2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase - Part XIV
And that’s a wrap on the 2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase! In our finale, we highlight miscellaneous student work that captures a range of topics. From centers celebrating Caribbean food culture and sea-farming operations to spaces for children and an urban crematorium, each project demonstrates skill and innovation.
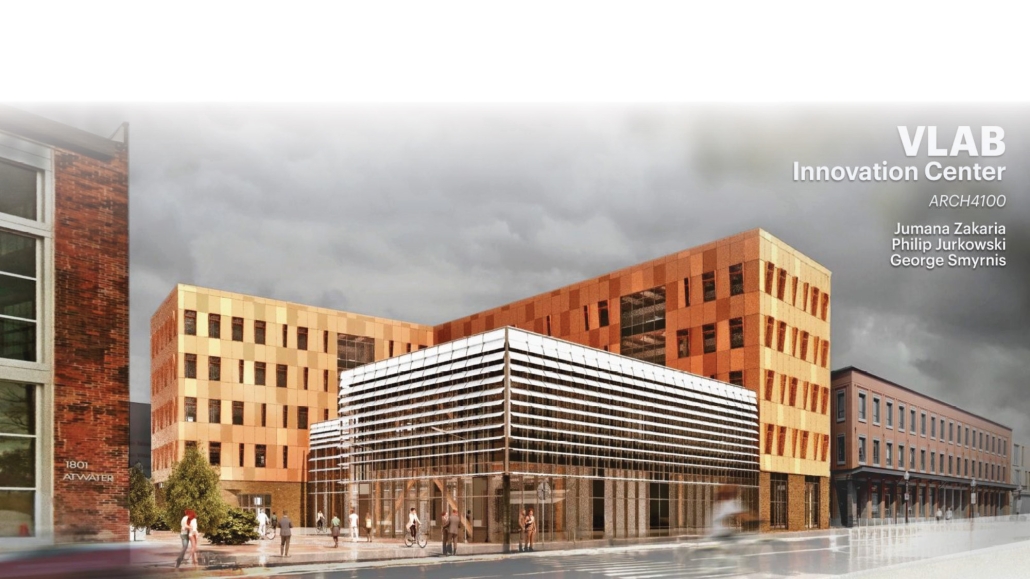
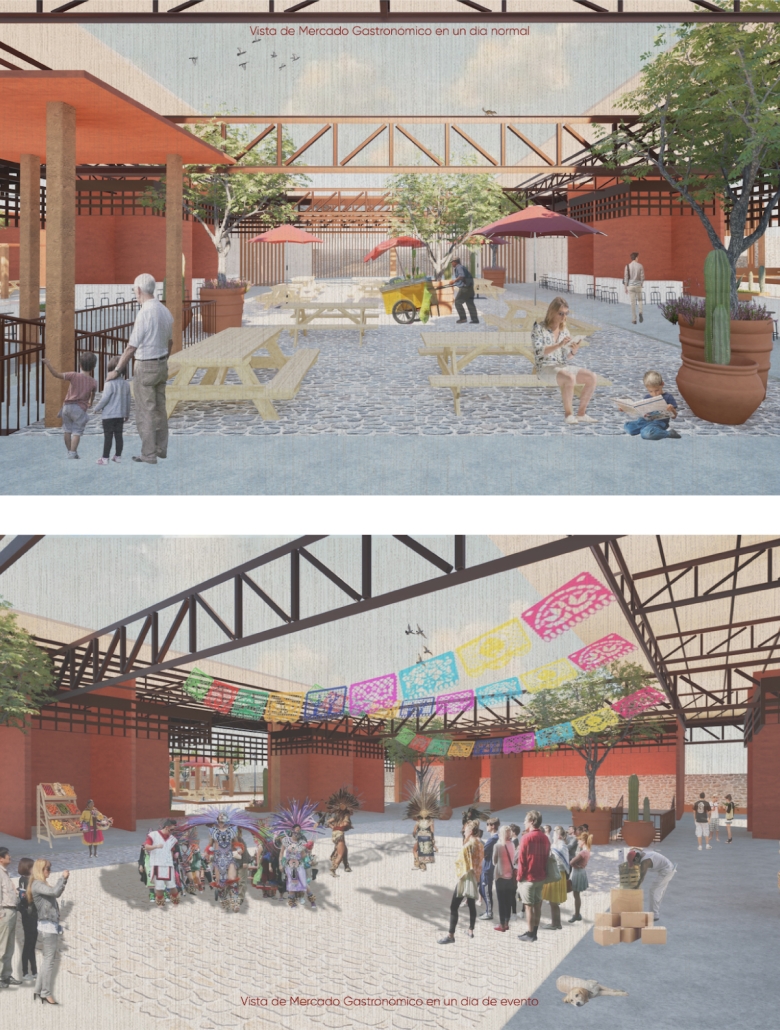
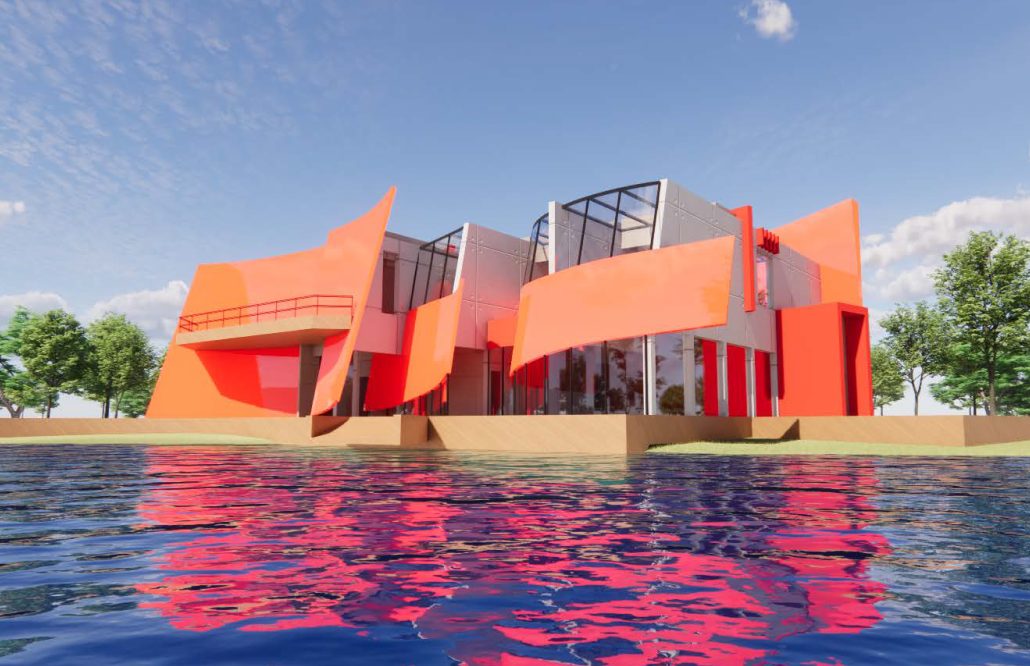
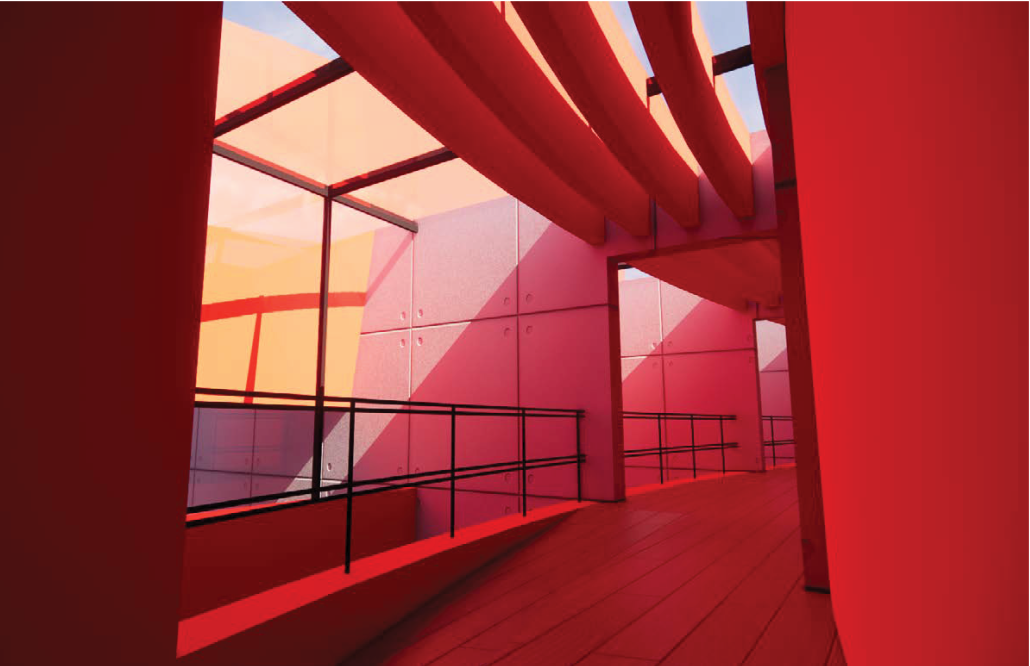
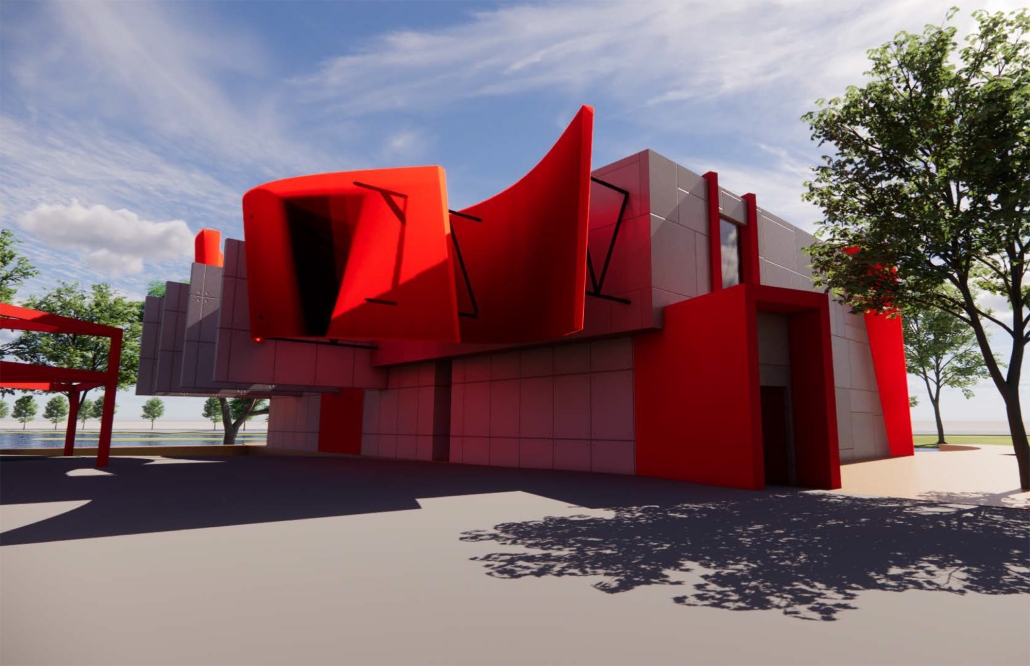
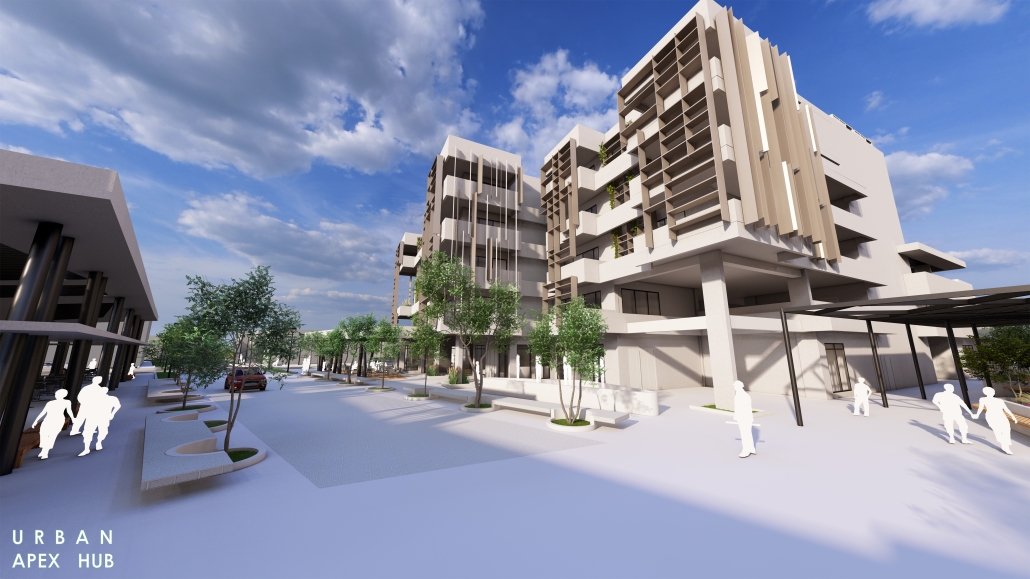
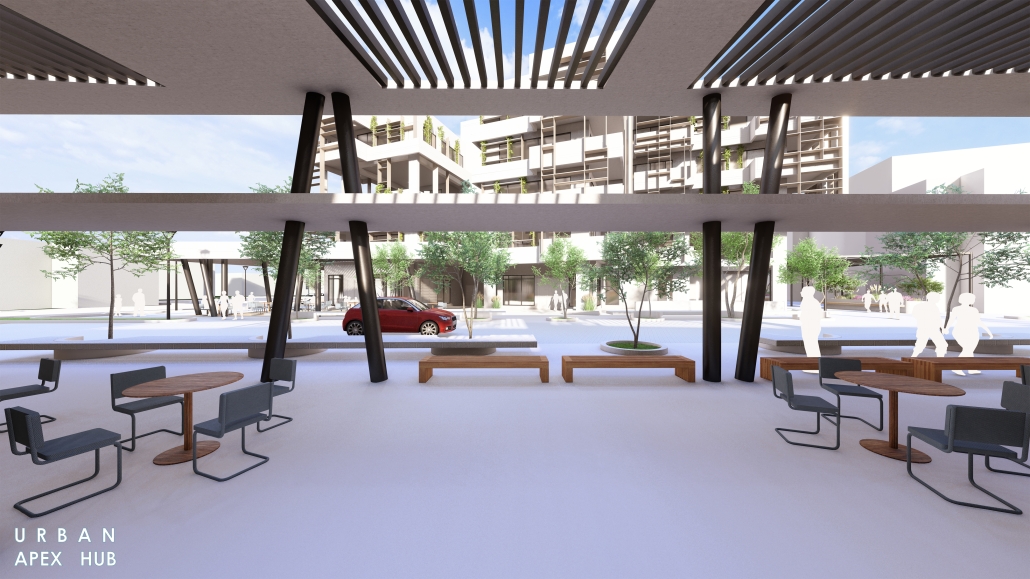
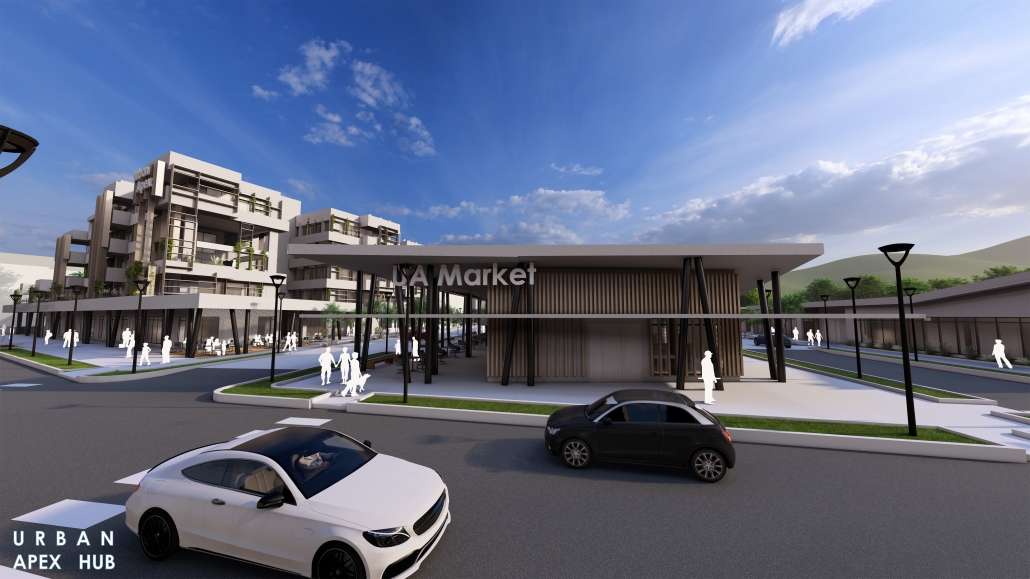
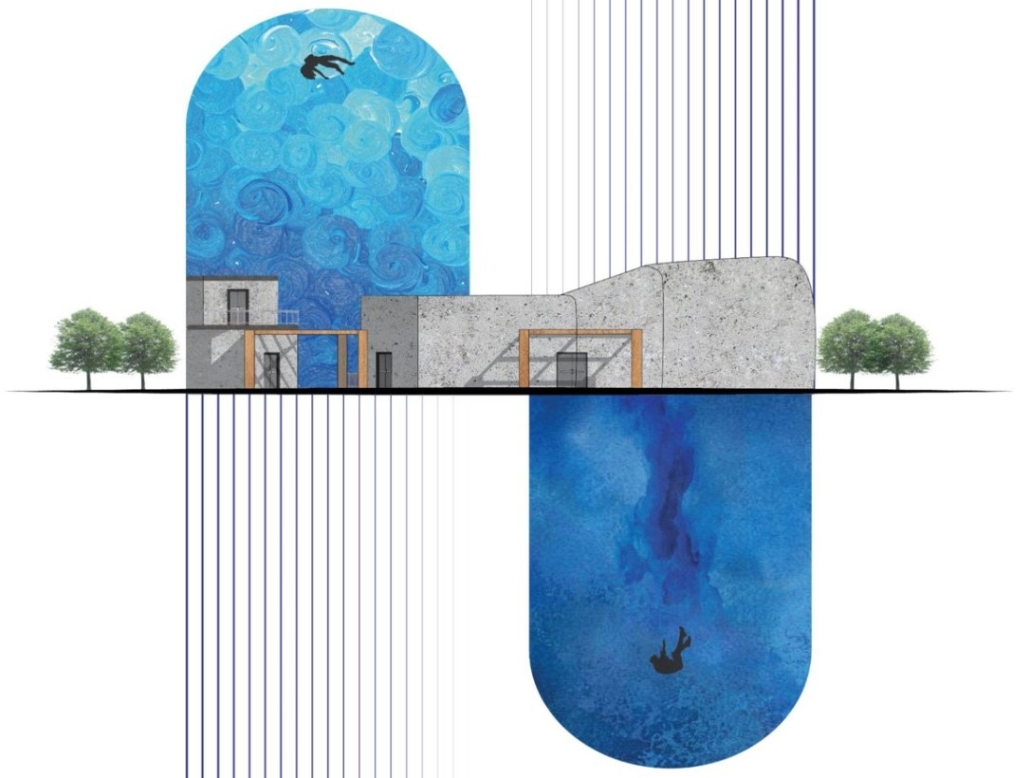
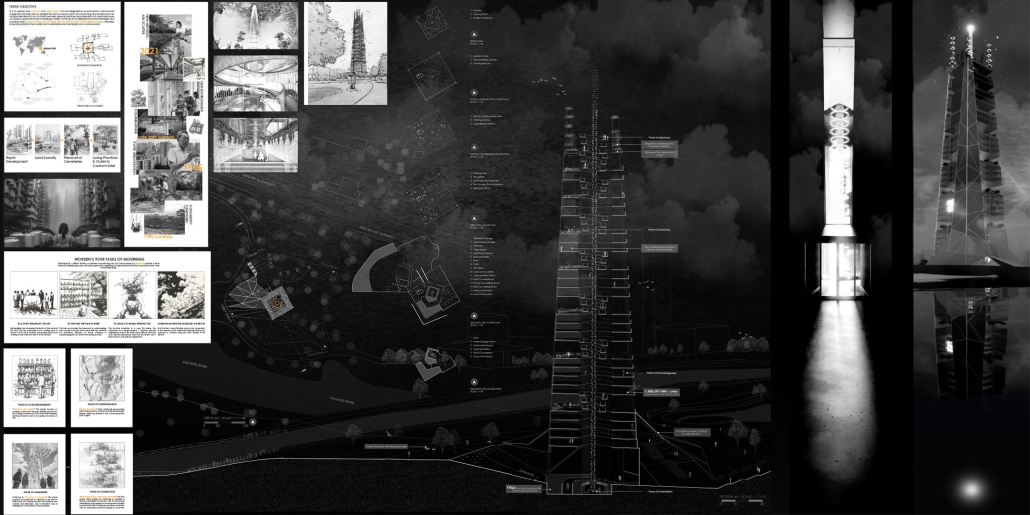
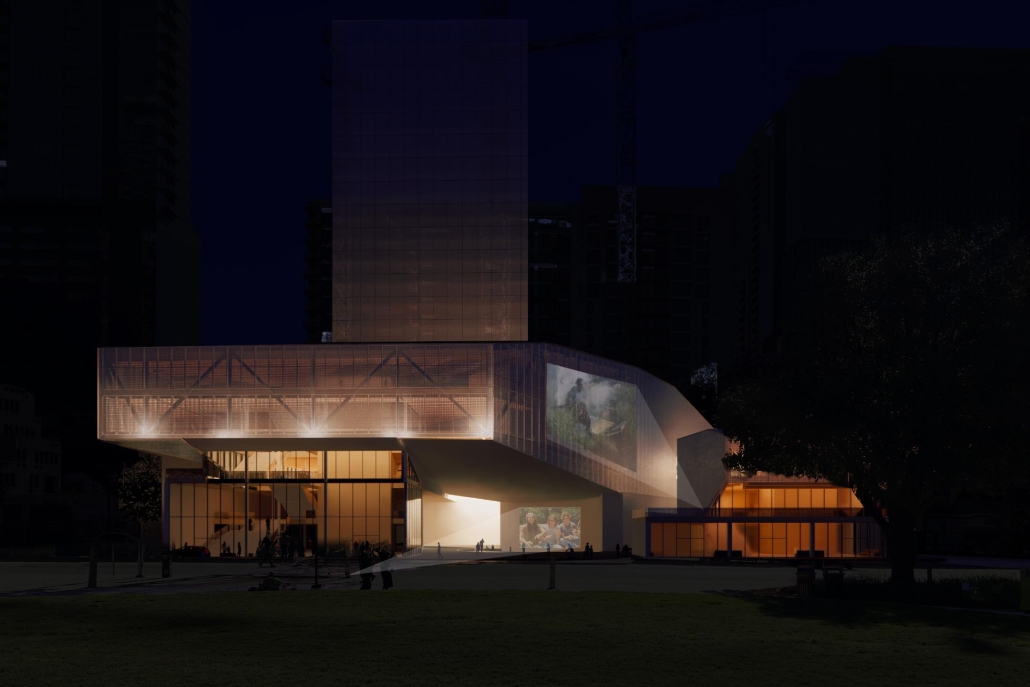
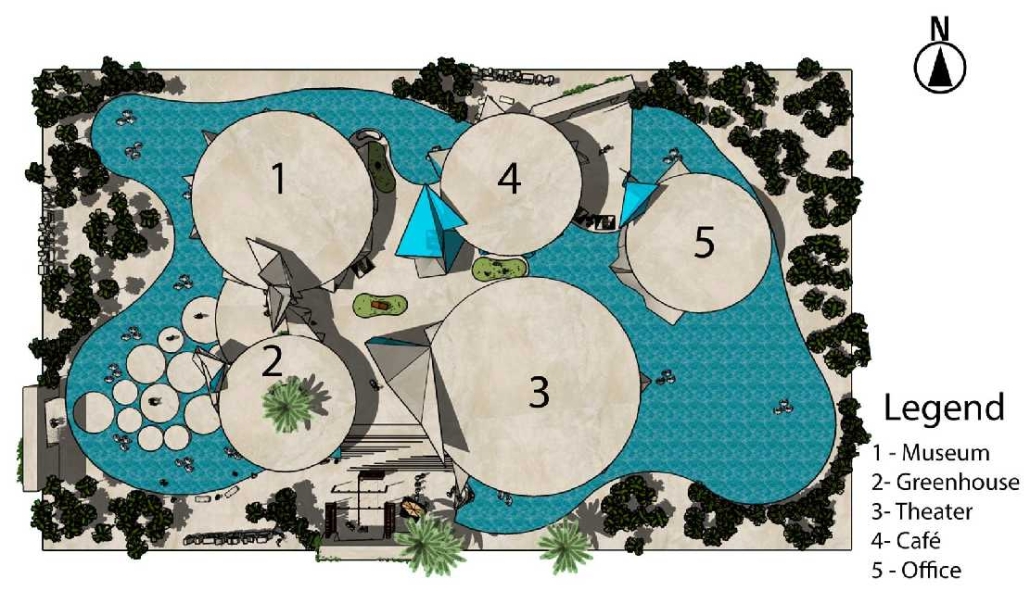
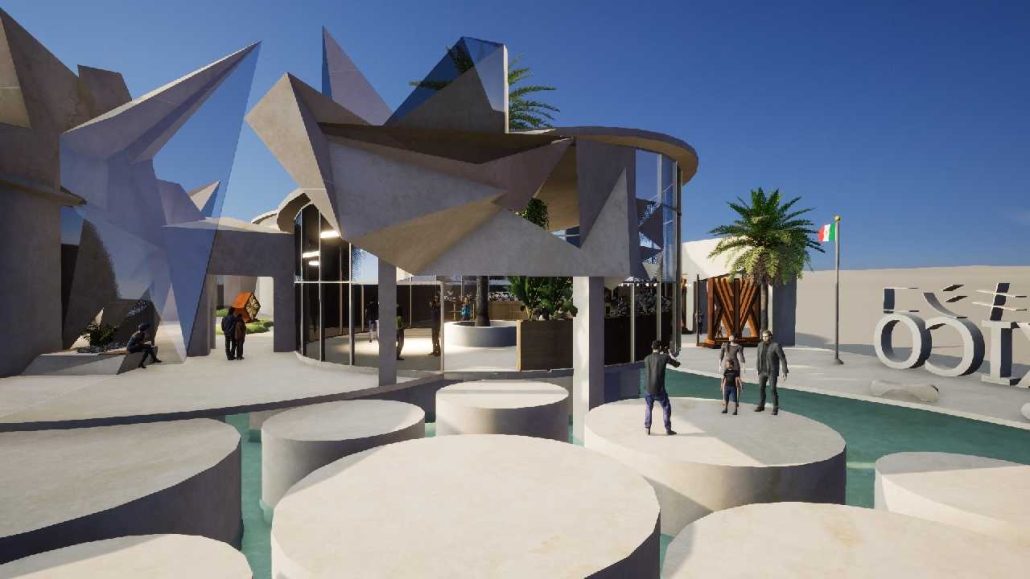
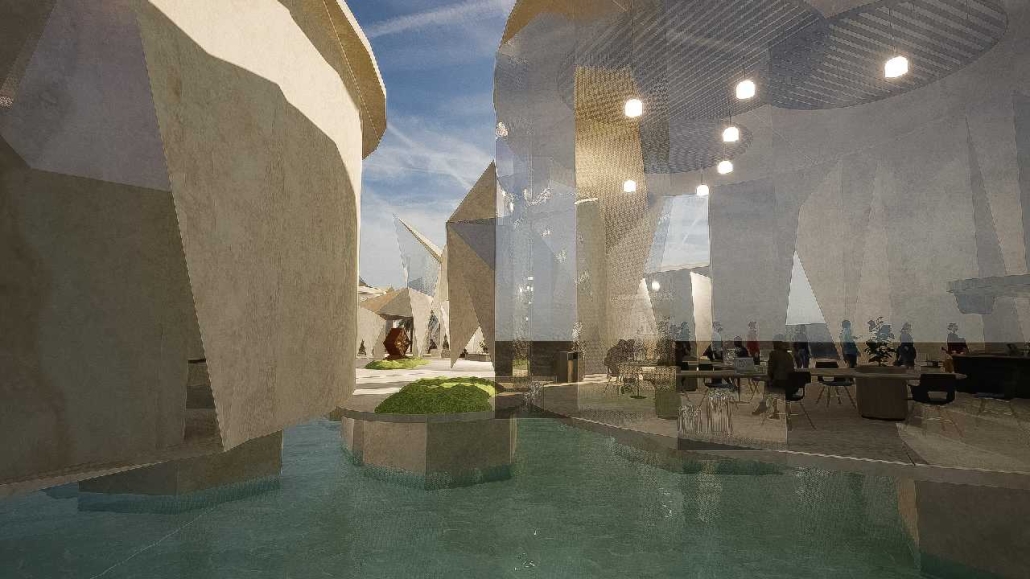
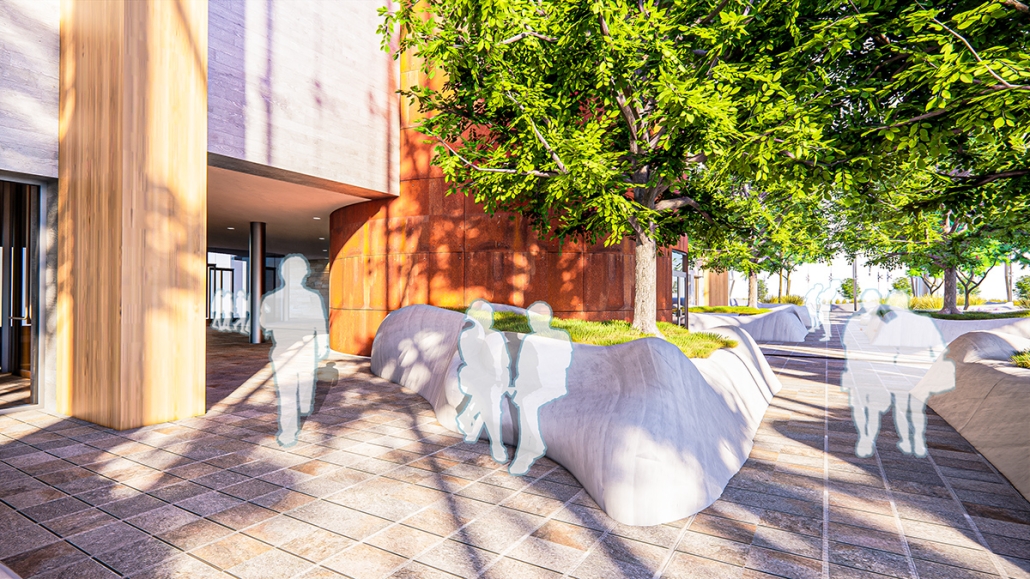
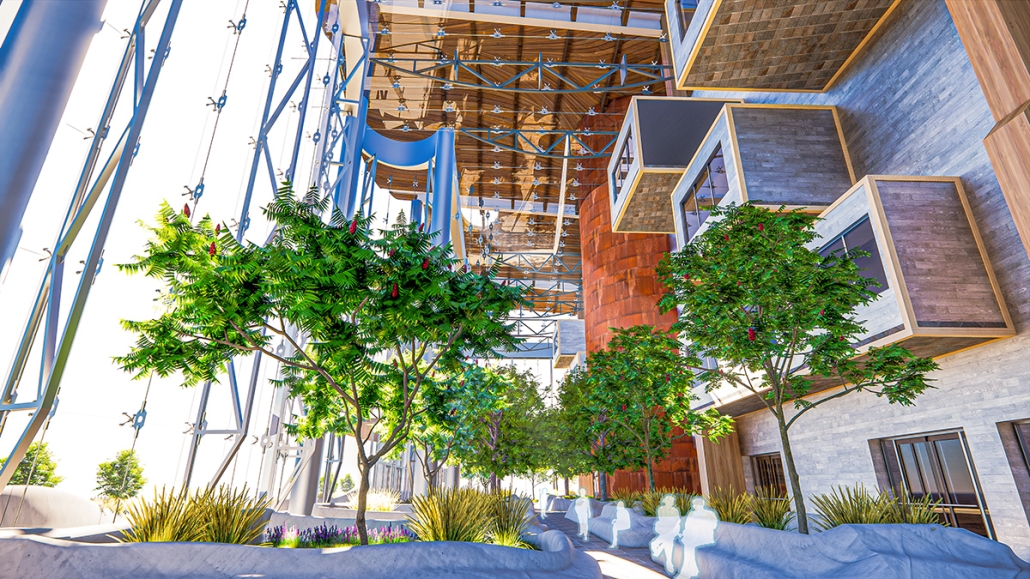
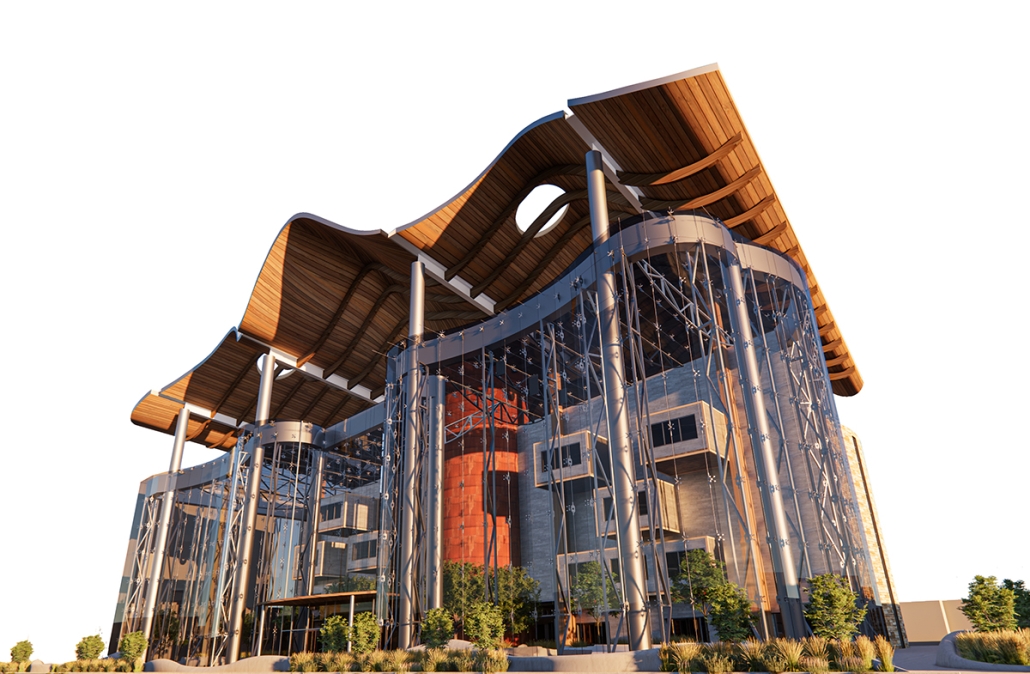
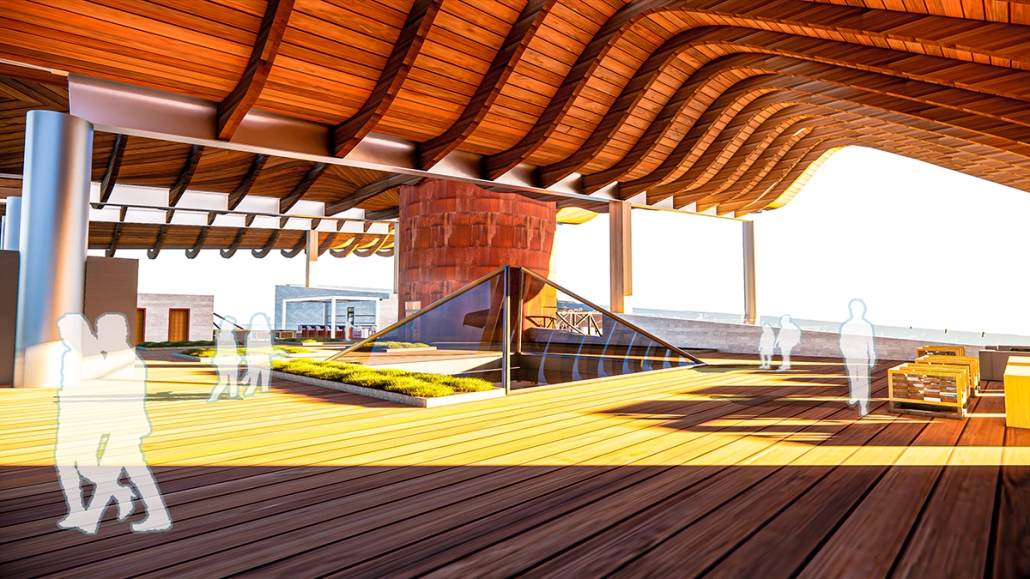
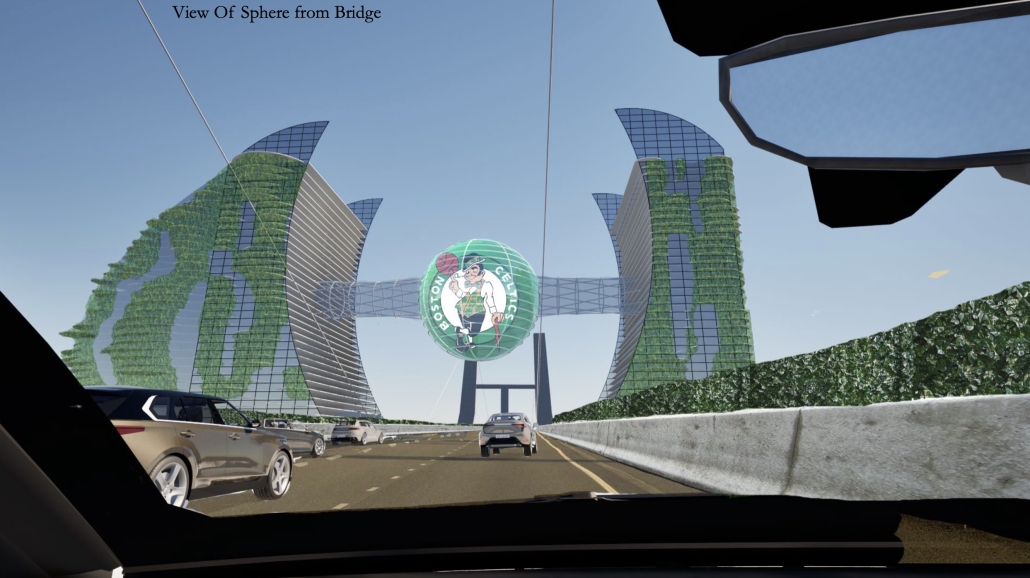
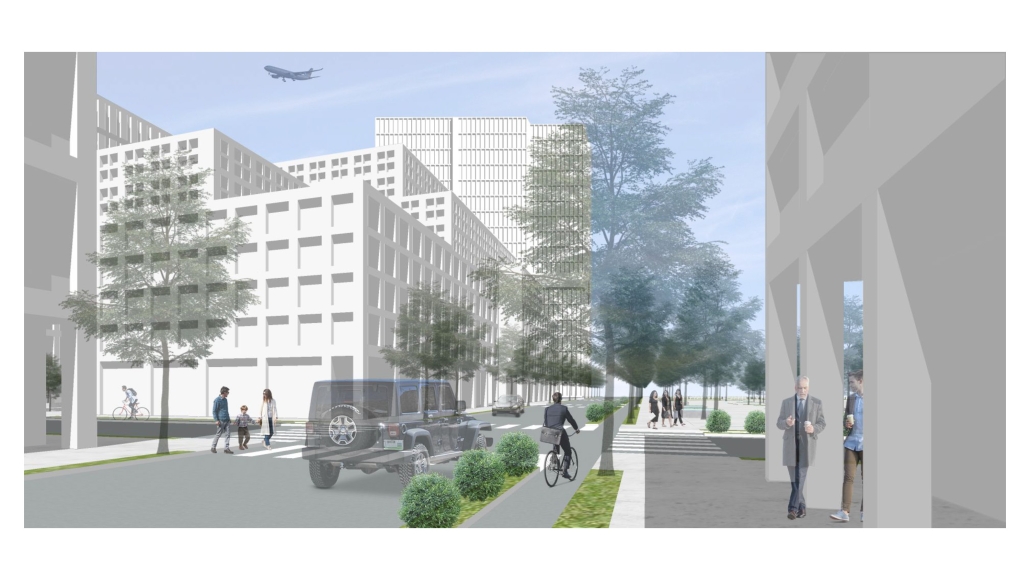
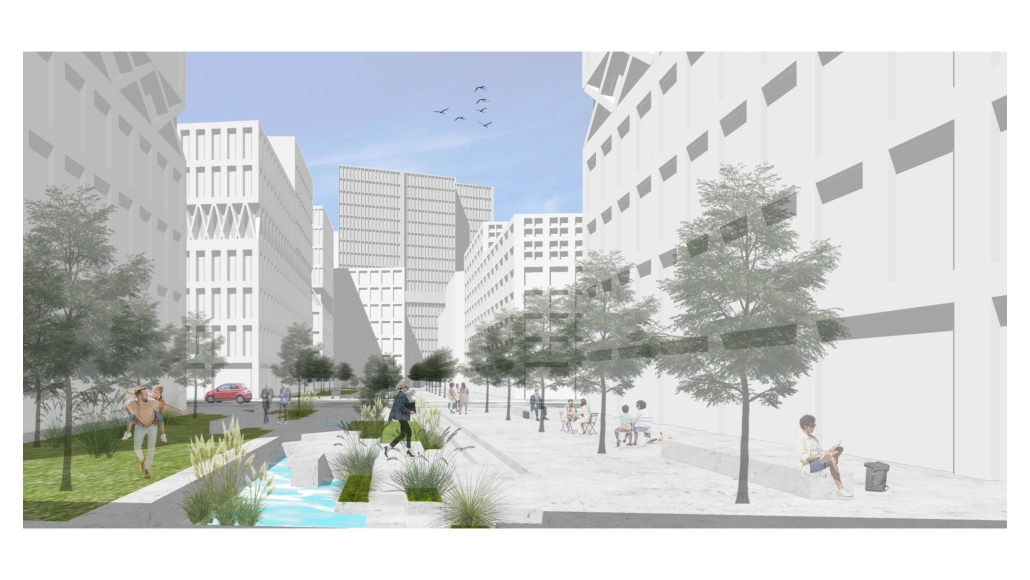
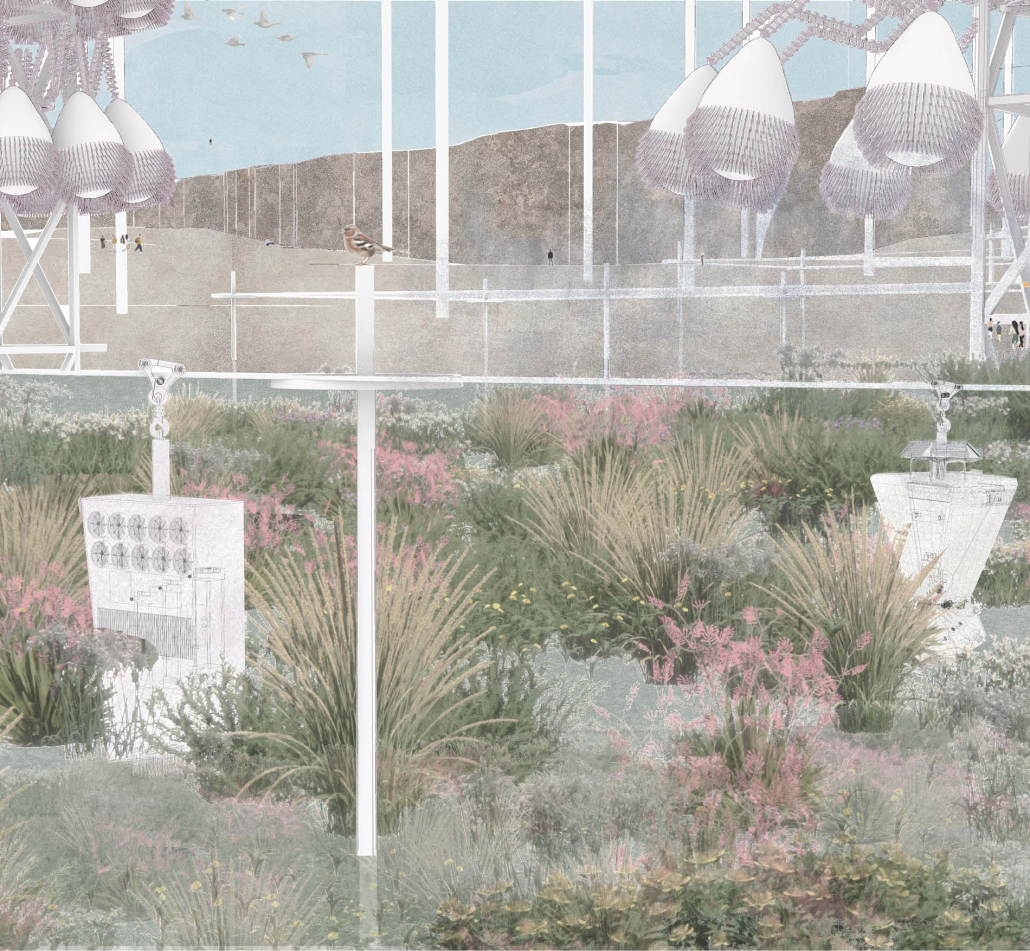
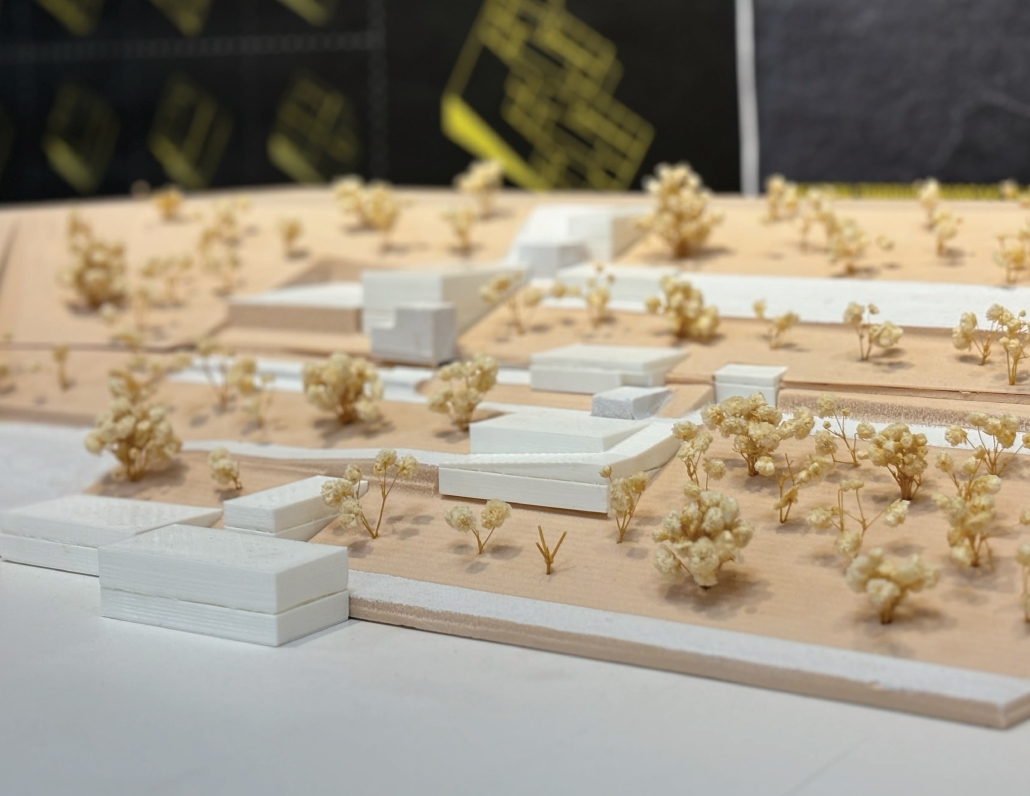
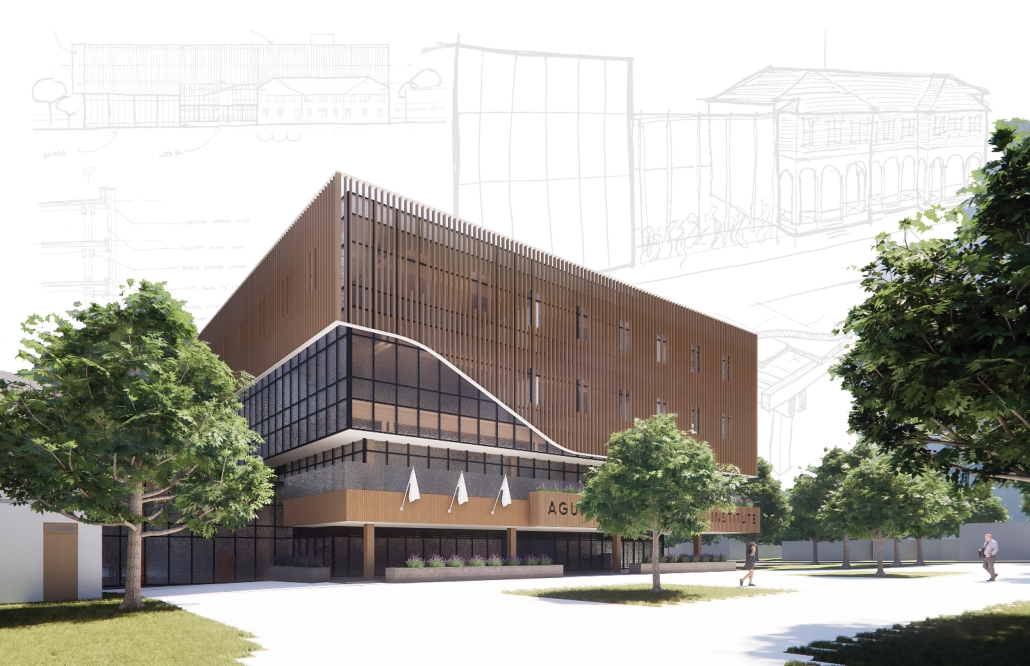
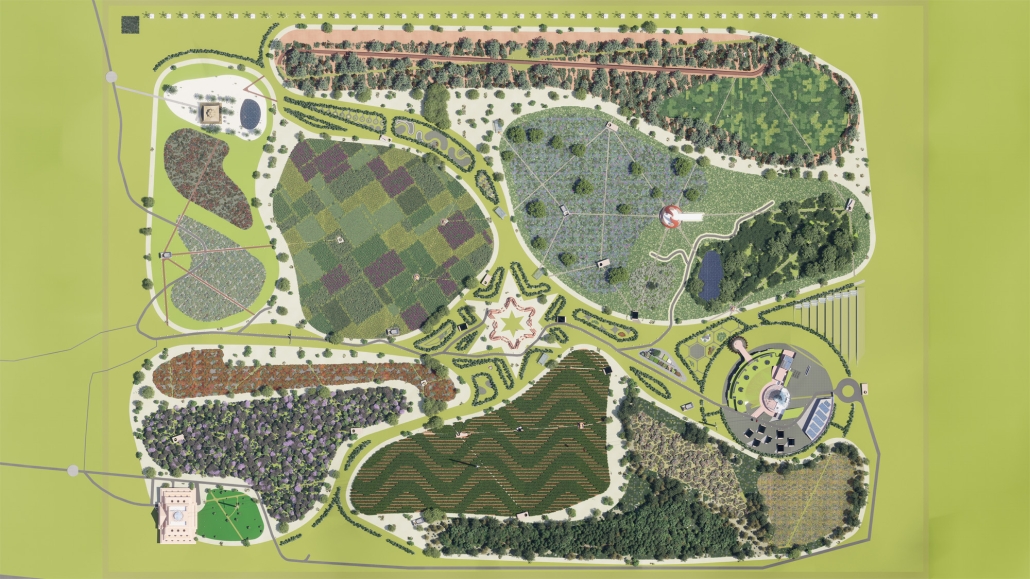
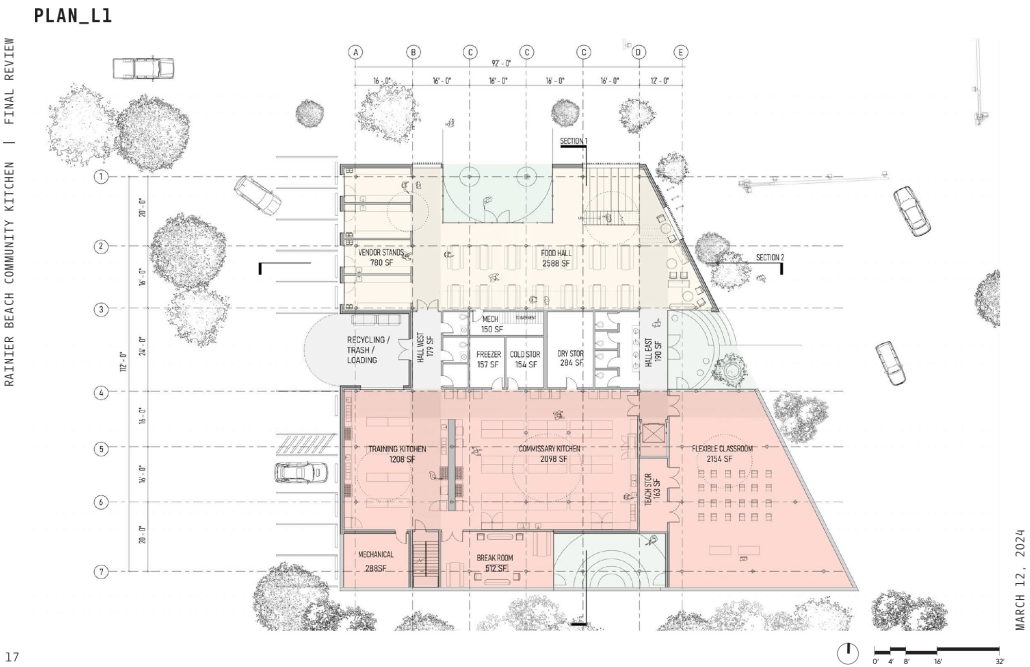
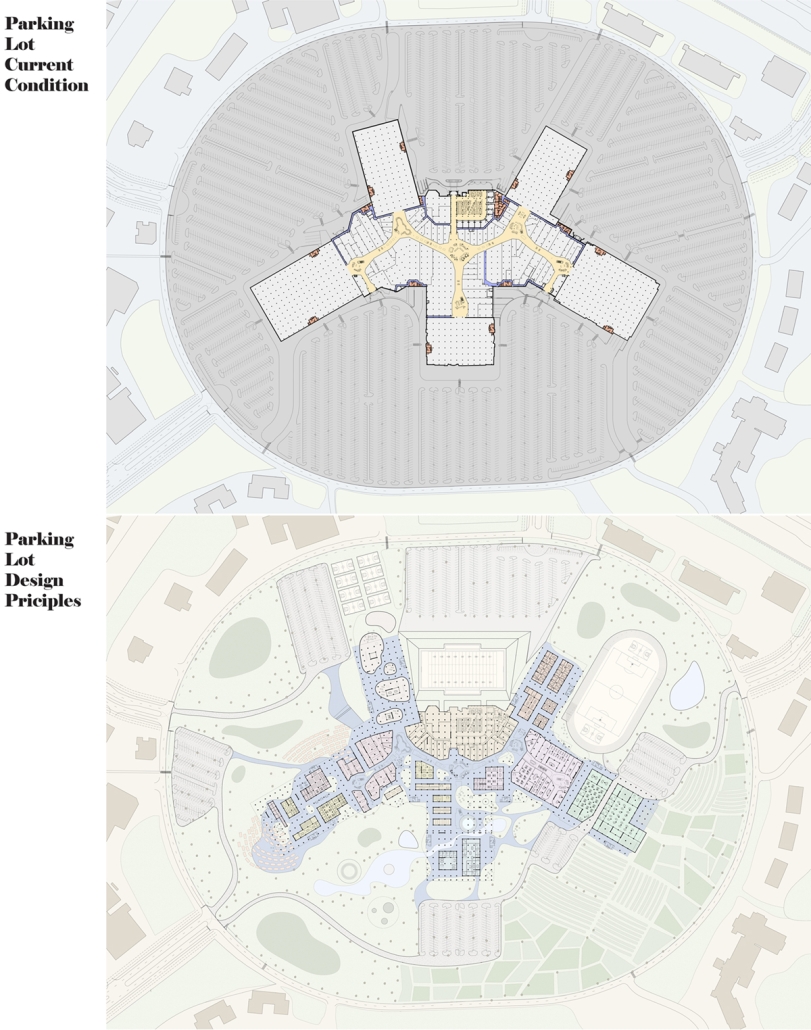
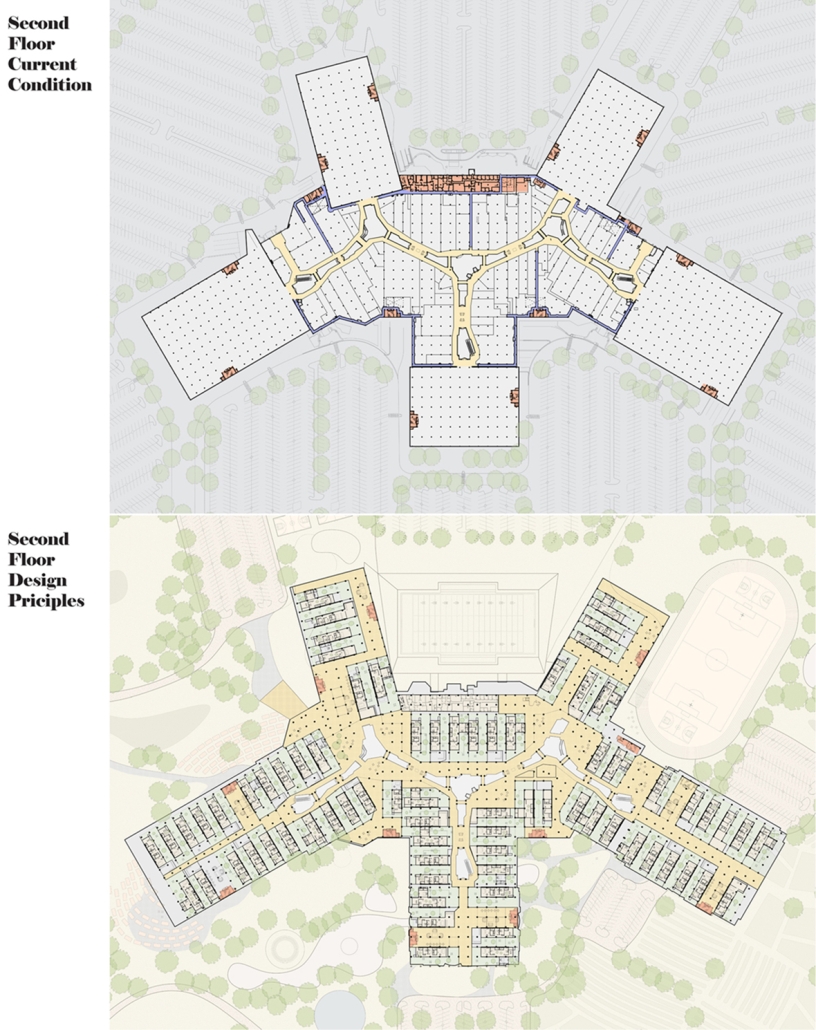
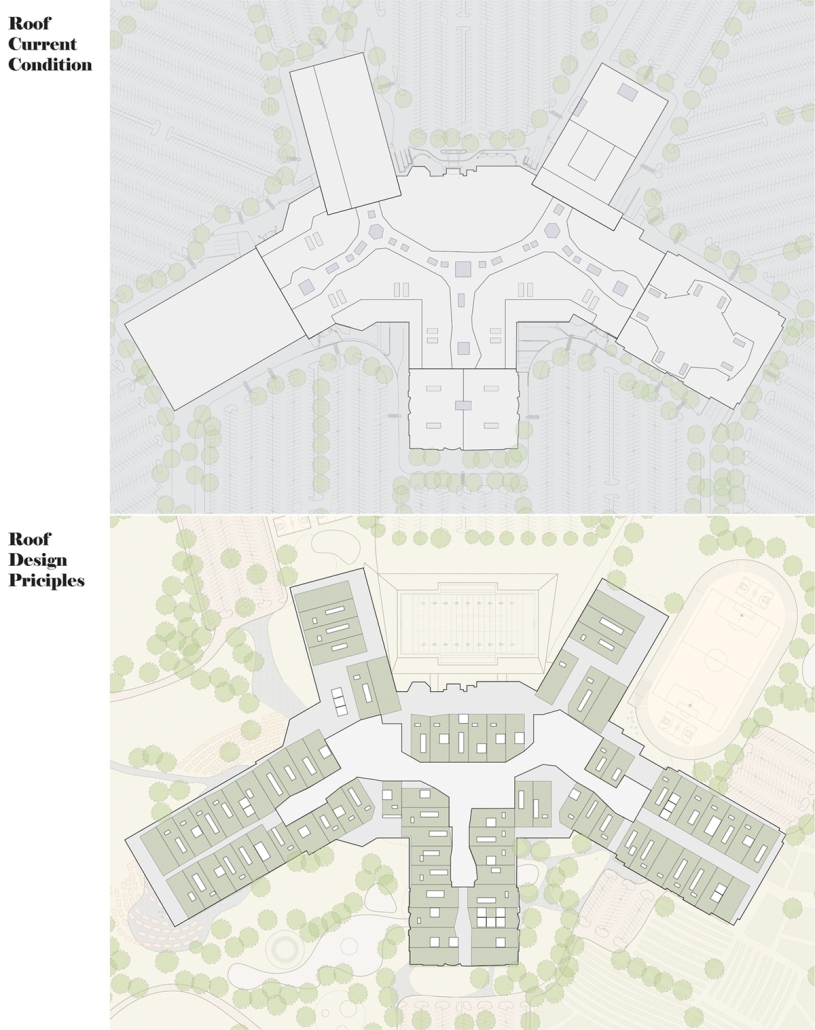
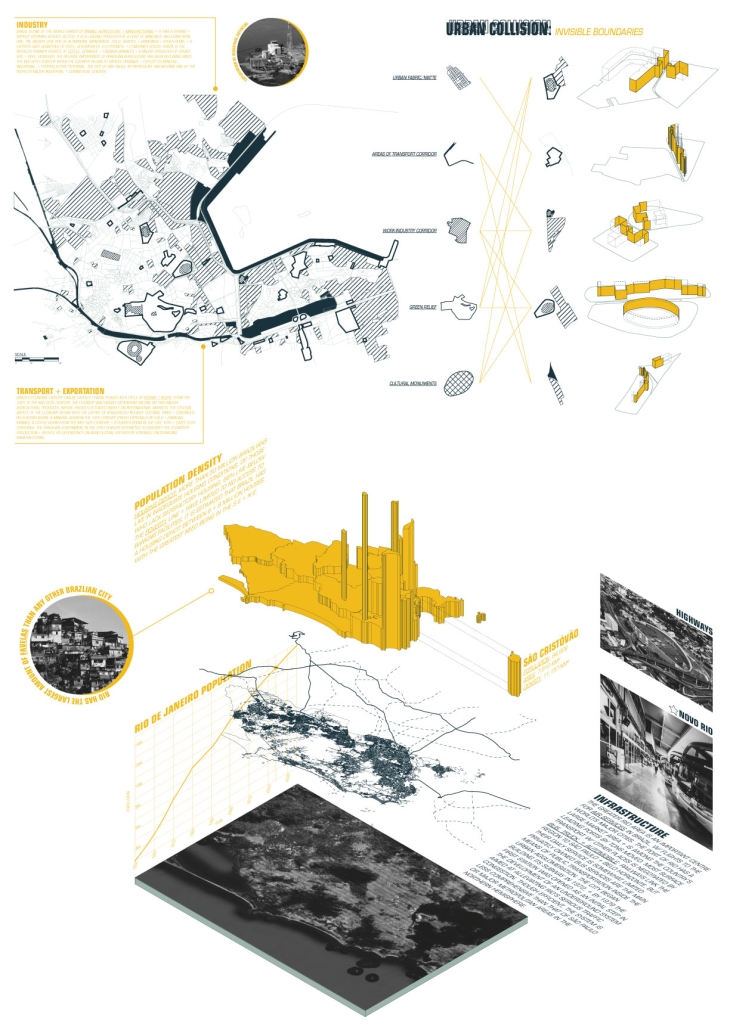
BREAKWATER: A Living Infrastructure for Food, Culture and Climate by Colin Cantwell, B.Arch ’25
The University of Texas at Austin | Advisor: Nichole Wiedemann
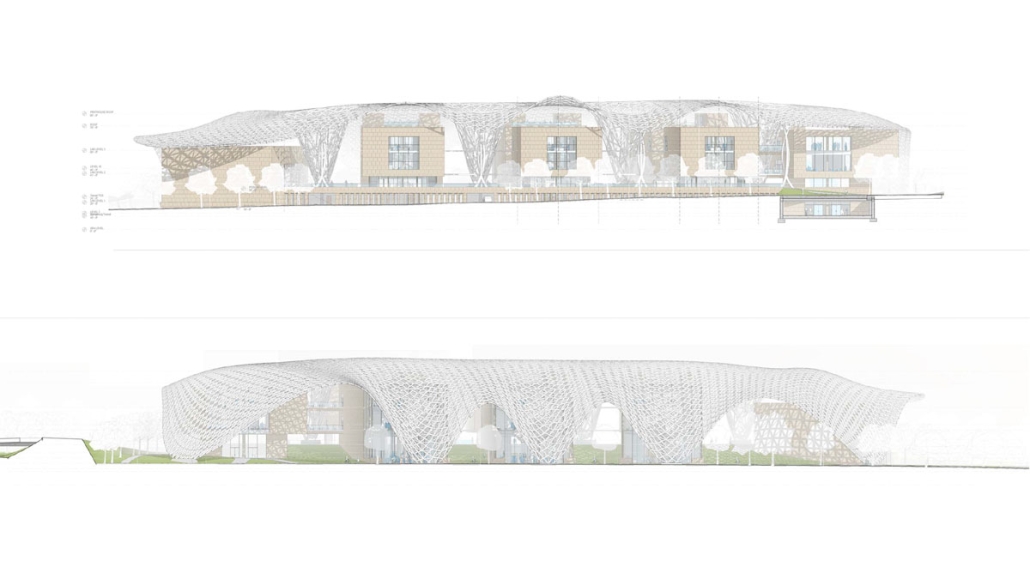
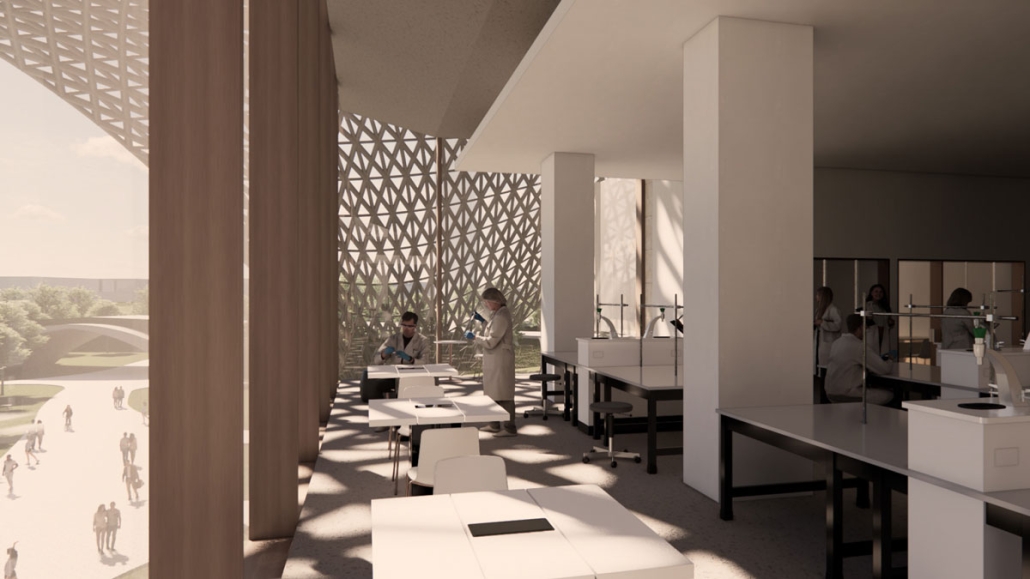
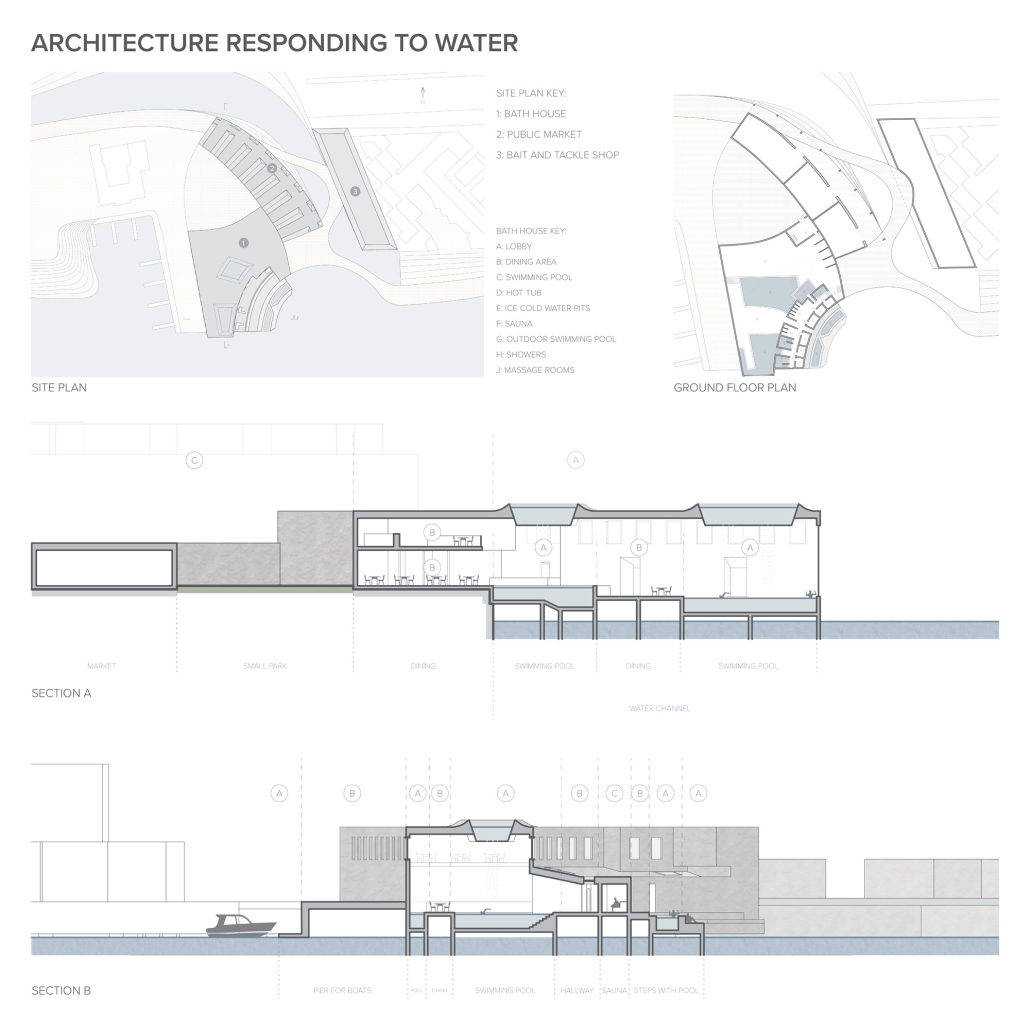
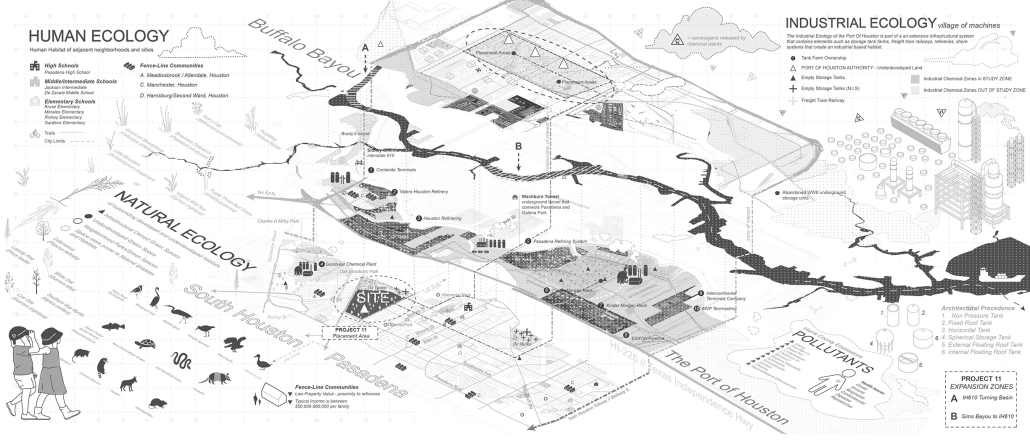
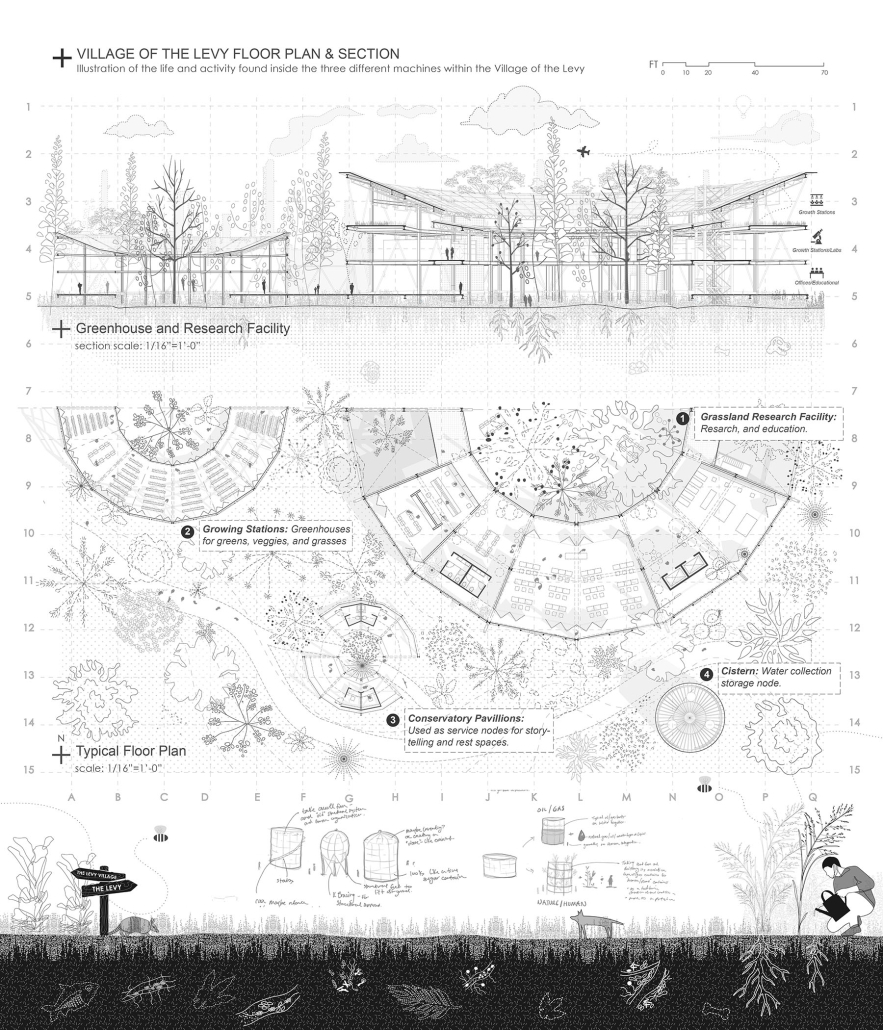
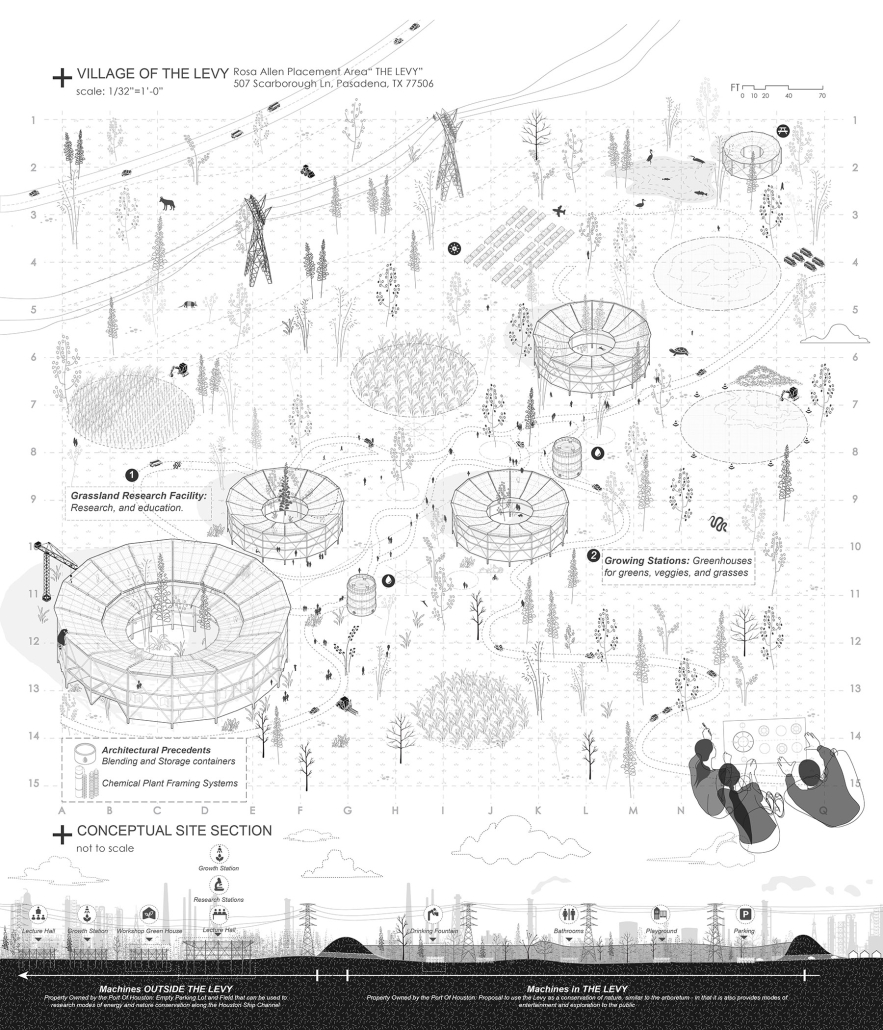
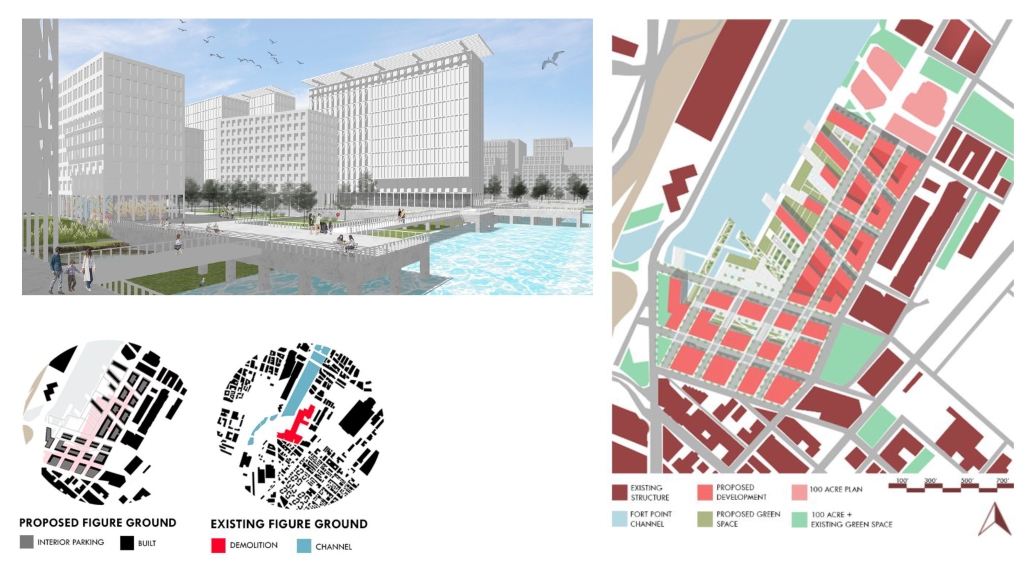
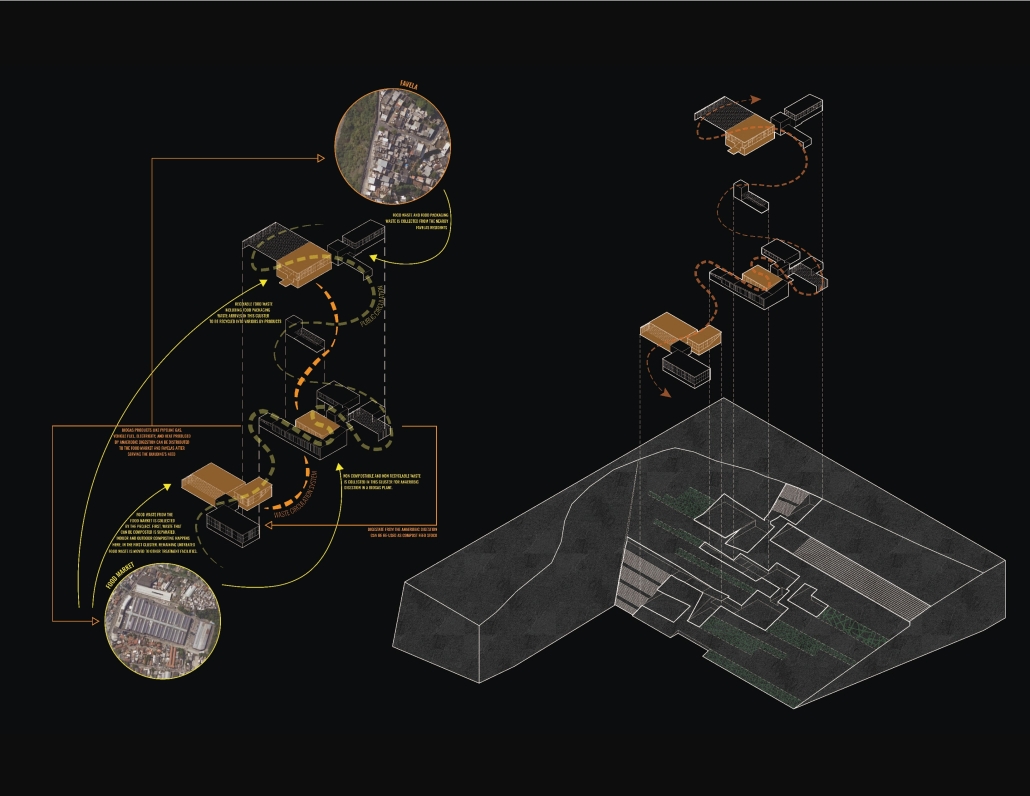
The defining characteristic of the Caribbean is perhaps interdependence. These resilient islands, marked in various ways by violent histories of colonialism, now face an unwritten future as newly independent nations. Central to this new regional identity is a cooperative and self-reliant system of food production and distribution, de-emphasizing international exports and strengthening local agriculture and trade.
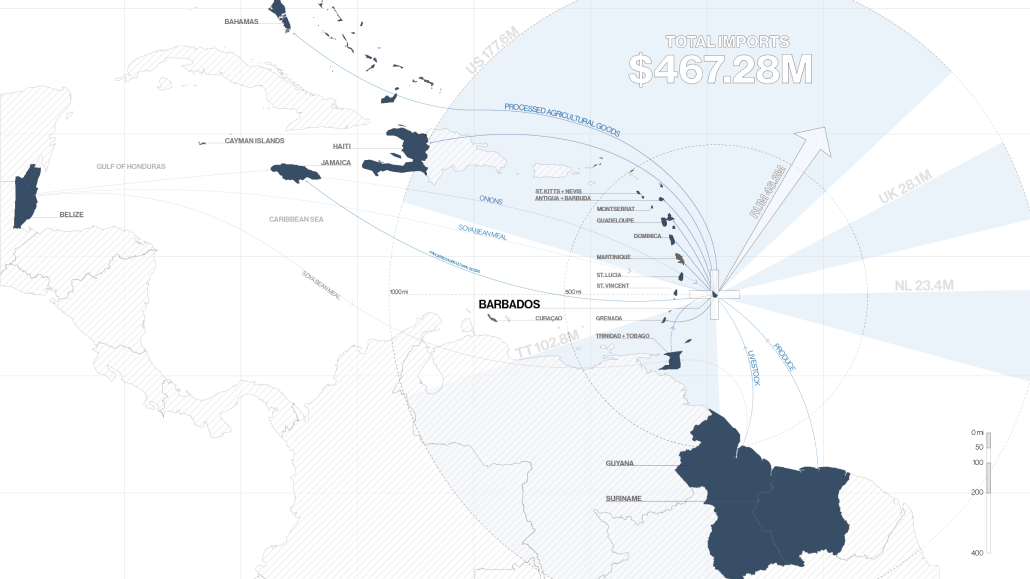
Barbados is poised to become a critical node in this network with the opening of the International Food Science Centre in Oistins, as well as the upcoming Barbados-Guyana food terminal outside Bridgetown. Within this context, how can architecture participate in a regional food culture? Can a restaurant not only nourish bodies but also fuel a network of food sovereignty?
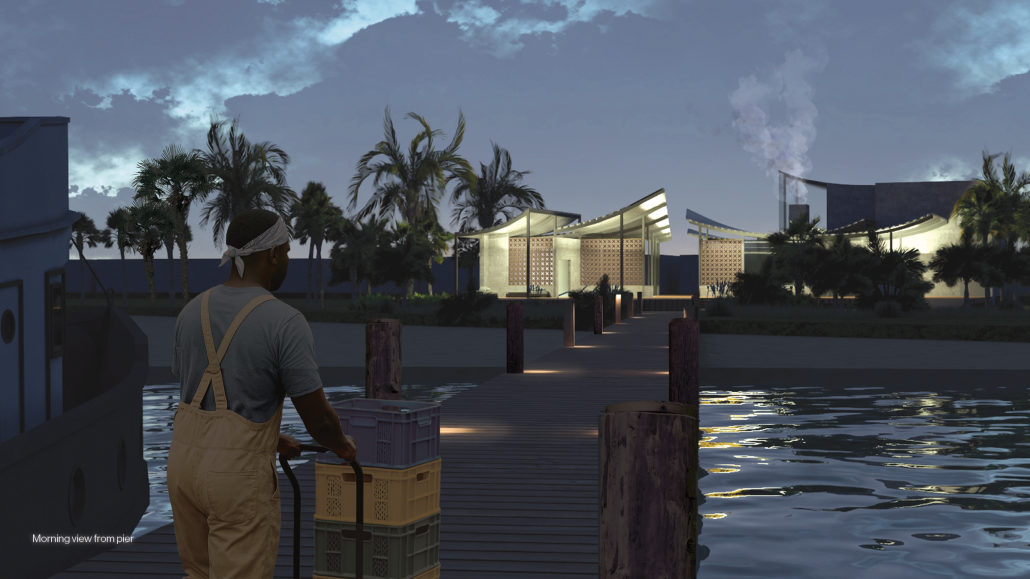
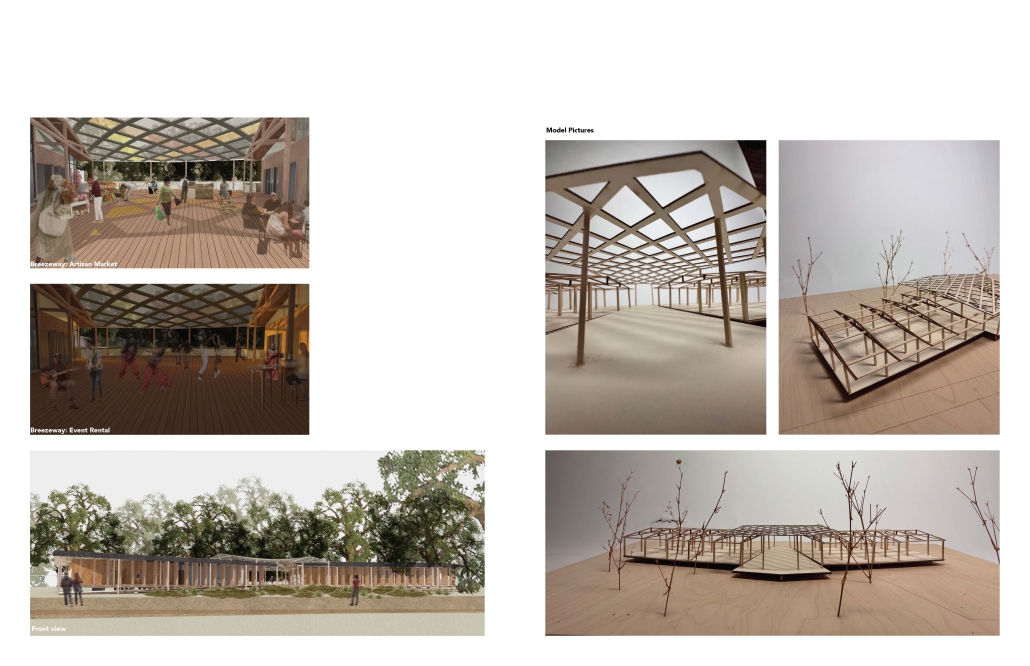
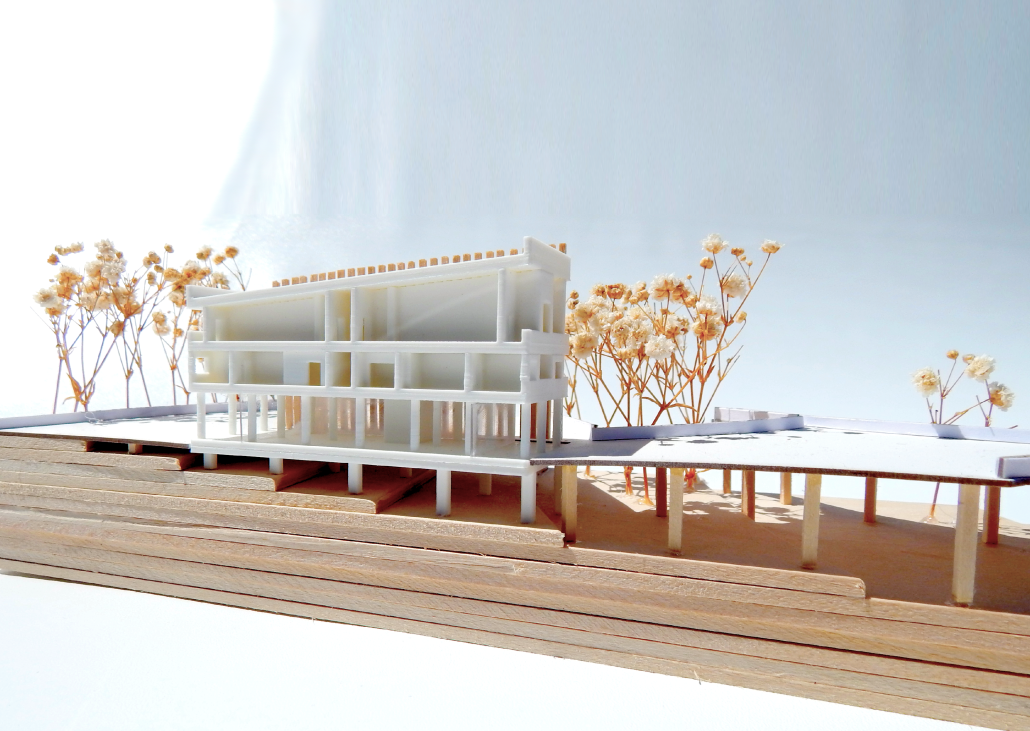
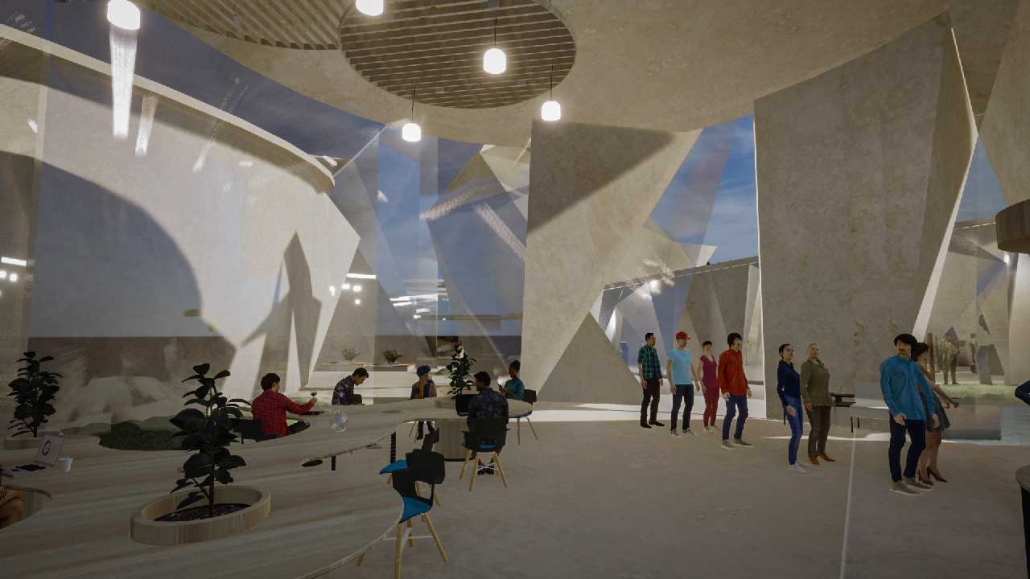
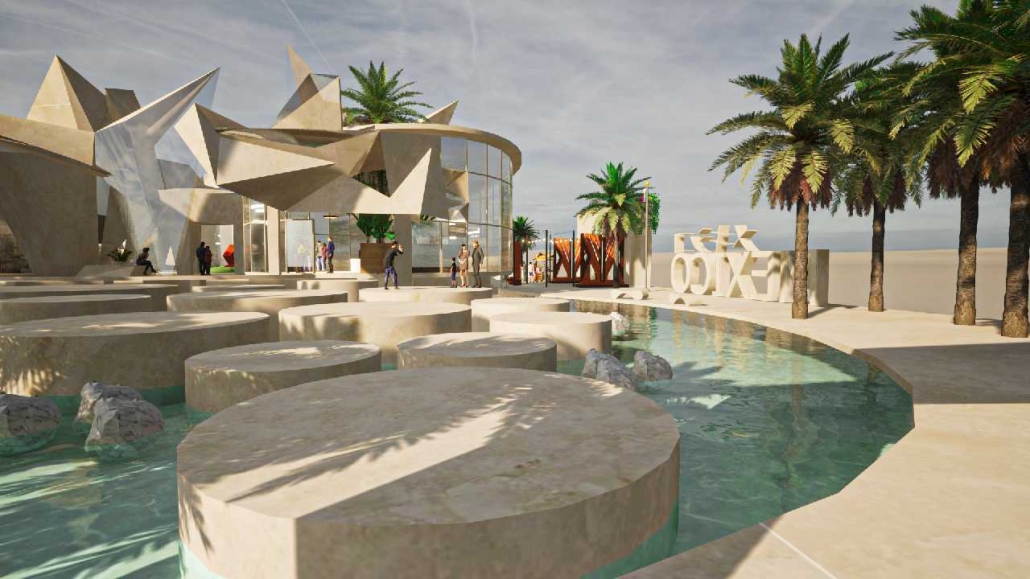
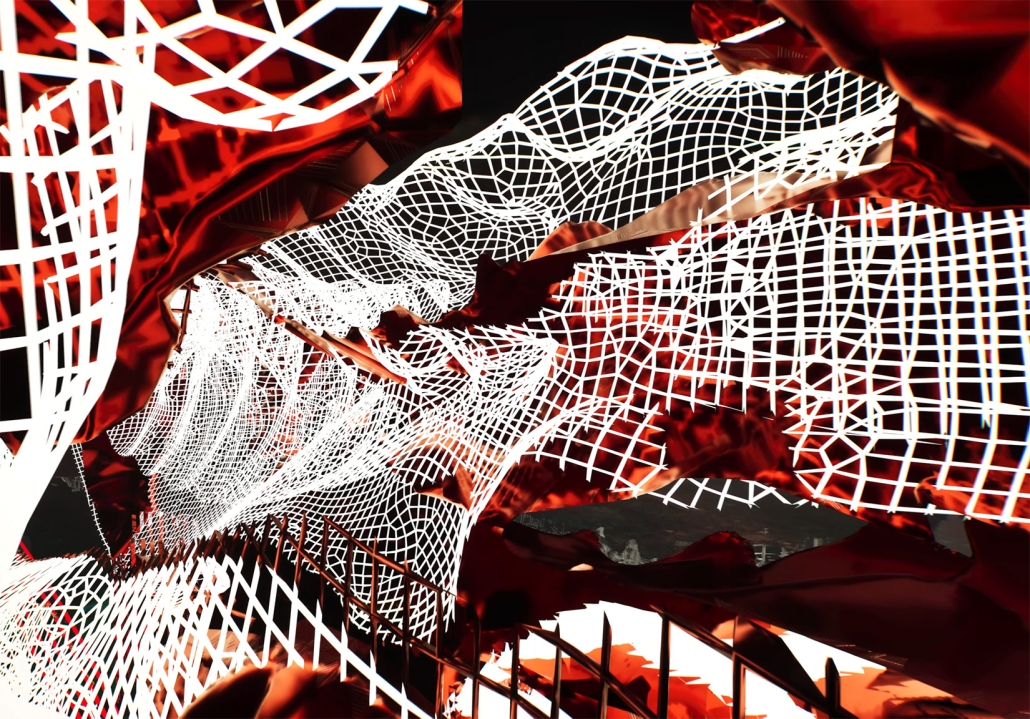
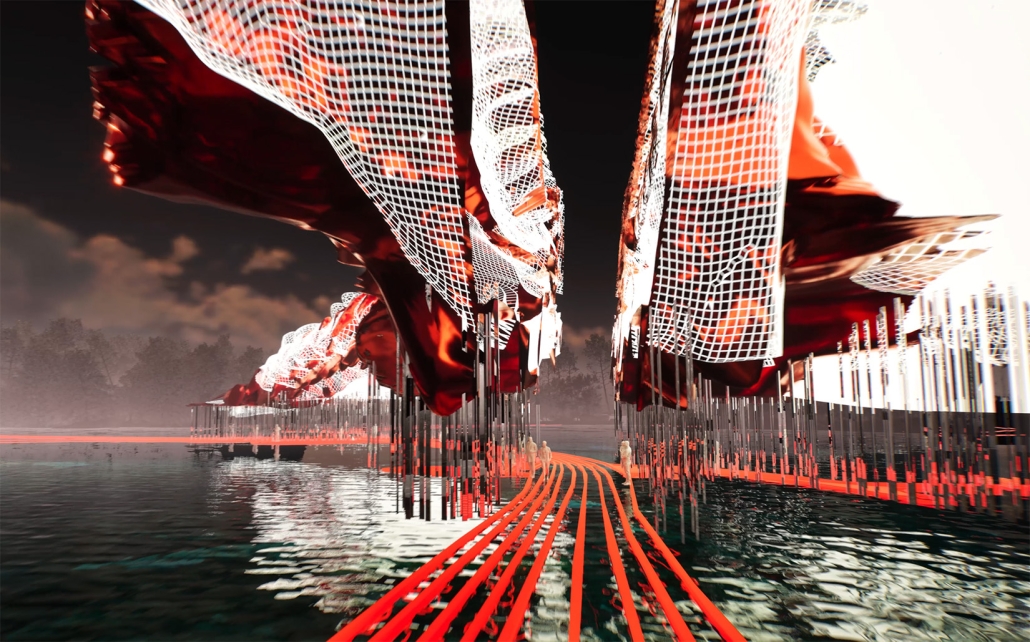
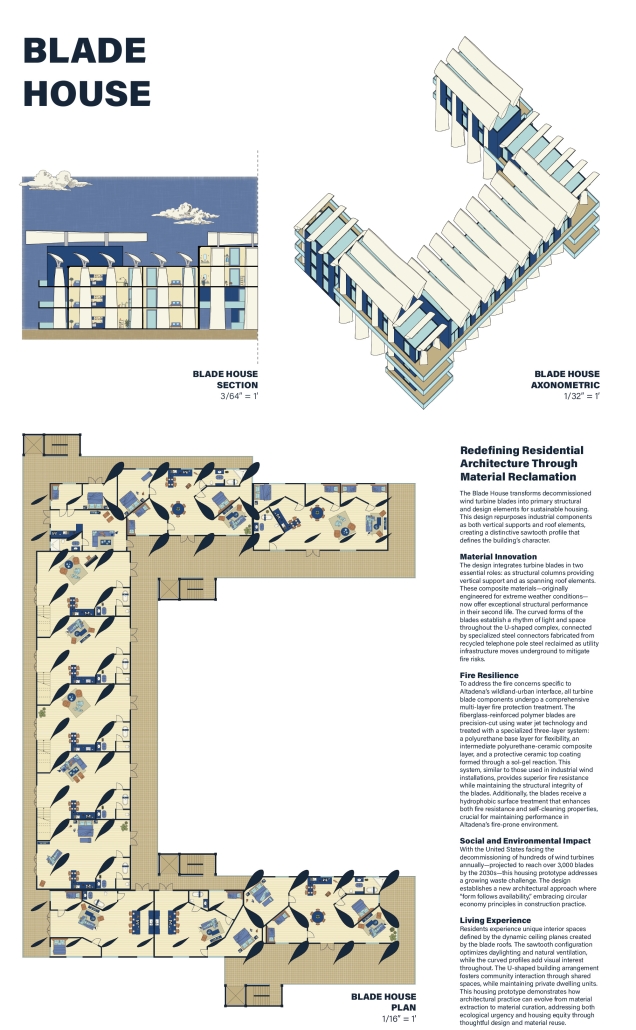
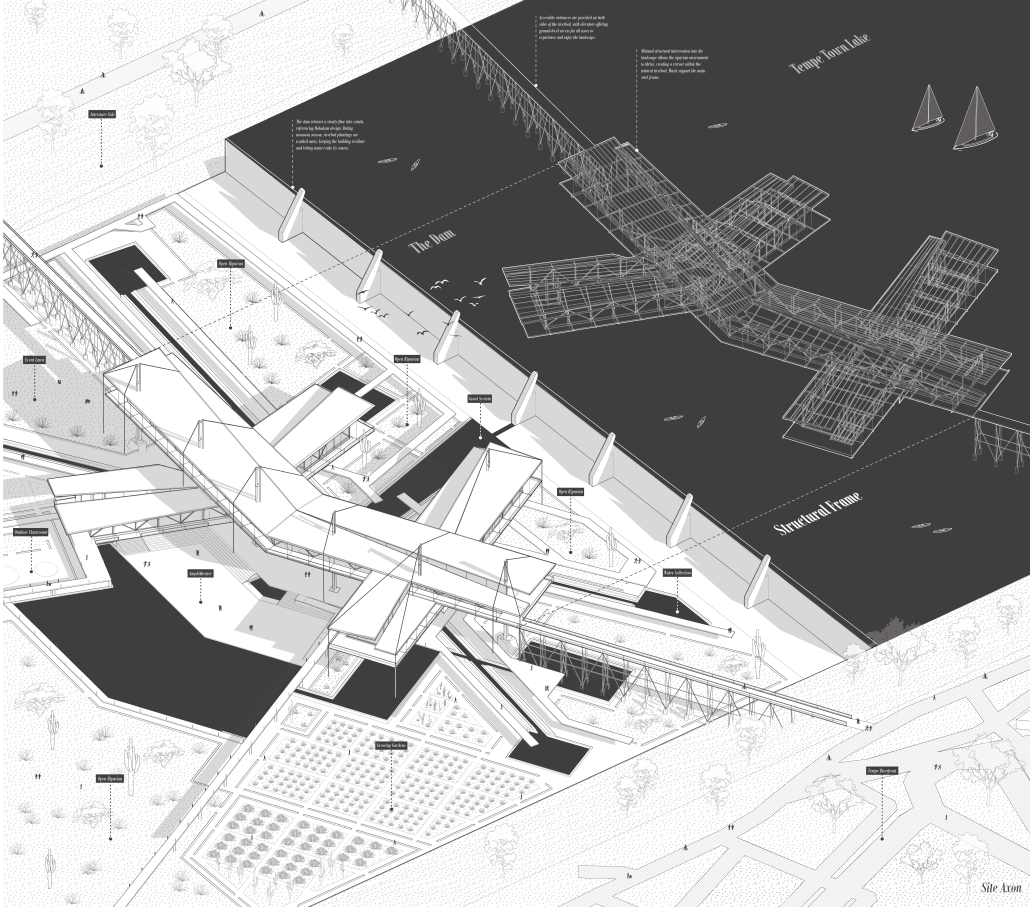
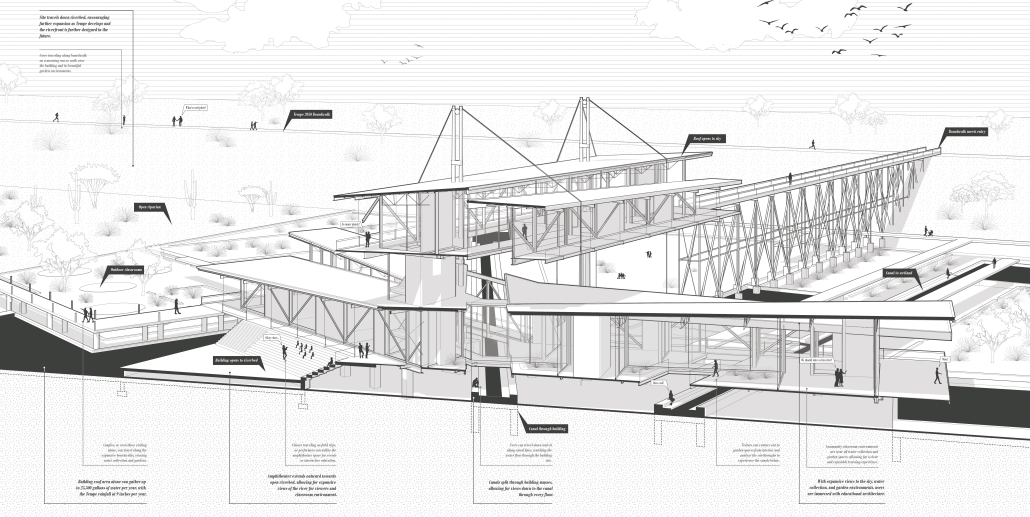
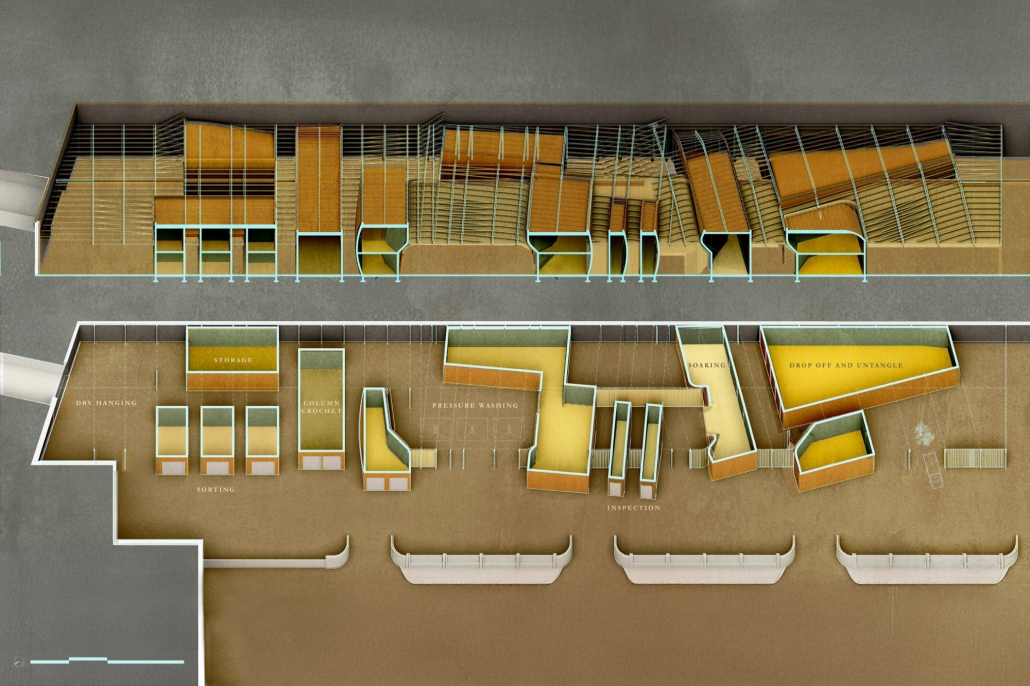
“Breakwater” is a hub for this evolving food future, a place where chefs and diners share not only cuisine, but knowledge, memory, and care. Emphasizing porosity, informality, and connection, the project acts as a framework that supports the emergence of a contemporary Caribbean food culture.
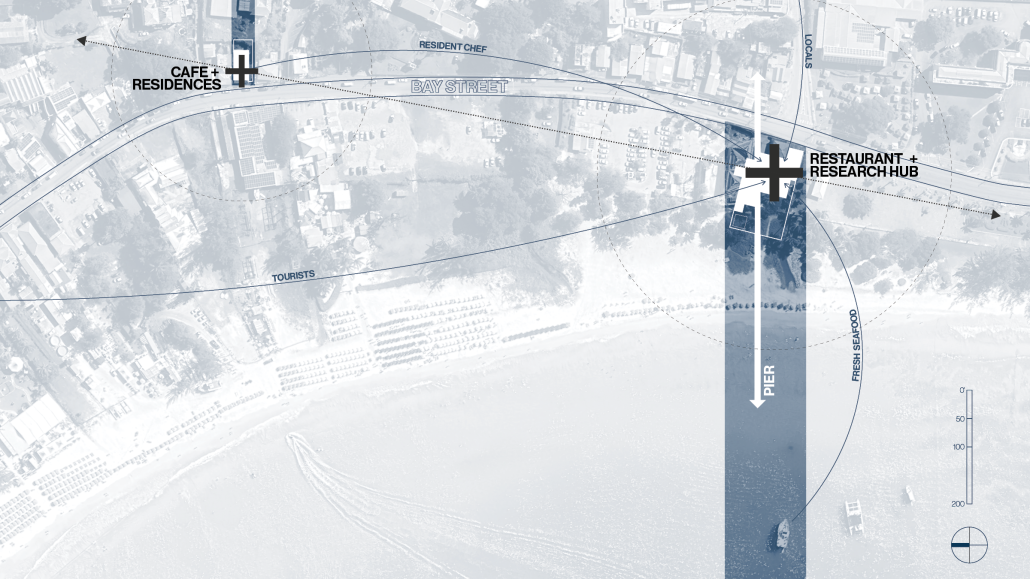
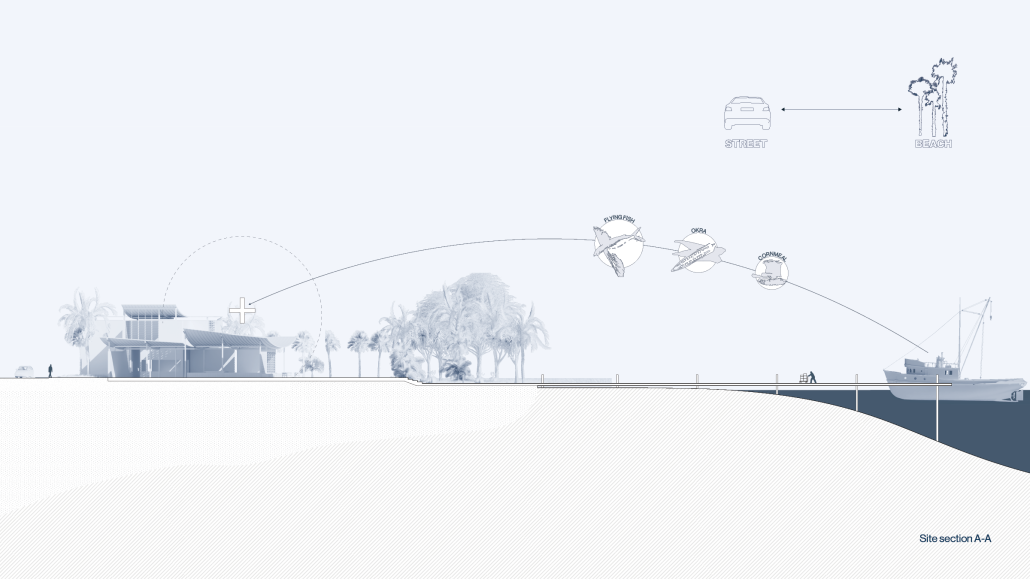
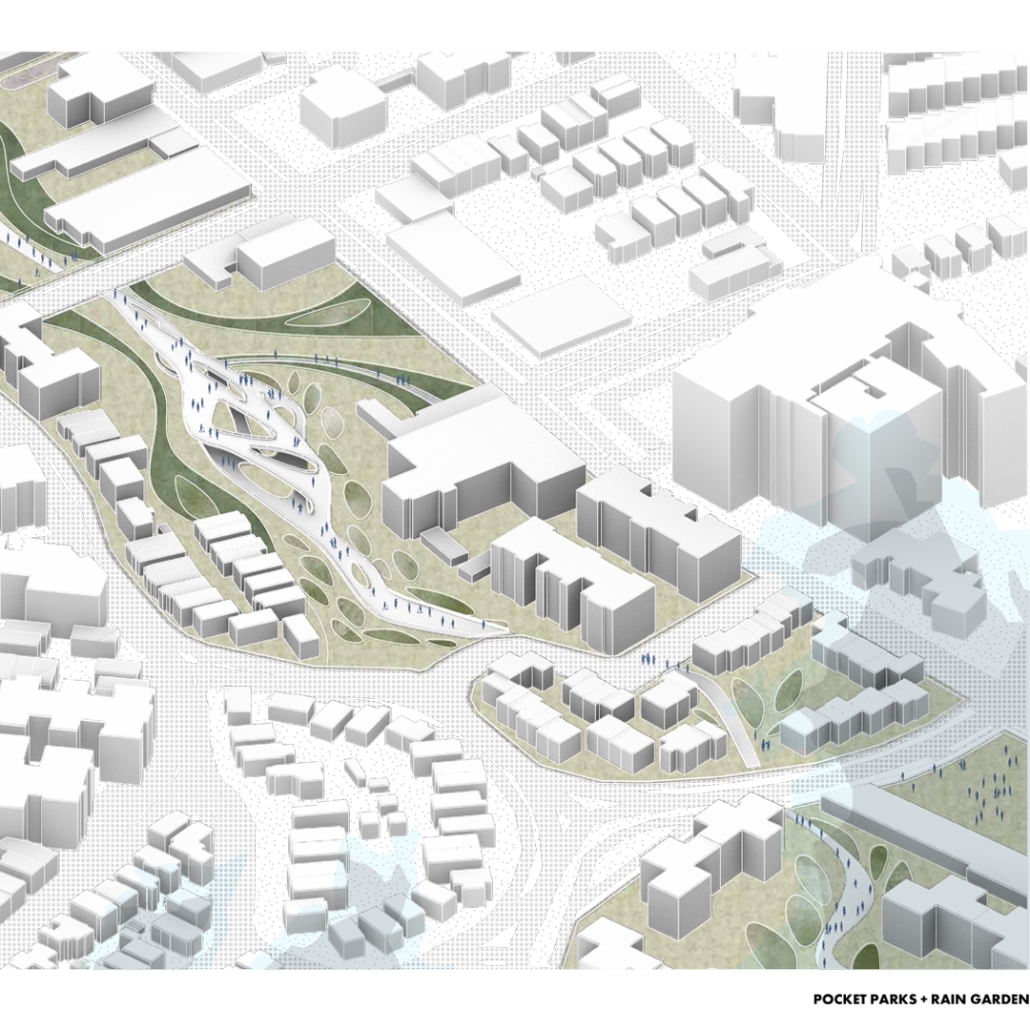
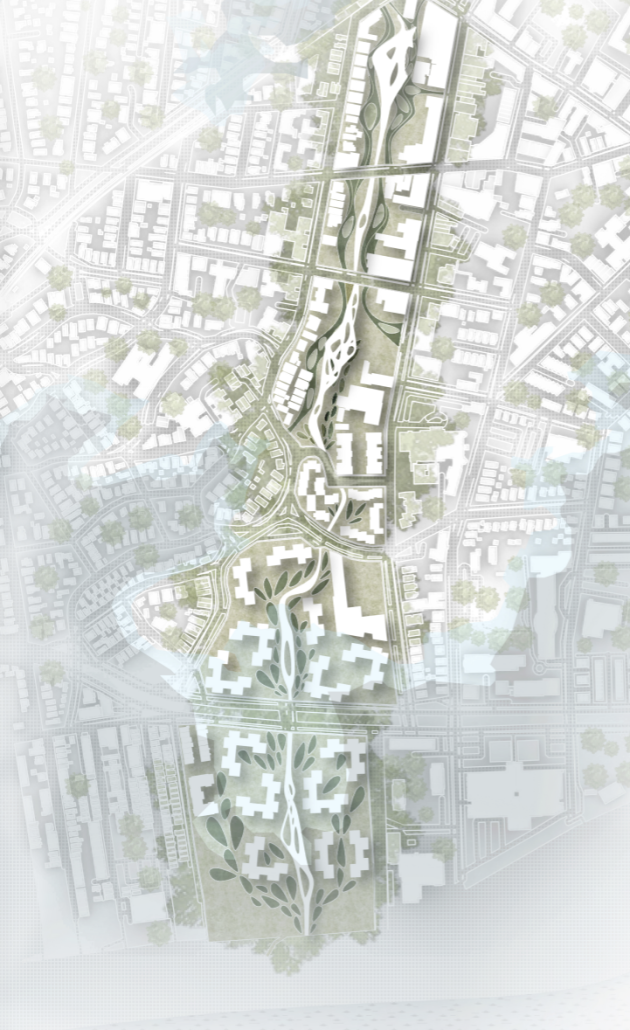
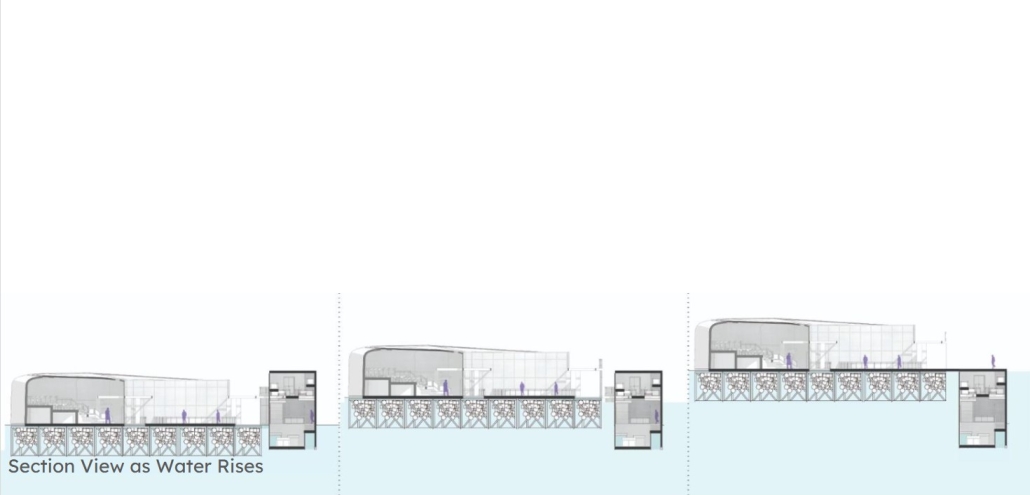
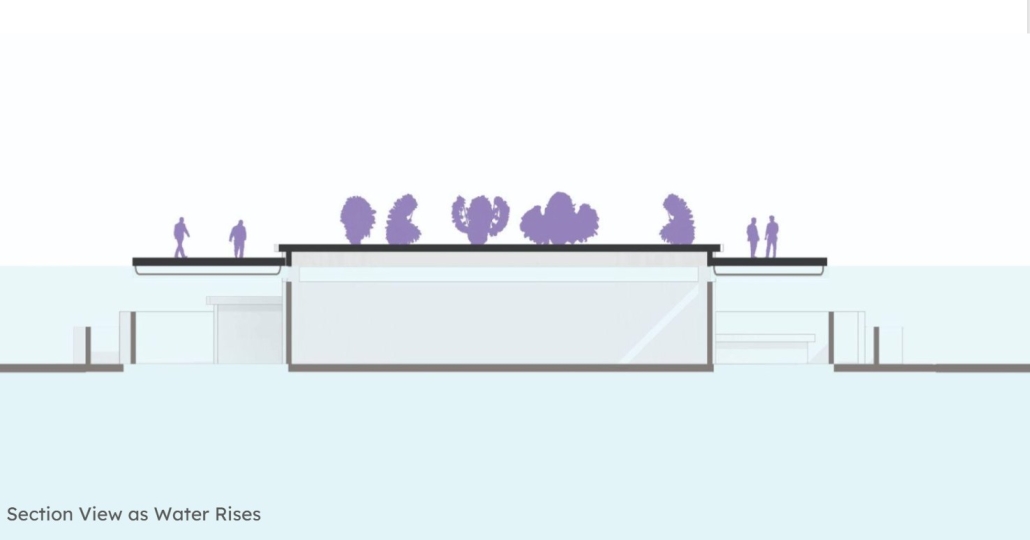
The restaurant and research center welcome the public with a direct path from city to sea. A 250-foot pier extends into the water, receiving fresh seafood and produce delivered by local and regional vessels. Breakwater is embedded within the rhythms of trade, supply, and cultural exchange that flow across the sea.
As Bajans move from cafe to restaurant or from street to beach, they can stop for a quick meal or be seated for a full-course experience guided by a visiting chef behind the counter. Spaces ebb and flow, creating opportunity for informal gatherings and chef-guest encounters. With two sites connected by the urban artery of Bay Street, Breakwater becomes a culinary campus: a space of hospitality and collaboration.
This project was entered in the Lyceum Competition.
Instagram: @fields0fblue, @nicholewiedemann
LookOut by Nick Alonzo, Nicole Roach, Jackson Franks & Olivia Tine, M.Arch ‘25
Northeastern University | Advisor: Jeremy Munn
Inspired by studio thesis topics, students worked in groups to develop an innovative business model by thinking critically about the skills they developed in pursuit of an Architecture degree and how to flex those skills to develop new value propositions.
The idea for LookOut sprouted from a personal experience. I spend a lot of time outdoors, biking from spot to spot, whether it be for birdwatching, hikes, runs, or anything else. I live in a city where there are plenty of parks, and thus plenty of new places for me to explore. Most people, including myself, when going to a new park would simply look it up on Google Maps to get information on directions, hours, and a general sense of quality. This was the case when I headed to Belle Isle Marsh in Boston. Once there, I quickly learned that there was more information that I should have known beforehand. The park was absolutely overrun by mosquitoes, to such an extent that it was unbearable to stand still or even walk. Despite a high Google Maps rating, and being a clearly great, scenic park, my experience at Belle Isle Marsh was unpleasant and brief. If I had somehow known about this mosquito situation, I could have dressed appropriately and packed bug spray.
This is just one example of the lack of relevant park information that Google Maps and similar apps are able to provide. LookOut analyzes open source data, GIS-centric algorithms, and crowd-sourced information to present users with comprehensive, yet simple visualizations – catered to their needs and interests – about the parks they want to visit. This allows our customers to get all the information they need without needing to learn it the hard way. Examples include environmental risks like mosquitoes and flooding, social risks like crime reports and disruptive events, as well as positive features including unique wildlife sightings or special events. Our hope is to make the ups and downs of the great outdoors a more accessible and safe experience for all!
Click here to view the full business plan.
Instagram: @jeremy.munn.001
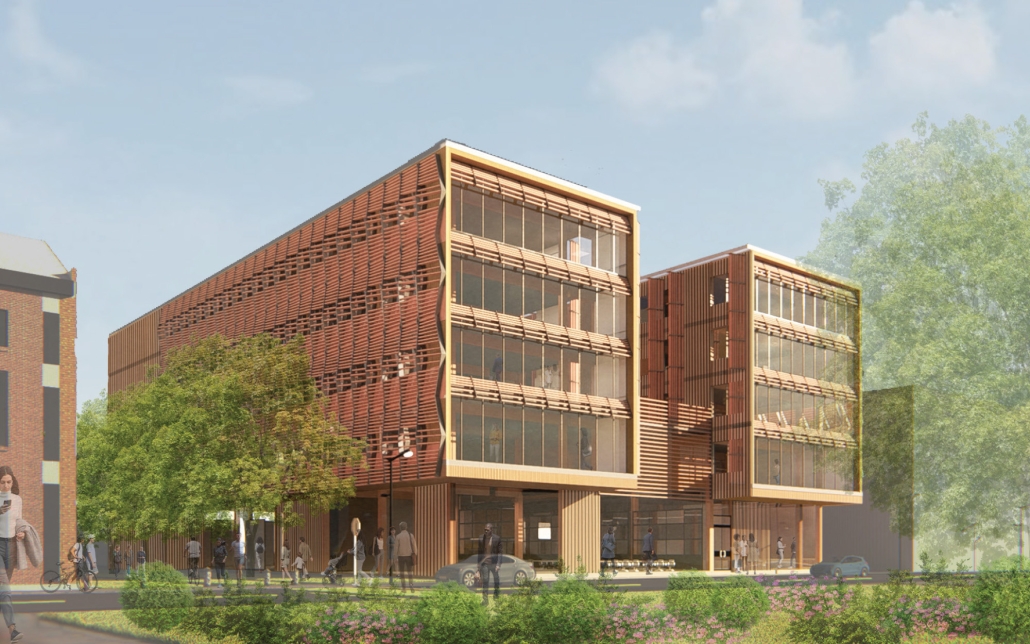
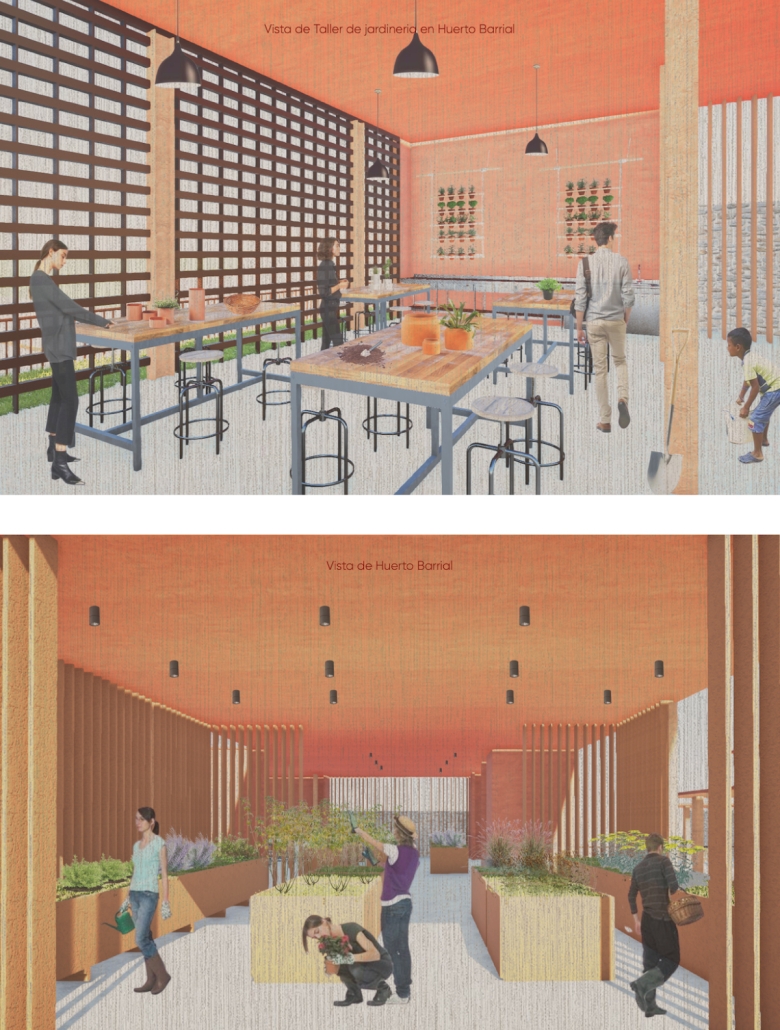
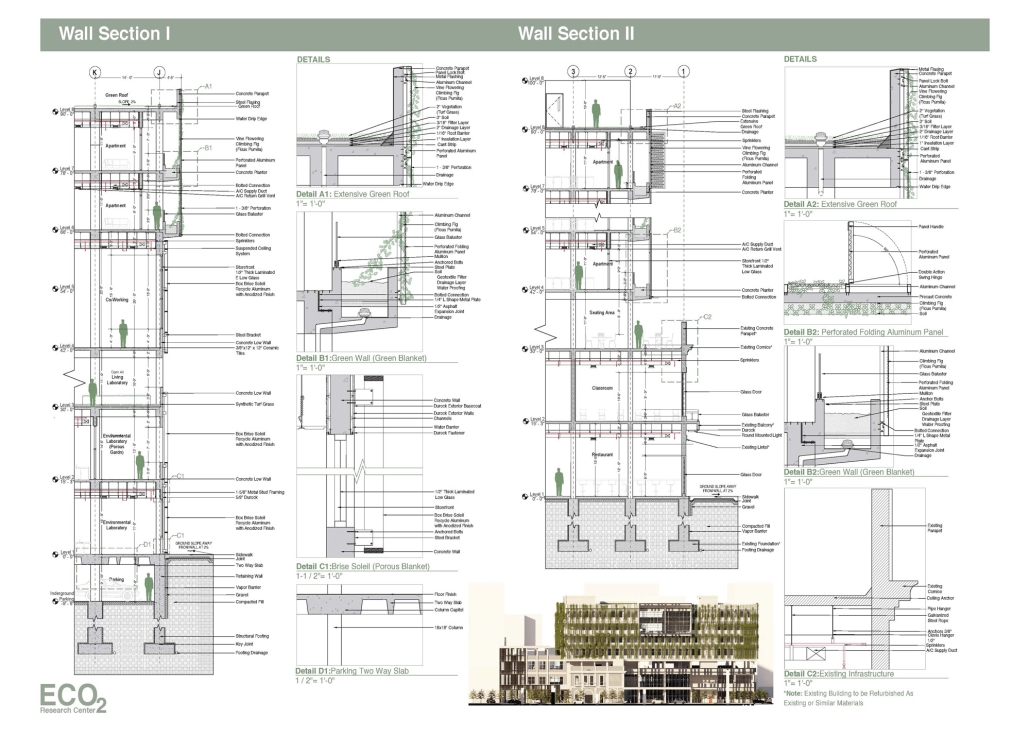
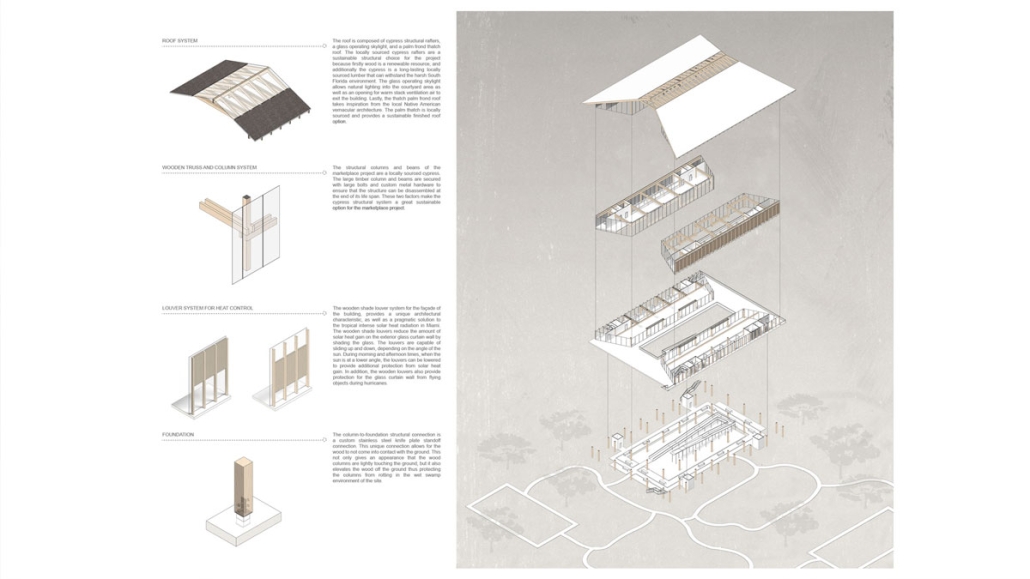
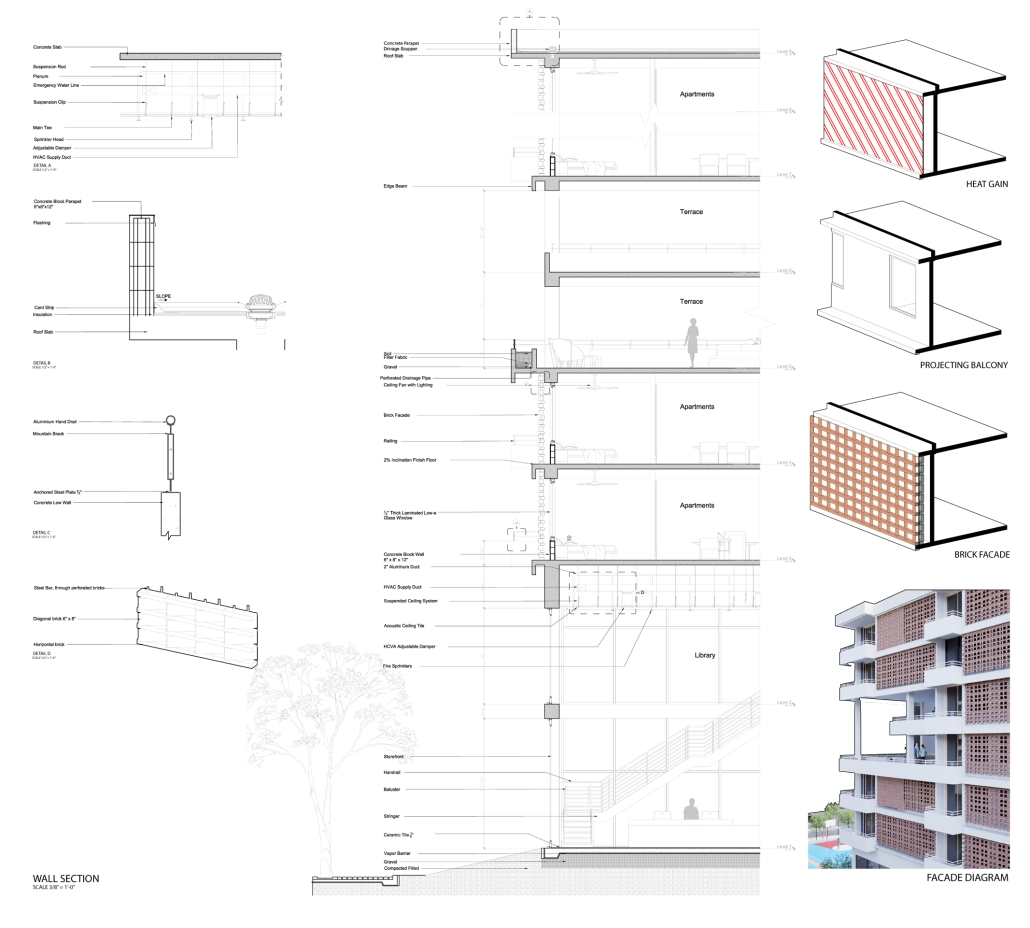
Cultivated Archive by Fredrick Ubah, B.Arch ’25
Texas Tech University | Advisor: Erin Hunt
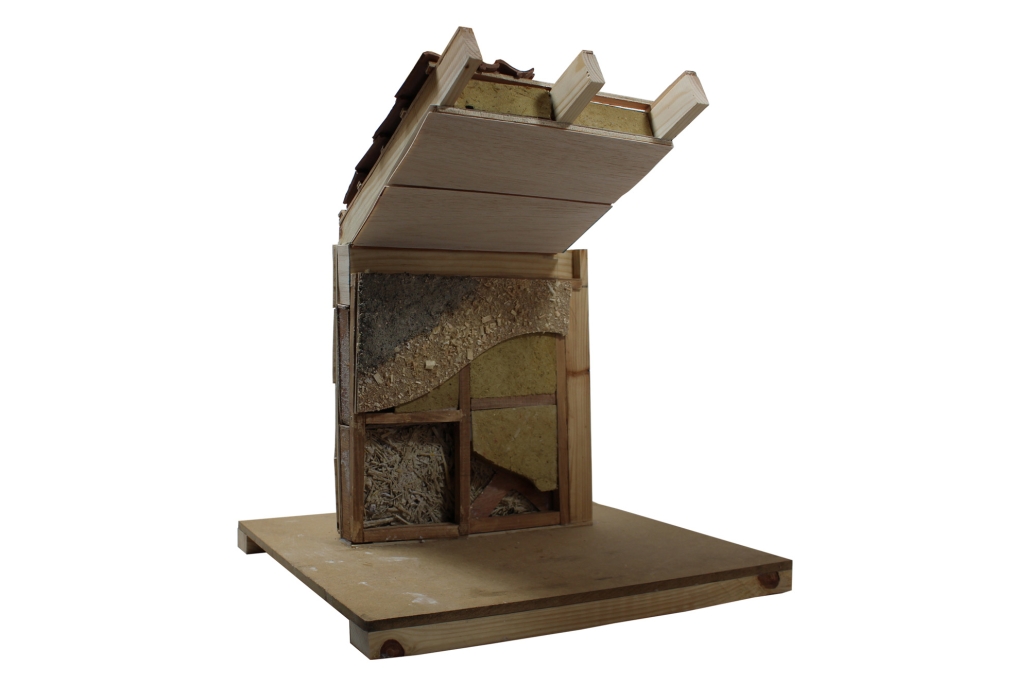
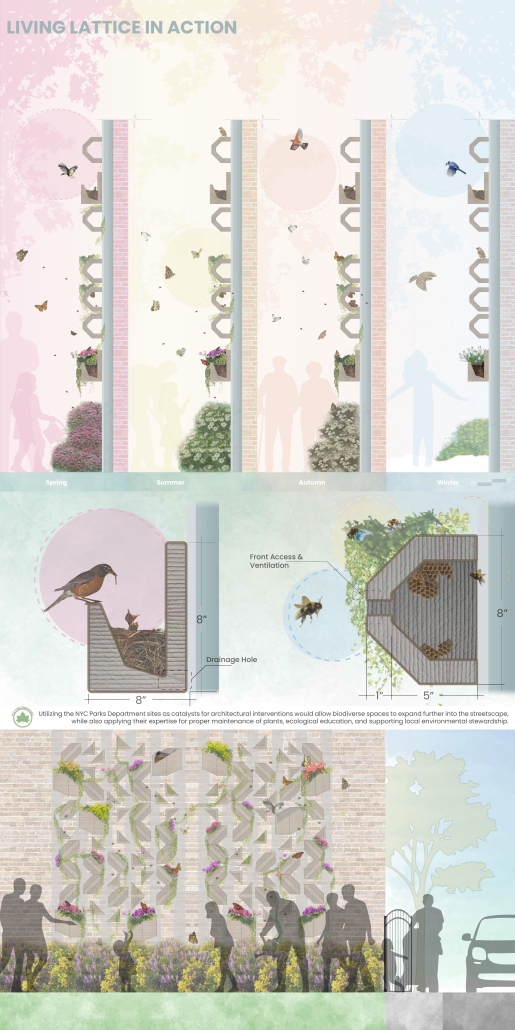
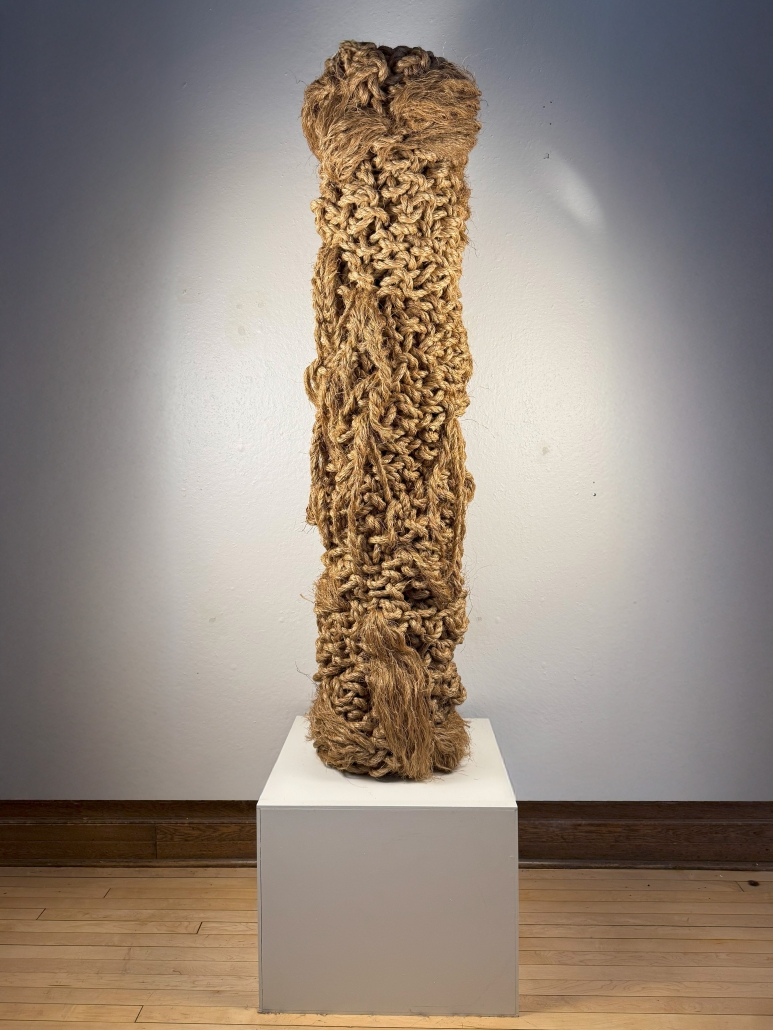
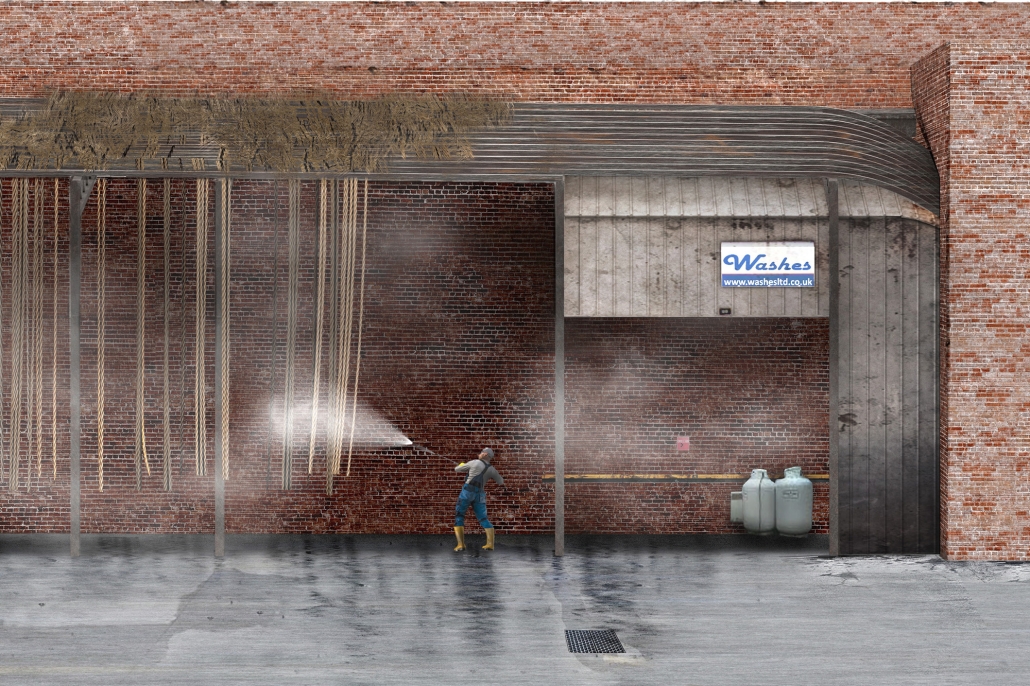
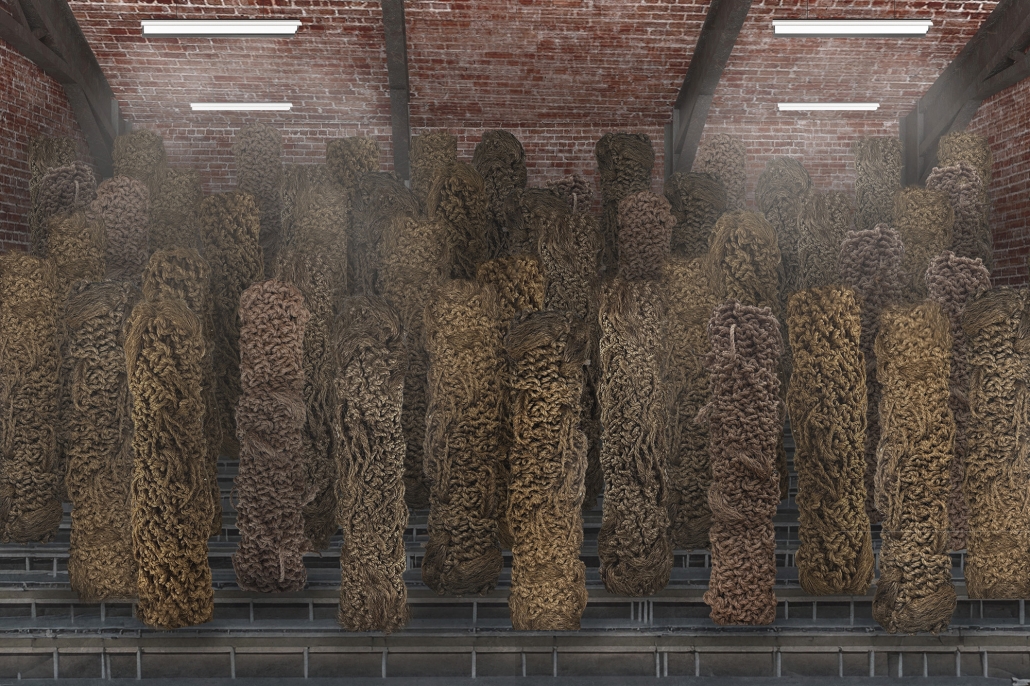
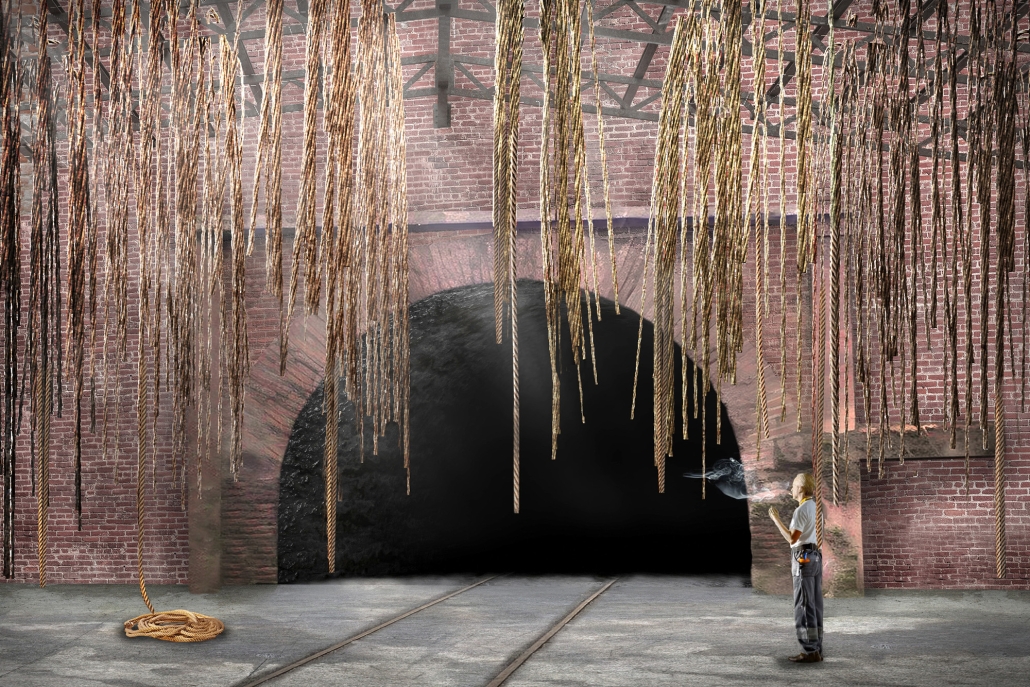
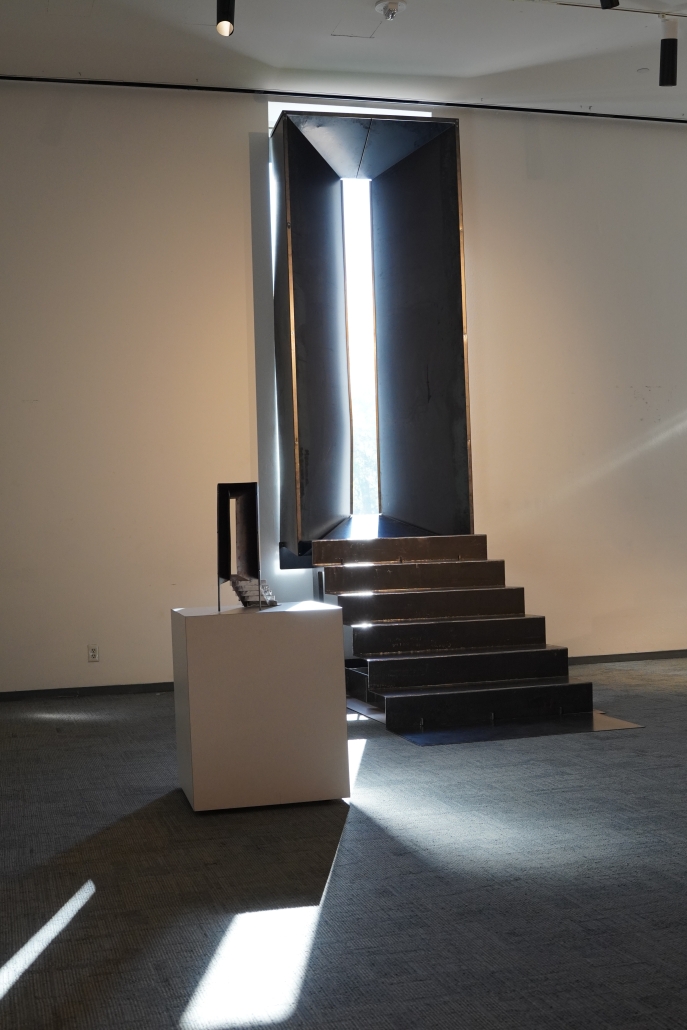
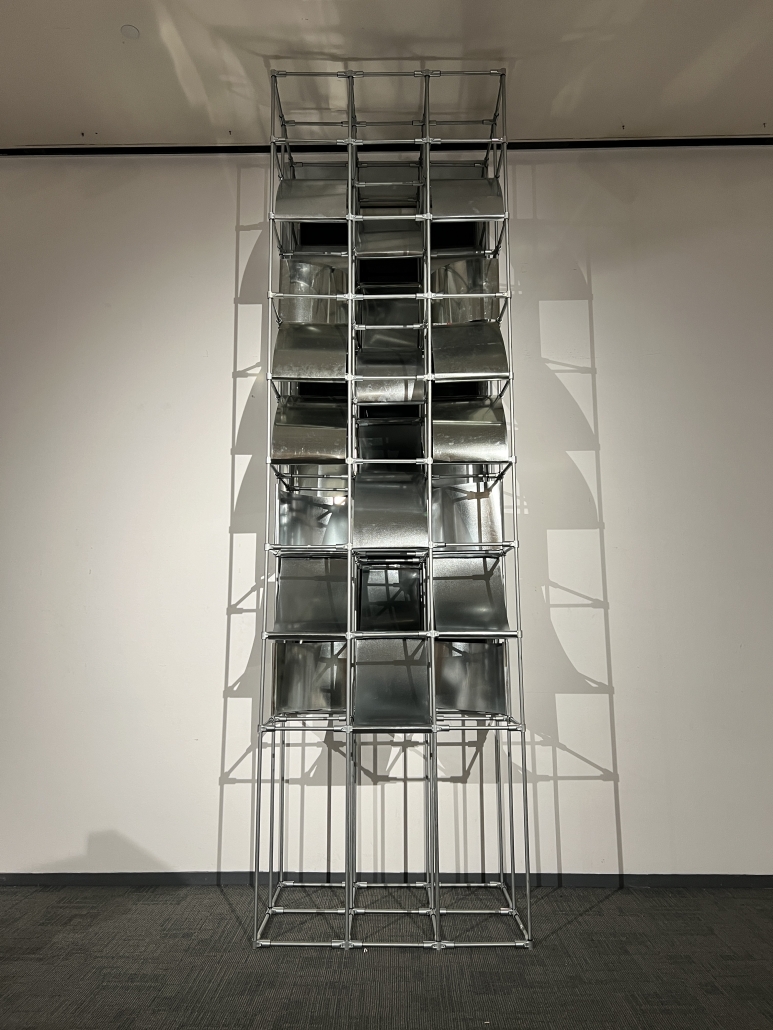
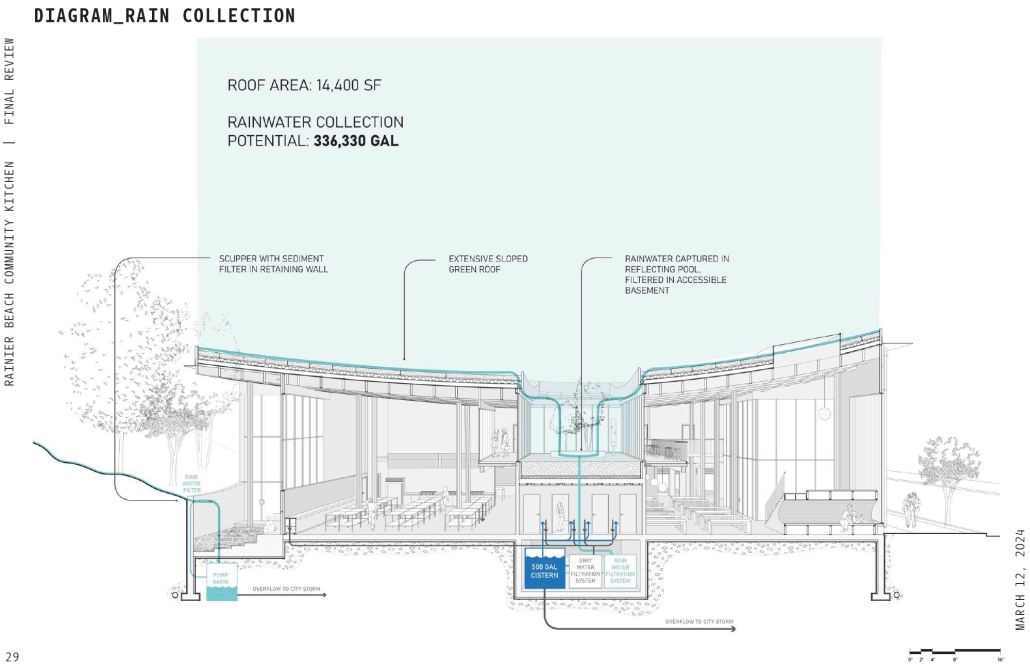
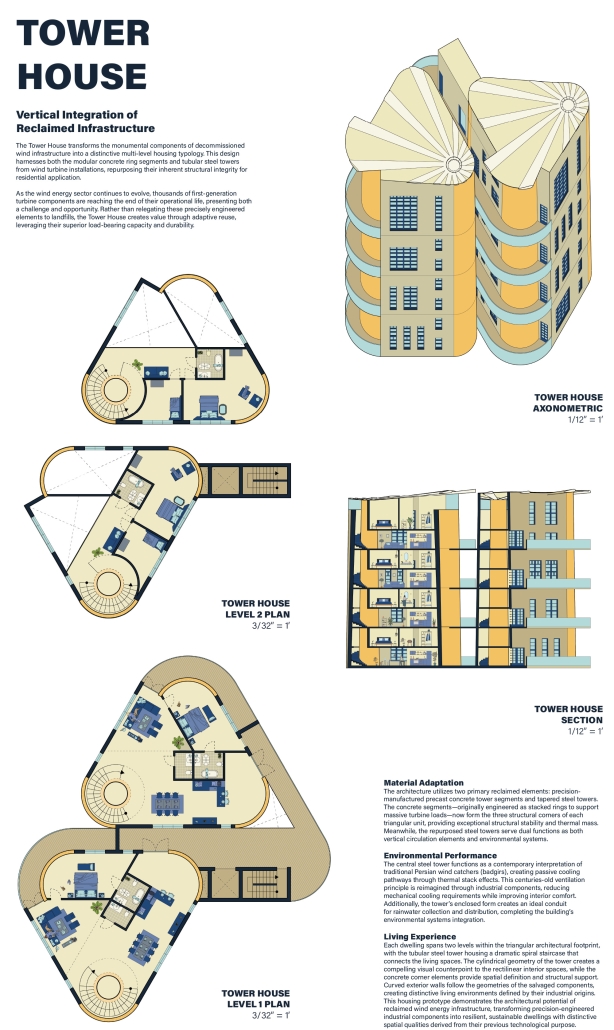
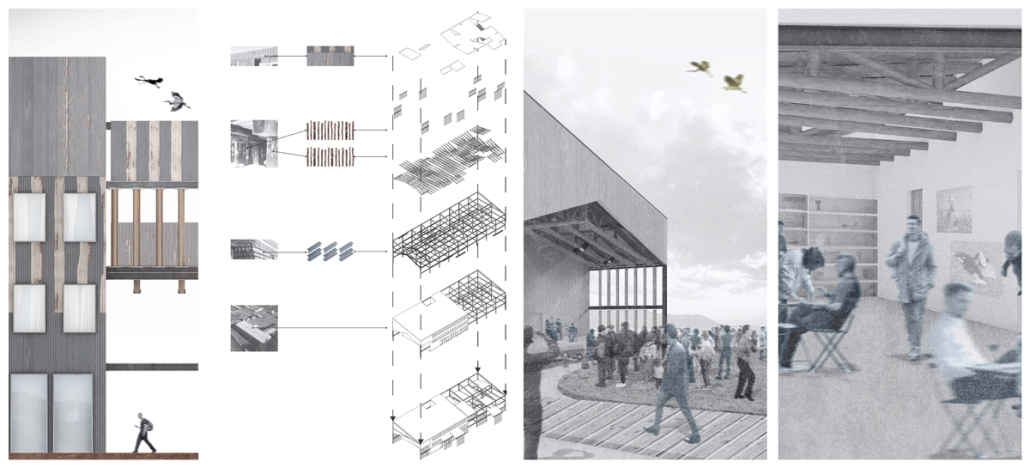
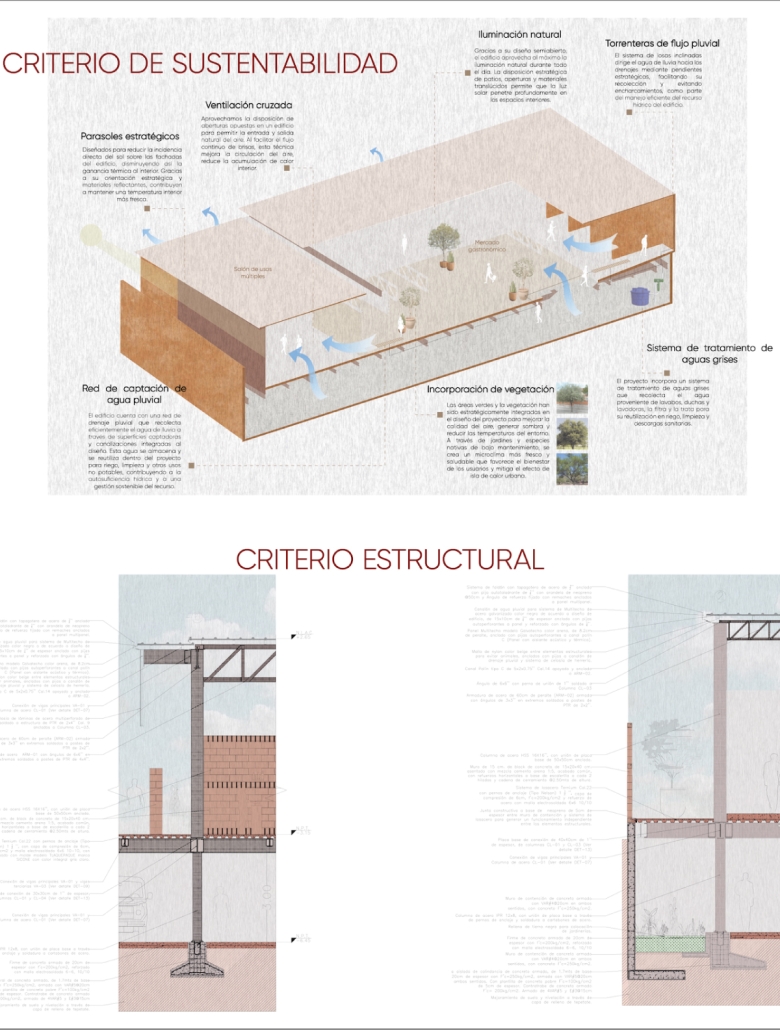
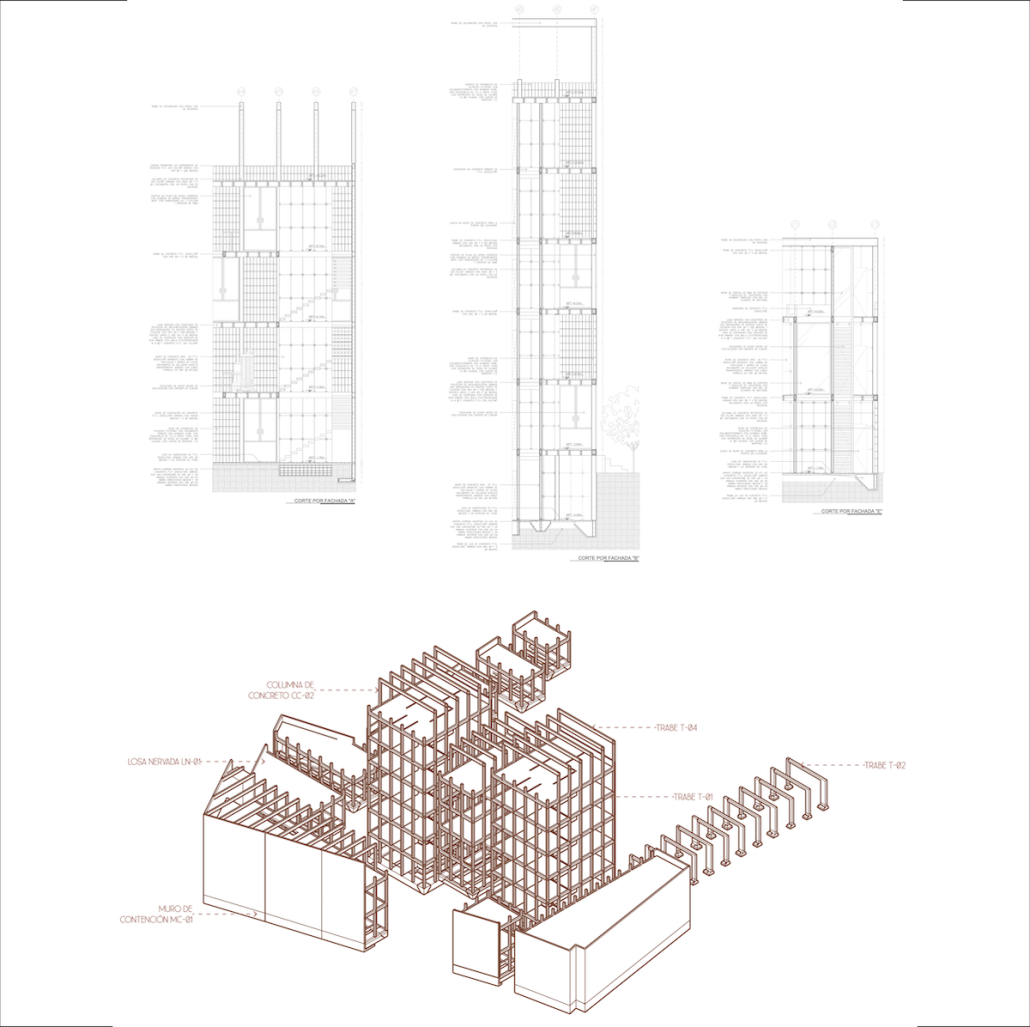
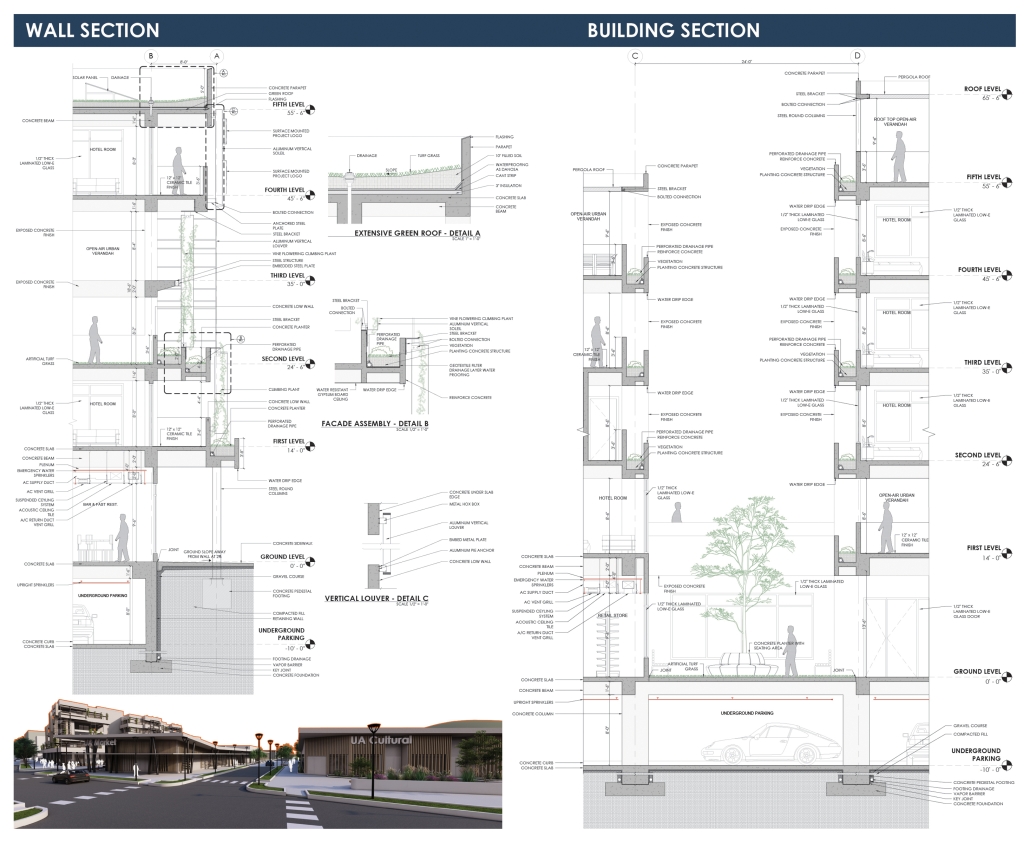
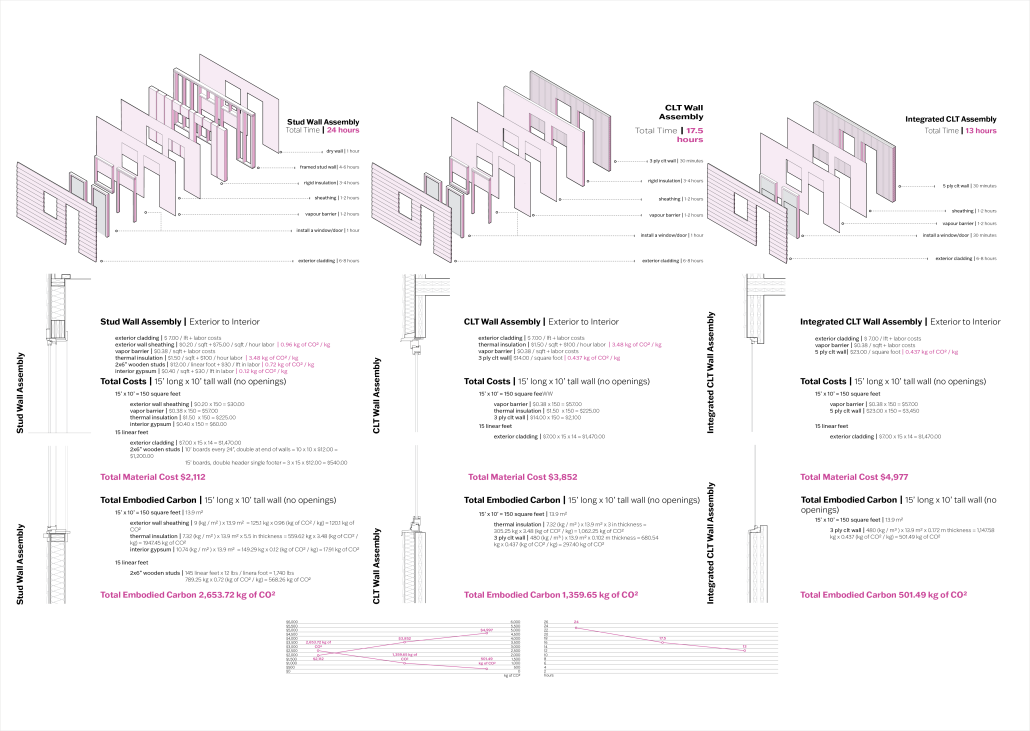
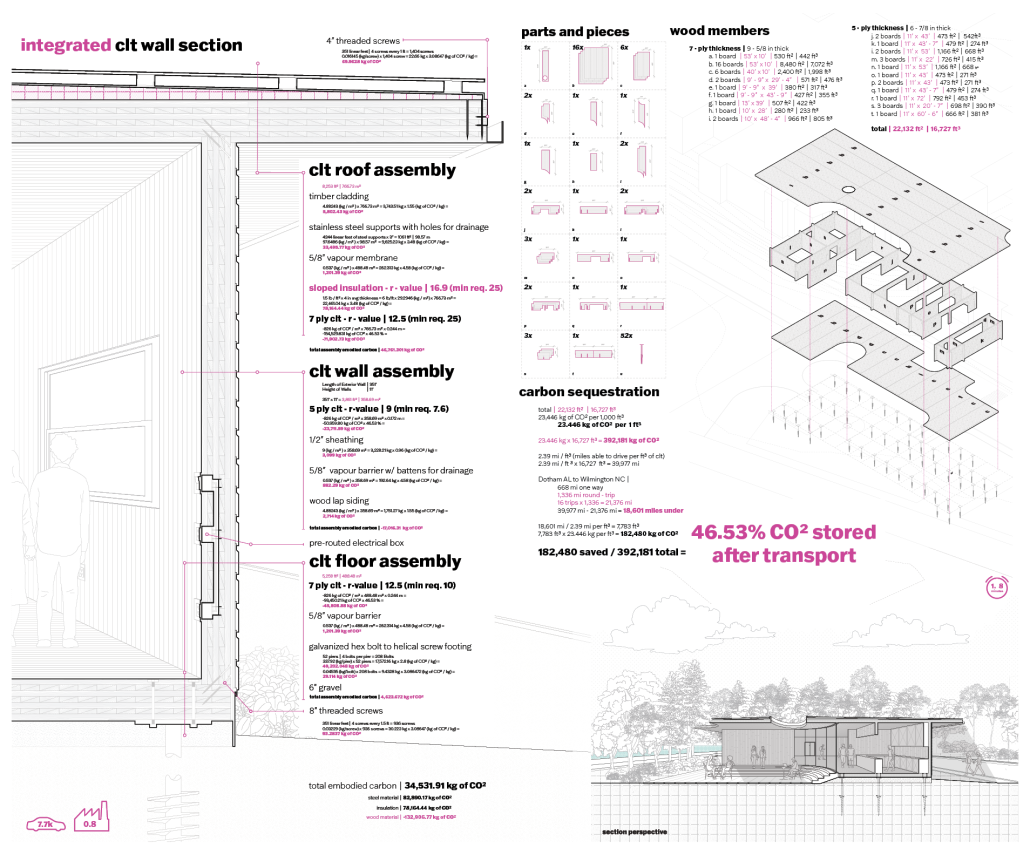
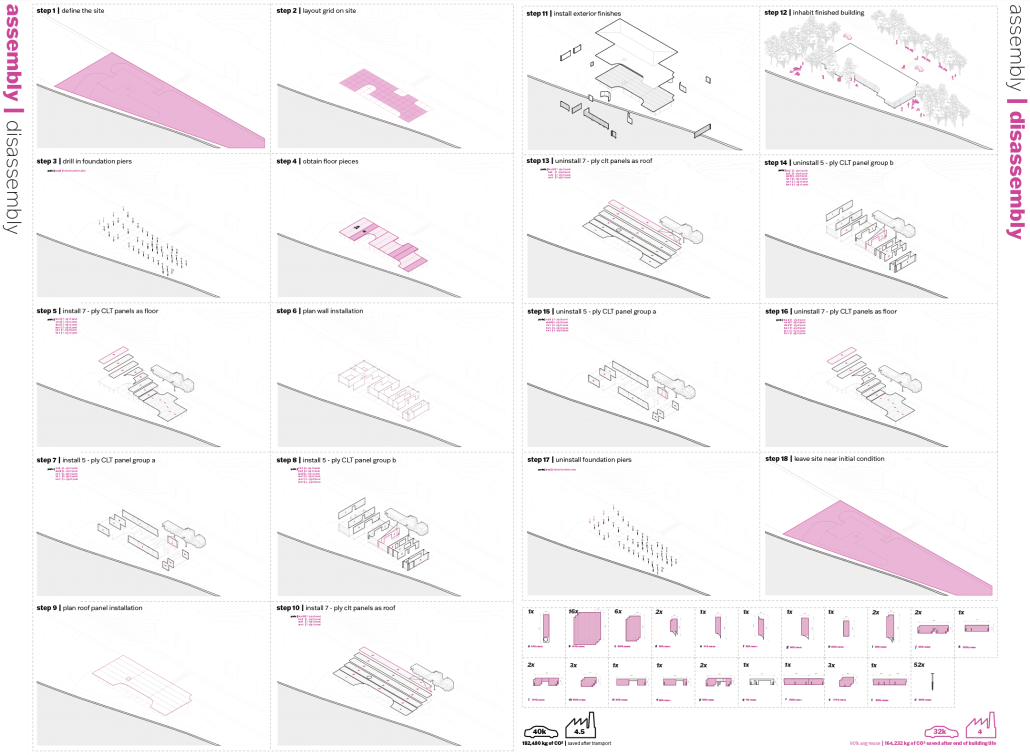
This project draws conceptual and formal inspiration from the utilitarian vertical gutters found along Austin’s East 6th Street, where concrete and wood are juxtaposed across historic and contemporary structures. These gutters, bridging rooflines to the ground, express a raw clarity that resonates with Modernism’s ideals of exposure, honesty, and tectonic legibility. The integration contrasts wood’s warmth and decorative softness with the stark presence of concrete, creating a balance between directness and welcome. The design explores vertical continuity while elevating functional components—such as exposed gutters—as aesthetic features. The facade merges disjointed yet deliberate elements of wood and concrete, reinforcing a Modernist commitment to revealing structure. Diagonal framing, influenced by Frankengram patterns and informed by fragmented urban stair logics, introduces an “implied organizational frame” that challenges conventional facade hierarchies and spatial expectations. Beyond form, the project incorporates sustainable water management through implied gutters that serve as active hydrological systems. Rainwater is guided through the structure into a passive aquaponics system, enabling ecological productivity without mechanical input. In Austin’s semi-arid context, this approach reduces runoff, enhances biodiversity, and mitigates heat.
Altogether, the facade becomes a layered system—materially honest, formally complex, and ecologically performative—bridging architectural expression with environmental stewardship.
Instagram: @Urfredrick, @erinlinseyhunt
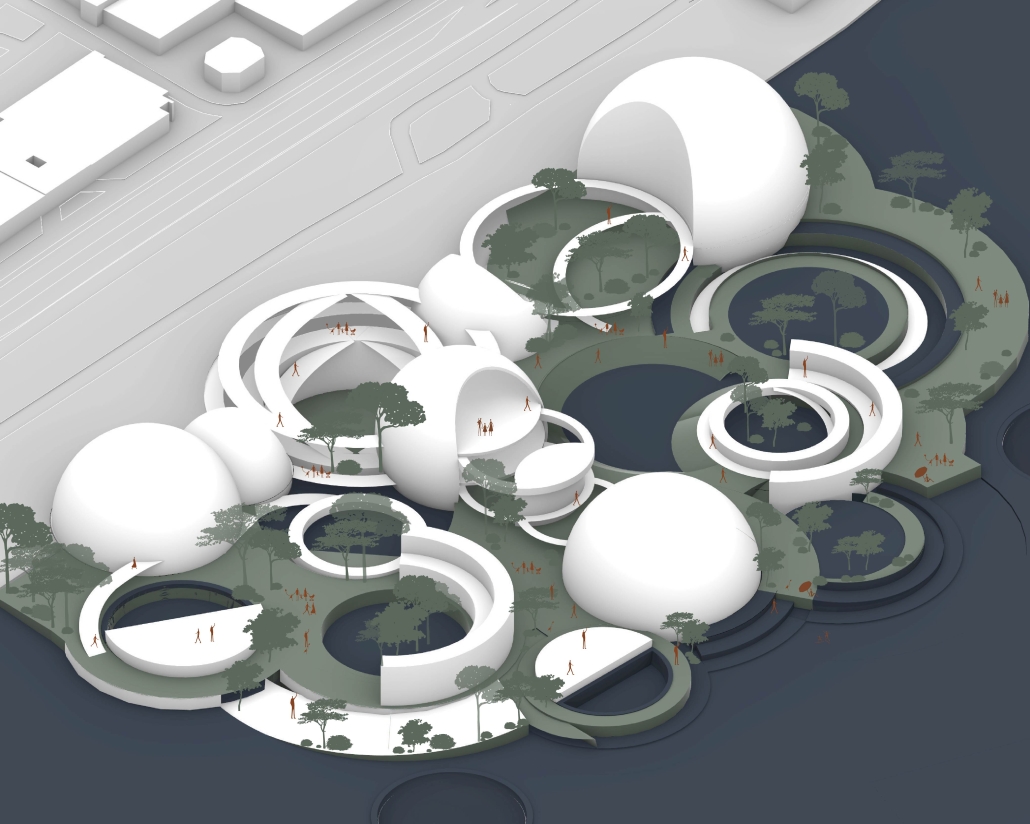
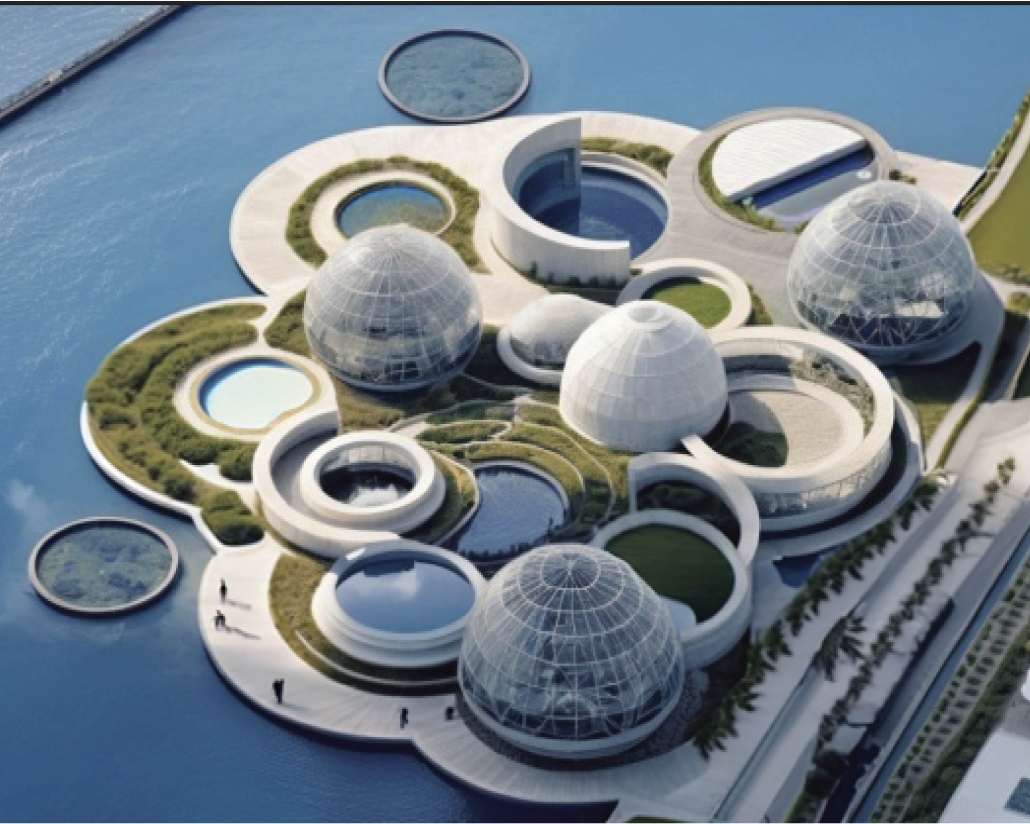
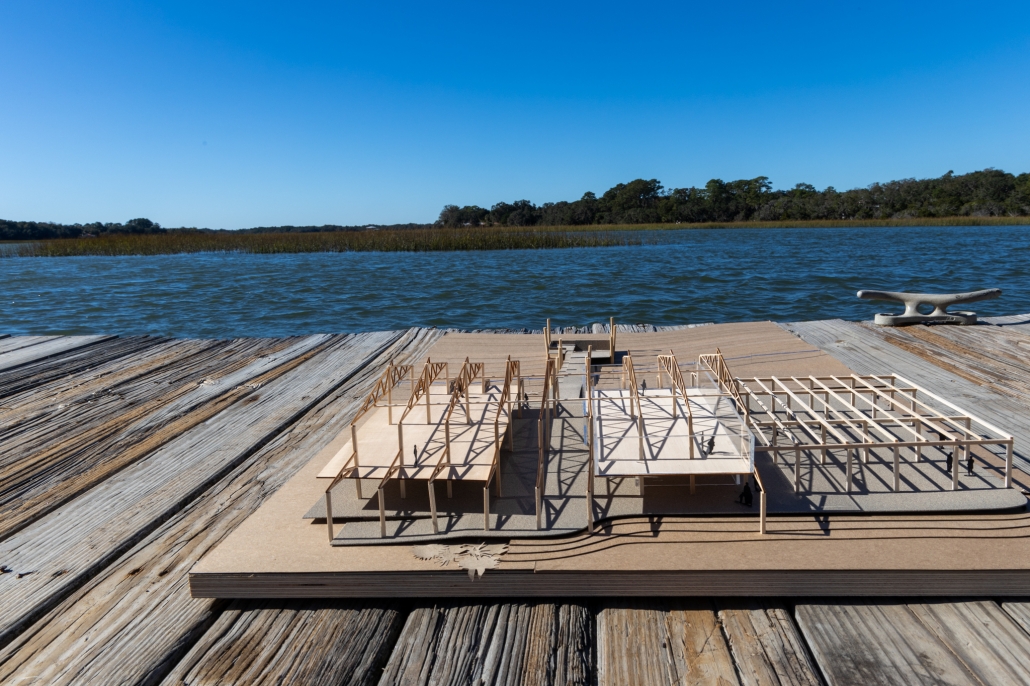
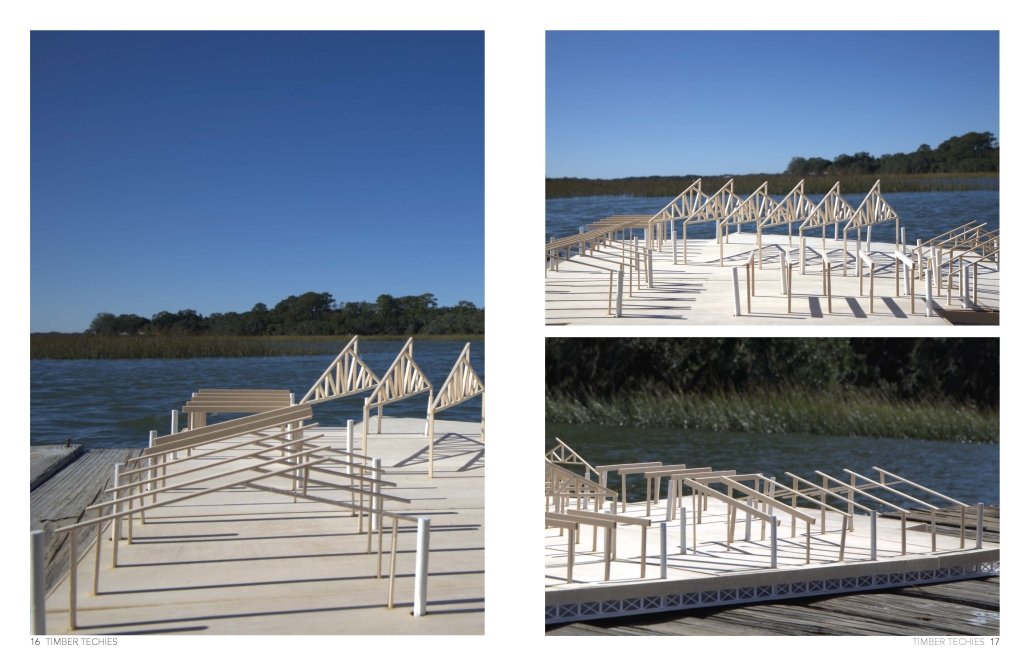
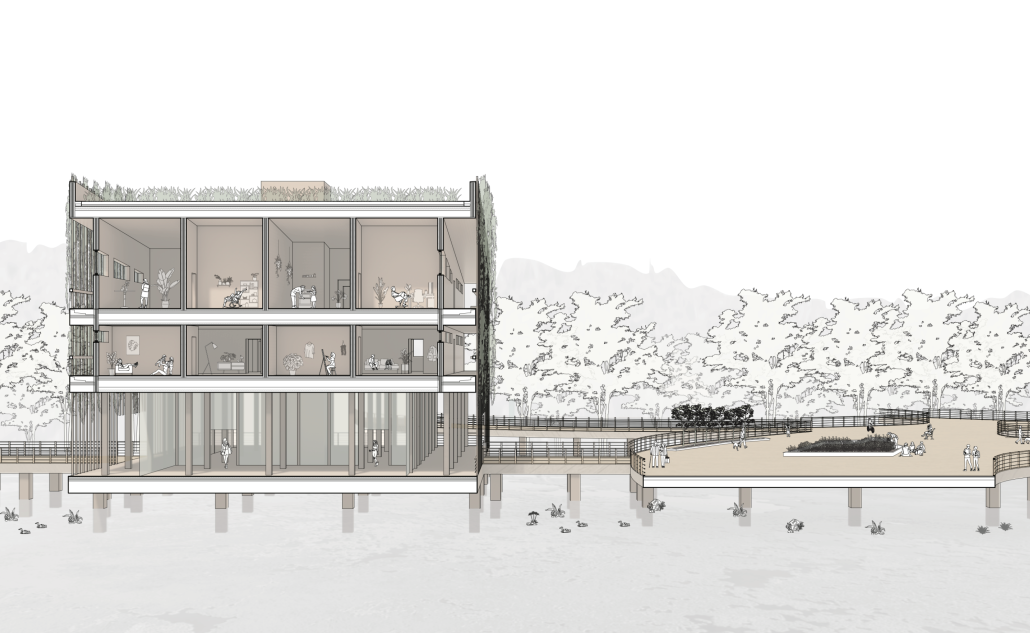
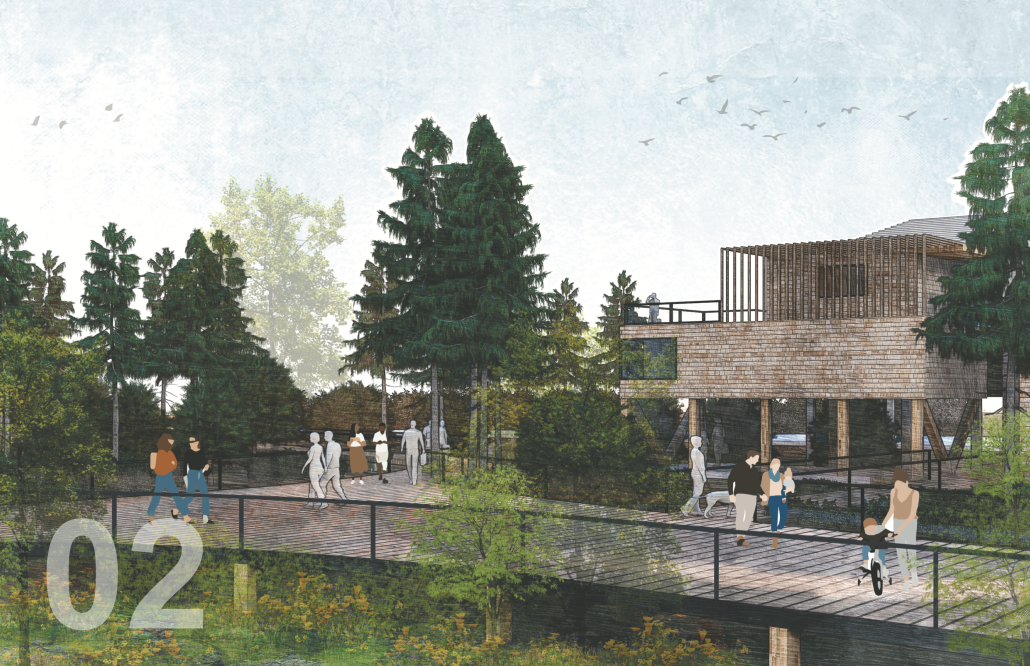
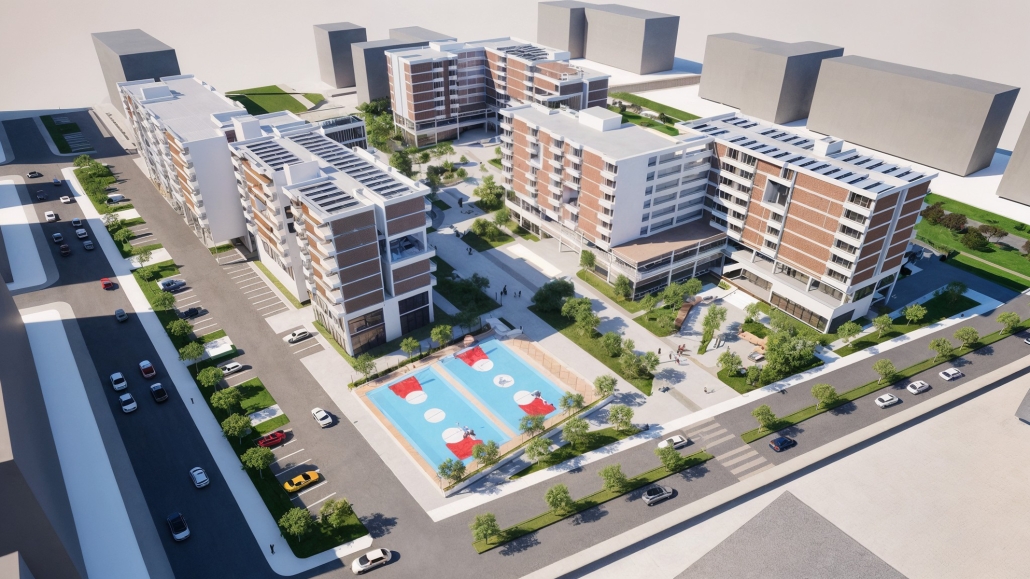
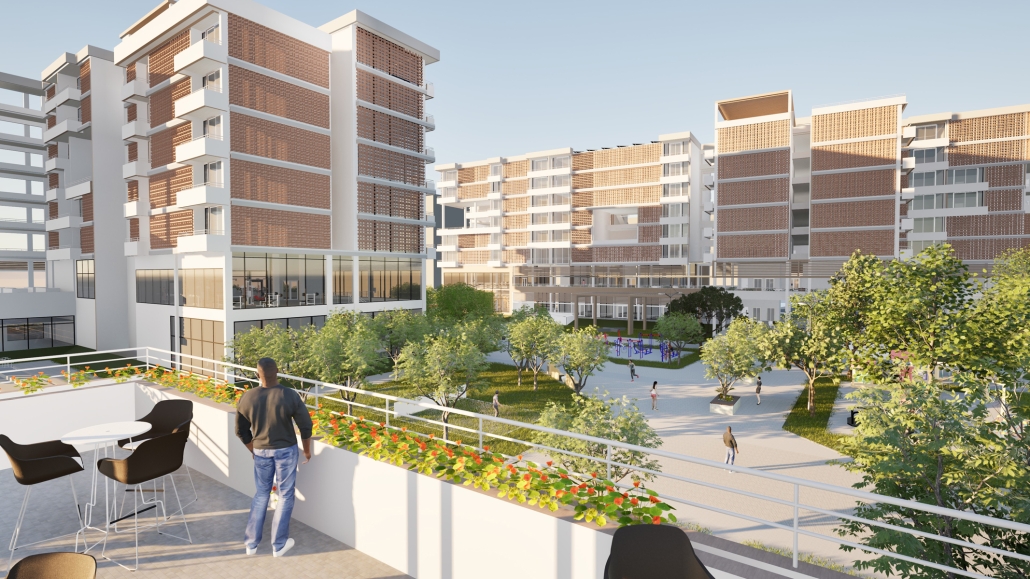
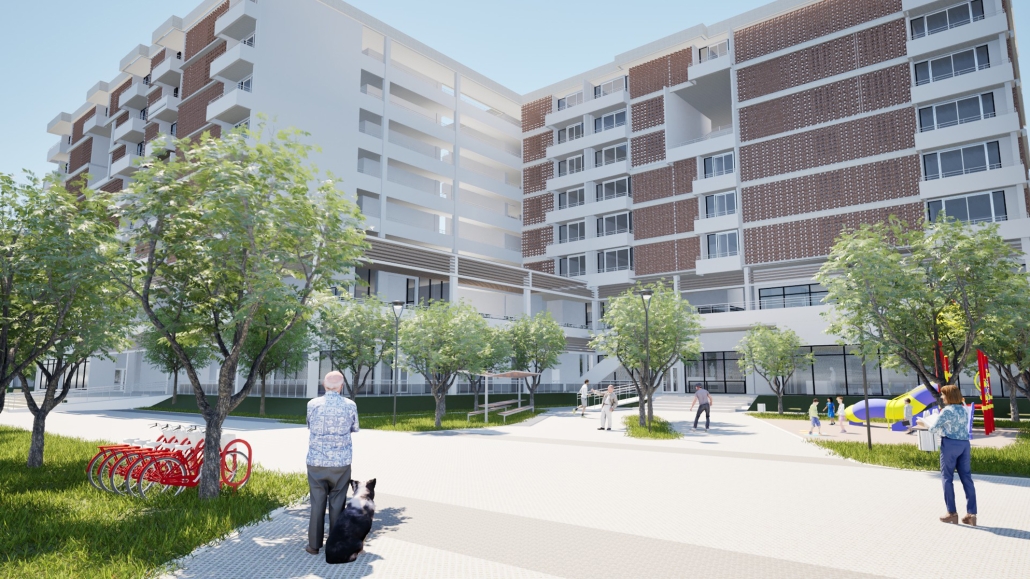
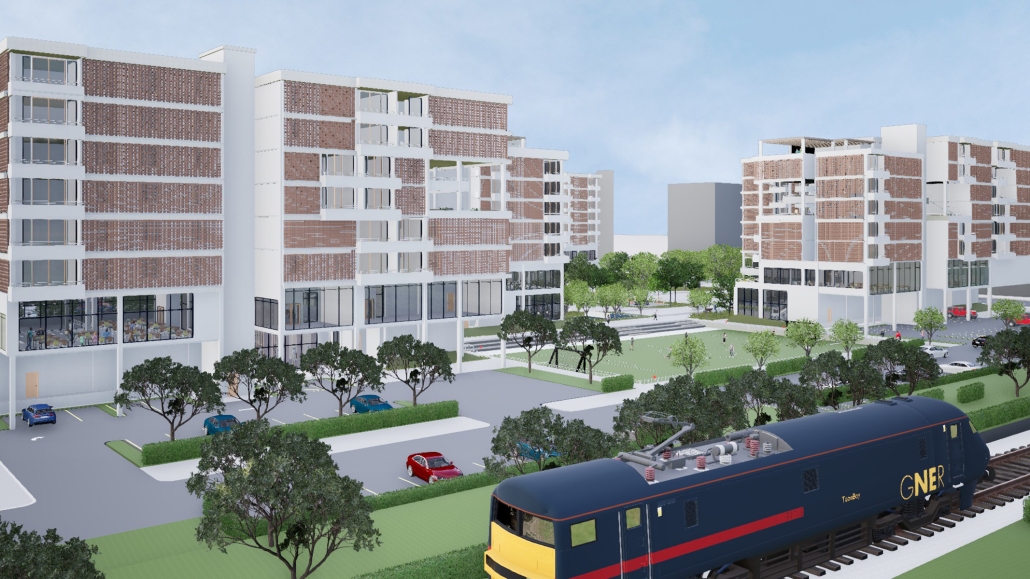
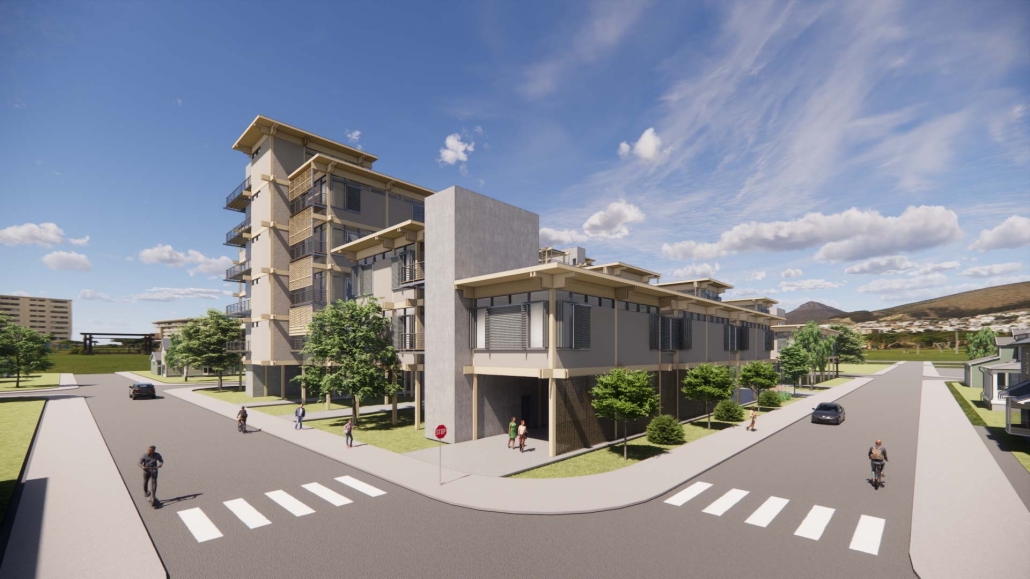
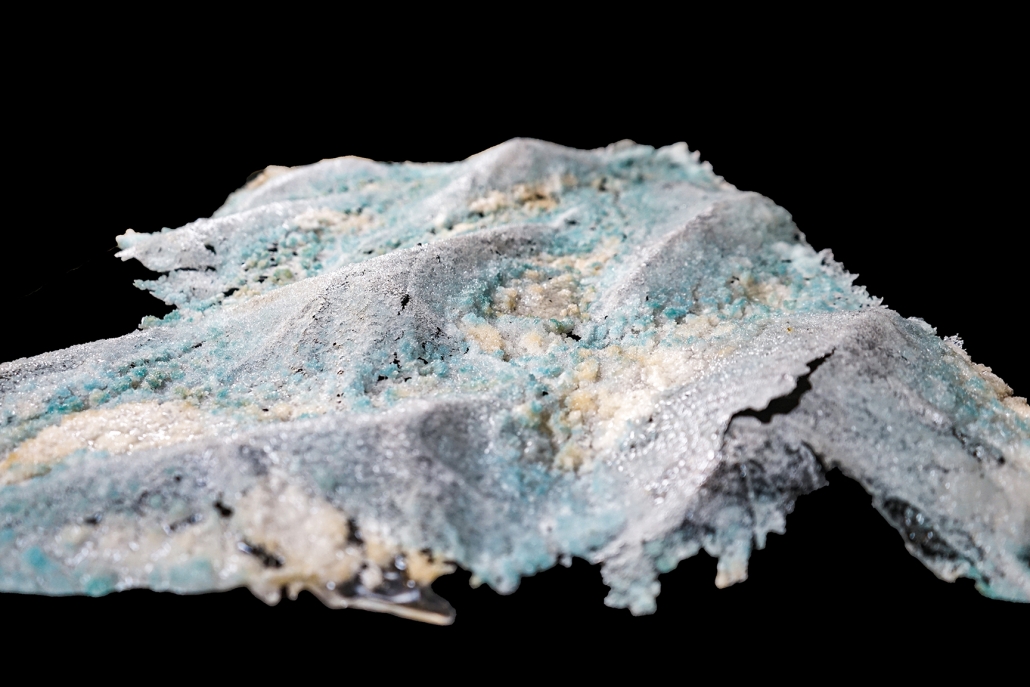
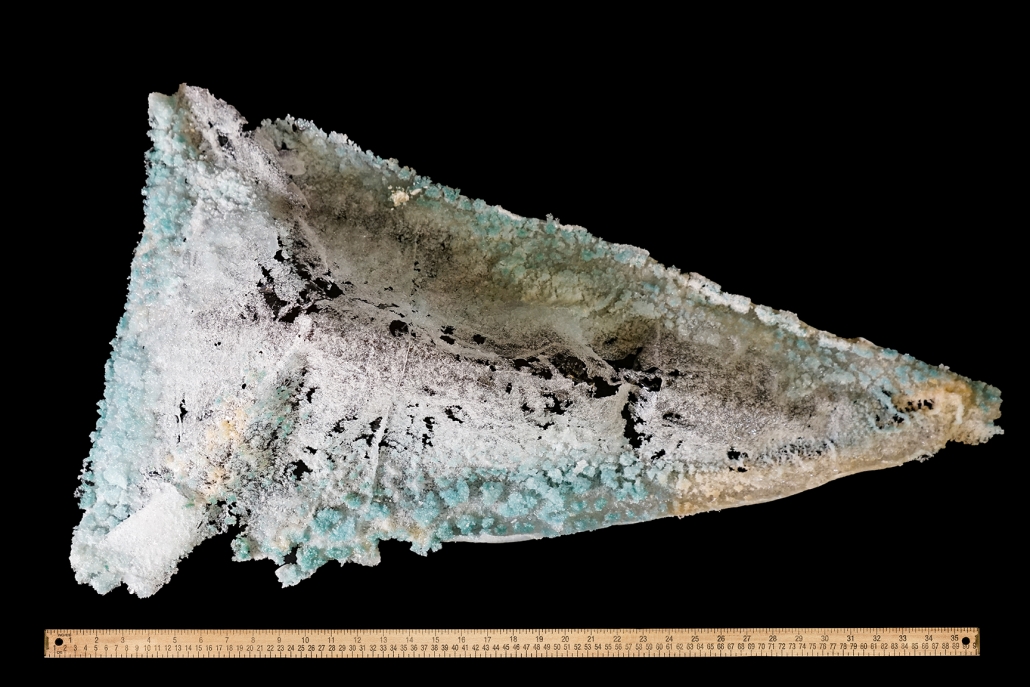
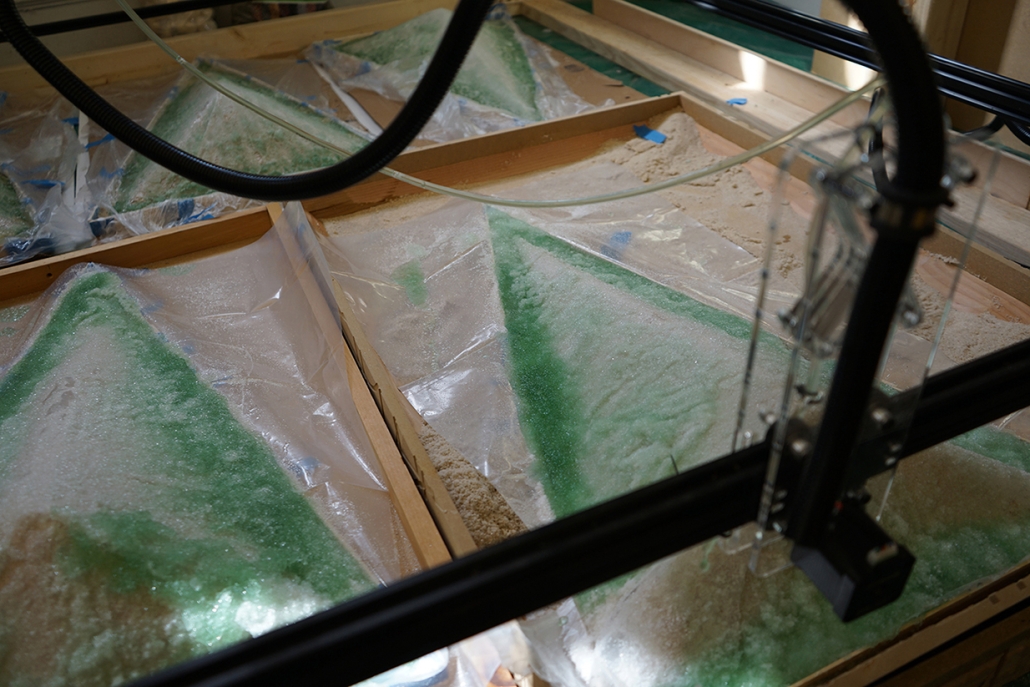
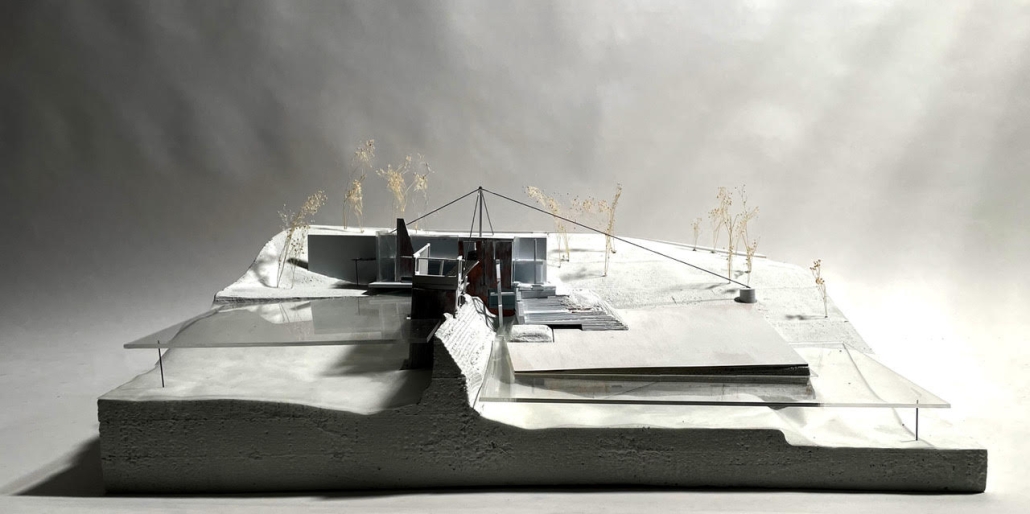
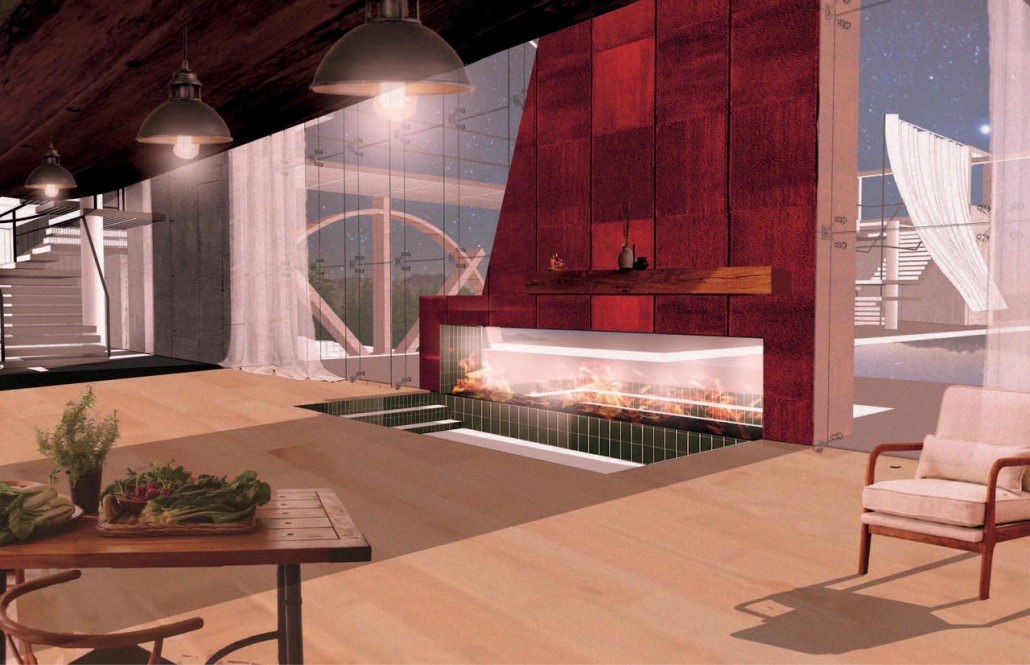
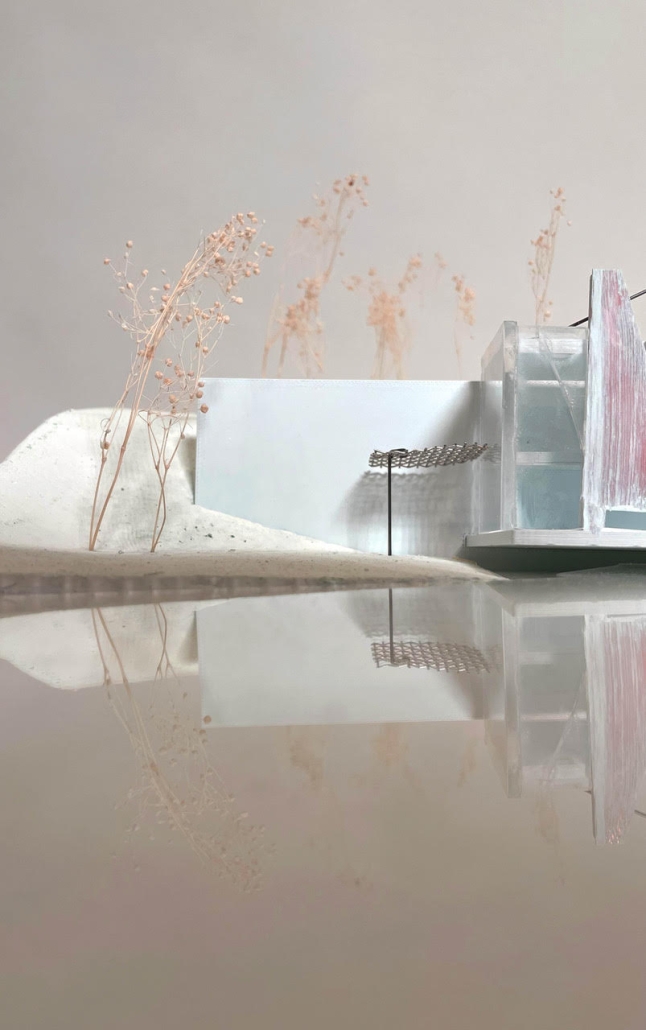
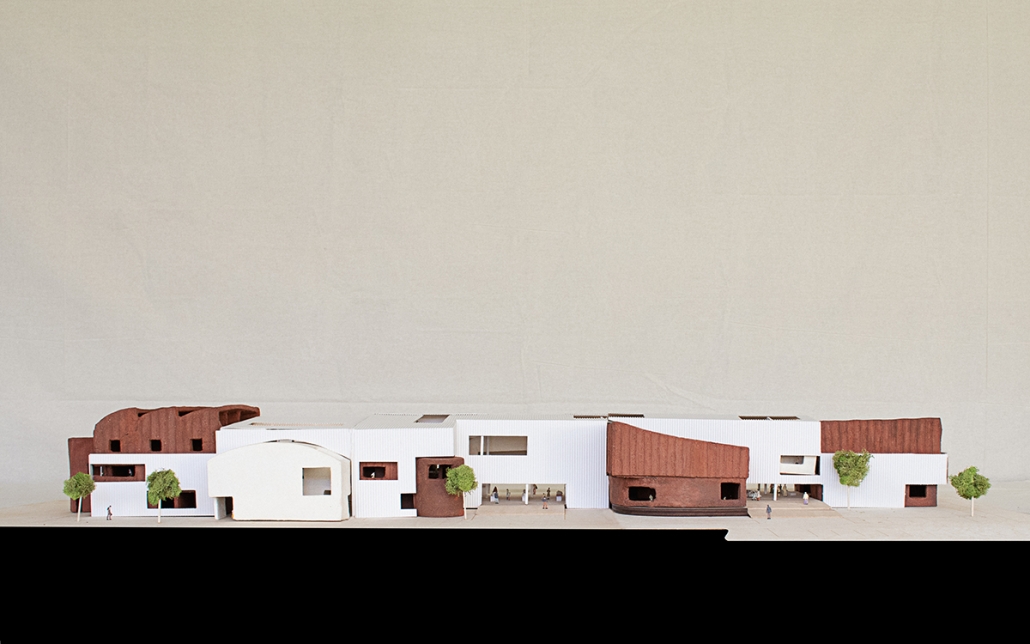
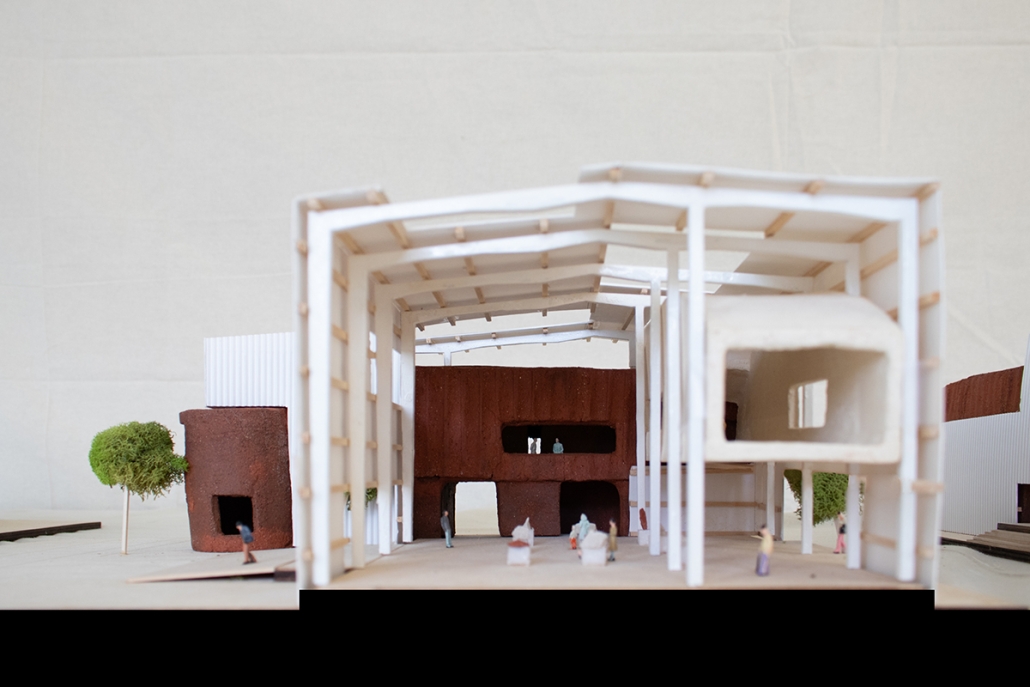
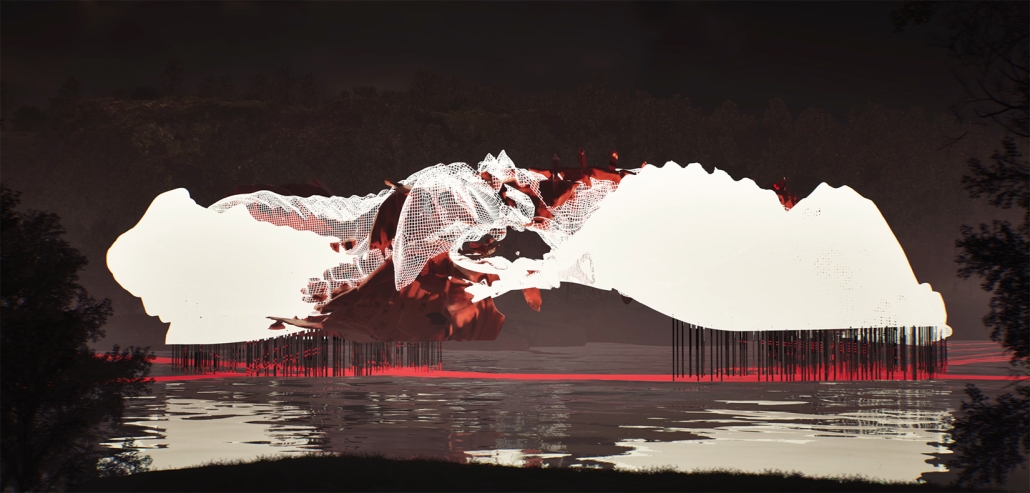
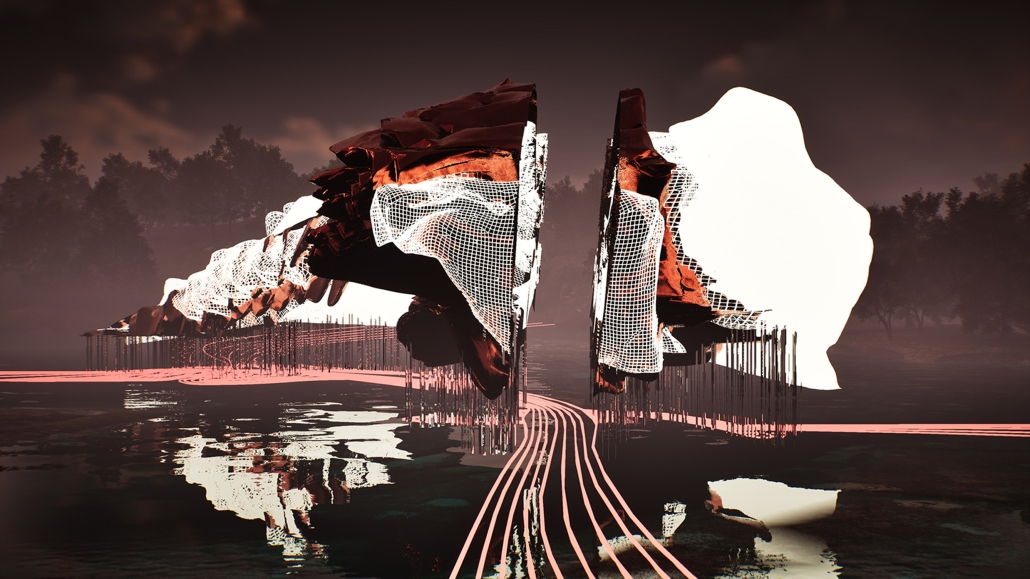
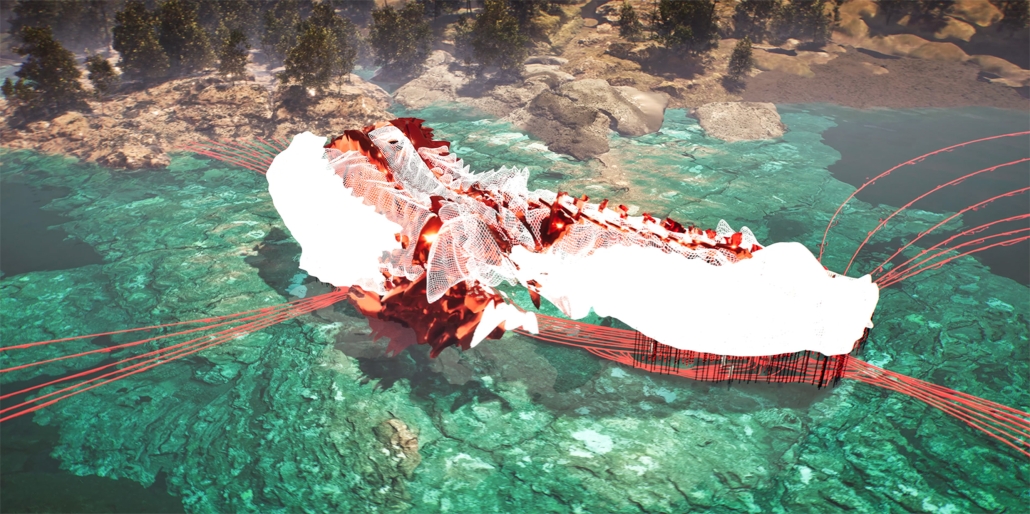
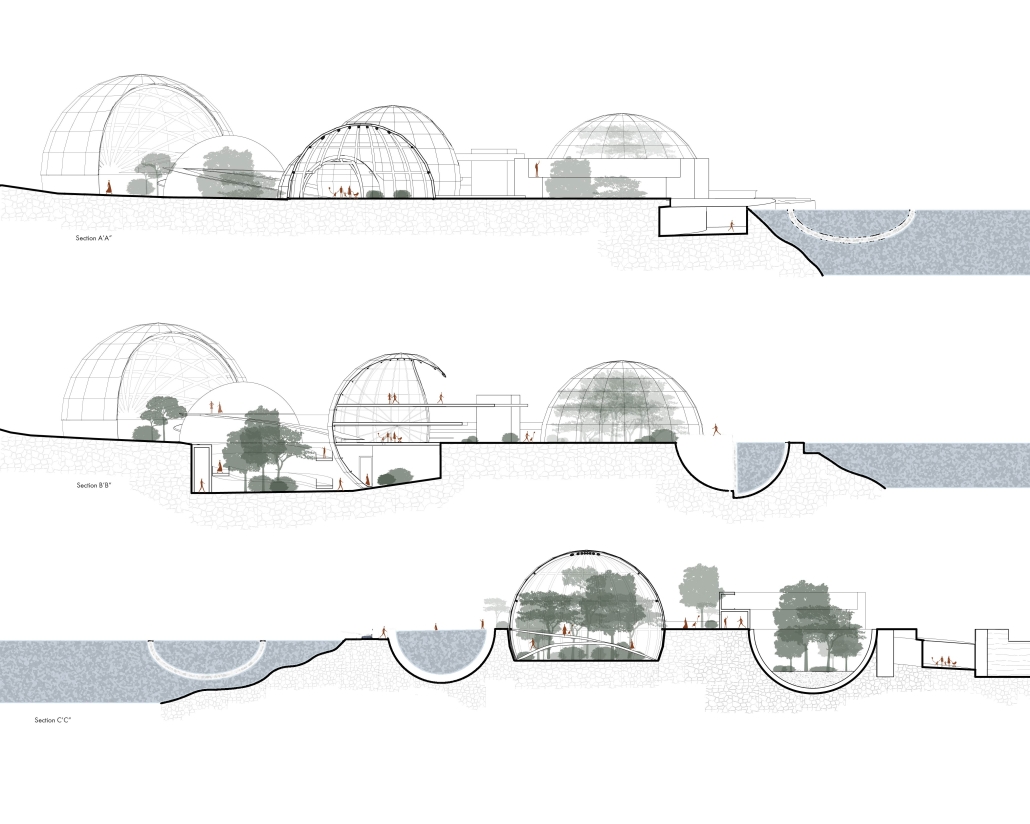
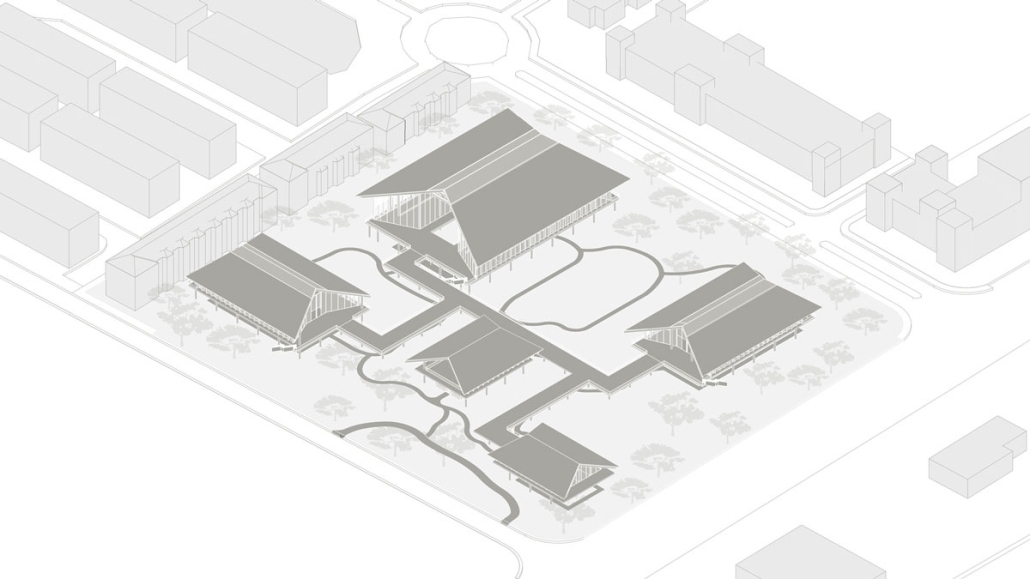
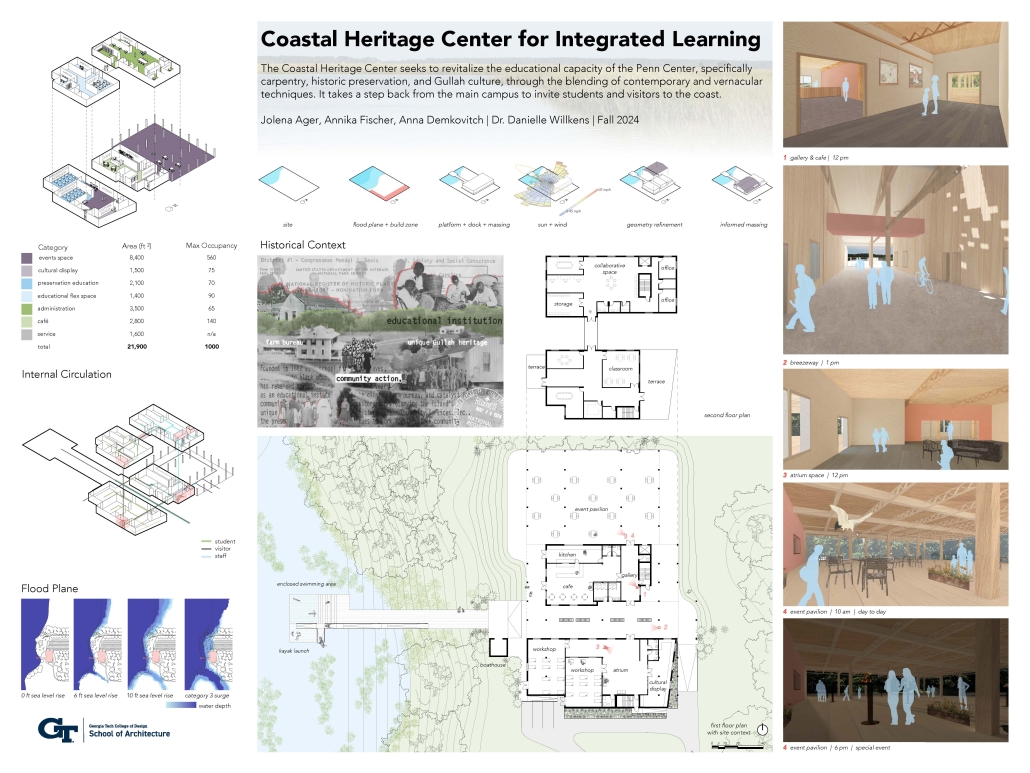
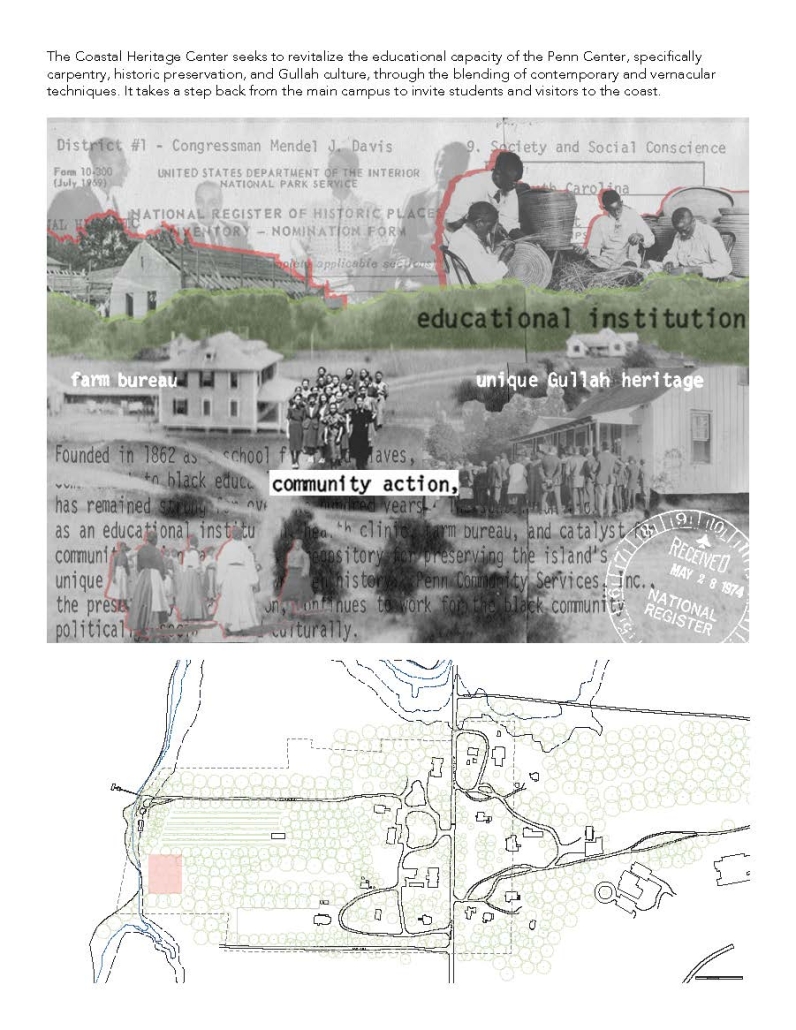
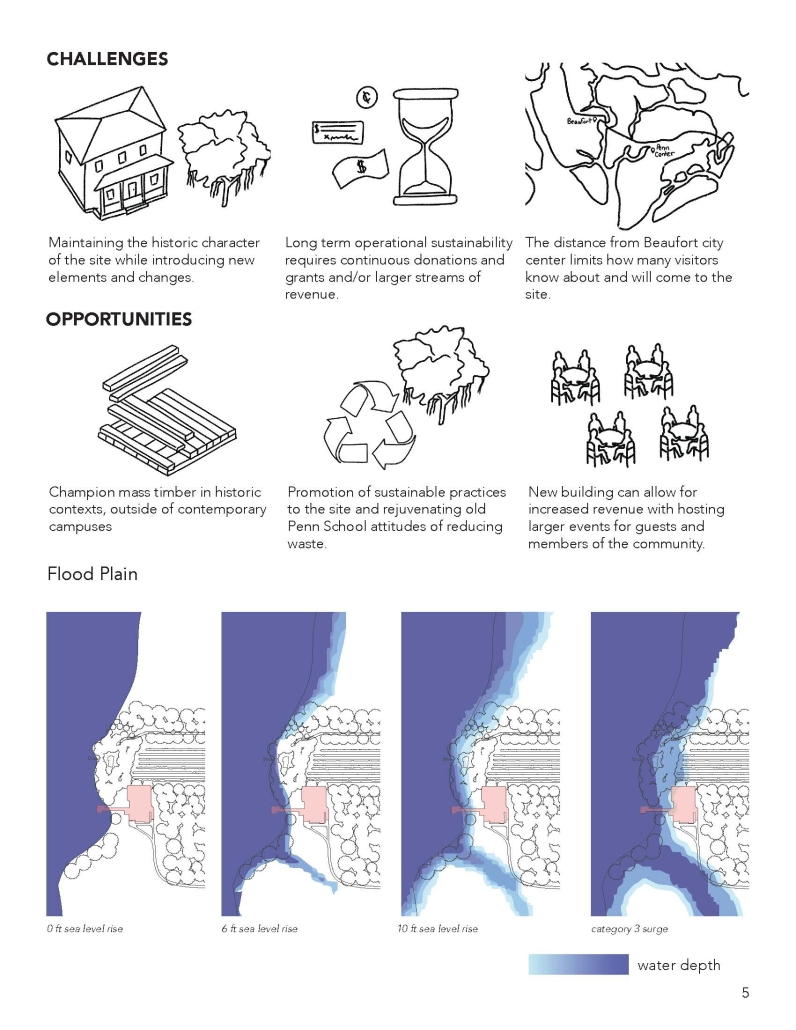
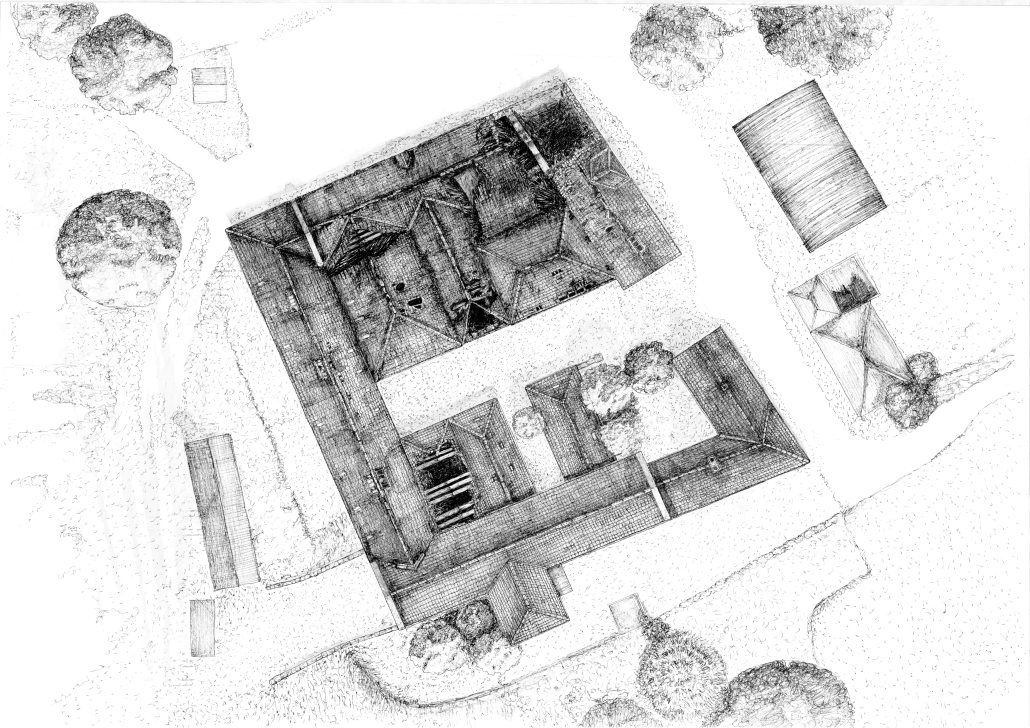
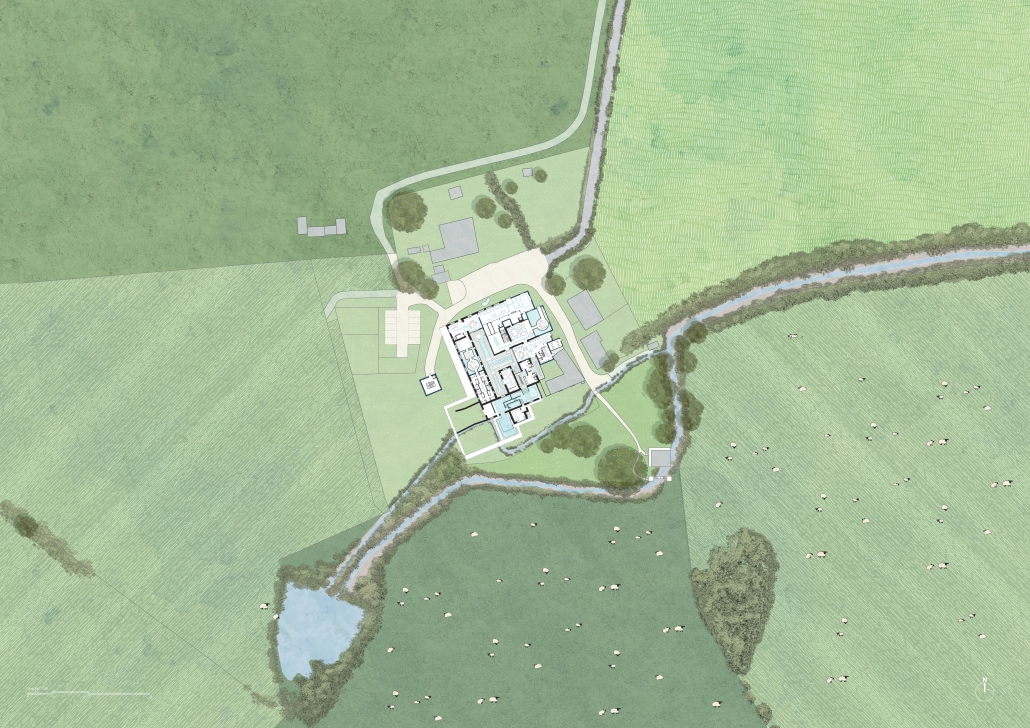
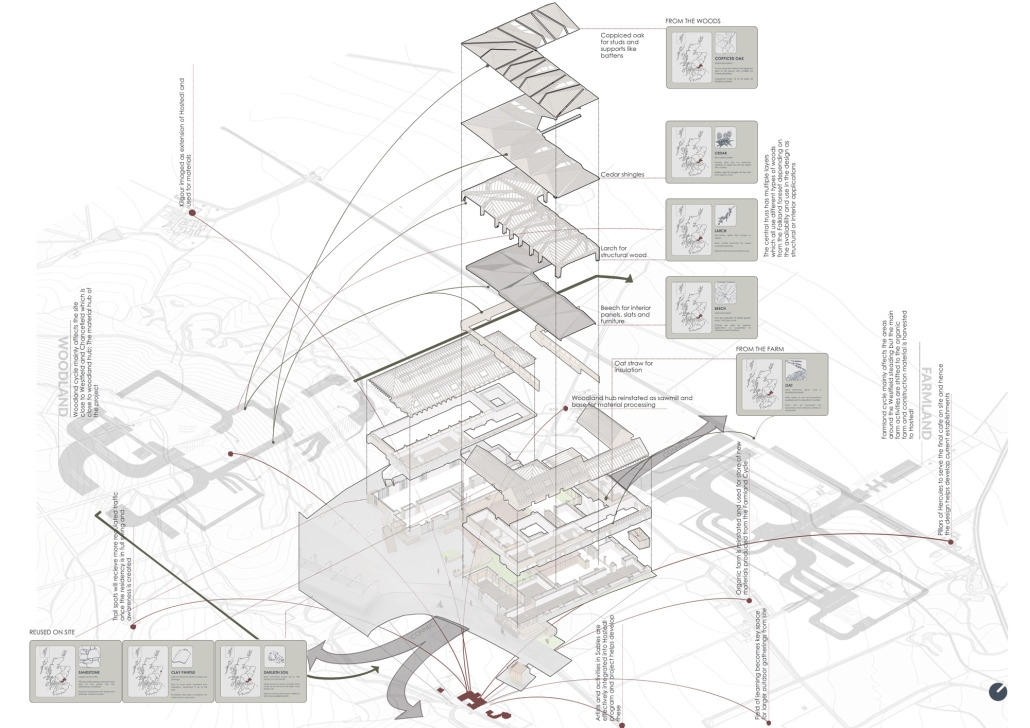
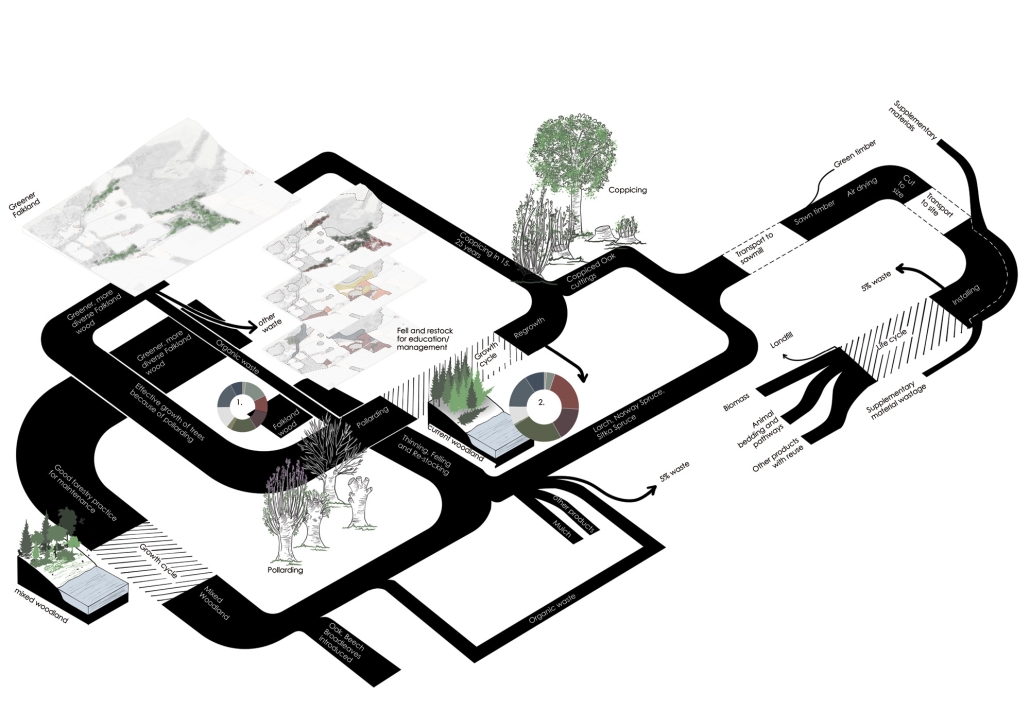
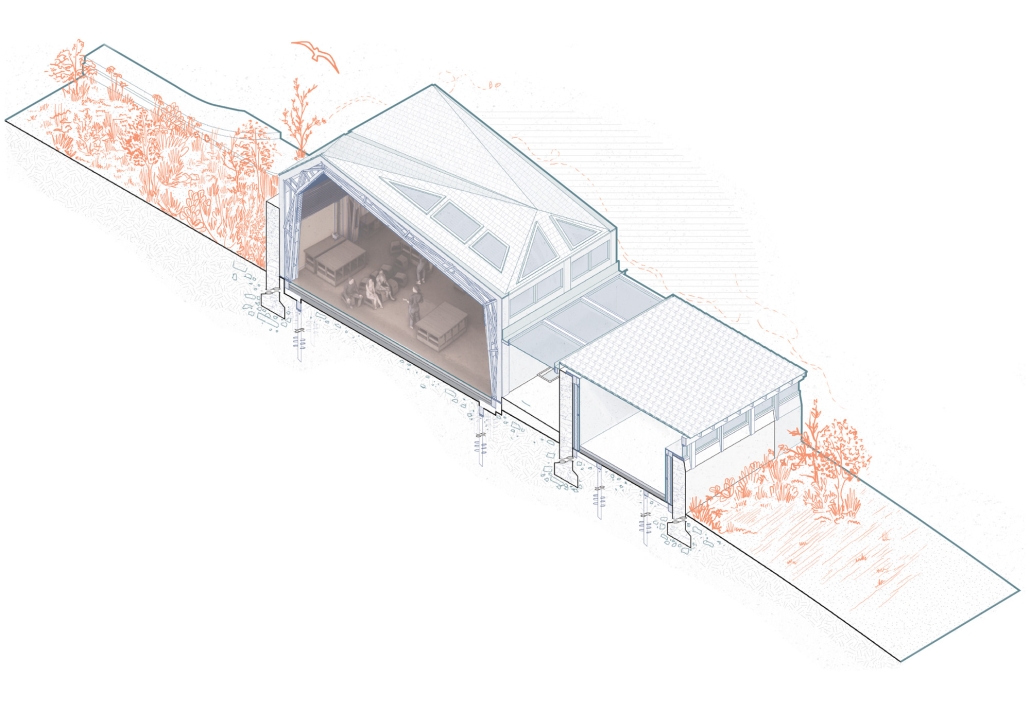
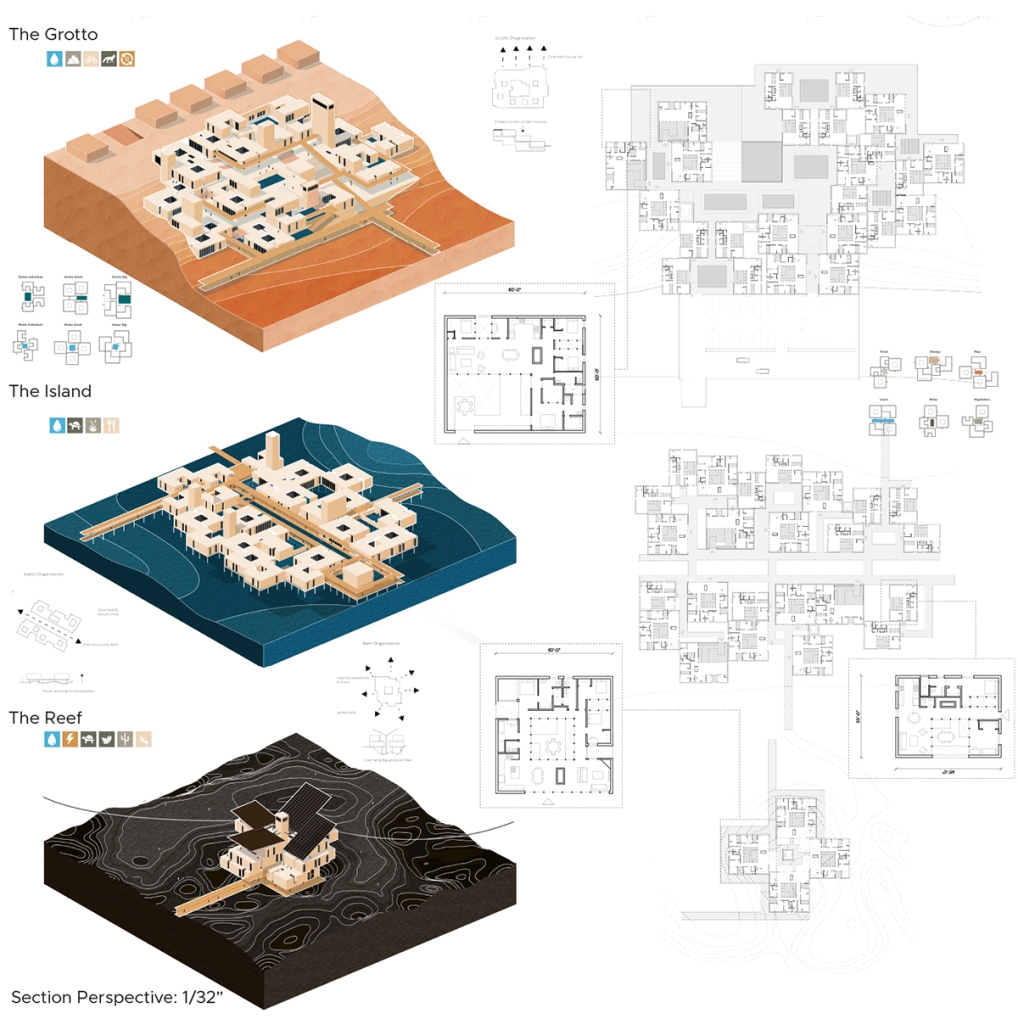
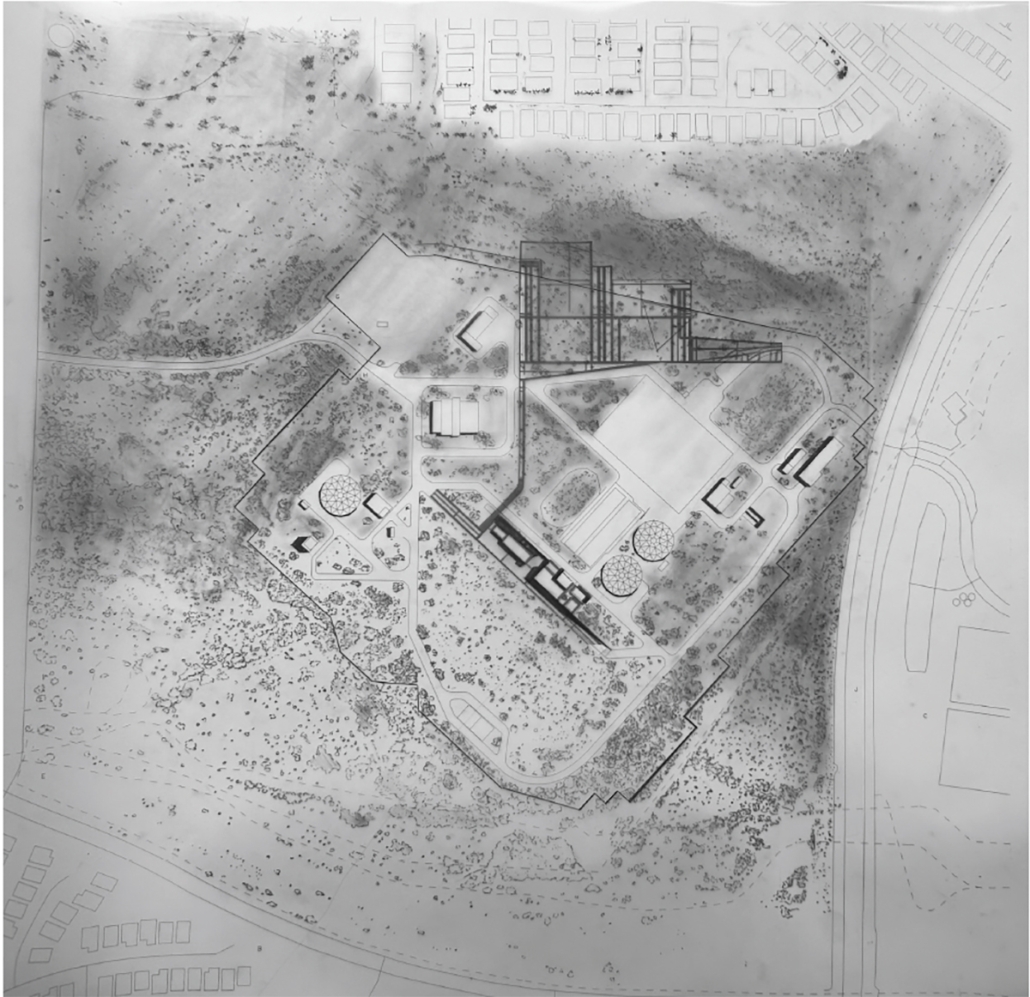
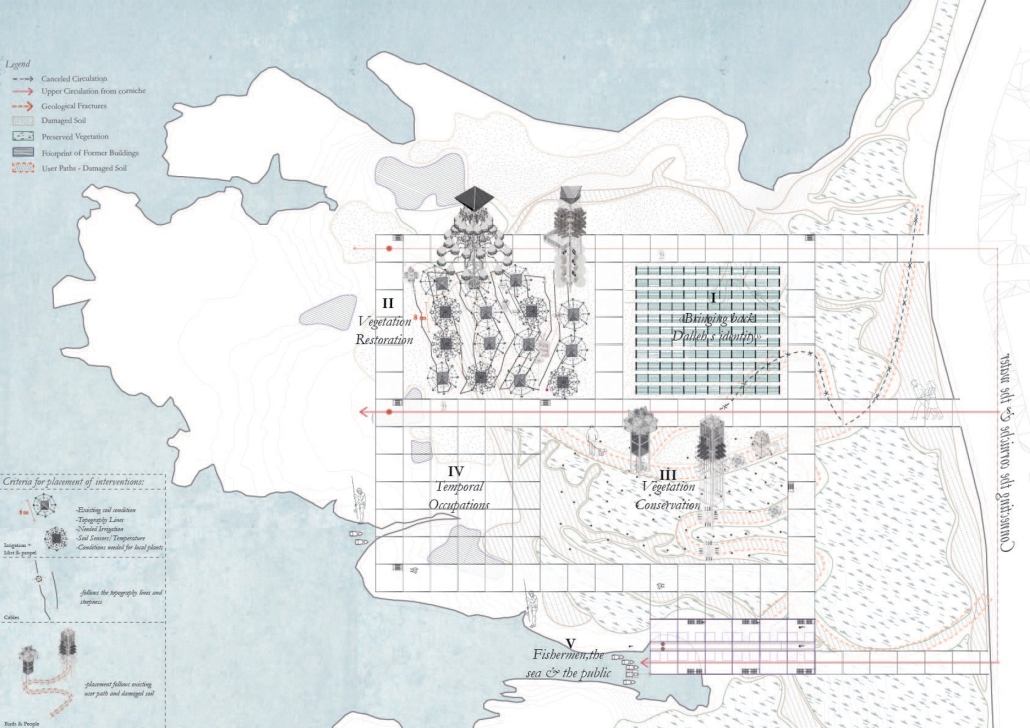
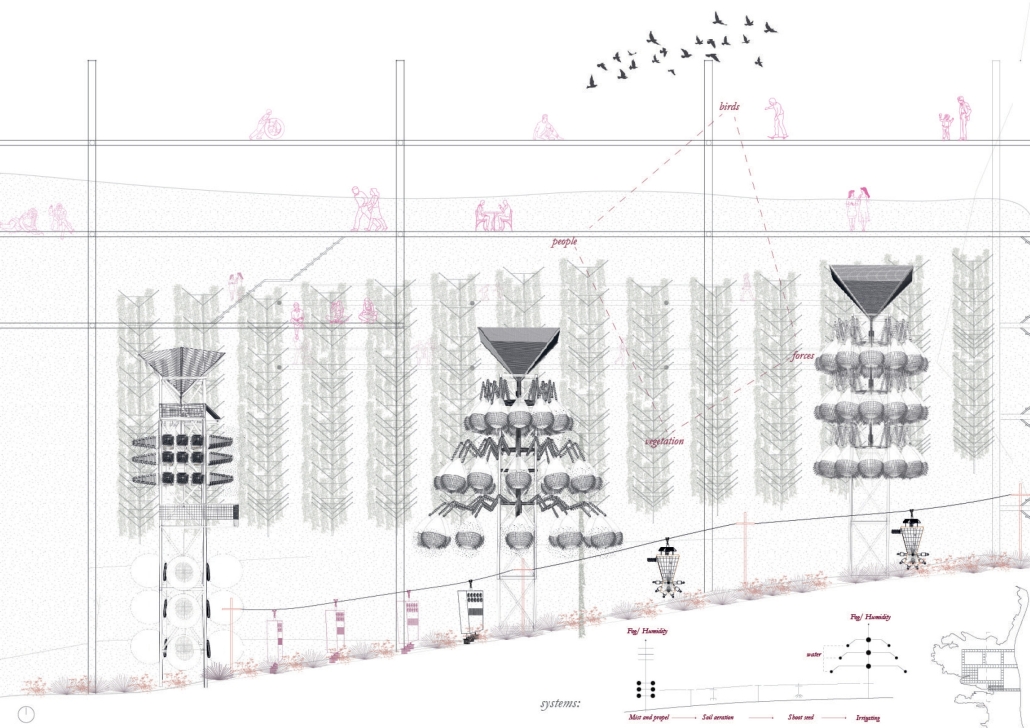
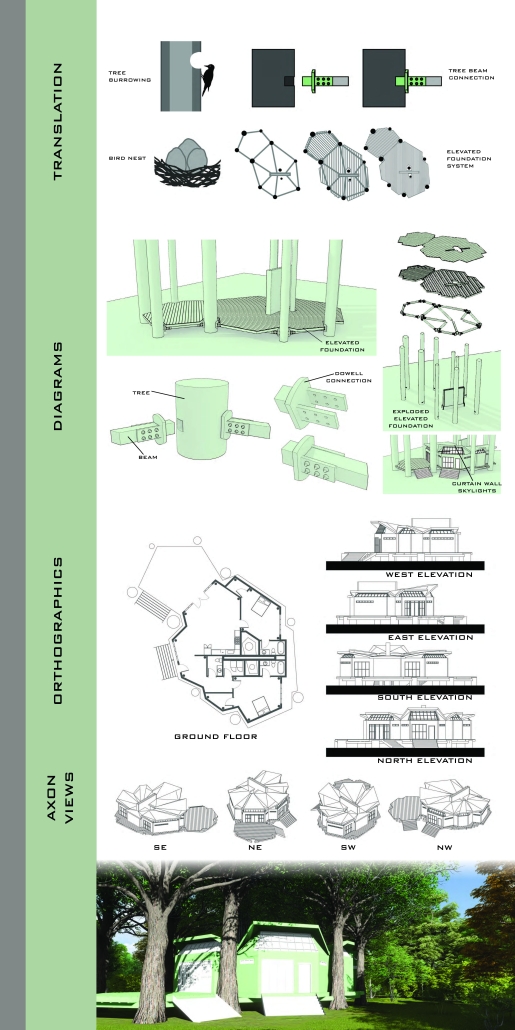
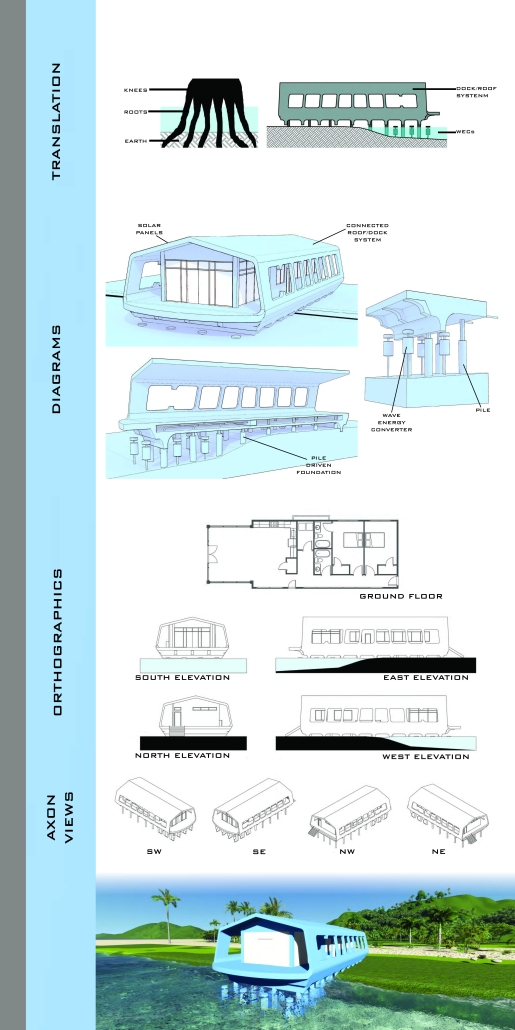
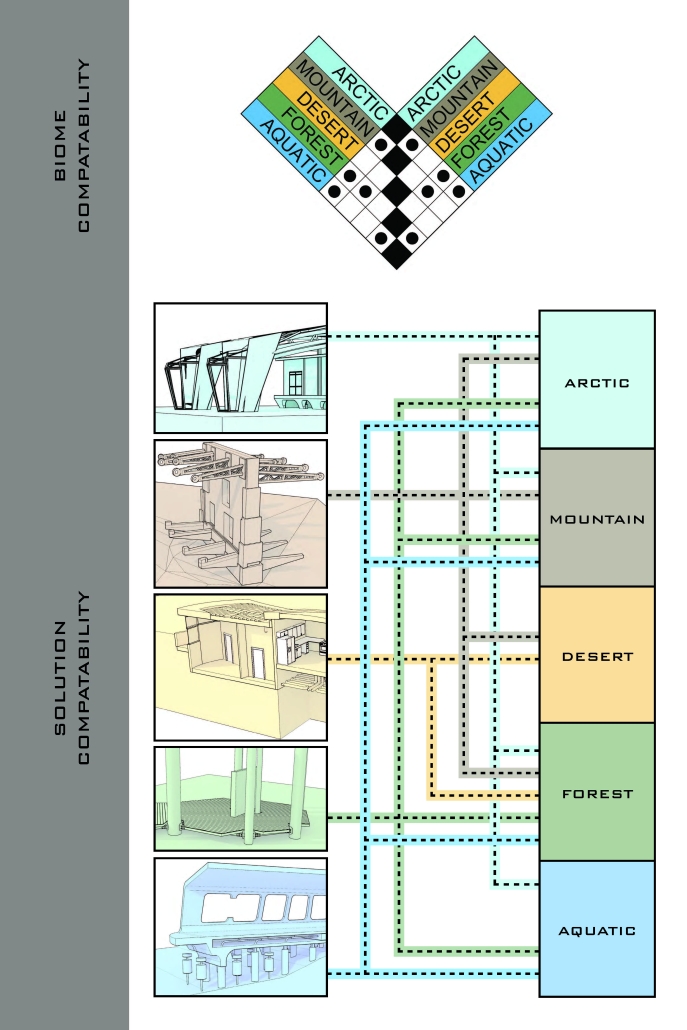
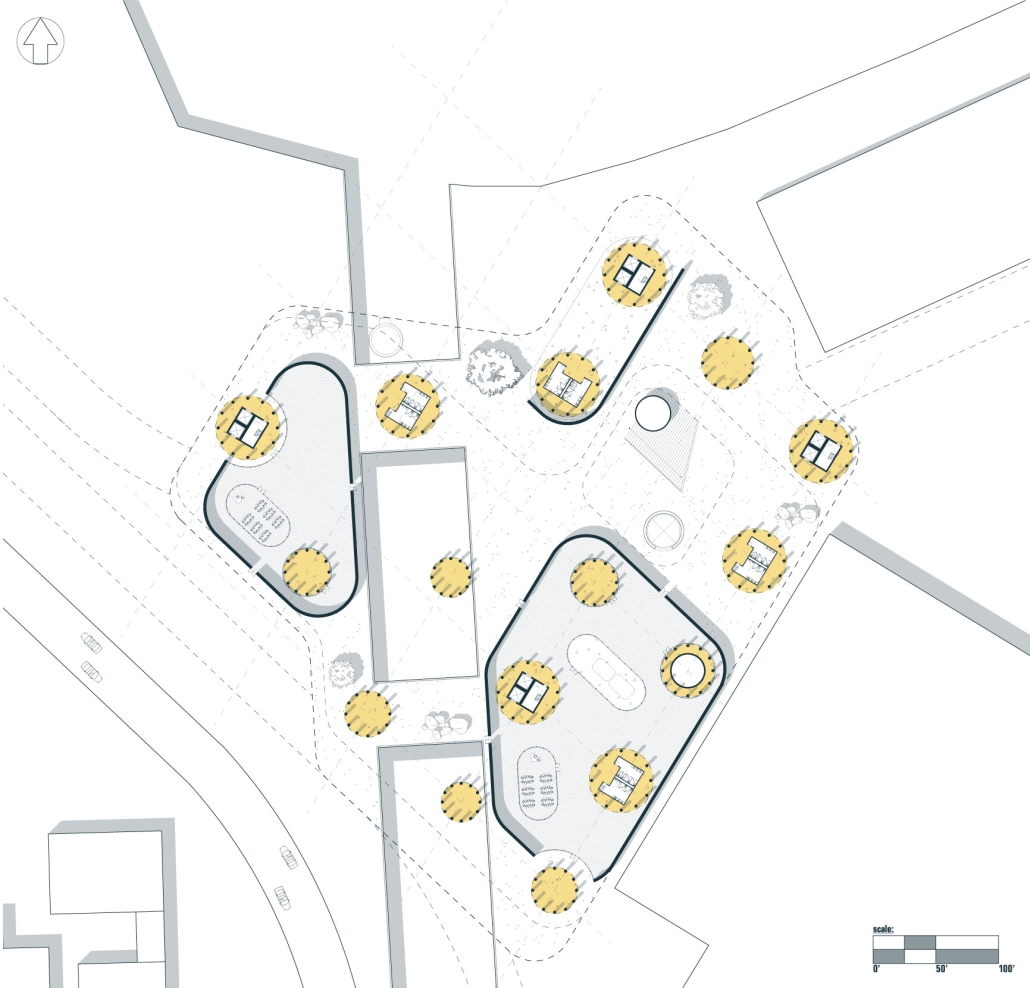
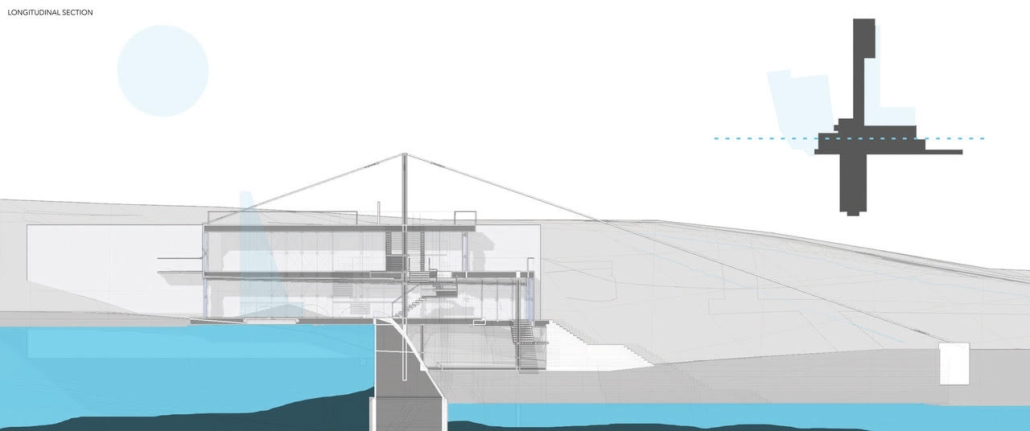
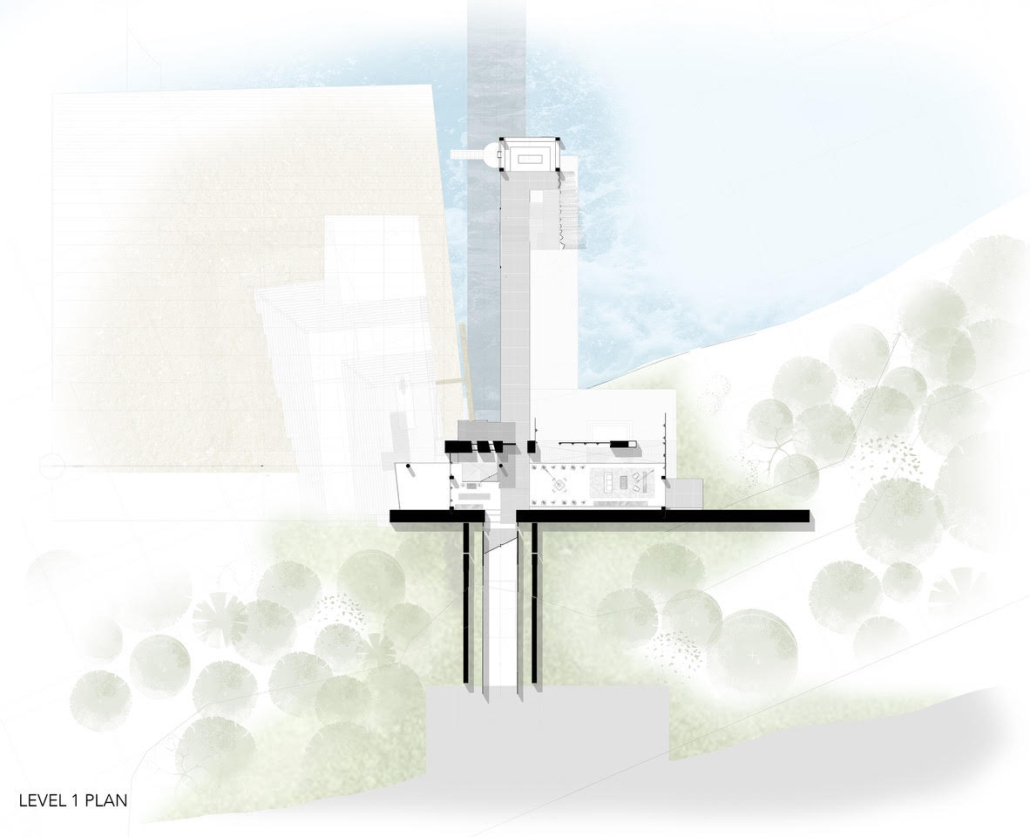
Convergence of Culture, Land, and Sea on a Barrier Island: A New Form of Community on Sapelo Island, Georgia by Cecilia Brock, B.S. in Architecture ’25
University of Virginia | Advisor: Peter Waldman
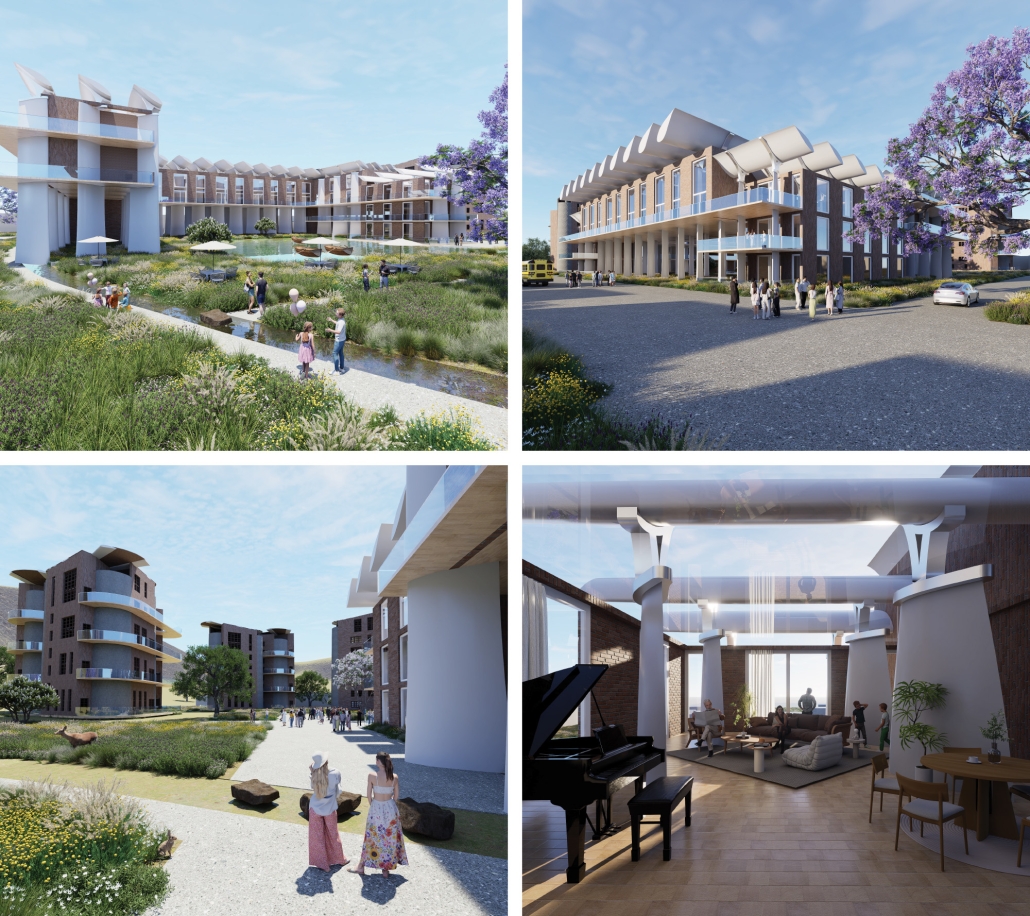
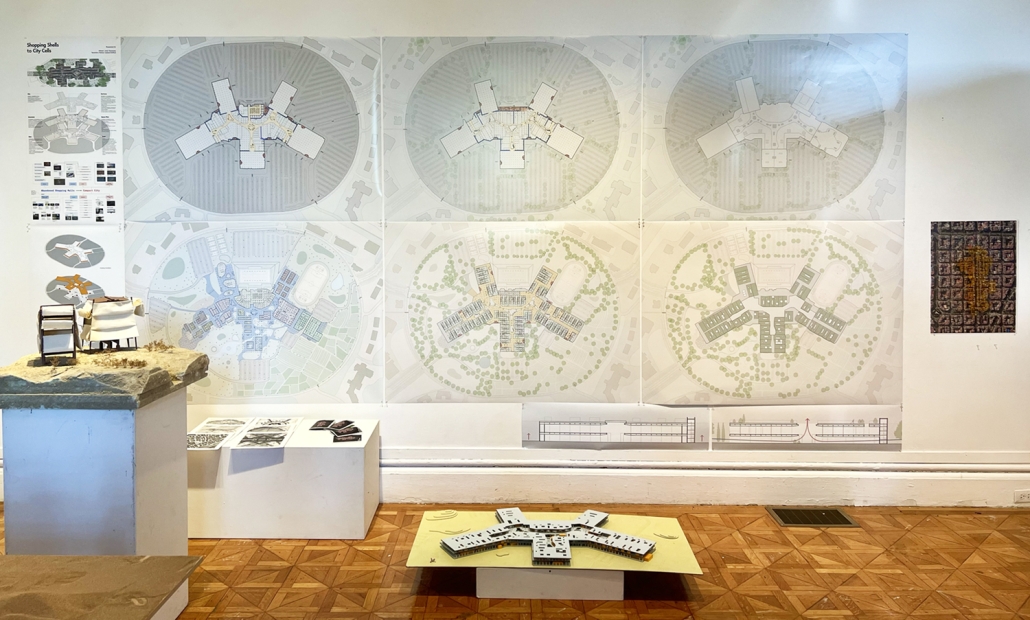
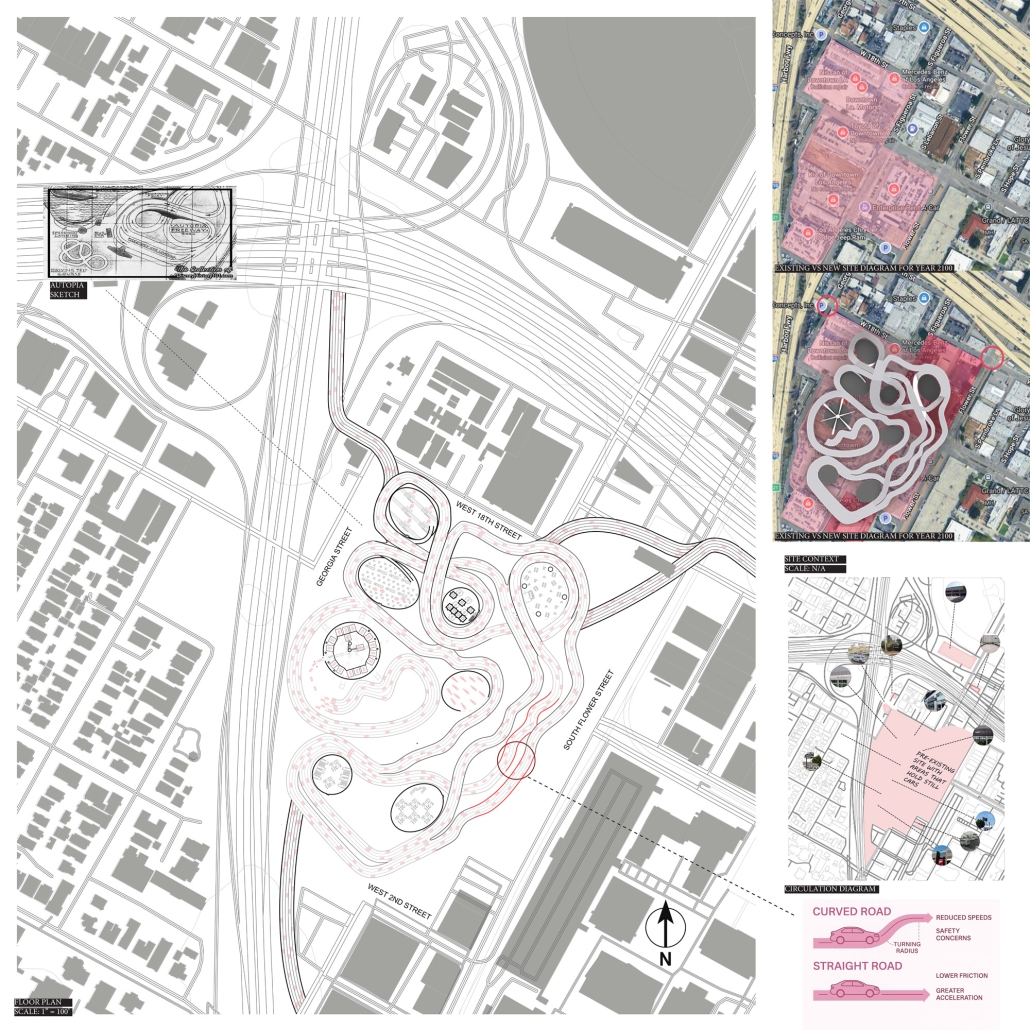
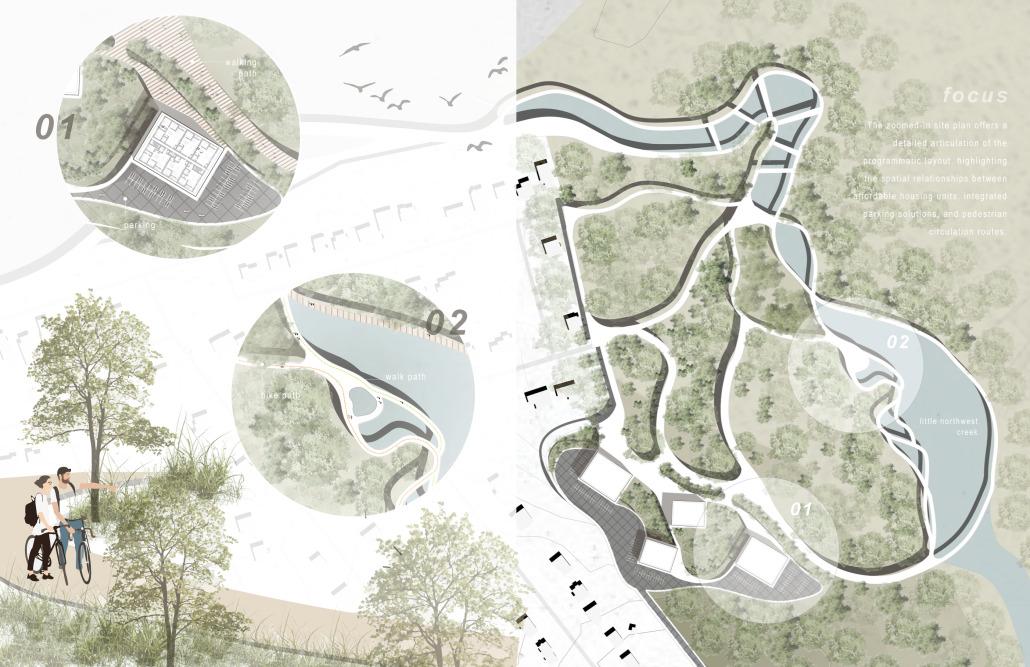
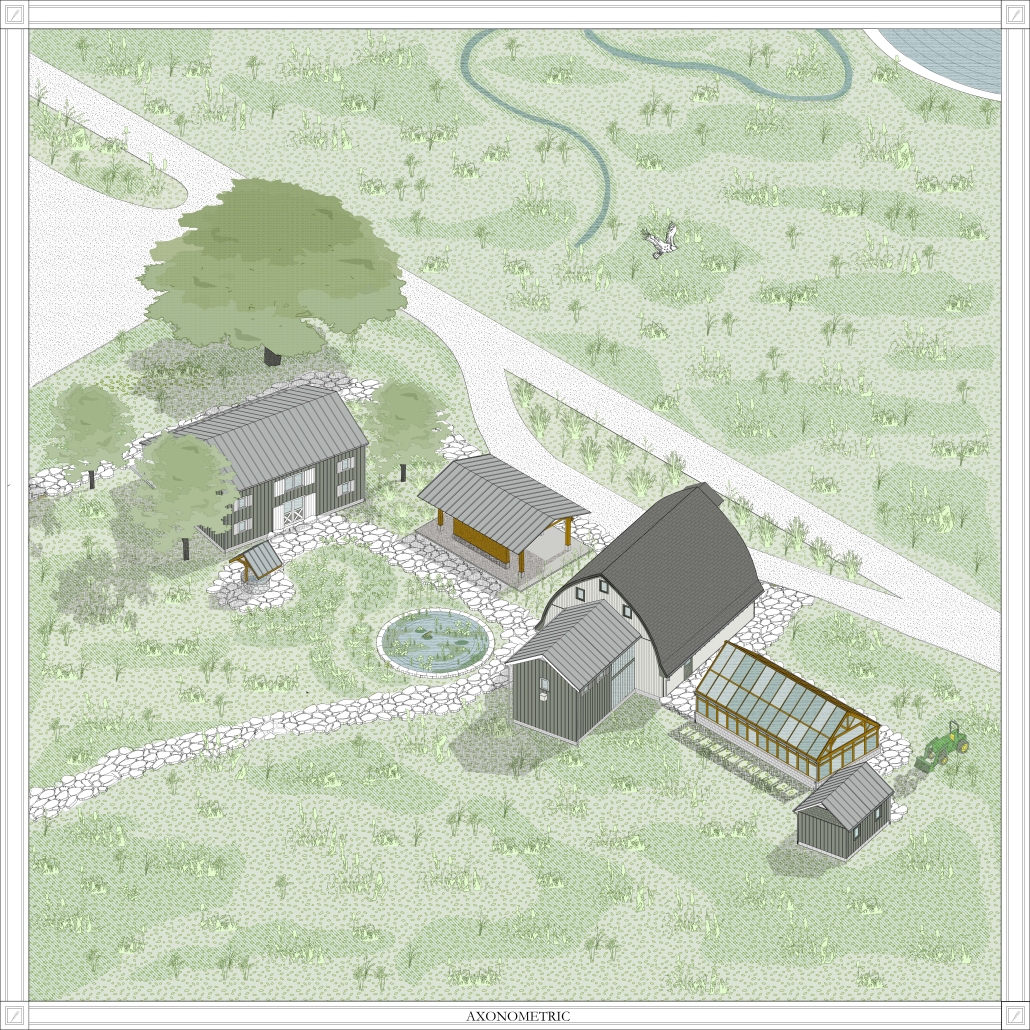
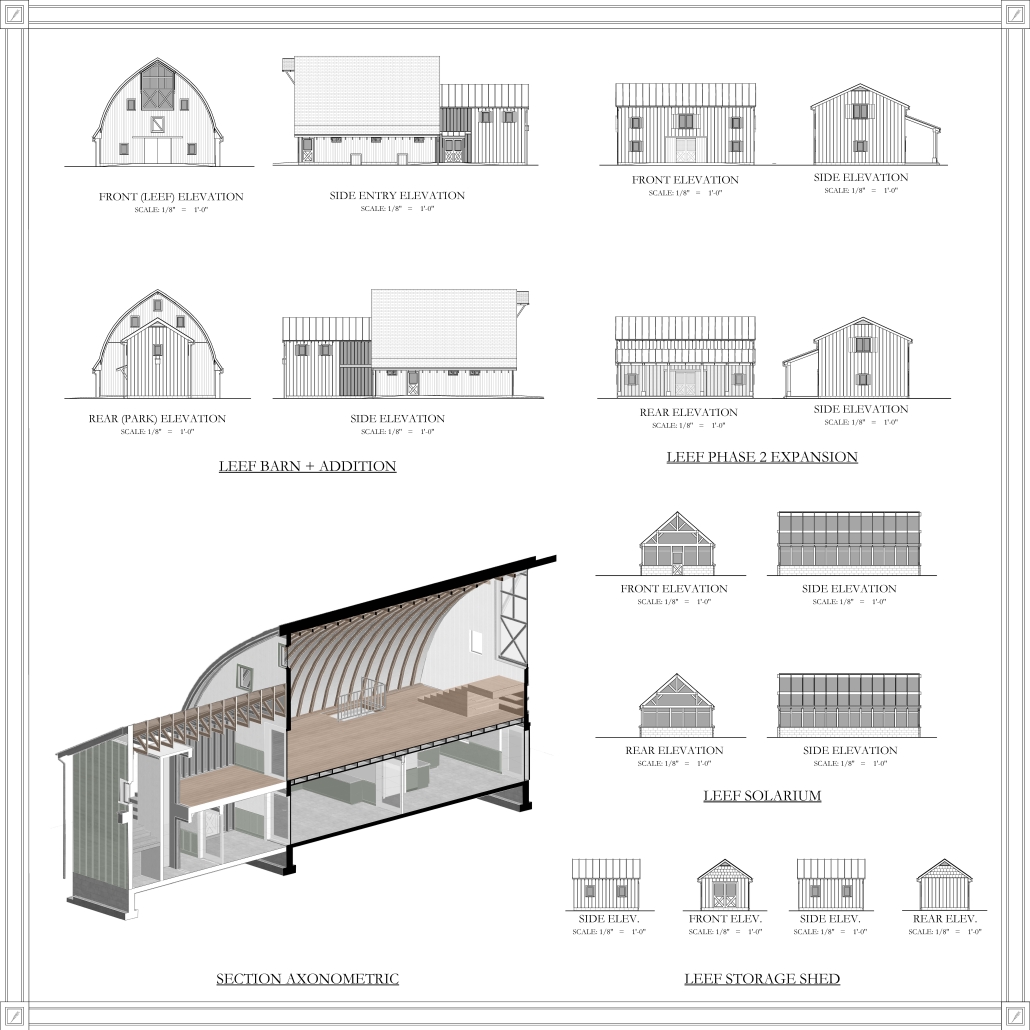
This thesis explores a new model of coastal community living on Sapelo Island, rooted in the cultural and environmental knowledge of the Gullah Geechee people of Coastal Georgia. Rather than simply preserving the existing community of Hogg Hammock, the project envisions a future community on the north end of the island where marine farming and agriculture sustain both the local economy and the local population.
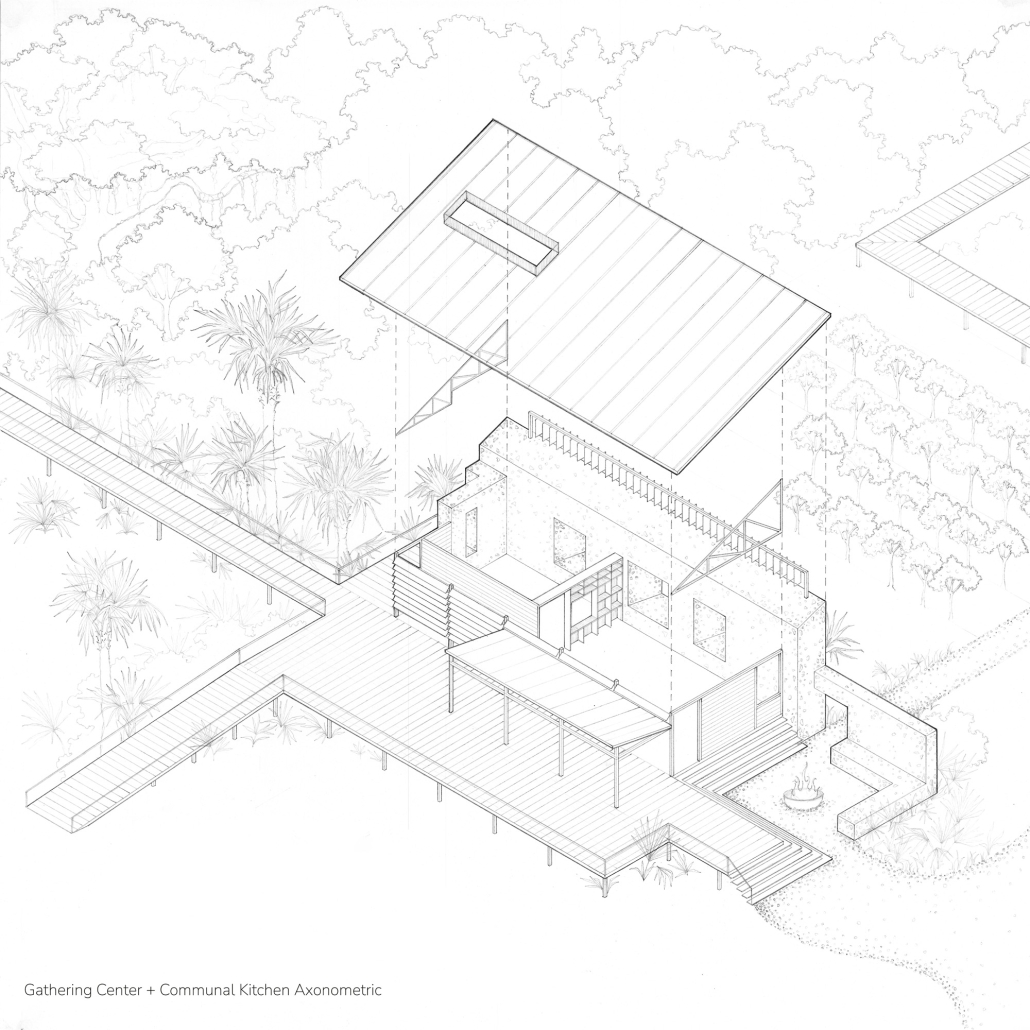
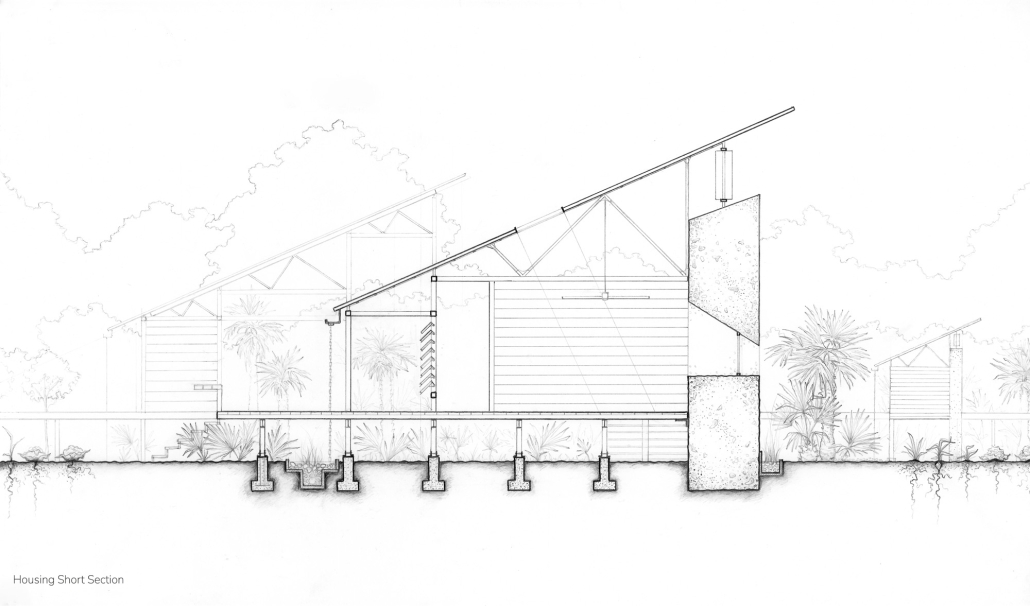
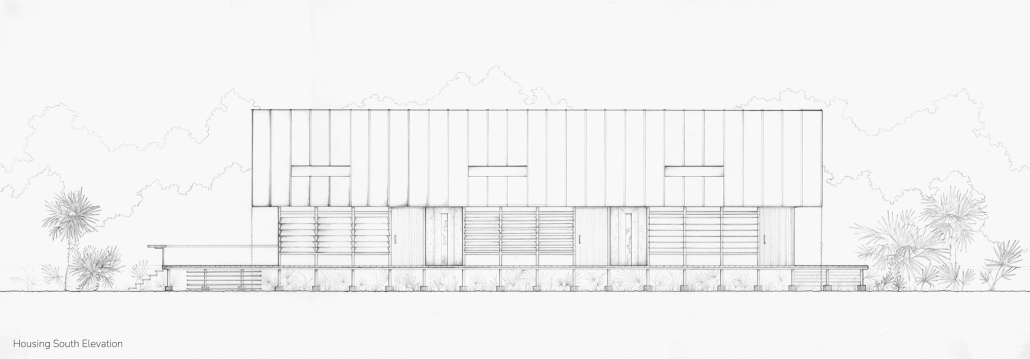
Explored entirely through hand-drawing, the design moves beyond conventional buildings, focusing on spaces defined by activity rather than form. It considers housing not as isolated structures but as a network of small, essential elements—tools for living that support daily rhythms, seasonal changes, and the evolving needs of the community. Inspired by the traditional Saltwater Geechee family compound, the proposal prioritizes flexible, interconnected spaces where work, gathering, and sustenance shape the built environment. Local materials are prioritized, with the structures being composed of wood from the site, tabby made from native oysters, and salvaged metal.
At the heart of the project is a sea-farming operation, extending from the land into the water as a continuous, working landscape from west to east. Housing clusters, gardens, porches and paths emerge from this axis, fostering a way of life where shelter, work, and nature are inseparable. This project ultimately serves as a temporary home for students from the University of Georgia Marine Institute and volunteers from Sapelo’s SOLO Program, who support the cultivation of the island’s three main agricultural products: Purple Sugarcane, sour oranges, and Sapelo Red Peas. By designing for the patterns of daily life—hour to hour, season to season—the project aims to create an adaptable, living architecture that strengthens both community and environment.
This project received Highest Honors for 4th year Thesis, University of Virginia Pre-Professional Program.
Instagram: @cecilia.brock
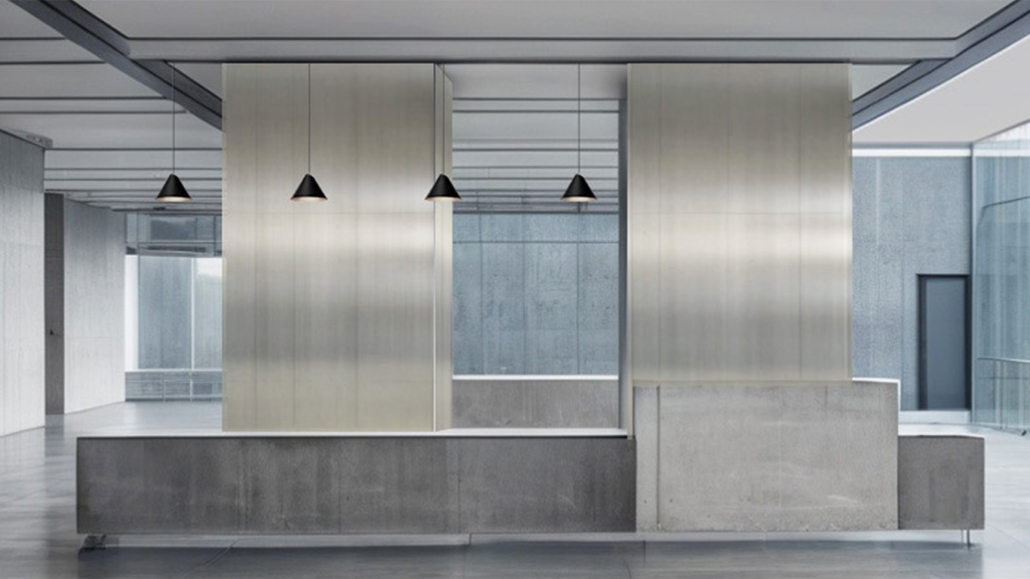
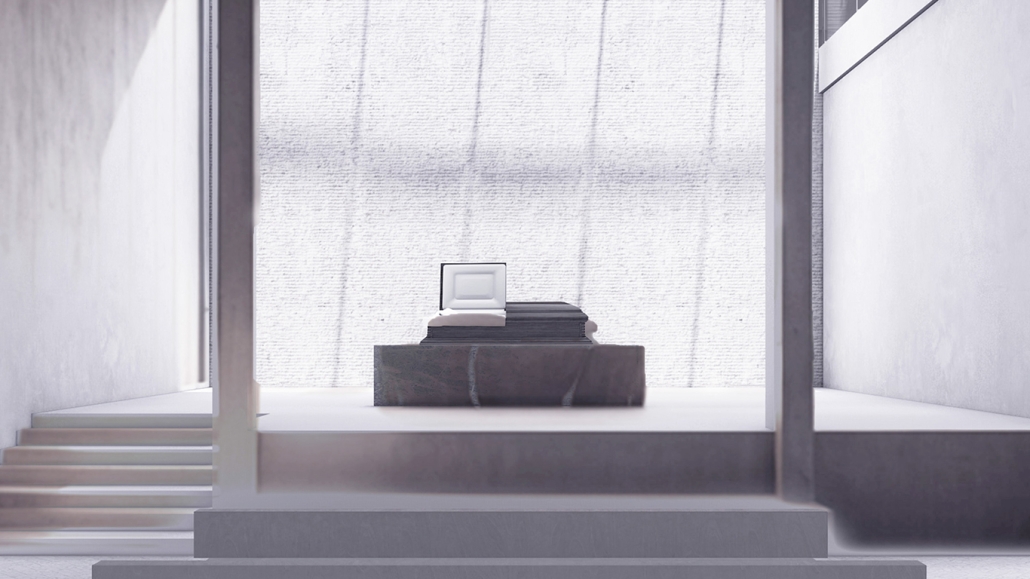
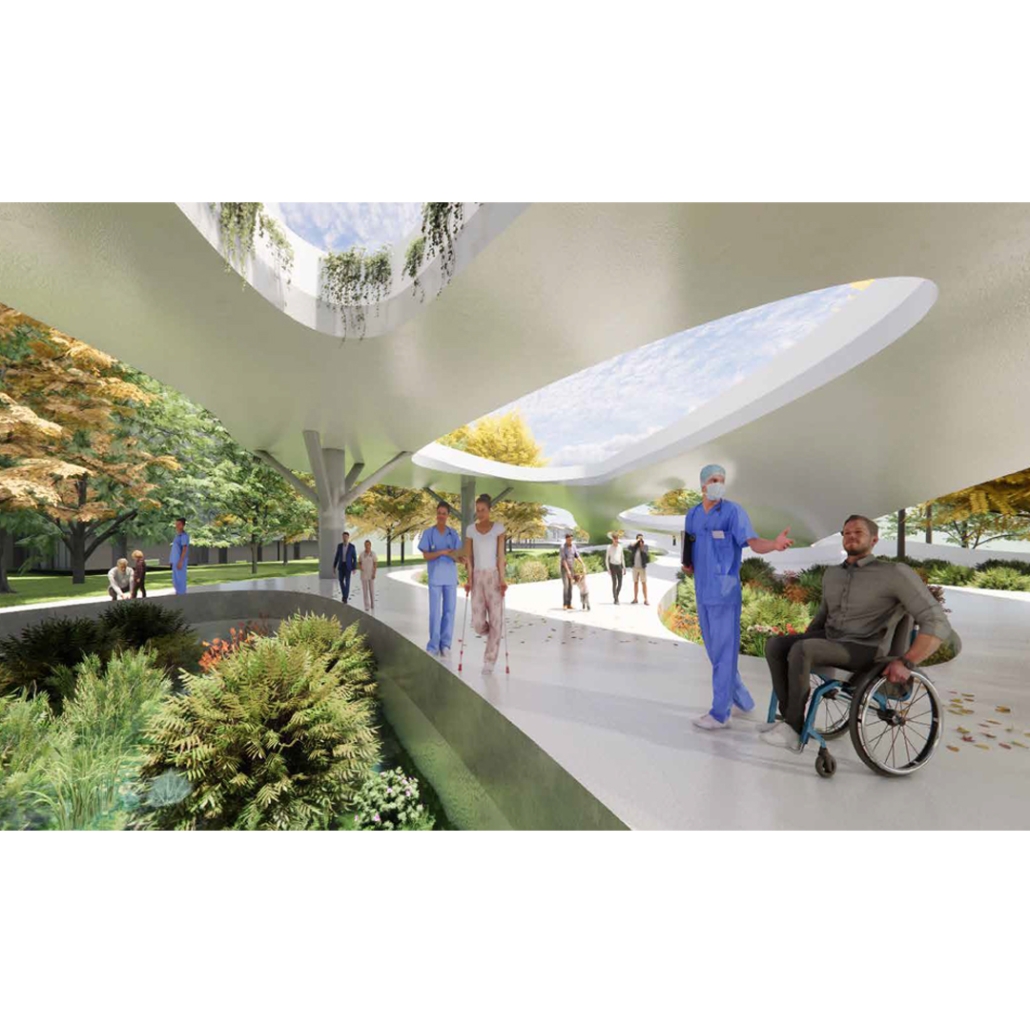
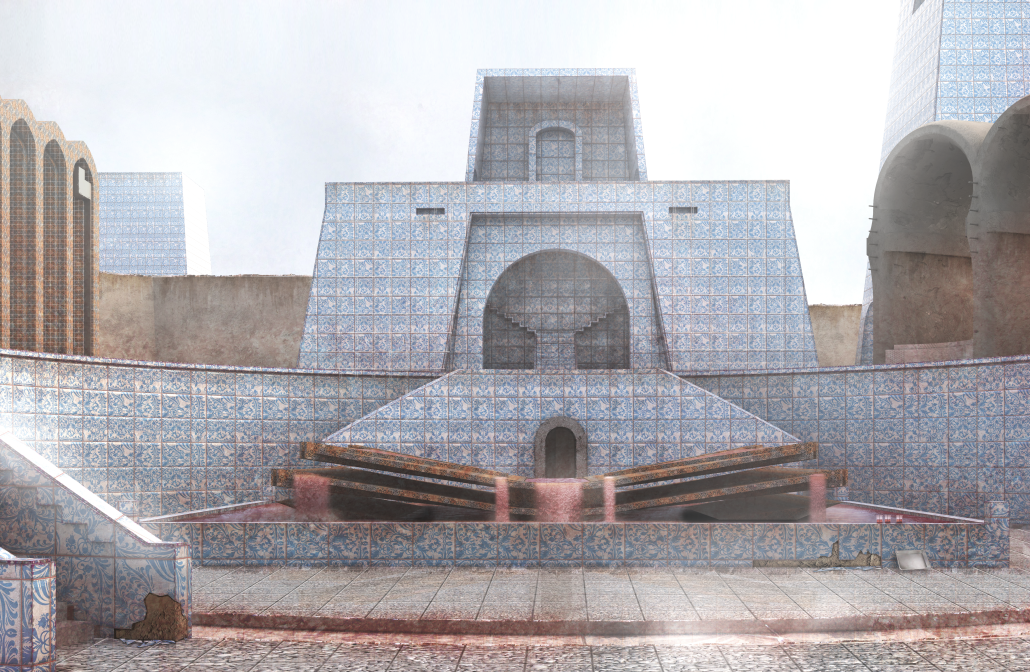
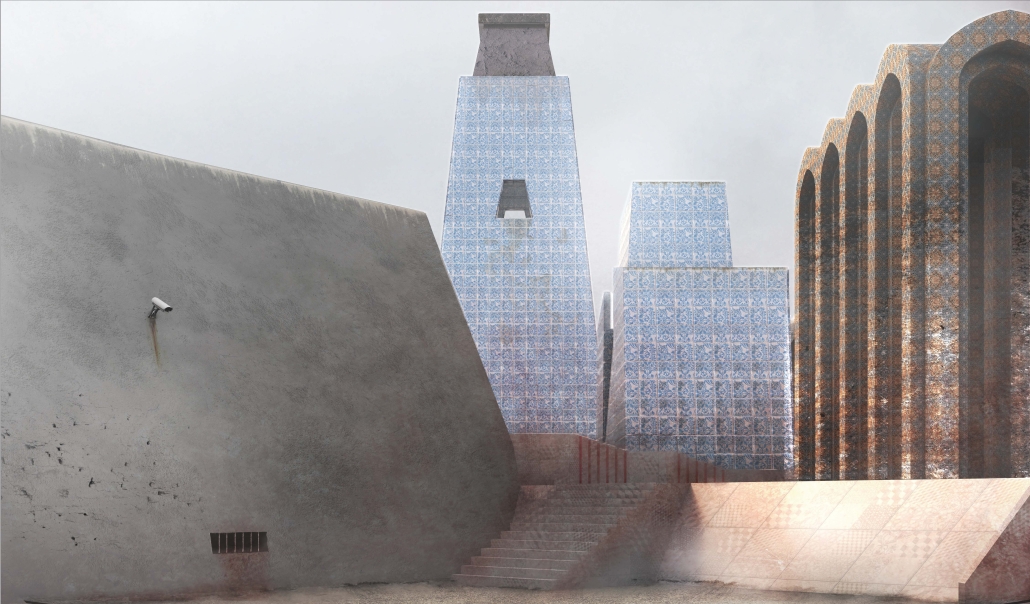
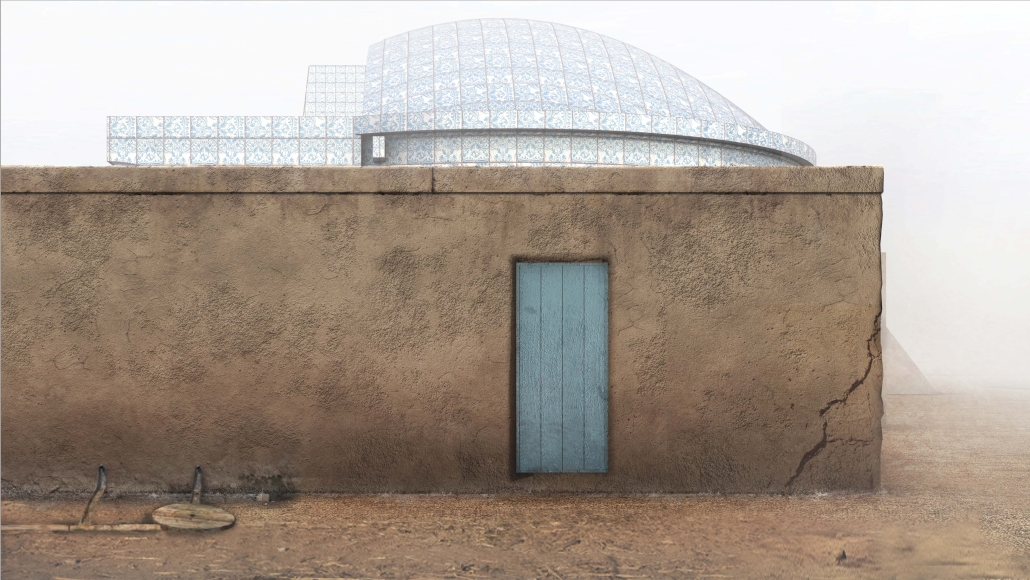
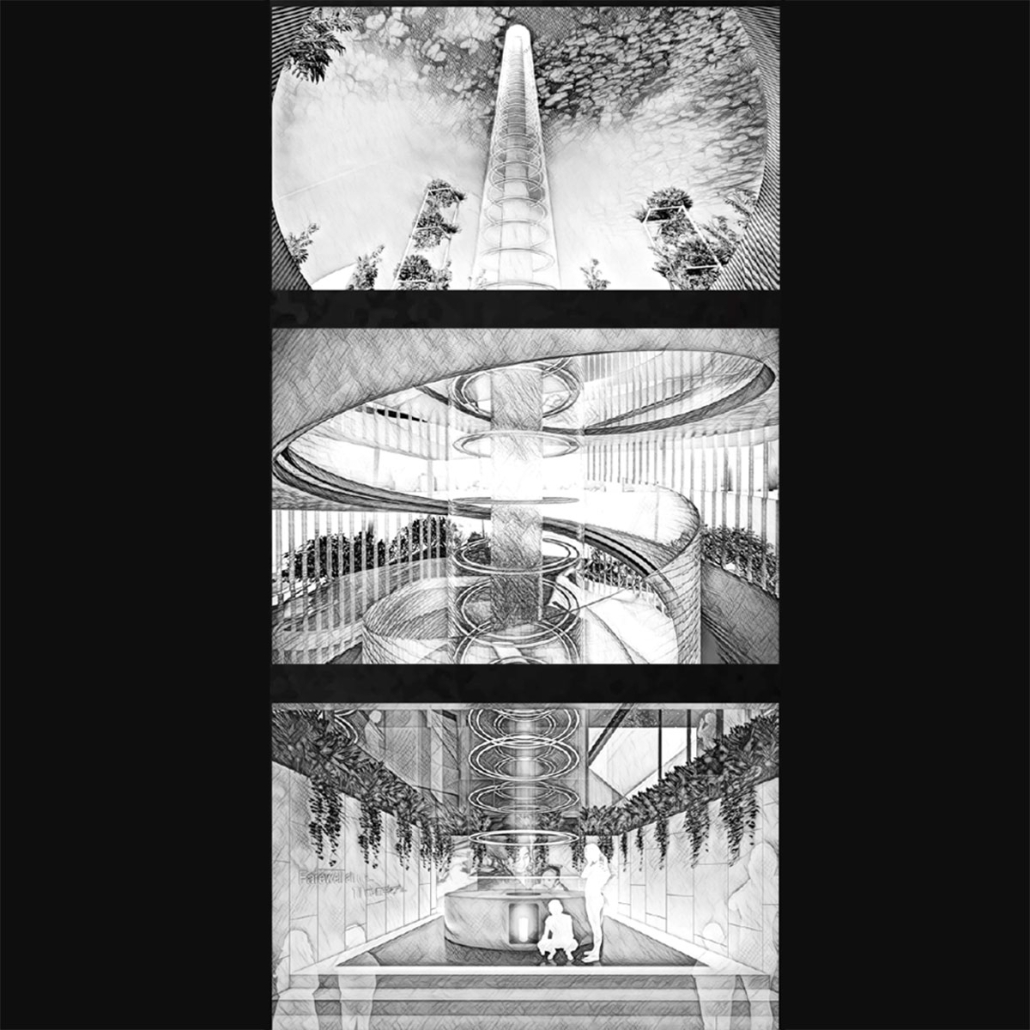
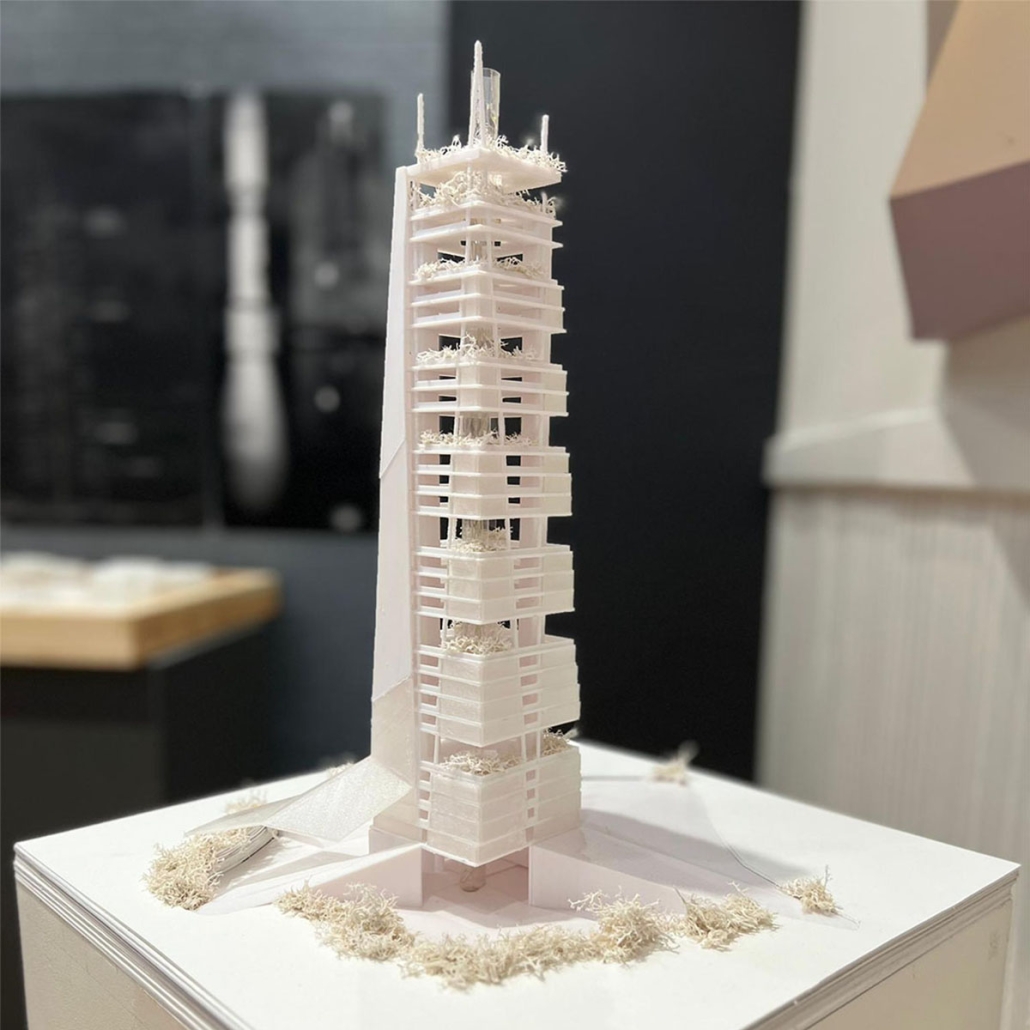
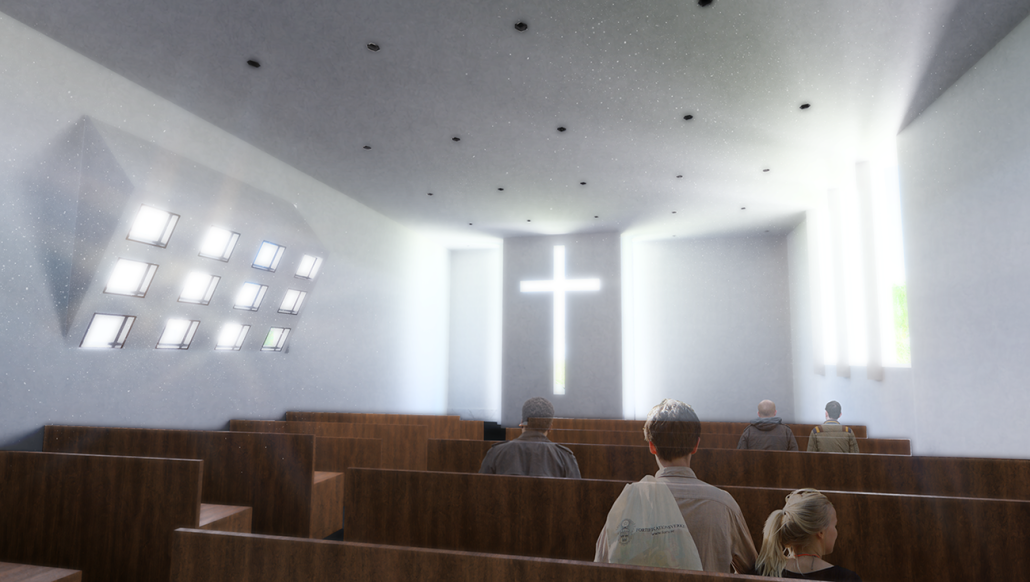
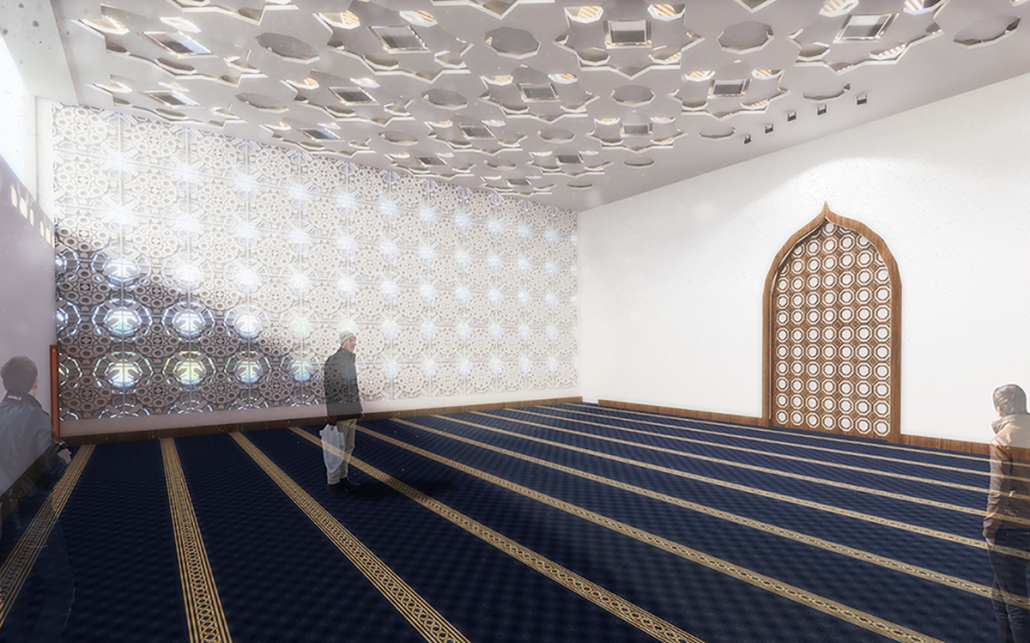
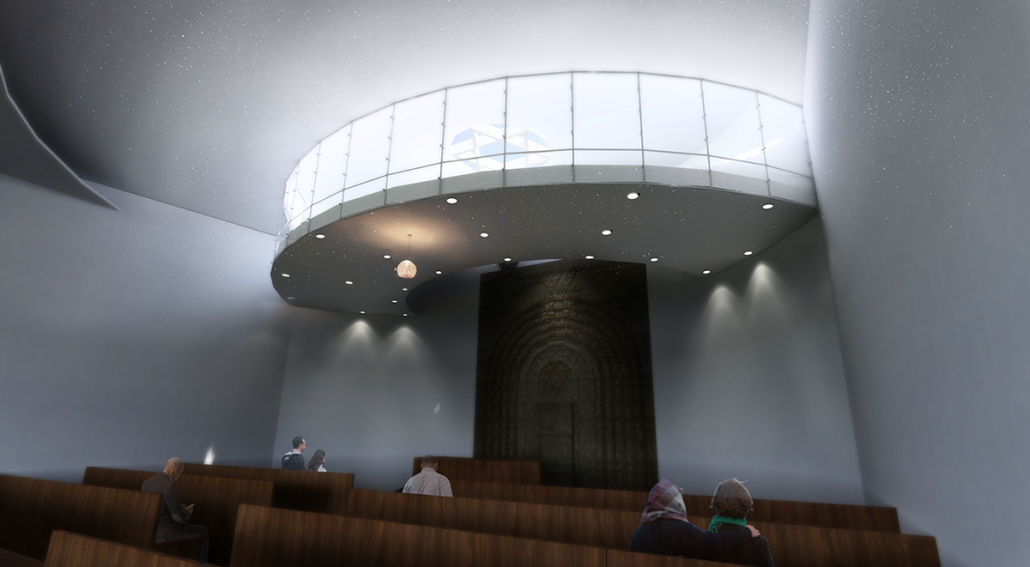
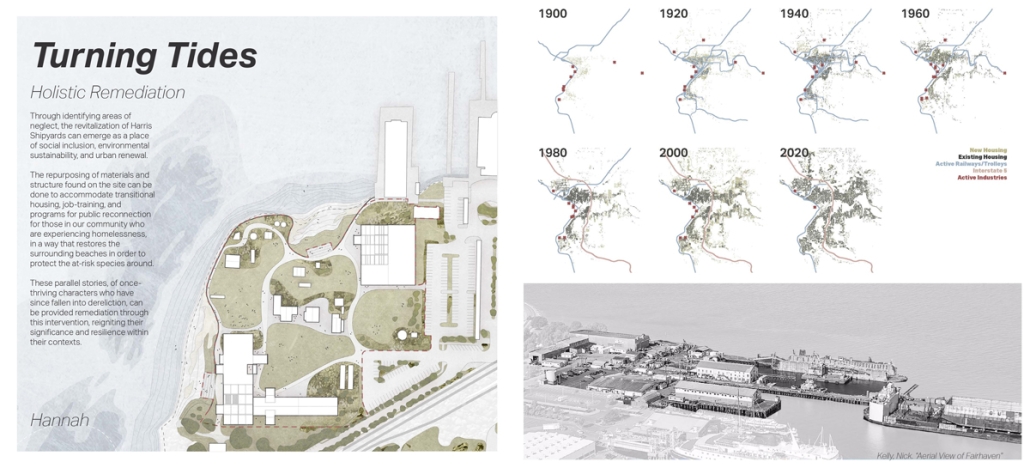
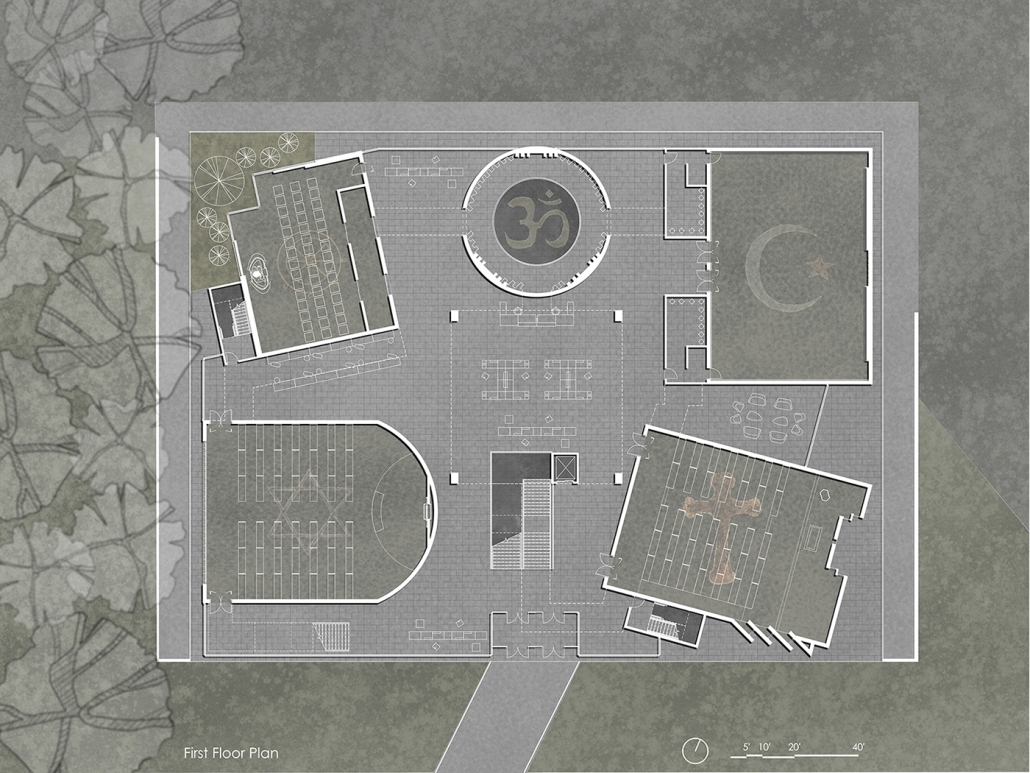
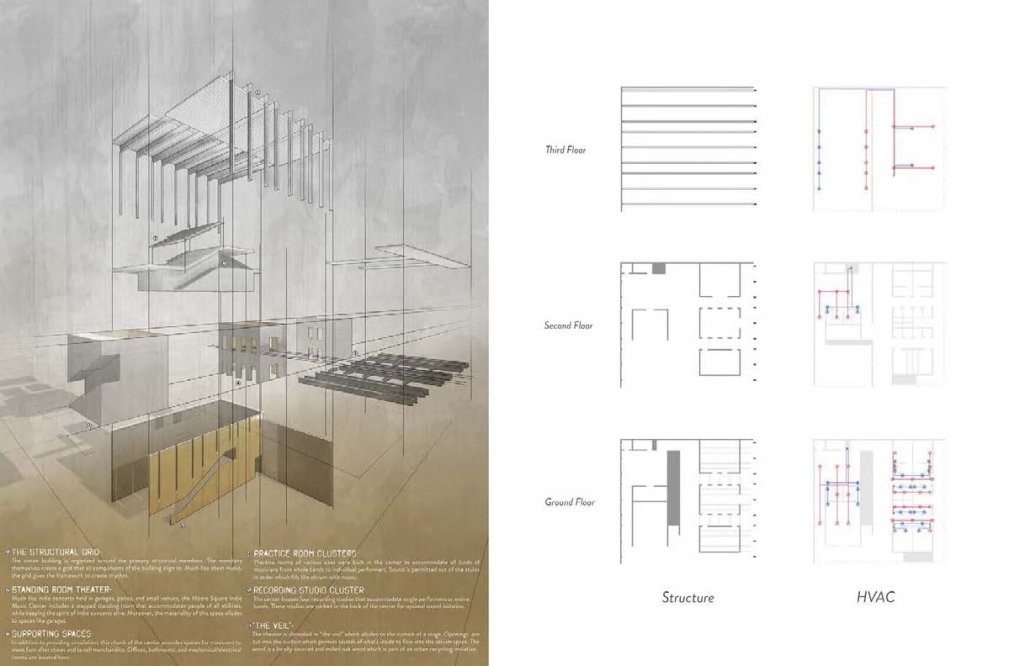
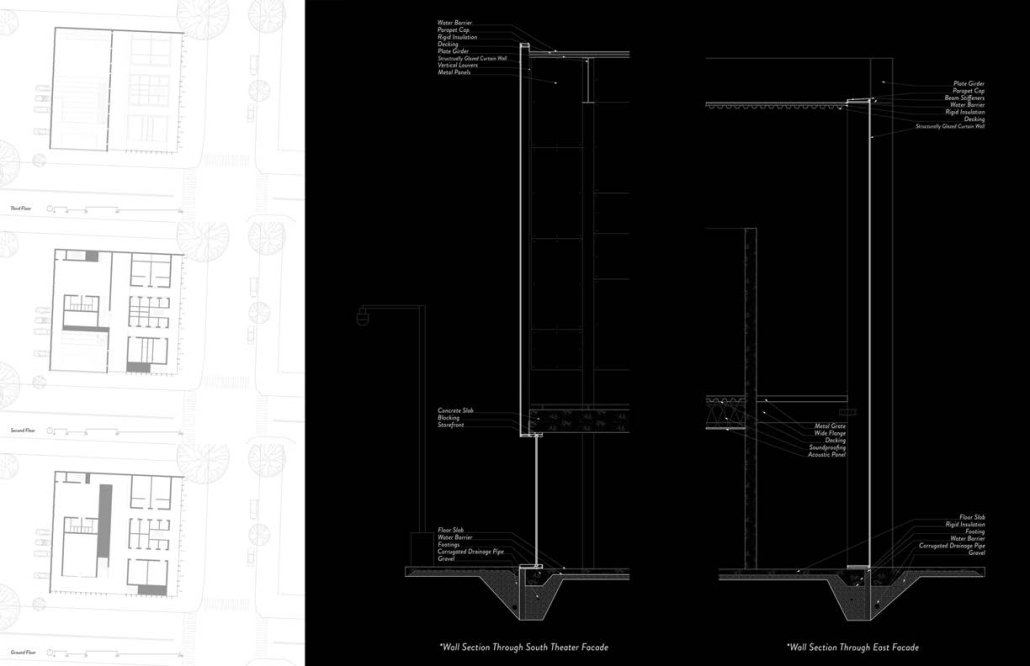
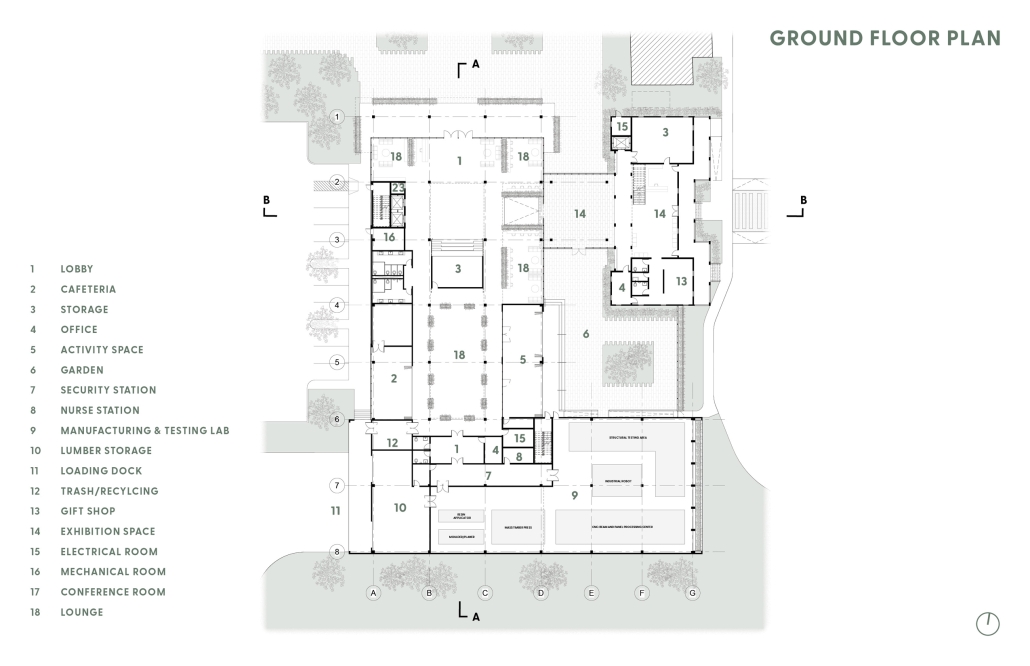
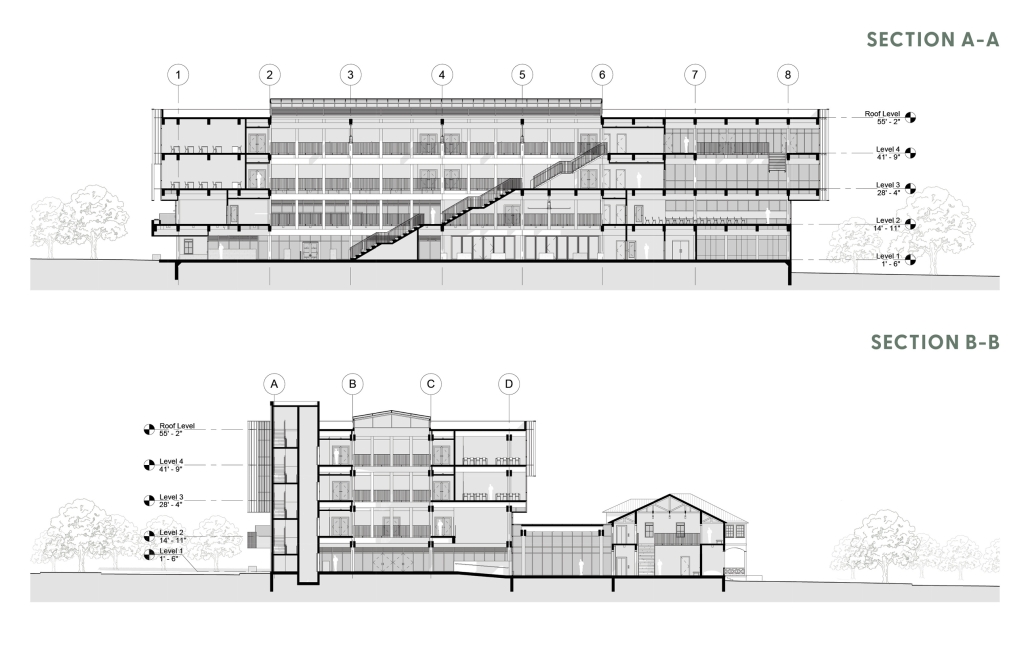
Memphis Urban Crematorium by Marah Al-Tal, M.Arch ’25
University of Memphis | Advisor: Brian Andrews
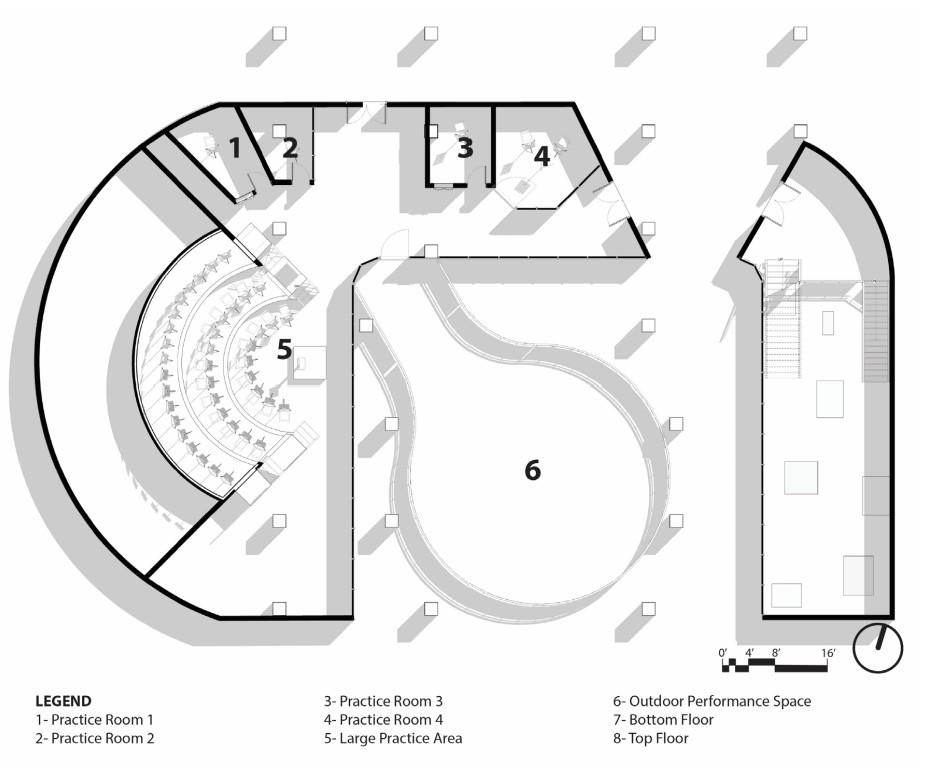
This urban crematorium project creates a meaningful path between the ceremony and cremation areas, connected by a symbolic bridge. This bridge allows mourners a reflective farewell and provides a journey for the departed. The urban crematorium includes spaces for administration, cremation, ceremonies, dining, accommodation, and a columbarium. The layout is organized by function, with the reception, cremation, and administrative areas on the first floor, the columbarium on the second floor, dining and ceremonial spaces on the third floor, and accommodation on the fourth floor. The concept centers on a gap between the ceremonial and cremation areas, joined by a bridge that creates a unique passage for the final farewell. This gap also houses the columbarium, symbolizing the connection between life and death. The design acknowledges our complex feelings about death—both distant and unavoidable—while creating a respectful place for final goodbyes.
This project received the 3rd-place AIA Memphis Student Award.
Instagram: @marah.tal, @aiasuofm
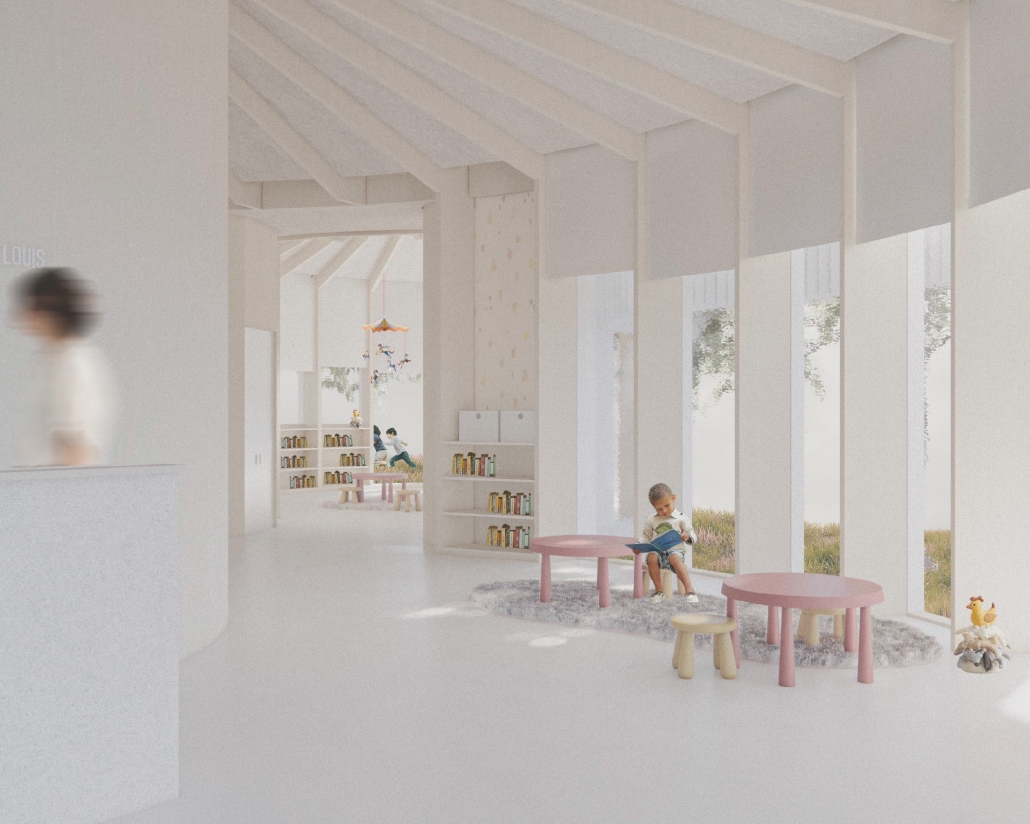
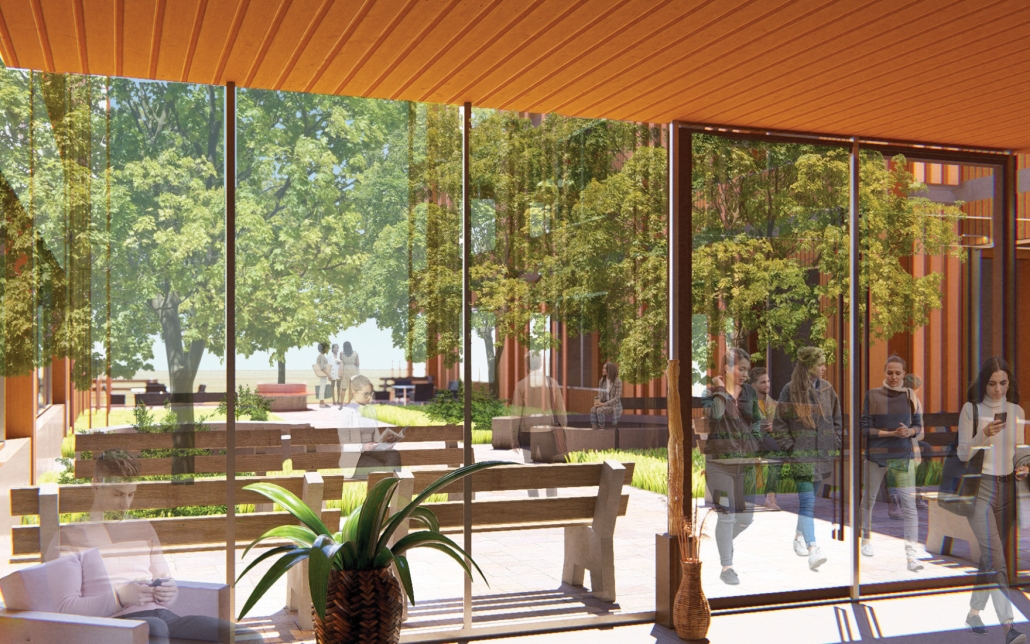
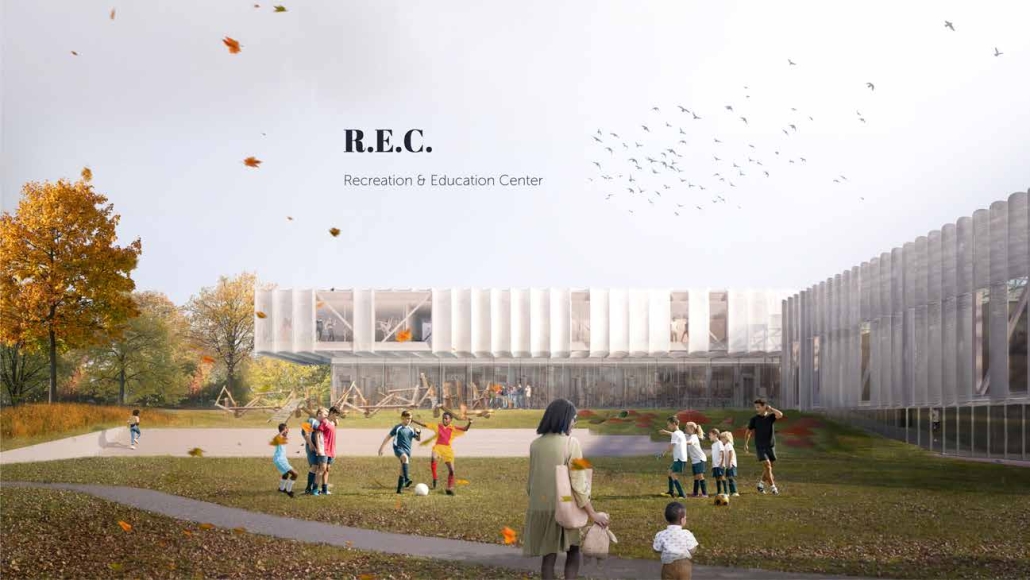
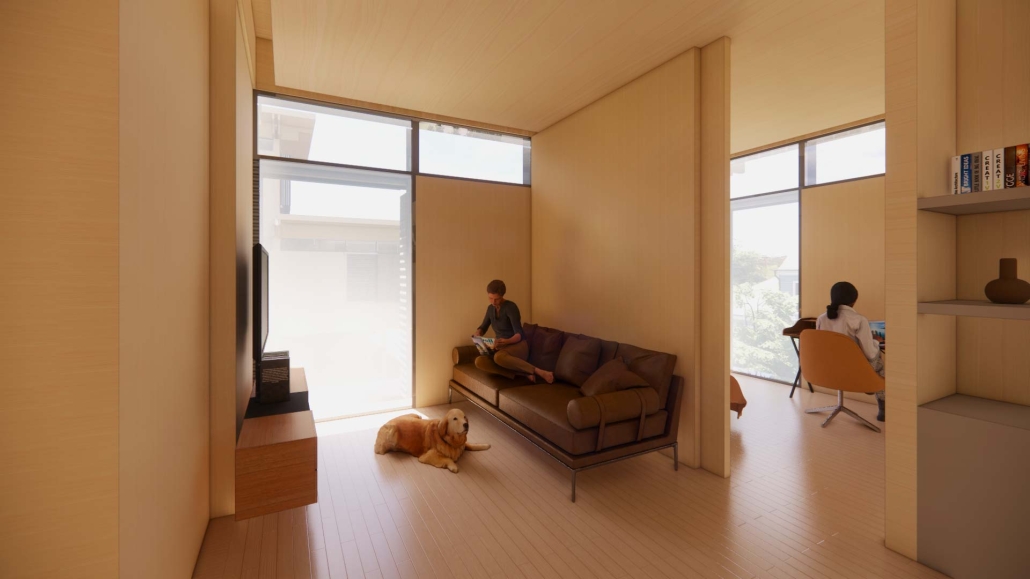
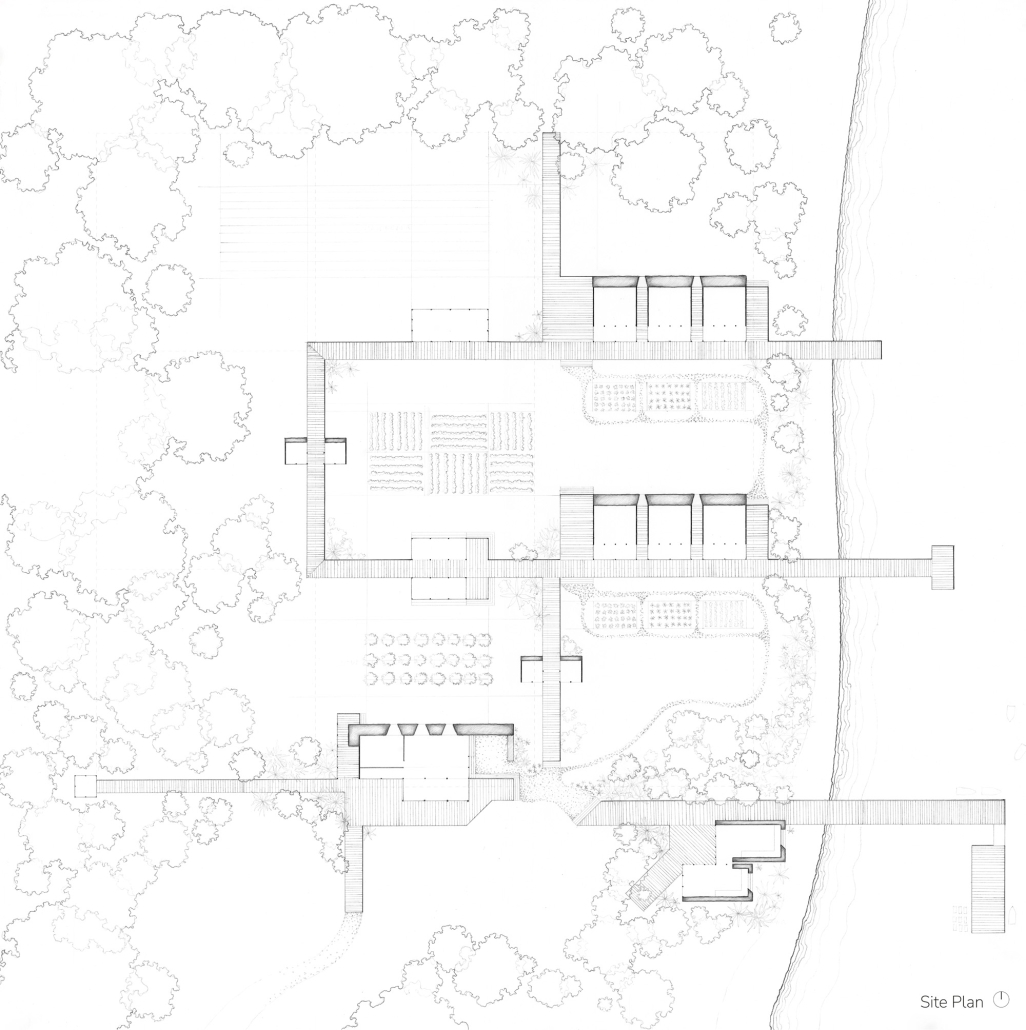
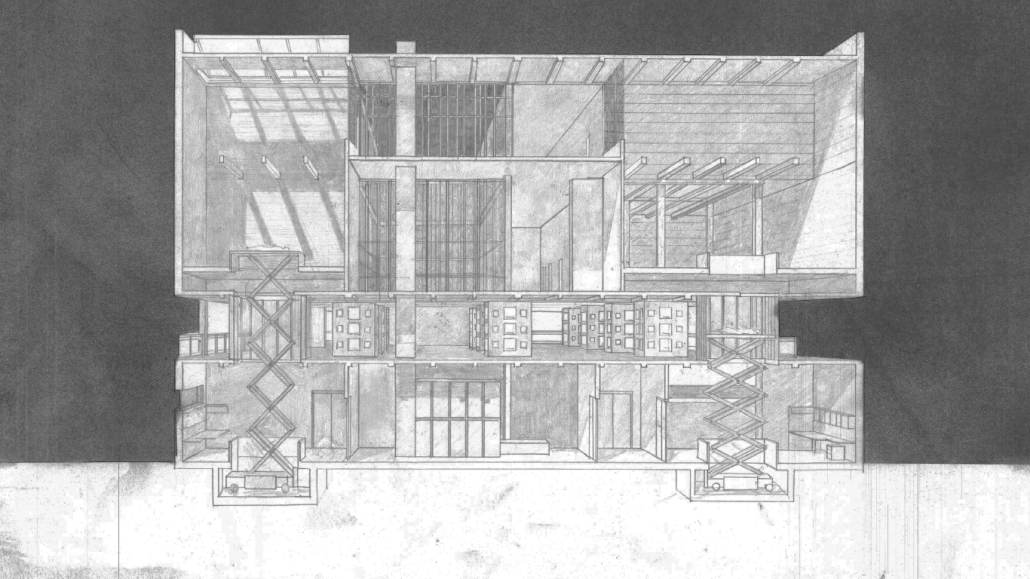
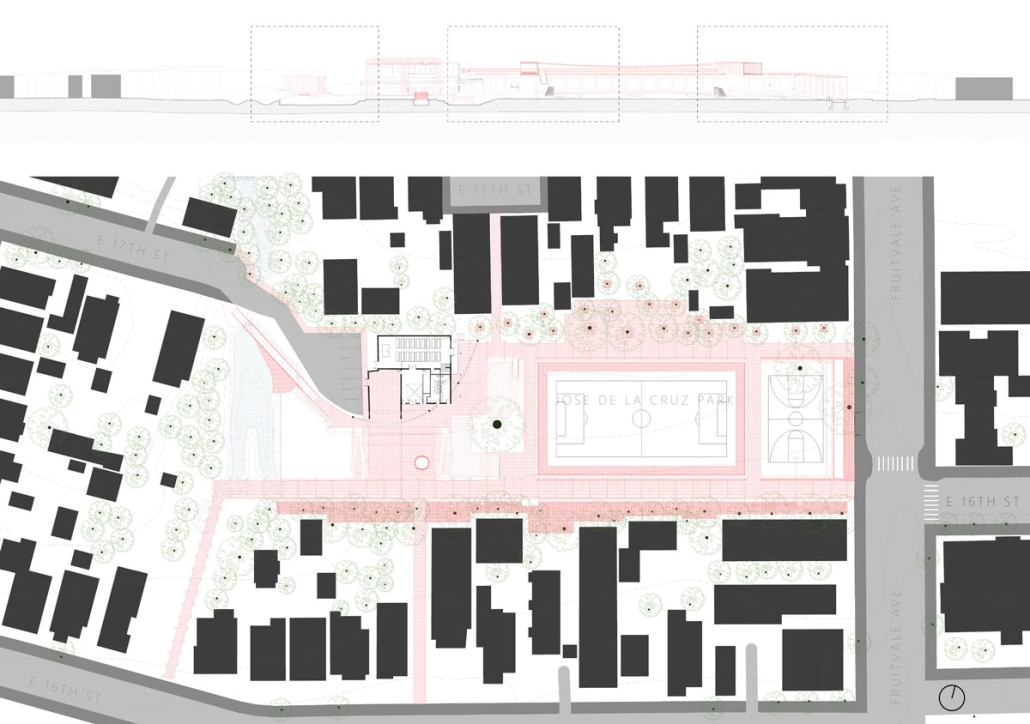
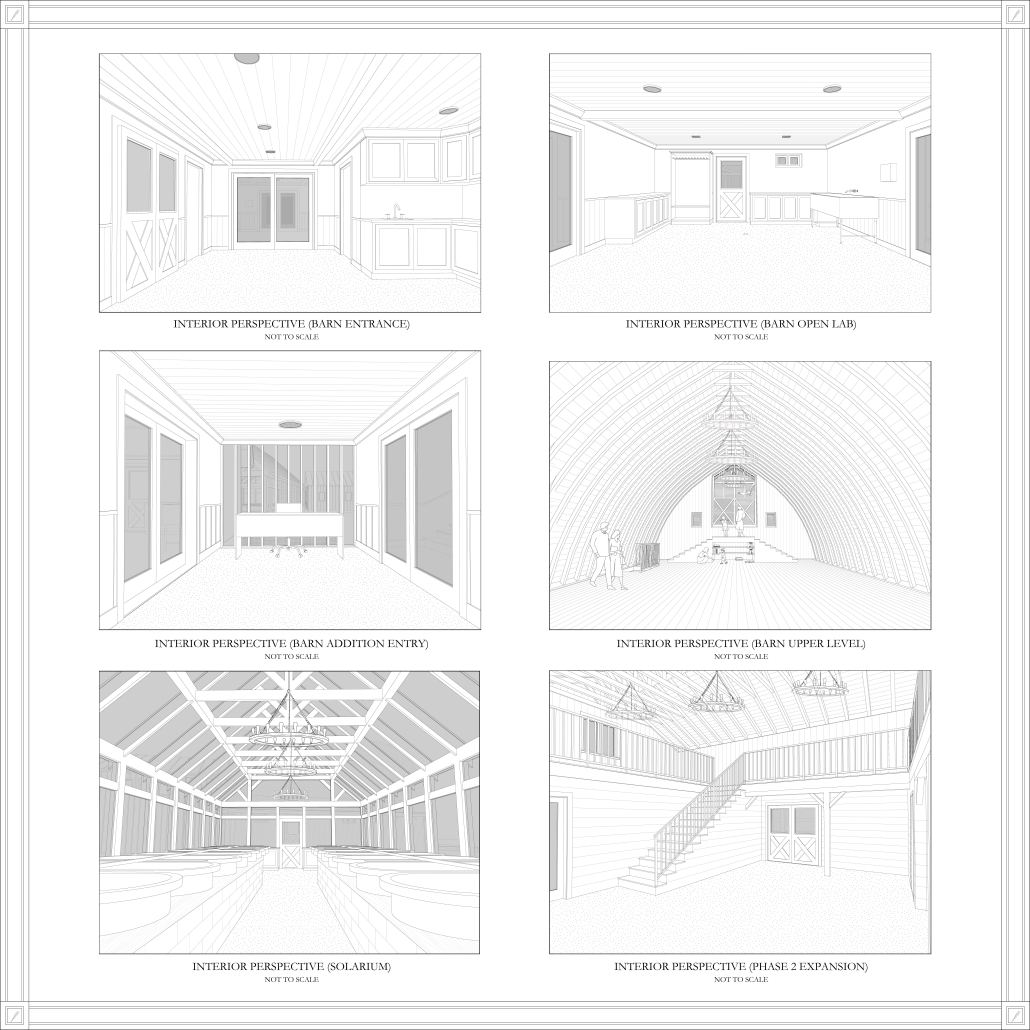
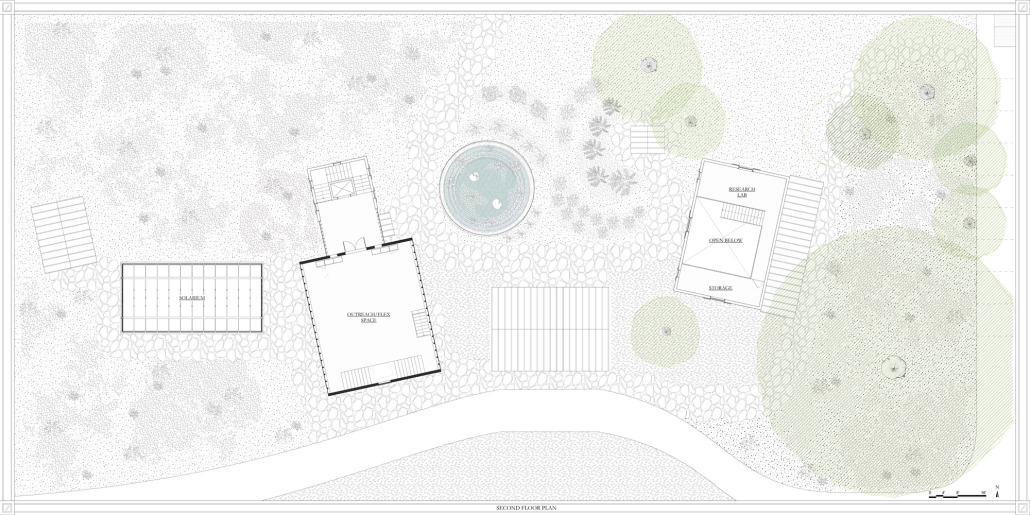
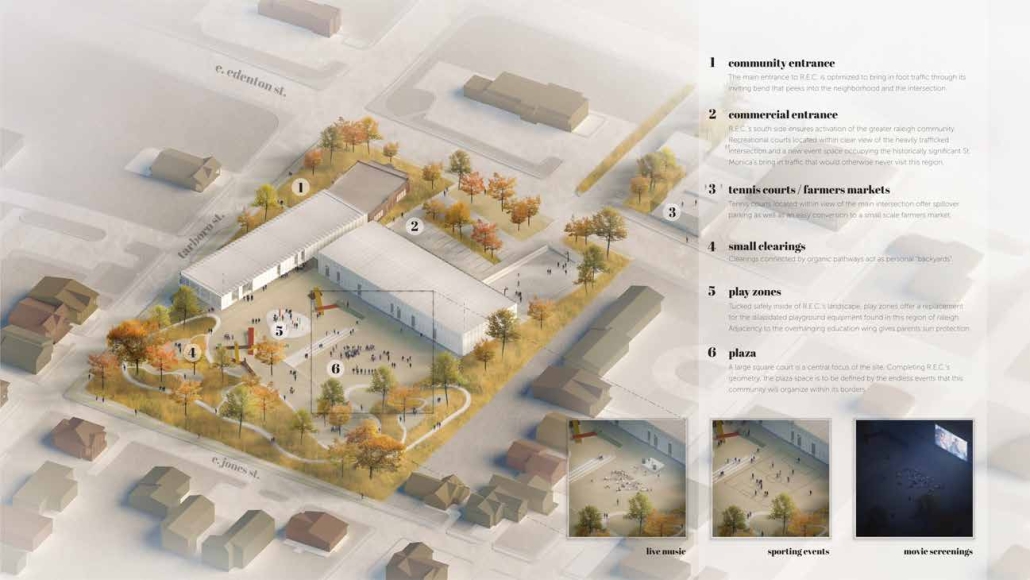
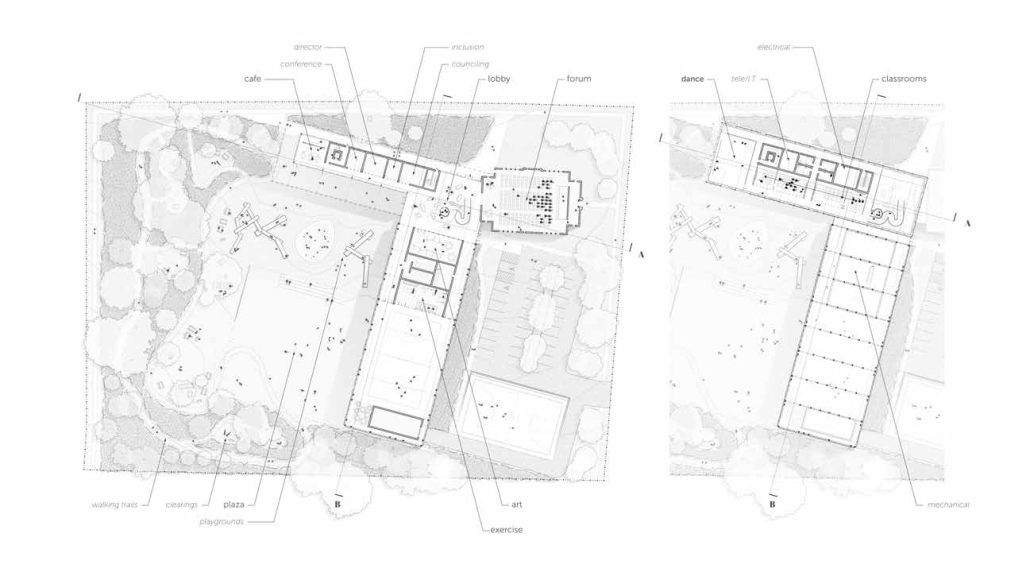
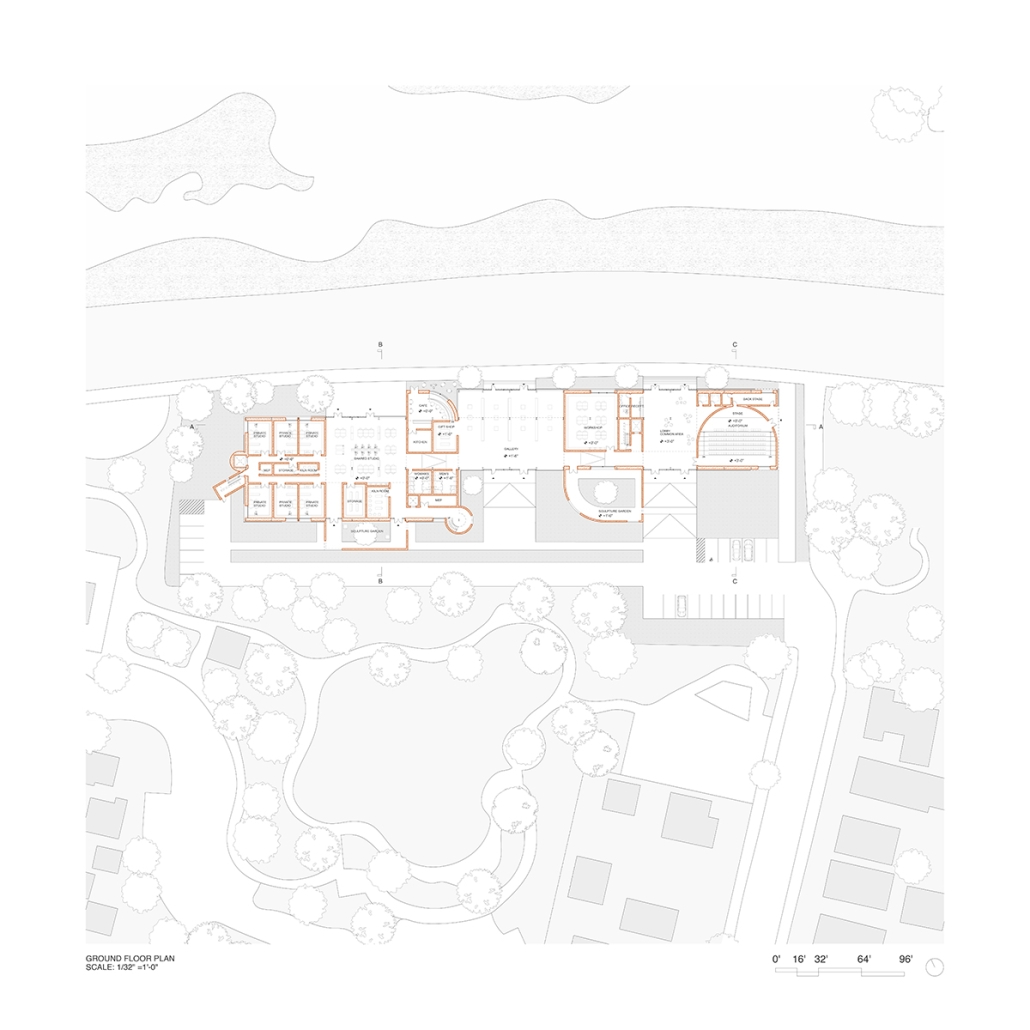
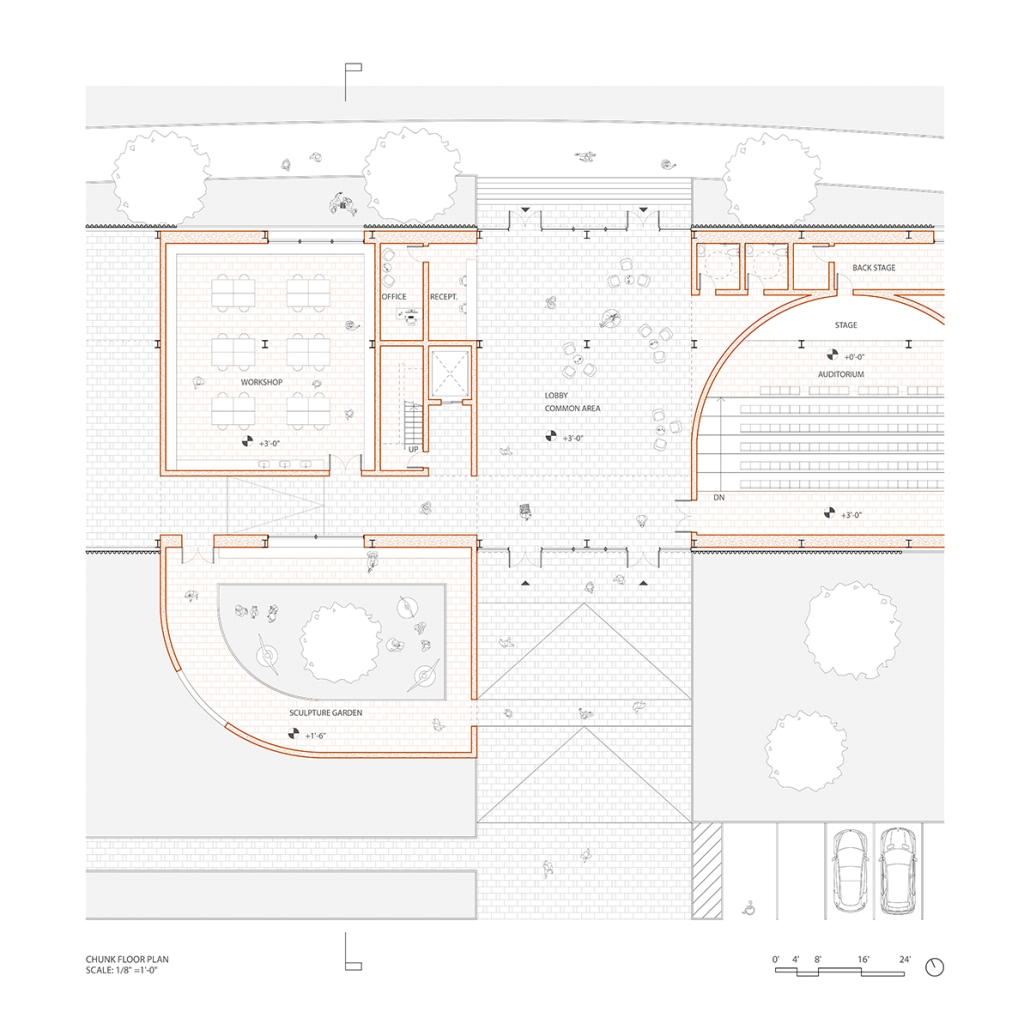
TURNING THE PAGE ON TRENDS: Children’s Library & Daycare In North St. Louis by Rebecca Spratt, M.Arch ’25
Washington University in St. Louis | Advisor: Julie Bauer
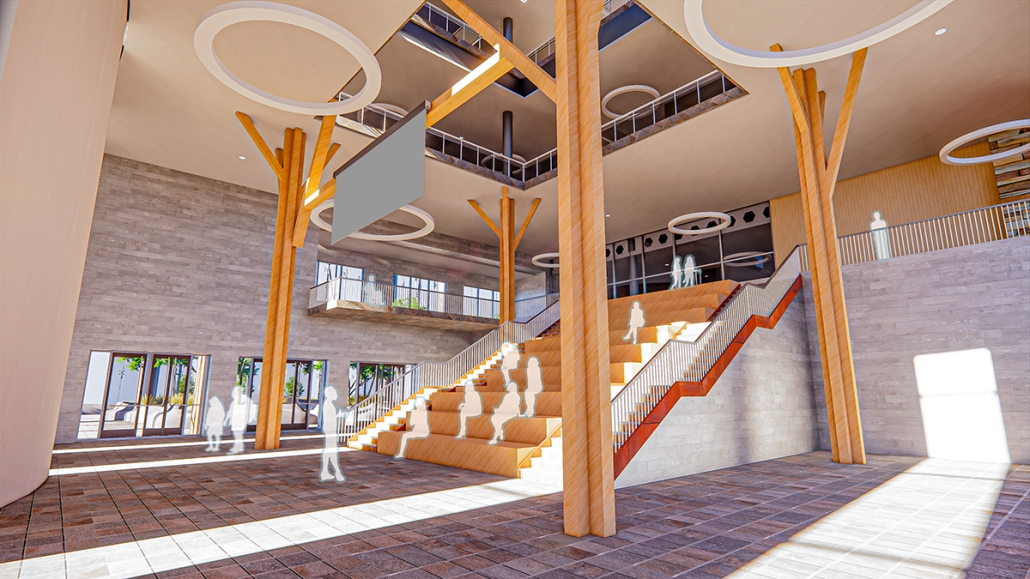
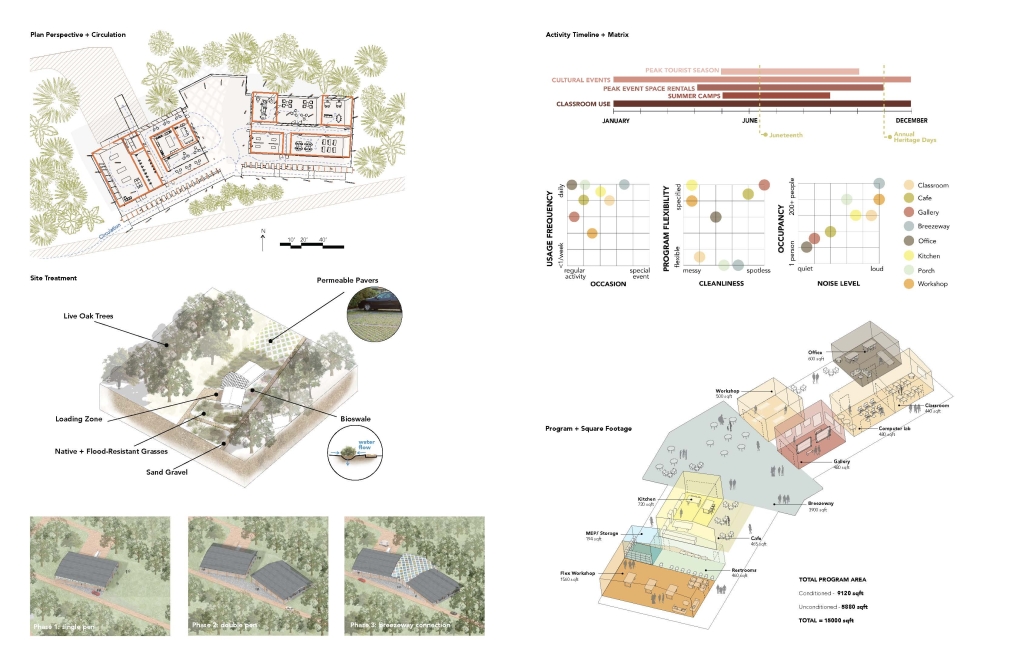
“Turning the Page on Trends” is a proposal that responds to the needs of children amidst the current social and socioeconomic climate of North St. Louis. Designed to improve reading comprehension rates among the youngest members of this community while providing a safe space for learning and play, this project is a hybrid proposal that combines a children’s daycare and library in the Grand Center neighborhood. The building includes reading rooms, play areas, dining space, a volunteer kitchen, a family resource center, and an exterior garden. The design is centered around the reading and garden spaces, keeping nature at the core of the educational experience. Beyond serving children, the project aspires to create meaningful engagement among youth, families, and the wider community. Architecturally, the project is influenced by the bookshelf, a modular element integrated throughout the design to embed the library into the structure of the building itself.
Instagram: @rebeccaspratt, @julie.e.bauer
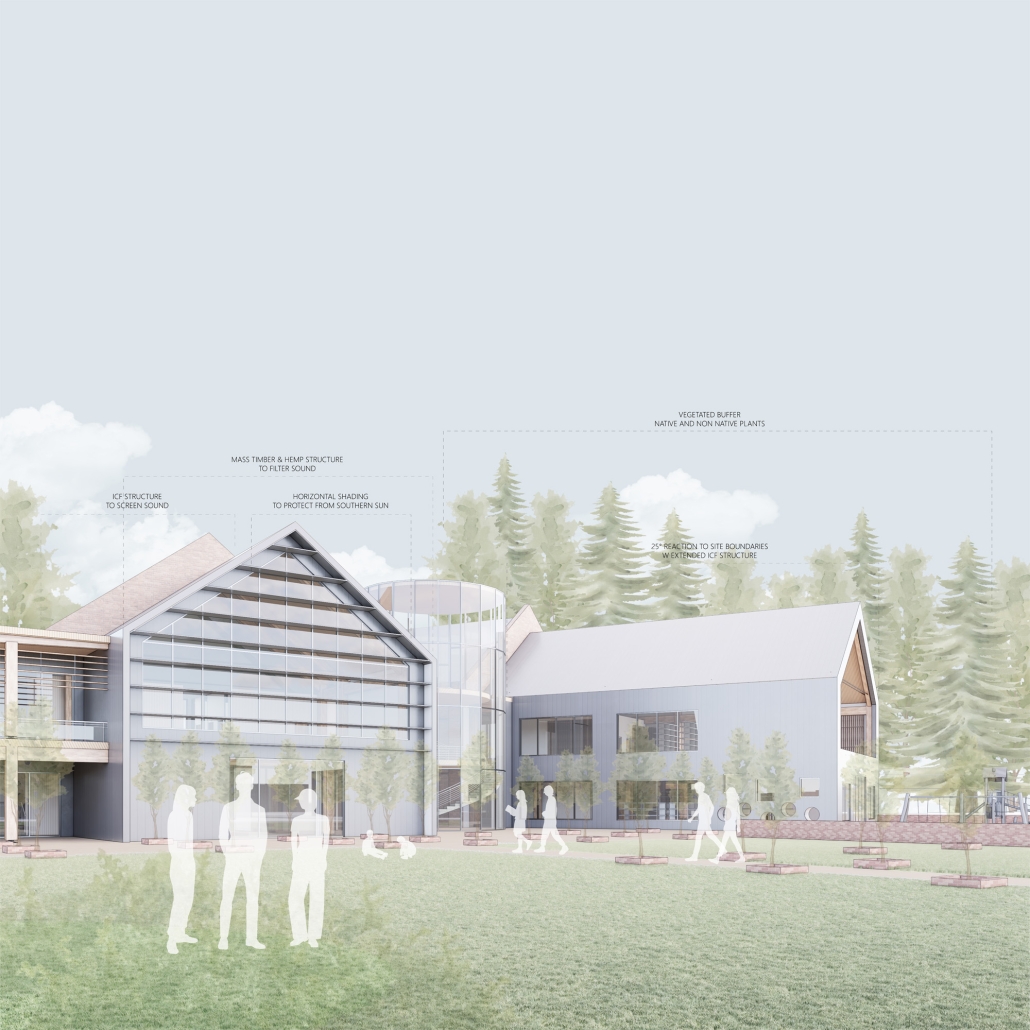
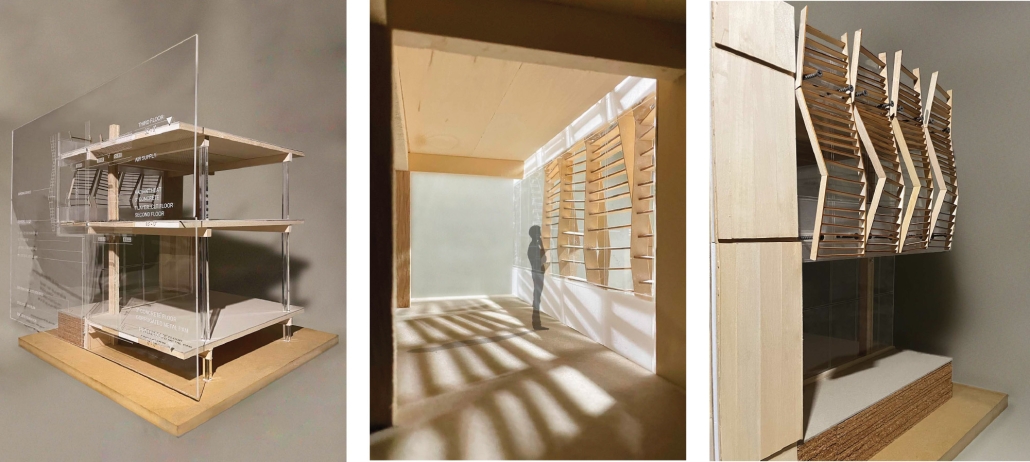
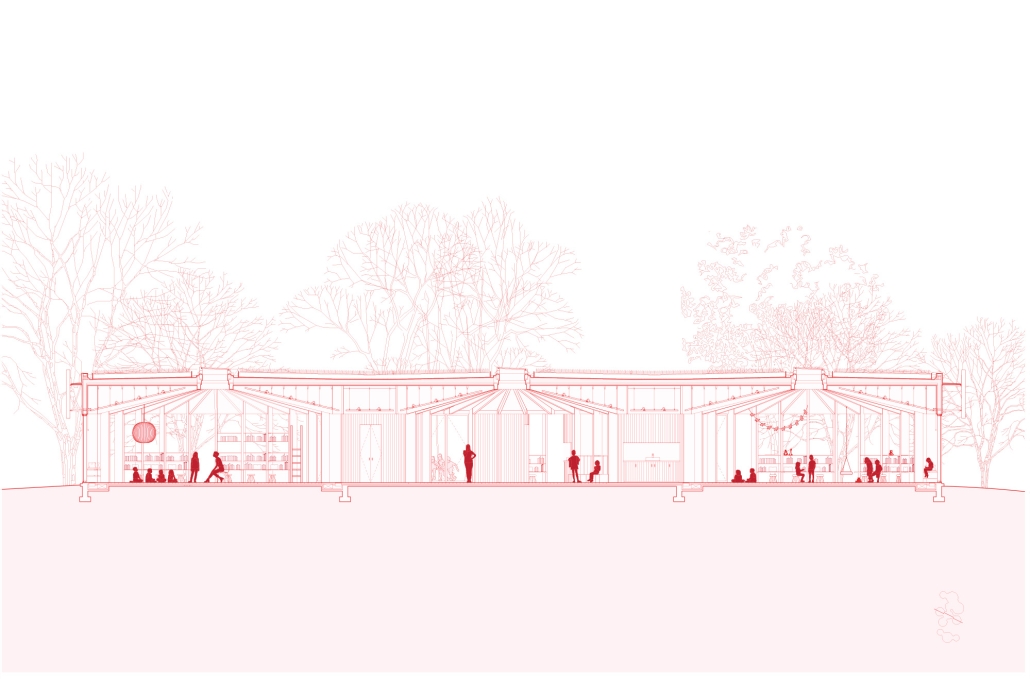
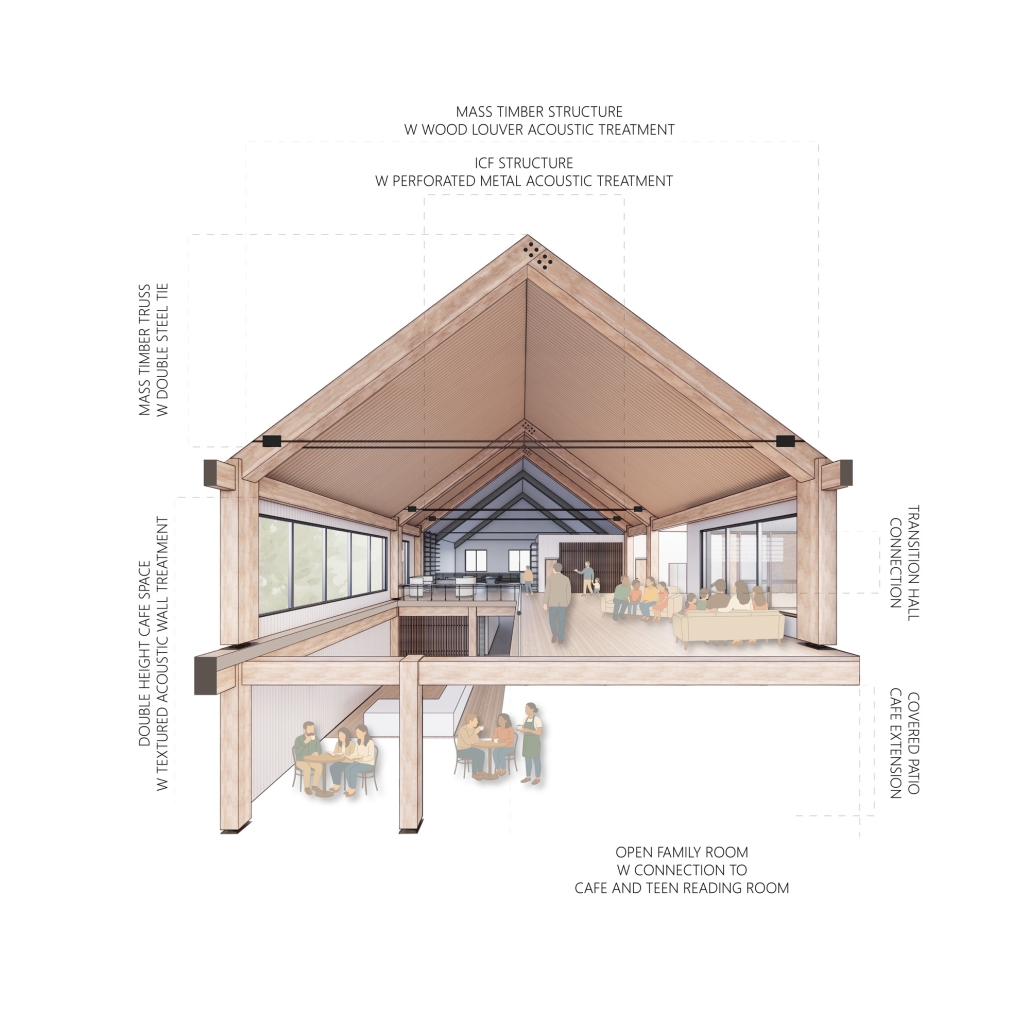
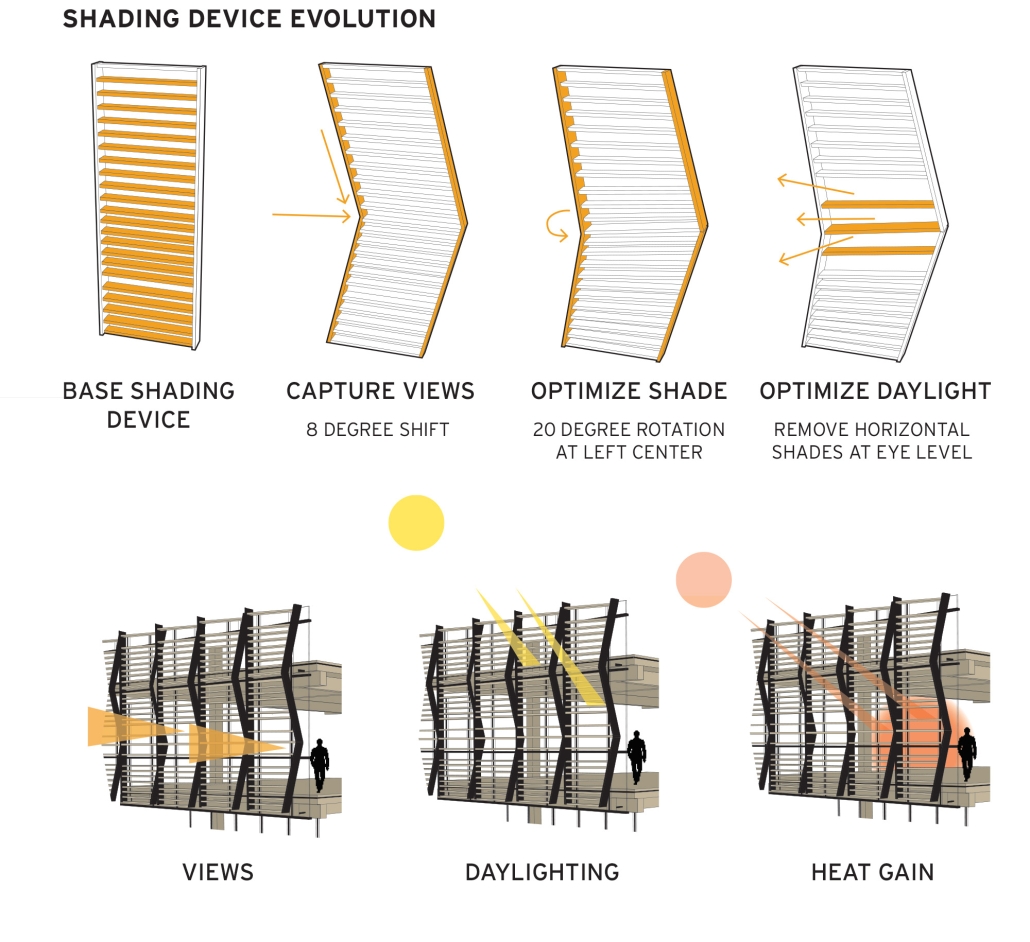
Soundscapes of Change by Sarah Jane Graven, M.Arch ’25
University of Maryland | Advisors: Brittany Williams, Brian Kelly & Julie Gabrielli
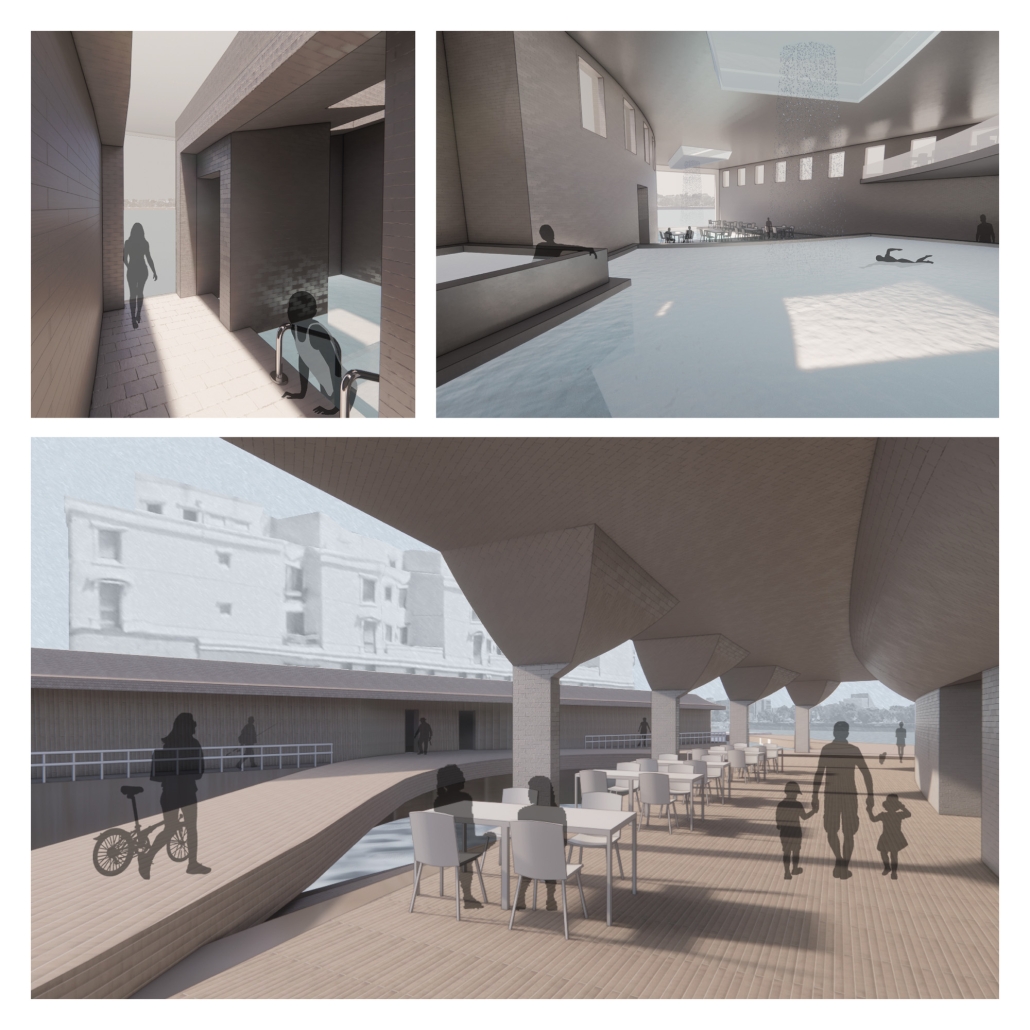
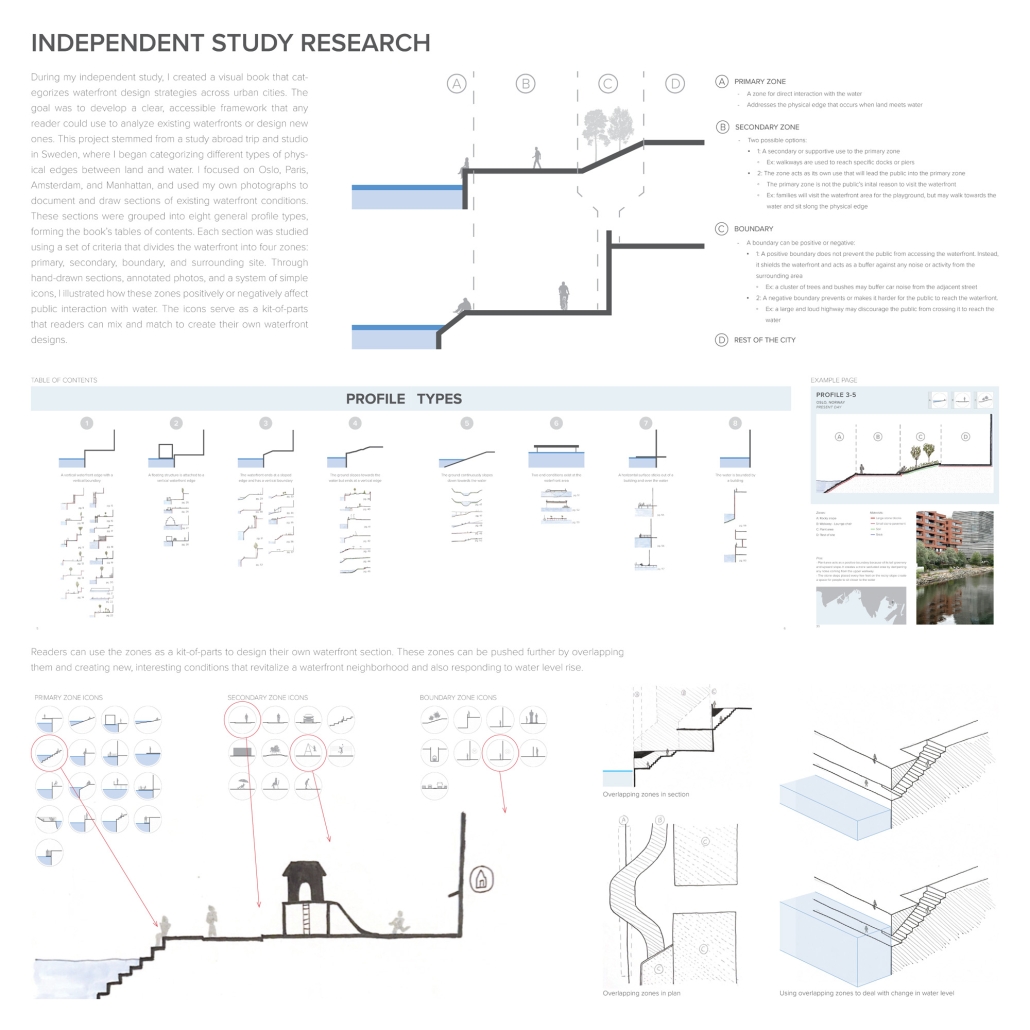
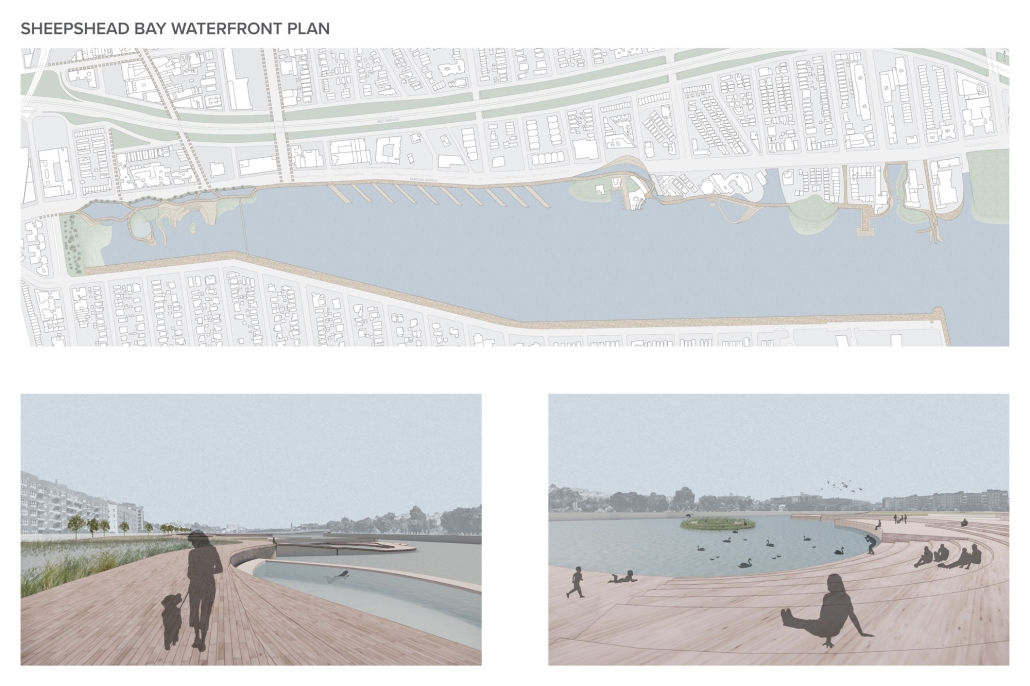
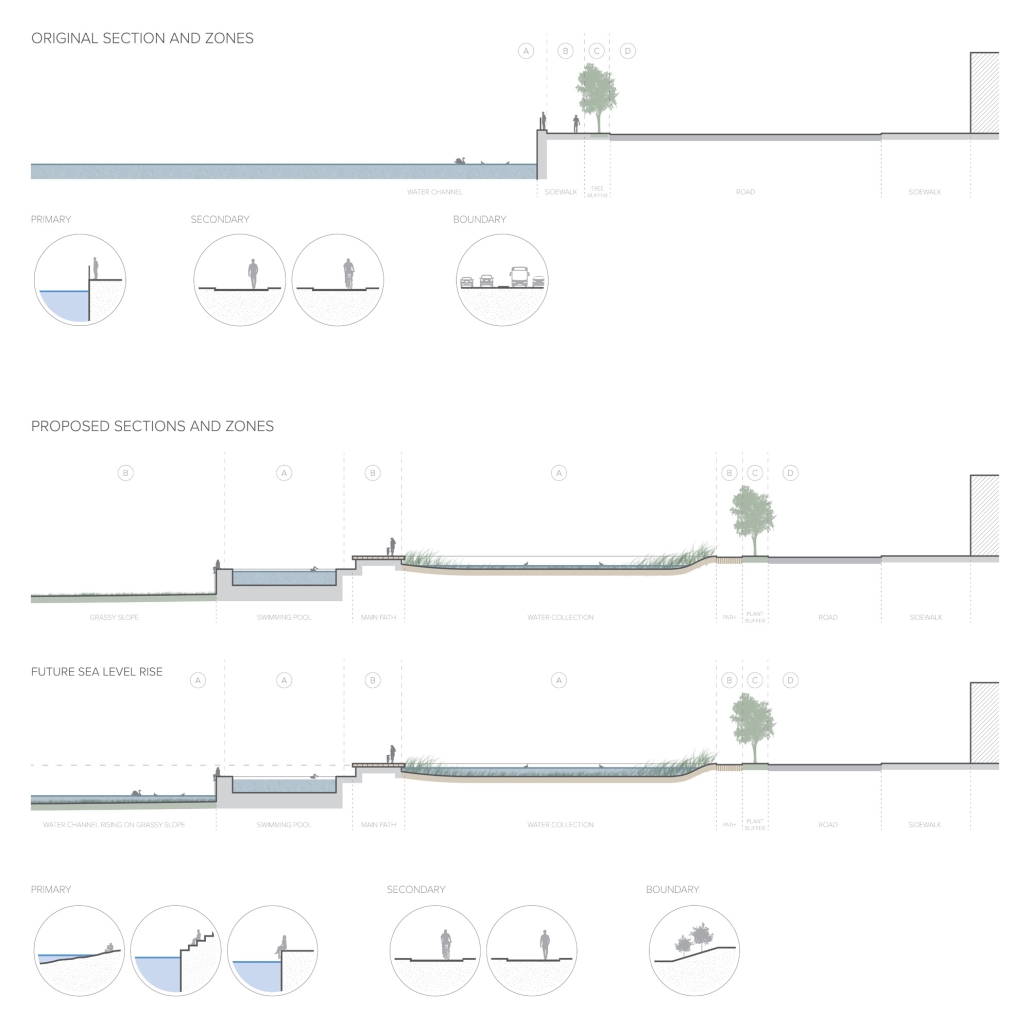
America’s approach to childcare often places additional stress on parenting and hinders child development. The United States is the only developed country that does not have a federally mandated paid parental leave policy. Without guaranteed parental leave, parents are forced to find childcare, which is often unaffordable and inaccessible. Not only is society and policy making childhood and parenthood difficult, the built environment is as well. The built environment is designed as though children do not exist. America’s hostility towards children has enforced a mindset that children should be seen, not heard. This research reorients the design process and puts acoustics at the center to rethink the built environment in a way that supports both children and parents. Children are our future, and they deserve to be a visible and welcome part of the present.
This thesis aims to explore how acoustic strategies can be implemented into traditionally quiet spaces to address, engage, and celebrate children and families in civic life. By designing spaces that are flexible and will fit the needs of the user, acoustic design will create environments where people of all ages can relax, enjoy, and learn. This thesis challenges the social norms in traditionally quiet spaces. By designing spaces with acoustics at the center of the process, spaces will be more comfortable and welcoming to children and families. This thesis aims to reimagine the design process and put acoustics at the center to integrate children and families into civic life.
Instagram: @sarahjanegraven, @br.ttw.ll
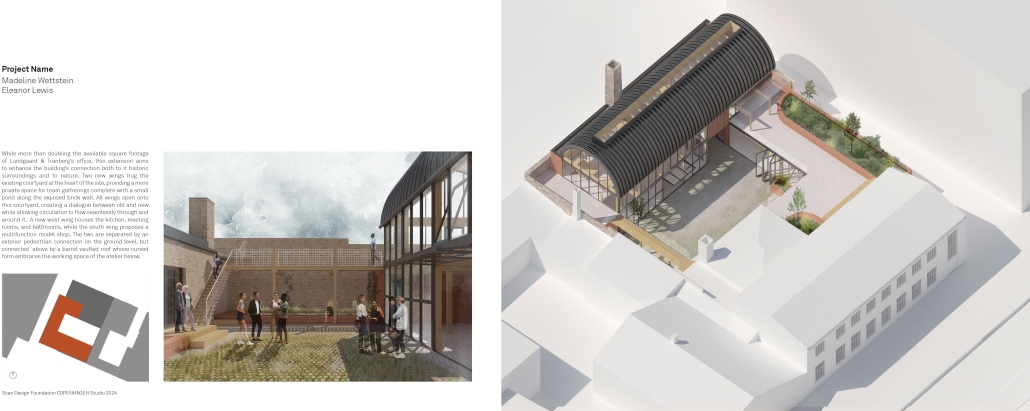
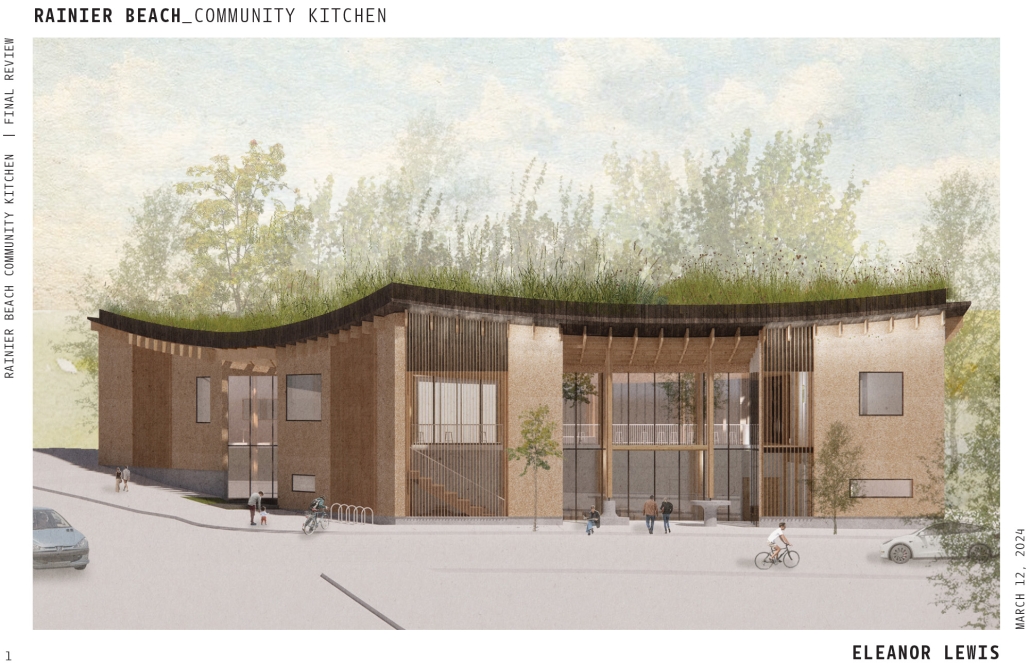
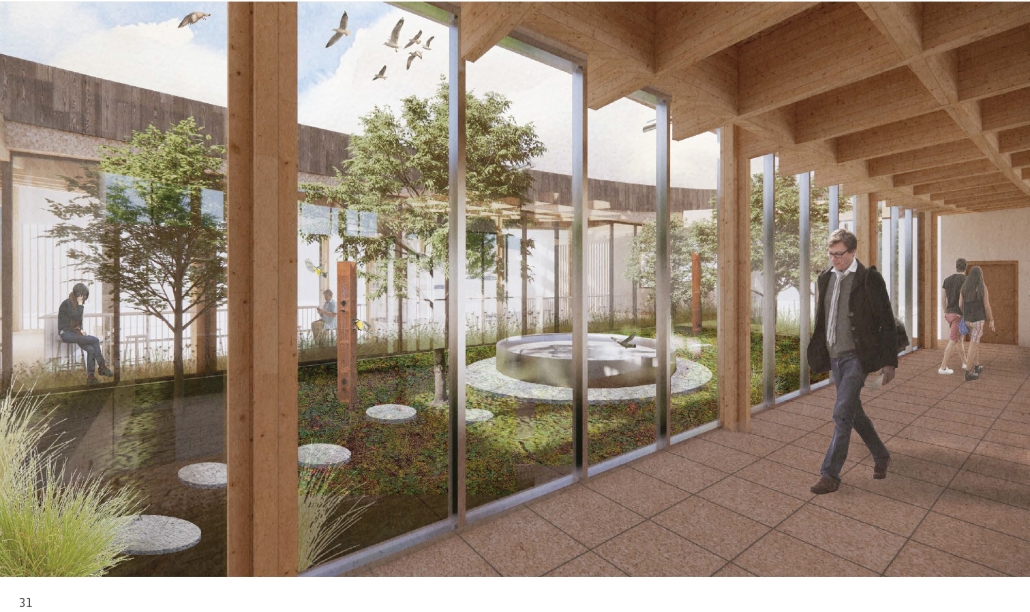
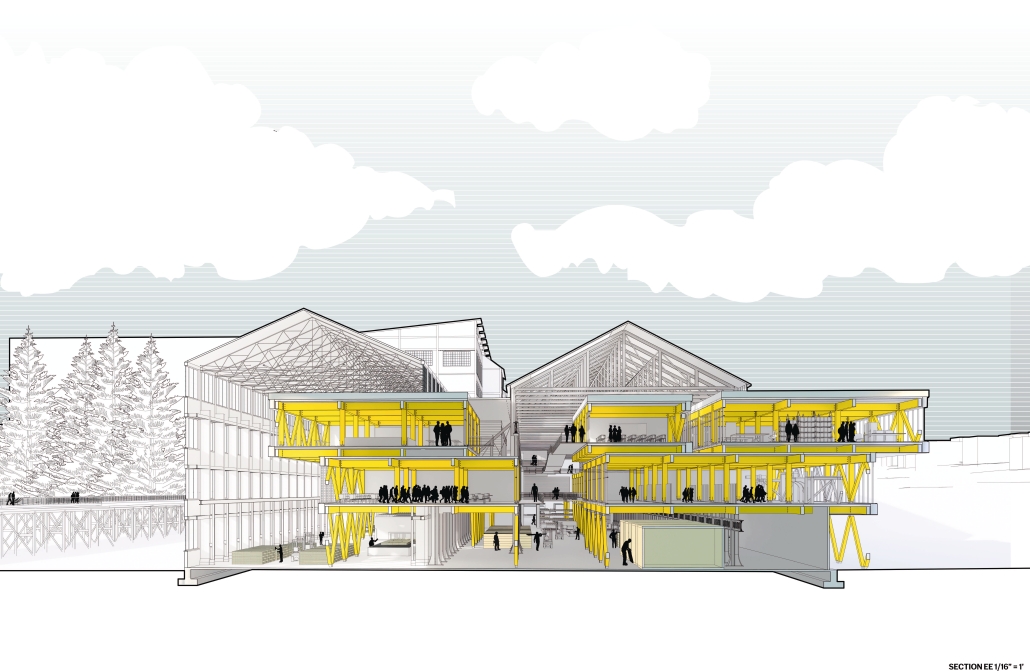
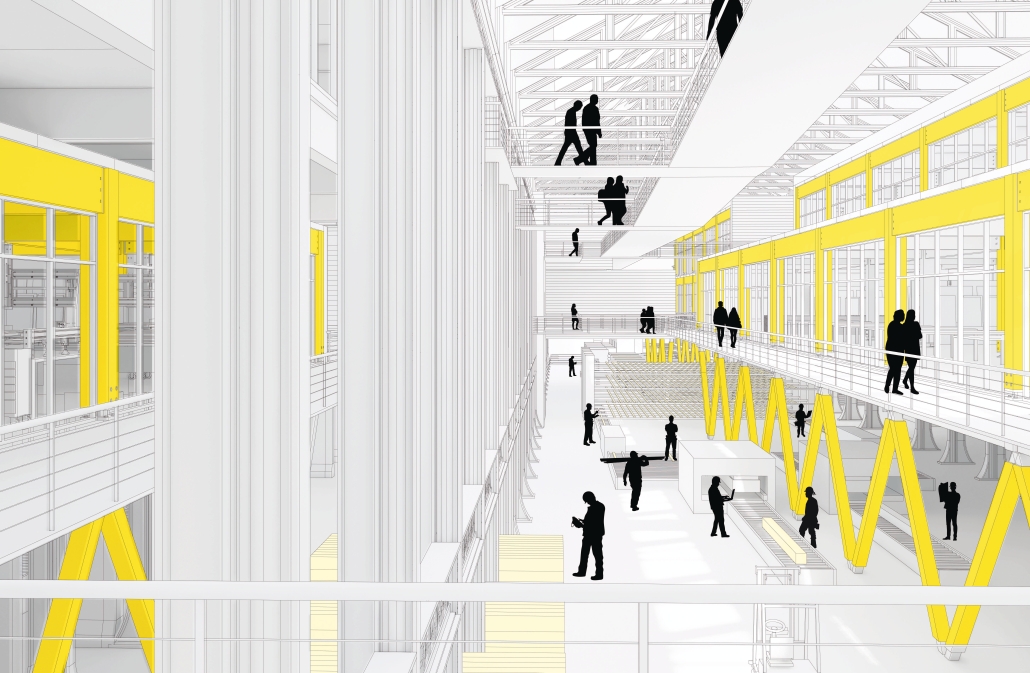
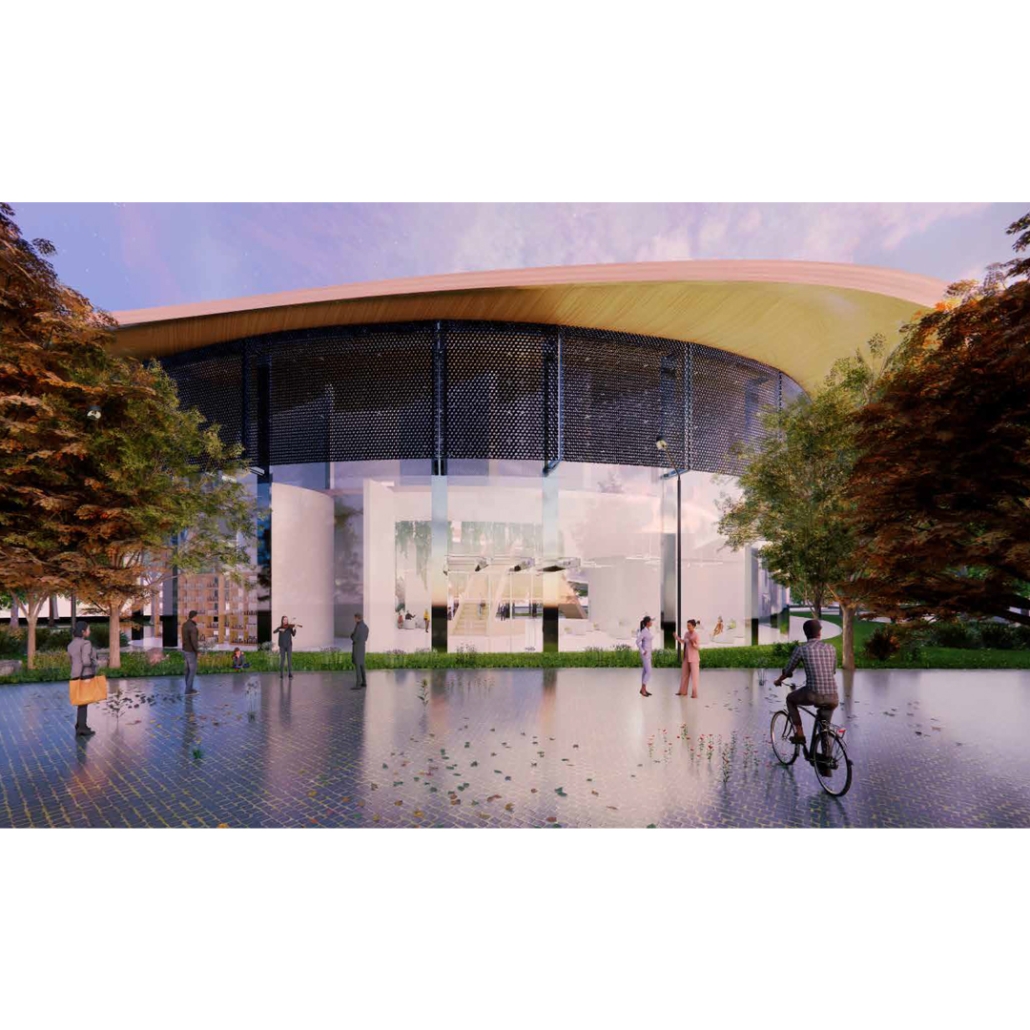
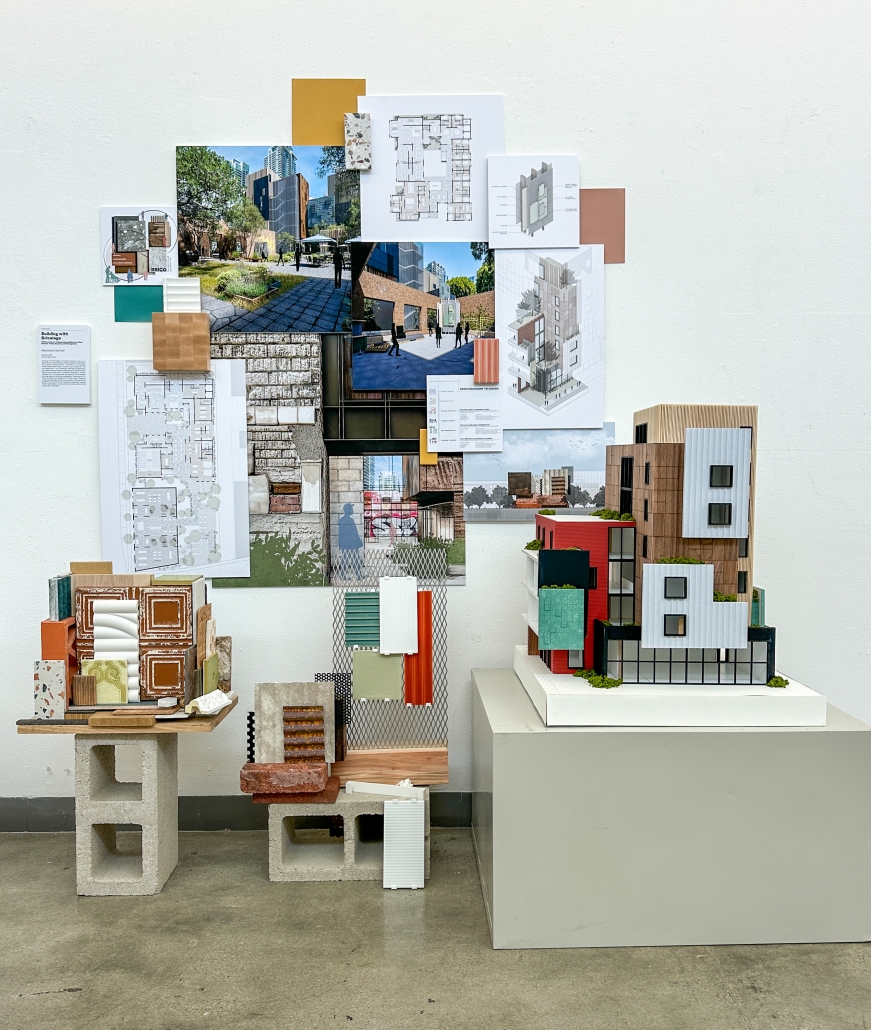
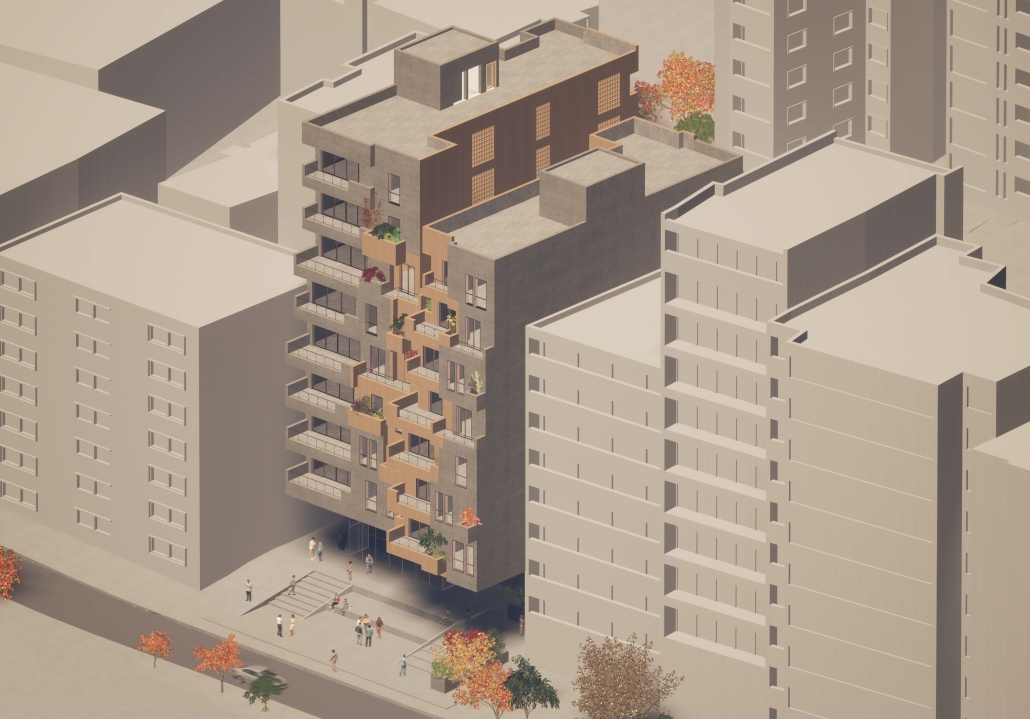
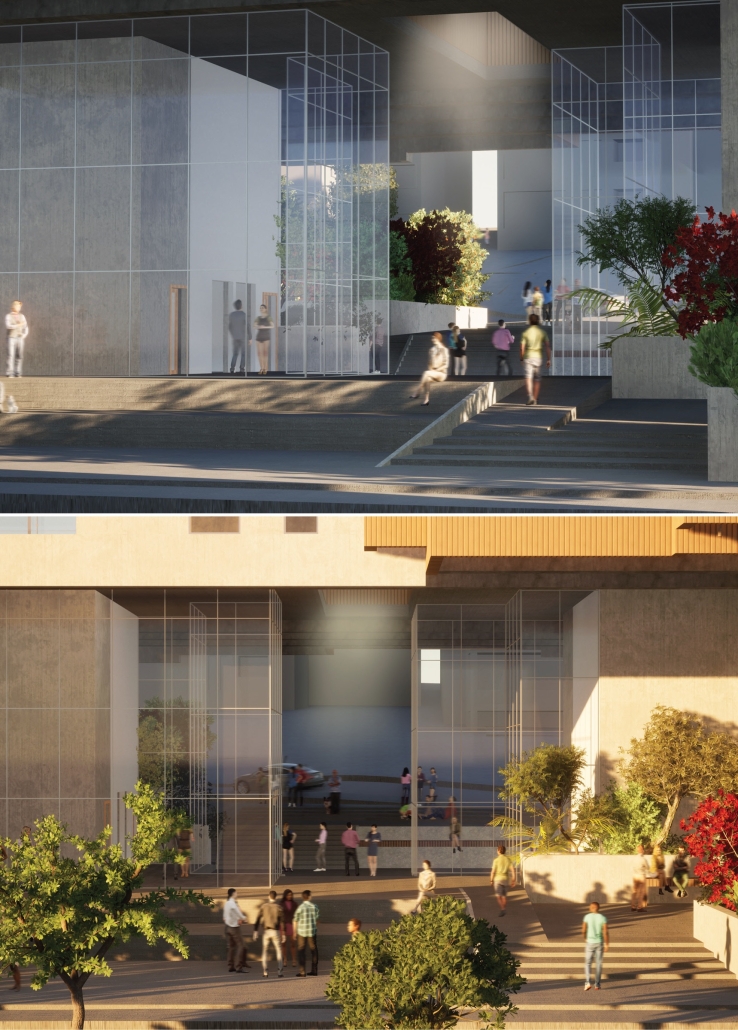
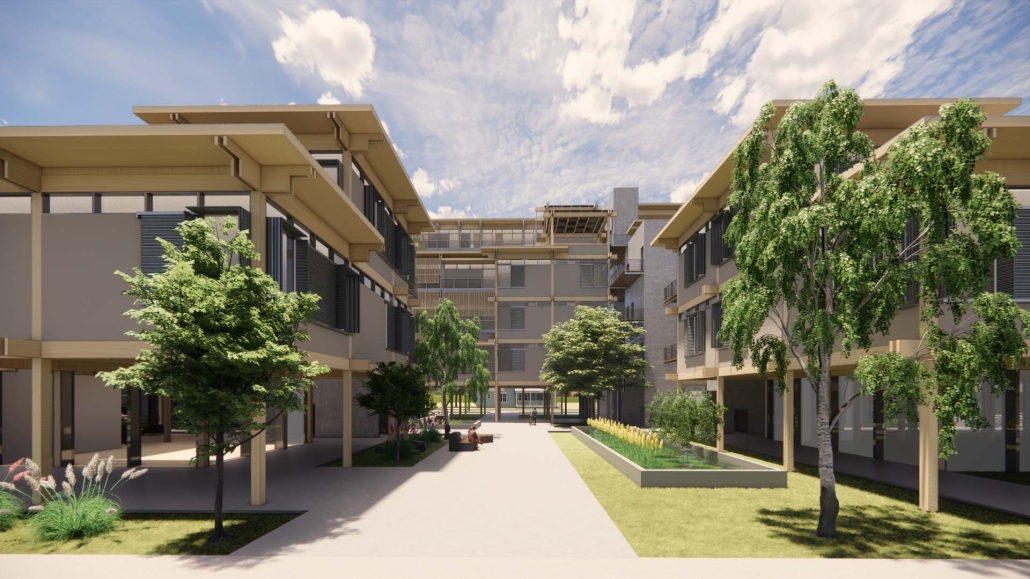
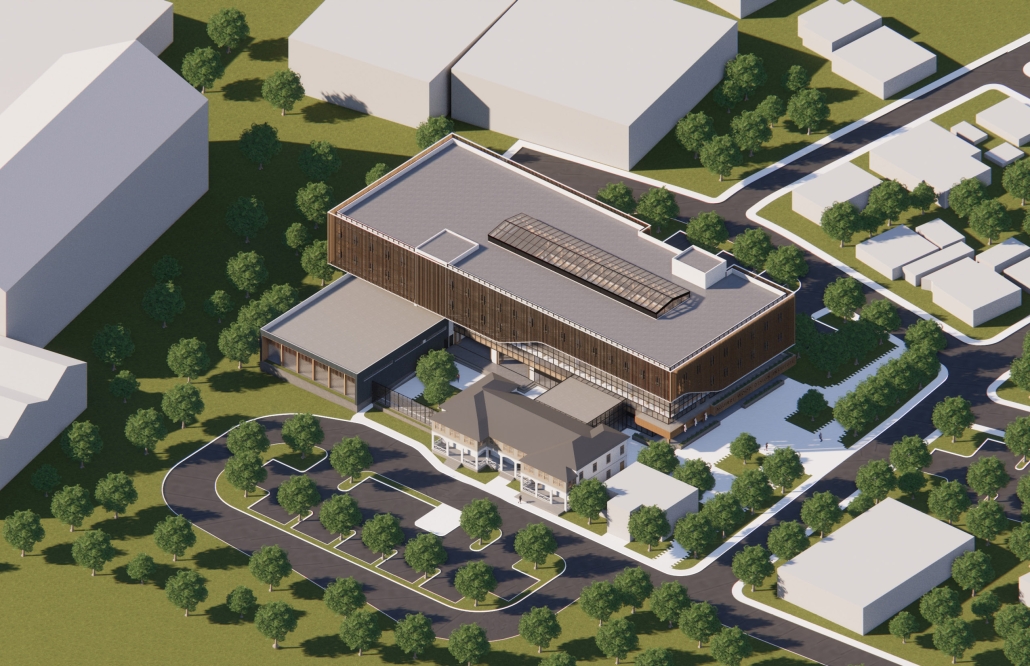
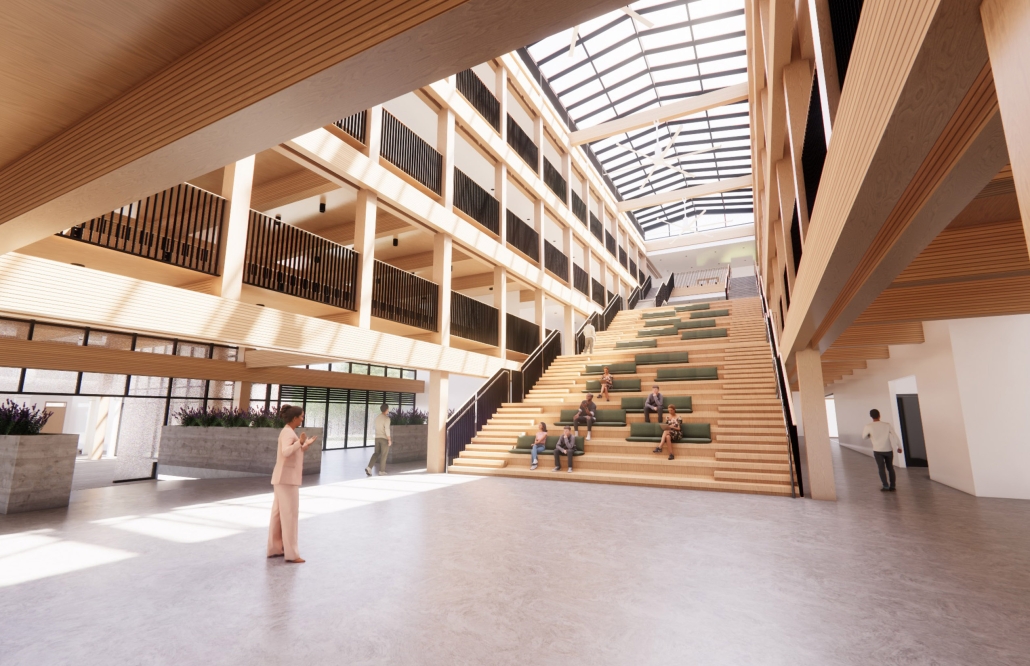
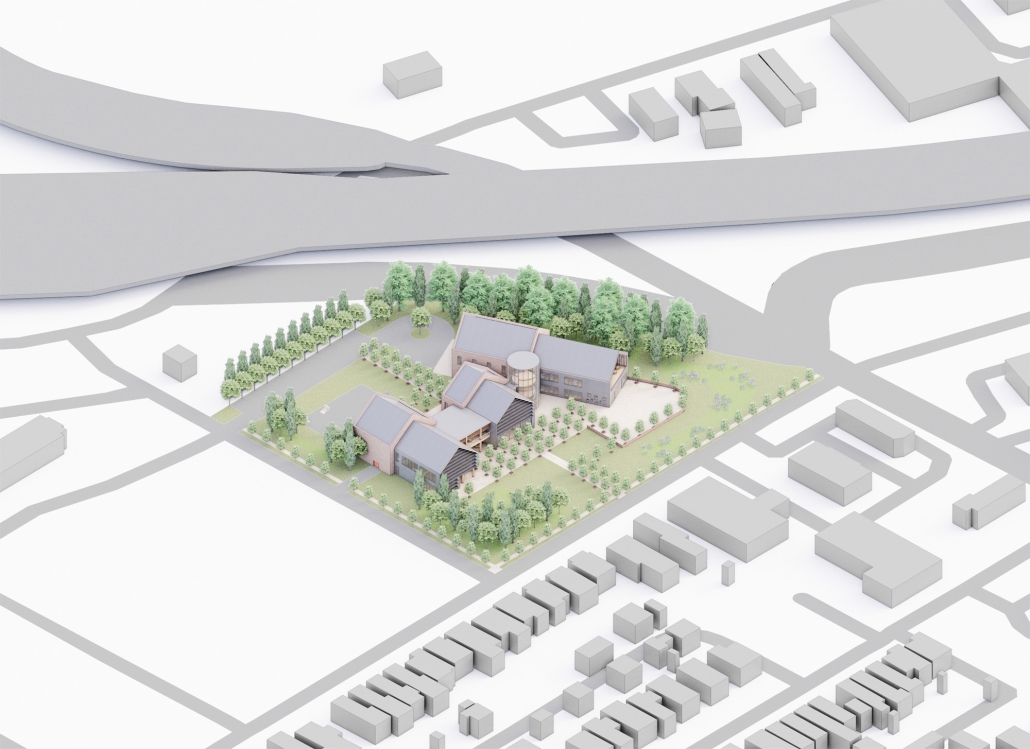
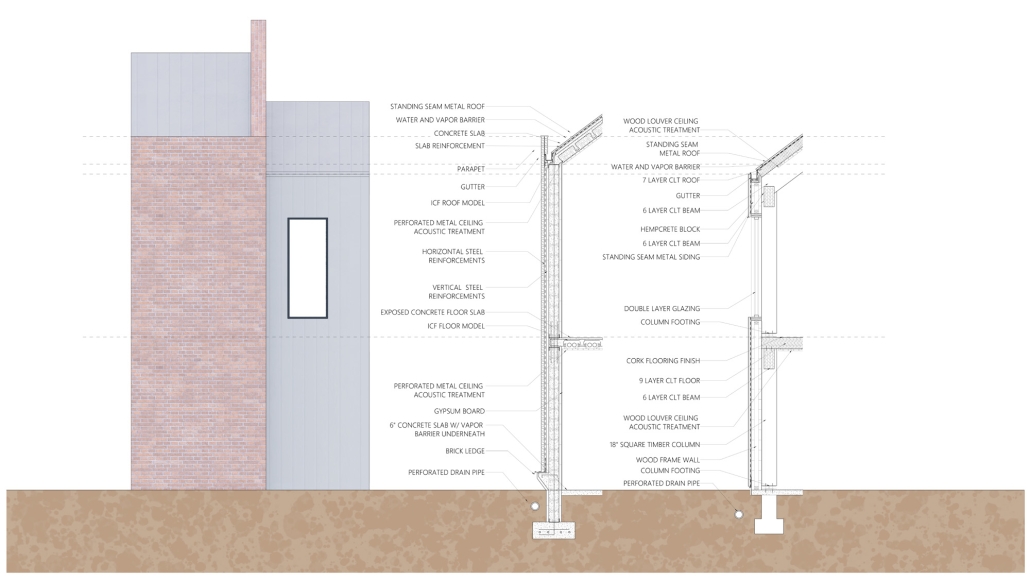
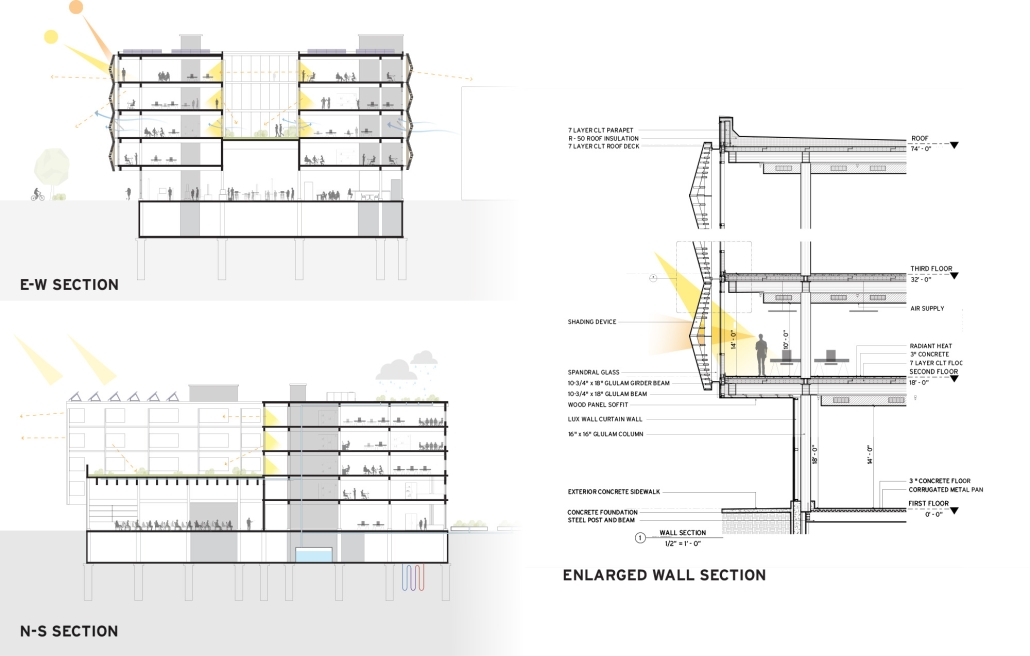
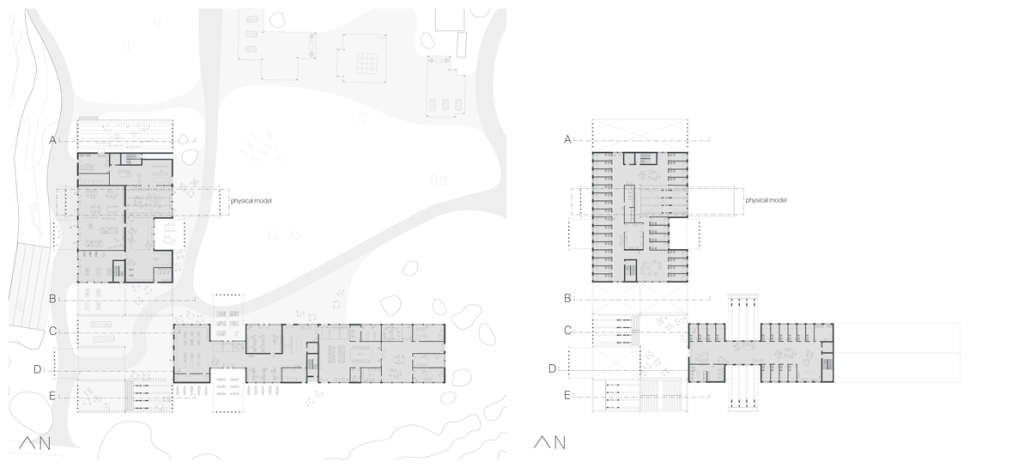
Extension to Lundgaard & Tranberg’s Architectural Office by Madeline Wettstein & Eleanor Lewis, M.Arch ’25
University of Washington | Advisors: Peter Cohan & Lene Tranberg
The project was assigned for the 2024 Scan Design Studio, co-taught by UW Professor Peter Cohan and famed Copenhagen-based architect Lene Tranberg of Lundgaard & Tranberg as Visiting Professor. The studio is generously funded by the Scan Design Foundation and provides student travel to Copenhagen before the studio commences, and allows the Visiting Professor to spend several weeks in Seattle working directly with students.
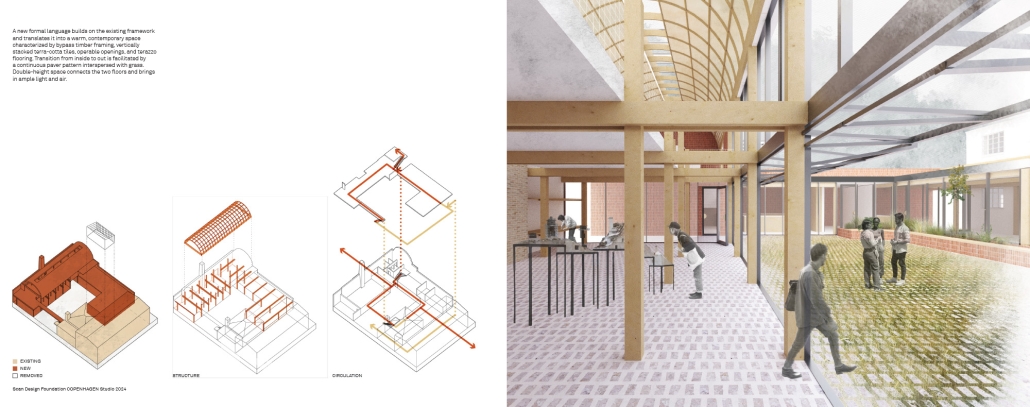
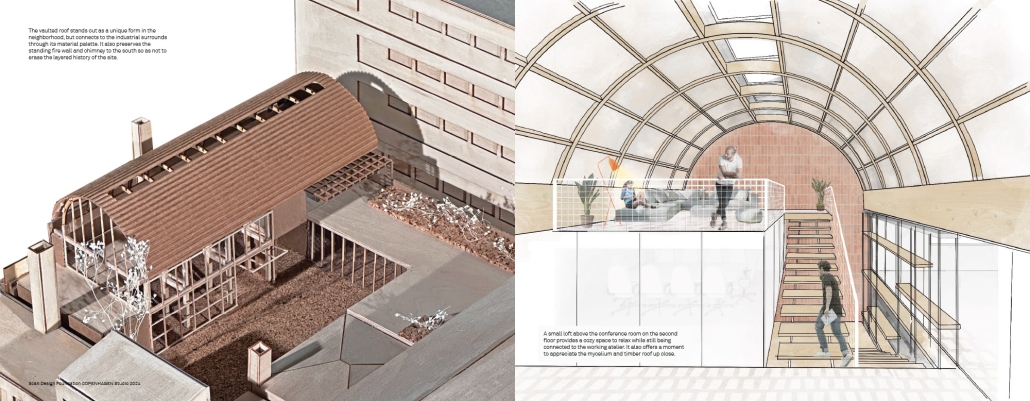
The assigned project was the expansion of Lundgaard & Tranberg’s office through the adaptive reuse of an existing building and addition. This proposal more than doubles the available square footage of the office and aims to enhance the building’s connection both to its historic surroundings and to nature. Two new wings hug the existing courtyard at the heart of the site, providing a more private space for team gatherings, complete with a small pond along the exposed brick wall. All wings open onto this courtyard, creating a dialogue between old and new while allowing circulation to flow seamlessly through and around it. A new west wing houses the kitchen, meeting rooms, and bathrooms, while the south wing proposes a multifunction model shop. The two are separated by an exterior pedestrian connection on the ground level, but connected above by a barrel vaulted roof whose curved form embraces the working space of the atelier below.
This project received commends for the studio.
Thanks for tuning in to the 2025 Study Architecture Student Showcase!