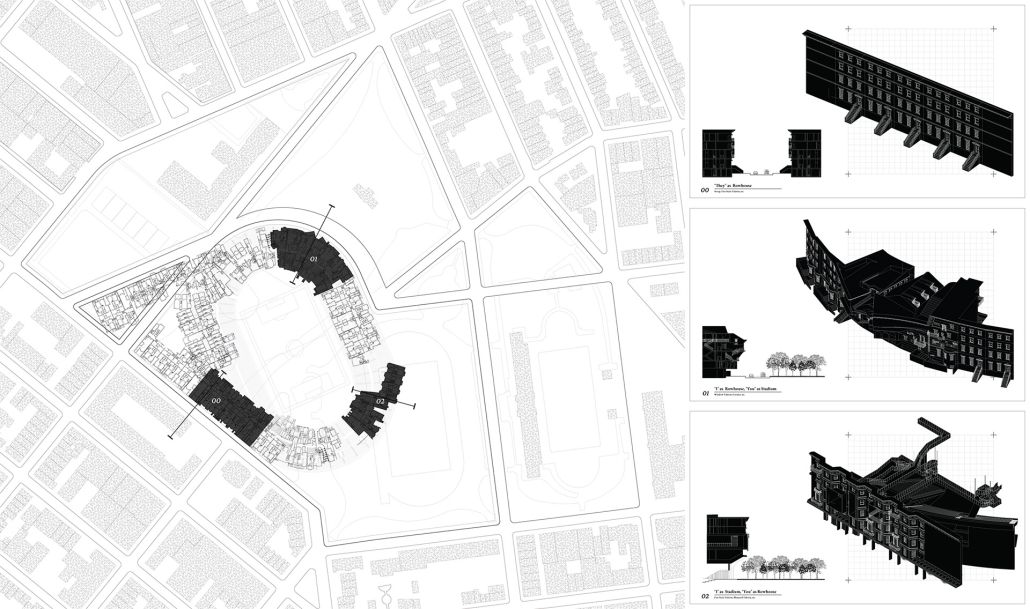
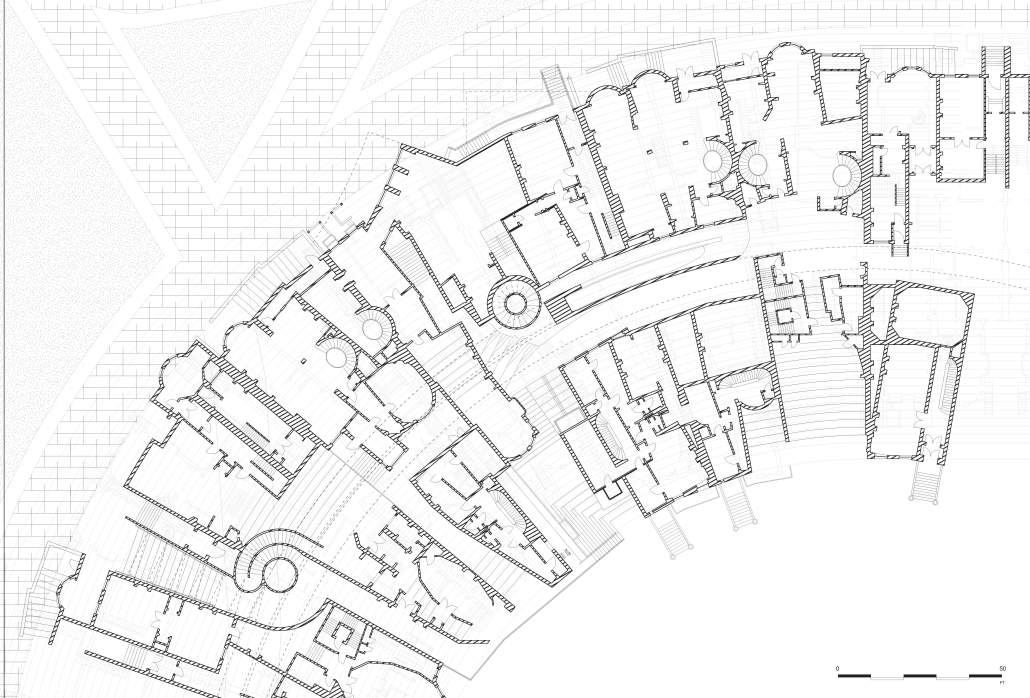
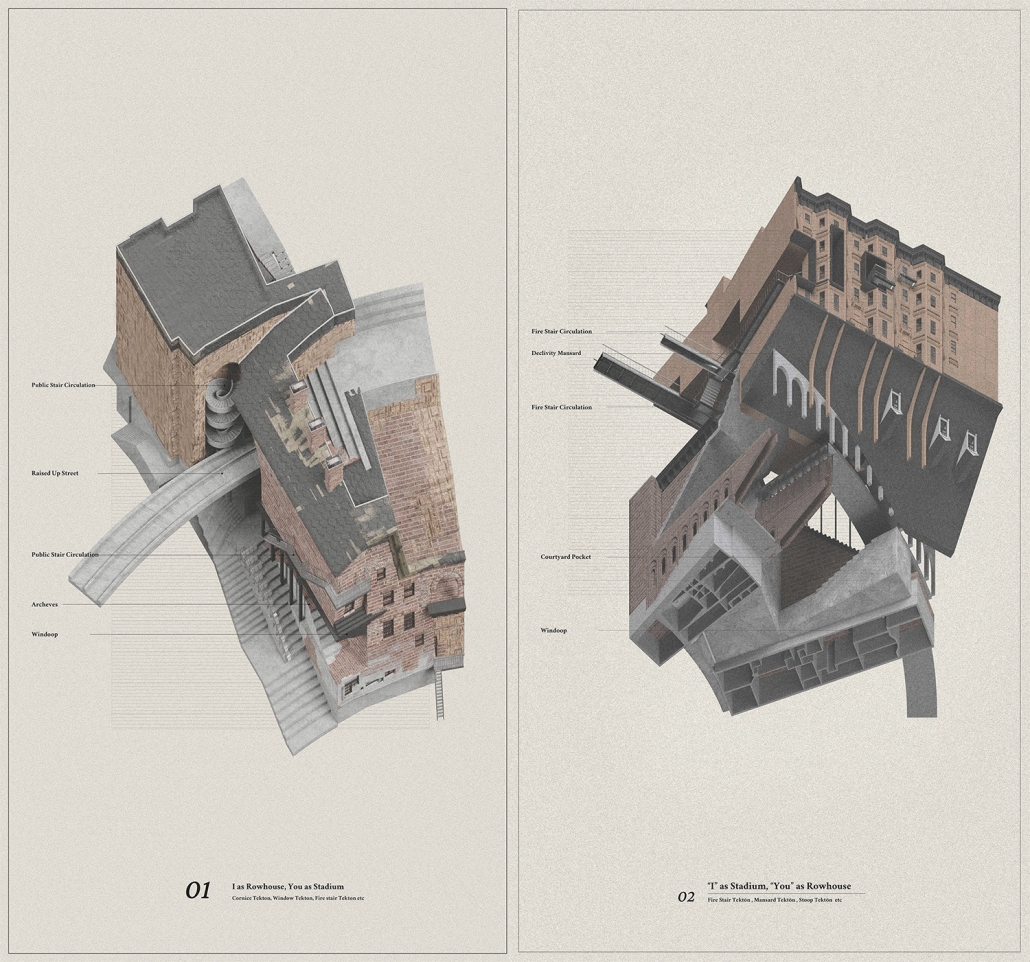
This project, “Residential Stadium,” is based on the brief of the public competition “Residential Stadium: Adaptive Reuse,” held in 2018 on a site in Brooklyn, New York. In this thesis, I first examine the ‘stoop’—a distinctive architectural element observed on the facades of Brooklyn rowhouses—investigating how a generic stair typology acquires its unique ‘stoop’ identity. Next, by overlaying the semi-public nature of the stoop with the function of stadium seating, I designed a program that integrates stair/stoop/stadium seating within a single stair typology. Furthermore, by extending this architectural element to other features characteristic of Brooklyn rowhouses, such as fire stairs, balconies, cornices, and windows, the design aims to create architectural devices that mediate between residential and stadium spaces. The activities occurring within these spaces are intended to expand the discussion beyond what traditional design methods with program blocks can capture.
At the massing scale, the relationship between the residential and stadium programs transforms into three typologies based on their degree of integration with the adjacent urban street.
In Chunk 0, typical rowhouses line North 12th Street, showcasing a standard Brooklyn rowhouse configuration. In Chunk 1, the floor plan of a generic stadium superimposed with Brooklyn rowhouses creates an unusual spatial relationship, with the adjacent roadway extending into McCarren Park. In Chunk 2, the roadway disappears, leaving Brooklyn rowhouses floating above the park’s meadow, detached from the urban street. The space is completely open at the ground level, with the stadium field connected to the park’s field.
This thesis reveals enigmatic objects from architectural and societal shifts, enhancing our understanding of their impact on society and identity.
Instagram: @ssasaki636, @karelnyla
Stay tuned for Part XI!